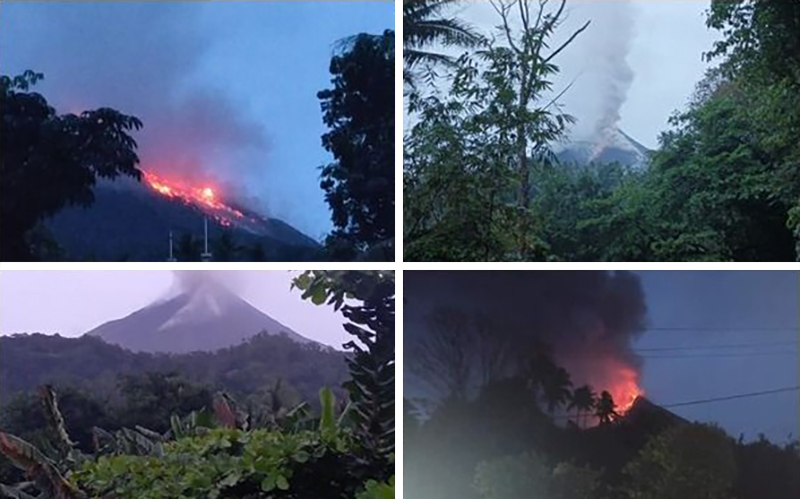
Recently Published Bulletin Reports
Manam (Papua New Guinea) Few ash plumes during November-December 2022
Krakatau (Indonesia) Strombolian activity and ash plumes during November 2022-April 2023
Stromboli (Italy) Strombolian explosions and lava flows continue during January-April 2023
Nishinoshima (Japan) Small ash plumes and fumarolic activity during November 2022 through April 2023
Karangetang (Indonesia) Lava flows, incandescent avalanches, and ash plumes during January-June 2023
Ahyi (United States) Intermittent hydroacoustic signals and discolored plumes during November 2022-June 2023
Kadovar (Papua New Guinea) An ash plume and weak thermal anomaly during May 2023
San Miguel (El Salvador) Small gas-and-ash explosions during March and May 2023
Semisopochnoi (United States) Occasional explosions, ash deposits, and gas-and-steam plumes during December 2022-May 2023
Ebeko (Russia) Continued explosions, ash plumes, and ashfall during October 2022-May 2023
Home Reef (Tonga) Discolored plumes continued during November 2022-April 2023
Ambae (Vanuatu) New lava flow, ash plumes, and sulfur dioxide plumes during February-May 2023
Manam (Papua New Guinea) — July 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Manam
Papua New Guinea
4.08°S, 145.037°E; summit elev. 1807 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
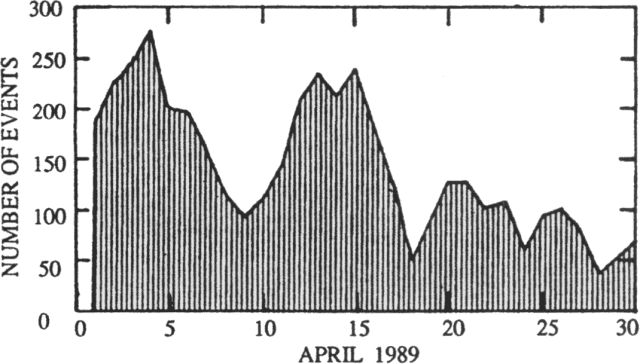
Few ash plumes during November-December 2022
Manam is a 10-km-wide island that consists of two active summit craters: the Main summit crater and the South summit crater and is located 13 km off the northern coast of mainland Papua New Guinea. Frequent mild-to-moderate eruptions have been recorded since 1616. The current eruption period began during June 2014 and has more recently been characterized by intermittent ash plumes and thermal activity (BGVN 47:11). This report updates activity that occurred from November 2022 through May 2023 based on information from the Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) and various satellite data.
Ash plumes were reported during November and December 2022 by the Darwin VAAC. On 7 November an ash plume rose to 2.1 km altitude and drifted NE based on satellite images and weather models. On 14 November an ash plume rose to 2.1 km altitude and drifted W based on RVO webcam images. On 20 November ash plumes rose to 1.8 km altitude and drifted NW. On 26 December an ash plume rose to 3 km altitude and drifted S and SSE.
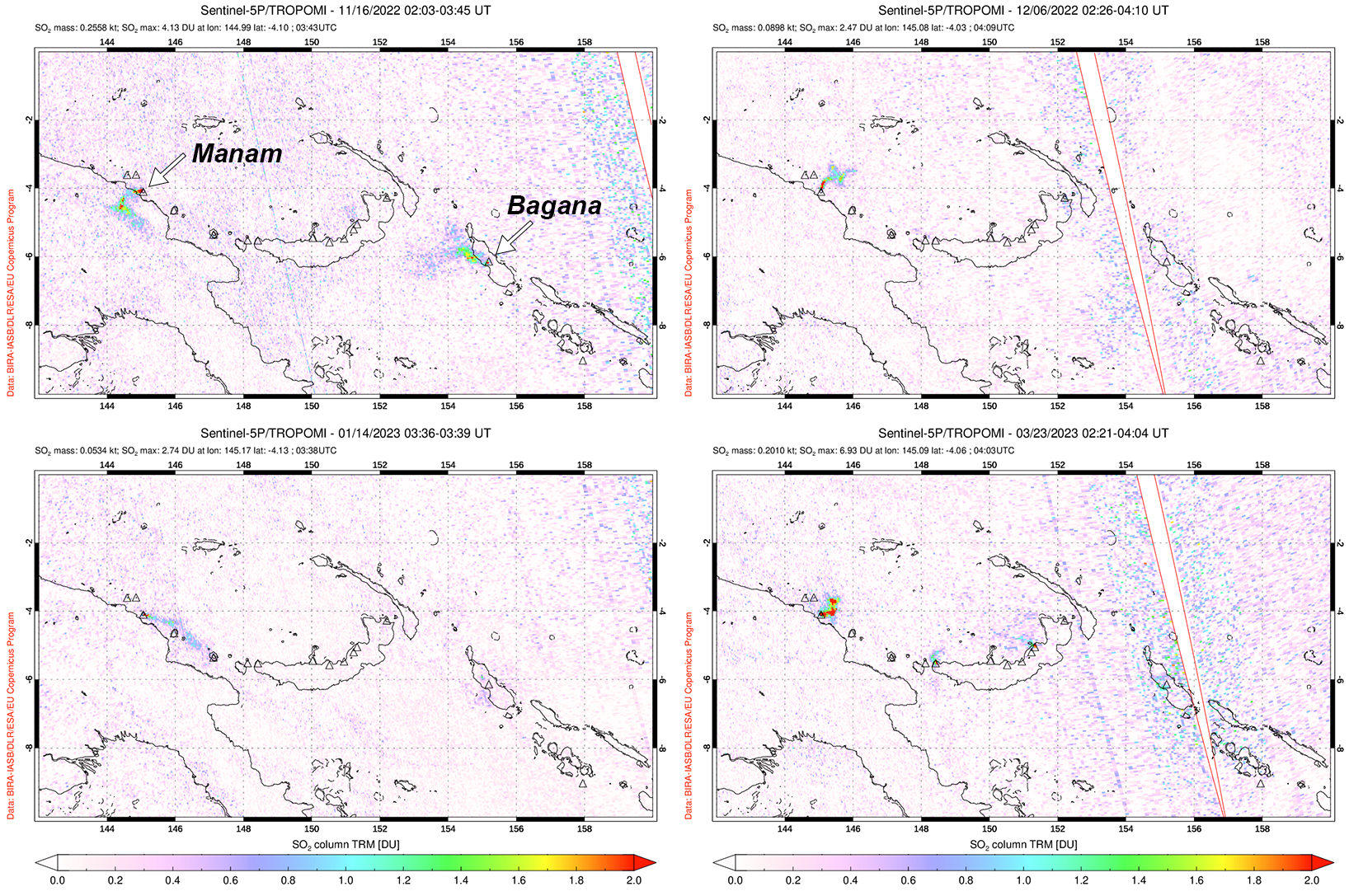
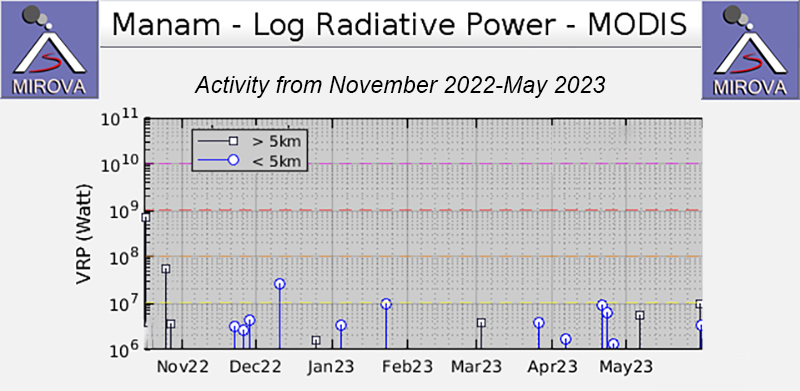
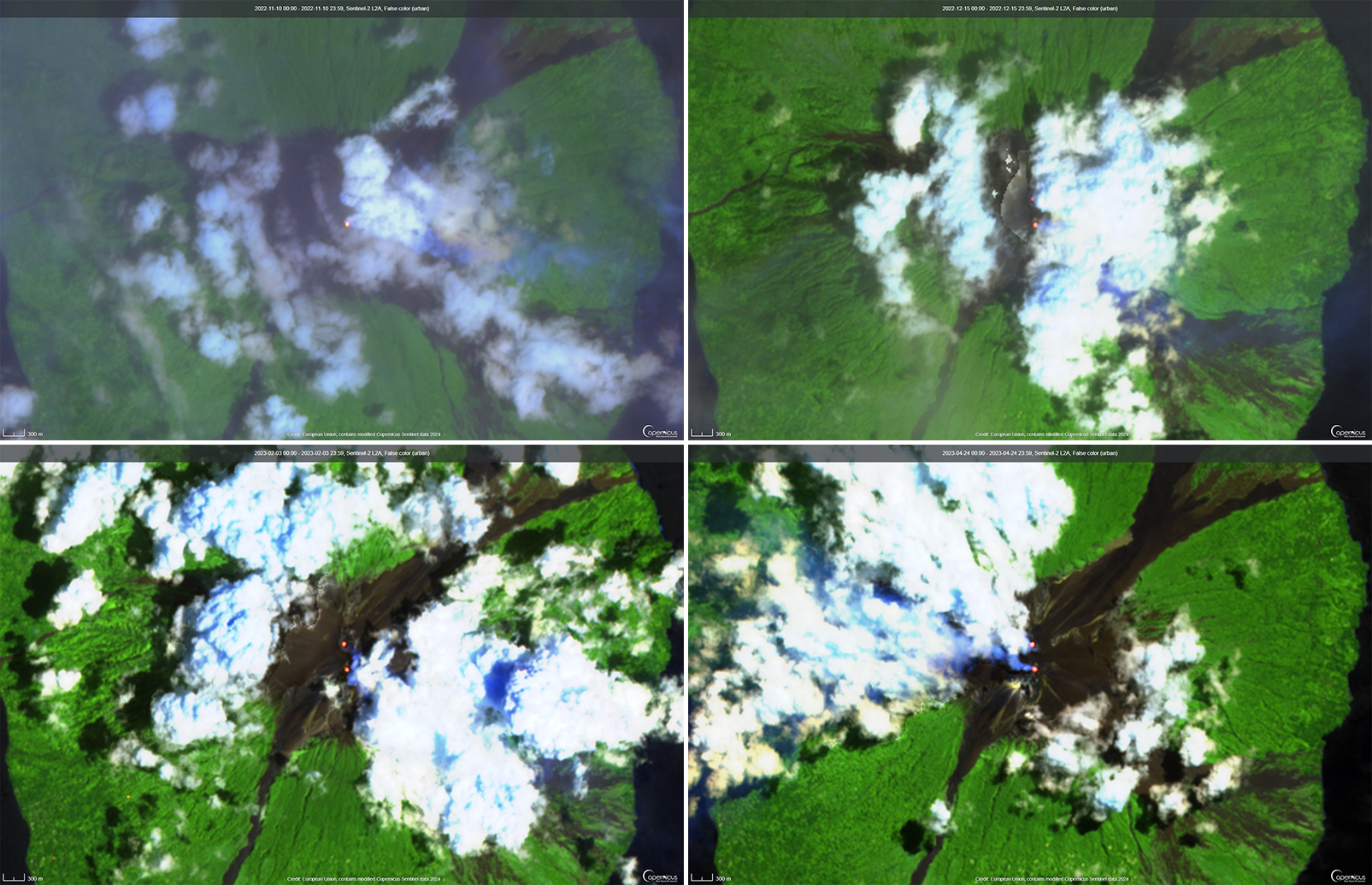
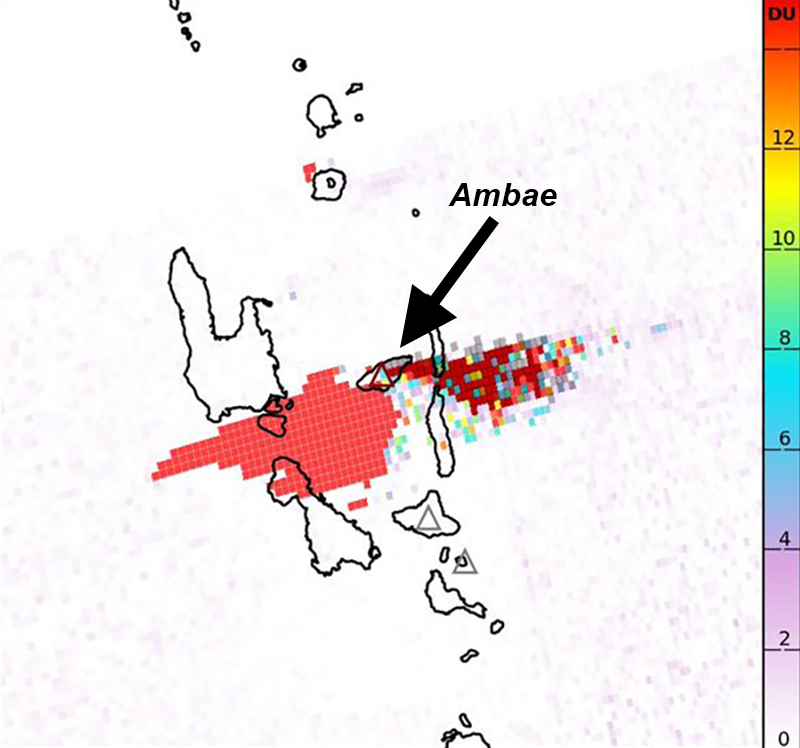
Intermittent sulfur dioxide plumes were detected using the TROPOMI instrument on the Sentinel-5P satellite, some of which exceeded at least two Dobson Units (DU) and drifted in different directions (figure 93). Occasional low-to-moderate power thermal anomalies were recorded by the MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) system; less than five anomalies were recorded each month during November 2022 through May 2023 (figure 94). Two thermal hotspots were detected by the MODVOLC thermal alerts system on 10 December 2022. On clear weather days, thermal activity was also captured in infrared satellite imagery in both the Main and South summit craters, accompanied by gas-and-steam emissions (figure 95).
Geologic Background. The 10-km-wide island of Manam, lying 13 km off the northern coast of mainland Papua New Guinea, is one of the country's most active volcanoes. Four large radial valleys extend from the unvegetated summit of the conical basaltic-andesitic stratovolcano to its lower flanks. These valleys channel lava flows and pyroclastic avalanches that have sometimes reached the coast. Five small satellitic centers are located near the island's shoreline on the northern, southern, and western sides. Two summit craters are present; both are active, although most observed eruptions have originated from the southern crater, concentrating eruptive products during much of the past century into the SE valley. Frequent eruptions, typically of mild-to-moderate scale, have been recorded since 1616. Occasional larger eruptions have produced pyroclastic flows and lava flows that reached flat-lying coastal areas and entered the sea, sometimes impacting populated areas.
Information Contacts: Rabaul Volcano Observatory (RVO), Geohazards Management Division, Department of Mineral Policy and Geohazards Management (DMPGM), PO Box 3386, Kokopo, East New Britain Province, Papua New Guinea; Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Bureau of Meteorology, Northern Territory Regional Office, PO Box 40050, Casuarina, NT 0811, Australia (URL: http://www.bom.gov.au/info/vaac/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); NASA Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Krakatau (Indonesia) — July 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Krakatau
Indonesia
6.1009°S, 105.4233°E; summit elev. 285 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
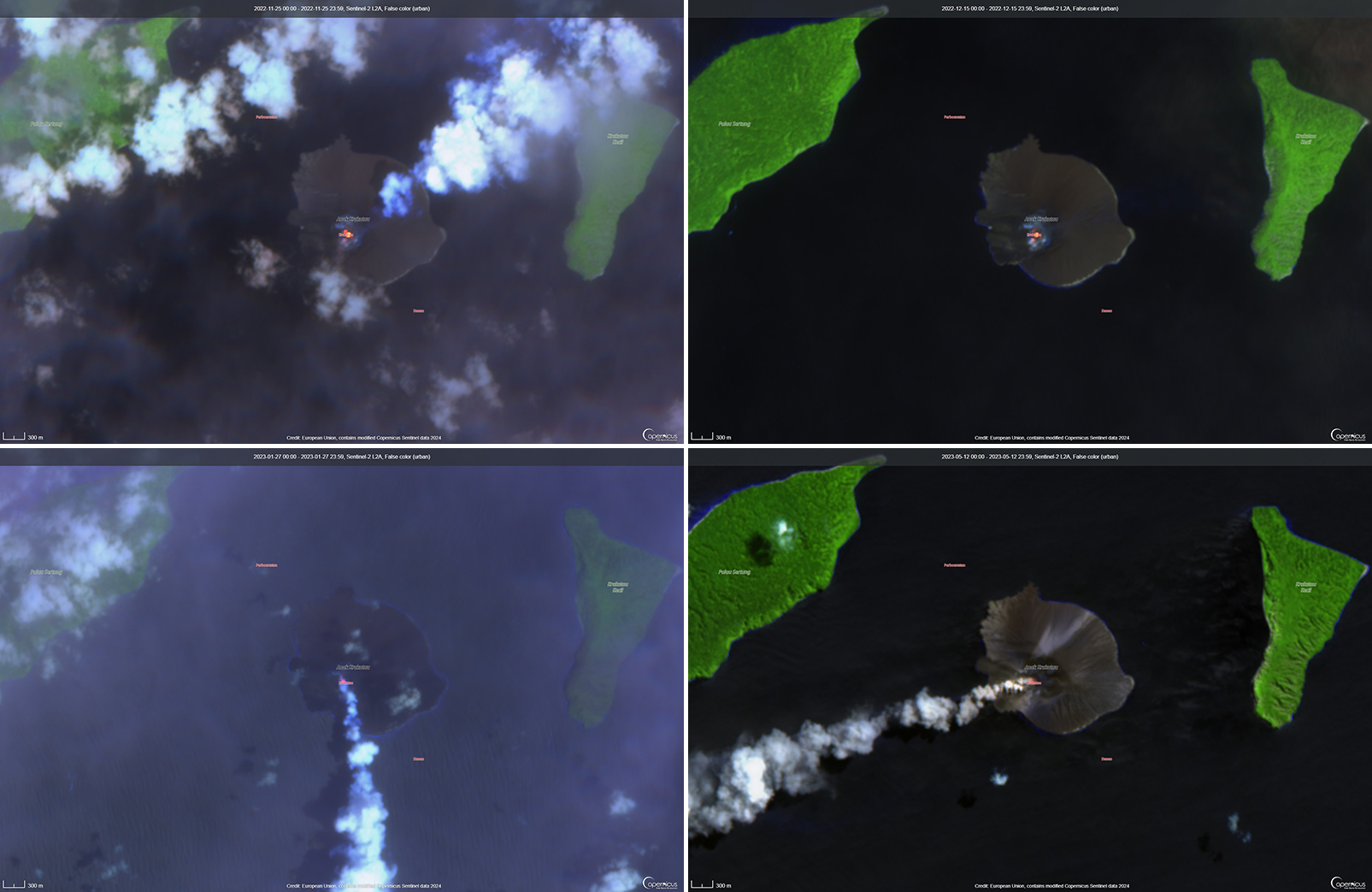
Strombolian activity and ash plumes during November 2022-April 2023
Krakatau is located in the Sunda Strait between Java and Sumatra, Indonesia. Caldera collapse during the catastrophic 1883 eruption destroyed Danan and Perbuwatan cones and left only a remnant of Rakata. The post-collapse cone of Anak Krakatau (Child of Krakatau) was constructed within the 1883 caldera at a point between the former Danan and Perbuwatan cones; it has been the site of frequent eruptions since 1927. The current eruption period began in May 2021 and has recently consisted of explosions, ash plumes, and thermal activity (BGVN 47:11). This report covers activity during November 2022 through April 2023 based on information provided by the Indonesian Center for Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation, referred to as Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG), MAGMA Indonesia, the Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), and several sources of satellite data.
Activity was relatively low during November and December 2022. Daily white gas-and-steam plumes rose 25-100 m above the summit and drifted in different directions. Gray ash plumes rose 200 m above the summit and drifted NE at 1047 and at 2343 on 11 November. On 14 November at 0933 ash plumes rose 300 m above the summit and drifted E. An ash plume was reported at 0935 on 15 December that rose 100 m above the summit and drifted NE. An eruptive event at 1031 later that day generated an ash plume that rose 700 m above the summit and drifted NE. A gray ash plume at 1910 rose 100 m above the summit and drifted E. Incandescent material was ejected above the vent based on an image taken at 1936.
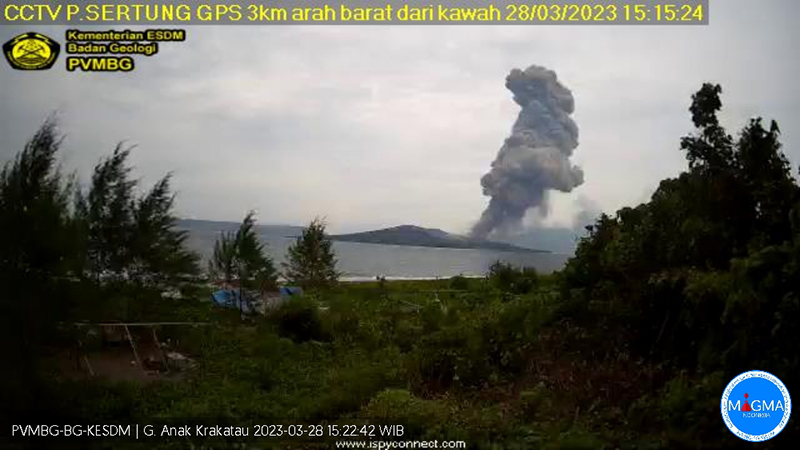
During January 2023 daily white gas-and-steam plumes rose 25-300 m above the summit and drifted in multiple directions. Gray-to-brown ash plumes were reported at 1638 on 3 January, at 1410 and 1509 on 4 January, and at 0013 on 5 January that rose 100-750 m above the summit and drifted NE and E; the gray-to-black ash plume at 1509 on 4 January rose as high as 3 km above the summit and drifted E. Gray ash plumes were recorded at 1754, 2241, and 2325 on 11 January and at 0046 on 12 January and rose 200-300 m above the summit and drifted NE. Toward the end of January, PVMBG reported that activity had intensified; Strombolian activity was visible in webcam images taken at 0041, 0043, and 0450 on 23 January. Multiple gray ash plumes throughout the day rose 200-500 m above the summit and drifted E and SE (figure 135). Webcam images showed progressively intensifying Strombolian activity at 1919, 1958, and 2113 on 24 January; a gray ash plume at 1957 rose 300 m above the summit and drifted E (figure 135). Eruptive events at 0231 and 2256 on 25 January and at 0003 on 26 January ejected incandescent material from the vent, based on webcam images. Gray ash plumes observed during 26-27 January rose 300-500 m above the summit and drifted NE, E, and SE.
Low levels of activity were reported during February and March. Daily white gas-and-steam plumes rose 25-300 m above the summit and drifted in different directions. The Darwin VAAC reported that continuous ash emissions rose to 1.5-1.8 km altitude and drifted W and NW during 1240-1300 on 10 March, based on satellite images, weather models, and PVMBG webcams. White-and-gray ash plumes rose 500 m and 300 m above the summit and drifted SW at 1446 and 1846 on 18 March, respectively. An eruptive event was recorded at 2143, though it was not visible due to darkness. Multiple ash plumes were reported during 27-29 March that rose as high as 2.5 km above the summit and drifted NE, W, and SW (figure 136). Webcam images captured incandescent ejecta above the vent at 0415 and around the summit area at 2003 on 28 March and at 0047 above the vent on 29 March.
Daily white gas-and-steam plumes rose 25-300 m above the summit and drifted in multiple directions during April and May. White-and-gray and black plumes rose 50-300 m above the summit on 2 and 9 April. On 11 May at 1241 a gray ash plume rose 1-3 km above the summit and drifted SW. On 12 May at 0920 a gray ash plume rose 2.5 km above the summit and drifted SW and at 2320 an ash plume rose 1.5 km above the summit and drifted SW. An accompanying webcam image showed incandescent ejecta. On 13 May at 0710 a gray ash plume rose 2 km above the summit and drifted SW (figure 137).
