Report on Popocatepetl (Mexico) — September 2019
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 44, no. 9 (September 2019)
Managing Editor: Edward Venzke.
Edited by Janine B. Krippner.
Popocatepetl (Mexico) Frequent explosions continue during March-August 2019
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 2019. Report on Popocatepetl (Mexico) (Krippner, J.B., and Venzke, E., eds.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 44:9. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.BGVN201909-341090
Popocatepetl
Mexico
19.023°N, 98.622°W; summit elev. 5393 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
The current eruptive period of Popocatépetl began on 9 January 2005 and it has since been producing frequent explosions accompanied by ash plumes, gas emissions, and ballistic ejecta that can impact several kilometers away from the crater, as well as dome growth and destruction. This activity continued through March-August 2019 with an increase in volcano alert level during 28 March-6 May. This report summarizes activity during this period and is based on information from Centro Nacional de Prevención de Desastres (CENAPRED), Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (UNAM), and various webcam and remote sensing data.
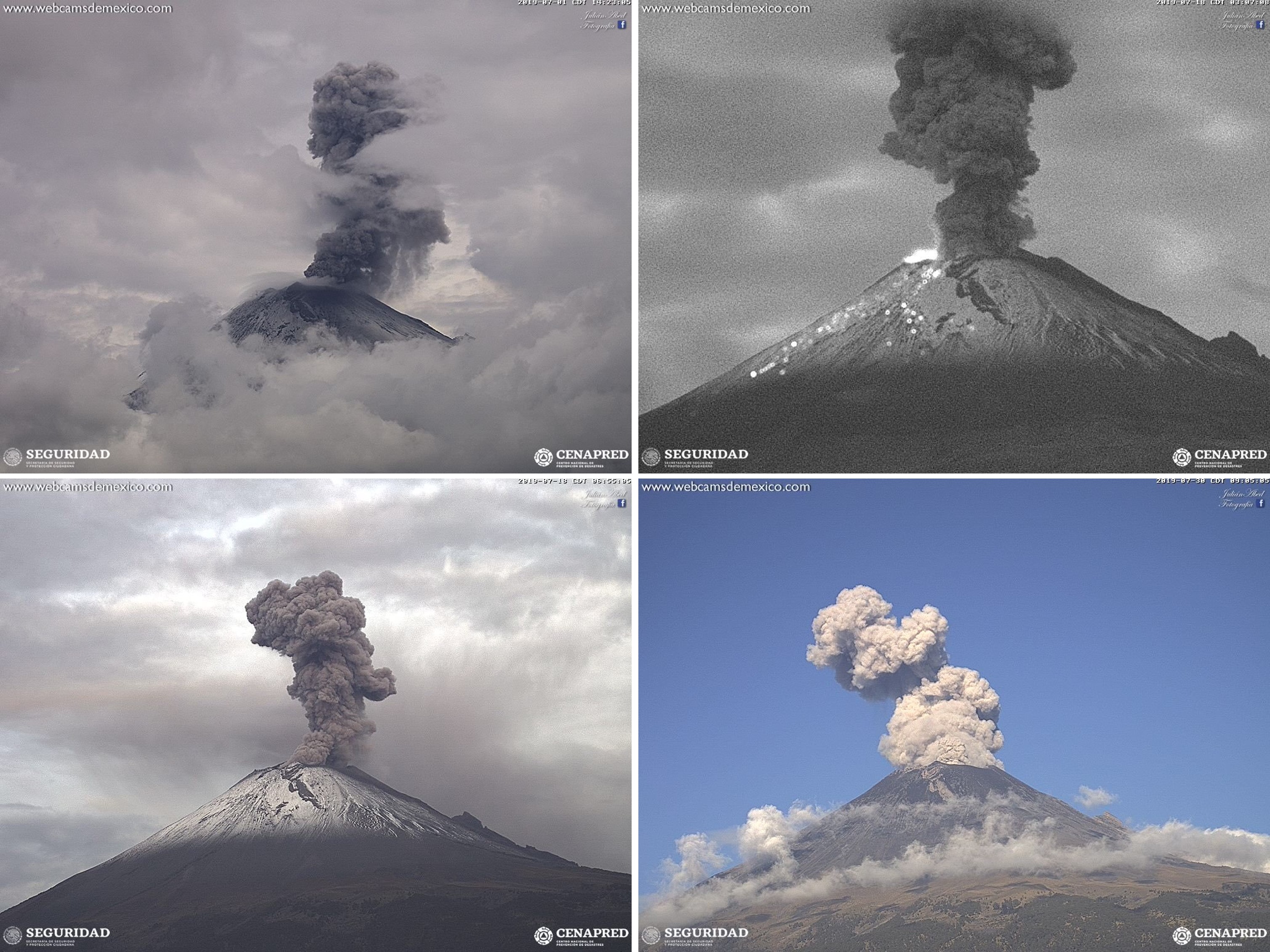
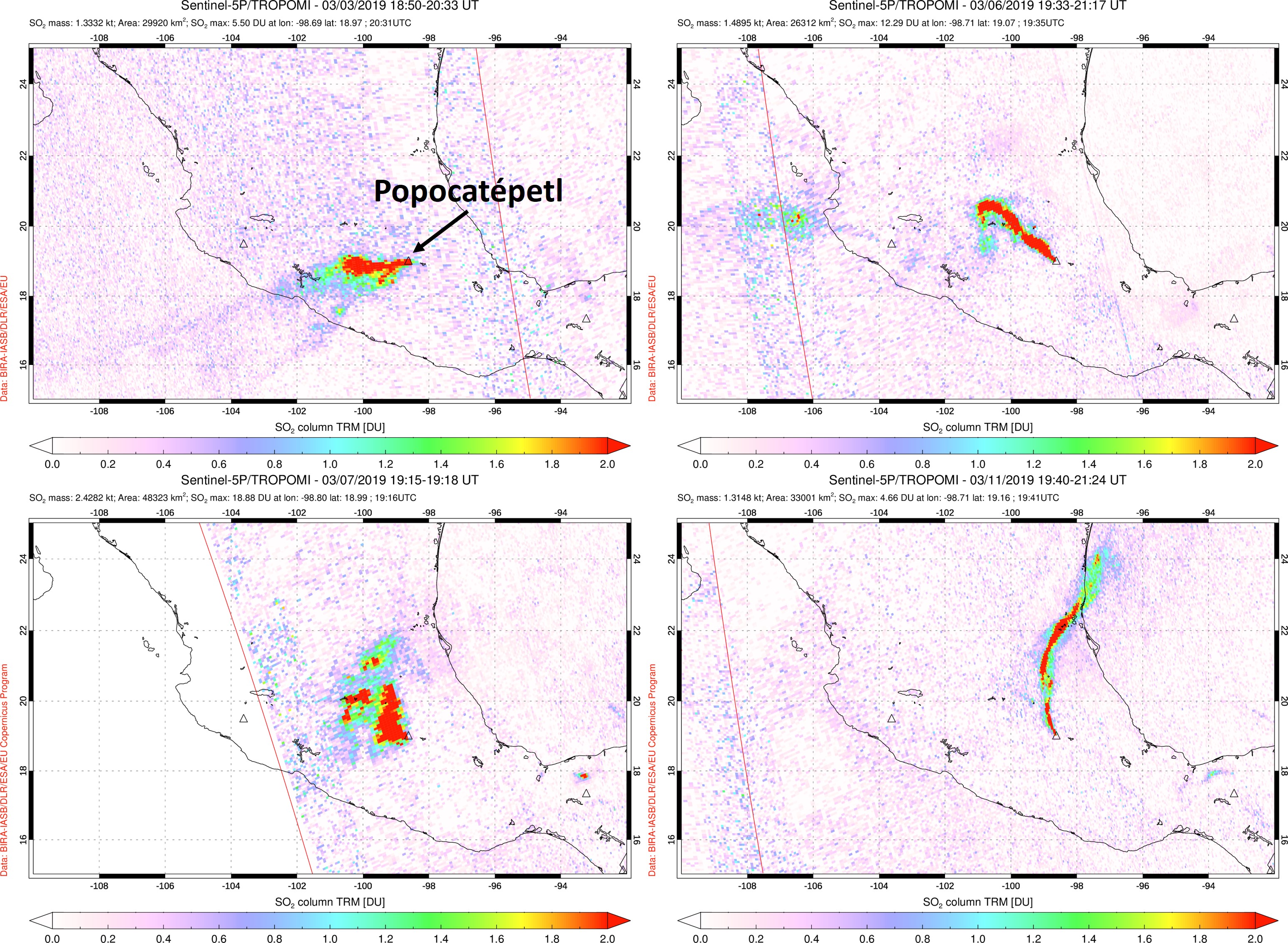
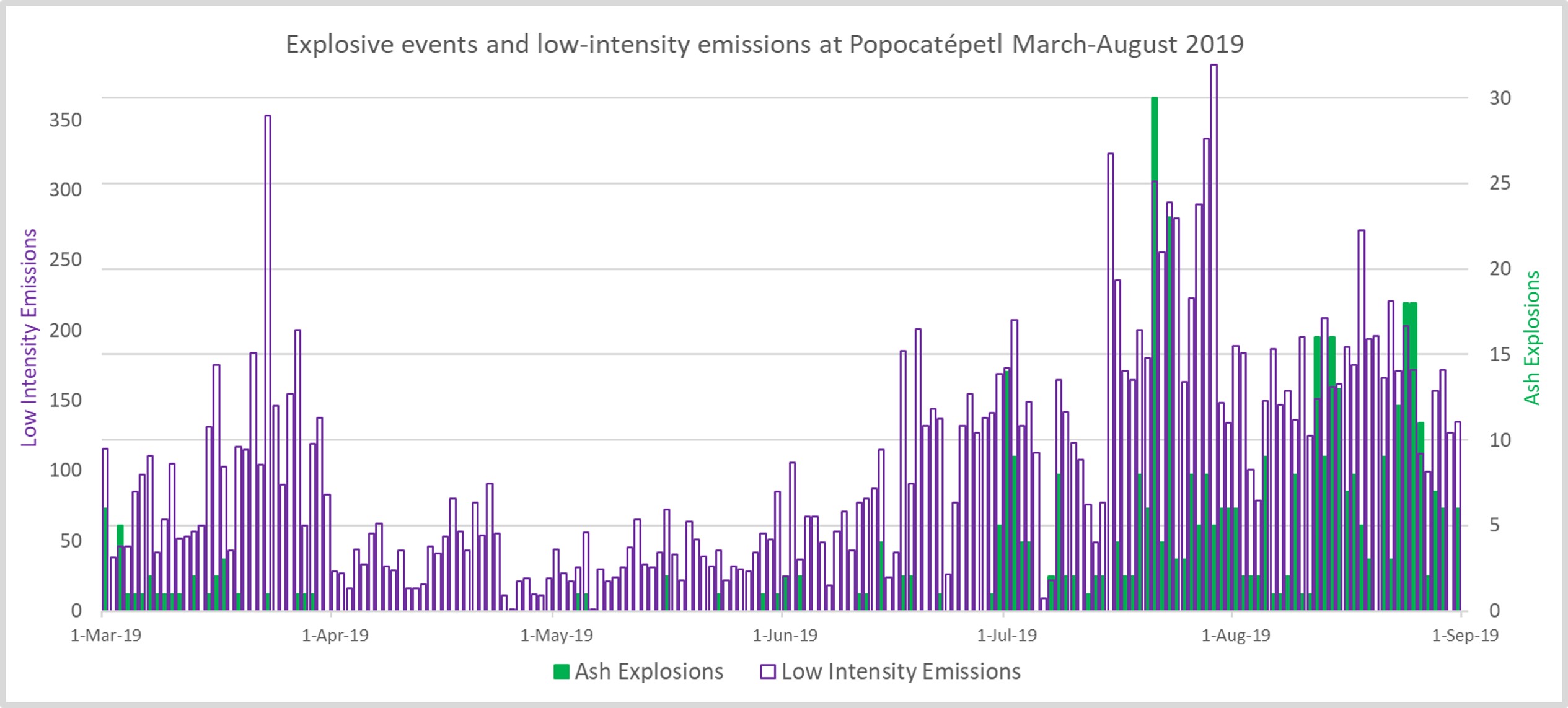
An overflight on 28 February confirmed that dome 82, which was first observed on 14 February, was still present and was 200 m in diameter. During March there were 3,291 observed low-intensity emissions, and 33 larger explosions that produced ash plumes to a maximum height of 5 km, accompanied by near-continuous emission of water vapor and volcanic gases. Explosions ejected blocks that fell on the flanks out to 1.2-2 km on 1, 10, 13, 17, 26, 27, and 29 March. The events on the 17th and 27th resulted in vegetation fires. Frequent sulfur dioxide (SO2) plumes were detected by TropOMI (figure 130). An overflight on 7 March showed intense degassing and an ash plume at 1142, preventing visibility into the crater (figure 131). On 13 March Strombolian activity was observed for approximately 15 minutes at 0500, accompanied by incandescent ejecta that deposited mainly on the ESE flank.
