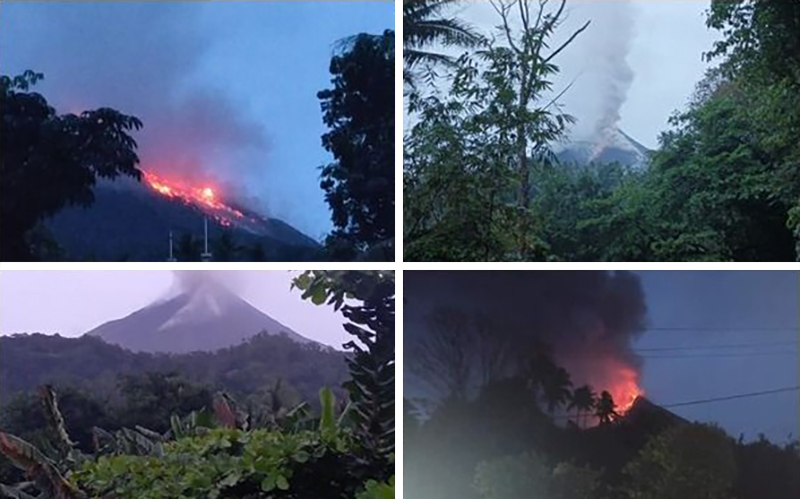
Recently Published Bulletin Reports
Manam (Papua New Guinea) Few ash plumes during November-December 2022
Krakatau (Indonesia) Strombolian activity and ash plumes during November 2022-April 2023
Stromboli (Italy) Strombolian explosions and lava flows continue during January-April 2023
Nishinoshima (Japan) Small ash plumes and fumarolic activity during November 2022 through April 2023
Karangetang (Indonesia) Lava flows, incandescent avalanches, and ash plumes during January-June 2023
Ahyi (United States) Intermittent hydroacoustic signals and discolored plumes during November 2022-June 2023
Kadovar (Papua New Guinea) An ash plume and weak thermal anomaly during May 2023
San Miguel (El Salvador) Small gas-and-ash explosions during March and May 2023
Semisopochnoi (United States) Occasional explosions, ash deposits, and gas-and-steam plumes during December 2022-May 2023
Ebeko (Russia) Continued explosions, ash plumes, and ashfall during October 2022-May 2023
Home Reef (Tonga) Discolored plumes continued during November 2022-April 2023
Ambae (Vanuatu) New lava flow, ash plumes, and sulfur dioxide plumes during February-May 2023
Manam (Papua New Guinea) — July 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Manam
Papua New Guinea
4.08°S, 145.037°E; summit elev. 1807 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Few ash plumes during November-December 2022
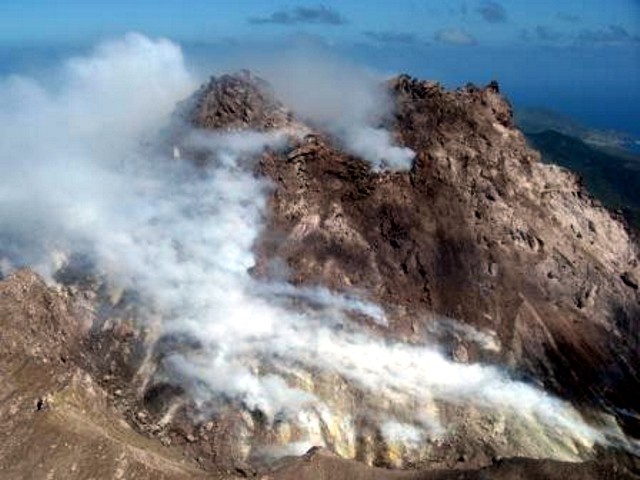
Manam is a 10-km-wide island that consists of two active summit craters: the Main summit crater and the South summit crater and is located 13 km off the northern coast of mainland Papua New Guinea. Frequent mild-to-moderate eruptions have been recorded since 1616. The current eruption period began during June 2014 and has more recently been characterized by intermittent ash plumes and thermal activity (BGVN 47:11). This report updates activity that occurred from November 2022 through May 2023 based on information from the Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) and various satellite data.
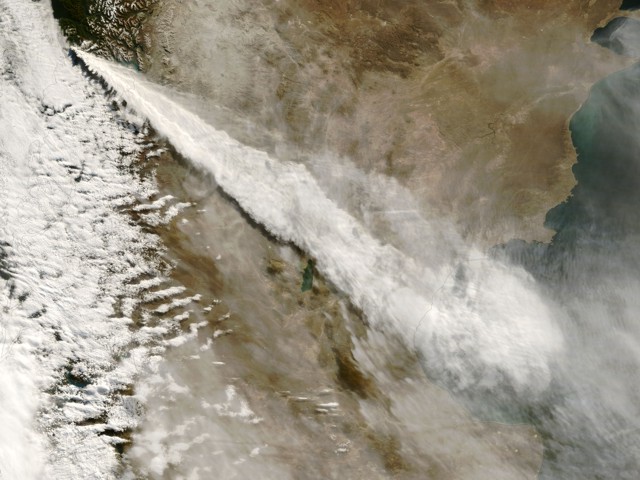
Ash plumes were reported during November and December 2022 by the Darwin VAAC. On 7 November an ash plume rose to 2.1 km altitude and drifted NE based on satellite images and weather models. On 14 November an ash plume rose to 2.1 km altitude and drifted W based on RVO webcam images. On 20 November ash plumes rose to 1.8 km altitude and drifted NW. On 26 December an ash plume rose to 3 km altitude and drifted S and SSE.
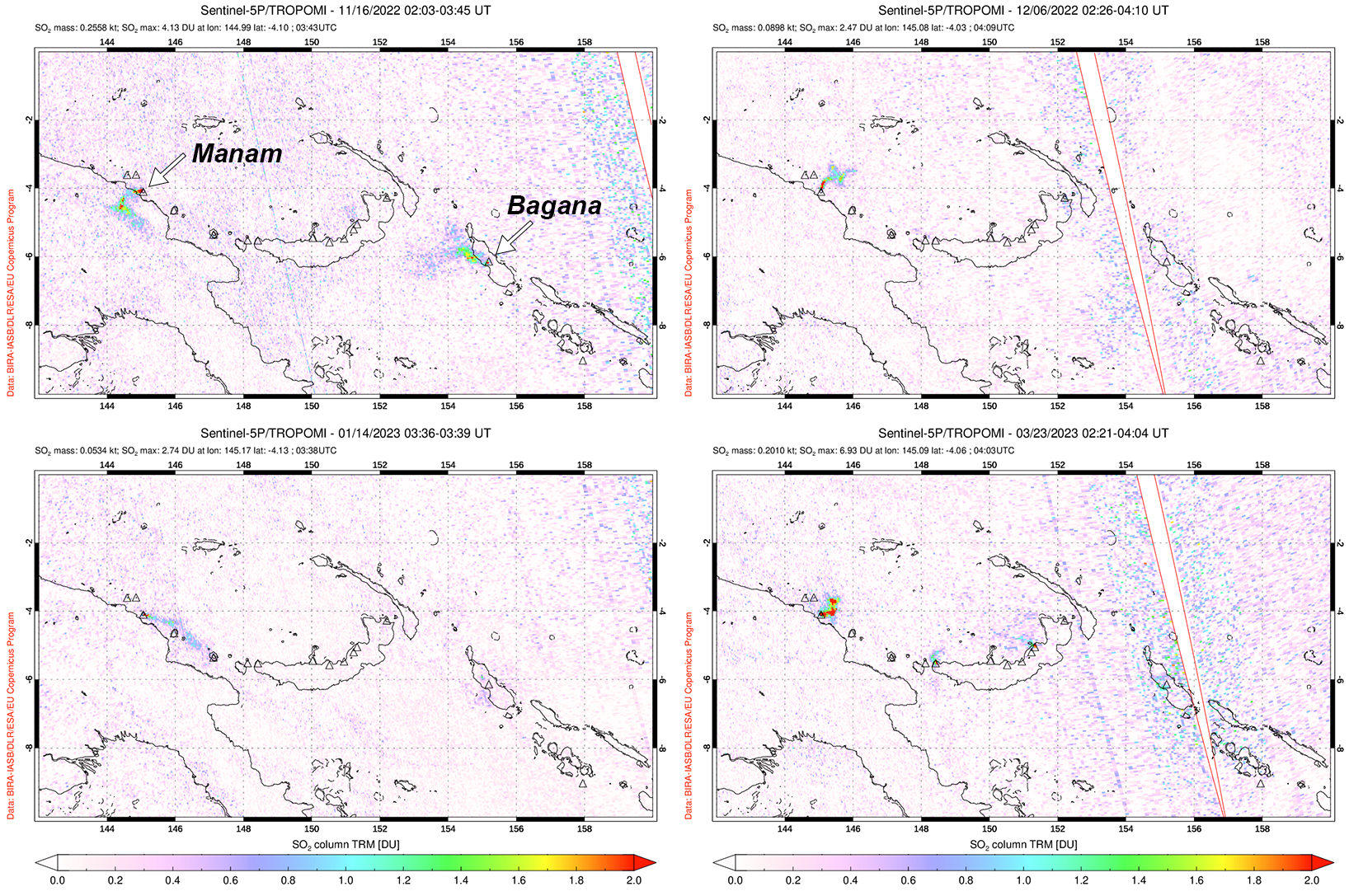
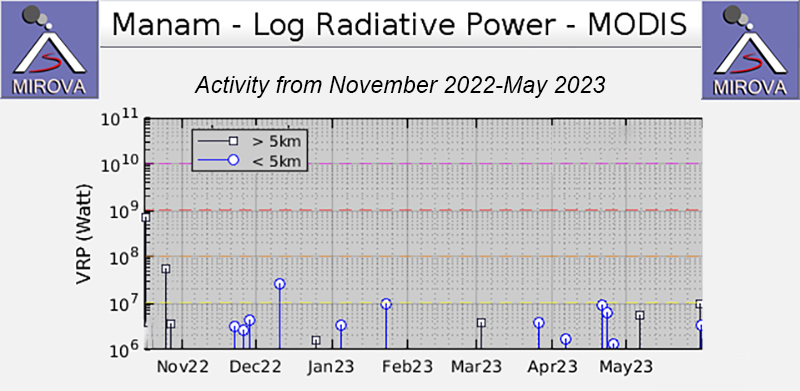
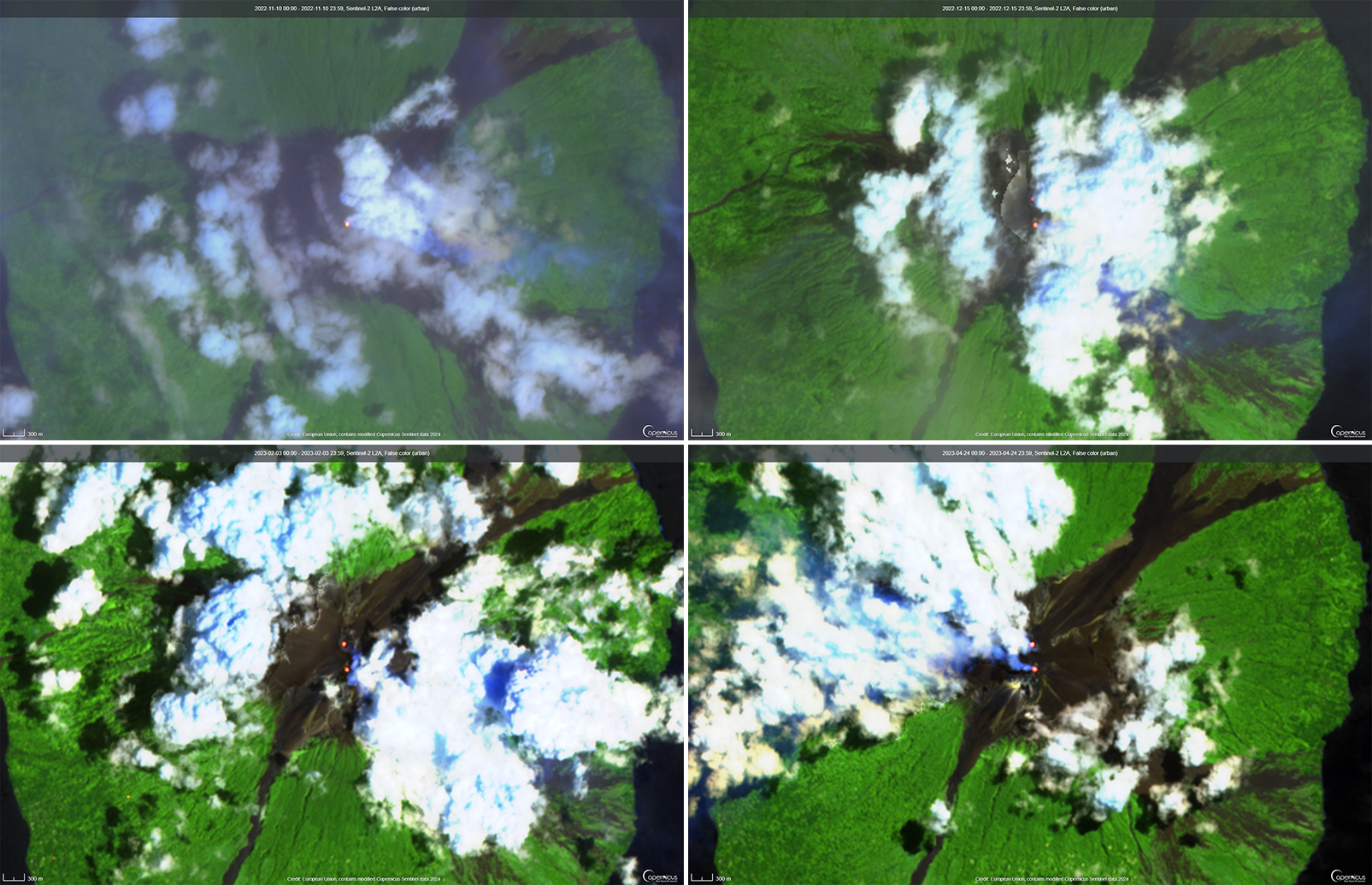
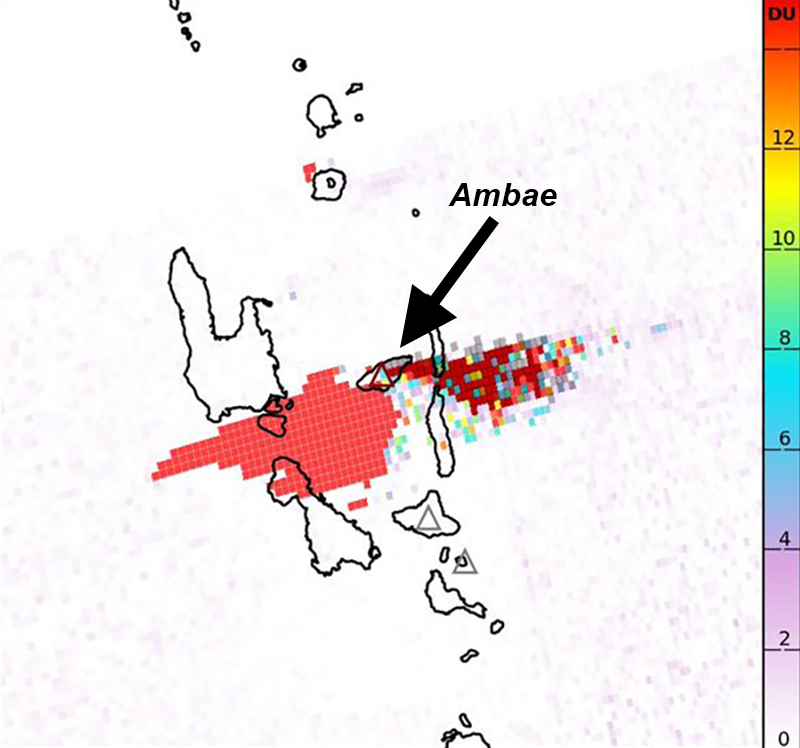
Intermittent sulfur dioxide plumes were detected using the TROPOMI instrument on the Sentinel-5P satellite, some of which exceeded at least two Dobson Units (DU) and drifted in different directions (figure 93). Occasional low-to-moderate power thermal anomalies were recorded by the MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) system; less than five anomalies were recorded each month during November 2022 through May 2023 (figure 94). Two thermal hotspots were detected by the MODVOLC thermal alerts system on 10 December 2022. On clear weather days, thermal activity was also captured in infrared satellite imagery in both the Main and South summit craters, accompanied by gas-and-steam emissions (figure 95).
Geologic Background. The 10-km-wide island of Manam, lying 13 km off the northern coast of mainland Papua New Guinea, is one of the country's most active volcanoes. Four large radial valleys extend from the unvegetated summit of the conical basaltic-andesitic stratovolcano to its lower flanks. These valleys channel lava flows and pyroclastic avalanches that have sometimes reached the coast. Five small satellitic centers are located near the island's shoreline on the northern, southern, and western sides. Two summit craters are present; both are active, although most observed eruptions have originated from the southern crater, concentrating eruptive products during much of the past century into the SE valley. Frequent eruptions, typically of mild-to-moderate scale, have been recorded since 1616. Occasional larger eruptions have produced pyroclastic flows and lava flows that reached flat-lying coastal areas and entered the sea, sometimes impacting populated areas.
Information Contacts: Rabaul Volcano Observatory (RVO), Geohazards Management Division, Department of Mineral Policy and Geohazards Management (DMPGM), PO Box 3386, Kokopo, East New Britain Province, Papua New Guinea; Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Bureau of Meteorology, Northern Territory Regional Office, PO Box 40050, Casuarina, NT 0811, Australia (URL: http://www.bom.gov.au/info/vaac/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); NASA Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Krakatau (Indonesia) — July 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Krakatau
Indonesia
6.1009°S, 105.4233°E; summit elev. 285 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
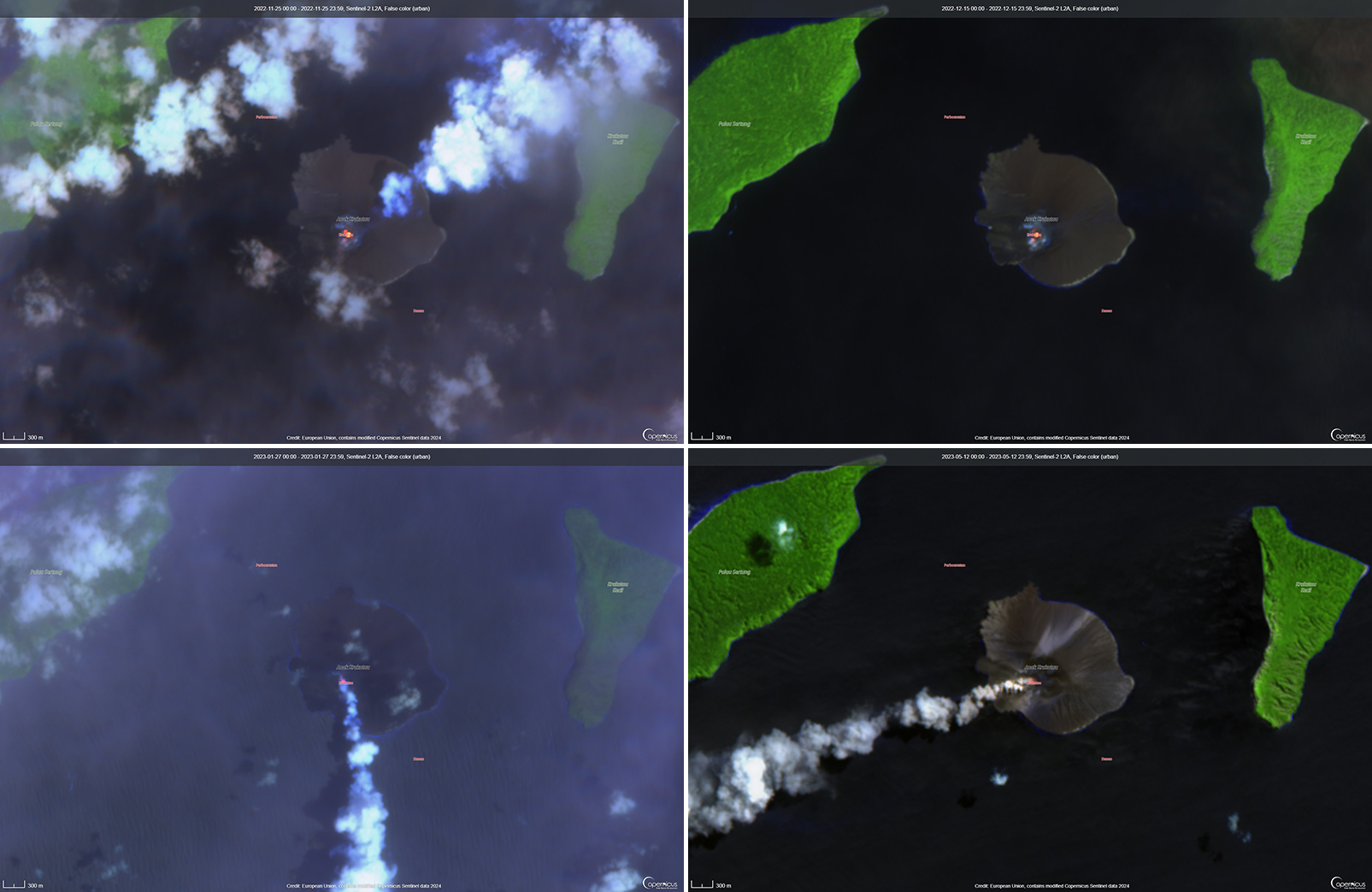
Strombolian activity and ash plumes during November 2022-April 2023
Krakatau is located in the Sunda Strait between Java and Sumatra, Indonesia. Caldera collapse during the catastrophic 1883 eruption destroyed Danan and Perbuwatan cones and left only a remnant of Rakata. The post-collapse cone of Anak Krakatau (Child of Krakatau) was constructed within the 1883 caldera at a point between the former Danan and Perbuwatan cones; it has been the site of frequent eruptions since 1927. The current eruption period began in May 2021 and has recently consisted of explosions, ash plumes, and thermal activity (BGVN 47:11). This report covers activity during November 2022 through April 2023 based on information provided by the Indonesian Center for Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation, referred to as Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG), MAGMA Indonesia, the Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), and several sources of satellite data.
Activity was relatively low during November and December 2022. Daily white gas-and-steam plumes rose 25-100 m above the summit and drifted in different directions. Gray ash plumes rose 200 m above the summit and drifted NE at 1047 and at 2343 on 11 November. On 14 November at 0933 ash plumes rose 300 m above the summit and drifted E. An ash plume was reported at 0935 on 15 December that rose 100 m above the summit and drifted NE. An eruptive event at 1031 later that day generated an ash plume that rose 700 m above the summit and drifted NE. A gray ash plume at 1910 rose 100 m above the summit and drifted E. Incandescent material was ejected above the vent based on an image taken at 1936.