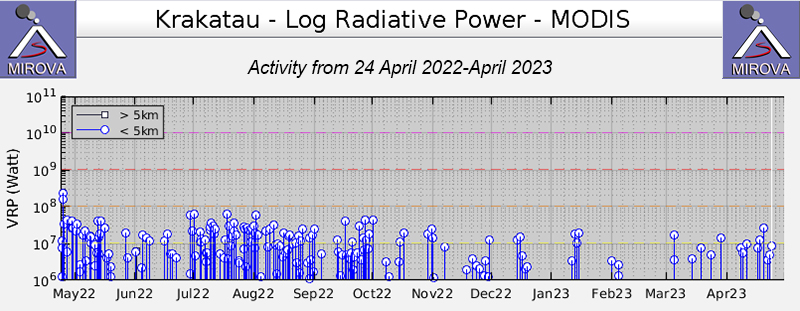
The MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) graph of MODIS thermal anomaly data showed intermittent low-to-moderate power thermal anomalies during November 2022 through April 2023 (figure 138). Some of this thermal activity was also visible in infrared satellite imagery at the crater, accompanied by gas-and-steam and ash plumes that drifted in different directions (figure 139).
Geologic Background. The renowned Krakatau (frequently mis-named as Krakatoa) volcano lies in the Sunda Strait between Java and Sumatra. Collapse of an older edifice, perhaps in 416 or 535 CE, formed a 7-km-wide caldera. Remnants of that volcano are preserved in Verlaten and Lang Islands; subsequently the Rakata, Danan, and Perbuwatan cones were formed, coalescing to create the pre-1883 Krakatau Island. Caldera collapse during the catastrophic 1883 eruption destroyed Danan and Perbuwatan, and left only a remnant of Rakata. This eruption caused more than 36,000 fatalities, most as a result of tsunamis that swept the adjacent coastlines of Sumatra and Java. Pyroclastic surges traveled 40 km across the Sunda Strait and reached the Sumatra coast. After a quiescence of less than a half century, the post-collapse cone of Anak Krakatau (Child of Krakatau) was constructed within the 1883 caldera at a point between the former Danan and Perbuwatan cones. Anak Krakatau has been the site of frequent eruptions since 1927.
Information Contacts: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as Indonesian Center for Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation, CVGHM), Jalan Diponegoro 57, Bandung 40122, Indonesia (URL: http://www.vsi.esdm.go.id/); MAGMA Indonesia, Kementerian Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral (URL: https://magma.esdm.go.id/v1); Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Bureau of Meteorology, Northern Territory Regional Office, PO Box 40050, Casuarina, NT 0811, Australia (URL: http://www.bom.gov.au/info/vaac/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Stromboli
Italy
38.789°N, 15.213°E; summit elev. 924 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Strombolian explosions and lava flows continue during January-April 2023
Stromboli, located in Italy, has exhibited nearly constant lava fountains for the past 2,000 years; recorded eruptions date back to 350 BCE. Eruptive activity occurs at the summit from multiple vents, which include a north crater area (N area) and a central-southern crater (CS area) on a terrace known as the ‘terrazza craterica’ at the head of the Sciara del Fuoco, a large scarp that runs from the summit down the NW side of the volcano-island. Activity typically consists of Strombolian explosions, incandescent ejecta, lava flows, and pyroclastic flows. Thermal and visual monitoring cameras are located on the nearby Pizzo Sopra La Fossa, above the terrazza craterica, and at multiple flank locations. The current eruption period has been ongoing since 1934 and recent activity has consisted of frequent Strombolian explosions and lava flows (BGVN 48:02). This report updates activity during January through April 2023 primarily characterized by Strombolian explosions and lava flows based on reports from Italy's Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV) and various satellite data.
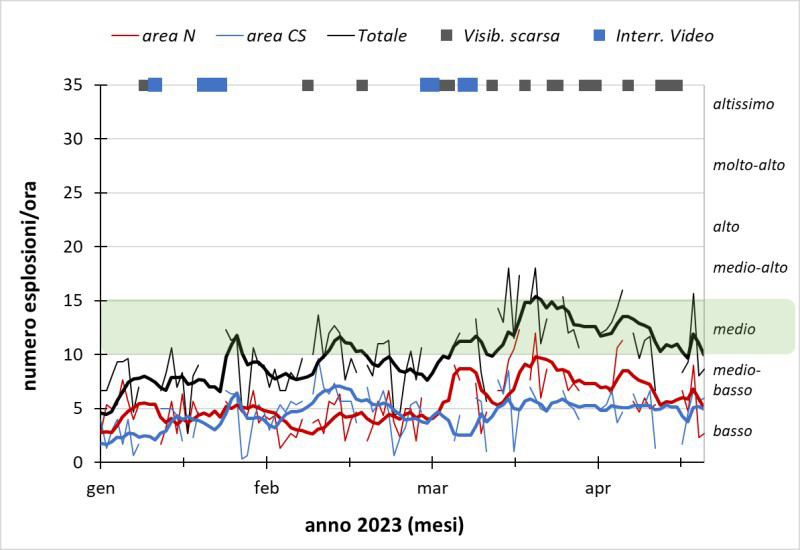
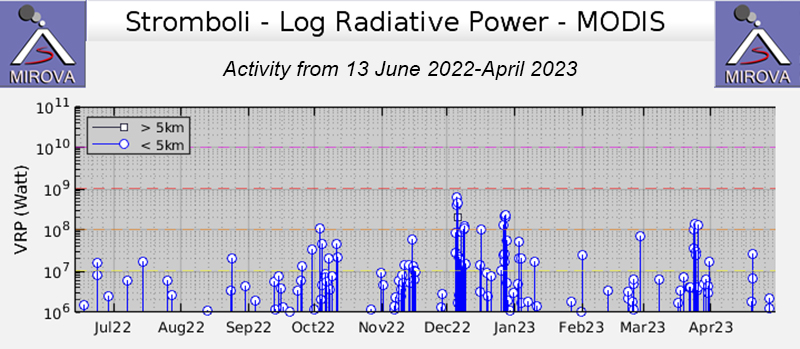
Frequent explosive activity continued throughout the reporting period, generally in the low-to-medium range, based on the number of hourly explosions in the summit crater (figure 253, table 16). Intermittent thermal activity was recorded by the MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) analysis of MODIS satellite data (figure 254). According to data collected by the MODVOLC thermal algorithm, a total of 9 thermal alerts were detected: one on 2 January 2023, one on 1 February, five on 24 March, and two on 26 March. The stronger pulses of thermal activity likely reflected lava flow events. Infrared satellite imagery captured relatively strong thermal hotspots at the two active summit craters on clear weather days, showing an especially strong event on 8 March (figure 255).
Table 16. Summary of type, frequency, and intensity of explosive activity at Stromboli by month during January-April 2023; information from webcam observations. Courtesy of INGV weekly reports.
| Month |
Explosive Activity |
| Jan 2023 |
Typical Strombolian activity with spattering and lava overflows in the N crater area. Explosions were reported from 4 vents in the N area and 1-2 vents in the CS area. The average hourly frequency of explosions was low-to-medium (1-12 events/hour). The intensity of the explosions varied from low (less than 80 m high) to medium (less than 150 m high) in the N crater area and up to high (greater than 150 m high) in the CS crater area. |
| Feb 2023 |
Typical Strombolian activity with spattering in the N crater area. Explosions were reported from 2-3 vents in the N area and 1-4 vents in the CS area. The average hourly frequency of explosions was low-to-medium (1-14 events/hour). The intensity of the explosions varied from low (less than 80 m high) to medium (less than 150 m high) in the N crater area and up to high (greater than 150 m high) in the CS crater area. |
| Mar 2023 |
Typical Strombolian activity with spattering and lava overflows in the N crater area. Explosions were reported from 2-3 vents in the N area and 2-4 vents in the CS area. The average hourly frequency of explosions was low-to-medium (1-18 events/hour). The intensity of the explosions varied from low (less than 80 m high) to medium (less than 150 m high) in the N crater area and up to high (greater than 150 m high) in the CS crater area. |
| Apr 2023 |
Typical Strombolian activity. Explosions were reported from 2 vents in the N area and 2-3 vents in the CS area. The average hourly frequency of explosions was low-to-high (1-16 events/hour). The intensity of the explosions varied from low (less than 80 m high) to medium (less than 150 m high) in both the N and CS crater areas. |
Activity during January-February 2023. Strombolian explosions were reported in the N crater area, as well as lava effusion. Explosive activity in the N crater area ejected coarse material (bombs and lapilli). Intense spattering was observed in both the N1 and N2 craters. In the CS crater area, explosions generally ejected fine material (ash), sometimes to heights greater than 250 m. The intensity of the explosions was characterized as low-to-medium in the N crater and medium-to-high in the CS crater. After intense spattering activity from the N crater area, a lava overflow began at 2136 on 2 January that flowed part way down the Sciara del Fuoco, possibly moving down the drainage that formed in October, out of view from webcams. The flow remained active for a couple of hours before stopping and beginning to cool. A second lava flow was reported at 0224 on 4 January that similarly remained active for a few hours before stopping and cooling. Intense spattering was observed on 11 and 13 January from the N1 crater. After intense spattering activity at the N2 crater at 1052 on 17 January another lava flow started to flow into the upper part of the Sciara del Fuoco (figure 256), dividing into two: one that traveled in the direction of the drainage formed in October, and the other one moving parallel to the point of emission. By the afternoon, the rate of the flow began to decrease, and at 1900 it started to cool. A lava flow was reported at 1519 on 24 January following intense spattering in the N2 area, which began to flow into the upper part of the Sciara del Fuoco. By the morning of 25 January, the lava flow had begun to cool. During 27 January the frequency of eruption in the CS crater area increased to 6-7 events/hour compared to the typical 1-7 events/hour; the following two days showed a decrease in frequency to less than 1 event/hour. Starting at 1007 on 30 January a high-energy explosive sequence was produced by vents in the CS crater area. The sequence began with an initial energetic pulse that lasted 45 seconds, ejecting predominantly coarse products 300 m above the crater that fell in an ESE direction. Subsequent and less intense explosions ejected material 100 m above the crater. The total duration of this event lasted approximately two minutes. During 31 January through 6, 13, and 24 February spattering activity was particularly intense for short periods in the N2 crater.
An explosive sequence was reported on 16 February that was characterized by a major explosion in the CS crater area (figure 257). The sequence began at 1817 near the S2 crater that ejected material radially. A few seconds later, lava fountains were observed in the central part of the crater. Three explosions of medium intensity (material was ejected less than 150 m high) were recorded at the S2 crater. The first part of this sequence lasted approximately one minute, according to INGV, and material rose 300 m above the crater and then was deposited along the Sciara del Fuoco. The second phase began at 1818 at the S1 crater; it lasted seven seconds and material was ejected 150 m above the crater. Another event 20 seconds later lasted 12 seconds, also ejecting material 150 m above the crater. The sequence ended with at least three explosions of mostly fine material from the S1 crater. The total duration of this sequence was about two minutes.
Short, intense spattering activity was noted above the N1 crater on 27 and 28 February. A lava overflow was first reported at 0657 from the N2 crater on 27 February that flowed into the October 2022 drainage. By 1900 the flow had stopped. A second lava overflow also in the N crater area occurred at 2149, which overlapped the first flow and then stopped by 0150 on 28 February. Material detached from both the lava overflows rolled down the Sciara del Fuoco, some of which was visible in webcam images.
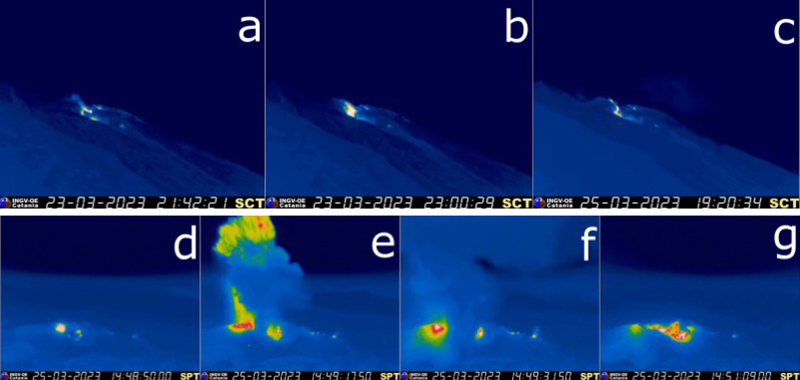
Activity during March-April 2023. Strombolian activity continued with spattering activity and lava overflows in the N crater area during March. Explosive activity at the N crater area varied from low (less than 80 m high) to medium (less than 150 m high) and ejected coarse material, such as bombs and lapilli. Spattering was observed above the N1 crater, while explosive activity at the CS crater area varied from medium to high (greater than 150 m high) and ejected coarse material. Intense spattering activity was observed for short periods on 6 March above the N1 crater. At approximately 0610 a lava overflow was reported around the N2 crater on 8 March, which then flowed into the October 2022 drainage. By 1700 the flow started to cool. A second overflow began at 1712 on 9 March and overlapped the previous flow. It had stopped by 2100. Material from both flows was deposited along the Sciara del Fuoco, though much of the activity was not visible in webcam images. On 11 March a lava overflow was observed at 0215 that overlapped the two previous flows in the October 2022 drainage. By late afternoon on 12 March, it had stopped.
During a field excursion on 16 March, scientists noted that a vent in the central crater area was degassing. Another vent showed occasional Strombolian activity that emitted ash and lapilli. During 1200-1430 low-to-medium intense activity was reported; the N1 crater emitted ash emissions and the N2 crater emitted both ash and coarse material. Some explosions also occurred in the CS crater area that ejected coarse material. The C crater in the CS crater area occasionally showed gas jetting and low intensity explosions on 17 and 22 March; no activity was observed at the S1 crater. Intense, longer periods of spattering were reported in the N1 crater on 19, 24, and 25 March. Around 2242 on 23 March a lava overflow began from the N1 crater that, after about an hour, began moving down the October 2022 drainage and flow along the Sciara del Fuoco (figure 258). Between 0200 and 0400 on 26 March the flow rate increased, which generated avalanches of material from collapses at the advancing flow front. By early afternoon, the flow began to cool. On 25 March at 1548 an explosive sequence began from one of the vents at S2 in the CS crater area (figure 258). Fine ash mixed with coarse material was ejected 300 m above the crater rim and drifted SSE. Some modest explosions around Vent C were detected at 1549 on 25 March, which included an explosion at 1551 that ejected coarse material. The entire explosive sequence lasted approximately three minutes.
During April explosions persisted in both the N and CS crater areas. Fine material was ejected less than 80 m above the N crater rim until 6 April, followed by ejection of coarser material. Fine material was also ejected less than 80 m above the CS crater rim. The C and S2 crater did not show significant eruptive activity. On 7 April an explosive sequence was detected in the CS crater area at 1203 (figure 259). The first explosion lasted approximately 18 seconds and ejected material 400 m above the crater rim, depositing pyroclastic material in the upper part of the Sciara del Fuoco. At 1204 a second, less intense explosion lasted approximately four seconds and deposited pyroclastic products outside the crater area and near Pizzo Sopra La Fossa. A third explosion at 1205 was mainly composed of ash that rose about 150 m above the crater and lasted roughly 20 seconds. A fourth explosion occurred at 1205 about 28 seconds after the third explosion and ejected a mixture of coarse and fine material about 200 m above the crater; the explosion lasted roughly seven seconds. Overall, the entire explosive sequence lasted about two minutes and 20 seconds. After the explosive sequence on 7 April, explosions in both the N and CS crater areas ejected material as high as 150 m above the crater.
On 21 April research scientists from INGV made field observations in the summit area of Stromboli, and some lapilli samples were collected. In the N crater area near the N1 crater, a small cone was observed with at least two active vents, one of which was characterized by Strombolian explosions. The other vent produced explosions that ejected ash and chunks of cooled lava. At the N2 crater at least one vent was active and frequently emitted ash. In the CS crater area, a small cone contained 2-3 degassing vents and a smaller, possible fissure area also showed signs of degassing close to the Pizzo Sopra La Fossa. In the S part of the crater, three vents were active: a small hornito was characterized by modest and rare explosions, a vent that intermittently produced weak Strombolian explosions, and a vent at the end of the terrace that produced frequent ash emissions. Near the S1 crater there was a hornito that generally emitted weak gas-and-steam emissions, sometimes associated with “gas rings”. On 22 April another field inspection was carried out that reported two large sliding surfaces on the Sciara del Fuoco that showed where blocks frequently descended toward the sea. A thermal anomaly was detected at 0150 on 29 April.
Geologic Background. Spectacular incandescent nighttime explosions at Stromboli have long attracted visitors to the "Lighthouse of the Mediterranean" in the NE Aeolian Islands. This volcano has lent its name to the frequent mild explosive activity that has characterized its eruptions throughout much of historical time. The small island is the emergent summit of a volcano that grew in two main eruptive cycles, the last of which formed the western portion of the island. The Neostromboli eruptive period took place between about 13,000 and 5,000 years ago. The active summit vents are located at the head of the Sciara del Fuoco, a prominent scarp that formed about 5,000 years ago due to a series of slope failures which extends to below sea level. The modern volcano has been constructed within this scarp, which funnels pyroclastic ejecta and lava flows to the NW. Essentially continuous mild Strombolian explosions, sometimes accompanied by lava flows, have been recorded for more than a millennium.
Information Contacts: Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV), Sezione di Catania, Piazza Roma 2, 95123 Catania, Italy, (URL: http://www.ct.ingv.it/en/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Nishinoshima (Japan) — July 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Nishinoshima
Japan
27.247°N, 140.874°E; summit elev. 100 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Small ash plumes and fumarolic activity during November 2022 through April 2023
Nishinoshima is a small island located about 1,000 km S of Tokyo in the Ogasawara Arc in Japan. The island is the summit of a massive submarine volcano that has prominent peaks to the S, W, and NE. Eruptions date back to 1973; the most recent eruption period began in October 2022 and was characterized by ash plumes and fumarolic activity (BGVN 47:12). This report describes ash plumes and fumarolic activity during November 2022 through April 2023 based on monthly reports from the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) monthly reports and satellite data.
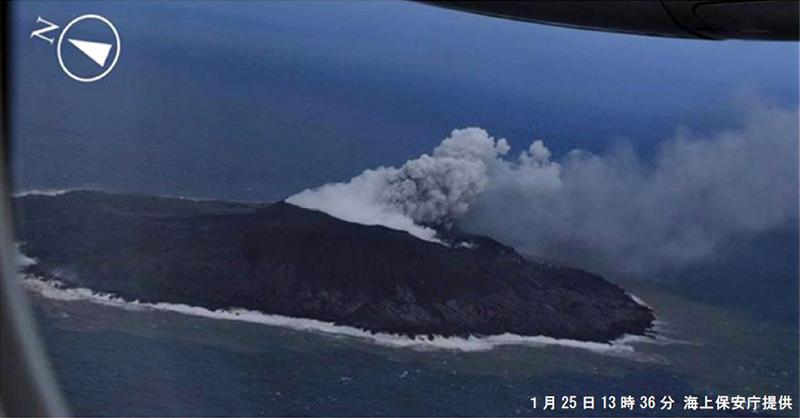
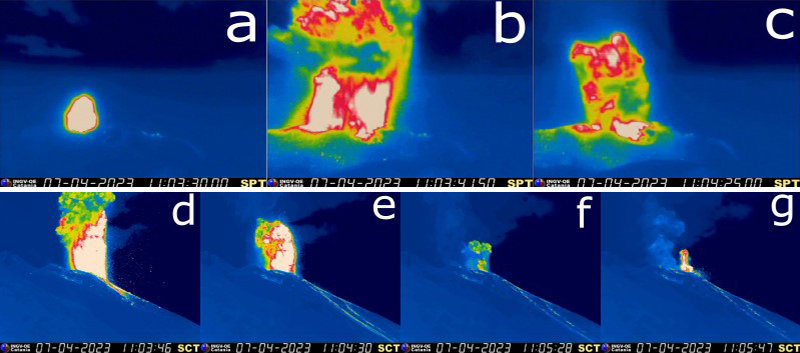
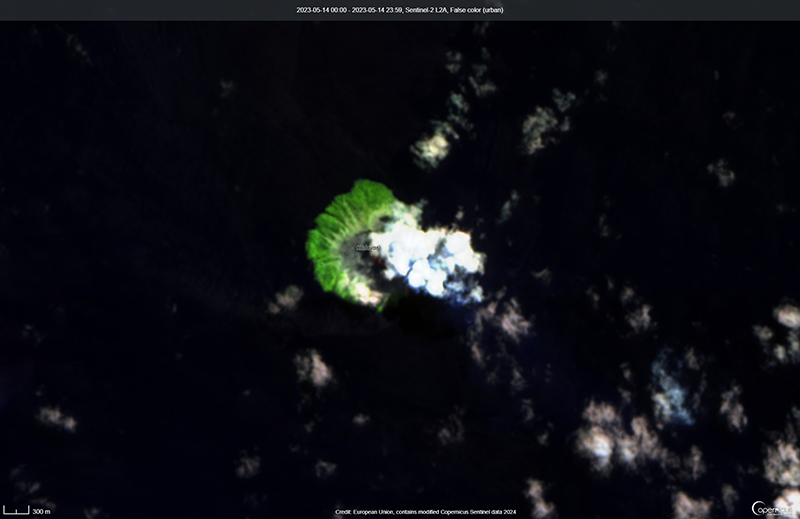
The most recent eruptive activity prior to the reporting internal occurred on 12 October 2022, when an ash plume rose 3.5 km above the crater rim. An aerial observation conducted by the Japan Coast Guard (JCG) on 25 November reported that white fumaroles rose approximately 200 m above the central crater of a pyroclastic cone (figure 119), and multiple plumes were observed on the ESE flank of the cone. Discolored water ranging from reddish-brown to brown and yellowish-green were visible around the perimeter of the island (figure 119). No significant activity was reported in December.
During an overflight conducted by JCG on 25 January 2023 intermittent activity and small, blackish-gray plumes rose 900 m above the central part of the crater were observed (figure 120). The fumarolic zone of the E flank and base of the cone had expanded and emissions had intensified. Dark brown discolored water was visible around the perimeter of the island.
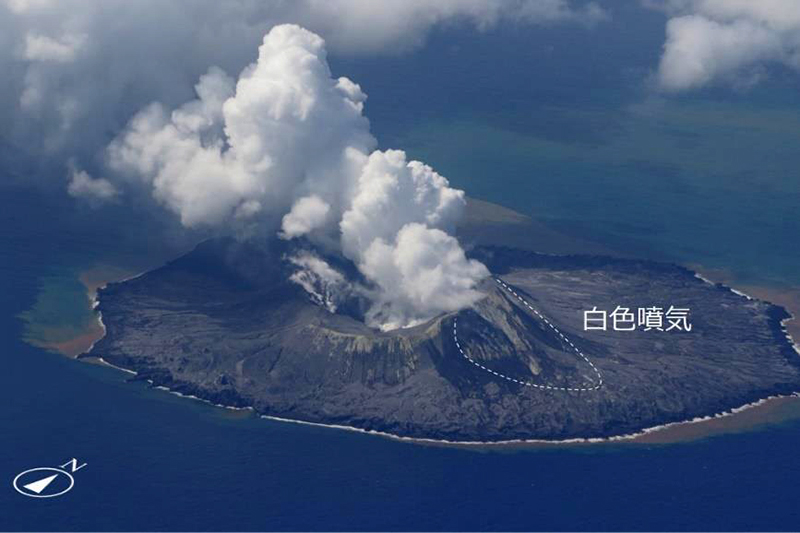
No significant activity was reported during February through March. Ash plumes at 1050 and 1420 on 11 April rose 1.9 km above the crater rim and drifted NW and N. These were the first ash plumes observed since 12 October 2022. On 14 April JCG carried out an overflight and reported that no further eruptive activity was visible, although white gas-and-steam plumes were visible from the central crater and rose 900 m high (figure 121). Brownish and yellow-green discolored water surrounded the island.
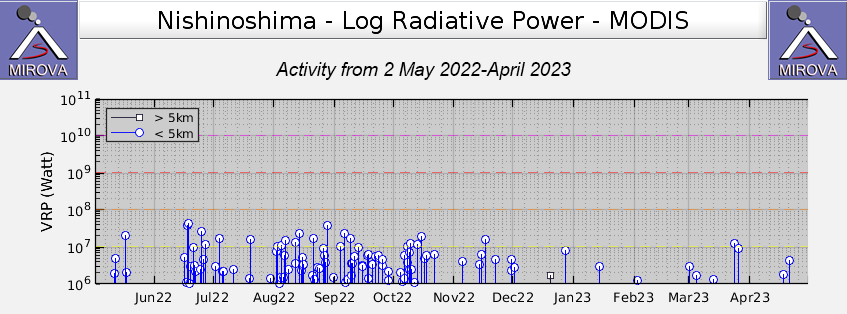
Intermittent low-to-moderate power thermal anomalies were recorded in the MIROVA graph (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) during November 2022 through April 2023 (figure 123). A cluster of six to eight anomalies were detected during November while a smaller number were detected during the following months: two to three during December, one during mid-January 2023, one during February, five during March, and two during April. Thermal activity was also reflected in infrared satellite data at the summit crater, accompanied by occasional gas-and-steam plumes (figure 124).