An overflight on 15 March was taken by CENAPRED and UNAM personnel to observe changes to the crater after explosions on the 13th and 14th. They reported that dome 82 had been destroyed and the crater maintained its previous dimensions of 300 m in diameter and 130 m deep. An explosion on the 27th ejected incandescent rocks out to 2 km from the crater and produced a 3-km-high ash plume that dispersed to the NE. Ashfall was reported in Santa Cruz, Atlixco, San Pedro, San Andrés, Santa Isabel Cholula, San Pedro Benito Juárez, and in the municipalities of Puebla, Hueyapan, Tetela del Volcán, and Morelos.
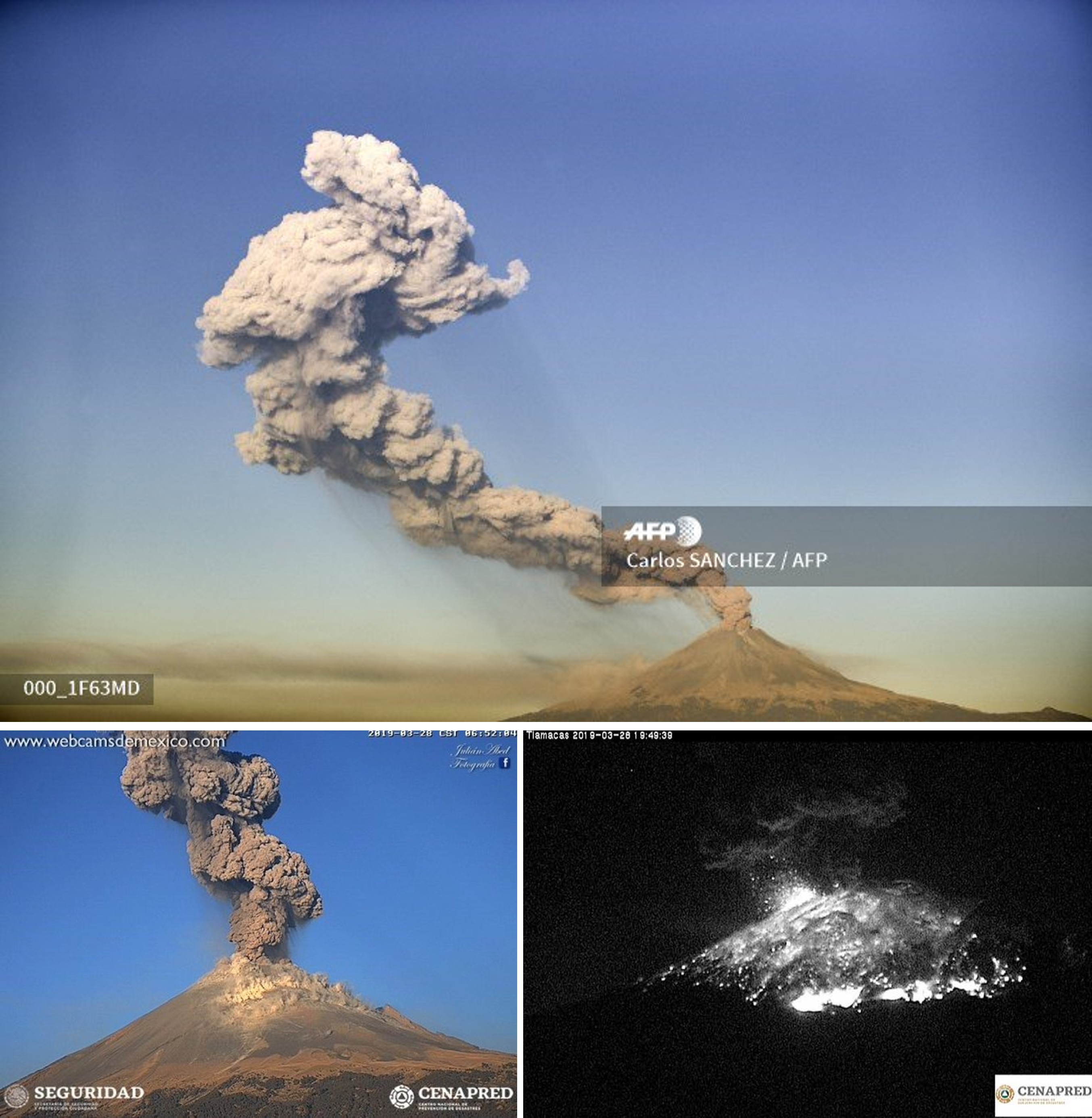
On 28 March an explosion at 0650 generated a 2.5-km-high ash plume and ejecta out to 1 km from the crater, and a 130-minute-long event produced gas and ah plumes (figure 132). On this day the volcano alert level was increased from Yellow Phase 2 to Yellow Phase 3. On the 29th an ash plume rose to 3 km and was accompanied by ejecta that reached 2 km away from the crater. Later that day a 20-minute-long event produced ash and gas. During a surveillance flight on 30 March a view into the crater showed no dome present, and the crater size had increased to 350 m in width and 250-300 m in depth after recent explosions (figure 131). On this day Strombolian activity was also observed lasting for 14 minutes, producing an ash plume to 800 m and ejecta out to 300 m from the crater. Incandescence at the crater was often seen during nighttime throughout the month.