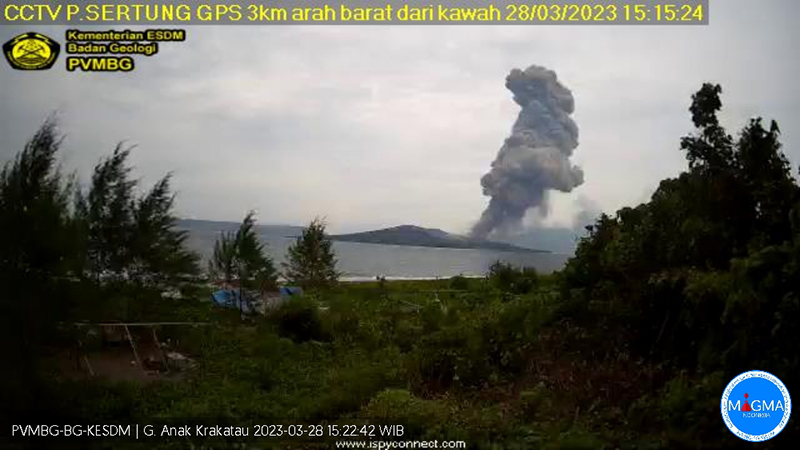
During January 2023 daily white gas-and-steam plumes rose 25-300 m above the summit and drifted in multiple directions. Gray-to-brown ash plumes were reported at 1638 on 3 January, at 1410 and 1509 on 4 January, and at 0013 on 5 January that rose 100-750 m above the summit and drifted NE and E; the gray-to-black ash plume at 1509 on 4 January rose as high as 3 km above the summit and drifted E. Gray ash plumes were recorded at 1754, 2241, and 2325 on 11 January and at 0046 on 12 January and rose 200-300 m above the summit and drifted NE. Toward the end of January, PVMBG reported that activity had intensified; Strombolian activity was visible in webcam images taken at 0041, 0043, and 0450 on 23 January. Multiple gray ash plumes throughout the day rose 200-500 m above the summit and drifted E and SE (figure 135). Webcam images showed progressively intensifying Strombolian activity at 1919, 1958, and 2113 on 24 January; a gray ash plume at 1957 rose 300 m above the summit and drifted E (figure 135). Eruptive events at 0231 and 2256 on 25 January and at 0003 on 26 January ejected incandescent material from the vent, based on webcam images. Gray ash plumes observed during 26-27 January rose 300-500 m above the summit and drifted NE, E, and SE.
Low levels of activity were reported during February and March. Daily white gas-and-steam plumes rose 25-300 m above the summit and drifted in different directions. The Darwin VAAC reported that continuous ash emissions rose to 1.5-1.8 km altitude and drifted W and NW during 1240-1300 on 10 March, based on satellite images, weather models, and PVMBG webcams. White-and-gray ash plumes rose 500 m and 300 m above the summit and drifted SW at 1446 and 1846 on 18 March, respectively. An eruptive event was recorded at 2143, though it was not visible due to darkness. Multiple ash plumes were reported during 27-29 March that rose as high as 2.5 km above the summit and drifted NE, W, and SW (figure 136). Webcam images captured incandescent ejecta above the vent at 0415 and around the summit area at 2003 on 28 March and at 0047 above the vent on 29 March.
Daily white gas-and-steam plumes rose 25-300 m above the summit and drifted in multiple directions during April and May. White-and-gray and black plumes rose 50-300 m above the summit on 2 and 9 April. On 11 May at 1241 a gray ash plume rose 1-3 km above the summit and drifted SW. On 12 May at 0920 a gray ash plume rose 2.5 km above the summit and drifted SW and at 2320 an ash plume rose 1.5 km above the summit and drifted SW. An accompanying webcam image showed incandescent ejecta. On 13 May at 0710 a gray ash plume rose 2 km above the summit and drifted SW (figure 137).
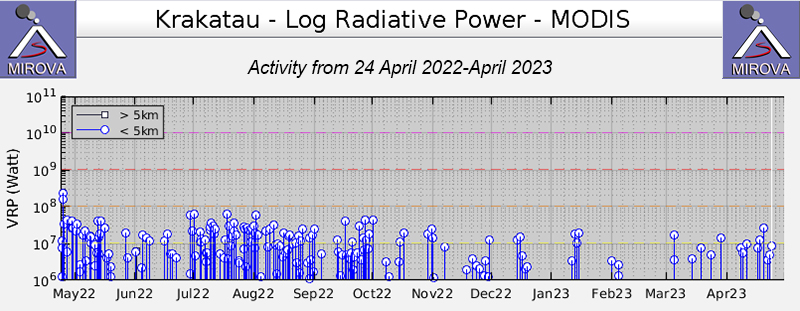
The MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) graph of MODIS thermal anomaly data showed intermittent low-to-moderate power thermal anomalies during November 2022 through April 2023 (figure 138). Some of this thermal activity was also visible in infrared satellite imagery at the crater, accompanied by gas-and-steam and ash plumes that drifted in different directions (figure 139).
Geologic Background. The renowned Krakatau (frequently mis-named as Krakatoa) volcano lies in the Sunda Strait between Java and Sumatra. Collapse of an older edifice, perhaps in 416 or 535 CE, formed a 7-km-wide caldera. Remnants of that volcano are preserved in Verlaten and Lang Islands; subsequently the Rakata, Danan, and Perbuwatan cones were formed, coalescing to create the pre-1883 Krakatau Island. Caldera collapse during the catastrophic 1883 eruption destroyed Danan and Perbuwatan, and left only a remnant of Rakata. This eruption caused more than 36,000 fatalities, most as a result of tsunamis that swept the adjacent coastlines of Sumatra and Java. Pyroclastic surges traveled 40 km across the Sunda Strait and reached the Sumatra coast. After a quiescence of less than a half century, the post-collapse cone of Anak Krakatau (Child of Krakatau) was constructed within the 1883 caldera at a point between the former Danan and Perbuwatan cones. Anak Krakatau has been the site of frequent eruptions since 1927.
Information Contacts: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as Indonesian Center for Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation, CVGHM), Jalan Diponegoro 57, Bandung 40122, Indonesia (URL: http://www.vsi.esdm.go.id/); MAGMA Indonesia, Kementerian Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral (URL: https://magma.esdm.go.id/v1); Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Bureau of Meteorology, Northern Territory Regional Office, PO Box 40050, Casuarina, NT 0811, Australia (URL: http://www.bom.gov.au/info/vaac/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Stromboli
Italy
38.789°N, 15.213°E; summit elev. 924 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Strombolian explosions and lava flows continue during January-April 2023
Stromboli, located in Italy, has exhibited nearly constant lava fountains for the past 2,000 years; recorded eruptions date back to 350 BCE. Eruptive activity occurs at the summit from multiple vents, which include a north crater area (N area) and a central-southern crater (CS area) on a terrace known as the ‘terrazza craterica’ at the head of the Sciara del Fuoco, a large scarp that runs from the summit down the NW side of the volcano-island. Activity typically consists of Strombolian explosions, incandescent ejecta, lava flows, and pyroclastic flows. Thermal and visual monitoring cameras are located on the nearby Pizzo Sopra La Fossa, above the terrazza craterica, and at multiple flank locations. The current eruption period has been ongoing since 1934 and recent activity has consisted of frequent Strombolian explosions and lava flows (BGVN 48:02). This report updates activity during January through April 2023 primarily characterized by Strombolian explosions and lava flows based on reports from Italy's Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV) and various satellite data.
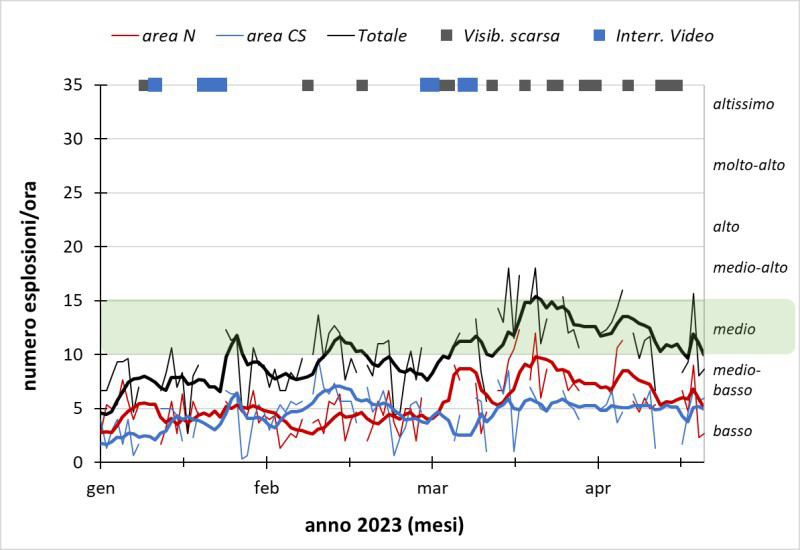
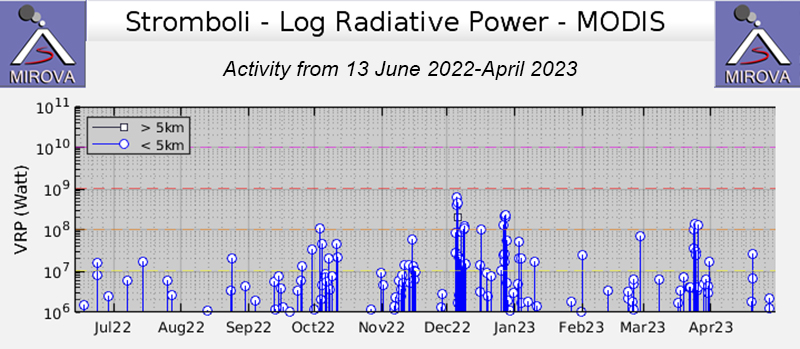
Frequent explosive activity continued throughout the reporting period, generally in the low-to-medium range, based on the number of hourly explosions in the summit crater (figure 253, table 16). Intermittent thermal activity was recorded by the MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) analysis of MODIS satellite data (figure 254). According to data collected by the MODVOLC thermal algorithm, a total of 9 thermal alerts were detected: one on 2 January 2023, one on 1 February, five on 24 March, and two on 26 March. The stronger pulses of thermal activity likely reflected lava flow events. Infrared satellite imagery captured relatively strong thermal hotspots at the two active summit craters on clear weather days, showing an especially strong event on 8 March (figure 255).
Table 16. Summary of type, frequency, and intensity of explosive activity at Stromboli by month during January-April 2023; information from webcam observations. Courtesy of INGV weekly reports.
| Month |
Explosive Activity |
| Jan 2023 |
Typical Strombolian activity with spattering and lava overflows in the N crater area. Explosions were reported from 4 vents in the N area and 1-2 vents in the CS area. The average hourly frequency of explosions was low-to-medium (1-12 events/hour). The intensity of the explosions varied from low (less than 80 m high) to medium (less than 150 m high) in the N crater area and up to high (greater than 150 m high) in the CS crater area. |
| Feb 2023 |
Typical Strombolian activity with spattering in the N crater area. Explosions were reported from 2-3 vents in the N area and 1-4 vents in the CS area. The average hourly frequency of explosions was low-to-medium (1-14 events/hour). The intensity of the explosions varied from low (less than 80 m high) to medium (less than 150 m high) in the N crater area and up to high (greater than 150 m high) in the CS crater area. |
| Mar 2023 |
Typical Strombolian activity with spattering and lava overflows in the N crater area. Explosions were reported from 2-3 vents in the N area and 2-4 vents in the CS area. The average hourly frequency of explosions was low-to-medium (1-18 events/hour). The intensity of the explosions varied from low (less than 80 m high) to medium (less than 150 m high) in the N crater area and up to high (greater than 150 m high) in the CS crater area. |
| Apr 2023 |
Typical Strombolian activity. Explosions were reported from 2 vents in the N area and 2-3 vents in the CS area. The average hourly frequency of explosions was low-to-high (1-16 events/hour). The intensity of the explosions varied from low (less than 80 m high) to medium (less than 150 m high) in both the N and CS crater areas. |
Activity during January-February 2023. Strombolian explosions were reported in the N crater area, as well as lava effusion. Explosive activity in the N crater area ejected coarse material (bombs and lapilli). Intense spattering was observed in both the N1 and N2 craters. In the CS crater area, explosions generally ejected fine material (ash), sometimes to heights greater than 250 m. The intensity of the explosions was characterized as low-to-medium in the N crater and medium-to-high in the CS crater. After intense spattering activity from the N crater area, a lava overflow began at 2136 on 2 January that flowed part way down the Sciara del Fuoco, possibly moving down the drainage that formed in October, out of view from webcams. The flow remained active for a couple of hours before stopping and beginning to cool. A second lava flow was reported at 0224 on 4 January that similarly remained active for a few hours before stopping and cooling. Intense spattering was observed on 11 and 13 January from the N1 crater. After intense spattering activity at the N2 crater at 1052 on 17 January another lava flow started to flow into the upper part of the Sciara del Fuoco (figure 256), dividing into two: one that traveled in the direction of the drainage formed in October, and the other one moving parallel to the point of emission. By the afternoon, the rate of the flow began to decrease, and at 1900 it started to cool. A lava flow was reported at 1519 on 24 January following intense spattering in the N2 area, which began to flow into the upper part of the Sciara del Fuoco. By the morning of 25 January, the lava flow had begun to cool. During 27 January the frequency of eruption in the CS crater area increased to 6-7 events/hour compared to the typical 1-7 events/hour; the following two days showed a decrease in frequency to less than 1 event/hour. Starting at 1007 on 30 January a high-energy explosive sequence was produced by vents in the CS crater area. The sequence began with an initial energetic pulse that lasted 45 seconds, ejecting predominantly coarse products 300 m above the crater that fell in an ESE direction. Subsequent and less intense explosions ejected material 100 m above the crater. The total duration of this event lasted approximately two minutes. During 31 January through 6, 13, and 24 February spattering activity was particularly intense for short periods in the N2 crater.
An explosive sequence was reported on 16 February that was characterized by a major explosion in the CS crater area (figure 257). The sequence began at 1817 near the S2 crater that ejected material radially. A few seconds later, lava fountains were observed in the central part of the crater. Three explosions of medium intensity (material was ejected less than 150 m high) were recorded at the S2 crater. The first part of this sequence lasted approximately one minute, according to INGV, and material rose 300 m above the crater and then was deposited along the Sciara del Fuoco. The second phase began at 1818 at the S1 crater; it lasted seven seconds and material was ejected 150 m above the crater. Another event 20 seconds later lasted 12 seconds, also ejecting material 150 m above the crater. The sequence ended with at least three explosions of mostly fine material from the S1 crater. The total duration of this sequence was about two minutes.
Short, intense spattering activity was noted above the N1 crater on 27 and 28 February. A lava overflow was first reported at 0657 from the N2 crater on 27 February that flowed into the October 2022 drainage. By 1900 the flow had stopped. A second lava overflow also in the N crater area occurred at 2149, which overlapped the first flow and then stopped by 0150 on 28 February. Material detached from both the lava overflows rolled down the Sciara del Fuoco, some of which was visible in webcam images.
Activity during March-April 2023. Strombolian activity continued with spattering activity and lava overflows in the N crater area during March. Explosive activity at the N crater area varied from low (less than 80 m high) to medium (less than 150 m high) and ejected coarse material, such as bombs and lapilli. Spattering was observed above the N1 crater, while explosive activity at the CS crater area varied from medium to high (greater than 150 m high) and ejected coarse material. Intense spattering activity was observed for short periods on 6 March above the N1 crater. At approximately 0610 a lava overflow was reported around the N2 crater on 8 March, which then flowed into the October 2022 drainage. By 1700 the flow started to cool. A second overflow began at 1712 on 9 March and overlapped the previous flow. It had stopped by 2100. Material from both flows was deposited along the Sciara del Fuoco, though much of the activity was not visible in webcam images. On 11 March a lava overflow was observed at 0215 that overlapped the two previous flows in the October 2022 drainage. By late afternoon on 12 March, it had stopped.
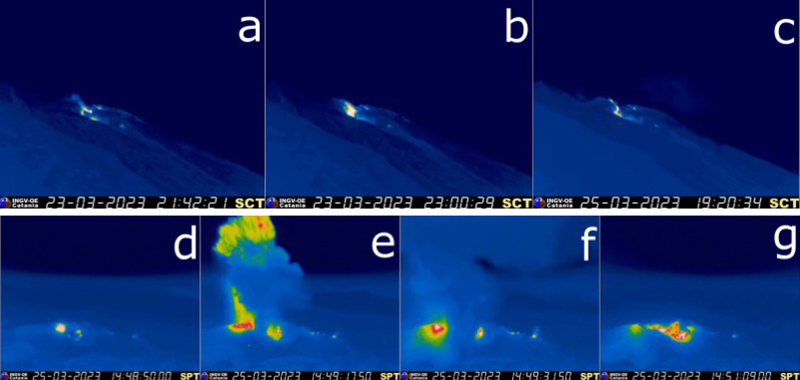
During a field excursion on 16 March, scientists noted that a vent in the central crater area was degassing. Another vent showed occasional Strombolian activity that emitted ash and lapilli. During 1200-1430 low-to-medium intense activity was reported; the N1 crater emitted ash emissions and the N2 crater emitted both ash and coarse material. Some explosions also occurred in the CS crater area that ejected coarse material. The C crater in the CS crater area occasionally showed gas jetting and low intensity explosions on 17 and 22 March; no activity was observed at the S1 crater. Intense, longer periods of spattering were reported in the N1 crater on 19, 24, and 25 March. Around 2242 on 23 March a lava overflow began from the N1 crater that, after about an hour, began moving down the October 2022 drainage and flow along the Sciara del Fuoco (figure 258). Between 0200 and 0400 on 26 March the flow rate increased, which generated avalanches of material from collapses at the advancing flow front. By early afternoon, the flow began to cool. On 25 March at 1548 an explosive sequence began from one of the vents at S2 in the CS crater area (figure 258). Fine ash mixed with coarse material was ejected 300 m above the crater rim and drifted SSE. Some modest explosions around Vent C were detected at 1549 on 25 March, which included an explosion at 1551 that ejected coarse material. The entire explosive sequence lasted approximately three minutes.
During April explosions persisted in both the N and CS crater areas. Fine material was ejected less than 80 m above the N crater rim until 6 April, followed by ejection of coarser material. Fine material was also ejected less than 80 m above the CS crater rim. The C and S2 crater did not show significant eruptive activity. On 7 April an explosive sequence was detected in the CS crater area at 1203 (figure 259). The first explosion lasted approximately 18 seconds and ejected material 400 m above the crater rim, depositing pyroclastic material in the upper part of the Sciara del Fuoco. At 1204 a second, less intense explosion lasted approximately four seconds and deposited pyroclastic products outside the crater area and near Pizzo Sopra La Fossa. A third explosion at 1205 was mainly composed of ash that rose about 150 m above the crater and lasted roughly 20 seconds. A fourth explosion occurred at 1205 about 28 seconds after the third explosion and ejected a mixture of coarse and fine material about 200 m above the crater; the explosion lasted roughly seven seconds. Overall, the entire explosive sequence lasted about two minutes and 20 seconds. After the explosive sequence on 7 April, explosions in both the N and CS crater areas ejected material as high as 150 m above the crater.
On 21 April research scientists from INGV made field observations in the summit area of Stromboli, and some lapilli samples were collected. In the N crater area near the N1 crater, a small cone was observed with at least two active vents, one of which was characterized by Strombolian explosions. The other vent produced explosions that ejected ash and chunks of cooled lava. At the N2 crater at least one vent was active and frequently emitted ash. In the CS crater area, a small cone contained 2-3 degassing vents and a smaller, possible fissure area also showed signs of degassing close to the Pizzo Sopra La Fossa. In the S part of the crater, three vents were active: a small hornito was characterized by modest and rare explosions, a vent that intermittently produced weak Strombolian explosions, and a vent at the end of the terrace that produced frequent ash emissions. Near the S1 crater there was a hornito that generally emitted weak gas-and-steam emissions, sometimes associated with “gas rings”. On 22 April another field inspection was carried out that reported two large sliding surfaces on the Sciara del Fuoco that showed where blocks frequently descended toward the sea. A thermal anomaly was detected at 0150 on 29 April.
Geologic Background. Spectacular incandescent nighttime explosions at Stromboli have long attracted visitors to the "Lighthouse of the Mediterranean" in the NE Aeolian Islands. This volcano has lent its name to the frequent mild explosive activity that has characterized its eruptions throughout much of historical time. The small island is the emergent summit of a volcano that grew in two main eruptive cycles, the last of which formed the western portion of the island. The Neostromboli eruptive period took place between about 13,000 and 5,000 years ago. The active summit vents are located at the head of the Sciara del Fuoco, a prominent scarp that formed about 5,000 years ago due to a series of slope failures which extends to below sea level. The modern volcano has been constructed within this scarp, which funnels pyroclastic ejecta and lava flows to the NW. Essentially continuous mild Strombolian explosions, sometimes accompanied by lava flows, have been recorded for more than a millennium.
Information Contacts: Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV), Sezione di Catania, Piazza Roma 2, 95123 Catania, Italy, (URL: http://www.ct.ingv.it/en/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Nishinoshima (Japan) — July 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Nishinoshima
Japan
27.247°N, 140.874°E; summit elev. 100 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Small ash plumes and fumarolic activity during November 2022 through April 2023
Nishinoshima is a small island located about 1,000 km S of Tokyo in the Ogasawara Arc in Japan. The island is the summit of a massive submarine volcano that has prominent peaks to the S, W, and NE. Eruptions date back to 1973; the most recent eruption period began in October 2022 and was characterized by ash plumes and fumarolic activity (BGVN 47:12). This report describes ash plumes and fumarolic activity during November 2022 through April 2023 based on monthly reports from the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) monthly reports and satellite data.