Geologic Background. The small island of Nishinoshima was enlarged when several new islands coalesced during an eruption in 1973-74. Multiple eruptions that began in 2013 completely covered the previous exposed surface and continued to enlarge the island. The island is the summit of a massive submarine volcano that has prominent peaks to the S, W, and NE. The summit of the southern cone rises to within 214 m of the ocean surface 9 km SSE.
Information Contacts: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA), 1-3-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8122, Japan (URL: http://www.jma.go.jp/jma/indexe.html); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Karangetang (Indonesia) — July 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Karangetang
Indonesia
2.781°N, 125.407°E; summit elev. 1797 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
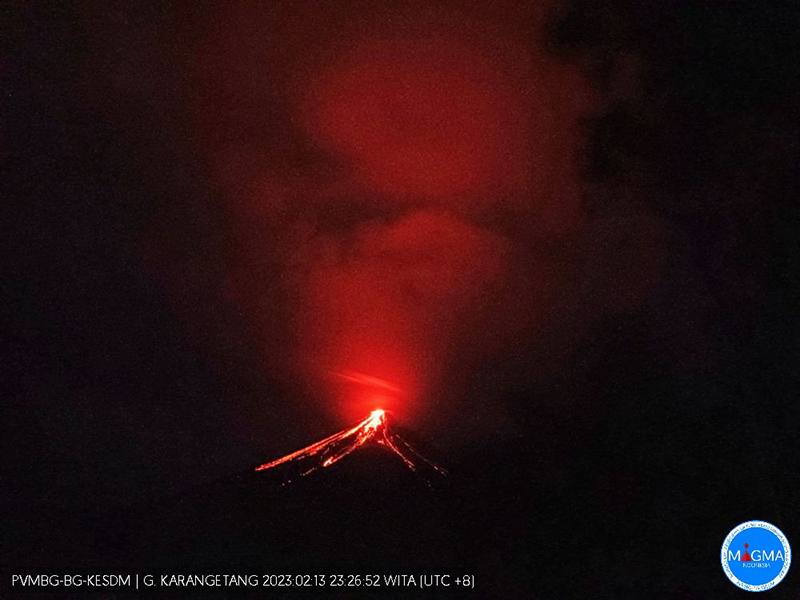
Lava flows, incandescent avalanches, and ash plumes during January-June 2023
Karangetang (also known as Api Siau), at the northern end of the island of Siau, Indonesia, contains five summit craters along a N-S line. More than 40 eruptions have been recorded since 1675; recent eruptions have included frequent explosive activity, sometimes accompanied by pyroclastic flows and lahars. Lava dome growth has occurred in the summit craters and collapses of lava flow fronts have produced pyroclastic flows. The two active summit craters are Kawah Dua (the N crater) and Kawah Utama (the S crater, also referred to as the “Main Crater”). The most recent eruption began in late November 2018 and has more recently consisted of weak thermal activity and gas-and-steam emissions (BGVN 48:01). This report updates activity characterized by lava flows, incandescent avalanches, and ash plumes during January through June 2023 using reports from Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as CVGHM, or the Center of Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation), MAGMA Indonesia, the Darwin VAAC (Volcano Ash Advisory Center), and satellite data.
Activity during January was relatively low and mainly consisted of white gas-and-steam emissions that rose 25-150 m above Main Crater (S crater) and drifted in different directions. Incandescence was visible from the lava dome in Kawah Dua (the N crater). Weather conditions often prevented clear views of the summit. On 18 January the number of seismic signals that indicated avalanches of material began to increase. In addition, there were a total of 71 earthquakes detected during the month.
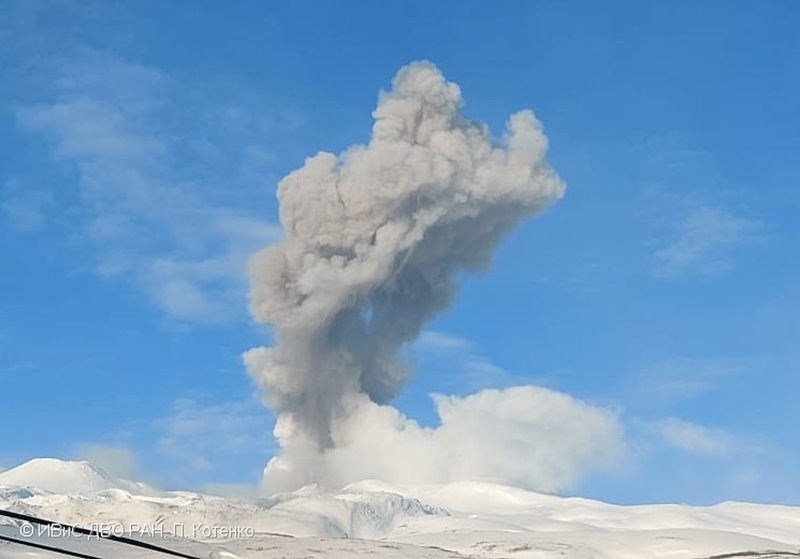
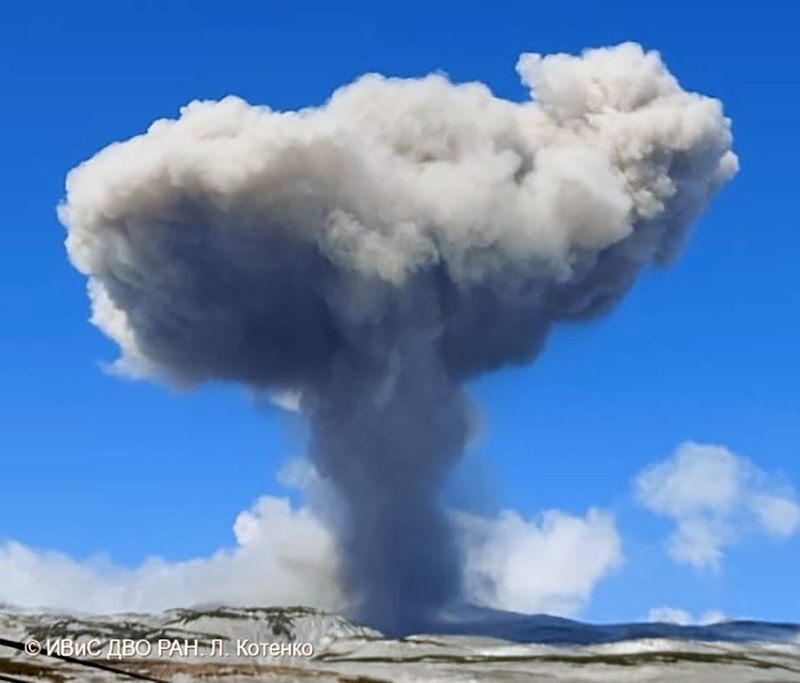
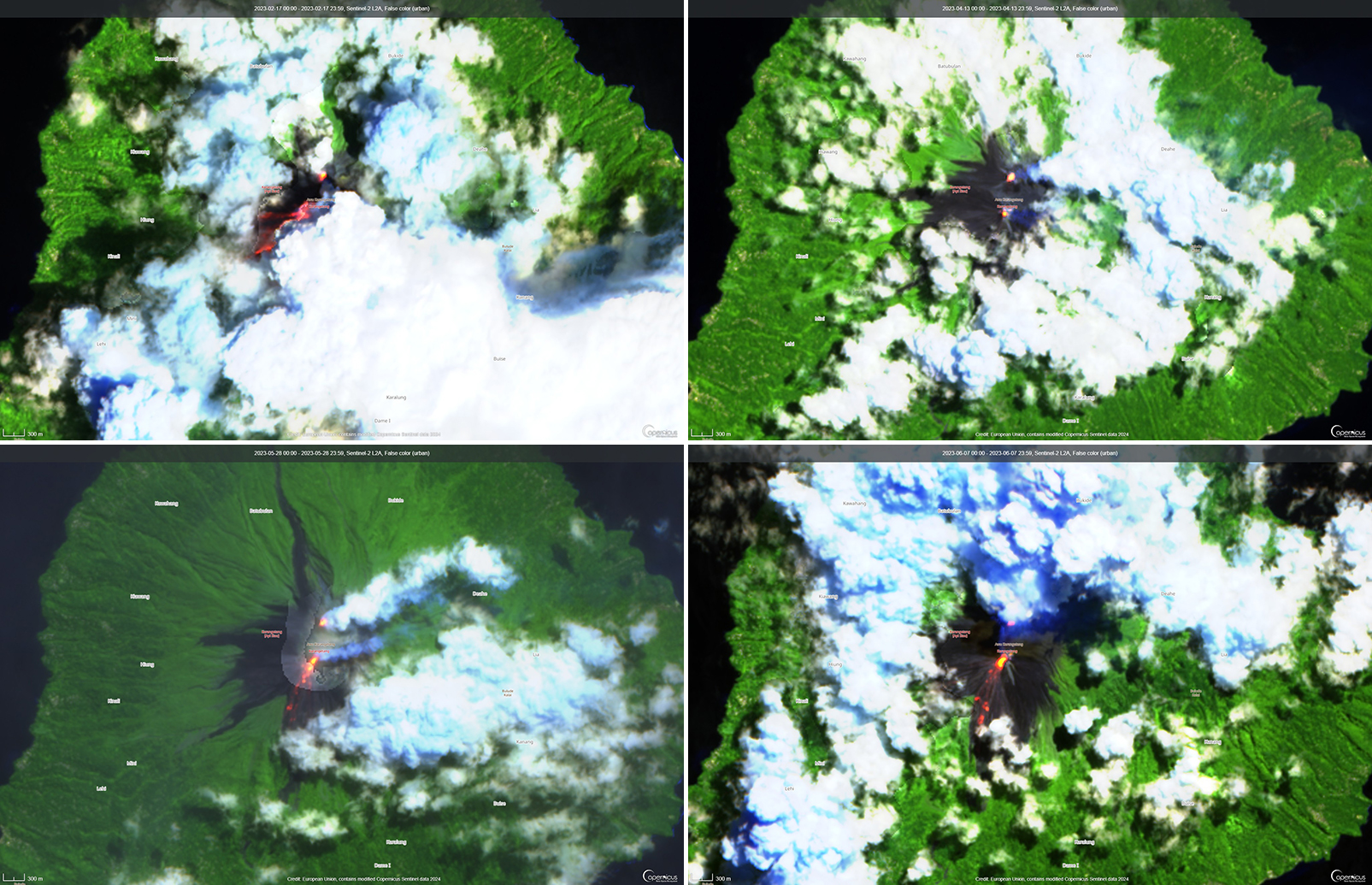
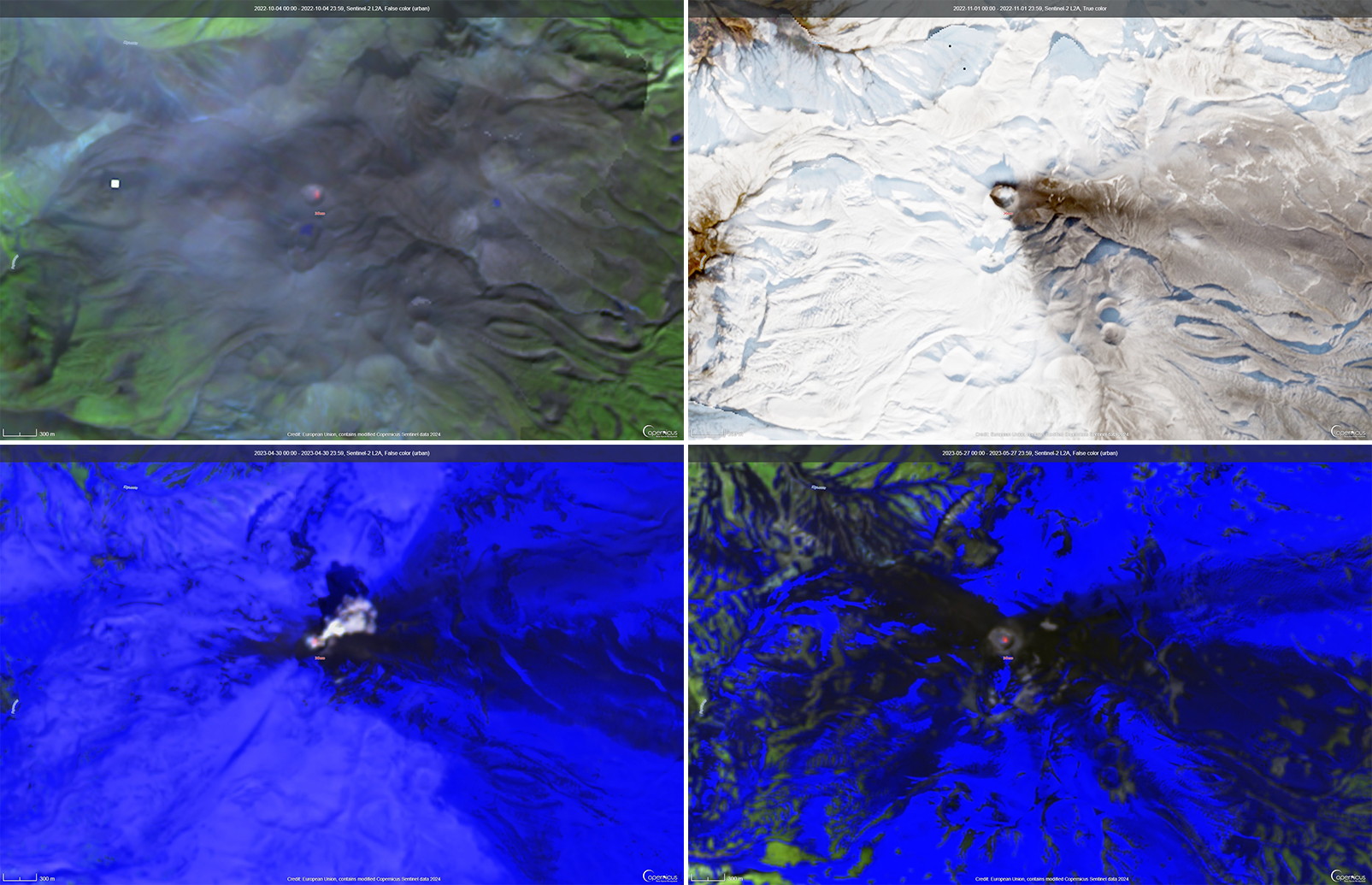
Activity continued to increase during the first week of February. Material from Main Crater traveled as far as 800 m down the Batuawang (S) and Batang (W) drainages and as far as 1 km W down the Beha (W) drainage on 4 February. On 6 February 43 earthquake events were recorded, and on 7 February, 62 events were recorded. White gas-and-steam emissions rose 25-250 m above both summit craters throughout the month. PVMBG reported an eruption began during the evening of 8 February around 1700. Photos showed incandescent material at Main Crater. Incandescent material had also descended the flank in at least two unconfirmed directions as far as 2 km from Main Crater, accompanied by ash plumes (figure 60). As a result, PVMBG increased the Volcano Alert Level (VAL) to 3 (the second highest level on a 1-4 scale).
Occasional nighttime webcam images showed three main incandescent lava flows of differing lengths traveling down the S, SW, and W flanks (figure 61). Incandescent rocks were visible on the upper flanks, possibly from ejected or collapsed material from the crater, and incandescence was the most intense at the summit. Based on analyses of satellite imagery and weather models, the Darwin VAAC reported that daily ash plumes during 16-20 February rose to 2.1-3 km altitude and drifted NNE, E, and SE. BNPB reported on 16 February that as many as 77 people were evacuated and relocated to the East Siau Museum. A webcam image taken at 2156 on 17 February possibly showed incandescent material descending the SE flank. Ash plumes rose to 2.1 km altitude and drifted SE during 22-23 February, according to the Darwin VAAC.
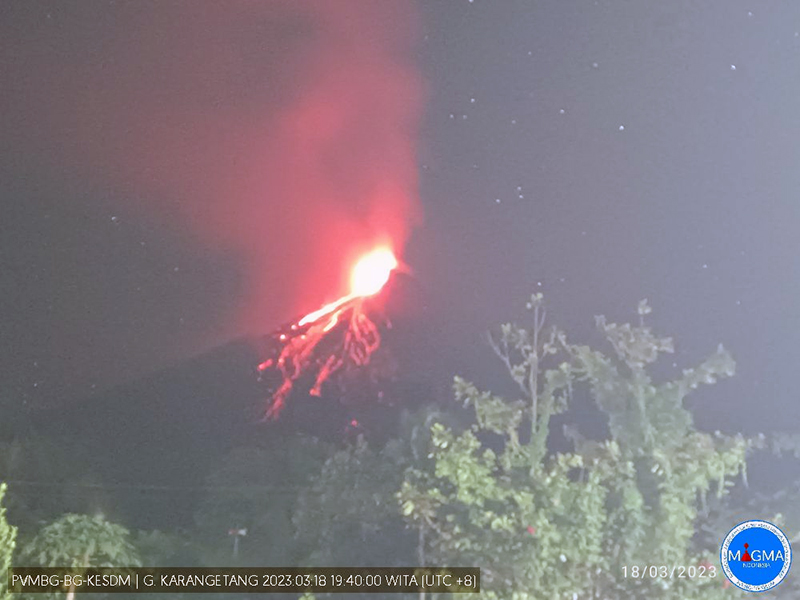
Incandescent avalanches of material and summit incandescence at Main Crater continued during March. White gas-and-steam emissions during March generally rose 25-150 m above the summit crater; on 31 March gas-and-steam emissions rose 200-400 m high. An ash plume rose to 2.4 km altitude and drifted S at 1710 on 9 March and a large thermal anomaly was visible in images taken at 0550 and 0930 on 10 March. Incandescent material was visible at the summit and on the flanks based on webcam images taken at 0007 and 2345 on 16 March, at 1828 on 17 March, at 1940 on 18 March, at 2311 on 19 March, and at 2351 on 20 March. Incandescence was most intense on 18 and 20 March and webcam images showed possible Strombolian explosions (figure 62). An ash plume rose to 2.4 km altitude and drifted SW on 18 March, accompanied by a thermal anomaly.
Summit crater incandescence at Main Crater and on the flanks persisted during April. Incandescent material at the S crater and on the flanks was reported at 0016 on 1 April. The lava flows had stopped by 1 April according to PVMBG, although incandescence was still visible up to 10 m high. Seismic signals indicating effusion decreased and by 6 April they were no longer detected. Incandescence was visible from both summit craters. On 26 April the VAL was lowered to 2 (the second lowest level on a 1-4 scale). White gas-and-steam emissions rose 25-200 m above the summit crater.
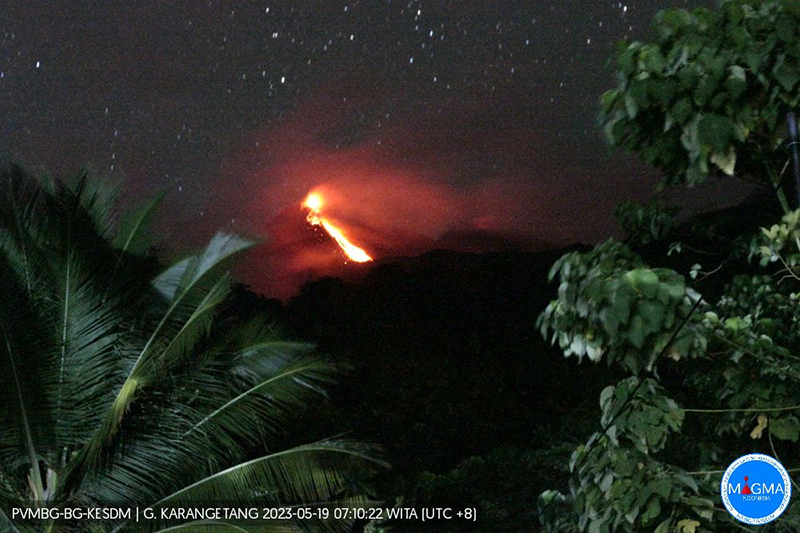
During May white gas-and-steam emissions generally rose 50-250 m above the summit, though it was often cloudy, which prevented clear views; on 21 May gas-and-steam emissions rose 50-400 m high. Nighttime N summit crater incandescence rose 10-25 m above the lava dome, and less intense incandescence was noted above Main Crater, which reached about 10 m above the dome. Sounds of falling rocks at Main Crater were heard on 15 May and the seismic network recorded 32 rockfall events in the crater on 17 May. Avalanches traveled as far as 1.5 km down the SW and S flanks, accompanied by rumbling sounds on 18 May. Incandescent material descending the flanks was captured in a webcam image at 2025 on 19 May (figure 63) and on 29 May; summit crater incandescence was observed in webcam images at 2332 on 26 May and at 2304 on 29 May. On 19 May the VAL was again raised to 3.
Occasional Main Crater incandescence was reported during June, as well as incandescent material on the flanks. White gas-and-steam emissions rose 10-200 m above the summit crater. Ash plumes rose to 2.1 km altitude and drifted SE and E during 2-4 June, according to the Darwin VAAC. Material on the flanks of Main Crater were observed at 2225 on 7 June, at 2051 on 9 June, at 0007 on 17 June, and at 0440 on 18 June. Webcam images taken on 21, 25, and 27 June showed incandescence at Main Crater and from material on the flanks.
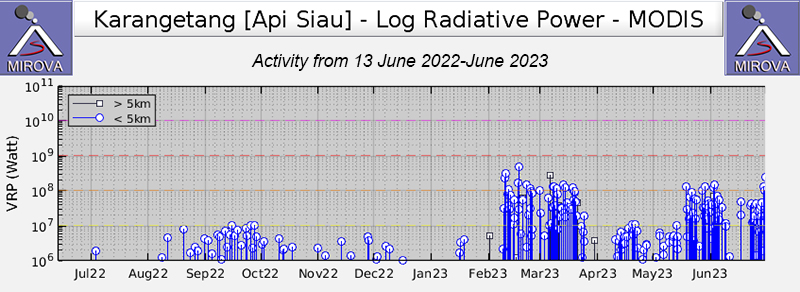
MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) analysis of MODIS satellite data showed strong thermal activity during mid-February through March and mid-May through June, which represented incandescent avalanches and lava flows (figure 64). During April through mid-May the power of the anomalies decreased but frequent anomalies were still detected. Brief gaps in activity occurred during late March through early April and during mid-June. Infrared satellite images showed strong lava flows mainly affecting the SW and S flanks, accompanied by gas-and-steam emissions (figure 65). According to data recorded by the MODVOLC thermal algorithm, there were a total of 79 thermal hotspots detected: 28 during February, 24 during March, one during April, five during May, and 21 during June.
Geologic Background. Karangetang (Api Siau) volcano lies at the northern end of the island of Siau, about 125 km NNE of the NE-most point of Sulawesi. The stratovolcano contains five summit craters along a N-S line. It is one of Indonesia's most active volcanoes, with more than 40 eruptions recorded since 1675 and many additional small eruptions that were not documented (Neumann van Padang, 1951). Twentieth-century eruptions have included frequent explosive activity sometimes accompanied by pyroclastic flows and lahars. Lava dome growth has occurred in the summit craters; collapse of lava flow fronts have produced pyroclastic flows.
Information Contacts: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as Indonesian Center for Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation, CVGHM), Jalan Diponegoro 57, Bandung 40122, Indonesia (URL: http://www.vsi.esdm.go.id/); MAGMA Indonesia, Kementerian Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral (URL: https://magma.esdm.go.id/v1); Badan Nasional Penanggulangan Bencana (BNPB), National Disaster Management Agency, Graha BNPB - Jl. Scout Kav.38, East Jakarta 13120, Indonesia (URL: http://www.bnpb.go.id/); Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Bureau of Meteorology, Northern Territory Regional Office, PO Box 40050, Casuarina, NT 0811, Australia (URL: http://www.bom.gov.au/info/vaac/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/); IDN Times, Jl. Jend. Gatot Subroto Kav. 27 3rd Floor Kuningan, Jakarta, Indonesia 12950, Status of Karangetang Volcano in Sitaro Islands Increases (URL: https://sulsel.idntimes.com/news/indonesia/savi/status-gunung-api-karangetang-di-kepulauan-sitaro-meningkat?page=all).
Ahyi (United States) — July 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Ahyi
United States
20.42°N, 145.03°E; summit elev. -75 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Intermittent hydroacoustic signals and discolored plumes during November 2022-June 2023
Ahyi seamount is a large, conical submarine volcano that rises to within 75 m of the ocean surface about 18 km SE of the island of Farallon de Pajaros in the Northern Marianas. The remote location of the seamount has made eruptions difficult to document, but seismic stations installed in the region confirmed an eruption in the vicinity in 2001. No new activity was detected until April-May 2014 when an eruption was detected by NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) divers, hydroacoustic sensors, and seismic stations (BGVN 42:04). New activity was first detected on 15 November by hydroacoustic sensors that were consistent with submarine volcanic activity. This report covers activity during November 2022 through June 2023 based on daily and weekly reports from the US Geological Survey.