There was a decrease in events during the next two months with 1,119 recorded low-intensity emissions and no larger ash explosions throughout April, followed by 1,210 low-intensity emissions and seven larger ash explosions through May (figure 133). Water vapor and volcanic gas emissions were frequently observed through this time and incandescence was observed some nights. A surveillance overflight on 26 April noted no new dome within the crater. On 6 May the alert level was lowered back to Yellow Phase 2. Another overflight on 9 May showed no change in the crater. An explosion at 1910 on 22 May produced an ash plume to 3.5 km above the crater with ashfall reported in Ozumba, Temamatla, Atlautla, Cocotitlán, Ayapango, Ecatzingo, Tenango del Aire and Tepetlixpa.
Through the month of June there were 2,820 low-intensity emissions and 21 larger ash explosions recorded. Gas emissions were observed throughout the month. Two explosions on 3 June produced ash plumes up to 3.5 and 2.8 km, with ejecta out to 2 km S during the first explosion. On 11 June an explosion produced an ash plume to 1 km above the crater and ballistic ejecta out to 1 km E. Observers on a surveillance overflight on the 12th reported no changes within the crater
Explosions with estimated plume heights of 5 km occurred on the 14th and 15th, with the latter producing ashfall in the municipalities of San Pablo del Monte, Tenancingo, Papantla, San Cosme Mazatencocho, San Luis Teolocholco, Acuamanala, Nativitas, Tepetitla, Santa Apolonia Teacalco, Santa Isabel Tetlatlahuaca, and Huamantla, in the state of Tlaxcala, as well as in Nealtican, San Nicolás de los Ranchos, Calpan, San Pedro Cholula, Juan C. Bonilla, Coronango, Atoyatempan, and Coatzingo, in the state of Puebla.
On 17 June an explosion produced an ash plume that reached 8 km above the crater and dispersed towards the SW. An ash plume rising 2.5 km high was accompanied by incandescent ejecta impacting a short distance from the crater on the 21st, and another ash plume reached 2.5 km on the 22nd. Explosions on 26, 29, and 30 June resulted in ash plumes reaching 1.5 km above the crater and ballistic ejecta impacting on the flanks out to 1 km.