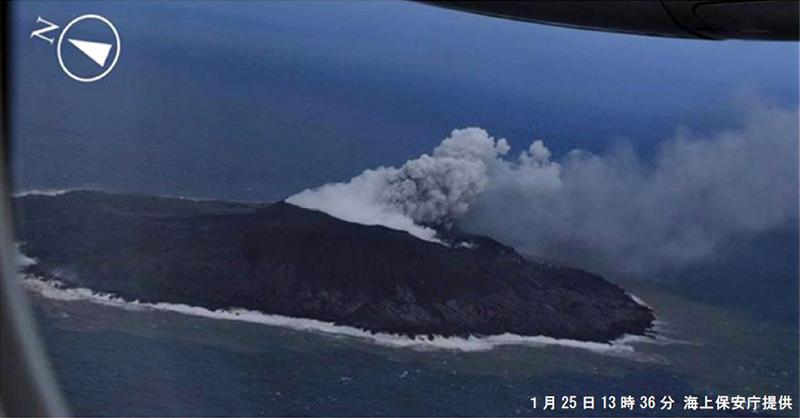
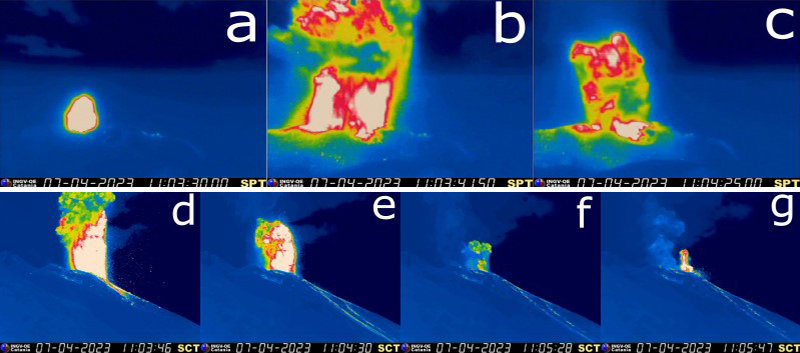
The most recent eruptive activity prior to the reporting internal occurred on 12 October 2022, when an ash plume rose 3.5 km above the crater rim. An aerial observation conducted by the Japan Coast Guard (JCG) on 25 November reported that white fumaroles rose approximately 200 m above the central crater of a pyroclastic cone (figure 119), and multiple plumes were observed on the ESE flank of the cone. Discolored water ranging from reddish-brown to brown and yellowish-green were visible around the perimeter of the island (figure 119). No significant activity was reported in December.
During an overflight conducted by JCG on 25 January 2023 intermittent activity and small, blackish-gray plumes rose 900 m above the central part of the crater were observed (figure 120). The fumarolic zone of the E flank and base of the cone had expanded and emissions had intensified. Dark brown discolored water was visible around the perimeter of the island.
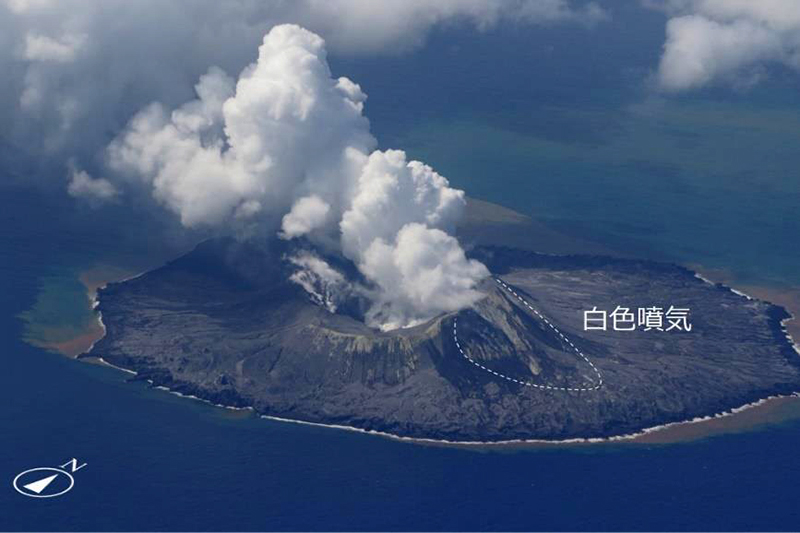
No significant activity was reported during February through March. Ash plumes at 1050 and 1420 on 11 April rose 1.9 km above the crater rim and drifted NW and N. These were the first ash plumes observed since 12 October 2022. On 14 April JCG carried out an overflight and reported that no further eruptive activity was visible, although white gas-and-steam plumes were visible from the central crater and rose 900 m high (figure 121). Brownish and yellow-green discolored water surrounded the island.
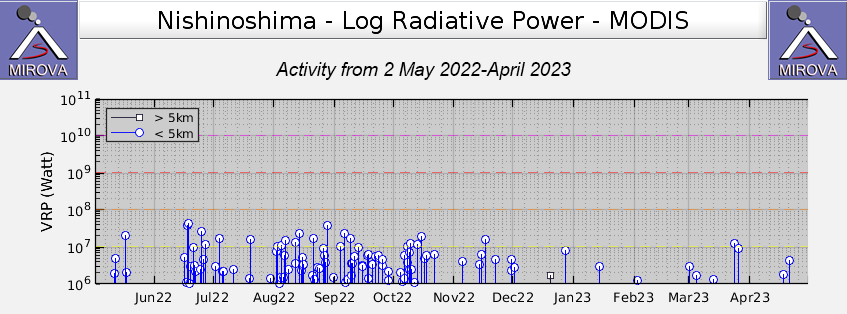
Intermittent low-to-moderate power thermal anomalies were recorded in the MIROVA graph (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) during November 2022 through April 2023 (figure 123). A cluster of six to eight anomalies were detected during November while a smaller number were detected during the following months: two to three during December, one during mid-January 2023, one during February, five during March, and two during April. Thermal activity was also reflected in infrared satellite data at the summit crater, accompanied by occasional gas-and-steam plumes (figure 124).
Geologic Background. The small island of Nishinoshima was enlarged when several new islands coalesced during an eruption in 1973-74. Multiple eruptions that began in 2013 completely covered the previous exposed surface and continued to enlarge the island. The island is the summit of a massive submarine volcano that has prominent peaks to the S, W, and NE. The summit of the southern cone rises to within 214 m of the ocean surface 9 km SSE.
Information Contacts: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA), 1-3-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8122, Japan (URL: http://www.jma.go.jp/jma/indexe.html); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Karangetang (Indonesia) — July 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Karangetang
Indonesia
2.781°N, 125.407°E; summit elev. 1797 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
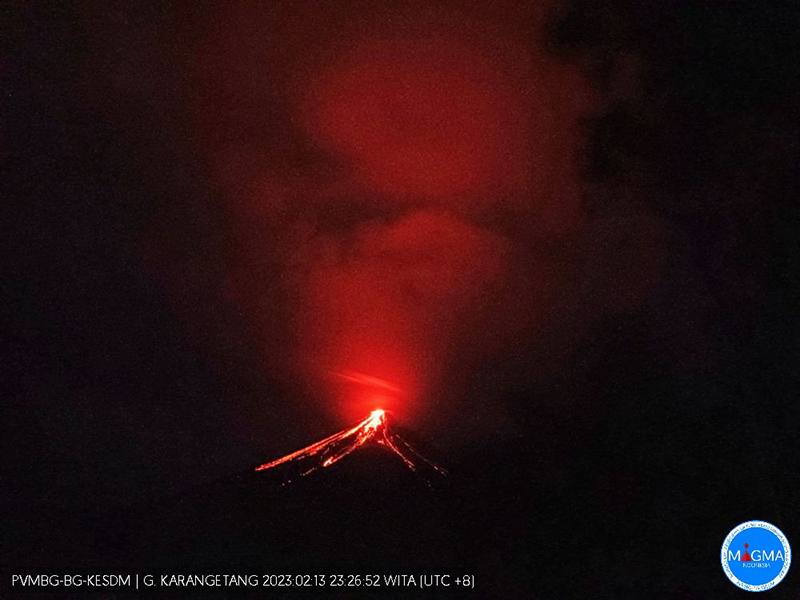
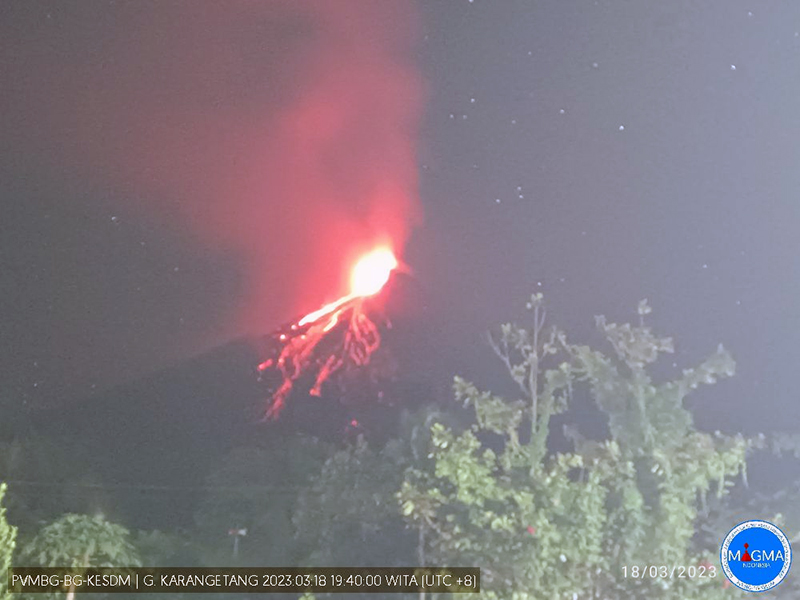
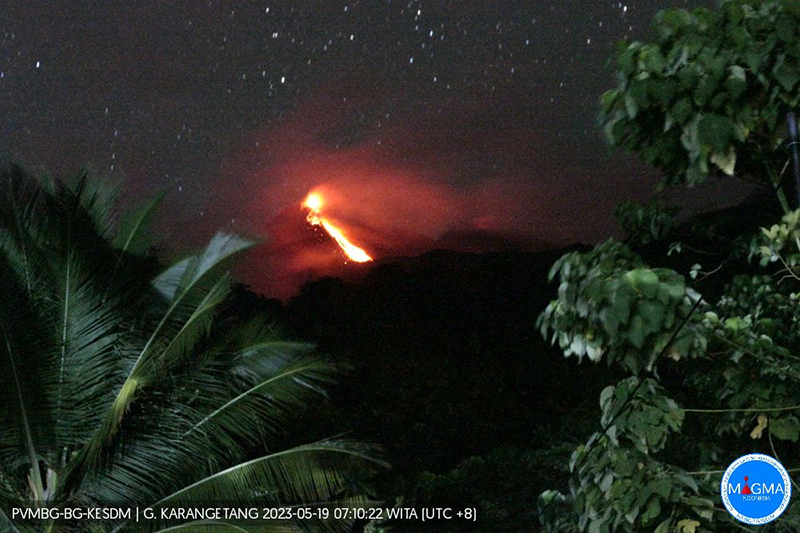
Lava flows, incandescent avalanches, and ash plumes during January-June 2023
Karangetang (also known as Api Siau), at the northern end of the island of Siau, Indonesia, contains five summit craters along a N-S line. More than 40 eruptions have been recorded since 1675; recent eruptions have included frequent explosive activity, sometimes accompanied by pyroclastic flows and lahars. Lava dome growth has occurred in the summit craters and collapses of lava flow fronts have produced pyroclastic flows. The two active summit craters are Kawah Dua (the N crater) and Kawah Utama (the S crater, also referred to as the “Main Crater”). The most recent eruption began in late November 2018 and has more recently consisted of weak thermal activity and gas-and-steam emissions (BGVN 48:01). This report updates activity characterized by lava flows, incandescent avalanches, and ash plumes during January through June 2023 using reports from Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as CVGHM, or the Center of Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation), MAGMA Indonesia, the Darwin VAAC (Volcano Ash Advisory Center), and satellite data.
Activity during January was relatively low and mainly consisted of white gas-and-steam emissions that rose 25-150 m above Main Crater (S crater) and drifted in different directions. Incandescence was visible from the lava dome in Kawah Dua (the N crater). Weather conditions often prevented clear views of the summit. On 18 January the number of seismic signals that indicated avalanches of material began to increase. In addition, there were a total of 71 earthquakes detected during the month.
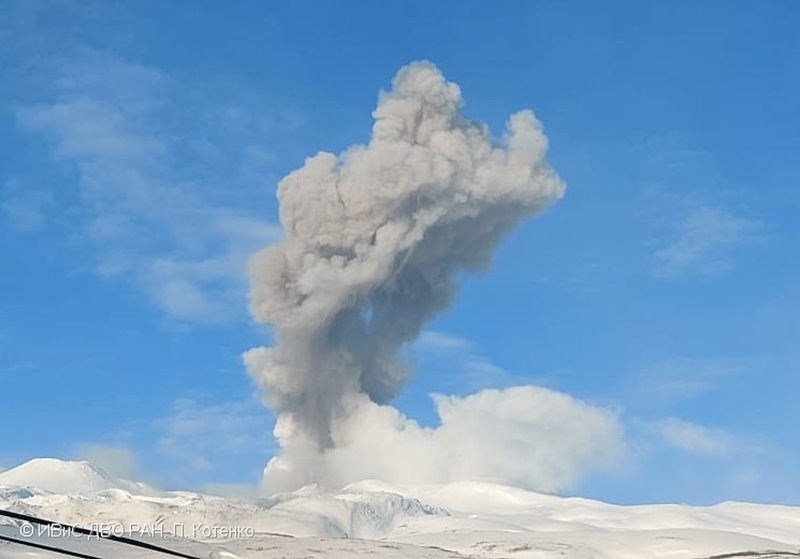
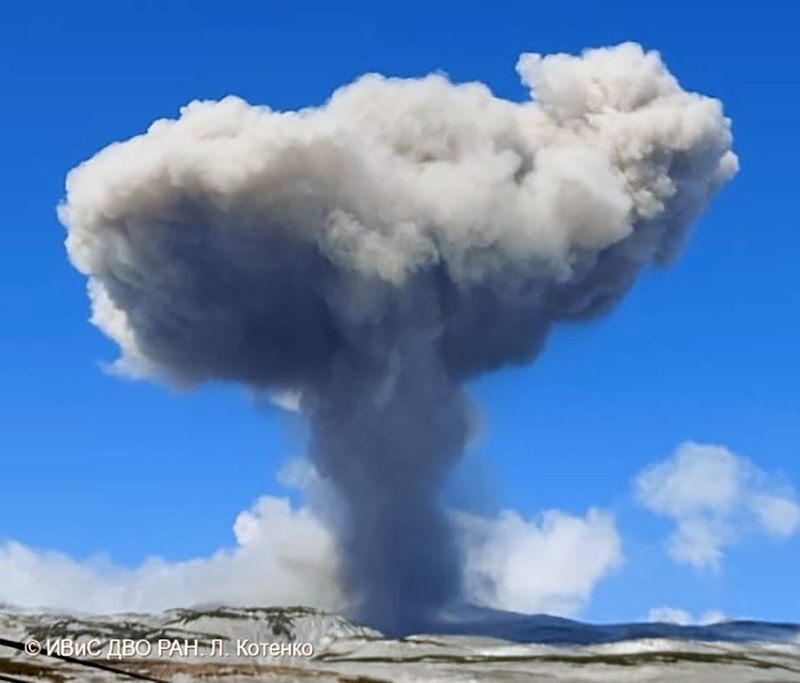
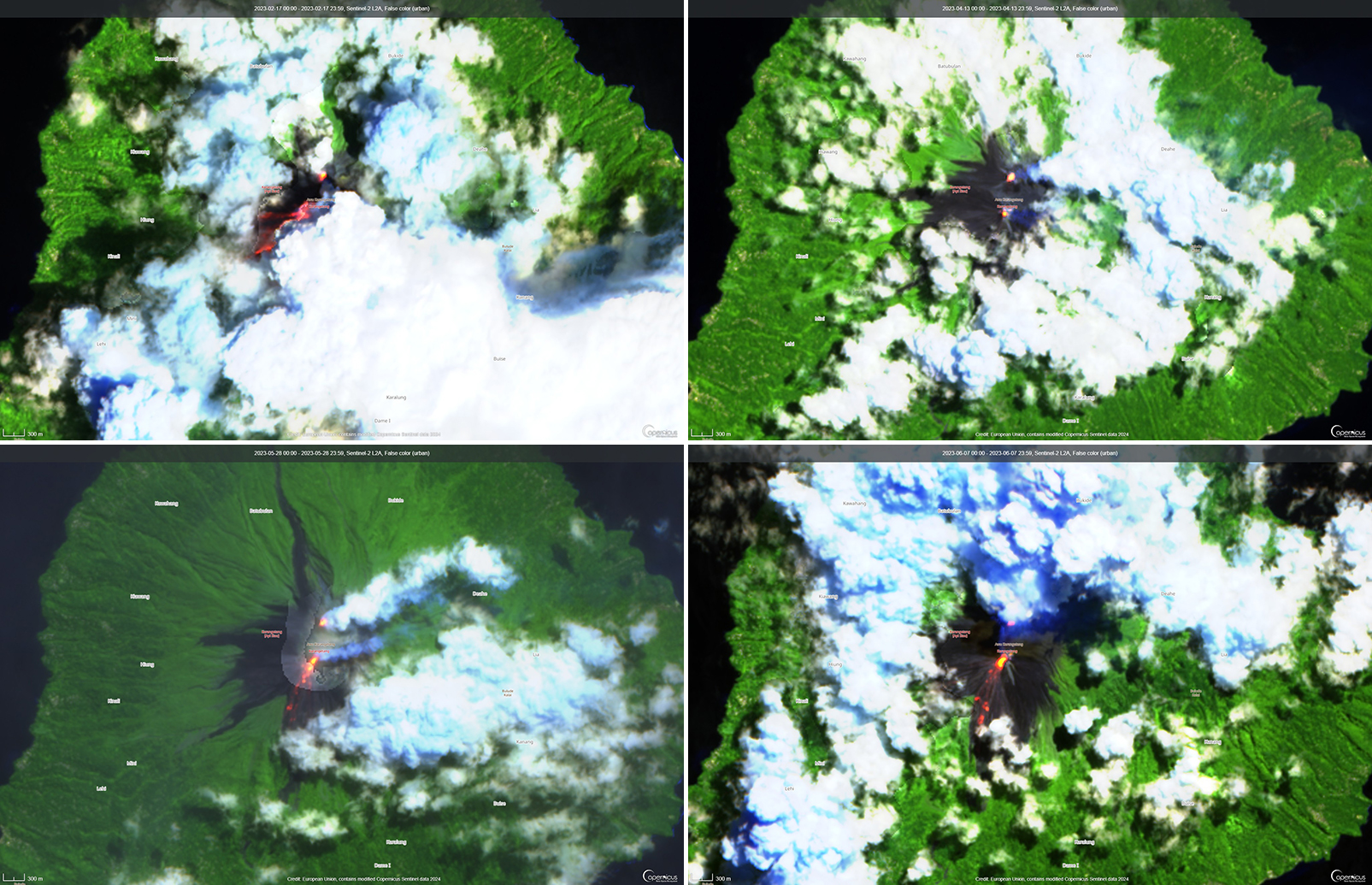
Activity continued to increase during the first week of February. Material from Main Crater traveled as far as 800 m down the Batuawang (S) and Batang (W) drainages and as far as 1 km W down the Beha (W) drainage on 4 February. On 6 February 43 earthquake events were recorded, and on 7 February, 62 events were recorded. White gas-and-steam emissions rose 25-250 m above both summit craters throughout the month. PVMBG reported an eruption began during the evening of 8 February around 1700. Photos showed incandescent material at Main Crater. Incandescent material had also descended the flank in at least two unconfirmed directions as far as 2 km from Main Crater, accompanied by ash plumes (figure 60). As a result, PVMBG increased the Volcano Alert Level (VAL) to 3 (the second highest level on a 1-4 scale).
Occasional nighttime webcam images showed three main incandescent lava flows of differing lengths traveling down the S, SW, and W flanks (figure 61). Incandescent rocks were visible on the upper flanks, possibly from ejected or collapsed material from the crater, and incandescence was the most intense at the summit. Based on analyses of satellite imagery and weather models, the Darwin VAAC reported that daily ash plumes during 16-20 February rose to 2.1-3 km altitude and drifted NNE, E, and SE. BNPB reported on 16 February that as many as 77 people were evacuated and relocated to the East Siau Museum. A webcam image taken at 2156 on 17 February possibly showed incandescent material descending the SE flank. Ash plumes rose to 2.1 km altitude and drifted SE during 22-23 February, according to the Darwin VAAC.
Incandescent avalanches of material and summit incandescence at Main Crater continued during March. White gas-and-steam emissions during March generally rose 25-150 m above the summit crater; on 31 March gas-and-steam emissions rose 200-400 m high. An ash plume rose to 2.4 km altitude and drifted S at 1710 on 9 March and a large thermal anomaly was visible in images taken at 0550 and 0930 on 10 March. Incandescent material was visible at the summit and on the flanks based on webcam images taken at 0007 and 2345 on 16 March, at 1828 on 17 March, at 1940 on 18 March, at 2311 on 19 March, and at 2351 on 20 March. Incandescence was most intense on 18 and 20 March and webcam images showed possible Strombolian explosions (figure 62). An ash plume rose to 2.4 km altitude and drifted SW on 18 March, accompanied by a thermal anomaly.
Summit crater incandescence at Main Crater and on the flanks persisted during April. Incandescent material at the S crater and on the flanks was reported at 0016 on 1 April. The lava flows had stopped by 1 April according to PVMBG, although incandescence was still visible up to 10 m high. Seismic signals indicating effusion decreased and by 6 April they were no longer detected. Incandescence was visible from both summit craters. On 26 April the VAL was lowered to 2 (the second lowest level on a 1-4 scale). White gas-and-steam emissions rose 25-200 m above the summit crater.
During May white gas-and-steam emissions generally rose 50-250 m above the summit, though it was often cloudy, which prevented clear views; on 21 May gas-and-steam emissions rose 50-400 m high. Nighttime N summit crater incandescence rose 10-25 m above the lava dome, and less intense incandescence was noted above Main Crater, which reached about 10 m above the dome. Sounds of falling rocks at Main Crater were heard on 15 May and the seismic network recorded 32 rockfall events in the crater on 17 May. Avalanches traveled as far as 1.5 km down the SW and S flanks, accompanied by rumbling sounds on 18 May. Incandescent material descending the flanks was captured in a webcam image at 2025 on 19 May (figure 63) and on 29 May; summit crater incandescence was observed in webcam images at 2332 on 26 May and at 2304 on 29 May. On 19 May the VAL was again raised to 3.
Occasional Main Crater incandescence was reported during June, as well as incandescent material on the flanks. White gas-and-steam emissions rose 10-200 m above the summit crater. Ash plumes rose to 2.1 km altitude and drifted SE and E during 2-4 June, according to the Darwin VAAC. Material on the flanks of Main Crater were observed at 2225 on 7 June, at 2051 on 9 June, at 0007 on 17 June, and at 0440 on 18 June. Webcam images taken on 21, 25, and 27 June showed incandescence at Main Crater and from material on the flanks.