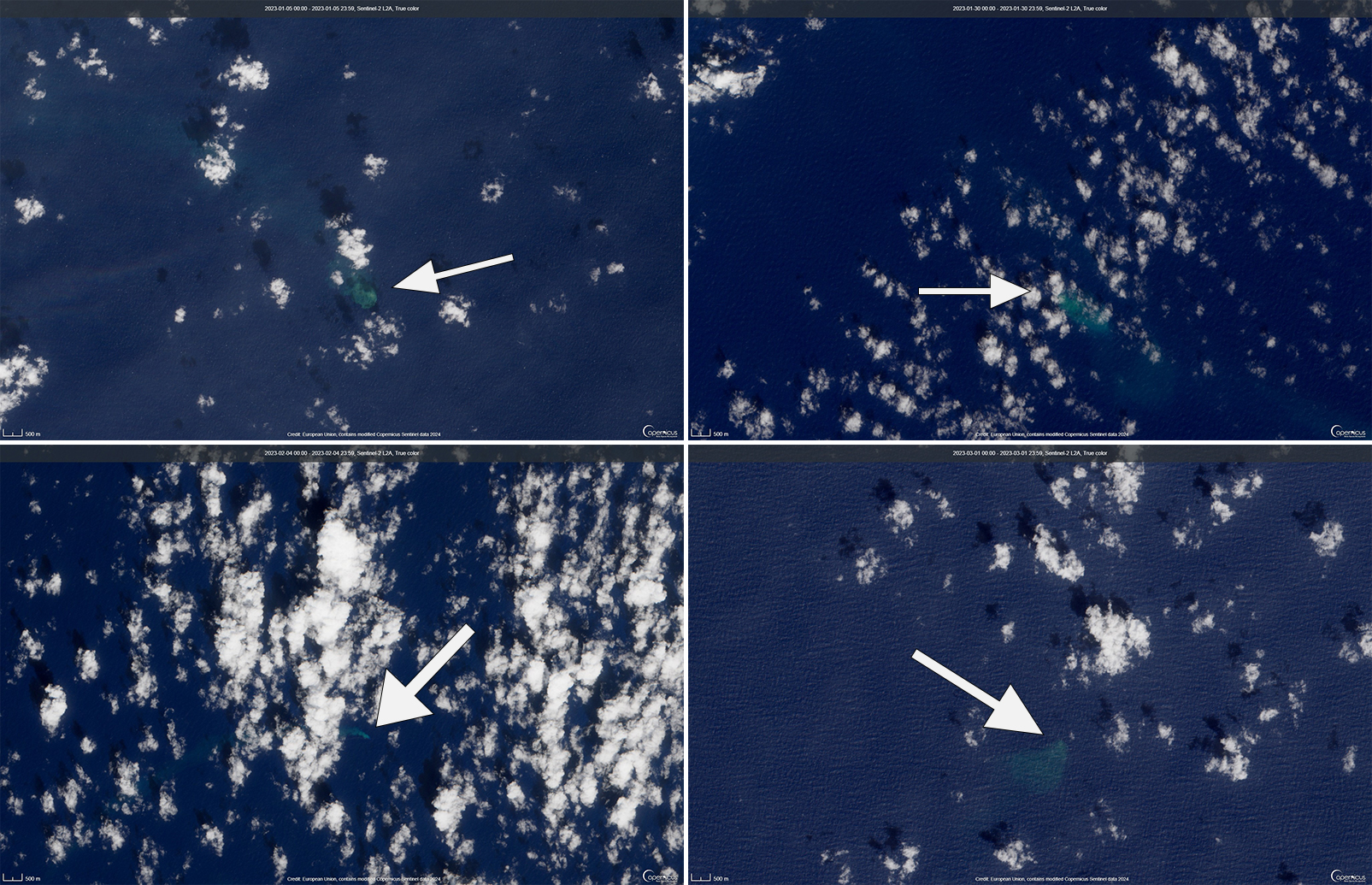
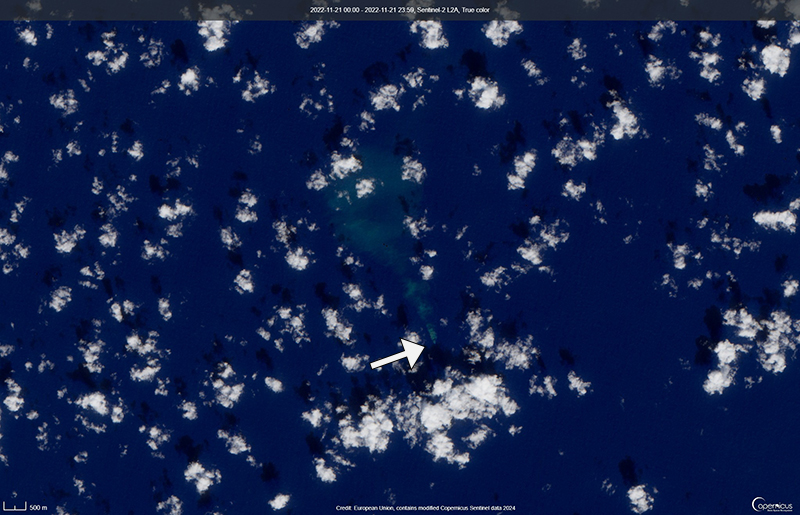
Starting in mid-October, hydroacoustic sensors at Wake Island (2.2 km E) recorded signals consistent with submarine volcanic activity, according to a report from the USGS issued on 15 November 2022. A combined analysis of the hydroacoustic signals and seismic stations located at Guam and Chichijima Island, Japan, suggested that the source of this activity was at or near the Ahyi seamount. After a re-analysis of a satellite image of the area that was captured on 6 November, USGS confirmed that there was no evidence of discoloration at the ocean surface. Few hydroacoustic and seismic signals continued through November, including on 18 November, which USGS suggested signified a decline or pause in unrest. A VONA (Volcano Observatory Notice for Aviation) reported that a discolored water plume was persistently visible in satellite data starting on 18 November (figure 6). Though clouds often obscured clear views of the volcano, another discolored water plume was captured in a satellite image on 26 November. The Aviation Color Code (ACC) was raised to Yellow (the second lowest level on a four-color scale) and the Volcano Alert Level (VAL) was raised to Advisory (the second lowest level on a four-level scale) on 29 November.
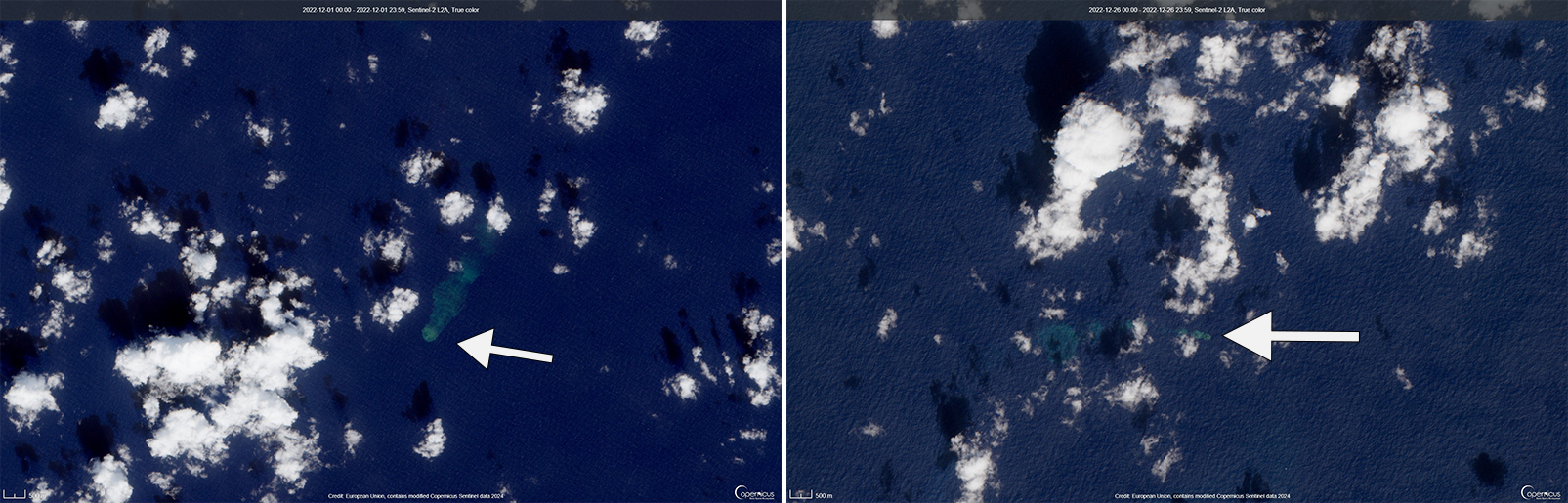
During December, occasional detections were recorded on the Wake Island hydrophone sensors and discolored water over the seamount remained visible. During 2-7, 10-12, and 16-31 December possible explosion signals were detected. A small area of discolored water was observed in high-resolution Sentinel-2 satellite images during 1-6 December (figure 7). High-resolution satellite images recorded discolored water plumes on 13 December that originated from the summit region; no observations indicated that activity breached the ocean surface. A possible underwater plume was visible in satellite images on 18 December, and during 19-20 December a definite but diffuse underwater plume located SSE from the main vent was reported. An underwater plume was visible in a satellite image taken on 26 December (figure 7).
Hydrophone sensors continued to detect signals consistent with possible explosions during 1-8 January 2023. USGS reported that the number of detections decreased during 4-5 January. The hydrophone sensors experienced a data outage that started at 0118 on 8 January and continued through 10 January, though according to USGS, possible explosions were recorded prior to the data outage and likely continued during the outage. A discolored water plume originating from the summit region was detected in a partly cloudy satellite image on 8 January. On 11-12 and 15-17 January possible explosion signals were recorded again. One small signal was detected during 22-23 January and several signals were recorded on 25 and 31 January. During 27-31 January a plume of discolored water was observed above the seamount in satellite imagery (figure 8).
Low levels of activity continued during February and March, based on data from pressure sensors on Wake Island. During 1 and 4-6 February activity was reported, and a submarine plume was observed on 4 February (figure 8). Possible explosion signals were detected during 7-8, 10, 13-14, and 24 February. During 1-2 and 3-5 March a plume of discolored water was observed in satellite imagery (figure 8). Almost continuous hydroacoustic signals were detected in remote pressure sensor data on Wake Island 2,270 km E from the volcano during 7-13 March. During 12-13 March water discoloration around the seamount was observed in satellite imagery, despite cloudy weather. By 14 March discolored water extended about 35 km, but no direction was noted. USGS reported that the continuous hydroacoustic signals detected during 13-14 March stopped abruptly on 14 March and no new detections were observed. Three 30 second hydroacoustic detections were reported during 17-19 March, but no activity was visible due to cloudy weather. A data outage was reported during 21-22 March, making pressure sensor data unavailable; a discolored water plume was, however, visible in satellite data. A possible underwater explosion signal was detected by pressure sensors at Wake Island on 26, 29, and 31 March, though the cause and origin of these events were unclear.
Similar low activity continued during April, May, and June. Several signals were detected during 1-3 April in pressure sensors at Wake Island. USGS suggested that these may be related to underwater explosions or earthquakes at the volcano, but no underwater plumes were visible in clear satellite images. The pressure sensors had data outages during 12-13 April and no data were recorded; no underwater plumes were visible in satellite images, although cloudy weather obscured most clear views. Eruptive activity was reported starting at 2210 on 21 May. On 22 May a discolored water plume that extended 4 km was visible in satellite images, though no direction was recorded. During 23-24 May some signals were detected by the underwater pressure sensors. Possible hydroacoustic signals were detected during 2-3 and 6-8 June. Multiple hydroacoustic signals were detected during 9-11 and 16-17 June, although no activity was visible in satellite images. One hydroacoustic signal was detected during 23-24 June, but there was some uncertainty about its association with volcanic activity. A single possible hydroacoustic signal was detected during 30 June to 1 July.
Geologic Background. Ahyi seamount is a large conical submarine volcano that rises to within 75 m of the ocean surface ~18 km SE of the island of Farallon de Pajaros in the northern Marianas. Water discoloration has been observed there, and in 1979 the crew of a fishing boat felt shocks over the summit area, followed by upwelling of sulfur-bearing water. On 24-25 April 2001 an explosive eruption was detected seismically by a station on Rangiroa Atoll, Tuamotu Archipelago. The event was well constrained (+/- 15 km) at a location near the southern base of Ahyi. An eruption in April-May 2014 was detected by NOAA divers, hydroacoustic sensors, and seismic stations.
Information Contacts: US Geological Survey, Volcano Hazards Program (USGS-VHP), 12201 Sunrise Valley Drive, Reston, VA, USA, https://volcanoes.usgs.gov/index.html; Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Kadovar (Papua New Guinea) — June 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Kadovar
Papua New Guinea
3.608°S, 144.588°E; summit elev. 365 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
An ash plume and weak thermal anomaly during May 2023
Kadovar is a 2-km-wide island that is the emergent summit of a Bismarck Sea stratovolcano. It lies off the coast of New Guinea, about 25 km N of the mouth of the Sepik River. Prior to an eruption that began in 2018, a lava dome formed the high point of the volcano, filling an arcuate landslide scarp open to the S. Submarine debris-avalanche deposits occur to the S of the island. The current eruption began in January 2018 and has comprised lava effusion from vents at the summit and at the E coast; more recent activity has consisted of ash plumes, weak thermal activity, and gas-and-steam plumes (BGVN 48:02). This report covers activity during February through May 2023 using information from the Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) and satellite data.
Activity during the reporting period was relatively low and mainly consisted of white gas-and-steam plumes that were visible in natural color satellite images on clear weather days (figure 67). According to a Darwin VAAC report, at 2040 on 6 May an ash plume rose to 4.6 km altitude and drifted W; by 2300 the plume had dissipated. MODIS satellite instruments using the MODVOLC thermal algorithm detected a single thermal hotspot on the SE side of the island on 7 May. Weak thermal activity was also detected in a satellite image on the E side of the island on 14 May, accompanied by a white gas-and-steam plume that drifted SE (figure 68).
Geologic Background. The 2-km-wide island of Kadovar is the emergent summit of a Bismarck Sea stratovolcano of Holocene age. It is part of the Schouten Islands, and lies off the coast of New Guinea, about 25 km N of the mouth of the Sepik River. Prior to an eruption that began in 2018, a lava dome formed the high point of the andesitic volcano, filling an arcuate landslide scarp open to the south; submarine debris-avalanche deposits occur in that direction. Thick lava flows with columnar jointing forms low cliffs along the coast. The youthful island lacks fringing or offshore reefs. A period of heightened thermal phenomena took place in 1976. An eruption began in January 2018 that included lava effusion from vents at the summit and at the E coast.
Information Contacts: Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Bureau of Meteorology, Northern Territory Regional Office, PO Box 40050, Casuarina, NT 0811, Australia (URL: http://www.bom.gov.au/info/vaac/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
San Miguel (El Salvador) — June 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
San Miguel
El Salvador
13.434°N, 88.269°W; summit elev. 2130 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Small gas-and-ash explosions during March and May 2023
San Miguel in El Salvador is a broad, deep crater complex that has been frequently modified by eruptions recorded since the early 16th century and consists of the summit known locally as Chaparrastique. Flank eruptions have produced lava flows that extended to the N, NE, and SE during the 17-19th centuries. The most recent activity has consisted of minor ash eruptions from the summit crater. The current eruption period began in November 2022 and has been characterized by frequent phreatic explosions, gas-and-ash emissions, and sulfur dioxide plumes (BGVN 47:12). This report describes small gas-and-ash explosions during December 2022 through May 2023 based on special reports from the Ministero de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (MARN).
Activity has been relatively low since the last recorded explosions on 29 November 2022. Seismicity recorded by the San Miguel Volcano Station (VSM) located on the N flank at 1.7 km elevation had decreased by 7 December. Sulfur dioxide gas measurements taken with DOAS (Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy) mobile equipment were below typical previously recorded values: 300 tons per day (t/d). During December, small explosions were recorded by the seismic network and manifested as gas-and-steam emissions.
Gas-and-ash explosions in the crater occurred during January 2023, which were recorded by the seismic network. Sulfur dioxide values remained low, between 300-400 t/d through 10 March. At 0817 on 14 January a gas-and-ash emission was visible in webcam images, rising just above the crater rim. Some mornings during February, small gas-and-steam plumes were visible in the crater. On 7 March at 2252 MARN noted an increase in degassing from the central crater; gas emissions were constantly observed through the early morning hours on 8 March. During the early morning of 8 March through the afternoon on 9 March, 12 emissions were registered, some accompanied by ash. The last gas-and-ash emission was recorded at 1210 on 9 March; very fine ashfall was reported in El Tránsito (10 km S), La Morita (6 km W), and La Piedrita (3 km W). The smell of sulfur was reported in Piedra Azul (5 km SW). On 16 March MARN reported that gas-and-steam emissions decreased.
Low degassing and very low seismicity were reported during April; no explosions have been detected between 9 March and 27 May. The sulfur dioxide emissions remained between 350-400 t/d; during 13-20 April sulfur dioxide values fluctuated between 30-300 t/d. Activity remained low through most of May; on 23 May seismicity increased. An explosion was detected at 1647 on 27 May generated a gas-and-ash plume that rose 700 m high (figure 32); a decrease in seismicity and gas emissions followed. The DOAS station installed on the W flank recorded sulfur dioxide values that reached 400 t/d on 27 May; subsequent measurements showed a decrease to 268 t/d on 28 May and 100 t/d on 29 May.
Geologic Background. The symmetrical cone of San Miguel, one of the most active volcanoes in El Salvador, rises from near sea level to form one of the country's most prominent landmarks. A broad, deep, crater complex that has been frequently modified by eruptions recorded since the early 16th century caps the truncated unvegetated summit, also known locally as Chaparrastique. Flanks eruptions of the basaltic-andesitic volcano have produced many lava flows, including several during the 17th-19th centuries that extended to the N, NE, and SE. The SE-flank flows are the largest and form broad, sparsely vegetated lava fields crossed by highways and a railroad skirting the base of the volcano. Flank vent locations have migrated higher on the edifice during historical time, and the most recent activity has consisted of minor ash eruptions from the summit crater.
Information Contacts: Ministero de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (MARN), Km. 5½ Carretera a Nueva San Salvador, Avenida las Mercedes, San Salvador, El Salvador (URL: http://www.snet.gob.sv/ver/vulcanologia).
Semisopochnoi (United States) — June 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Semisopochnoi
United States
51.93°N, 179.58°E; summit elev. 1221 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Occasional explosions, ash deposits, and gas-and-steam plumes during December 2022-May 2023
Semisopochnoi is located in the western Aleutians, is 20-km-wide at sea level, and contains an 8-km-wide caldera. The three-peaked Mount Young (formerly Cerberus) was constructed within the caldera during the Holocene. Each of these peaks contains a summit crater; the lava flows on the N flank appear younger than those on the S side. The current eruption period began in early February 2021 and has more recently consisted of intermittent explosions and ash emissions (BGVN 47:12). This report updates activity during December 2022 through May 2023 using daily, weekly, and special reports from the Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO). AVO monitors the volcano using local seismic and infrasound sensors, satellite data, web cameras, and remote infrasound and lightning networks.
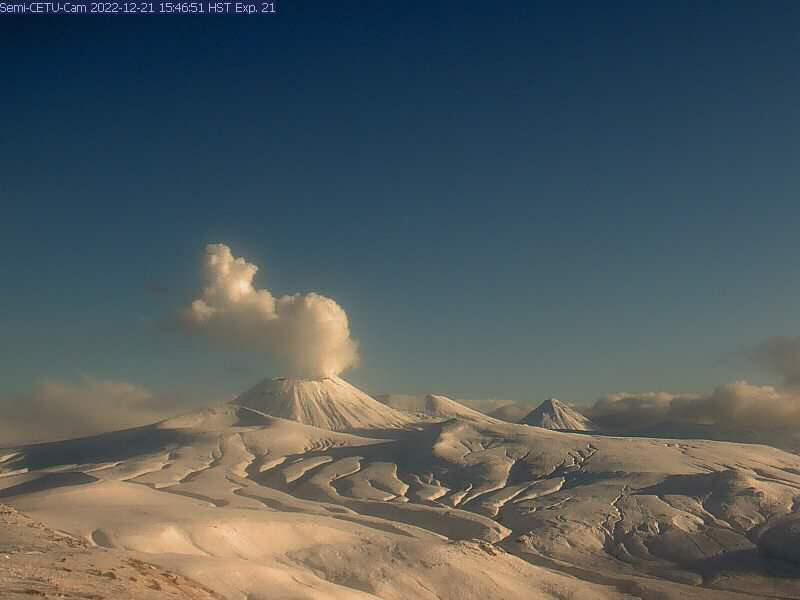
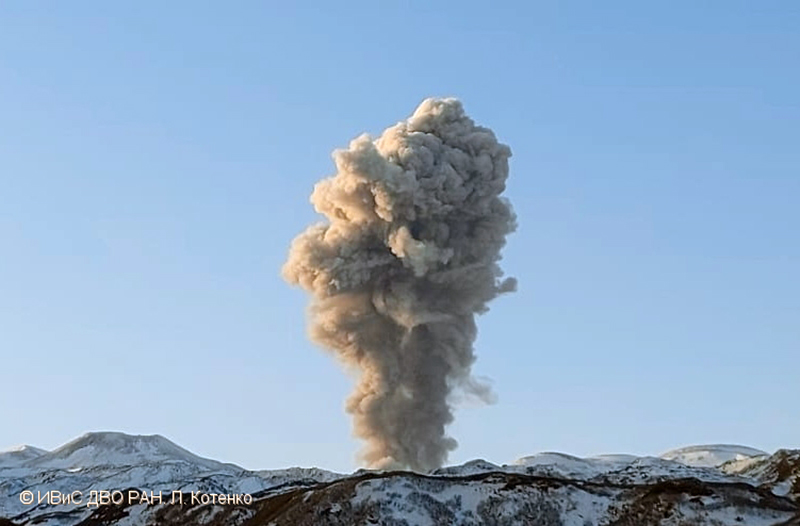
Activity during most of December 2022 was relatively quiet; according to AVO no eruptive or explosive activity was observed since 7 November 2022. Intermittent tremor and occasional small earthquakes were observed in geophysical data. Continuous gas-and-steam emissions were observed from the N crater of Mount Young in webcam images on clear weather days (figure 25). On 24 December, there was a slight increase in earthquake activity and several small possible explosion signals were detected in infrasound data. Eruptive activity resumed on 27 December at the N crater of Mount Young; AVO issued a Volcano Activity Notice (VAN) that reported minor ash deposits on the flanks of Mount Young that extended as far as 1 km from the vent, according to webcam images taken during 27-28 December (figure 26). No ash plumes were observed in webcam or satellite imagery, but a persistent gas-and-steam plume that might have contained some ash rose to 1.5 km altitude. As a result, AVO raised the Aviation Color Code (ACC) to Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale) and the Volcano Alert Level (VAL) to Watch (the second highest level on a four-level scale). Possible explosions were detected during 21 December 2022 through 1 January 2023 and seismic tremor was recorded during 30-31 December.
During January 2023 eruptive activity continued at the active N crater of Mount Young. Minor ash deposits were observed on the flanks, extending about 2 km SSW, based on webcam images from 1 and 3 January. A possible explosion occurred during 1-2 January based on elevated seismicity recorded on local seismometers and an infrasound signal recorded minutes later by an array at Adak. Though no ash plumes were observed in webcam or satellite imagery, a persistent gas-and-steam plume rose to 1.5 km altitude that might have carried minor traces of ash. Ash deposits were accompanied by periods of elevated seismicity and infrasound signals from the local geophysical network, which AVO reported were likely due to weak explosive activity. Low-level explosive activity was also detected during 2-3 January, with minor gas-and-steam emissions and a new ash deposit that was visible in webcam images. Low-level explosive activity was detected in geophysical data during 4-5 January, with elevated seismicity and infrasound signals observed on local stations. Volcanic tremor was detected during 7-9 January and very weak explosive activity was detected in seismic and infrasound data on 9 January. Weak seismic and infrasound signals were recorded on 17 January, which indicated minor explosive activity, but no ash emissions were observed in clear webcam images; a gas-and-steam plume continued to rise to 1.5 km altitude. During 29-30 January, ash deposits near the summit were observed on fresh snow, according to webcam images.