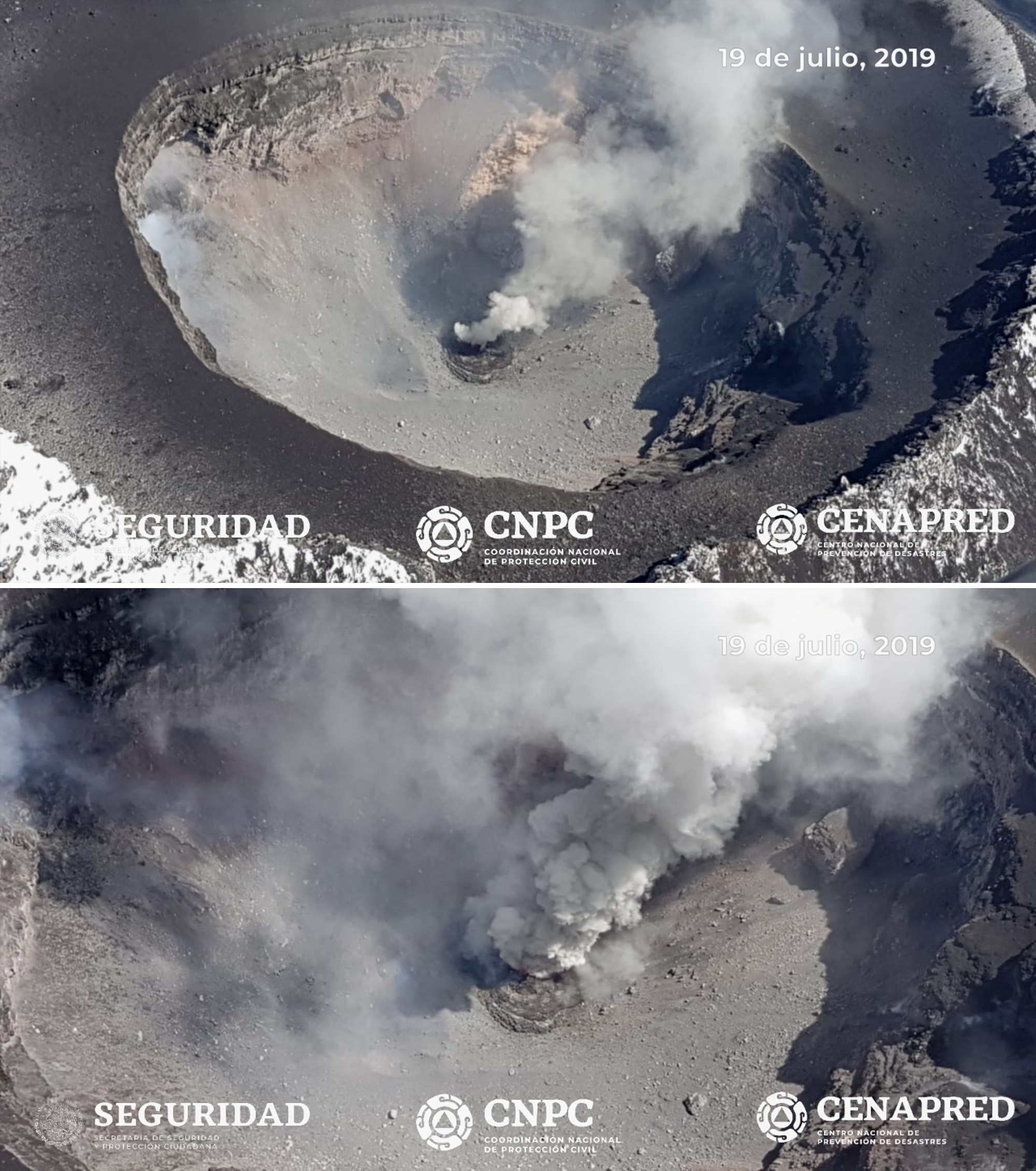
For the month of July there was an increased total of 5,637 recorded low-intensity emissions, and 173 larger ash explosions (figure 134). On 8 July an explosion produced ballistic ejecta out to 1.5 km and an ash plume up to 1 km above the crater. An ash plume up to 2.6 km was produced on the 12th. On 19 July a surveillance overflight observed a new dome (dome 83) with a diameter of 70 m and a thickness of 15 m (figure 135). Explosions on 20 July produced ashfall, and minor explosions that ejected incandescent ballistics onto the slopes. An event on the 24th produced an ash plume that reached 1.2 km, and ash plumes the following day reached 1 km. An overflight on 27 July confirmed that these explosions destroyed dome 83, and the crater dimensions remained the same (figure 136). The following day, ash plumes reached up to 1.6 km above the crater, and up to 2 km on the 29th. Minor ashfall was reported in the municipality of Ozumba on 30 June.
Throughout August the number of recorded events was higher than previous months, with 5,091 low-intensity emissions and 204 larger ash explosions (figure 137). Two explosions generated ash plumes and incandescent ejecta on 2 August, the first with a plume up to 1.5 km with ejecta impacting the slopes, and the second with an 800 m plume and ejecta landing back in the crater. Ashfall from the events was reported in in the municipalities of Tenango del Aire, Ayapango and Amecameca. On the 14th ashfall was reported in Juchitepec, Ayapango, and Ozumba. Explosions on 16 August produced ash plumes up to 2 km that dispersed to the WSW. Over the following two days ash plumes reached 1.2 km and resulted in ashfall in Cuernavaca, Tepoztlán, Tlalnepantla, Morelos, Ozumba, and Ecatzingo. Over 30-31 August ash plumes reached between 1-2 km above the crater and ashfall was reported in Amecameca, Atlautla, Ozumba, and Tlalmanalco. Incandescence was sometimes observed at the crater through the month.