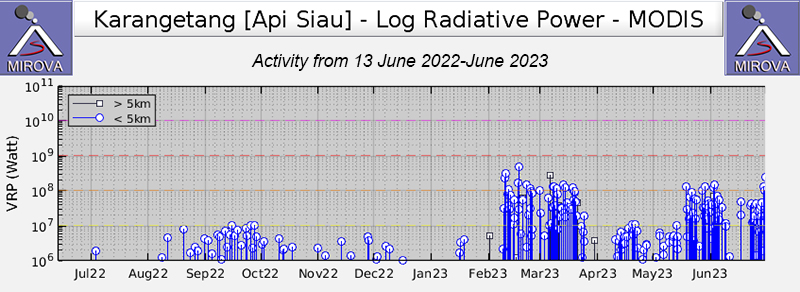
MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) analysis of MODIS satellite data showed strong thermal activity during mid-February through March and mid-May through June, which represented incandescent avalanches and lava flows (figure 64). During April through mid-May the power of the anomalies decreased but frequent anomalies were still detected. Brief gaps in activity occurred during late March through early April and during mid-June. Infrared satellite images showed strong lava flows mainly affecting the SW and S flanks, accompanied by gas-and-steam emissions (figure 65). According to data recorded by the MODVOLC thermal algorithm, there were a total of 79 thermal hotspots detected: 28 during February, 24 during March, one during April, five during May, and 21 during June.
Geologic Background. Karangetang (Api Siau) volcano lies at the northern end of the island of Siau, about 125 km NNE of the NE-most point of Sulawesi. The stratovolcano contains five summit craters along a N-S line. It is one of Indonesia's most active volcanoes, with more than 40 eruptions recorded since 1675 and many additional small eruptions that were not documented (Neumann van Padang, 1951). Twentieth-century eruptions have included frequent explosive activity sometimes accompanied by pyroclastic flows and lahars. Lava dome growth has occurred in the summit craters; collapse of lava flow fronts have produced pyroclastic flows.
Information Contacts: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as Indonesian Center for Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation, CVGHM), Jalan Diponegoro 57, Bandung 40122, Indonesia (URL: http://www.vsi.esdm.go.id/); MAGMA Indonesia, Kementerian Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral (URL: https://magma.esdm.go.id/v1); Badan Nasional Penanggulangan Bencana (BNPB), National Disaster Management Agency, Graha BNPB - Jl. Scout Kav.38, East Jakarta 13120, Indonesia (URL: http://www.bnpb.go.id/); Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Bureau of Meteorology, Northern Territory Regional Office, PO Box 40050, Casuarina, NT 0811, Australia (URL: http://www.bom.gov.au/info/vaac/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/); IDN Times, Jl. Jend. Gatot Subroto Kav. 27 3rd Floor Kuningan, Jakarta, Indonesia 12950, Status of Karangetang Volcano in Sitaro Islands Increases (URL: https://sulsel.idntimes.com/news/indonesia/savi/status-gunung-api-karangetang-di-kepulauan-sitaro-meningkat?page=all).
Ahyi (United States) — July 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Ahyi
United States
20.42°N, 145.03°E; summit elev. -75 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Intermittent hydroacoustic signals and discolored plumes during November 2022-June 2023
Ahyi seamount is a large, conical submarine volcano that rises to within 75 m of the ocean surface about 18 km SE of the island of Farallon de Pajaros in the Northern Marianas. The remote location of the seamount has made eruptions difficult to document, but seismic stations installed in the region confirmed an eruption in the vicinity in 2001. No new activity was detected until April-May 2014 when an eruption was detected by NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) divers, hydroacoustic sensors, and seismic stations (BGVN 42:04). New activity was first detected on 15 November by hydroacoustic sensors that were consistent with submarine volcanic activity. This report covers activity during November 2022 through June 2023 based on daily and weekly reports from the US Geological Survey.
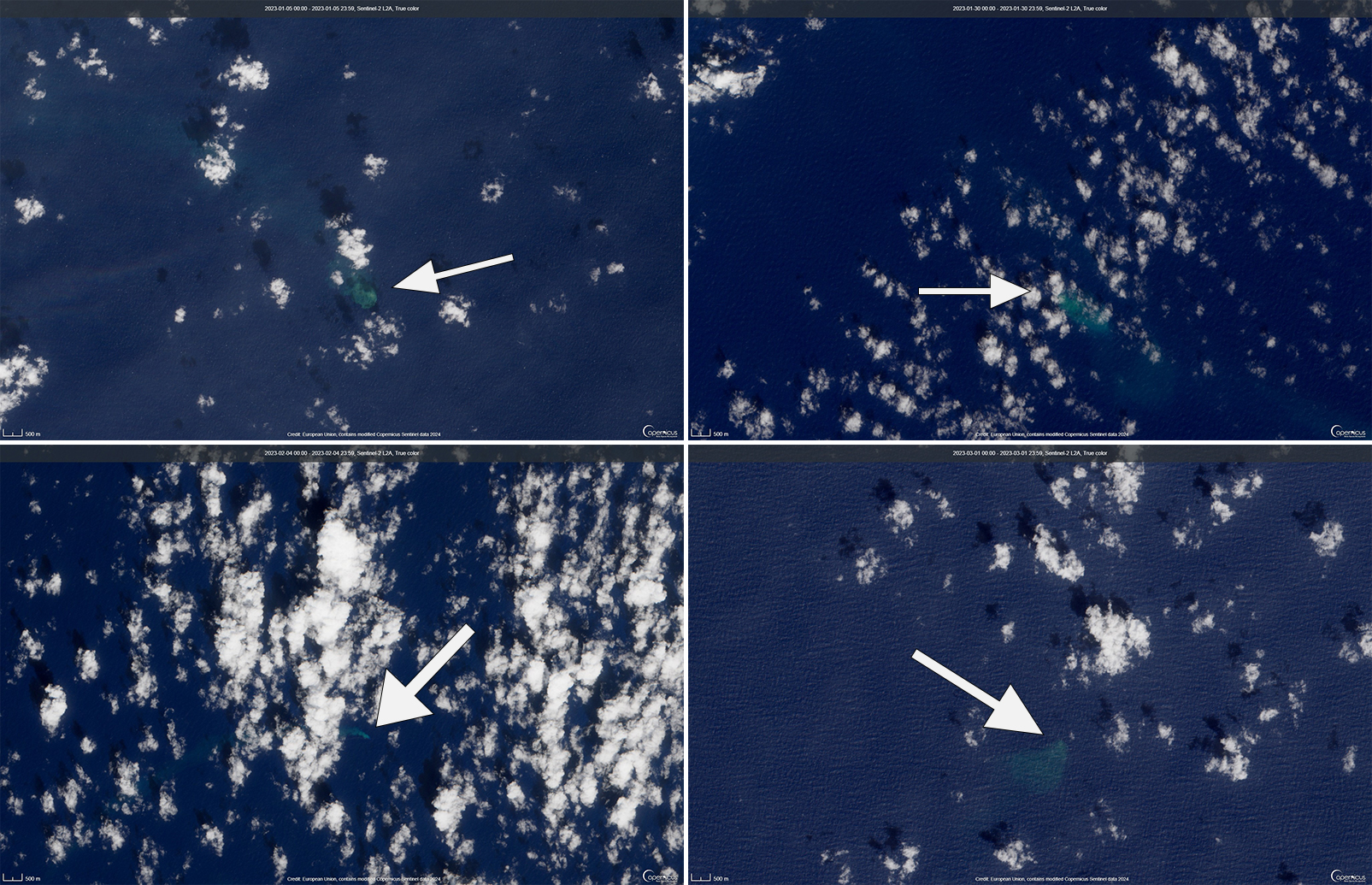
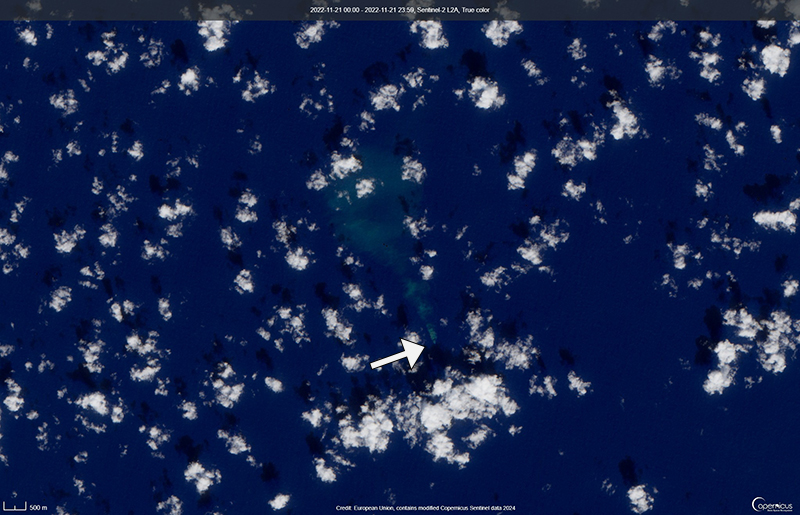
Starting in mid-October, hydroacoustic sensors at Wake Island (2.2 km E) recorded signals consistent with submarine volcanic activity, according to a report from the USGS issued on 15 November 2022. A combined analysis of the hydroacoustic signals and seismic stations located at Guam and Chichijima Island, Japan, suggested that the source of this activity was at or near the Ahyi seamount. After a re-analysis of a satellite image of the area that was captured on 6 November, USGS confirmed that there was no evidence of discoloration at the ocean surface. Few hydroacoustic and seismic signals continued through November, including on 18 November, which USGS suggested signified a decline or pause in unrest. A VONA (Volcano Observatory Notice for Aviation) reported that a discolored water plume was persistently visible in satellite data starting on 18 November (figure 6). Though clouds often obscured clear views of the volcano, another discolored water plume was captured in a satellite image on 26 November. The Aviation Color Code (ACC) was raised to Yellow (the second lowest level on a four-color scale) and the Volcano Alert Level (VAL) was raised to Advisory (the second lowest level on a four-level scale) on 29 November.
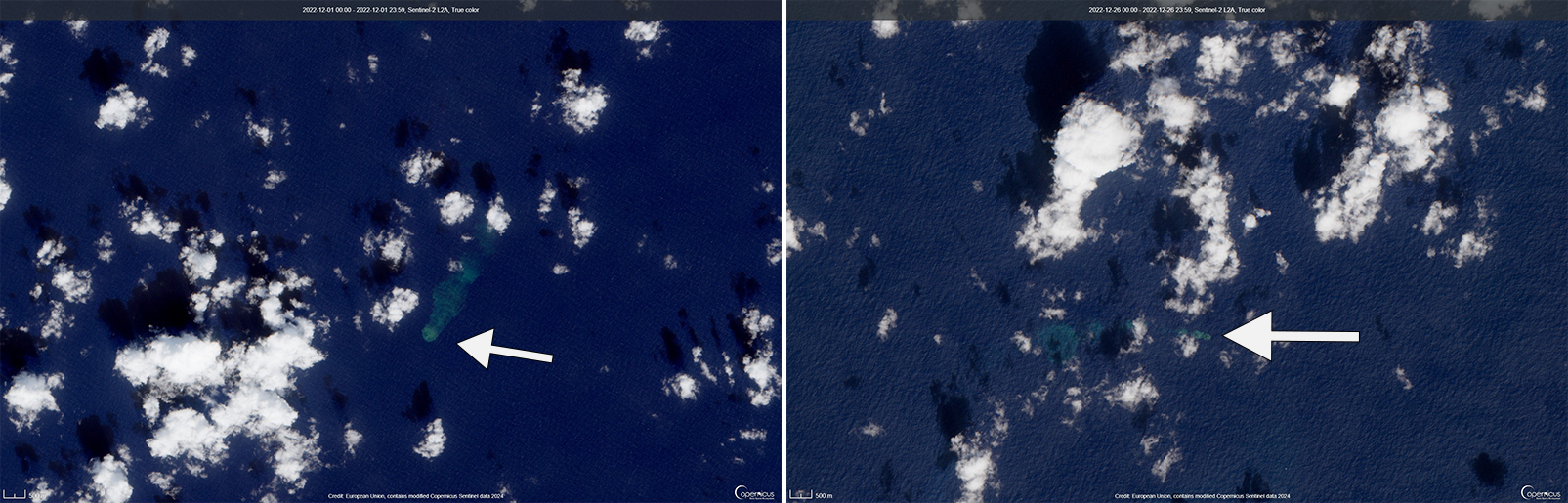
During December, occasional detections were recorded on the Wake Island hydrophone sensors and discolored water over the seamount remained visible. During 2-7, 10-12, and 16-31 December possible explosion signals were detected. A small area of discolored water was observed in high-resolution Sentinel-2 satellite images during 1-6 December (figure 7). High-resolution satellite images recorded discolored water plumes on 13 December that originated from the summit region; no observations indicated that activity breached the ocean surface. A possible underwater plume was visible in satellite images on 18 December, and during 19-20 December a definite but diffuse underwater plume located SSE from the main vent was reported. An underwater plume was visible in a satellite image taken on 26 December (figure 7).
Hydrophone sensors continued to detect signals consistent with possible explosions during 1-8 January 2023. USGS reported that the number of detections decreased during 4-5 January. The hydrophone sensors experienced a data outage that started at 0118 on 8 January and continued through 10 January, though according to USGS, possible explosions were recorded prior to the data outage and likely continued during the outage. A discolored water plume originating from the summit region was detected in a partly cloudy satellite image on 8 January. On 11-12 and 15-17 January possible explosion signals were recorded again. One small signal was detected during 22-23 January and several signals were recorded on 25 and 31 January. During 27-31 January a plume of discolored water was observed above the seamount in satellite imagery (figure 8).
Low levels of activity continued during February and March, based on data from pressure sensors on Wake Island. During 1 and 4-6 February activity was reported, and a submarine plume was observed on 4 February (figure 8). Possible explosion signals were detected during 7-8, 10, 13-14, and 24 February. During 1-2 and 3-5 March a plume of discolored water was observed in satellite imagery (figure 8). Almost continuous hydroacoustic signals were detected in remote pressure sensor data on Wake Island 2,270 km E from the volcano during 7-13 March. During 12-13 March water discoloration around the seamount was observed in satellite imagery, despite cloudy weather. By 14 March discolored water extended about 35 km, but no direction was noted. USGS reported that the continuous hydroacoustic signals detected during 13-14 March stopped abruptly on 14 March and no new detections were observed. Three 30 second hydroacoustic detections were reported during 17-19 March, but no activity was visible due to cloudy weather. A data outage was reported during 21-22 March, making pressure sensor data unavailable; a discolored water plume was, however, visible in satellite data. A possible underwater explosion signal was detected by pressure sensors at Wake Island on 26, 29, and 31 March, though the cause and origin of these events were unclear.
Similar low activity continued during April, May, and June. Several signals were detected during 1-3 April in pressure sensors at Wake Island. USGS suggested that these may be related to underwater explosions or earthquakes at the volcano, but no underwater plumes were visible in clear satellite images. The pressure sensors had data outages during 12-13 April and no data were recorded; no underwater plumes were visible in satellite images, although cloudy weather obscured most clear views. Eruptive activity was reported starting at 2210 on 21 May. On 22 May a discolored water plume that extended 4 km was visible in satellite images, though no direction was recorded. During 23-24 May some signals were detected by the underwater pressure sensors. Possible hydroacoustic signals were detected during 2-3 and 6-8 June. Multiple hydroacoustic signals were detected during 9-11 and 16-17 June, although no activity was visible in satellite images. One hydroacoustic signal was detected during 23-24 June, but there was some uncertainty about its association with volcanic activity. A single possible hydroacoustic signal was detected during 30 June to 1 July.
Geologic Background. Ahyi seamount is a large conical submarine volcano that rises to within 75 m of the ocean surface ~18 km SE of the island of Farallon de Pajaros in the northern Marianas. Water discoloration has been observed there, and in 1979 the crew of a fishing boat felt shocks over the summit area, followed by upwelling of sulfur-bearing water. On 24-25 April 2001 an explosive eruption was detected seismically by a station on Rangiroa Atoll, Tuamotu Archipelago. The event was well constrained (+/- 15 km) at a location near the southern base of Ahyi. An eruption in April-May 2014 was detected by NOAA divers, hydroacoustic sensors, and seismic stations.
Information Contacts: US Geological Survey, Volcano Hazards Program (USGS-VHP), 12201 Sunrise Valley Drive, Reston, VA, USA, https://volcanoes.usgs.gov/index.html; Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Kadovar (Papua New Guinea) — June 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Kadovar
Papua New Guinea
3.608°S, 144.588°E; summit elev. 365 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
An ash plume and weak thermal anomaly during May 2023
Kadovar is a 2-km-wide island that is the emergent summit of a Bismarck Sea stratovolcano. It lies off the coast of New Guinea, about 25 km N of the mouth of the Sepik River. Prior to an eruption that began in 2018, a lava dome formed the high point of the volcano, filling an arcuate landslide scarp open to the S. Submarine debris-avalanche deposits occur to the S of the island. The current eruption began in January 2018 and has comprised lava effusion from vents at the summit and at the E coast; more recent activity has consisted of ash plumes, weak thermal activity, and gas-and-steam plumes (BGVN 48:02). This report covers activity during February through May 2023 using information from the Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) and satellite data.
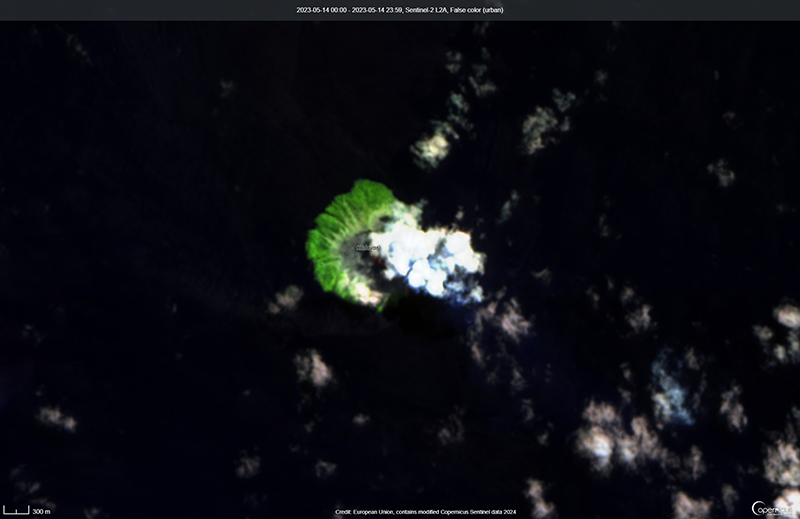
Activity during the reporting period was relatively low and mainly consisted of white gas-and-steam plumes that were visible in natural color satellite images on clear weather days (figure 67). According to a Darwin VAAC report, at 2040 on 6 May an ash plume rose to 4.6 km altitude and drifted W; by 2300 the plume had dissipated. MODIS satellite instruments using the MODVOLC thermal algorithm detected a single thermal hotspot on the SE side of the island on 7 May. Weak thermal activity was also detected in a satellite image on the E side of the island on 14 May, accompanied by a white gas-and-steam plume that drifted SE (figure 68).
Geologic Background. The 2-km-wide island of Kadovar is the emergent summit of a Bismarck Sea stratovolcano of Holocene age. It is part of the Schouten Islands, and lies off the coast of New Guinea, about 25 km N of the mouth of the Sepik River. Prior to an eruption that began in 2018, a lava dome formed the high point of the andesitic volcano, filling an arcuate landslide scarp open to the south; submarine debris-avalanche deposits occur in that direction. Thick lava flows with columnar jointing forms low cliffs along the coast. The youthful island lacks fringing or offshore reefs. A period of heightened thermal phenomena took place in 1976. An eruption began in January 2018 that included lava effusion from vents at the summit and at the E coast.
Information Contacts: Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Bureau of Meteorology, Northern Territory Regional Office, PO Box 40050, Casuarina, NT 0811, Australia (URL: http://www.bom.gov.au/info/vaac/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
San Miguel (El Salvador) — June 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
San Miguel
El Salvador
13.434°N, 88.269°W; summit elev. 2130 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Small gas-and-ash explosions during March and May 2023
San Miguel in El Salvador is a broad, deep crater complex that has been frequently modified by eruptions recorded since the early 16th century and consists of the summit known locally as Chaparrastique. Flank eruptions have produced lava flows that extended to the N, NE, and SE during the 17-19th centuries. The most recent activity has consisted of minor ash eruptions from the summit crater. The current eruption period began in November 2022 and has been characterized by frequent phreatic explosions, gas-and-ash emissions, and sulfur dioxide plumes (BGVN 47:12). This report describes small gas-and-ash explosions during December 2022 through May 2023 based on special reports from the Ministero de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (MARN).
Activity has been relatively low since the last recorded explosions on 29 November 2022. Seismicity recorded by the San Miguel Volcano Station (VSM) located on the N flank at 1.7 km elevation had decreased by 7 December. Sulfur dioxide gas measurements taken with DOAS (Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy) mobile equipment were below typical previously recorded values: 300 tons per day (t/d). During December, small explosions were recorded by the seismic network and manifested as gas-and-steam emissions.
Gas-and-ash explosions in the crater occurred during January 2023, which were recorded by the seismic network. Sulfur dioxide values remained low, between 300-400 t/d through 10 March. At 0817 on 14 January a gas-and-ash emission was visible in webcam images, rising just above the crater rim. Some mornings during February, small gas-and-steam plumes were visible in the crater. On 7 March at 2252 MARN noted an increase in degassing from the central crater; gas emissions were constantly observed through the early morning hours on 8 March. During the early morning of 8 March through the afternoon on 9 March, 12 emissions were registered, some accompanied by ash. The last gas-and-ash emission was recorded at 1210 on 9 March; very fine ashfall was reported in El Tránsito (10 km S), La Morita (6 km W), and La Piedrita (3 km W). The smell of sulfur was reported in Piedra Azul (5 km SW). On 16 March MARN reported that gas-and-steam emissions decreased.
Low degassing and very low seismicity were reported during April; no explosions have been detected between 9 March and 27 May. The sulfur dioxide emissions remained between 350-400 t/d; during 13-20 April sulfur dioxide values fluctuated between 30-300 t/d. Activity remained low through most of May; on 23 May seismicity increased. An explosion was detected at 1647 on 27 May generated a gas-and-ash plume that rose 700 m high (figure 32); a decrease in seismicity and gas emissions followed. The DOAS station installed on the W flank recorded sulfur dioxide values that reached 400 t/d on 27 May; subsequent measurements showed a decrease to 268 t/d on 28 May and 100 t/d on 29 May.
Geologic Background. The symmetrical cone of San Miguel, one of the most active volcanoes in El Salvador, rises from near sea level to form one of the country's most prominent landmarks. A broad, deep, crater complex that has been frequently modified by eruptions recorded since the early 16th century caps the truncated unvegetated summit, also known locally as Chaparrastique. Flanks eruptions of the basaltic-andesitic volcano have produced many lava flows, including several during the 17th-19th centuries that extended to the N, NE, and SE. The SE-flank flows are the largest and form broad, sparsely vegetated lava fields crossed by highways and a railroad skirting the base of the volcano. Flank vent locations have migrated higher on the edifice during historical time, and the most recent activity has consisted of minor ash eruptions from the summit crater.
Information Contacts: Ministero de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (MARN), Km. 5½ Carretera a Nueva San Salvador, Avenida las Mercedes, San Salvador, El Salvador (URL: http://www.snet.gob.sv/ver/vulcanologia).