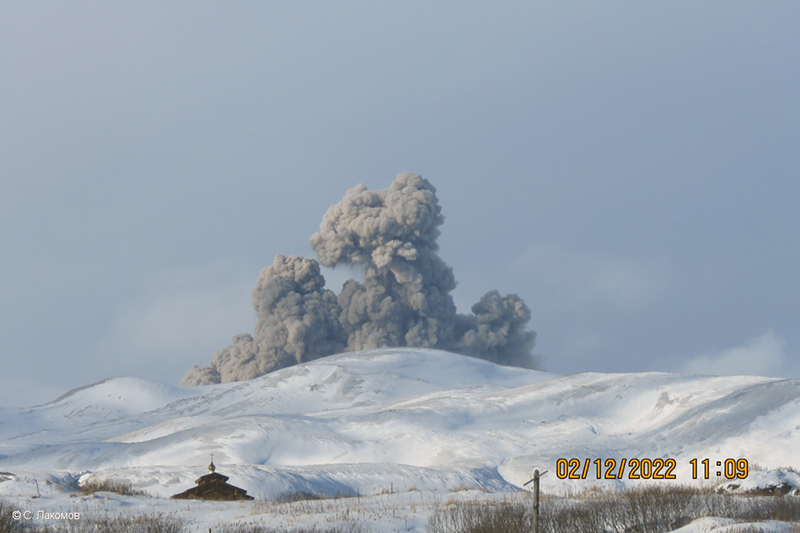
The active N cone at Mount Young continued to produce a gas-and-steam plume during February, but no ash emissions or explosive events were detected. Seismicity remained elevated with faint tremor during early February. Gas-and-steam emissions from the N crater were observed in clear webcam images on 11-13 and 16 February; no explosive activity was detected in seismic, infrasound, or satellite data. Seismicity has also decreased, with no significant seismic tremor observed since 25 January. Therefore, the ACC was lowered to Yellow (the second lowest level on a four-color scale) and the VAL was lowered to Advisory (the second lowest level on a four-color scale) on 22 February.
Gas-and-steam emissions persisted during March from the N cone of Mount Young, based on clear webcam images. A few brief episodes of weak tremor were detected in seismic data, although seismicity decreased over the month. A gas-and-steam plume detected in satellite data extended 150 km on 18 March. Low-level ash emissions from the N cone at Mount Young were observed in several webcam images during 18-19 March, in addition to small explosions and volcanic tremor. The ACC was raised to Orange and the VAL increased to Watch on 19 March. A small explosion was detected in seismic and infrasound data on 21 March.
Low-level unrest continued during April, although cloudy weather often obscured views of the summit; periods of seismic tremor and local earthquakes were recorded. During 3-4 April a gas-and-steam plume was visible traveling more than 200 km overnight; no ash was evident in the plume, according to AVO. A gas-and-steam plume was observed during 4-6 April that extended 400 km but did not seem to contain ash. Small explosions were detected in seismic and infrasound data on 5 April. Occasional clear webcam images showed continuing gas-and-steam emissions rose from Mount Young, but no ash deposits were observed on the snow. On 19 April small explosions and tremor were detected in seismic and infrasound data. A period of seismic tremor was detected during 22-25 April, with possible weak explosions on 25 April. Ash deposits were visible near the crater rim, but it was unclear if these deposits were recent or due to older deposits.
Occasional small earthquakes were recorded during May, but there were no signs of explosive activity seen in geophysical data. Gas-and-steam emissions continued from the N crater of Mount Young, based on webcam images, and seismicity remained slightly elevated. A new, light ash deposit was visible during the morning of 5 May on fresh snow on the NW flank of Mount Young. During 10 May periods of volcanic tremor were observed. The ACC was lowered to Yellow and the VAL to Advisory on 17 May due to no additional evidence of activity.
Geologic Background. Semisopochnoi, the largest subaerial volcano of the western Aleutians, is 20 km wide at sea level and contains an 8-km-wide caldera. It formed as a result of collapse of a low-angle, dominantly basaltic volcano following the eruption of a large volume of dacitic pumice. The high point of the island is Anvil Peak, a double-peaked late-Pleistocene cone that forms much of the island's northern part. The three-peaked Mount Cerberus (renamed Mount Young in 2023) was constructed within the caldera during the Holocene. Each of the peaks contains a summit crater; lava flows on the N flank appear younger than those on the south side. Other post-caldera volcanoes include the symmetrical Sugarloaf Peak SSE of the caldera and Lakeshore Cone, a small cinder cone at the edge of Fenner Lake in the NE part of the caldera. Most documented eruptions have originated from Young, although Coats (1950) considered that both Sugarloaf and Lakeshore Cone could have been recently active.
Information Contacts: Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667 USA (URL: https://avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA (URL: http://dggs.alaska.gov/).
Ebeko
Russia
50.686°N, 156.014°E; summit elev. 1103 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Continued explosions, ash plumes, and ashfall during October 2022-May 2023
Ebeko, located on the N end of Paramushir Island in the Kuril Islands, consists of three summit craters along a SSW-NNE line at the northern end of a complex of five volcanic cones. Eruptions date back to the late 18th century and have been characterized as small-to-moderate explosions from the summit crater, accompanied by intense fumarolic activity. The current eruption period began in June 2022 and has recently consisted of frequent explosions, ash plumes, and thermal activity (BGVN 47:10). This report covers similar activity during October 2022 through May 2023, based on information from the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT) and satellite data.
Activity during October consisted of explosive activity, ash plumes, and occasional thermal anomalies. Visual data by volcanologists from Severo-Kurilsk showed explosions producing ash clouds up to 2.1-3 km altitude which drifted E, N, NE, and SE during 1-8, 10, 16, and 18 October. KVERT issued several Volcano Observatory Notices for Aviation (VONA) on 7, 13-15, and 27 October 2022, stating that explosions generated ash plumes that rose to 2.3-4 km altitude and drifted 5 km E, NE, and SE. Ashfall was reported in Severo-Kurilsk (Paramushir Island, about 7 km E) on 7 and 13 October. Satellite data showed a thermal anomaly over the volcano on 15-16 October. Visual data showed ash plumes rising to 2.5-3.6 km altitude on 22, 25-29, and 31 October and moving NE due to constant explosions.
Similar activity continued during November, with explosions, ash plumes, and ashfall occurring. KVERT issued VONAs on 1-2, 4, 6-7, 9, 13, and 16 November that reported explosions and resulting ash plumes that rose to 1.7-3.6 km altitude and drifted 3-5 km SE, ESE, E, and NE. On 1 November ash plumes extended as far as 110 km SE. On 5, 8, 12, and 24-25 November explosions and ash plumes rose to 2-3.1 km altitude and drifted N and E. Ashfall was observed in Severo-Kurilsk on 7 and 16 November. A thermal anomaly was visible during 1-4, 16, and 20 November. Explosions during 26 November rose as high as 2.7 km altitude and drifted NE (figure 45).
Explosions and ash plumes continued to occur in December. During 1-2 and 4 December volcanologists from Severo-Kurilsk observed explosions that sent ash to 1.9-2.5 km altitude and drifted NE and SE (figure 46). VONAs were issued on 5, 9, and 16 December reporting that explosions generated ash plumes rising to 1.9 km, 2.6 km, and 2.4 km altitude and drifted 5 km SE, E, and NE, respectively. A thermal anomaly was visible in satellite imagery on 16 December. On 18 and 27-28 December explosions produced ash plumes that rose to 2.5 km altitude and drifted NE and SE. On 31 December an ash plume rose to 2 km altitude and drifted NE.
Explosions continued during January 2023, based on visual observations by volcanologists from Severo-Kurilsk. During 1-7 January explosions generated ash plumes that rose to 4 km altitude and drifted NE, E, W, and SE. According to VONAs issued by KVERT on 2, 4, 10, and 23 January, explosions produced ash plumes that rose to 2-4 km altitude and drifted 5 km N, NE, E, and ENE; the ash plume that rose to 4 km altitude occurred on 10 January (figure 47). Satellite data showed a thermal anomaly during 3-4, 10, 13, 16, 21, 22, and 31 January. KVERT reported that an ash cloud on 4 January moved 12 km NE. On 6 and 9-11 January explosions sent ash plumes to 4.5 km altitude and drifted W and ESE. On 13 January an ash plume rose to 3 km altitude and drifted SE. During 20-24 January ash plumes from explosions rose to 3.7 km altitude and drifted SE, N, and NE. On 21 January the ash plume drifted as far as 40 km NE. During 28-29 and 31 January and 1 February ash plumes rose to 4 km altitude and drifted NE.
During February, explosions, ash plumes, and ashfall were reported. During 1, 4-5 and 7-8 February explosions generated ash plumes that rose to 4.5 km altitude and drifted E and NE; ashfall was observed on 5 and 8 February. On 6 February an explosion produced an ash plume that rose to 3 km altitude and drifted 7 km E, causing ashfall in Severo-Kurilsk. A thermal anomaly was visible in satellite data on 8, 9, 13, and 21 February. Explosions on 9 and 12-13 February produced ash plumes that rose to 4 km altitude and drifted E and NE; the ash cloud on 12 February extended as far as 45 km E. On 22 February explosions sent ash to 3 km altitude that drifted E. During 24 and 26-27 February ash plumes rose to 4 km altitude and drifted E. On 28 February an explosion sent ash to 2.5-3 km altitude and drifted 5 km E; ashfall was observed in Severo-Kurilsk.
Activity continued during March; visual observations showed that explosions generated ash plumes that rose to 3.6 km altitude on 3, 5-7, and 9-12 March and drifted E, NE, and NW. Thermal anomalies were visible on 10, 13, and 29-30 March in satellite imagery. On 18, 21-23, 26, and 29-30 March explosions produced ash plumes that rose to 2.8 km altitude and drifted NE and E; the ash plumes during 22-23 March extended up to 76 km E. A VONA issued on 21 March reported an explosion that produced an ash plume that rose to 2.8 km altitude and drifted 5 km E. Another VONA issued on 23 March reported that satellite data showed an ash plume rising to 3 km altitude and drifted 14 km E.
Explosions during April continued to generate ash plumes. On 1 and 4 April an ash plume rose to 2.8-3.5 km altitude and drifted SE and NE. A thermal anomaly was visible in satellite imagery during 1-6 April. Satellite data showed ash plumes and clouds rising to 2-3 km altitude and drifting up to 12 km SW and E on 3 and 6 April (figure 48). KVERT issued VONAs on 3, 5, 14, 16 April describing explosions that produced ash plumes rising to 3 km, 3.5 km, 3.5 km, and 3 km altitude and drifting 5 km S, 5 km NE and SE, 72 km NNE, and 5 km NE, respectively. According to satellite data, the resulting ash cloud from the explosion on 14 April was 25 x 7 km in size and drifted 72-104 km NNE during 14-15 April. According to visual data by volcanologists from Severo-Kurilsk explosions sent ash up to 3.5 km altitude that drifted NE and E during 15-16, 22, 25-26, and 29 April.
The explosive eruption continued during May. Explosions during 3-4, 6-7, and 9-10 May generated ash plumes that rose to 4 km altitude and drifted SW and E. Satellite data showed a thermal anomaly on 3, 9, 13-14, and 24 May. During 12-16, 23-25, and 27-28 May ash plumes rose to 3.5 km altitude and drifted in different directions due to explosions. Two VONA notices were issued on 16 and 25 May, describing explosions that generated ash plumes rising to 3 km and 3.5 km altitude, respectively and extending 5 km E. The ash cloud on 25 May drifted 75 km SE.
Thermal activity in the summit crater, occasionally accompanied by ash plumes and ash deposits on the SE and E flanks due to frequent explosions, were visible in infrared and true color satellite images (figure 49).
Geologic Background. The flat-topped summit of the central cone of Ebeko volcano, one of the most active in the Kuril Islands, occupies the northern end of Paramushir Island. Three summit craters located along a SSW-NNE line form Ebeko volcano proper, at the northern end of a complex of five volcanic cones. Blocky lava flows extend west from Ebeko and SE from the neighboring Nezametnyi cone. The eastern part of the southern crater contains strong solfataras and a large boiling spring. The central crater is filled by a lake about 20 m deep whose shores are lined with steaming solfataras; the northern crater lies across a narrow, low barrier from the central crater and contains a small, cold crescentic lake. Historical activity, recorded since the late-18th century, has been restricted to small-to-moderate explosive eruptions from the summit craters. Intense fumarolic activity occurs in the summit craters, on the outer flanks of the cone, and in lateral explosion craters.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Home Reef
Tonga
18.992°S, 174.775°W; summit elev. -10 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Discolored plumes continued during November 2022-April 2023
Home Reef is a submarine volcano located in the central Tonga islands between Lateiki (Metis Shoal) and Late Island. The first recorded eruption occurred in the mid-19th century, when an ephemeral island formed. An eruption in 1984 produced a 12-km-high eruption plume, a large volume of floating pumice, and an ephemeral island 500 x 1,500 m wide, with cliffs 30-50 m high that enclosed a water-filled crater. Another island-forming eruption in 2006 produced widespread pumice rafts that drifted as far as Australia; by 2008 the island had eroded below sea level. The previous eruption occurred during October 2022 and was characterized by a new island-forming eruption, lava effusion, ash plumes, discolored water, and gas-and-steam plumes (BGVN 47:11). This report covers discolored water plumes during November 2022 through April 2023 using satellite data.
Discolored plumes continued during the reporting period and were observed in true color satellite images on clear weather days. Satellite images show light green-yellow discolored water extending W on 8 and 28 November 2022 (figure 31), and SW on 18 November. Light green-yellow plumes extended W on 3 December, S on 13 December, SW on 18 December, and W and S on 23 December (figure 31). On 12 January 2023 discolored green-yellow plumes extended to the NE, E, SE, and N. The plume moved SE on 17 January and NW on 22 January. Faint discolored water in February was visible moving NE on 1 February. A discolored plume extended NW on 8 and 28 March and NW on 13 March (figure 31). During April, clear weather showed green-blue discolored plumes moving S on 2 April, W on 7 April, and NE and S on 12 April. A strong green-yellow discolored plume extended E and NE on 22 April for several kilometers (figure 31).
Geologic Background. Home Reef, a submarine volcano midway between Metis Shoal and Late Island in the central Tonga islands, was first reported active in the mid-19th century, when an ephemeral island formed. An eruption in 1984 produced a 12-km-high eruption plume, large amounts of floating pumice, and an ephemeral 500 x 1,500 m island, with cliffs 30-50 m high that enclosed a water-filled crater. In 2006 an island-forming eruption produced widespread dacitic pumice rafts that drifted as far as Australia. Another island was built during a September-October 2022 eruption.
Information Contacts: Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Ambae
Vanuatu
15.389°S, 167.835°E; summit elev. 1496 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
New lava flow, ash plumes, and sulfur dioxide plumes during February-May 2023
Ambae, also known as Aoba, is a large basaltic shield volcano in Vanuatu. A broad pyroclastic cone containing three crater lakes (Manaro Ngoru, Voui, and Manaro Lakua) is located at the summit within the youngest of at least two nested calderas. Periodic phreatic and pyroclastic explosions have been reported since the 16th century. A large eruption more than 400 years ago resulted in a volcanic cone within the summit crater that is now filled by Lake Voui; the similarly sized Lake Manaro fills the western third of the caldera. The previous eruption ended in August 2022 that was characterized by gas-and-steam and ash emissions and explosions of wet tephra (BGVN 47:10). This report covers a new eruption during February through May 2023 that consisted of a new lava flow, ash plumes, and sulfur dioxide emissions, using information from the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) and satellite data.
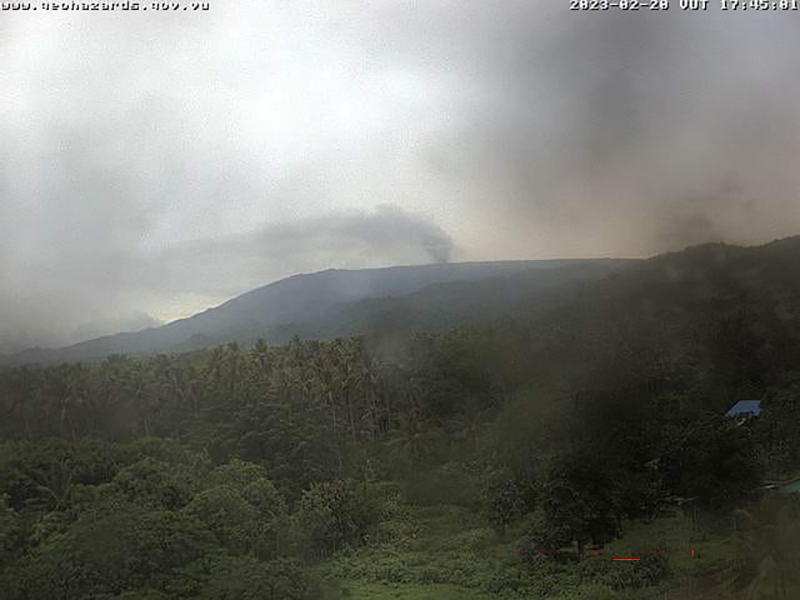
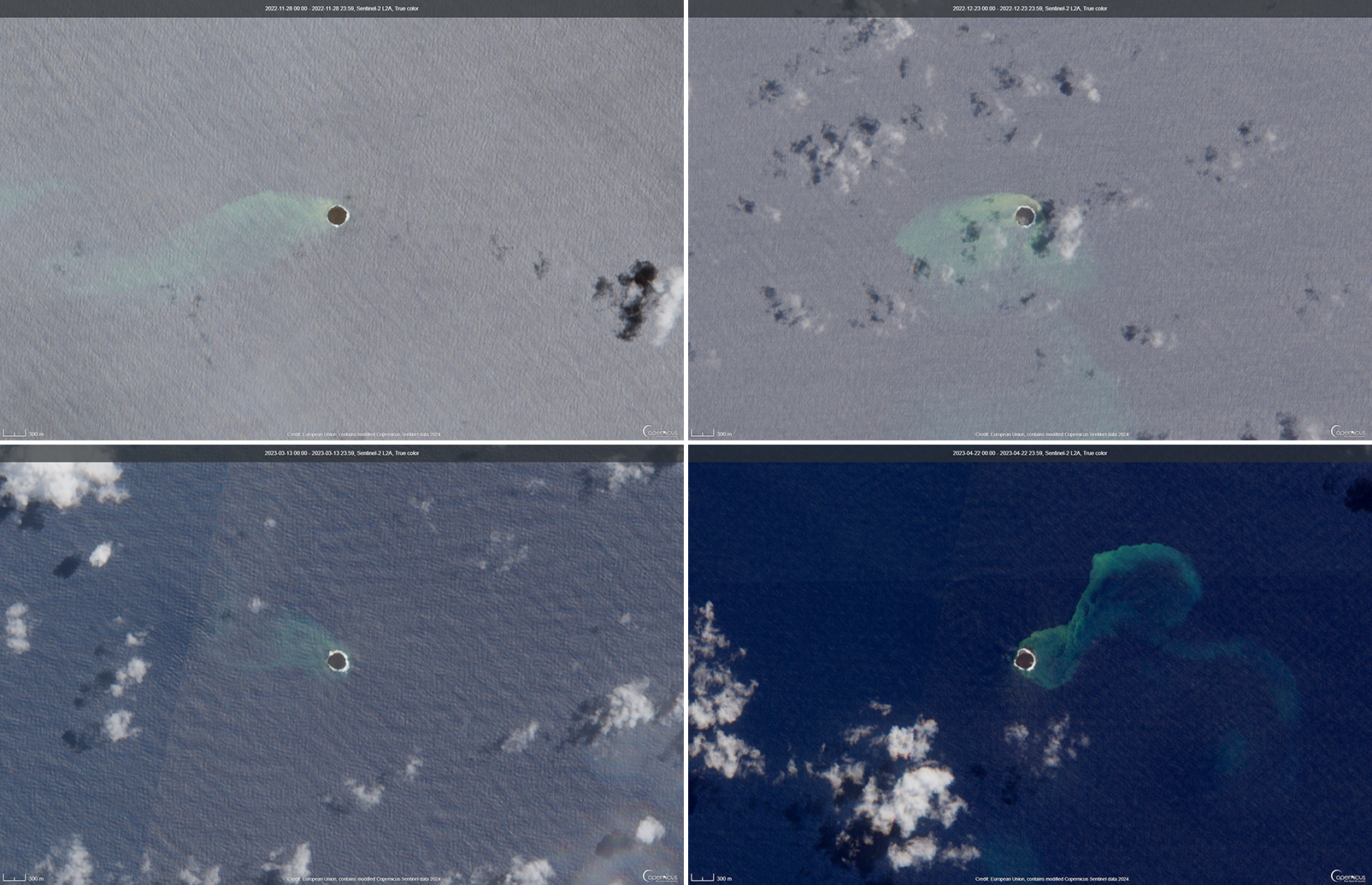
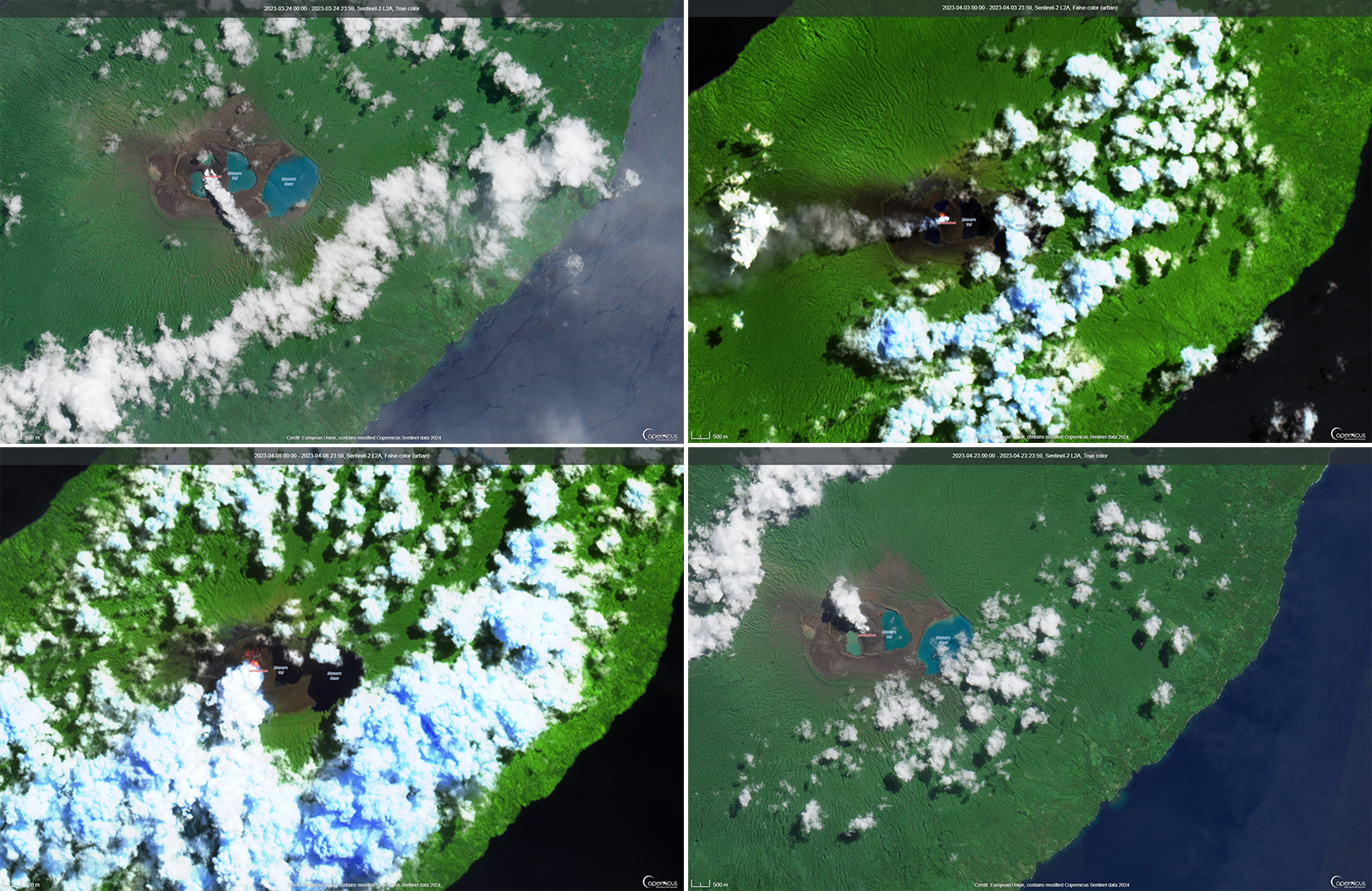
During the reporting period, the Alert Level remained at a 2 (on a scale of 0-5), which has been in place since December 2021. Activity during October 2022 through March 2023 remained relatively low and mostly consisted of gas-and-steam emissions in Lake Voui. VMGD reported that at 1300 on 15 November a satellite image captured a strong amount of sulfur dioxide rising above the volcano (figure 99), and that seismicity slightly increased. The southern and northern part of the island reported a strong sulfur dioxide smell and heard explosions. On 20 February 2023 a gas-and-ash plume rose 1.3 km above the summit and drifted SSW, according to a webcam image (figure 100). Gas-and-steam and possibly ash emissions continued on 23 February and volcanic earthquakes were recorded by the seismic network.