Semisopochnoi (United States) — June 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Semisopochnoi
United States
51.93°N, 179.58°E; summit elev. 1221 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Occasional explosions, ash deposits, and gas-and-steam plumes during December 2022-May 2023
Semisopochnoi is located in the western Aleutians, is 20-km-wide at sea level, and contains an 8-km-wide caldera. The three-peaked Mount Young (formerly Cerberus) was constructed within the caldera during the Holocene. Each of these peaks contains a summit crater; the lava flows on the N flank appear younger than those on the S side. The current eruption period began in early February 2021 and has more recently consisted of intermittent explosions and ash emissions (BGVN 47:12). This report updates activity during December 2022 through May 2023 using daily, weekly, and special reports from the Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO). AVO monitors the volcano using local seismic and infrasound sensors, satellite data, web cameras, and remote infrasound and lightning networks.
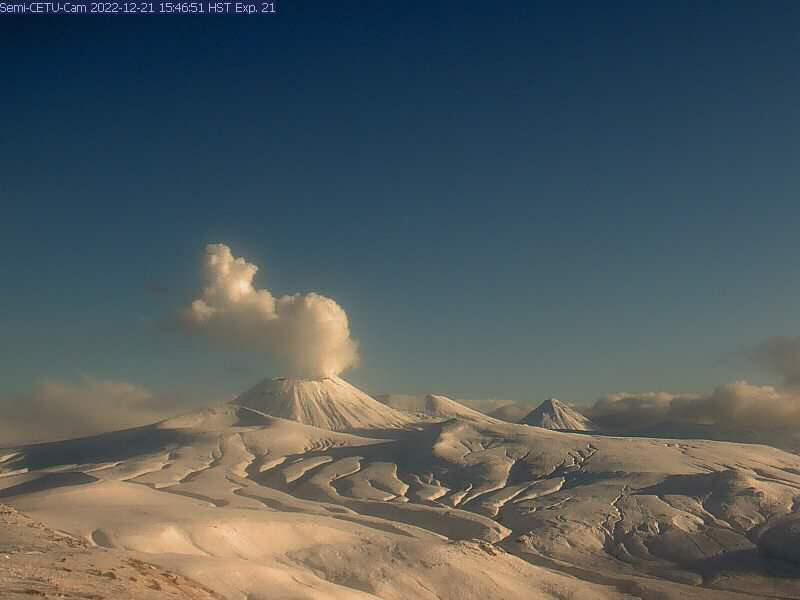
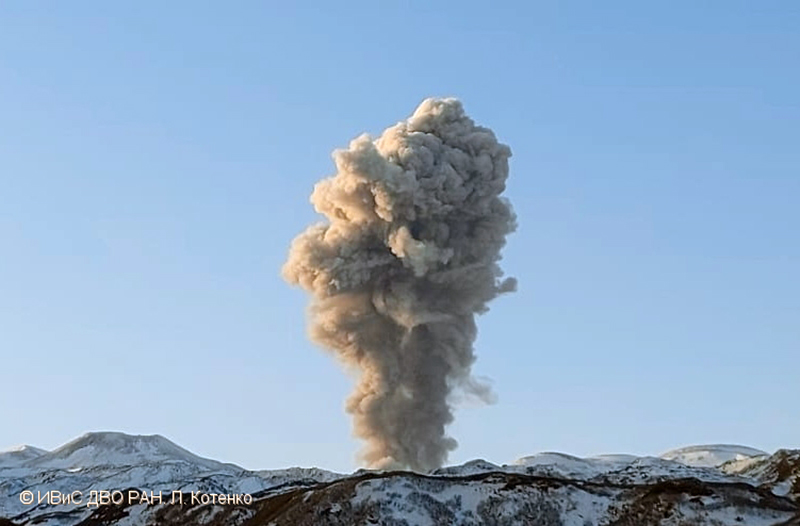
Activity during most of December 2022 was relatively quiet; according to AVO no eruptive or explosive activity was observed since 7 November 2022. Intermittent tremor and occasional small earthquakes were observed in geophysical data. Continuous gas-and-steam emissions were observed from the N crater of Mount Young in webcam images on clear weather days (figure 25). On 24 December, there was a slight increase in earthquake activity and several small possible explosion signals were detected in infrasound data. Eruptive activity resumed on 27 December at the N crater of Mount Young; AVO issued a Volcano Activity Notice (VAN) that reported minor ash deposits on the flanks of Mount Young that extended as far as 1 km from the vent, according to webcam images taken during 27-28 December (figure 26). No ash plumes were observed in webcam or satellite imagery, but a persistent gas-and-steam plume that might have contained some ash rose to 1.5 km altitude. As a result, AVO raised the Aviation Color Code (ACC) to Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale) and the Volcano Alert Level (VAL) to Watch (the second highest level on a four-level scale). Possible explosions were detected during 21 December 2022 through 1 January 2023 and seismic tremor was recorded during 30-31 December.
During January 2023 eruptive activity continued at the active N crater of Mount Young. Minor ash deposits were observed on the flanks, extending about 2 km SSW, based on webcam images from 1 and 3 January. A possible explosion occurred during 1-2 January based on elevated seismicity recorded on local seismometers and an infrasound signal recorded minutes later by an array at Adak. Though no ash plumes were observed in webcam or satellite imagery, a persistent gas-and-steam plume rose to 1.5 km altitude that might have carried minor traces of ash. Ash deposits were accompanied by periods of elevated seismicity and infrasound signals from the local geophysical network, which AVO reported were likely due to weak explosive activity. Low-level explosive activity was also detected during 2-3 January, with minor gas-and-steam emissions and a new ash deposit that was visible in webcam images. Low-level explosive activity was detected in geophysical data during 4-5 January, with elevated seismicity and infrasound signals observed on local stations. Volcanic tremor was detected during 7-9 January and very weak explosive activity was detected in seismic and infrasound data on 9 January. Weak seismic and infrasound signals were recorded on 17 January, which indicated minor explosive activity, but no ash emissions were observed in clear webcam images; a gas-and-steam plume continued to rise to 1.5 km altitude. During 29-30 January, ash deposits near the summit were observed on fresh snow, according to webcam images.
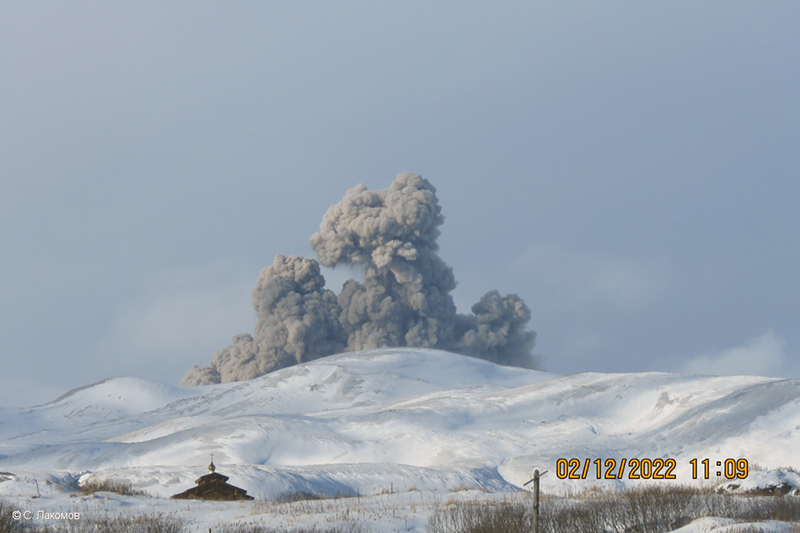
The active N cone at Mount Young continued to produce a gas-and-steam plume during February, but no ash emissions or explosive events were detected. Seismicity remained elevated with faint tremor during early February. Gas-and-steam emissions from the N crater were observed in clear webcam images on 11-13 and 16 February; no explosive activity was detected in seismic, infrasound, or satellite data. Seismicity has also decreased, with no significant seismic tremor observed since 25 January. Therefore, the ACC was lowered to Yellow (the second lowest level on a four-color scale) and the VAL was lowered to Advisory (the second lowest level on a four-color scale) on 22 February.
Gas-and-steam emissions persisted during March from the N cone of Mount Young, based on clear webcam images. A few brief episodes of weak tremor were detected in seismic data, although seismicity decreased over the month. A gas-and-steam plume detected in satellite data extended 150 km on 18 March. Low-level ash emissions from the N cone at Mount Young were observed in several webcam images during 18-19 March, in addition to small explosions and volcanic tremor. The ACC was raised to Orange and the VAL increased to Watch on 19 March. A small explosion was detected in seismic and infrasound data on 21 March.
Low-level unrest continued during April, although cloudy weather often obscured views of the summit; periods of seismic tremor and local earthquakes were recorded. During 3-4 April a gas-and-steam plume was visible traveling more than 200 km overnight; no ash was evident in the plume, according to AVO. A gas-and-steam plume was observed during 4-6 April that extended 400 km but did not seem to contain ash. Small explosions were detected in seismic and infrasound data on 5 April. Occasional clear webcam images showed continuing gas-and-steam emissions rose from Mount Young, but no ash deposits were observed on the snow. On 19 April small explosions and tremor were detected in seismic and infrasound data. A period of seismic tremor was detected during 22-25 April, with possible weak explosions on 25 April. Ash deposits were visible near the crater rim, but it was unclear if these deposits were recent or due to older deposits.
Occasional small earthquakes were recorded during May, but there were no signs of explosive activity seen in geophysical data. Gas-and-steam emissions continued from the N crater of Mount Young, based on webcam images, and seismicity remained slightly elevated. A new, light ash deposit was visible during the morning of 5 May on fresh snow on the NW flank of Mount Young. During 10 May periods of volcanic tremor were observed. The ACC was lowered to Yellow and the VAL to Advisory on 17 May due to no additional evidence of activity.
Geologic Background. Semisopochnoi, the largest subaerial volcano of the western Aleutians, is 20 km wide at sea level and contains an 8-km-wide caldera. It formed as a result of collapse of a low-angle, dominantly basaltic volcano following the eruption of a large volume of dacitic pumice. The high point of the island is Anvil Peak, a double-peaked late-Pleistocene cone that forms much of the island's northern part. The three-peaked Mount Cerberus (renamed Mount Young in 2023) was constructed within the caldera during the Holocene. Each of the peaks contains a summit crater; lava flows on the N flank appear younger than those on the south side. Other post-caldera volcanoes include the symmetrical Sugarloaf Peak SSE of the caldera and Lakeshore Cone, a small cinder cone at the edge of Fenner Lake in the NE part of the caldera. Most documented eruptions have originated from Young, although Coats (1950) considered that both Sugarloaf and Lakeshore Cone could have been recently active.
Information Contacts: Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667 USA (URL: https://avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA (URL: http://dggs.alaska.gov/).
Ebeko
Russia
50.686°N, 156.014°E; summit elev. 1103 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Continued explosions, ash plumes, and ashfall during October 2022-May 2023
Ebeko, located on the N end of Paramushir Island in the Kuril Islands, consists of three summit craters along a SSW-NNE line at the northern end of a complex of five volcanic cones. Eruptions date back to the late 18th century and have been characterized as small-to-moderate explosions from the summit crater, accompanied by intense fumarolic activity. The current eruption period began in June 2022 and has recently consisted of frequent explosions, ash plumes, and thermal activity (BGVN 47:10). This report covers similar activity during October 2022 through May 2023, based on information from the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT) and satellite data.
Activity during October consisted of explosive activity, ash plumes, and occasional thermal anomalies. Visual data by volcanologists from Severo-Kurilsk showed explosions producing ash clouds up to 2.1-3 km altitude which drifted E, N, NE, and SE during 1-8, 10, 16, and 18 October. KVERT issued several Volcano Observatory Notices for Aviation (VONA) on 7, 13-15, and 27 October 2022, stating that explosions generated ash plumes that rose to 2.3-4 km altitude and drifted 5 km E, NE, and SE. Ashfall was reported in Severo-Kurilsk (Paramushir Island, about 7 km E) on 7 and 13 October. Satellite data showed a thermal anomaly over the volcano on 15-16 October. Visual data showed ash plumes rising to 2.5-3.6 km altitude on 22, 25-29, and 31 October and moving NE due to constant explosions.
Similar activity continued during November, with explosions, ash plumes, and ashfall occurring. KVERT issued VONAs on 1-2, 4, 6-7, 9, 13, and 16 November that reported explosions and resulting ash plumes that rose to 1.7-3.6 km altitude and drifted 3-5 km SE, ESE, E, and NE. On 1 November ash plumes extended as far as 110 km SE. On 5, 8, 12, and 24-25 November explosions and ash plumes rose to 2-3.1 km altitude and drifted N and E. Ashfall was observed in Severo-Kurilsk on 7 and 16 November. A thermal anomaly was visible during 1-4, 16, and 20 November. Explosions during 26 November rose as high as 2.7 km altitude and drifted NE (figure 45).
Explosions and ash plumes continued to occur in December. During 1-2 and 4 December volcanologists from Severo-Kurilsk observed explosions that sent ash to 1.9-2.5 km altitude and drifted NE and SE (figure 46). VONAs were issued on 5, 9, and 16 December reporting that explosions generated ash plumes rising to 1.9 km, 2.6 km, and 2.4 km altitude and drifted 5 km SE, E, and NE, respectively. A thermal anomaly was visible in satellite imagery on 16 December. On 18 and 27-28 December explosions produced ash plumes that rose to 2.5 km altitude and drifted NE and SE. On 31 December an ash plume rose to 2 km altitude and drifted NE.
Explosions continued during January 2023, based on visual observations by volcanologists from Severo-Kurilsk. During 1-7 January explosions generated ash plumes that rose to 4 km altitude and drifted NE, E, W, and SE. According to VONAs issued by KVERT on 2, 4, 10, and 23 January, explosions produced ash plumes that rose to 2-4 km altitude and drifted 5 km N, NE, E, and ENE; the ash plume that rose to 4 km altitude occurred on 10 January (figure 47). Satellite data showed a thermal anomaly during 3-4, 10, 13, 16, 21, 22, and 31 January. KVERT reported that an ash cloud on 4 January moved 12 km NE. On 6 and 9-11 January explosions sent ash plumes to 4.5 km altitude and drifted W and ESE. On 13 January an ash plume rose to 3 km altitude and drifted SE. During 20-24 January ash plumes from explosions rose to 3.7 km altitude and drifted SE, N, and NE. On 21 January the ash plume drifted as far as 40 km NE. During 28-29 and 31 January and 1 February ash plumes rose to 4 km altitude and drifted NE.
During February, explosions, ash plumes, and ashfall were reported. During 1, 4-5 and 7-8 February explosions generated ash plumes that rose to 4.5 km altitude and drifted E and NE; ashfall was observed on 5 and 8 February. On 6 February an explosion produced an ash plume that rose to 3 km altitude and drifted 7 km E, causing ashfall in Severo-Kurilsk. A thermal anomaly was visible in satellite data on 8, 9, 13, and 21 February. Explosions on 9 and 12-13 February produced ash plumes that rose to 4 km altitude and drifted E and NE; the ash cloud on 12 February extended as far as 45 km E. On 22 February explosions sent ash to 3 km altitude that drifted E. During 24 and 26-27 February ash plumes rose to 4 km altitude and drifted E. On 28 February an explosion sent ash to 2.5-3 km altitude and drifted 5 km E; ashfall was observed in Severo-Kurilsk.
Activity continued during March; visual observations showed that explosions generated ash plumes that rose to 3.6 km altitude on 3, 5-7, and 9-12 March and drifted E, NE, and NW. Thermal anomalies were visible on 10, 13, and 29-30 March in satellite imagery. On 18, 21-23, 26, and 29-30 March explosions produced ash plumes that rose to 2.8 km altitude and drifted NE and E; the ash plumes during 22-23 March extended up to 76 km E. A VONA issued on 21 March reported an explosion that produced an ash plume that rose to 2.8 km altitude and drifted 5 km E. Another VONA issued on 23 March reported that satellite data showed an ash plume rising to 3 km altitude and drifted 14 km E.
Explosions during April continued to generate ash plumes. On 1 and 4 April an ash plume rose to 2.8-3.5 km altitude and drifted SE and NE. A thermal anomaly was visible in satellite imagery during 1-6 April. Satellite data showed ash plumes and clouds rising to 2-3 km altitude and drifting up to 12 km SW and E on 3 and 6 April (figure 48). KVERT issued VONAs on 3, 5, 14, 16 April describing explosions that produced ash plumes rising to 3 km, 3.5 km, 3.5 km, and 3 km altitude and drifting 5 km S, 5 km NE and SE, 72 km NNE, and 5 km NE, respectively. According to satellite data, the resulting ash cloud from the explosion on 14 April was 25 x 7 km in size and drifted 72-104 km NNE during 14-15 April. According to visual data by volcanologists from Severo-Kurilsk explosions sent ash up to 3.5 km altitude that drifted NE and E during 15-16, 22, 25-26, and 29 April.
The explosive eruption continued during May. Explosions during 3-4, 6-7, and 9-10 May generated ash plumes that rose to 4 km altitude and drifted SW and E. Satellite data showed a thermal anomaly on 3, 9, 13-14, and 24 May. During 12-16, 23-25, and 27-28 May ash plumes rose to 3.5 km altitude and drifted in different directions due to explosions. Two VONA notices were issued on 16 and 25 May, describing explosions that generated ash plumes rising to 3 km and 3.5 km altitude, respectively and extending 5 km E. The ash cloud on 25 May drifted 75 km SE.
Thermal activity in the summit crater, occasionally accompanied by ash plumes and ash deposits on the SE and E flanks due to frequent explosions, were visible in infrared and true color satellite images (figure 49).
Geologic Background. The flat-topped summit of the central cone of Ebeko volcano, one of the most active in the Kuril Islands, occupies the northern end of Paramushir Island. Three summit craters located along a SSW-NNE line form Ebeko volcano proper, at the northern end of a complex of five volcanic cones. Blocky lava flows extend west from Ebeko and SE from the neighboring Nezametnyi cone. The eastern part of the southern crater contains strong solfataras and a large boiling spring. The central crater is filled by a lake about 20 m deep whose shores are lined with steaming solfataras; the northern crater lies across a narrow, low barrier from the central crater and contains a small, cold crescentic lake. Historical activity, recorded since the late-18th century, has been restricted to small-to-moderate explosive eruptions from the summit craters. Intense fumarolic activity occurs in the summit craters, on the outer flanks of the cone, and in lateral explosion craters.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Home Reef
Tonga
18.992°S, 174.775°W; summit elev. -10 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Discolored plumes continued during November 2022-April 2023
Home Reef is a submarine volcano located in the central Tonga islands between Lateiki (Metis Shoal) and Late Island. The first recorded eruption occurred in the mid-19th century, when an ephemeral island formed. An eruption in 1984 produced a 12-km-high eruption plume, a large volume of floating pumice, and an ephemeral island 500 x 1,500 m wide, with cliffs 30-50 m high that enclosed a water-filled crater. Another island-forming eruption in 2006 produced widespread pumice rafts that drifted as far as Australia; by 2008 the island had eroded below sea level. The previous eruption occurred during October 2022 and was characterized by a new island-forming eruption, lava effusion, ash plumes, discolored water, and gas-and-steam plumes (BGVN 47:11). This report covers discolored water plumes during November 2022 through April 2023 using satellite data.
Discolored plumes continued during the reporting period and were observed in true color satellite images on clear weather days. Satellite images show light green-yellow discolored water extending W on 8 and 28 November 2022 (figure 31), and SW on 18 November. Light green-yellow plumes extended W on 3 December, S on 13 December, SW on 18 December, and W and S on 23 December (figure 31). On 12 January 2023 discolored green-yellow plumes extended to the NE, E, SE, and N. The plume moved SE on 17 January and NW on 22 January. Faint discolored water in February was visible moving NE on 1 February. A discolored plume extended NW on 8 and 28 March and NW on 13 March (figure 31). During April, clear weather showed green-blue discolored plumes moving S on 2 April, W on 7 April, and NE and S on 12 April. A strong green-yellow discolored plume extended E and NE on 22 April for several kilometers (figure 31).
Geologic Background. Home Reef, a submarine volcano midway between Metis Shoal and Late Island in the central Tonga islands, was first reported active in the mid-19th century, when an ephemeral island formed. An eruption in 1984 produced a 12-km-high eruption plume, large amounts of floating pumice, and an ephemeral 500 x 1,500 m island, with cliffs 30-50 m high that enclosed a water-filled crater. In 2006 an island-forming eruption produced widespread dacitic pumice rafts that drifted as far as Australia. Another island was built during a September-October 2022 eruption.
Information Contacts: Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Ambae
Vanuatu
15.389°S, 167.835°E; summit elev. 1496 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
New lava flow, ash plumes, and sulfur dioxide plumes during February-May 2023
Ambae, also known as Aoba, is a large basaltic shield volcano in Vanuatu. A broad pyroclastic cone containing three crater lakes (Manaro Ngoru, Voui, and Manaro Lakua) is located at the summit within the youngest of at least two nested calderas. Periodic phreatic and pyroclastic explosions have been reported since the 16th century. A large eruption more than 400 years ago resulted in a volcanic cone within the summit crater that is now filled by Lake Voui; the similarly sized Lake Manaro fills the western third of the caldera. The previous eruption ended in August 2022 that was characterized by gas-and-steam and ash emissions and explosions of wet tephra (BGVN 47:10). This report covers a new eruption during February through May 2023 that consisted of a new lava flow, ash plumes, and sulfur dioxide emissions, using information from the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) and satellite data.
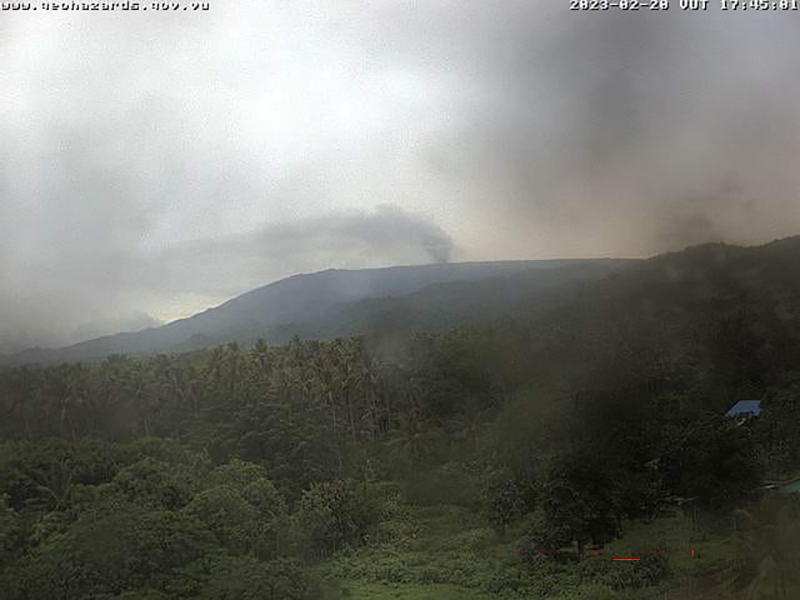
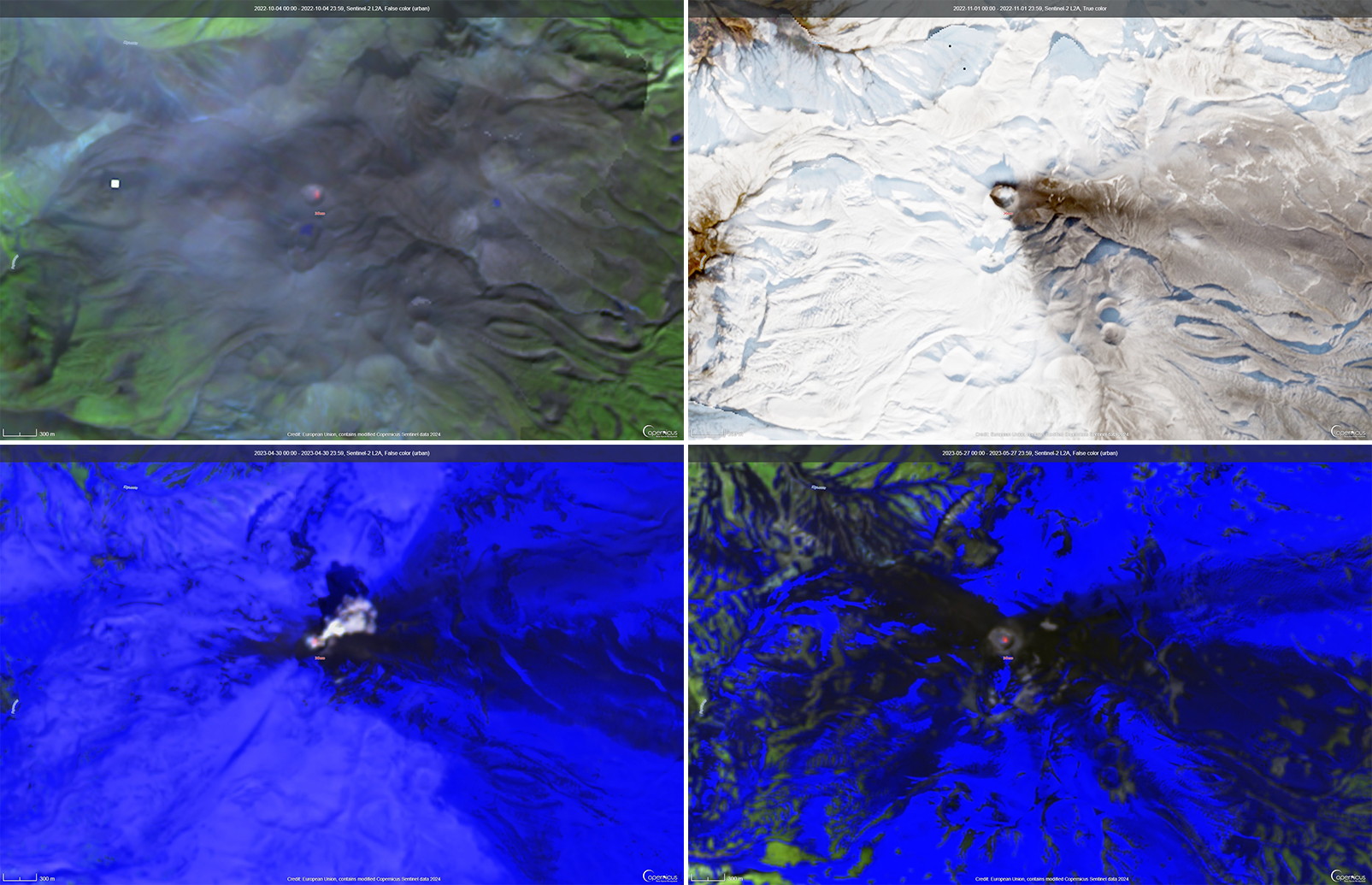
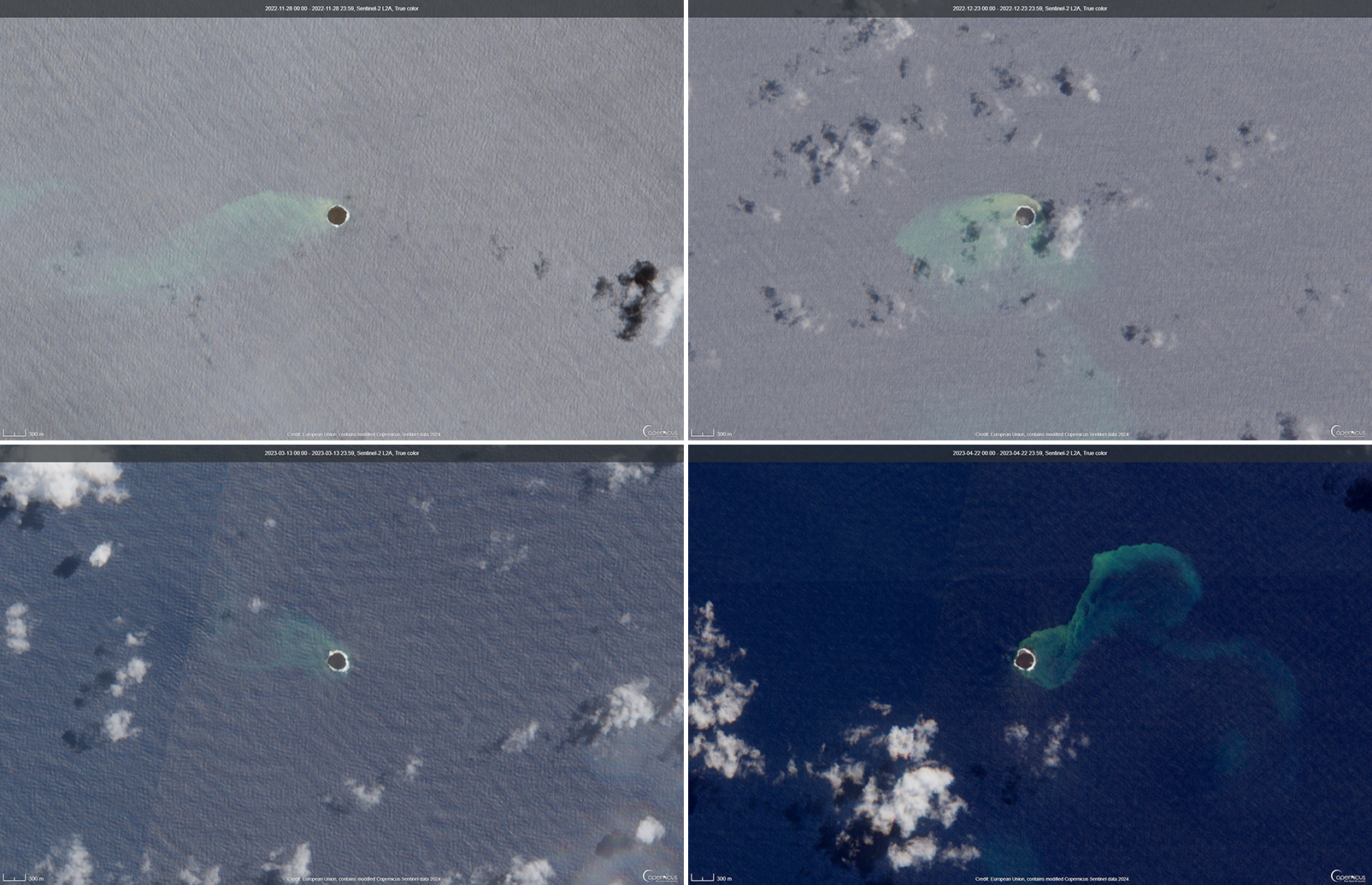
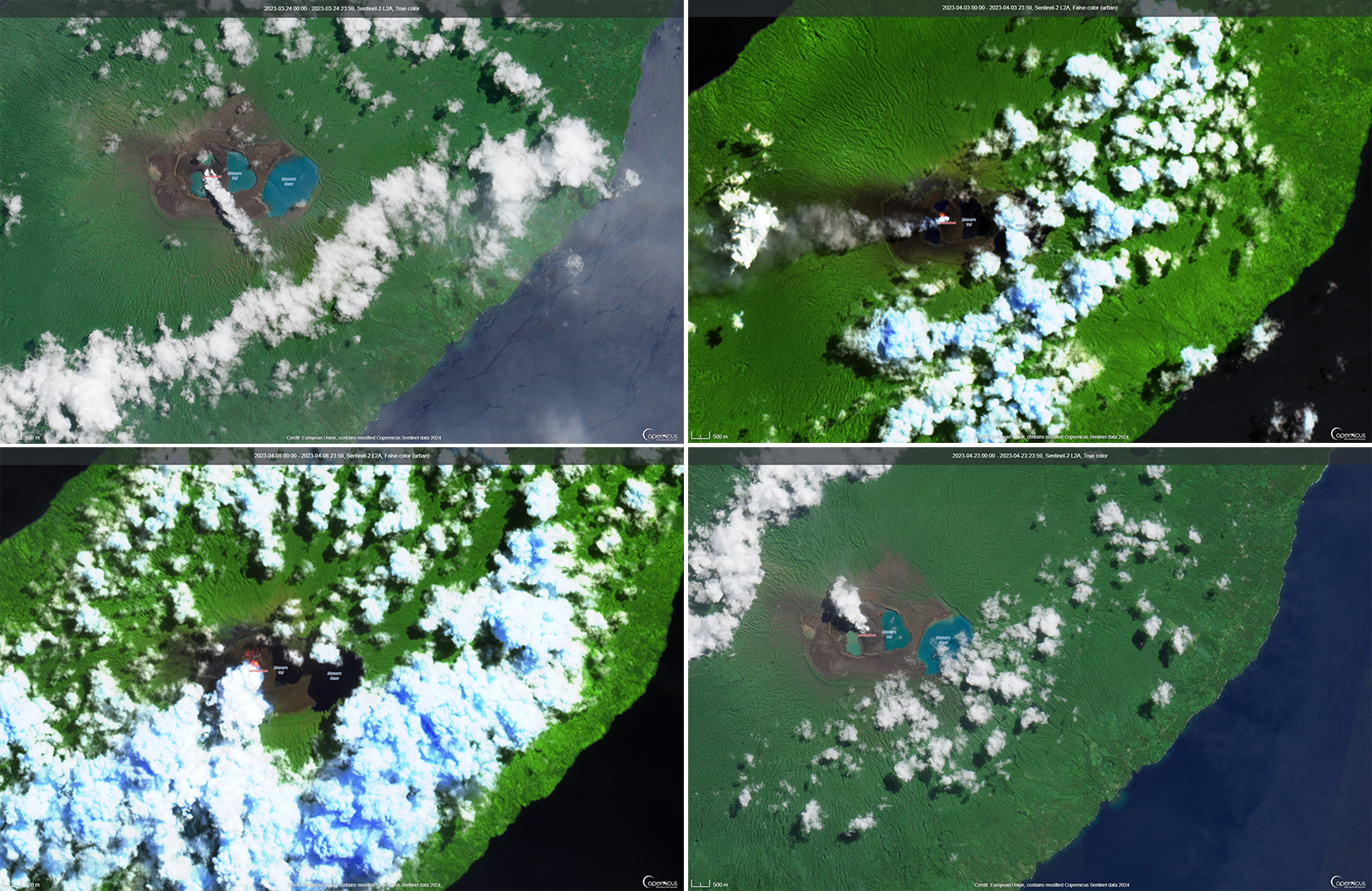
During the reporting period, the Alert Level remained at a 2 (on a scale of 0-5), which has been in place since December 2021. Activity during October 2022 through March 2023 remained relatively low and mostly consisted of gas-and-steam emissions in Lake Voui. VMGD reported that at 1300 on 15 November a satellite image captured a strong amount of sulfur dioxide rising above the volcano (figure 99), and that seismicity slightly increased. The southern and northern part of the island reported a strong sulfur dioxide smell and heard explosions. On 20 February 2023 a gas-and-ash plume rose 1.3 km above the summit and drifted SSW, according to a webcam image (figure 100). Gas-and-steam and possibly ash emissions continued on 23 February and volcanic earthquakes were recorded by the seismic network.
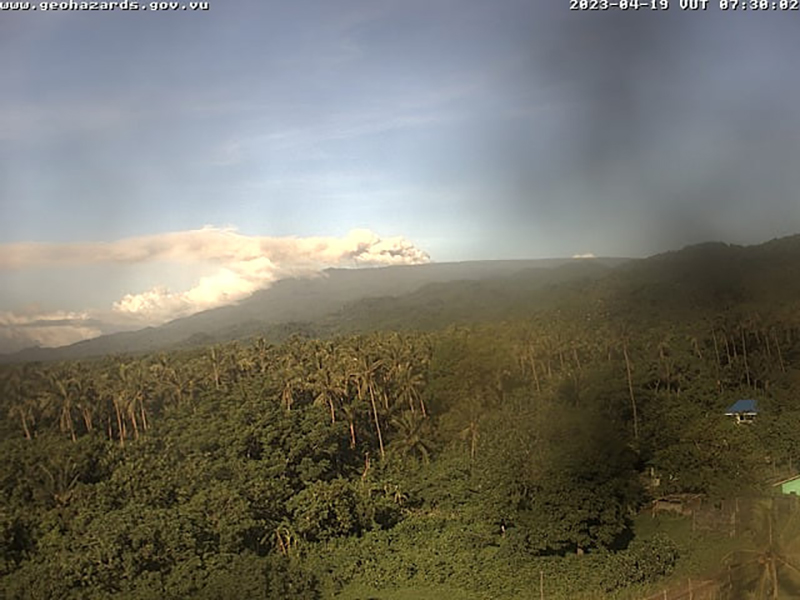
During April, volcanic earthquakes and gas-and-steam and ash emissions were reported from the cone in Lake Voui. VMGD reported that activity increased during 5-7 April; high gas-and-steam and ash plumes were visible, accompanied by nighttime incandescence. According to a Wellington VAAC report, a low-level ash plume rose as high as 2.5 km above the summit and drifted W and SW on 5 April, based on satellite imagery. Reports in Saratamata stated that a dark ash plume drifted to the WSW, but no loud explosion was heard. Webcam images from 2100 showed incandescence above the crater and reflected in the clouds. According to an aerial survey, field observations, and satellite data, water was no longer present in the lake. A lava flow was reported effusing from the vent and traveling N into the dry Lake Voui, which lasted three days. The next morning at 0745 on 6 April a gas-and-steam and ash plume rose 5.4 km above the summit and drifted ESE, based on information from VMGD (figure 101). The Wellington VAAC also reported that light ashfall was observed on the island. Intermittent gas-and-steam and ash emissions were visible on 7 April, some of which rose to an estimated 3 km above the summit and drifted E. Webcam images during 0107-0730 on 7 April showed continuing ash emissions. A gas-and-steam and ash plume rose 695 m above the summit crater at 0730 on 19 April and drifted ESE, based on a webcam image (figure 102).
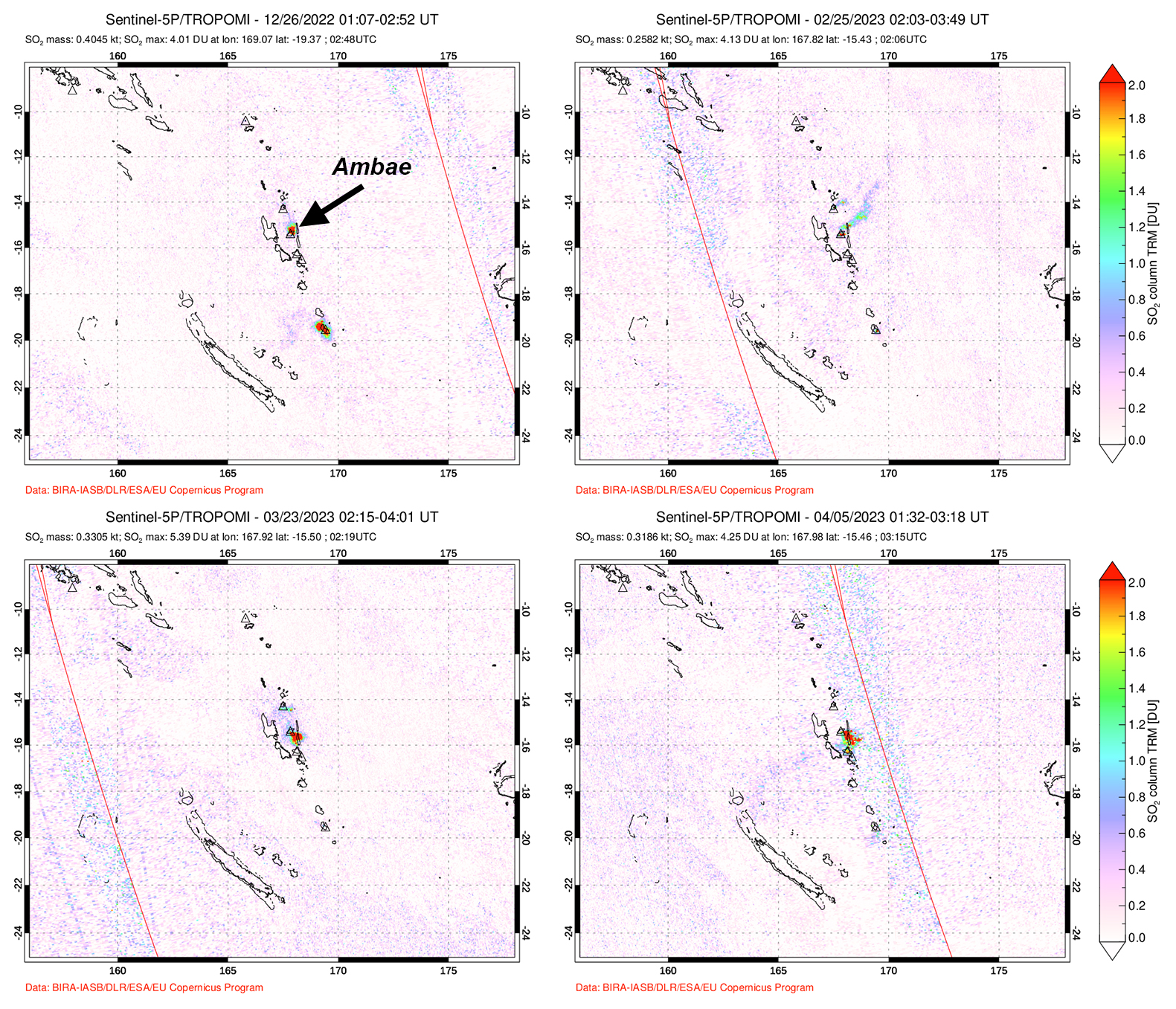
According to visual and infrared satellite data, water was visible in Lake Voui as late as 24 March 2023 (figure 103). The vent in the caldera showed a gas-and-steam plume drifted SE. On 3 April thermal activity was first detected, accompanied by a gas-and-ash plume that drifted W (figure 103). The lava flow moved N within the dry lake and was shown cooling by 8 April. By 23 April much of the water in the lake had returned. Occasional sulfur dioxide plumes were detected by the TROPOMI instrument on the Sentinel-5P satellite that exceeded 2 Dobson Units (DU) and drifted in different directions (figure 104).
Geologic Background. The island of Ambae, also known as Aoba, is a massive 2,500 km3 basaltic shield that is the most voluminous volcano of the New Hebrides archipelago. A pronounced NE-SW-trending rift zone with numerous scoria cones gives the 16 x 38 km island an elongated form. A broad pyroclastic cone containing three crater lakes (Manaro Ngoru, Voui, and Manaro Lakua) is located at the summit within the youngest of at least two nested calderas, the largest of which is 6 km in diameter. That large central edifice is also called Manaro Voui or Lombenben volcano. Post-caldera explosive eruptions formed the summit craters about 360 years ago. A tuff cone was constructed within Lake Voui (or Vui) about 60 years later. The latest known flank eruption, about 300 years ago, destroyed the population of the Nduindui area near the western coast.
Information Contacts: Geo-Hazards Division, Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD), Ministry of Climate Change Adaptation, Meteorology, Geo-Hazards, Energy, Environment and Disaster Management, Private Mail Bag 9054, Lini Highway, Port Vila, Vanuatu (URL: http://www.vmgd.gov.vu/, https://www.facebook.com/VanuatuGeohazardsObservatory/); Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Meteorological Service of New Zealand Ltd (MetService), PO Box 722, Wellington, New Zealand (URL: http://www.metservice.com/vaac/, http://www.ssd.noaa.gov/VAAC/OTH/NZ/messages.html); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Search Bulletin Archive by Publication Date
Select a month and year from the drop-downs and click "Show Issue" to have that issue displayed in this tab.
The default month and year is the latest issue available.
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network - Volume 33, Number 04 (April 2008)
Managing Editor: Richard Wunderman
Chaiten (Chile)
First recorded eruption generates large ash plume; thousands evacuated
Colima (Mexico)
By 8 March 2008, the last year's dome growth filled ~30% of the crater
Manam (Papua New Guinea)
Low-level eruptions continue in late 2007 and early 2008
Reventador (Ecuador)
Quiet, January 2006-February 2007; emissions, March-October 2007
Saunders (United Kingdom)
No thermal anomalies detected since December 2006
Sheveluch (Russia)
Emissions continue since January 2008 as lava dome grows; morphology
Slamet (Indonesia)
Heavy rains trigger steam plumes during 28 March-3 April 2007
Soufriere Hills (United Kingdom)
Halt in dome growth during March 2007-May 2008
Tair, Jebel at (Yemen)
Eruptive cloud entered stratosphere; decaying thermal anomalies
Chaiten
Chile
42.8349°S, 72.6514°W; summit elev. 1122 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
First recorded eruption generates large ash plume; thousands evacuated
The first historical eruption at Chaitén began on the morning of 2 May 2008, following increased seismicity in the region the day before. Chaitén, located W of the larger Minchinmávida (or Michinmahuida) stratovolcano, is a small 3-km-diameter post-glacial caldera or explosion crater (figure 1) which probably was formed ~ 9.4 ka BP, based on dating of scoria-rich surge deposits (Naranjo and Stern, 2004). Within the explosion crater lies an obsidian lava dome of rhyolite composition.
Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería (SERNAGEOMIN) reported that a pulsating white-to-gray ash plume on 2 May rose to an estimated altitude greater than 21 km and drifted SSE. Based on observations of satellite imagery and pilot reports, the Buenos Aires VAAC reported an ash plume at altitudes of 13.7-16.8 km that drifted NE. According to news articles, Chile's government declared a state of emergency on 2 May and several hundred people were evacuated from the coastal town of Chaitén (10 km SE).