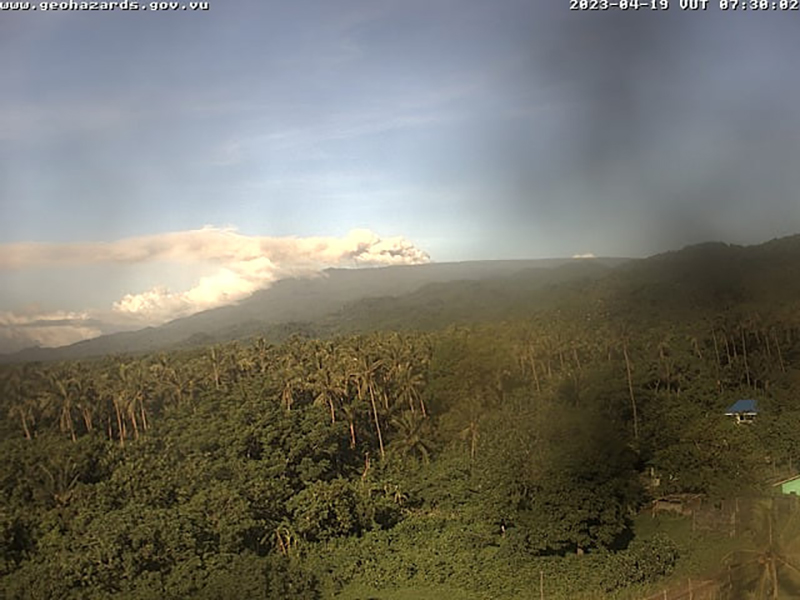
During April, volcanic earthquakes and gas-and-steam and ash emissions were reported from the cone in Lake Voui. VMGD reported that activity increased during 5-7 April; high gas-and-steam and ash plumes were visible, accompanied by nighttime incandescence. According to a Wellington VAAC report, a low-level ash plume rose as high as 2.5 km above the summit and drifted W and SW on 5 April, based on satellite imagery. Reports in Saratamata stated that a dark ash plume drifted to the WSW, but no loud explosion was heard. Webcam images from 2100 showed incandescence above the crater and reflected in the clouds. According to an aerial survey, field observations, and satellite data, water was no longer present in the lake. A lava flow was reported effusing from the vent and traveling N into the dry Lake Voui, which lasted three days. The next morning at 0745 on 6 April a gas-and-steam and ash plume rose 5.4 km above the summit and drifted ESE, based on information from VMGD (figure 101). The Wellington VAAC also reported that light ashfall was observed on the island. Intermittent gas-and-steam and ash emissions were visible on 7 April, some of which rose to an estimated 3 km above the summit and drifted E. Webcam images during 0107-0730 on 7 April showed continuing ash emissions. A gas-and-steam and ash plume rose 695 m above the summit crater at 0730 on 19 April and drifted ESE, based on a webcam image (figure 102).
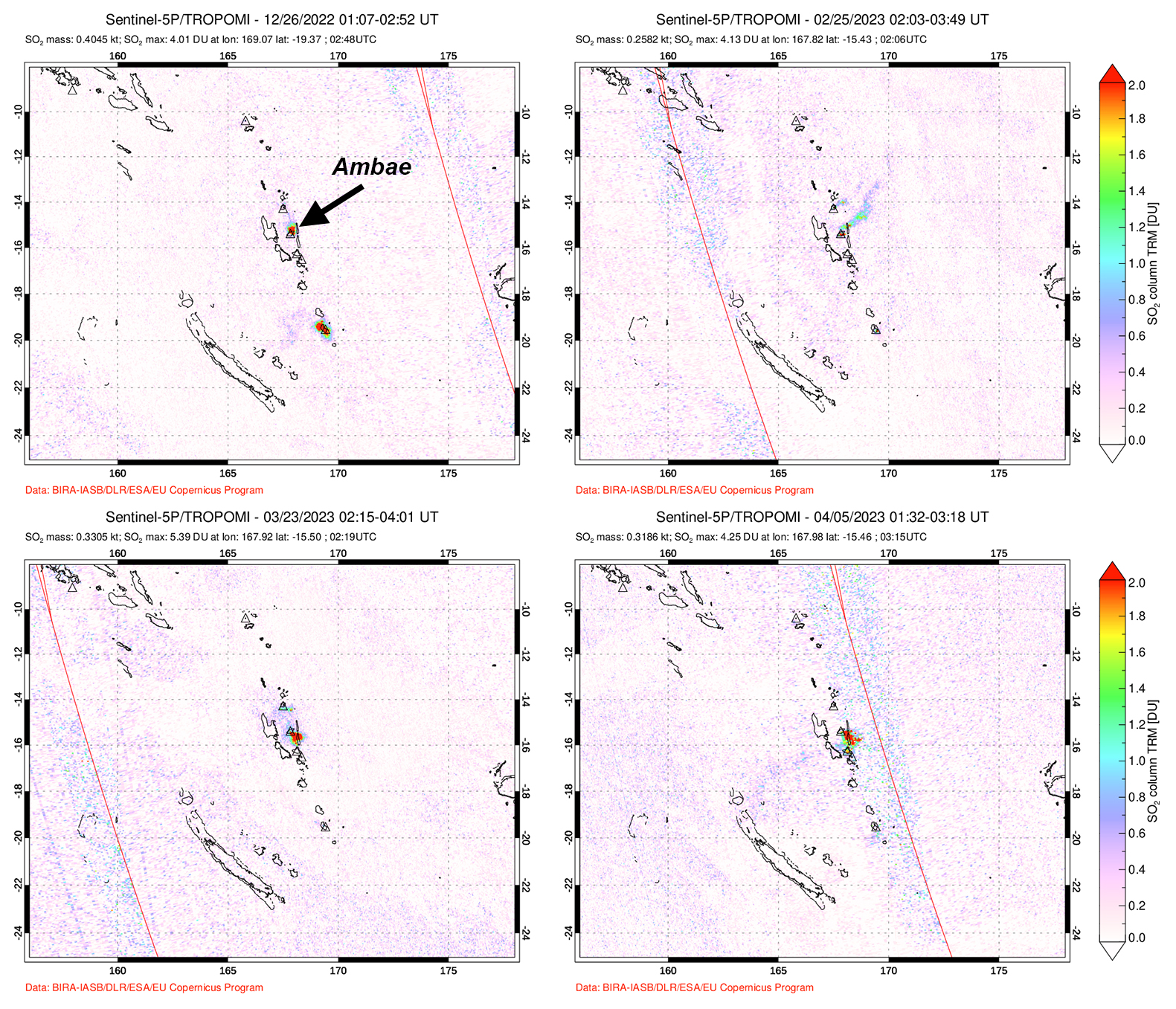
According to visual and infrared satellite data, water was visible in Lake Voui as late as 24 March 2023 (figure 103). The vent in the caldera showed a gas-and-steam plume drifted SE. On 3 April thermal activity was first detected, accompanied by a gas-and-ash plume that drifted W (figure 103). The lava flow moved N within the dry lake and was shown cooling by 8 April. By 23 April much of the water in the lake had returned. Occasional sulfur dioxide plumes were detected by the TROPOMI instrument on the Sentinel-5P satellite that exceeded 2 Dobson Units (DU) and drifted in different directions (figure 104).
Geologic Background. The island of Ambae, also known as Aoba, is a massive 2,500 km3 basaltic shield that is the most voluminous volcano of the New Hebrides archipelago. A pronounced NE-SW-trending rift zone with numerous scoria cones gives the 16 x 38 km island an elongated form. A broad pyroclastic cone containing three crater lakes (Manaro Ngoru, Voui, and Manaro Lakua) is located at the summit within the youngest of at least two nested calderas, the largest of which is 6 km in diameter. That large central edifice is also called Manaro Voui or Lombenben volcano. Post-caldera explosive eruptions formed the summit craters about 360 years ago. A tuff cone was constructed within Lake Voui (or Vui) about 60 years later. The latest known flank eruption, about 300 years ago, destroyed the population of the Nduindui area near the western coast.
Information Contacts: Geo-Hazards Division, Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD), Ministry of Climate Change Adaptation, Meteorology, Geo-Hazards, Energy, Environment and Disaster Management, Private Mail Bag 9054, Lini Highway, Port Vila, Vanuatu (URL: http://www.vmgd.gov.vu/, https://www.facebook.com/VanuatuGeohazardsObservatory/); Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Meteorological Service of New Zealand Ltd (MetService), PO Box 722, Wellington, New Zealand (URL: http://www.metservice.com/vaac/, http://www.ssd.noaa.gov/VAAC/OTH/NZ/messages.html); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Search Bulletin Archive by Publication Date
Select a month and year from the drop-downs and click "Show Issue" to have that issue displayed in this tab.
The default month and year is the latest issue available.
Scientific Event Alert Network Bulletin - Volume 14, Number 04 (April 1989)
Managing Editor: Lindsay McClelland
Aira (Japan)
Summit explosions diminish
Akutan (United States)
Small ash ejections resume
Ambrym (Vanuatu)
Ash plume and lava flow; recent eruption history
Apoyeque (Nicaragua)
Lake temperature measured
Asosan (Japan)
Brief ash emission
Atmospheric Effects (1980-1989) (Unknown)
No new stratospheric aerosols
Bagana (Papua New Guinea)
Lava flow advances; new avalanche deposits
Concepcion (Nicaragua)
Strong fuming
Galeras (Colombia)
Ash emission and strong seismicity; area residents alerted
Kilauea (United States)
Lava flows threaten houses
Langila (Papua New Guinea)
Moderate ash ejections and glow
Lengai, Ol Doinyo (Tanzania)
January inspection reveals no new lava
Lonquimay (Chile)
Continued tephra emission; cattle sickened by ash
Manam (Papua New Guinea)
Incandescent ejections and vapor release
Masaya (Nicaragua)
Lava lake drains; rockslides; gas emission
Momotombo (Nicaragua)
Burning gases from fumaroles
Niigata-Yakeyama (Japan)
Increased steaming, small ash eruption
Nyamulagira (DR Congo)
Lava erupts from summit and E flank
Poas (Costa Rica)
Crater lake gone; explosions and molten sulfur ponds
Popocatepetl (Mexico)
New fumaroles and large sulfur deposits
Rabaul (Papua New Guinea)
Seismicity and deformation at background level
Rincon de la Vieja (Costa Rica)
Crater lake sampled
Ruapehu (New Zealand)
Heat flow declines
Ruiz, Nevado del (Colombia)
Seismicity decreases
Soputan (Indonesia)
Ashfall damages houses and crops
Ulawun (Papua New Guinea)
Small ash emissions, minor seismic increases
Whakaari/White Island (New Zealand)
Tephra ejections continue
Aira
Japan
31.5772°N, 130.6589°E; summit elev. 1117 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Summit explosions diminish
Activity . . . in April was lower than in previous years. Single explosions were registered on the 1st, 5th, and 13th. The highest cloud rose 1,600 m on 13 April. Monthly ash accumulation at the observatory was 119 g/m2.
Geologic Background. The Aira caldera in the northern half of Kagoshima Bay contains the post-caldera Sakurajima volcano, one of Japan's most active. Eruption of the voluminous Ito pyroclastic flow accompanied formation of the 17 x 23 km caldera about 22,000 years ago. The smaller Wakamiko caldera was formed during the early Holocene in the NE corner of the caldera, along with several post-caldera cones. The construction of Sakurajima began about 13,000 years ago on the southern rim and built an island that was joined to the Osumi Peninsula during the major explosive and effusive eruption of 1914. Activity at the Kitadake summit cone ended about 4,850 years ago, after which eruptions took place at Minamidake. Frequent eruptions since the 8th century have deposited ash on the city of Kagoshima, located across Kagoshima Bay only 8 km from the summit. The largest recorded eruption took place during 1471-76.
Information Contacts: JMA.
Akutan (United States) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Akutan
United States
54.134°N, 165.986°W; summit elev. 1303 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Small ash ejections resume
Small ash ejections resumed in February 1989. Observer's initials, in brackets, follow their information in the chronology below.
27 February, 1200: A small, short-lived, vertical blast of ash and steam from the summit tephra cone was observed from a small boat on the N side of Akutan Island. The plume was probably <500 m high [LP].
15 March: An atmospheric shock wave was felt at 0900 by a pilot [NS] over the W shore of Akutan volcano. A black summit eruption plume rose rapidly, its top disappearing into cloud cover at 1,800 m altitude. Near Akutan village, the plume was observed at 0900 [RP] through a break in the clouds. Black ash quickly reached an estimated 2,300 m above the volcano. During the next several hours, emissions diminished and turned gray, with only a small white steam plume evident just before noon. At 1430, a small dark-gray eruption plume was observed from the village, drifting S [DM]. During an overflight at 1500, the summit tephra cone emitted dark steam [NS and HW]. Observations of the W and SW flanks revealed fresh ash covering the snow above 600 m elevation.
16 March, morning: A very light dusting of ash that had fallen the previous night was noticed in Akutan village [DM]. At 1100 the volcano's summit region was white with fresh snow [HW].
Between 17 and 31 March: A crater on the E side of the summit cone began to emit steam at some time during this period [DM]. Previously, steam had emerged only from the cone's W side.
28-29 March: Akutan's summit was black with fresh-looking ash. Minor amounts of steam were emitted [CL].
31 March, about 1945: A large white plume was observed at least 600 m above Akutan from a U.S. Coast Guard plane [SR]. The plume top had drifted 7 km S. No eruptive activity had been seen from near the village at 1900 [LL]. No further activity was observed from 31 March until the end of the report period on 7 April.
Observers (initials in brackets): Lawrence Prokopioff, Richard Petre, David McGlashan, Harold Wilson, and Linda Logan, Akutan Village and vicinity; Nick Sias, Peninsula Airways; Craig Leth, FAA; Lieutenant Commander Steve Rapalus and his crew, U.S. Coast Guard.
Geologic Background. Akutan contains a 2-km-wide caldera with a large cinder cone in the NE part of the caldera that has been the source of frequent explosive eruptions and occasional lava effusion that covers the caldera floor. An older, largely buried caldera was formed during the late Pleistocene or early Holocene. Two volcanic centers are located on the NW flank. Lava Peak is of Pleistocene age, and a cinder cone lower on the flank produced a lava flow in 1852 that extended the shoreline of the island and forms Lava Point. The 60-365 m deep younger caldera was formed during a major explosive eruption about 1,600 years ago and contains at least three lakes. A lava flow in 1978 traveled through a narrow breach in the north caldera rim almost to the coast. Fumaroles occur at the base of the caldera cinder cone, and hot springs are located NE of the caldera at the head of Hot Springs Bay valley and along the shores of Hot Springs Bay.
Information Contacts: J. Reeder, ADGGS.
Ambrym
Vanuatu
16.25°S, 168.12°E; summit elev. 1334 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Ash plume and lava flow; recent eruption history
On 31 April at 0730, the meteorological service in Wellington, New Zealand detected volcanic ash clouds near 16.1°S, 168.1°E on satellite images. The main cloud had an estimated diameter of 15-30 km, with streamers to 115 km NNE, and moved at a speed of ~30 km/hour. The plume height was estimated at ~6 km from an aircraft at 0350. The meteorological service in Darwin, Australia also located a steam/ash cloud on visible satellite images at 1030. NOAA infrared and visible images showed only a small cloud on 31 April at 1344 during clear weather. The following is a report from J.P. Eissen, M. Lardy, M. Monzier, L. Mollard, and D. Charley of ORSTOM (Nouméa and Port Vila).
Description and history. "Ambrym, a large stratovolcano with a 15-km-wide caldera (figure 1), is one of the most active volcanoes of the New Hebrides arc, which includes Yasur (Tanna Island), Lopevi (Lopevi Island), and the shallow submarine volcano Karua (between Epi and Tongoa Islands).
". . . . In the historical period, at least five types of activity can be distinguished. From the most to least frequent, these are: 1) intra-caldera, intermittent, Strombolian-type activity with mild extra-caldera ashfalls, but without lava flows (occurs almost every year); 2) intracaldera eruption frequently preceded by lava lake formation in the crater — generally starts with emission of a Plinian column that produces extra-caldera ashfalls, followed by intra-caldera lava flows; 3) activity similar to (2) followed by lava overflowing from the caldera (1863 (?), 1913-14, 1942 eruptions); 4) extra-caldera lava emission from fissures (1894, 1913, 1929, 1936 eruptions) — sometimes evolves toward 5) formation of pyroclastic cones, sometimes accompanied by lava flows (1888, 1915, 1929 eruptions). Several of these types of actvity have occurred consecutively in the different phases of a single eruption (as in 1913-14 and 1929, the two major Ambrym eruptions).
"On 13 November 1986, an aircraft pilot reported an increase in activity at the volcano. Ash emission became significant 17 November, but activity decreased 19-20 November. A new cone formed (Cheney, 1986) 3 km E of the active Marum cone (figure 1) and produced an intra-caldera lava flow ~4 km long (Melchior, 1988).
May 1988 activity. "On 27 May 1988, a lava lake ~50 m in diameter was observed in Mbwelesu's crater. Benbow was emitting white clouds whereas Marum and Mbwelesu were emitting dark grey clouds (Melchior, 1988). On 10 August, intracaldera lava flowed S more than 1.5 km from what appeared to be a new cone, but was possibly an extension of Mbwelesu (Cheney, 1988). The flow (still warm) extended ~5 km S (Charley, 1988). This eruption had ended by 23 August.
April 1989 activity. "At 1000 on 24 April 1989, a pilot observed a large plume rising ~3,500 m above the volcano. A lava flow from the the 1988 cone was following the same path as the 1988 flow but was a few kilometers longer. It followed the creek near Endou village (figure 1) and may or may not have extended outside the caldera [but see 14:10]. About 1 km2 of Otas village was reported to be burned. On the night of 29 April, large areas of red glow were seen from boats cruising in the area, and winds carried ash NW. Young vegetation on the S flank was burned (possibly by acid rain), and rain water had a strong taste. Local inhabitants said that the eruption was normal for the volcano even though there were more loud roaring noises and small earthquakes than in 1986 or 1988. A local pilots' strike prevented further observation of the eruption, but on 10 May the volcano was still active." The eruption apparently stopped sometime before 14 May.
References. Charley, D., 1988, Rapport de Mission à Ambrym en Aout 1988: Document ORSTOM, Port Vila, 5 p.
Cheney, C.S., 1986, New volcanic eruption near Endu, SE Ambrym: Geology Dept Memo, 24 November 1986, 1 p.
Cheney, C.S., 1988, Volcanic activity report, Ambrym and Epi: Geology Dept Memo, 17 August 1988, 1 p.
Melchior, A.H., 1988, Rapport de Mission de Reconnaissance Volcanologique Ambrym (25-28 May 1988) et à Tanna (14 May 1988): Document ORSTOM, Nouméa, 10 p.
Quantin, P., 1978, Archipel des Nouvelles-Hébrides: Atlas des Sols et de quelques Données du Milieu: Cartes Pédologiques, des Formes du Relief, Géologiques et de la Végétation; ORSTOM (18 sheets).
Stephenson, P.J., McCall, G.J.H., Le Maitre, R.W., and Robinson, G.P., 1968, The Ambrym Island Research Project, in Warden, A.J., ed., New Hebrides Geological Survey Annual Report 1966: Port Vila, p. 9-15.
Geologic Background. Ambrym, a large basaltic volcano with a 12-km-wide caldera, is one of the most active volcanoes of the New Hebrides Arc. A thick, almost exclusively pyroclastic sequence, initially dacitic then basaltic, overlies lava flows of a pre-caldera shield volcano. The caldera was formed during a major Plinian eruption with dacitic pyroclastic flows about 1,900 years ago. Post-caldera eruptions, primarily from Marum and Benbow cones, have partially filled the caldera floor and produced lava flows that ponded on the floor or overflowed through gaps in the caldera rim. Post-caldera eruptions have also formed a series of scoria cones and maars along a fissure system oriented ENE-WSW. Eruptions have apparently occurred almost yearly during historical time from cones within the caldera or from flank vents. However, from 1850 to 1950, reporting was mostly limited to extra-caldera eruptions that would have affected local populations.
Information Contacts: J. Eissen, M. Lardy, M. Monzier, ORSTOM, New Caledonia; L. Mollard, and D. Chaney, ORSTOM, Vanuatu; J. Latter, DSIR Geophysics, Wellington; S. Kusselson, SAB; J. Temakon, Dept of Geology, Mines, and Rural Water Supply, Port Vila.
Apoyeque (Nicaragua) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Apoyeque
Nicaragua
12.242°N, 86.342°W; summit elev. 518 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Lake temperature measured
Surface temperature of the lake (measured with an 8-14 micrometer bandpass radiometer) varied between 28 and 30°C during fieldwork 8 April. A water temperature measured near the N shore was 25.5°C.
Geologic Background. The Apoyeque volcanic complex occupies the broad Chiltepe Peninsula, which extends into south-central Lake Managua. The peninsula is part of the Chiltepe pyroclastic shield volcano, one of three large ignimbrite shields on the Nicaraguan volcanic front. A 2.8-km wide, 400-m-deep, lake-filled caldera whose floor lies near sea level truncates the low Apoyeque edifice, which rises only about 500 m above the lake shore. The caldera was the source of a thick deposit of dacitic pumice that covers the surrounding area. The 2.5 x 3 km lake-filled Xiloá (Jiloá) maar is located immediately SE of Apoyeque. The Talpetatl lava dome was constructed between Laguna Xiloá and Lake Managua. Pumiceous pyroclastic flows from Laguna Xiloá were erupted about 6,100 years ago and overlie deposits of comparable age from the Masaya Plinian eruption.
Information Contacts: C. Oppenheimer, Open Univ.
Asosan
Japan
32.8849°N, 131.085°E; summit elev. 1592 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Brief ash emission
On 27 April, the staff of AWS visited the crater rim as they have every day for the past 20 years. A vent on the SE floor of Crater 1 was releasing yellow vapor and ash to 30 m, accompanied by larger tephra. The Aso Volcano Disaster Prevention Authority closed a 1-km area near the crater to tourists. The area was reopened 2 May, when a field survey revealed only white vapor reaching ~5-6 m above the vent.
Glow on the crater floor has been observed every night since October 1988. A maximum temperature of 232°C was measured (with a infrared radiation thermometer) at a glowing site on 18 April.
Isolated tremor remained frequent in April. The daily number of tremor episodes was 100-250, with a monthly total of ~5,760 (figure 10). Amplitude of continuous tremor remained the same.
Geologic Background. The 24-km-wide Asosan caldera was formed during four major explosive eruptions from 300,000 to 90,000 years ago. These produced voluminous pyroclastic flows that covered much of Kyushu. The last of these, the Aso-4 eruption, produced more than 600 km3 of airfall tephra and pyroclastic-flow deposits. A group of 17 central cones was constructed in the middle of the caldera, one of which, Nakadake, is one of Japan's most active volcanoes. It was the location of Japan's first documented historical eruption in 553 CE. The Nakadake complex has remained active throughout the Holocene. Several other cones have been active during the Holocene, including the Kometsuka scoria cone as recently as about 210 CE. Historical eruptions have largely consisted of basaltic to basaltic-andesite ash emission with periodic strombolian and phreatomagmatic activity. The summit crater of Nakadake is accessible by toll road and cable car, and is one of Kyushu's most popular tourist destinations.
Information Contacts: JMA.
Atmospheric Effects (1980-1989) (Unknown) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Atmospheric Effects (1980-1989)
Unknown
Unknown, Unknown; summit elev. m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
No new stratospheric aerosols
Recent eruptions have apparently contributed little new aerosol material to the stratosphere. Aerosol concentrations over Obninsk and Teplocluchenka, USSR increased slightly during fall and winter 1988 from spring and summer values (figure 66). Poor weather limited observations from Mauna Loa, Hawaii; the one successful April 1989 observation registered the lowest integrated aerosol backscattering measured since before the 1982 eruption of El Chichón.
Geologic Background. The enormous aerosol cloud from the March-April 1982 eruption of Mexico's El Chichón persisted for years in the stratosphere, and led to the Atmospheric Effects section becoming a regular feature of the Bulletin. Descriptions of the initial dispersal of major eruption clouds remain with the individual eruption reports, but observations of long-term stratospheric aerosol loading will be found here.
Information Contacts: Sergei Khmelevtsov, Yu. Kaufman, and B. Chen, Institute of Experimental Meteorology, Lenin St. 82, Obninsk, Kaluga Reg., USSR; Thomas DeFoor, Mauna Loa Observatory, P. O. Box 275, Hilo, HI 96720 USA.
Bagana (Papua New Guinea) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Bagana
Papua New Guinea
6.137°S, 155.196°E; summit elev. 1855 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Lava flow advances; new avalanche deposits
"Observer reports and recorded seismicity indicate that increased activity . . . is continuing. Inspections on 3 and 4 March by personnel from Bougainville Island Copper Ltd. revealed that a new deposit of avalanche debris was present on the SE flank. The deposit was dark in colour and extended from the summit . . . to the mid-flank level (~1,000 m altitude). Vegetation around the edges of the deposit had been killed. The avalanche occurred sometime between 3 February and 3 March. The profile of E flank lava flow's terminus had changed, suggesting overriding of older parts of the flow by new lobes and possible advance of the flow nose.
"On 18 March, the pilot of a passing aircraft reported a lava flow on the SE flank and copious ash around and above the volcano. However, an inspection on 12 April indicated that the deposit was probably formed by a rockfall from the inactive nose of of the E flank lava flow (at ~880 m altitude). The proximal part of the flow was still active. It appeared that a new thin lobe was overriding older lava in the main flow channel. An ash mantle on the upper E flank indicated that rockfalls (detected seismically) were occurring in this area. The flow was bent to the S at ~1,150 m altitude. It may be significant that the first lobe of this now compound flow terminated at about this point.
"Since 8 March (when seismic recording . . . was restored) seismicity has been dominated by relatively long-duration, low-frequency, spindle-shaped events. This activity is attributed to rockfalls on the margin of the active lava flow. Daily totals of these events ranged between ~90 and 300. Summit activity has continued to consist of moderate to strong emission of white vapour rich in sulphur dioxide."
Geologic Background. Bagana volcano, in a remote portion of central Bougainville Island, is frequently active. This massive symmetrical cone was largely constructed by an accumulation of viscous andesitic lava flows. The entire edifice could have been constructed in about 300 years at its present rate of lava production. Eruptive activity is characterized by non-explosive effusion of viscous lava that maintains a small lava dome in the summit crater, although occasional explosive activity produces pyroclastic flows. Lava flows with tongue-shaped lobes up to 50 m thick and prominent levees descend the flanks on all sides.
Information Contacts: C. McKee, RVO.
Concepcion (Nicaragua) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Concepcion
Nicaragua
11.538°N, 85.622°W; summit elev. 1700 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Strong fuming
During fieldwork 24 March, fuming obscured the interior of the summit crater. Most of the gas appeared to originate below a step in the crater's inner NE wall. A zone of weak fumaroles about 30 m below the rim on the inner E crater wall had a maximum surface temperature of 42°C (measured by an 8-14 micrometer bandpass infrared thermometer from a distance of about 300 m), suggesting gas temperatures of around 100°C.
Geologic Background. Volcán Concepción is one of Nicaragua's highest and most active volcanoes. The symmetrical basaltic-to-dacitic stratovolcano forms the NW half of the dumbbell-shaped island of Ometepe in Lake Nicaragua and is connected to neighboring Madera volcano by a narrow isthmus. A steep-walled summit crater is 250 m deep and has a higher western rim. N-S-trending fractures on the flanks have produced chains of spatter cones, cinder cones, lava domes, and maars located on the NW, NE, SE, and southern sides extending in some cases down to Lake Nicaragua. Concepción was constructed above a basement of lake sediments, and the modern cone grew above a largely buried caldera, a small remnant of which forms a break in slope about halfway up the N flank. Frequent explosive eruptions during the past half century have increased the height of the summit significantly above that shown on current topographic maps and have kept the upper part of the volcano unvegetated.
Information Contacts: C. Oppenheimer, Open Univ.
Galeras
Colombia
1.22°N, 77.37°W; summit elev. 4276 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Ash emission and strong seismicity; area residents alerted
Frequent ash ejection in early May was accompanied by increased seismicity (figure 1) and SO2 emission. The strong seismic swarm that began 5 April at 1000 and saturated one seismograph was not associated with eruptive activity. COSPEC measurements the next day showed a sharp rise in SO2 emission to >1,200 metric tons/day (t/d) from 30-40 t/d 19-20 March [SO2 flux rose above 1,000 t/d on four days in April, see figure 12]. Glow was observed within the active (El Pinta) vent and by mid-April rocks 2 m below the rim had reached almost 600°C. The seismic swarm and glow prompted officials to increase the alert status to "yellow." A hazard map was published in a local newspaper and residents of areas designated as hazardous were urged to move, if possible, to a safer region. As of late April, a dense water-rich gas plume continued to rise 1-2 km above the crater and low-level seismicity persisted, but no deformation was evident.
4-5 May. After 10 hours of gradual increases in both background tremor (<1 mm peak to peak) and small long-period seismic events, ash was erupted between 0613 and 0830 on 4 May. Although emission rates were low, column heights reached 3.3 km. Ash composed of lithic particles and some plagioclase crystals fell towards the SW and E; a light dusting of ash fell on Pasto (population 350,000) at the volcano's E foot. Seismicity fluctuated between low and moderate levels for the next 11 hours before ash emission resumed at 1743. There were no recognizable immediate seismic precursors but the onset of the activity was accompanied by increased tremor. The rate of ash emission was again low, with the column pulsing at times to 2.9 km height. Both the plume and tremor diminished to low levels at 1855, but ash emission continued until 1940. Most of the ash was blown SW, and 1 mm of dust-sized tephra fell on Consaca, roughly 13 km WSW of the vent. EDM lines showed no change during the activity.
The ash eruption resumed at 0638, accompanied by an impulsive seismic signal, and tremor increased rapidly to an average peak-to-peak amplitude of 2 mm. The column grew to 1.2 km height by 0712, 1.9 km by 0726, and stabilized as a pulsing column to 2.8 km height between 0728 and 0825. The eruption column and tremor then decreased rapidly to low levels. The plume was broad and dense, dropping sheets of ash mainly within a few kilometers W of the vent. On the vent's E rim, the new deposit was ~25 cm thick, with the first layer a wet mud, probably from the lake that had occupied the bottom of the vent. Surge units were found in the deposit, as were lithic blocks that averaged about 15 cm in diameter. Only a thin film of ash fell at Consaca and other areas to the W and SW. However, the press reported that rescue workers evacuated ~2,000 residents of the Consacá area because of the ashfall. Activity around 1100 was accompanied by pulses of 4-5-Hz tremor and some long-period events. Ash was blown to the N, falling over La Florida and Nariño (8 km NNW and 7.5 km N of the vent). The EDM line across the caldera showed no change after the 4-5 May activity, but there may have been slight deflation on lines from the caldera rim to the active cone.
6 May. Ash emission resumed on 6 May at about 0900, producing a broad, pulsing column that fluctuated between 2.5 and 3.2 km height until darkness prevented further observations (about 1800). The rate of ash emission was intermediate between that of 4 May and the more vigorous activity of 5 May. Only low-level tremor and occasional long-period events accompanied the 6 May activity.
7-9 May. Harmonic tremor (1.3-1.4 Hz) began on 7 May at 0730 and continued for 38 minutes. Amplitudes reached 5 mm peak-to-peak and the tremor could be detected throughout the seismic net to 10 km from the vent. A similar signal reappeared at 0900, lasting for 40 minutes, and a pattern of intermittent tremor continued until 1400, with each episode building to larger amplitudes (as much as 1.5 cm peak-to-peak). The tremor typically occurred in 1.35-Hz packets with wavelengths of 10 seconds. The next-to-last tremor episode ceased abruptly after two large A-type events were recorded. During the last and strongest episode, many small A-type shocks were imbedded in the tremor. The A-type events were centered 3-3.5 km below the vent and 1-7 km to its S. The strong tremor was succeeded by bands of higher frequency tremor with much lower amplitude (<1 mm peak-to-peak). Minor ash emission continued 7 and 8 May. Ash was blown N on 7 May but did not reach La Florida, Nariño, or Jenoy (6 km NNE of the vent). The 8 May ash fell only near the crater. Frequent tremor episodes continued 8 May: 45 minutes of 2-3-Hz tremor that began gradually at 0614; low-frequency (1.54 Hz) banded tremor that began at 0800 and reached 23 mm amplitude about noon, decreasing in amplitude around 1540; amplitude increased again at 1600, to 20 mm, before declining at 1650 and stabilizing at 2-3 mm. Tremor decreased gradually from 9 May at 2000, to a maximum of 1 mm amplitude. Ash emission then stopped, and eruptive activity had not resumed as of 16 May.
The five days of ash emission prompted school closings and an increase in alert status to "orange" on 9 May. No immediate evacuations were ordered but officials asked residents to be ready for instructions if an eruption occurs. The Galeras Volcano Workshop that began 8 May with 50 participants from Central and South America will study the activity and hazards response.
Tephra deposits. An area of ~33 km2 was enclosed within the 3 mm ashfall isopach, including the TELECOM and television sites, 1.5 km to the S, and Nariño, 7.5 km N of the crater. The volume of tephra deposits was calculated at ~4 x 105 m3. The 7 cm of fine ash deposited at the S rim of El Pinta crater 19 February-3 May was overlain by more than 5 m of tephra that accumulated 4-9 May. A preliminary grain-size analysis shows a large fraction of fine (<1 mm) material (table 1). Some coarser layers of the early May tephra included scoria; in one layer (G) it was clearly altered, but in another horizon (E) it included abundant crystals in a very glassy matrix.
Table 1. Grain-size distribution of tephra deposited 4-9 May at Galeras, on the S rim of El Pinta crater. Thicknesses of individual layers (in cm) are supplemented by cumulative thickness of post-19 February tephra; only 7 cm of the section fell 19 February-3 May. The weight percent of six size fractions: <0.5, 0.5-1, 1-2, 2-4, 4-6.5, and >6.5 cm are shown. Courtesy of INGEOMINAS.
| Layer ID |
Layer Thickness |
Cumulative Thickness |
0-0.5 cm |
0.5-1 cm |
1-2 cm |
2-4 cm |
4-6.5 cm |
6.5+ cm |
| B |
3 cm |
501 cm |
26.6 |
32.2 |
27.3 |
8.6 |
5.5 |
-- |
| C |
7 cm |
498 cm |
96.0 |
2.3 |
1.0 |
0.5 |
0.3 |
-- |
| D |
12 cm |
491 cm |
44.6 |
27.3 |
20.4 |
6.1 |
1.6 |
-- |
| E |
22 cm |
469 cm |
5.0 |
4.1 |
6.1 |
7.9 |
30.9 |
46.0 |
| F |
32 cm |
447 cm |
38.8 |
33.0 |
17.9 |
5.2 |
5.2 |
-- |
| G |
43 cm |
415 cm |
6.9 |
8.1 |
7.5 |
6.5 |
6.5 |
24.1 |
Geologic Background. Galeras, a stratovolcano with a large breached caldera located immediately west of the city of Pasto, is one of Colombia's most frequently active volcanoes. The dominantly andesitic complex has been active for more than 1 million years, and two major caldera collapse eruptions took place during the late Pleistocene. Long-term extensive hydrothermal alteration has contributed to large-scale edifice collapse on at least three occasions, producing debris avalanches that swept to the west and left a large open caldera inside which the modern cone has been constructed. Major explosive eruptions since the mid-Holocene have produced widespread tephra deposits and pyroclastic flows that swept all but the southern flanks. A central cone slightly lower than the caldera rim has been the site of numerous small-to-moderate eruptions since the time of the Spanish conquistadors.
Information Contacts: H. Cepeda and B. Pulgarin, INGEOMINAS, Popayán; M. Calvache, F. Muñoz, and R. Méndez, INGEOMINAS, Manizales; I. Mejía and E. Parra, INGEOMINAS, Medellín; M. Mercado, Popayán; N. Banks, USGS; Deutche Presse-Agentur; Agence France-Presse.
Kilauea (United States) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Kilauea
United States
19.421°N, 155.287°W; summit elev. 1222 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Lava flows threaten houses
Kīlauea's . . . eruption continued to feed lava through tubes into the ocean near Kupapau Point during April. Surface lava breakouts along the W tube were active 1-12 April and extended from ~300 m (top of the fault scarp) to 70 m altitude. Lava traveled along the W side of the flow field, entering the E margin of the Royal Gardens subdivision (figure 60). A major breakout on the 13th at ~500 m elevation remained active throughout the month. Large surface flows burned forest to the W and on 25 April passed within 50 m of an occupied home . . . . Access to the upper subdivision, as well as several houses, were threatened. By the end of the month, the flow had reached 60 m elevation and slowed, but was still active. Surface activity from the E tube at the top of the fault scarp was sporadic in early April but ceased after the 10th. The terminus of a breakout from the central tube was active just above the Kapaahu kipuka but stagnated after the 12th. The lava breakouts from the W tube on the 13th apparently lowered the magma supply to the E and central tubes, causing their flows to stagnate. The active portion of the seacoast bench that had formed since the 23 March collapse measured 160 x 60 m at the beginning of the month. Following two large collapses on 13 April (at 2024) and 22 April (at 2307), the bench continued to rebuild.
The lava pond at Kupaianaha was 20-25 m below the rim during April. Lava was observed in the crater bottom of Pu`u `O`o . . . for most of the month, ranging from spatter to a sizeable lava pond that covered much of the crater floor. Gas pistoning events were witnessed at mid-month. By the 25th, only glowing holes in the rubble at the crater bottom could be seen.
Most of April's 18 strongly recorded seismic events . . . were tightly clustered beneath Kīlauea's summit and S flank. Shallow events (0-5 km depth) continued to be recorded. The number of intermediate-depth long-period events beneath the summit decreased and developed a fluctuating pattern after a persistent high rate in March. Increasingly longer bursts of deep tremor (40-60 km depth), at near-regular time intervals during the first half of the month decreased thereafter. Low-level tremor continued beneath Pu`u `O`o and Kupaianaha. Relatively steady tremor amplitude beneath Pu`u `O`o was interrupted 13-17 April by short gas piston bursts and long intervals of banded tremor, correlated with increased activity in the crater. Tremor returned to a relatively steady state in the latter part of the month. Low-amplitude signals from lava entering the sea near Kupapau Point continued to be recorded.
Geologic Background. Kilauea overlaps the E flank of the massive Mauna Loa shield volcano in the island of Hawaii. Eruptions are prominent in Polynesian legends; written documentation since 1820 records frequent summit and flank lava flow eruptions interspersed with periods of long-term lava lake activity at Halemaumau crater in the summit caldera until 1924. The 3 x 5 km caldera was formed in several stages about 1,500 years ago and during the 18th century; eruptions have also originated from the lengthy East and Southwest rift zones, which extend to the ocean in both directions. About 90% of the surface of the basaltic shield volcano is formed of lava flows less than about 1,100 years old; 70% of the surface is younger than 600 years. The long-term eruption from the East rift zone between 1983 and 2018 produced lava flows covering more than 100 km2, destroyed hundreds of houses, and added new coastline.
Information Contacts: C. Heliker and R. Koyanagi, HVO.
Langila (Papua New Guinea) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Langila
Papua New Guinea
5.525°S, 148.42°E; summit elev. 1330 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Moderate ash ejections and glow
"The slightly stronger activity from Crater 2 reported in March continued in April, although fluctuations in the level of activity were evident. The volcano was quiet at the beginning of the month. Between 5 and 23 April, moderate ash emissions were observed, accompanied by weak to strong rumbling sounds. Most ash fell near the volcano. On most nights during this period, weak red glow was observed above Crater 2. Activity subsided between 24 and 28 April, but on the 29th and 30th returned to the levels seen at mid-month. Seismic records were unavailable between 14 and 30 April. During the first half of the month, seismicity was at a low level with only 0-1 explosion earthquakes/day."
Geologic Background. Langila, one of the most active volcanoes of New Britain, consists of a group of four small overlapping composite basaltic-andesitic cones on the lower E flank of the extinct Talawe volcano in the Cape Gloucester area of NW New Britain. A rectangular, 2.5-km-long crater is breached widely to the SE; Langila was constructed NE of the breached crater of Talawe. An extensive lava field reaches the coast on the N and NE sides of Langila. Frequent mild-to-moderate explosive eruptions, sometimes accompanied by lava flows, have been recorded since the 19th century from three active craters at the summit. The youngest and smallest crater (no. 3 crater) was formed in 1960 and has a diameter of 150 m.
Information Contacts: C. McKee, RVO.
Ol Doinyo Lengai (Tanzania) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Ol Doinyo Lengai
Tanzania
2.764°S, 35.914°E; summit elev. 2962 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
January inspection reveals no new lava
On 12 January, a field party heard magma bubbling at depth but saw no liquid lava. Photographs taken from the E rim by Mr. [Bay] Forrest indicated that hornitos within the crater remained unchanged since the last inspections in late November and mid-December 1988. The extent of lava that had entered the S crater in December had not changed, and the crater floors were covered by light-colored, older lava, with no signs of dark, fresh flows. The darkest feature was a cone (T10) near the base of the E wall. Although minor spattering similar to that observed at T4/T7 in June 1988 could have covered T10's surface, there had been no significant change in its shape. Fumaroles were visible on the E part of the saddle, but the crater walls and W part of the saddle were largely cloud-covered.
Geologic Background. The symmetrical Ol Doinyo Lengai is the only volcano known to have erupted carbonatite tephras and lavas in historical time. The prominent stratovolcano, known to the Maasai as "The Mountain of God," rises abruptly above the broad plain south of Lake Natron in the Gregory Rift Valley. The cone-building stage ended about 15,000 years ago and was followed by periodic ejection of natrocarbonatitic and nephelinite tephra during the Holocene. Historical eruptions have consisted of smaller tephra ejections and emission of numerous natrocarbonatitic lava flows on the floor of the summit crater and occasionally down the upper flanks. The depth and morphology of the northern crater have changed dramatically during the course of historical eruptions, ranging from steep crater walls about 200 m deep in the mid-20th century to shallow platforms mostly filling the crater. Long-term lava effusion in the summit crater beginning in 1983 had by the turn of the century mostly filled the northern crater; by late 1998 lava had begun overflowing the crater rim.
Information Contacts: C. Nyamweru, Kenyatta Univ; B. Forrest, Rift Valley Academy, Kijabe, Kenya.
Lonquimay
Chile
38.379°S, 71.586°W; summit elev. 2832 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Continued tephra emission; cattle sickened by ash
The eruption . . . was continuing in early May. Eruption clouds in April and early May, composed mainly of dark brown ash and water vapor, rose 500-1,500 m from Navidad Crater. The number of recorded seismic events had declined to 2-3/day.
Estimates of the volume of the lava flow vary, and are made difficult by the flow's very irregular thickness, which has been increasing faster than the area covered by lava. Hugo Moreno estimated that through March ~150 x 106 m3 of lava had been extruded. The lava flow's W lobe essentially stopped advancing in mid-February, but the E front continued to move down the Lolco River valley. Little additional advance of the lava flow was noted in April and early May. The position of the flow as of 5 April is shown in figure 11.
About 10,000 cattle have been suffering the effects of ashfall since December. Many have lost >100 kg in weight and are dying. Analyses by specialists at the Univ Austral determined that the animals are being affected by overdoses of fluorine from the ash. Ash has fallen in various directions (see table 5). The localities most affected are Maillin del Treile, El Naranjo (both roughly 20 km ESE of the active crater), and Comunidad Bernardo Nanco, home to about 80 families, the majority of which depend for their livelihoods on animal raising. Losses are estimated at about $2,000,000 (US). Local authorities and the Ministries of Agriculture and Health are taking emergency measures. Forest fires have burned valuable native trees, including coigüe (Nothfogus dombeyi) and araucaria (Araucaria araucana).
Geologic Background. Lonquimay is a small, flat-topped, symmetrical stratovolcano of late-Pleistocene to dominantly Holocene age immediately SE of Tolguaca volcano. A glacier fills its summit crater and flows down the S flank. It is dominantly andesitic, but basalt and dacite are also found. The prominent NE-SW Cordón Fissural Oriental fissure zone cuts across the entire volcano. A series of NE-flank vents and scoria cones were built along an E-W fissure, some of which have been the source of voluminous lava flows, including those during 1887-90 and 1988-90, that extended out to 10 km.
Information Contacts: O. González-Ferrán, Univ de Chile; G. Fuentealba and P. Riffo, Univ de la Frontera; H. Moreno, Univ de Chile.
Manam (Papua New Guinea) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Manam
Papua New Guinea
4.08°S, 145.037°E; summit elev. 1807 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Incandescent ejections and vapor release
"Activity remained at a low inter-eruptive level during April. Both Southern and Main Craters released white vapours at weak to moderate rates. Blue vapour was also emitted from Southern Crater on 9, 13, and 22-23 April. Weak deep rumbling sounds from Southern Crater were heard occasionally 11-30 April. The summit was obscured by clouds on most nights, but during clear conditions on the 11th, glow and weak ejections of incandescent lava fragments were observed above Southern Crater. Volcano-seismicity remained at a normal inter-eruptive level with daily earthquake totals ranging between ~700 and 1,200. Tilt measurements showed no trends."
Geologic Background. The 10-km-wide island of Manam, lying 13 km off the northern coast of mainland Papua New Guinea, is one of the country's most active volcanoes. Four large radial valleys extend from the unvegetated summit of the conical basaltic-andesitic stratovolcano to its lower flanks. These valleys channel lava flows and pyroclastic avalanches that have sometimes reached the coast. Five small satellitic centers are located near the island's shoreline on the northern, southern, and western sides. Two summit craters are present; both are active, although most observed eruptions have originated from the southern crater, concentrating eruptive products during much of the past century into the SE valley. Frequent eruptions, typically of mild-to-moderate scale, have been recorded since 1616. Occasional larger eruptions have produced pyroclastic flows and lava flows that reached flat-lying coastal areas and entered the sea, sometimes impacting populated areas.
Information Contacts: C. McKee, RVO.
Masaya
Nicaragua
11.9844°N, 86.1688°W; summit elev. 594 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Lava lake drains; rockslides; gas emission
A local newspaper (the Barricada, citing Alain Creusot) reported that on 7 March, the level of the active lava lake in Santiago's crater had dropped considerably (since late February). Spatter was occasionally ejected outside the vent. The lake apparently drained on 9 March. Geologists visited the crater on 14 March and measured a temperature of 76.6°C on the surface of the frozen lake (all reported temperatures were measured by an 8-14 micrometer bandpass infrared thermometer from a distance of about 300 m unless otherwise stated). The two incandescent vents that first appeared on 23 February (14:02) were still present in the lake's N corner. The temperature of the hottest glowing vent was 667°C. On 16 and 18 March, fumes collected in the crater and limited observations. By 28 March, debris from rockslides on the SW inner wall of the crater had covered the site of the former lake, at least 175 m below the floor of Santiago Crater. Gas emission was strong. The two incandescent vents (maximum surface temperature 607°C) remained visible at night. On 12 April, the frequency of rockslides (audible about every 5 minutes) had increased significantly. Most occurred on the SW inner wall of the crater and many lasted for minutes. When geologists drove past Masaya on 18 April the amount of fuming appeared to have dramatically decreased.
Geologic Background. Masaya volcano in Nicaragua has erupted frequently since the time of the Spanish Conquistadors, when an active lava lake prompted attempts to extract the volcano's molten "gold" until it was found to be basalt rock upon cooling. It lies within the massive Pleistocene Las Sierras caldera and is itself a broad, 6 x 11 km basaltic caldera with steep-sided walls up to 300 m high. The caldera is filled on its NW end by more than a dozen vents that erupted along a circular, 4-km-diameter fracture system. The Nindirí and Masaya cones, the source of observed eruptions, were constructed at the southern end of the fracture system and contain multiple summit craters, including the currently active Santiago crater. A major basaltic Plinian tephra erupted from Masaya about 6,500 years ago. Recent lava flows cover much of the caldera floor and there is a lake at the far eastern end. A lava flow from the 1670 eruption overtopped the north caldera rim. Periods of long-term vigorous gas emission at roughly quarter-century intervals have caused health hazards and crop damage.
Information Contacts: C. Oppenheimer, Open Univ.
Momotombo (Nicaragua) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Momotombo
Nicaragua
12.423°N, 86.539°W; summit elev. 1270 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Burning gases from fumaroles
A maximum gas temperature of 880°C was measured (by a thermocouple) at fumarole ##9, inside the crater, on 15 April. Flames that extended up to 40 cm from vents were visible at night. Most were pale orange but some gases burned with a blue flame.
Geologic Background. Momotombo is a young stratovolcano that rises prominently above the NW shore of Lake Managua, forming one of Nicaragua's most familiar landmarks. Momotombo began growing about 4500 years ago at the SE end of the Marrabios Range and consists of a somma from an older edifice that is surmounted by a symmetrical younger cone with a 150 x 250 m wide summit crater. Young lava flows extend down the NW flank into the 4-km-wide Monte Galán caldera. The youthful cone of Momotombito forms an island offshore in Lake Managua. Momotombo has a long record of Strombolian eruptions, punctuated by occasional stronger explosive activity. The latest eruption, in 1905, produced a lava flow that traveled from the summit to the lower NE base. A small black plume was seen above the crater after a 10 April 1996 earthquake, but later observations noted no significant changes in the crater. A major geothermal field is located on the south flank.
Information Contacts: C. Oppenheimer, Open Univ.
Niigata-Yakeyama (Japan) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Niigata-Yakeyama
Japan
36.921°N, 138.036°E; summit elev. 2400 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Increased steaming, small ash eruption
A white steam plume was rising from the volcano's upper E flank during observations by the staff of Takada Weather Station (from sites 10-20 km away) 1 May 1987-September 1988. Emissions gradually declined, and after a 9 November 1988 visit, no plume was observed.
Moderate steam emission was seen again on 30 March 1989, with a white vapor plume rising 100-150 m from 2 areas on the upper E flank. Steam from the upper NE flank rose about 30-50 m on 15 April. Four days later, steam with a small amount of ash was emitted to about 100-150 m above the upper E flank, the first sighting of a gray plume since May 1987. Observations from Sasagamine (about 8 km SE) on 26 April revealed gray plumes rising 250-300 m from many sites on the upper E flank. A 30 April steam plume, about 300-400 m high and blown 600 m by the wind (figure 2), was the highest since May 1987. Access to the volcano has been closed to tourists.