According to news sources, ashfall was reported during 2-6 May both locally and up to hundreds of kilometers away, affecting water supplies and roads. Based on observations of satellite imagery and pilot reports, the Buenos Aires VAAC reported that during 3-6 May ash plumes rose as high as 10.7 km altitude and drifted variably to the SE (figure 2), E, W, and NE. News sources indicated that about 4,000-5,000 people were evacuated from the town of Chaitén and surrounding areas as the eruption continued. On 5 May, ONEMI (Oficina Nacional de Emergencia - Ministerio del Interior) reported that evacuations also took place in Futaleufú, about 65 km ESE of Chaitén, where ~ 30 cm of ash accumulated. One elderly person died during the evacuation efforts. On 6 May, ONEMI and SERNAGEOMIN reported that the eruption became more forceful and generated a wider and darker gray ash plume rising to an estimated altitude of 30 km. All remaining people in Chaitén were ordered to evacuate, as well as anyone within 50 km of the volcano.
Activity continued, and a lava dome began growing from a vent on the upper flank of the old dome. Lahars and floods also inundated the town of Chaitén, causing widespread destruction. Additional details will be provided in future reports.
References. Naranjo, J.A., and Stern, C.R., 2004, Holocene tephrochronology of the southernmost part (42°30'-45°S) of the Andean Southern Volcanic Zone: Revista Geológica de Chile, v. 31, no. 2, p. 225-240.
Geologic Background. Chaitén is a small caldera (~3 km in diameter) located 10 km NE of the town of Chaitén on the Gulf of Corcovado. Multiple explosive eruptions throughout the Holocene have been identified. A rhyolitic obsidian lava dome occupies much of the caldera floor. Obsidian cobbles from this dome found in the Blanco River are the source of artifacts from archaeological sites along the Pacific coast as far as 400 km from the volcano to the N and S. The caldera is breached on the SW side by a river that drains to the bay of Chaitén. The first recorded eruption, beginning in 2008, produced major rhyolitic explosive activity and building a new dome and tephra cone on the older rhyolite dome.
Information Contacts: Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería (SERNAGEOMIN), Avda Sta María No 0104, Santiago, Chile (URL: http://www.sernageomin.cl/); Oficina Nacional de Emergencia - Ministerio del Interior (ONEMI), Beaucheff 1637 / 1671, Santiago, Chile (URL: http://www.onemi.cl/); José Antonio Naranjo, Departamento de Geología Aplicada, SERNAGEOMIN; Buenos Aires Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), Buenos Aires, Argentina (URL: http://www.smn.gov.ar/vaac/buenosaires/productos.php); Rick Wessels, Alaska Volcano Observatory, U.S. Geological Survey, Anchorage, AK, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/); NASA Earth Observatory (URL: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/); Associated Press (URL: http://www.ap.org/); Agence France-Presse (URL: http://www.afp.com/).
Colima
Mexico
19.514°N, 103.62°W; summit elev. 3850 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
By 8 March 2008, the last year's dome growth filled ~30% of the crater
A new episode of lava dome growth in the crater was first observed on 1 February 2007 (figure 84). Dome growth continued during February-September, changing its volume from 15,000 m3 to 110,000 m3, with a low mean-effusion rate of about 0.0045 m3/s (figure 85).
During October 2007, Colima's effusion rate began to increase significantly (up to 0.033 m3/s) and on 8 March 2008 the dome's volume reached about 600,000 m3, filling ~ 30% of the crater (figure 86). This dome growth was accompanied by 3-5 small explosions daily.
Geologic Background. The Colima complex is the most prominent volcanic center of the western Mexican Volcanic Belt. It consists of two southward-younging volcanoes, Nevado de Colima (the high point of the complex) on the north and the historically active Volcán de Colima at the south. A group of late-Pleistocene cinder cones is located on the floor of the Colima graben west and east of the complex. Volcán de Colima (also known as Volcán Fuego) is a youthful stratovolcano constructed within a 5-km-wide scarp, breached to the south, that has been the source of large debris avalanches. Major slope failures have occurred repeatedly from both the Nevado and Colima cones, producing thick debris-avalanche deposits on three sides of the complex. Frequent recorded eruptions date back to the 16th century. Occasional major explosive eruptions have destroyed the summit (most recently in 1913) and left a deep, steep-sided crater that was slowly refilled and then overtopped by lava dome growth.
Information Contacts: Observatorio Vulcanológico de la Universidad de Colima, Colima, Col., 28045, México (URL: https://portal.ucol.mx/cueiv/).
Manam (Papua New Guinea) — April 2008  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Manam
Papua New Guinea
4.08°S, 145.037°E; summit elev. 1807 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Low-level eruptions continue in late 2007 and early 2008
Low-level seismicity and mild eruptions occurred from mid-May 2007 through mid-September 2007 (BGVN 32:08). This report addresses activity between the end of September 2007 through mid-May 2008, with gaps in reporting as noted. For the most part, Manam remained at a low eruptive level, but four fatalities from the early 2007 activity were noted in news reports.
According to the Rabaul Volcano Observatory (RVO), ash plumes were occasionally emitted both during the first half of October 2007, during 5-8 November 2007, and on 27 December 2007. The Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC) noted that one plume rose to 3.7 km during 3-9 October and another rose to 3 km on 27 December. White vapor plumes were also emitted occasionally during October and November, and incandescence was reported on 29 September, 1 October, 10-11 October, 30 October, and 4-5 November. Roaring noises were heard on 30 October.
Manam remained quiet during January and February 2008. Both the Main Crater and South Crater continued to release thin to thick white vapor. At Main Crater, a weak red glow was visible at night on 10 January, and a fluctuating red glow was visible from the Main Crater during 8-11 February and 22-25 February. Seismic activity was at the low-to-moderate level through 14 January, when lightning struck the monitoring equipment. The number of daily low-frequency volcanic earthquakes up through the lightning strike ranged between 500 and 970. The equipment was fixed on 28 February. On 29 February, 770 low frequency earthquakes were recorded. On 9-10 February, pale gray ash clouds were emitted from the Main Crater.
RVO reports covering the interval March and April 2008 were unavailable at the time of this writing. RVO reported Manam as quiet during May 2008, emitting only variable amounts of white vapor. Glow was reported from Main Crater on the nights of 16-20 May.
Editors searched MODVOLC thermal alerts on 10 June 2008 and found that they occurred on six days during the interval April-July 2007. After previously mentioned alerts on 16 and 23 May 2007 (UTC)(BGVN 32:08), the only subsequent alerts occurred on 8 June and 26 July 2007 (UTC).
The Darwin VAAC reported plumes to altitudes of several kilometers from Manam on 2 April, 14-15 April (ash-and-steam), 23-29 April, and 11-12 May 2008. The plumes during 11-12 May rose to an altitude of 3 km and extended ~ 36 km laterally.
Fatalities and injury. To supplement our previous report (BGVN 32:08), we note that an article by Reuters on 20 March 2007 reported that during the past week a mudslide on Manam killed four people in "an avalanche of ash and mud," and that a fifth person was seriously injured. RVO noted that they received word of the event on the 15th, suggesting the event was probably on 14 or 15 March. It occurred in a valley on the island's N side.
The news account quoted Health Minister Sir Peter Barter as saying, "The valleys are very dangerous and I am appealing to everyone not to venture into any of the valleys as there are huge quantities of ash and mud deposited on higher slopes. After heavy rain that has been experienced, the mud and loose material becomes a major risk for anyone venturing into the potential path of an avalanche."
Geologic Background. The 10-km-wide island of Manam, lying 13 km off the northern coast of mainland Papua New Guinea, is one of the country's most active volcanoes. Four large radial valleys extend from the unvegetated summit of the conical basaltic-andesitic stratovolcano to its lower flanks. These valleys channel lava flows and pyroclastic avalanches that have sometimes reached the coast. Five small satellitic centers are located near the island's shoreline on the northern, southern, and western sides. Two summit craters are present; both are active, although most observed eruptions have originated from the southern crater, concentrating eruptive products during much of the past century into the SE valley. Frequent eruptions, typically of mild-to-moderate scale, have been recorded since 1616. Occasional larger eruptions have produced pyroclastic flows and lava flows that reached flat-lying coastal areas and entered the sea, sometimes impacting populated areas.
Information Contacts: Herman Patia and Steve Saunders, Rabaul Volcano Observatory (RVO), P.O. Box 386, Rabaul, Papua New Guinea; Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Bureau of Meteorology, Northern Territory Regional Office, PO Box 40050, Casuarina, Northern Territory 0811, Australia (URL: http://www.bom.gov.au/info/vaac/).
Reventador (Ecuador) — April 2008  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Reventador
Ecuador
0.077°S, 77.656°W; summit elev. 3562 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Quiet, January 2006-February 2007; emissions, March-October 2007
Our previous report on Reventador documented intermittent explosive eruptions through September 2005, with Strombolian activity and short-duration Vulcanian events. These events were accompanied by small pyroclastic flows, small lava flows, large bombs, and ash columns (BGVN 30:08). This report discusses reported events into 2008.
According to the Instituto Geofísico (Escuela Politécnica Nacional) (IG), seismicity at Reventador was low at the end of December 2005. There were no reports on this volcano during January 2006 through February 2007. The volcano was apparently only weakly eruptive or non-eruptive around this interval. MODVOLC thermal alerts were absent during late December 2005 to late March 2006.
In early March 2007, however, the IG reported an increase in the number of tectonic earthquakes at Reventador. Steam-and-ash plumes were sporadically visible and occasionally rose to altitudes of 4 km during 8-22 March. On 21 March, noises were reported. The next day, seismic signals changed that indicated possible emissions. On 24 March, local residents saw ash plumes and incandescent material near the crater and heard roaring noises. An explosion produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 6.6 km and drifted W. Based on reports from IG, the Washington VAAC reported an ash plume during 26-27 March that reached an altitude of 3.7-7 km and drifted NE and WNW. A thermal anomaly was present on satellite imagery during 24-27 March.
On 28 March, observers reported roaring noises and an ash column from Reventador that rose to an altitude of 5.6 km and drifted W. A small lava flow traveled 200 m down the S flank. Incandescent material and ash emissions were observed during 29-31 March. On 1 April, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 7.6 km and incandescent rocks were ejected about 50 m above the crater. Incandescent material was again seen at the summit on 2 April. The Washington VAAC reported that a strong hotspot was present on satellite imagery during 1-3 April. Based on pilot reports, IG reported that a steam-and-gas plume with little ash content rose to an altitude of 6.1 km and drifted W on 3 April.
On 3-4 April, incandescent blocks ejected from the summit subsequently rolled down the S flanks. Satellite imagery revealed ash plumes drifting W and a large thermal anomaly over the crater. On 4 April, a plume rose to an altitude of 4.6 km. Crater incandescence was observed on 4 and 6 April and "cannon shots" were heard on 6 April. Ash-and-steam emissions were observed during 8-9 April. Steam emissions from the flanks on 8 April possibly originated from a lava flow.
On 11 April, a steam plume from Reventador rose to an altitude of 3.8 km. Visual observations were hindered during 12-17 April due to inclement weather. On 13 April, the lava flow on the S flank, first observed on 28 March, was 15 m thick and possibly active.
On 18, 20, and 23 April, steam-and-gas emissions from Reventador hung near the summit. On 18 April, a plume was seen drifting NW on satellite imagery. On 20 April, a bluish haze of gases was observed. Clouds occasionally inhibited views of the summit during 18-24 April.
On 27 April, a steam plume from Reventador rose to an altitude of 3.7 km. Later that night, incandescent material was ejected from the crater. On 30 April, a steam plume was observed on satellite imagery drifting NW. Based on the Guayaquil Meteorological Watch Office (MWO) and satellite imagery, the Washington VAAC reported that an ash plume rose to an altitude of 3.7 km and drifted NW. Visual observations were hindered during 25 April-1 May due to inclement weather.
On 16 May, the IG reported that a steam plume from Reventador rose to an altitude of 3.6 km and drifted to the NW. The plume was visible on satellite imagery. On 18 May, strong rains resulted in a lahar that lasted approximately 40 minutes. A lahar was also noted on 22 May. Visual observations were hindered during most of the reporting period due to inclement weather.
On 18 May, an ash plume from Reventador rose to an altitude of 3.7 km and drifted NW. Ash was not observed on satellite imagery. Lahars occurred on the flanks of Reventador on 15, 19, 20, 21, and 23 June. Clouds inhibited visual observations during 20-24 June.
MODVOLC thermal alerts were frequent during late March and throughout April 2007. One alert occurred in late May 2007; two also appeared on 6 August 2007 (local dates and times). No further alerts were issued in data accessed 9 June 2008.
A VAAC report noted an eruption on 11 October 2007. It emitted an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 4.6 km and drifted S. Ash was not observed on satellite imagery due to cloud cover.
Geologic Background. Volcán El Reventador is the most frequently active of a chain of Ecuadorian volcanoes in the Cordillera Real, well east of the principal volcanic axis. The forested, dominantly andesitic stratovolcano has 4-km-wide avalanche scarp open to the E formed by edifice collapse. A young, unvegetated, cone rises from the amphitheater floor to a height comparable to the rim. It has been the source of numerous lava flows as well as explosive eruptions visible from Quito, about 90 km ESE. Frequent lahars in this region of heavy rainfall have left extensive deposits on the scarp slope. The largest recorded eruption took place in 2002, producing a 17-km-high eruption column, pyroclastic flows that traveled up to 8 km, and lava flows from summit and flank vents.
Information Contacts: Washington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center, Satellite Analysis Branch (SAB), NOAA/NESDIS E/SP23, NOAA Science Center Room 401, 5200 Auth Rd, Camp Springs, MD 20746, USA (URL: http://www.ospo.noaa.gov/Products/atmosphere/vaac/); P. Ramón, Instituto Geofísico-Departamento de Geofísica (IG), Escuela Politécnica Nacional, Casilla 17-01-2759, Quito, Ecuador.
Saunders (United Kingdom) — April 2008  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Saunders
United Kingdom
57.8°S, 26.483°W; summit elev. 843 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
No thermal anomalies detected since December 2006
The frigid, remote, and uninhabited region of Michael volcano is seldom visited. Thermal anomalies detected by satellite-based MODIS instruments, processed using the MODVOLC algorithm by the Thermal Alerts System of the Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology, provide some data about possible eruptive activity (BGVN 28:02, 29:03, 31:04, and 31:10). During 3-6 October 2005 there were three days with thermal anomalies (BGVN 31:04). MODIS data indicates that anomalous pixels were also detected on 19 December 2005 (20 December UTC) and on 20 January 2006 (21 January UTC) (BGVN 31:10). The most recently reported MODIS thermal anomalies indicated activity during 19-21 October 2006 (20-21 October UTC) and again on 31 October-1 November 2006 (BGVN 31:10). The source of these anomalies was an inferred lava lake in a central vent as shown on an Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) image collected 28 October 2006 (BGVN 31:10). Additional anomalies occurred on 13 November and 6 December 2006 (7 December UTC). No anomalies were measured after that date through May 2008. Since August 2000 there have been six periods when thermal anomalies were detected in satellite imagery (table 2).
Table 2. Eruptive periods at Michael as inferred from MODIS thermal data from January 2000 through May 2008. Courtesy of the Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology Thermal Alerts System.
| Date (UTC) |
Thermal pixel data |
Bulletin reference |
| 30 Aug 2000-03 Feb 2001 |
3 days with pixels |
BGVN 28:02 |
| 05 Aug 2001-21 Nov 2001 |
10 days with pixels |
BGVN 28:02 |
| 05 Jul 2002-01 Nov 2002 |
12 days with pixels |
BGVN 28:02 |
| 07 May 2003 |
2 anomalous pixels |
BGVN 29:03 |
| 03 Oct 2005-21 Jan 2006 |
5 days with pixels, three during 3-6 Oct |
BGVN 31:04, 31:10 |
| 09 Jun 2006-07 Dec 2006 |
9 days with pixels |
BGVN 31:10, 33:04 |
Geologic Background. Saunders Island consists of a large central volcanic edifice intersected by two seamount chains, as shown by bathymetric mapping (Leat et al., 2013). The young Mount Michael stratovolcano dominates the glacier-covered island, while two submarine plateaus, Harpers Bank and Saunders Bank, extend north. The symmetrical Michael has a 500-m-wide summit crater and a remnant of a somma rim to the SE. Tephra layers visible in ice cliffs surrounding the island are evidence of recent eruptions. Ash clouds were reported from the summit crater in 1819, and an effusive eruption was inferred to have occurred from a N-flank fissure around the end of the 19th century and beginning of the 20th century. A low ice-free lava platform, Blackstone Plain, is located on the north coast, surrounding a group of former sea stacks. A cluster of cones on the SE flank, the Ashen Hills, appear to have been modified since 1820 (LeMasurier and Thomson, 1990). Analysis of satellite imagery available since 1989 (Gray et al., 2019; MODVOLC) suggests frequent eruptive activity (when weather conditions allow), volcanic clouds, steam plumes, and thermal anomalies indicative of a persistent, or at least frequently active, lava lake in the summit crater. Due to this observational bias, there has been a presumption when defining eruptive periods that activity has been ongoing unless there is no evidence for at least 10 months.
Information Contacts: Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/).
Sheveluch
Russia
56.653°N, 161.36°E; summit elev. 3283 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Emissions continue since January 2008 as lava dome grows; morphology
From the January to May 2008, dome growth at Shiveluch has consistently been accompanied by shallow, low-amplitude earthquakes, satellite thermal anomalies, and tremor. According to the Kamchatka Branch of the Geophysical Service of the Russian Academy of Sciences (KB GS RAS), several cases of elevated magnitude seismic signals occurred (figure 14). In some cases, these signals took place during times of zero visibility and the signals were interpreted to suggest a plume above to 4 km altitude.
On 3 March a plume of gas stretched 31 km to the SW of the volcano, and ash clouds rose up to ~ 4.5 km altitude. During the last two weeks of March, reports noted gas-and-ash emissions to ~ 3.5-4.5 km altitude; hot avalanches occurred each day (figure 15).
Background on the edifice and deposits. Shiveluch is the northern-most active volcano of the Kamchatka peninsula, Russian Far East (figure 16a). The volcano forms a large isolated edifice surrounded by lowlands of the northern part of the Central Kamchatka depression. Two basic structural elements of the volcano are clear on figure 16b where Young Shiveluch is seen located inside the caldera of Old Shiveluch.
Old Shiveluch includes a thick sequence of basaltic and andesitic pyroclastic layers exposed in the base of the caldera wall; the NE and SW parts of the complex contain a folded sequence of pyroclastic deposits overlapped by basaltic-basaltic andesite flows and broken through by numerous radial dikes. The lava flows and domes of Young Shiveluch are richer in silica (59.5-62.5%) than those of Old Shiveluch (54.5-56.5%). Young Shiveluch (figures 16 and 17) has produced numerous Plinian tephras.
References. Belousov, A., Belousova, M., and Voight, B., 1999, Multiple edifice failures, debris avalanches and associated eruptions in the Holocene history of Shiveluch volcano, Kamchatka, Russia: Bulletin of Volcanology, v. 61, p. 324-342.
Gorbach, N., 2007, Bulletin of activity at Shiveluch volcano, (title approximate translated from Russian issued 31 July 2007) available (in Russian) at URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/volcanoes/inform_messages/2007/Shiveluch_072007/Shiveluch_072007.html).
Geologic Background. The high, isolated massif of Sheveluch volcano (also spelled Shiveluch) rises above the lowlands NNE of the Kliuchevskaya volcano group. The 1,300 km3 andesitic volcano is one of Kamchatka's largest and most active volcanic structures, with at least 60 large eruptions during the Holocene. The summit of roughly 65,000-year-old Stary Shiveluch is truncated by a broad 9-km-wide late-Pleistocene caldera breached to the south. Many lava domes occur on its outer flanks. The Molodoy Shiveluch lava dome complex was constructed during the Holocene within the large open caldera; Holocene lava dome extrusion also took place on the flanks of Stary Shiveluch. Widespread tephra layers from these eruptions have provided valuable time markers for dating volcanic events in Kamchatka. Frequent collapses of dome complexes, most recently in 1964, have produced debris avalanches whose deposits cover much of the floor of the breached caldera.
Information Contacts: Yuri Demyanchuk, Natasha Gorbsch, and theKamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/); Kamchatka Branch of the Geophysical Service of the Russian Academy of Sciences (KB GS RAS), Russia (URL: http://www.emsd.ru/); Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), the Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Slamet
Indonesia
7.242°S, 109.208°E; summit elev. 3428 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Heavy rains trigger steam plumes during 28 March-3 April 2007
Our last review of Slamet's activity was in November 2000, reporting a white, gas-rich plume from the stratovolcano (BGVN 25:11). We are unaware of subsequent reporting until 28 March 2007. Starting that day and through 3 April, a volcano observer reported that plumes had increased in intensity and frequency. This 7-day interval took place after two weeks of heavy rains. The plumes were of sufficient magnitude to be visible in the provincial capital, Semarang, over 138 km to the ENE. The plumes did not significantly impact residents in vicinity of the volcano. Thermal anomalies (MODVOLC) have been absent on the upper cone during 2000 through 5 June 2008.
Geologic Background. Slamet, Java's second highest volcano at 3428 m and one of its most active, has a cluster of about three dozen cinder cones on its lower SE-NE flanks and a single cinder cone on the western flank. It is composed of two overlapping edifices, an older basaltic-andesite to andesitic volcano on the west and a younger basaltic to basaltic-andesite one on the east. Gunung Malang II cinder cone on the upper E flank on the younger edifice fed a lava flow that extends 6 km E. Four craters occur at the summit of Gunung Slamet, with activity migrating to the SW over time. Historical eruptions, recorded since the 18th century, have originated from a 150-m-deep, 450-m-wide, steep-walled crater at the western part of the summit and have consisted of explosive eruptions generally lasting a few days to a few weeks.
Information Contacts: Dali Ahmad, Center of Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation, Saut Simatupang, 57, Bandung 40122, Indonesia (URL: http://vsi.esdm.go.id/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/).
Soufriere Hills (United Kingdom) — April 2008  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Soufriere Hills
United Kingdom
16.72°N, 62.18°W; summit elev. 915 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Halt in dome growth during March 2007-May 2008
Our previous report on Soufrière Hills characterized the eruptive behavior and monitoring between 16 June 2006 and 25 May 2007 (BGVN 32:04). The current report describes activity between the end of May 2007 through May 2008.
Summary report. A report of a 14 and 16 April 2008 meeting by an advisory committee provides a convenient summary of recent behavior (SAC10, 2008). With minor stylistic changes, important paragraphs are quoted below.
The report indicated that by about mid-March 2007 the volcano stopped extruding dome lava. The authors said that since about October 2007 volcanism at the surface of the volcano has been at a very low level. Further, they noted, "Whilst there have been no major collapses of the dome, or explosions, rockfalls and minor pyroclastic flows [traveling E] into the Tar River Valley have occurred that have eroded the eastern side of the dome. However, the main mass of the 2006-2007 lava dome remains intact, and whilst it remains so it is capable of generating major pyroclastic flows for years to come. Also, the flow of gas continues to stream through the dome from the magma deep in the Earth, forming the visible plume.