Geologic Background. Niigata-Yakeyama, one of several Japanese volcanoes named Yakeyama ("Burning Mountain"), is an andesitic-to-dacitic lava dome in Niigata prefecture in west-central Honshu, about 20 km from the coast. The volcano was constructed on a base of Tertiary mountains beginning about 3,100 years ago. Three major eruptions in the past 1,000 years have produced pyroclastic flows and lava flows that traveled mainly down the Hayakawa river valley to the N and NW. The first of these eruptions, in 887 CE (and possibly 989 CE), produced the Hayakawa pyroclastic flow, which reached the coast, and the massive Mae-yama lava flow, which traveled about 6.5 km down the Hayakawa river valley. The summit lava dome was emplaced during the 1361 CE eruption, and the last magmatic eruption took place in 1773 CE. Eruptive activity since 1773 has consisted of relatively minor phreatic explosions from several radial fissures and explosion craters that cut the summit and flanks of the dome.
Information Contacts: JMA.
Nyamulagira (DR Congo) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Nyamulagira
DR Congo
1.408°S, 29.2°E; summit elev. 3058 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Lava erupts from summit and E flank
An eruption that began on 23 April in Nyamuragira's summit crater was reported by the Vice Conservator of the Institut Zairois pour la Conservation de la Nature, Parc National des Virunga. On the 24th at 1418, three lava fountains emerged from a fissure on the SSE flank of the volcano. Incandescence was visible from the village of Gisenyi, Rwanda, roughly 30 km from the vent. The resulting lava flow passed between Kitazungurwa and Rugarambiro cones, diverted around Gitebe cone, and flowed along lava erupted in 1981-82 from Rugarambiro (figure 6). By the 26th, the flow had reached Nyasheke-South and was ~6 km from Kakomero, the base camp for climbers at the park entrance.
On the night of the 26th, lava emerged from the W side of the Kanamaharagi cone (formed during the 1905 eruption), building a new parasitic cone (also named Kanamaharagi) at ~1,860 m altitude. Lava fountains up to 200 m high and large amounts of tephra were emitted 30 April-1 May. As of 6 May, the volcano was still erupting.
Geologic Background. Africa's most active volcano, Nyamulagira (also known as Nyamuragira), is a massive high-potassium basaltic shield about 25 km N of Lake Kivu and 13 km NNW of the steep-sided Nyiragongo volcano. The summit is truncated by a small 2 x 2.3 km caldera that has walls up to about 100 m high. Documented eruptions have occurred within the summit caldera, as well as from the numerous flank fissures and cinder cones. A lava lake in the summit crater, active since at least 1921, drained in 1938, at the time of a major flank eruption. Recent lava flows extend down the flanks more than 30 km from the summit as far as Lake Kivu; extensive lava flows from this volcano have covered 1,500 km2 of the western branch of the East African Rift.
Information Contacts: S. Peyer and H. Peyer, Gisenyi, Rwanda; H-L. Hody, GEOVAR, Kigali, Rwanda.
Poas
Costa Rica
10.2°N, 84.233°W; summit elev. 2697 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Crater lake gone; explosions and molten sulfur ponds
Until mid-April, thermal activity remained similar to that observed in March, with boiling mud springs and vigorous fumaroles in the crater lake, which has been shrinking since early 1987. Two ponds of molten sulfur (115°C) have persisted since 16 March at the former site of small sulfur and mud cones 50 m SE of the center of the inner crater (figure 14). Small pyroclastic sulfur cones surrounded the lakes, collapsing occasionally.
On 12 April, the crater lake was convecting vigorously, but shallow areas were visible. The lake level dropped about 2 m during the following week, and by 19 April only a few small mud pools remained. The characteristic geyser-type phreatic activity through the crater lake changed 18-19 April with the lake's near disappearance. Cypressoid vertical columns continuously rose about 25 m above the former center of the lake and began to build a mud/pyroclastic cone. On 19 April, small bursts of gas and mud that contained sulfur particles emerged through the mud surface to heights of about 10 m, rarely to 25-30 m. Steaming was continuous. Activity had increased slightly the next day, but magnetometer traverses that passed about 100 m from the active area showed no changes since the last measurements on 3 April. Phreatic bursts reached about 50 m height on 21 April. Using a thermocouple, Jorge Barquero measured a liquid temperature of 116°C in one of the sulfur ponds. On 22 April at around 1000, a dark mushroom-shaped column developed, convecting to 200-300 m height. Fine mud, sulfur, and burning gases (possibly hydrogen) were ejected until 1032. Fine yellow material fell on the W side of the inner crater [see also 14:05]. Ejection of lithic material stopped suddenly and the plume reverted to its normal white color. About 15 minutes later, continuous geysering of dark sediment and gas was observed for 2-3 minutes. Clouds obscured the summit at 1130. At 2100, after weather had cleared, the base of the plume was suddenly illuminated by a pink-orange light for about 2 minutes. No sounds were audible other than those accompanying the continuing phreatic activity. The light stopped suddenly and was thought to have been generated by burning gases.
During observations on 23 April, a thick white plume coalesced from numerous vents, two of which were discharging a mixture of white condensed steam and yellow sulfur. Dark cypressoid plumes were emitted every few seconds. At least one vent continuously discharged fine dark material. At 0717, a pink-orange light was again seen at the base of a continuous white plume on the SW side of the crater bottom. The light remained visible for 2.5 minutes, and geologists believed that it was generated by burning gases. A brightness temperature of 158°C was recorded (with an 8-14 micrometer bandpass infrared thermometer), but the measurement was made from almost 1 km distance and geologists suspected that the temperature was probably several hundred degrees higher. Phreatic activity from at least six of the vents expelled blocks to about 50 m height and occasionally to 100 m or more, generally vertically but sometimes obliquely. Most of the ejecta fell within 10-20 m of the vents, building cones to about 10 m height with funnel-shaped craters up to 5 m in diameter. The ejecta appeared dry and included blocks more than 20 cm across. Radiant temperatures of dark plumes were only about 80°C as measured from about 150 m away. Activity occasionally reached a level at which at least one of the six or more phreatic vents was erupting at a given time. Booming noises and sounds like a jet engine were occasionally heard. From nearer the vents, sounds like pistol shots were audible.
The two ponds of dark brown, very fluid, bubbling liquid, apparently sulfur, were about 50 cm below the former crater lake floor in steep-sided pits. One, roughly elliptical, was about 20 m across, while the other was dumbbell-shaped and about 10 m long. A terrace of solid sulfur had developed at the edge of the liquid, and the sides and rims of the pits were coated by bright yellow sulfur sublimates. A moderate amount of visible condensate rose from their surfaces and the smell of SO2 was strong. No surface burning was evident. Blocks of pale-colored altered rock (probably former lake sediments) floated on the sulfur ponds, suggesting a density substantially above 1 g/cm3. Remnants of the former crater lake had a maximum surface infrared radiometer temperature of 97°C.
Four geologists (G. Alvarado, M. Fernández, G. Soto, and D. Stevenson) descended to the bottom of the inner crater on 25 April. The activity had built at least three new cones, aligned with the sulfur ponds along a N30°W trend. The cones, 10-12 m high, were continuously active, emitting vertical columns of mud, sulfur, gases, and rocks to 30-70 m (occasionally 100 m) height for some seconds. Optical radiometer temperatures of the plumes were 75-90°C. Lesser thermal features (fumaroles, small hot lakes, and boiling mud springs) were found around the periphery of the cones. A small fault scarp, parallel to the line of cones, cut the sediments. The faulting was interpreted as the result of subsidence caused by the removal of the eruptive products, and a decrease in the internal pore pressure of the subsurface hydrothermal regime. At noon, the geologists were surprised by (but escaped unscathed from) a sudden eruption of sulfur, mud, and gases (some burning) that formed a thick vertical column nearly 400 m high, with a minimum radiometer temperature of 459°C. Sulfur and mud fell on the W wall of the crater and over the rim (toward Cerro Pelón). Other similar eruptions deposited greenish-gray mud within the crater.
The column from a larger eruption on 28 April between 0500 and 0600 reached an estimated height of 1.5-2 km and dropped fine mud to 2.5 km S of the source [see also 14:05]. The next day, the central mud cone (which had reached about 20 m height) ejected vertical columns of mud and sulfur to 200 m height. The small SW mud cone was in nearly continuous activity, emitting brown-gray lithic ash that was carried W by the wind. The gases were sulfurous, strongly yellow- and orange-colored, and rose in a vertical convective column to 350 m height. Eruptive characteristics were similar on 30 April and 1 May, but with columns to 1-1.5 km high on the 1st. The wind carried the fine lithic ash and mud toward the W onto various towns (including Bajos de Toro, Zarcero, and Sarchí).
Activity decreased 2 and 3 May. On the 3rd, ash was measured on the crater rim, reaching 1 mm thickness at point A (figure 15) and 2 mm at point B. Particles reached medium-grained ash size and were lithic, dominantly mud/clay granules of sulfide/sulfate sediments with a high percentage of solutes.
Seismicity has visibly declined. Volcanic earthquakes totaled 4,240 in April, for a mean of 141/day (figure 16). Seismicity continued to be dominated by B-type events, although their number had decreased. The most significant change was the appearance of tremor episodes with durations of 4-10 minutes. The change in seismic pattern was interpreted by Morales et al. (1988) as the change from magma-water interaction in a medium that is not open (B-type signals) to one that is partially open (continuous train of B-type signals or tremors).
Reference. Morales, L.D., Soley, J.F., Alvarado, G.E., Borgia, A., and Soto, G., 1988, análisise espectral de algunas señales sísmicas y su relación con la actividad de los volcanes Arenal y Poás, Costa Rica: Boletín del Observatorio Vulcanológico del Arenal, año 1, no. 2, p. 1-25.
Geologic Background. The broad vegetated edifice of Poás, one of the most active volcanoes of Costa Rica, contains three craters along a N-S line. The frequently visited multi-hued summit crater lakes of the basaltic-to-dacitic volcano are easily accessible by vehicle from the nearby capital city of San José. A N-S-trending fissure cutting the complex stratovolcano extends to the lower N flank, where it has produced the Congo stratovolcano and several lake-filled maars. The southernmost of the two summit crater lakes, Botos, last erupted about 7,500 years ago. The more prominent geothermally heated northern lake, Laguna Caliente, is one of the world's most acidic natural lakes, with a pH of near zero. It has been the site of frequent phreatic and phreatomagmatic eruptions since an eruption was reported in 1828. Eruptions often include geyser-like ejections of crater-lake water.
Information Contacts: G. Soto, Mario Fernández, and Héctor Flores, UCR; Guillermo Alvarado, R. Barquero, and Ileana Boschini, ICE; David Stevenson and C.M.M. Oppenheimer, Open Univ.
Popocatepetl (Mexico) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Popocatepetl
Mexico
19.023°N, 98.622°W; summit elev. 5393 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
New fumaroles and large sulfur deposits
During 1986-87, a seasonal, nearly circular lake occasionally occupied the summit crater. The lake's pH was 2-2.7 and the temperature was 30°C. Continuous fumarolic activity began in August 1988. A March 1989 summit visit by Alejandro Rivera Domínguez revealed large sulfur deposits in the main and inner craters. New fumaroles (not observed in 1987-88) on the main crater wall emitted high-pressure sulfurous gas and steam to 300 m. No significant microseismicity or tilt was detected.
The Grupo de Montañismo y Exploración de la UNAM, led by Prof. José Manuel Casanova Becerra, climbed the volcano on 9 April. More than 20 new fumaroles were observed on the outer S flank about 200 m below the crater rim. These vents (up to 1 m in diameter) were not observed when the group visited the area 2 years ago. Steam columns reached 20 m height and there was a mild sulfur odor. The steam's temperature was probably near the boiling point (at about 5,100 m altitude). The average altitude of the crater rim was 5,300 m with the crater bottom 340 m below. Increased steaming (common during the season) was observed inside the crater.
One seismograph is sited near the volcano . . . . Researchers hope to build an observatory 12 km from the volcano with telemetric data capture. Current monitoring is from the Meteorological Observatory, Geophysics Dept, Univ Autónoma de Puebla, and from Yancuitlalpan Village, S of the volcano.
Geologic Background. Volcán Popocatépetl, whose name is the Aztec word for smoking mountain, rises 70 km SE of Mexico City to form North America's 2nd-highest volcano. The glacier-clad stratovolcano contains a steep-walled, 400 x 600 m wide crater. The generally symmetrical volcano is modified by the sharp-peaked Ventorrillo on the NW, a remnant of an earlier volcano. At least three previous major cones were destroyed by gravitational failure during the Pleistocene, producing massive debris-avalanche deposits covering broad areas to the south. The modern volcano was constructed south of the late-Pleistocene to Holocene El Fraile cone. Three major Plinian eruptions, the most recent of which took place about 800 CE, have occurred since the mid-Holocene, accompanied by pyroclastic flows and voluminous lahars that swept basins below the volcano. Frequent historical eruptions, first recorded in Aztec codices, have occurred since Pre-Columbian time.
Information Contacts: S. De la Cruz-Reyna, UNAM; Alejandro Rivera Domínguez, Univ Autónoma de Puebla.
Rabaul (Papua New Guinea) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Rabaul
Papua New Guinea
4.2459°S, 152.1937°E; summit elev. 688 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Seismicity and deformation at background level
"Activity remained at a low (background) level in April. The total number of caldera earthquakes was 146. All of the events were small (ML 0.5-1.5) and none could be located. The daily earthquake count ranged from 0 to 17. Ground deformation measurements showed no significant changes."
Geologic Background. The low-lying Rabaul caldera on the tip of the Gazelle Peninsula at the NE end of New Britain forms a broad sheltered harbor utilized by what was the island's largest city prior to a major eruption in 1994. The outer flanks of the asymmetrical shield volcano are formed by thick pyroclastic-flow deposits. The 8 x 14 km caldera is widely breached on the east, where its floor is flooded by Blanche Bay and was formed about 1,400 years ago. An earlier caldera-forming eruption about 7,100 years ago is thought to have originated from Tavui caldera, offshore to the north. Three small stratovolcanoes lie outside the N and NE caldera rims. Post-caldera eruptions built basaltic-to-dacitic pyroclastic cones on the caldera floor near the NE and W caldera walls. Several of these, including Vulcan cone, which was formed during a large eruption in 1878, have produced major explosive activity during historical time. A powerful explosive eruption in 1994 occurred simultaneously from Vulcan and Tavurvur volcanoes and forced the temporary abandonment of Rabaul city.
Information Contacts: C. McKee, RVO.
Rincon de la Vieja (Costa Rica) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Rincon de la Vieja
Costa Rica
10.83°N, 85.324°W; summit elev. 1916 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Crater lake sampled
Geologists sampled the crater lake on 6 April. The lake temperature was 45°C, determined by throwing a bottle 100 m into the lake, measuring the resulting sample with a thermocouple, and applying a cooling correction.
Geologic Background. Rincón de la Vieja, the largest volcano in NW Costa Rica, is a remote volcanic complex in the Guanacaste Range. The volcano consists of an elongated, arcuate NW-SE-trending ridge constructed within the 15-km-wide early Pleistocene Guachipelín caldera, whose rim is exposed on the south side. Sometimes known as the "Colossus of Guanacaste," it has an estimated volume of 130 km3 and contains at least nine major eruptive centers. Activity has migrated to the SE, where the youngest-looking craters are located. The twin cone of Santa María volcano, the highest peak of the complex, is located at the eastern end of a smaller, 5-km-wide caldera and has a 500-m-wide crater. A Plinian eruption producing the 0.25 km3 Río Blanca tephra about 3,500 years ago was the last major magmatic eruption. All subsequent eruptions, including numerous historical eruptions possibly dating back to the 16th century, have been from the prominent active crater containing a 500-m-wide acid lake located ENE of Von Seebach crater.
Information Contacts: David Stevenson, Open Univ.
Ruapehu (New Zealand) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Ruapehu
New Zealand
39.28°S, 175.57°E; summit elev. 2797 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Heat flow declines
Since February, no discrete eruptions have been reported although steam passively rising from Crater Lake has occasionally been witnessed. When geologists visited the volcano 21-22 March, slight upwelling in the N vent area formed broken sulfur slicks. Crater Lake's temperature had fallen to 32°C (a 10.5° drop over 23 days) representing a decline in heat flow to ~10% of its previous rate. Lake level had decreased to 100-150 mm below overflow. Lake chemistry was stable, showing little change in Mg/Cl since 11 January. Minor inflation was measured across the N crater rim. On 5 April, geologists observed slightly increased upwelling in the N vent area. The lake temperature was 31.3°C. N-rim inflation had largely disappeared. NZGS geologists noted that some previous pulses of inflation/deflation have been followed by renewed lake heating (or strong seismicity). Few tremor episodes and volcanic earthquakes were recorded on seismic records through . . . 5 April.
Geologic Background. Ruapehu, one of New Zealand's most active volcanoes, is a complex stratovolcano constructed during at least four cone-building episodes dating back to about 200,000 years ago. The dominantly andesitic 110 km3 volcanic massif is elongated in a NNE-SSW direction and surrounded by another 100 km3 ring plain of volcaniclastic debris, including the NW-flank Murimoto debris-avalanche deposit. A series of subplinian eruptions took place between about 22,600 and 10,000 years ago, but pyroclastic flows have been infrequent. The broad summait area and flank contain at least six vents active during the Holocene. Frequent mild-to-moderate explosive eruptions have been recorded from the Te Wai a-Moe (Crater Lake) vent, and tephra characteristics suggest that the crater lake may have formed as recently as 3,000 years ago. Lahars resulting from phreatic eruptions at the summit crater lake are a hazard to a ski area on the upper flanks and lower river valleys.
Information Contacts: P. Otway, NZGS Wairakei.
Nevado del Ruiz (Colombia) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Nevado del Ruiz
Colombia
4.892°N, 75.324°W; summit elev. 5279 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Seismicity decreases
Seismic activity (high- and low-frequency earthquakes, long-period events, and tremor) significantly decreased in April, continuing a 2-month trend. SO2 emissions measured by COSPEC varied between 700 and 3,700 t/d with a monthly average of 1,800 t/d (figure 26). No significant changes in deformation were measured.
Geologic Background. Nevado del Ruiz is a broad, glacier-covered volcano in central Colombia that covers more than 200 km2. Three major edifices, composed of andesitic and dacitic lavas and andesitic pyroclastics, have been constructed since the beginning of the Pleistocene. The modern cone consists of a broad cluster of lava domes built within the caldera of an older edifice. The 1-km-wide, 240-m-deep Arenas crater occupies the summit. The prominent La Olleta pyroclastic cone located on the SW flank may also have been active in historical time. Steep headwalls of massive landslides cut the flanks. Melting of its summit icecap during historical eruptions, which date back to the 16th century, has resulted in devastating lahars, including one in 1985 that was South America's deadliest eruption.
Information Contacts: C. Carvajal, INGEOMINAS, Manizales.
Soputan (Indonesia) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Soputan
Indonesia
1.112°N, 124.737°E; summit elev. 1785 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Ashfall damages houses and crops
On 22 April, Soputan erupted for the first time since May 1985 (10:05), sending ash and lapilli to 1,000-1,500 m above the summit. Newspapers, quoting VSI director Subroto Modjo, reported that the eruption consisted of three explosions (at 1027, 1535, and 1752), the second of which ejected most of the tephra. Earthquakes were recorded by a nearby seismograph and were felt 25 km away. As much as 15-20 cm of ash (carried E by the wind) fell nearby in parts of Tumaratas (11 km NE of Soputan) and Taraitak, and in Ampreng, Raringis, and Noongan. At least 500 houses were damaged and three classrooms collapsed [but see 14:5] in Noongan, a gathering hall collapsed in Paslaten Langowan (13 km ENE), and many trees, especially in the Gunung Potong forest area (7 km E) were knocked down. No ashfall was reported in Manado, 45 km NNE. Damage to buildings and crops was estimated at about $114,000. As a precaution, hazard warning maps were given to residents. . . . No casualties or additional explosions had been reported as of 26 April.
Geologic Background. The Soputan stratovolcano on the southern rim of the Quaternary Tondano caldera on the northern arm of Sulawesi Island is one of Sulawesi's most active volcanoes. The youthful, largely unvegetated volcano is the only active cone in the Sempu-Soputan volcanic complex, which includes the Soputan caldera, Rindengan, and Manimporok (3.5 km ESE). Kawah Masem maar was formed in the W part of the caldera and contains a crater lake; sulfur has been extracted from fumarolic areas in the maar since 1938. Recent eruptions have originated at both the summit crater and Aeseput, a prominent NE-flank vent that formed in 1906 and was the source of intermittent major lava flows until 1924.
Information Contacts: OFDA; R. Austin, Englehard Engineering, USA.
Ulawun (Papua New Guinea) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Ulawun
Papua New Guinea
5.05°S, 151.33°E; summit elev. 2334 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Small ash emissions, minor seismic increases
"Mild, intermittent, eruptive activity continued in April. Ash emissions occurred 6, 8, 11, 20-22, and 28 April, but their ash content was low, and no significant ashfalls were reported. A strong correlation between activity and preceding heavy rainfall (as observed in March) was not evident. When not producing ash, the volcano emitted white vapours at moderate rates.
"For most of the month, the volcano-seismicity consisted of occasional, small, low-frequency events. Periods of low-amplitude, discontinuous and irregular tremor were recorded between 16 and 18 April. During the last week of April (perhaps correlating with a period of moderate rainfall) discrete events were more numerous, with periods of continuous and discontinuous irregular tremor of low-moderate amplitude."
Geologic Background. The symmetrical basaltic-to-andesitic Ulawun stratovolcano is the highest volcano of the Bismarck arc, and one of Papua New Guinea's most frequently active. The volcano, also known as the Father, rises above the N coast of the island of New Britain across a low saddle NE of Bamus volcano, the South Son. The upper 1,000 m is unvegetated. A prominent E-W escarpment on the south may be the result of large-scale slumping. Satellitic cones occupy the NW and E flanks. A steep-walled valley cuts the NW side, and a flank lava-flow complex lies to the south of this valley. Historical eruptions date back to the beginning of the 18th century. Twentieth-century eruptions were mildly explosive until 1967, but after 1970 several larger eruptions produced lava flows and basaltic pyroclastic flows, greatly modifying the summit crater.
Information Contacts: C. McKee, RVO.
Whakaari/White Island (New Zealand) — April 1989  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Whakaari/White Island
New Zealand
37.52°S, 177.18°E; summit elev. 294 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Tephra ejections continue
Donald Duck vent has intermittently ejected tephra since its formation in late January in a zone of strong fumarolic activity ~100 m NE of eruptive vents in 1978 crater (figure 11). Photographs by Geoff Green of a 4 March eruption (at about 1500-1530) show a 500-m, vigorously convoluting ash column with an incandescent base. The eruption continued for at least 45 minutes, and ash emission also began from R.F. Crater. A larger eruption between 16 and 20 March, apparently not witnessed, presumably generated a larger column. During April, Donald Duck vent continued to eject ash and threw lithic blocks to as much as 200 m S. Intermittent ash, block, and bomb ejections also continued from R.F. Crater during the month. Two bomb-ejecting eruptions from R.F. Crater since 20 March were followed by widespread ash deposition.
During 26 April fieldwork, Donald Duck vent emitted voluminous clouds of light gray gas from a vent at the base of its N wall. New ash-covered scoria bombs (first noted in early April) were present S of Donald Mound, reaching more than l m in diameter near the 1978 Crater rim. R.F. Crater (appearing deep with vertical walls) discharged a dilute cloud of gas and fine pink ash. Ash covered much of the main crater floor and walls. Impact craters and lithic blocks a few days old were abundant around Donald Mound and Donald Duck vent. Congress Crater was quiet.
Fumarole temperatures and emissions had decreased at most vents except Noisy Nellie, which continued to emit voluminous high-pressure gas. Geologists suggested that Donald Duck and R.F. Crater have been capturing heat from surrounding areas, which are cooling as a result. General deflation, in progress since mid-l987, continued with strong subsidence of the Donald Mound area. Seismicity through late April remained similar to previous months, with microearthquakes recorded most days. Activity was conspicuously banded, with individual bands lasting 1.5-24 hours, containing up to 10 medium-frequency events/minute. Activity was most prolonged around 1-2 April. Small E-type events were recorded in April on the 3rd (0854) and 8th (0115, 0931, and 2008), while small A-types occurred most days. Very few B-types were recorded.
Geologic Background. The uninhabited Whakaari/White Island is the 2 x 2.4 km emergent summit of a 16 x 18 km submarine volcano in the Bay of Plenty about 50 km offshore of North Island. The island consists of two overlapping andesitic-to-dacitic stratovolcanoes. The SE side of the crater is open at sea level, with the recent activity centered about 1 km from the shore close to the rear crater wall. Volckner Rocks, sea stacks that are remnants of a lava dome, lie 5 km NW. Descriptions of volcanism since 1826 have included intermittent moderate phreatic, phreatomagmatic, and Strombolian eruptions; activity there also forms a prominent part of Maori legends. The formation of many new vents during the 19th and 20th centuries caused rapid changes in crater floor topography. Collapse of the crater wall in 1914 produced a debris avalanche that buried buildings and workers at a sulfur-mining project. Explosive activity in December 2019 took place while tourists were present, resulting in many fatalities. The official government name Whakaari/White Island is a combination of the full Maori name of Te Puia o Whakaari ("The Dramatic Volcano") and White Island (referencing the constant steam plume) given by Captain James Cook in 1769.
Information Contacts: I. Nairn, NZGS Rotorua.