"A lidar survey of the shape of the dome undertaken in March 2008 gave an estimate of 195 million cubic meters for the volume of the dome. This figure is within the bounds of uncertainty of the volume estimate of 203 million cubic meters derived from photogrammetry in April 2007.
"The three distinct lobes of lava at the summit of the dome, present at the end of lava extrusion in April 2007, remain. There have been a number of rockfalls and a few minor pyroclastic flows from the dome into the Tar River Valley. As a result of these, the uppermost part of the talus has been removed on the eastern side exposing a steep band of core lava below which a chute channels material to lower levels. Similarly, erosion of talus has begun to re-expose the buried northern crater rim.
"Gases escape from the dome in several areas. On the southern and northern talus slopes multiple gas vents release mainly water-rich gas. Sulphur deposits are evident around the southern vents. These locations have been a common feature for much of the eruption. On the western side of the upper dome, just inside the buried Gage's Wall, is a vent releasing a large flux of gas with a pale blue tint, indicative of sulphur dioxide. This vent formed in February 2006 and has been the source of weak ash generation in the past, roaring noises, and the cause of minor erosion of the Gage's Wall (September 2006).
"The low levels of rockfall seismicity seen in 2007 declined even further during 2008. There were two minor swarms of long-period earthquakes on 23 November 2007 and 28 January 2008, the latter being co-incident with roaring from the Gage's Wall vent. Volcano-tectonic earthquakes occurred between the surface and 4 km below the dome. These may be caused by stress changes around the conduit.
"The reference GPS line between the South Soufrière (SOUF) and old MVO (MVO1) receivers continued the same extensional trend that began when extrusion stopped in April 2007. This extension is slower than the equivalent contracting trend seen during lava extrusion, but is comparable to the extension measured during the first year of the last pause in activity. This pattern is confirmed by most of the other GPS stations and the EDM lines on the northern side of the volcano. This extension is consistent with an island-wide pattern of surface inflation due to the magma reservoir re-charging at depth. Any deformation due to the effects of surface loading by the dome dies away over a much shorter distance from the volcano than that being monitored between MVO1 and SOUF.
"The lack of any fresh, degassing andesite magma high in the conduit was confirmed by low measured HCl/SO2 ratios. Sulphur dioxide was emitted at a rate above the long-term average (about 500 tonnes/day). Because several instruments in the measurement network have failed, there are some doubts about the absolute values, but a gradually increasing long-term trend seems real. This indicates not only that basalt degassing is ongoing, but also that the system may be becoming more permeable to deep gas loss or that gas production has increased. High values of sulphur dioxide measured by ground-based diffusion tubes to the west of the volcano have been recorded, as was also seen during the previous pause in 2005.
"Ongoing retrospective petrological analysis of the lava erupted over the last few years indicates that the amount of the basalt magma incorporated into the andesite lava that appears at the surface may be greater than previously appreciated. Understanding the mass balance of this interchange and being able to monitor it through time would help to understand the dynamics of the magma chamber.
"The current pause is 13 months long. Previous pauses have lasted 20 months (March 1998?November 1999) and 24 months (July 2003?August 2005). Despite the presence of a large dome, the "residual" surface activity now is far less than was the case during the first pause, when there was also a dome, and is much more like the second pause when there was no dome. The main difference between the first year of this pause and the first year of the second pause is the increasing trend of sulphur dioxide output in 2007-8. A few months prior to the ends of both previous pauses, the level of seismicity, and particularly long period seismicity, increased and there was a resumption of steam-rich explosions."
MVO and other reports. In accord with the summary above, the Montserrat Volcano Observatory (MVO) noted very low seismicity since May 2007. However, at the end of this reporting interval (May 2008), monitoring suggested that volcanic activity seemed headed for an upturn.
Despite the lack of dome growth (or dome destruction) during the entire period of this report the Alert Level remained at 4 (on a scale of 0-5). Authorities prohibited access to many areas near the volcano, including some areas ranging from 2 to 4 km offshore.
The Washington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (W-VAAC) noted several ash plumes during mid-May 2007 through December 2007 (11 June, 22-28 August, 16 September, 12 October, 15-19 November) and 2008 (7 and 10 January, 10 April, 5 May, 13 -19, 23 and 29 May). Some of the plumes resulted from rockfalls (19 November, and 7 January).
Plumes on 11 June and 15-16 November may have reached 3.7 km altitude. Those on 13 and 29 May rose to 3 km altitude.
Pyroclastic flows were indicated in MVO reports for the May-December 2007 part of the reporting interval on at least 16 days. Particularly noteworthy were days with multiple pyroclastic flows, including 11 June (2), 23 August (4), and 29 November (4). The latter sequence of pyroclastic flows followed minutes after a regional M 7.4 earthquake. A 30 July pyroclastic flow traveled N for a 1.5 km runout distance.
Pyroclastic flows during January-May 2008 occurred on at least five days, and on one of those days, two occurred. One on 15 January had a 2 km runout distance. A pyroclastic flow on 29 May 2008 descended a few hundred meters to the W of the dome and was associated with the above-mentioned ash plume rising to 3 km altitude. An overflight the next day suggested that the explosion and pyroclastic flow originated from the Gages vent.
Lahars were indicated in MVO reports, often one or more per month and sometimes one or more per week, during the 2007-8 reporting interval, typically associated with heavy rains and fresh deposition. Lahars were numerous on 23 October 2007 (descending all drainages), vigorous around 25-26 October 2007, abundant the week of 13-19 February 2008, and noteworthy on 5 May 2008.
A photo shows the little-changing dome as it appeared on 7 January 2008 (figure 77). The photo emphasizes the dome's steep sides and craggy summit, as well as wide areas with emerging plumes. SAC (2008) noted that, although seemingly static, the dome is far from stable and large pyroclastic flows are possible from dome disruptions in the future. In the past, many of the pyroclastic flows traveled E. SAC (2008) noted the possibility (and discussed probabilities) for their transit from the dome towards the WNW along various areas just N of Plymouth.
According to MVO, the level of volcano-tectonic (VT) earthquakes at Soufrière Hills increased during the week of 25 April-2 May 2008, and was the highest since February 2006. During this week, degassing from a vent above Gages Wall was audible in the St. George's Hill area to the NW, and steaming from the area above Tyre's Ghaut to the NW was visible. Light ashfall was reported in the Old Town area about 9 km NW, and in other nearby areas.
During 9-19 May 2008, activity increased. On 13 May a single long-period earthquake occurred, accompanied by a blue sulfur-dioxide plume. An ash plume that rose to an altitude of 3 km drifted NW (dropping ash over much of Iles Bay, Belham, Old Town, and Olveston). Ash emissions from two areas in the Gages vent to the W were observed on 15 May, but may have started the previous day. The resultant ash plume rose about 200 m above the lava dome and drifted W. Both a small rockfall and gentle roaring noises were reported. A new fumarolic area was seen on the SE side of Chances Peak. Ash emissions from Gages vent continued on 16 May. During the week of 17-23 May, activity decreased slightly.
A weekly summary of seismicity and SO2 fluxes between 25 May 2007 and 30 May 2008 is indicated in table 65. In addition to the rockfall data in the table, there was one long-period rockfall event during each of the weeks of 23-30 November, 4-11 January, and 11-18 January. The long-term SO2 average is 550 tons/day.
Table 65. Soufrière Hills seismicity and sulfur dioxide flux between 25 May 2007 and 30 May 2008. Courtesy of MVO.
| Date |
Hybrid EQ's |
Volcano-tectonic EQ's |
Long-period EQ's |
Rockfall signals |
SO2 flux (metric tons/day) |
| 25 May-01 Jun 2007 |
1 |
1 |
-- |
5 |
230 |
| 01 Jun-08 Jun 2007 |
-- |
1 |
1 |
5 |
175 |
| 08 Jun-15 Jun 2007 |
-- |
1 |
-- |
10 |
288 |
| 15 Jun-22 Jun 2007 |
-- |
1 |
1 |
10 |
165 |
| 22 Jun-29 Jun 2007 |
-- |
1 |
-- |
3 |
203 |
| 29 Jun-06 Jul 2007 |
-- |
1 |
1 |
10 |
200 |
| 06 Jul-13 Jul 2007 |
-- |
1 |
-- |
4 |
-- |
| 13 Jul-20 Jul 2007 |
-- |
1 |
1 |
6 |
300 |
| 20 Jul-27 Jul 2007 |
-- |
3 |
-- |
5 |
-- |
| 27 Jul-03 Aug 2007 |
-- |
2 |
2 |
11 |
639 |
| 03 Aug-10 Aug 2007 |
-- |
2 |
-- |
5 |
-- |
| 10 Aug-17 Aug 2007 |
-- |
2 |
-- |
4 |
818 |
| 17 Aug-24 Aug 2007 |
-- |
4 |
-- |
4 |
509 |
| 24 Aug-31 Aug 2007 |
-- |
13 |
1 |
17 |
740 |
| 31 Aug-07 Sep 2007 |
-- |
1 |
1 |
7 |
575 |
| 07 Sep-14 Sep 2007 |
-- |
5 |
-- |
6 |
688 |
| 14 Sep-21 Sep 2007 |
-- |
12 |
-- |
8 |
-- |
| 21 Sep-28 Sep 2007 |
-- |
4 |
-- |
9 |
300 |
| 28 Sep-05 Oct 2007 |
-- |
1 |
2 |
3 |
384 |
| 05 Oct-12 Oct 2007 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
10 |
508 |
| 12 Oct-19 Oct 2007 |
-- |
5 |
-- |
3 |
691 |
| 19 Oct-26 Oct 2007 |
-- |
-- |
1 |
9 |
518 |
| 26 Oct-02 Nov 2007 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
9 |
618 |
| 02 Nov-09 Nov 2007 |
-- |
12 |
-- |
16 |
596 |
| 09 Nov-16 Nov 2007 |
-- |
2 |
-- |
11 |
698 |
| 16 Nov-23 Nov 2007 |
-- |
-- |
20 |
7 |
685 |
| 23 Nov-30 Nov 2007 |
-- |
-- |
46 |
4 |
868 |
| 30 Nov-07 Dec 2007 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
4 |
405 |
| 07 Dec-14 Dec 2007 |
-- |
1 |
-- |
2 |
811 |
| 14 Dec-21 Dec 2007 |
-- |
9 |
-- |
2 |
865 |
| 21 Dec-28 Dec 2007 |
-- |
4 |
-- |
8 |
861 |
| 28 Dec-04 Jan 2008 |
-- |
1 |
-- |
2 |
615 |
| 04 Jan-11 Jan 2008 |
-- |
8 |
1 |
2 |
513 |
| 11 Jan-18 Jan 2008 |
-- |
13 |
2 |
3 |
568 |
| 18 Jan-25 Jan 2008 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
2 |
734 |
| 25 Jan-01 Feb 2008 |
-- |
3 |
25 |
-- |
468 |
| 01 Feb-08 Feb 2008 |
1 |
3 |
-- |
2 |
881 |
| 08 Feb-15 Feb 2008 |
1 |
-- |
-- |
1 |
1,004 |
| 15 Feb-22 Feb 2008 |
1 |
-- |
1 |
1 |
872 |
| 22 Feb-29 Feb 2008 |
4 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
972 |
| 29 Feb-07 Mar 2008 |
1 |
1 |
-- |
-- |
824 |
| 07 Mar-14 Mar 2008 |
-- |
4 |
-- |
3 |
766 |
| 14 Mar-21 Mar 2008 |
2 |
2 |
-- |
3 |
1,070 |
| 21 Mar-25 Apr 2008 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
| 25 Apr-02 May 2008 |
-- |
48 |
3 |
1 |
574 |
| 02 May-09 May 2008 |
-- |
10 |
5 |
5 |
630 |
| 09 May-16 May 2008 |
-- |
25 |
1 |
17 |
506 |
| 16 May-23 May 2008 |
-- |
3 |
2 |
11 |
653 |
| 23 May-30 May 2008 |
-- |
8 |
2 |
10 |
-- |
Since 2002, MVO has been monitoring the SO2 emission rate in real-time, with spectra telemetered back to the observatory from an array of three fixed, scanning UV spectrometers. MVO has also calculated the HCl:SO2 ratio by measuring the HCl emission rates indirectly using an open-path Fourier Transform Infrared spectrometer (FTIR). These ratios may be used to evaluate changes in the eruption rate and dome growth. Such mass ratios determined since August 2007 ranged from 0.28 to 0.46, with one ratio at 0.67 (during 9-16 November 2007).
MVO's weekly report for the third week of May states "observations show continuing unrest ... with a gradual increase over the last few weeks. The events of this week suggest that fresh magma is rising beneath the dome. There is now a distinct possibility that lava extrusion will start from the Gages vent without any warning. If this happens, it will probably not be long before there are small pyroclastic flows to the W. Even if lava extrusion does not restart, the dome is still a very large mass of very hot material which is capable of collapsing or exploding at any time."
Seismic signals. Five main seismic signal types have been recognized at many volcanoes, including Soufrière Hills. These include volcano-tectonic (VT) earthquakes, long-period (LP) earthquakes, hybrid earthquakes, rockfall or pyroclastic flow signals, and explosion signals. McNutt (2000) presents illustrations of characteristic seismic traces.
MVO defines a VT earthquake as having an impulsive (i.e., large amplitude) start and then rapidly decreasing in amplitude. These earthquakes often appear in swarms and are predominantly high-frequency signals (over 2 Hz). They are interpreted as due to rock fracturing.
An LP earthquake, as defined by MVO, has a more emergent start (i.e., amplitude growing with time) and generally low, narrow-band frequency content (1-2 Hz). These are interpreted as the result of signal resonance due to gas or magma inside the volcanic conduit.
MVO defines a hybrid (HB) earthquake as a mixture between VTs and LPs; hence they tend to have impulsive starts but contain significant amount of low-frequency signal. They are thought to represent magma forcing its way to the surface. These signals are often associated with periods of rapid dome growth, and are sometimes precursors to major dome collapses or switches in the direction of lava extrusion at the surface. These signals often merge into continuous tremor, which sometimes occurs in bands spaced 4-24 hours apart.
According to MVO, rockfall or pyroclastic flow signals have often been a dominant type of seismic signal recorded here (e.g., table 65). They have an emergent start and a gradual tapering towards the end of the signal and a wide frequency range. They are interpreted as being due to material falling off the dome and traveling down the flanks. Pyroclastic flow signals are similar to those of rockfalls but are generally of longer duration and higher amplitude.
Pyroclastic deposits in the ocean. Trofimovs and others (2006) reported that more than 90% of the pyroclastic material erupted at Soufrière Hills has been deposited in the ocean. The authors describe the characteristics of the deposits at different distances from shore. The coarse material forms steep-sided, near-linear ridges that intercalate to form a submarine fan. The finer materials form turbidity currents that flow to distances greater than 30 km from the shore.
MVO management. For almost 10 years the British Geological Survey (BGS) managed MVO. Beginning 1 April 2008, this service shifted to the Eastern Caribbean's two major geo-hazard organizations, the Seismic Research Unit (SRU) of the University of the West Indies, Trinidad and Tobago and the Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris (IPGP), France. The SRU carried out long-term monitoring prior to the 1995 eruption episode. They were assisted by others as the eruption began. A statement on the new situation included the following paragraph.
"The SRU monitors earthquakes and volcanoes for most of the English-speaking Eastern Caribbean countries. The IPGP has volcano observatories on Martinique and Guadeloupe, i.e. the main French-speaking Antilles. Island arcs such as the Lesser Antilles are regions where complex real-life hazards exist, not only the better known volcanic eruptions, but also the generation of a tsunami by a submarine earthquake or a volcanic landslide. The linking of these two research institutions will provide greater opportunities for studying volcanism and earthquake activity at arc-scale rather than the scale of individual islands, a logical and innovative step towards disaster risk reduction regionally and globally."
Reference. McNutt, S.R., 2000, Volcanic seismicity, in H. Sigurdsson (ed), Encyclopedia of Volcanoes, Academic Press, San Diego, p. 1015-1033.
Trofimovs, J., Amy, L., Boudon, G., Deplus, C., Doyle, E., Fournier, N., Hart, M.B., Komorowski, J.C., Le Friant, A., Lock, E.J., Pudsey, C., Ryan, G., Sparks, R.S.J., and Talling, P.J., 2006, Submarine pyroclastic deposits formed at the Soufrière Hills volcano, Montserrat (1995-2003): What happens when pyroclastic flows enter the ocean?: Geology, v. 34, no. 7, p. 549-552.
SAC10, 13 May 2008, Assessment of the hazards and risks associated with the Soufriere Hills volcano, Montserrat, Tenth Report of the Scientific Advisory Committee on Montserrat, Volcanic Activity, based on a meeting held between 14 and 16 April 2008 at the Montserrat Volcano Observatory, Montserrat (Part I: Main Report), 23 pp. (URL: http://www.mvo.ms/).
Geologic Background. The complex, dominantly andesitic Soufrière Hills volcano occupies the southern half of the island of Montserrat. The summit area consists primarily of a series of lava domes emplaced along an ESE-trending zone. The volcano is flanked by Pleistocene complexes to the north and south. English's Crater, a 1-km-wide crater breached widely to the east by edifice collapse, was formed about 2000 years ago as a result of the youngest of several collapse events producing submarine debris-avalanche deposits. Block-and-ash flow and surge deposits associated with dome growth predominate in flank deposits, including those from an eruption that likely preceded the 1632 CE settlement of the island, allowing cultivation on recently devegetated land to near the summit. Non-eruptive seismic swarms occurred at 30-year intervals in the 20th century, but no historical eruptions were recorded until 1995. Long-term small-to-moderate ash eruptions beginning in that year were later accompanied by lava-dome growth and pyroclastic flows that forced evacuation of the southern half of the island and ultimately destroyed the capital city of Plymouth, causing major social and economic disruption.
Information Contacts: Montserrat Volcano Observatory (MVO), Fleming, Montserrat, West Indies (URL: http://www.mvo.ms/); Washington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center, Satellite Analysis Branch (SAB), NOAA/NESDIS E/SP23, NOAA Science Center Room 401, 5200 Auth Road, Camp Springs, MD 20746, USA (URL: http://www.ssd.noaa.gov/).
Jebel at Tair (Yemen) — April 2008  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Jebel at Tair
Yemen
15.55°N, 41.83°E; summit elev. 244 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Eruptive cloud entered stratosphere; decaying thermal anomalies
On 30 September 2007 an eruption began on the island of Jebel at Tair (BGVN 32:10) that generated a large SO2 plume, sent lava flows into the sea, and resulted in the deaths of Yemeni soldiers. Observations of continuing activity were made in late November-early December 2007, and also in mid-January 2008, but no other eyewitness reports have been received since that time. However, satellite data indicated continuing thermal anomalies, indicative of hot lava flows, into mid-May 2008.
Thermal anomalies detected by the MODIS instrument on the Terra and Aqua satellites were recorded daily from the beginning of the eruption through 14 January 2008 (figure 10). After that time the detections of anomalies became more intermittent, and fewer alert pixels were recorded each time. Only single-pixel anomalies were observed after 19 February, and the 19-22 February period was the last time anomalies were recorded for more than two consecutive days. Single anomalous pixels were later noted on 13 days from 26 February through May 2008, all apparently located on the N or NW slopes; the last one was on 18 May. [Another thermal anomaly was later detected on 14 June local time.]
News media reports about the continuing eruption published in early December 2007 stated that at least eight soldiers had been killed during the initial activity on 30 September. Following a magnitude 2.7 earthquake in the Red Sea on 3 December reported by the Yemen Earthquake Observation Center (EOC), other officials were quoted as saying the eruption was "strong" with lava "shooting high in the air." The news stories also noted that two seismic stations had been installed on the Red Sea islands of Zuqar and Hunaish in late November 2007.
A later news report from 13 January 2008 indicated that a third seismic station was placed on the island of Kamaran. The 13 January story in the Yemen Times also included information from the head of the General Authority for Developing Yemeni Islands (GADYI), a government agency, indicating that "smoke steam" plumes were still rising from the crater.
Satellite data analysis. Eckhardt and others (2008) developed an "inverse modeling technique for estimating the vertical profile of SO2 emissions from a volcanic eruption, using total column measurements of SO2 from satellites and a Lagrangian particle dispersion model." Cloud-free satellite views of the 30 September 2007 eruption at Jebel at Tair and the long-range SO2 transport made for an "ideal" test case of the model. Modeling results will not be presented here, but the data analysis undertaken to initialize and test the model produced additional information about the eruption itself. The eruption began earlier than previously reported, and the plume reached stratospheric altitudes.
The onset of the eruption was not well documented, but soldiers reported entering the water to escape the eruption at 1530 local time (BGVN 32:10). By that time the water was described as "boiling" by survivors. Eckhardt and others (2008) looked for signs of the eruption onset using SEVIRI (Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infra-red Imager) satellite imagery (12µ channel). Their analysis of the temperature data suggested that the initial eruption took place before 1427 local time (1127 UTC). Temperature profiles also showed that the eruption cloud penetrated the tropopause, the atmospheric boundary found here at 15.3 km altitude (Eckhardt and others, 2008). Their initial eruption findings were summarized as follows: satellite observations combined with ECMWF (European Center for Medium range Weather Forecasting) and radiosonde profiles suggested an initial eruption no later than 1427; the plume reached neutral buoyancy no earlier than 1500; the minimum value of the 12µ brightness temperature was at 1557, and the plume reached an altitude above 16 km.
Total SO2 column measurements from AIRS (Atmospheric Infrared Sounder), OMI (Ozone Monitoring Instrument), and SEVIRI enabled Eckhardt and others (2008) to estimate a total emission of 80 (± 20) kt of SO2 into the atmosphere. Some instruments observed the plume dispersion for over a week, as it stretched across Asia and the Pacific Ocean.
Reference. Eckhardt, S., Prata, A.J., Seibert, P., Stebel, K., and Stohl, A., 2008, Estimation of the vertical profile of sulfur dioxide injection into the atmosphere by a volcanic eruption using satellite column measurements and inverse transport modeling: Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions, v. 8, p. 3761-3805.
Geologic Background. The basaltic Jebel at Tair volcano rises from 1,200 m depth in the south-central Red Sea, forming an oval-shaped island about 3 km long. It is the northernmost known Holocene volcano in the Red Sea and lies SW of the Farisan Islands. Youthful basaltic pahoehoe lava flows from the steep-sided central vent, Jebel Duchan, cover most of the island, draping a circular cliff cut by wave erosion of an older edifice and extending beyond it to form a flat coastal plain. Pyroclastic cones are located along the NW and S coasts, and fumarolic activity occurs from two uneroded scoria cones at the summit. Radial fissures extend from the summit, some of which were the sources of lava flows. Explosive eruptions were reported in the 18th and 19th centuries, prior to an eruption in 2007-2008.
Information Contacts: Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Yemen Times (URL: http://yementimes.com/); Yemen Observer (URL: http://www.yobserver.com/).