 |
Figure 137. Ash plumes at Popocatépetl on 7 August (top) and 26 August 2019 (bottom). Courtesy of CENAPRED and Webcams de Mexico. |
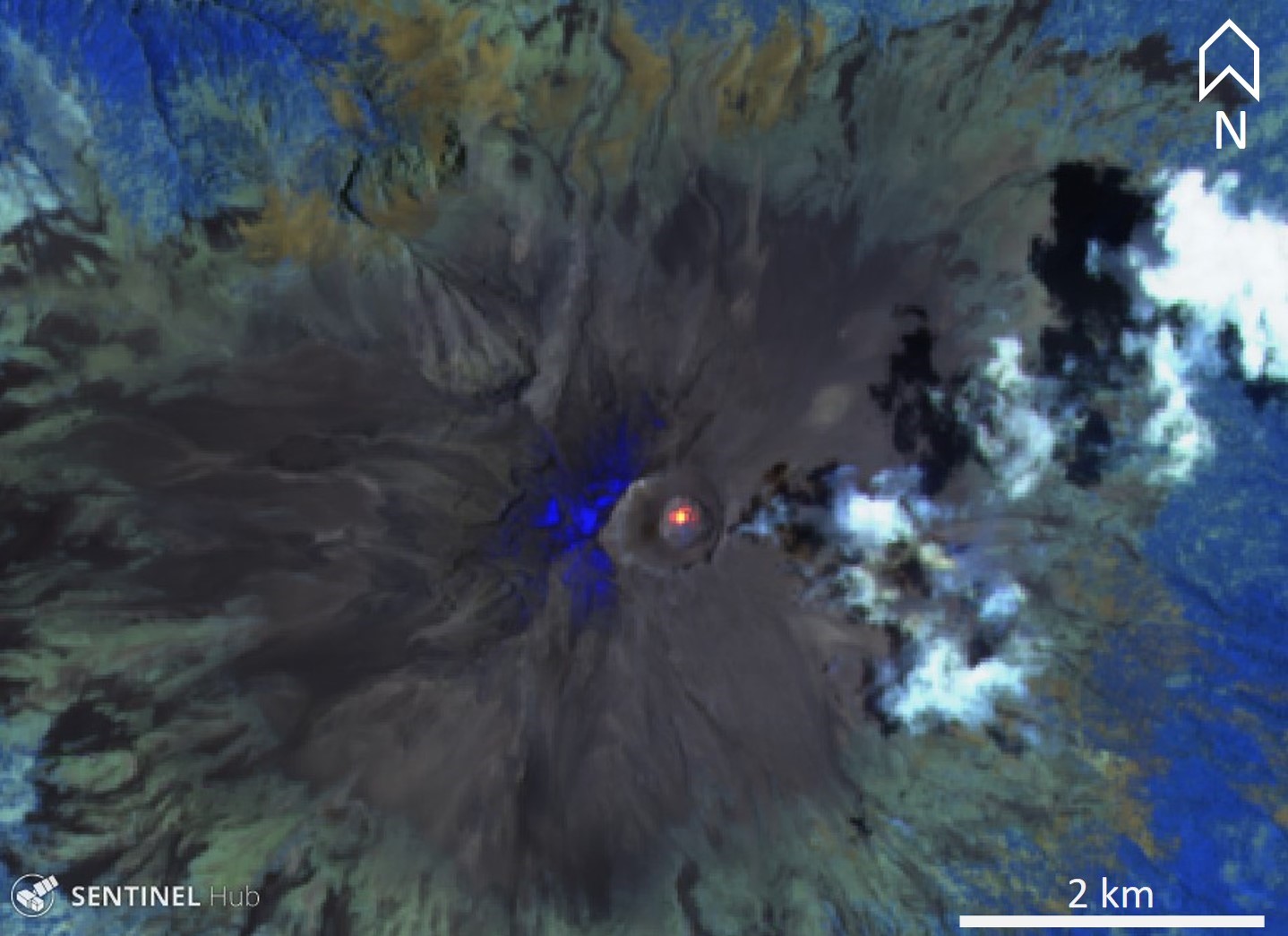
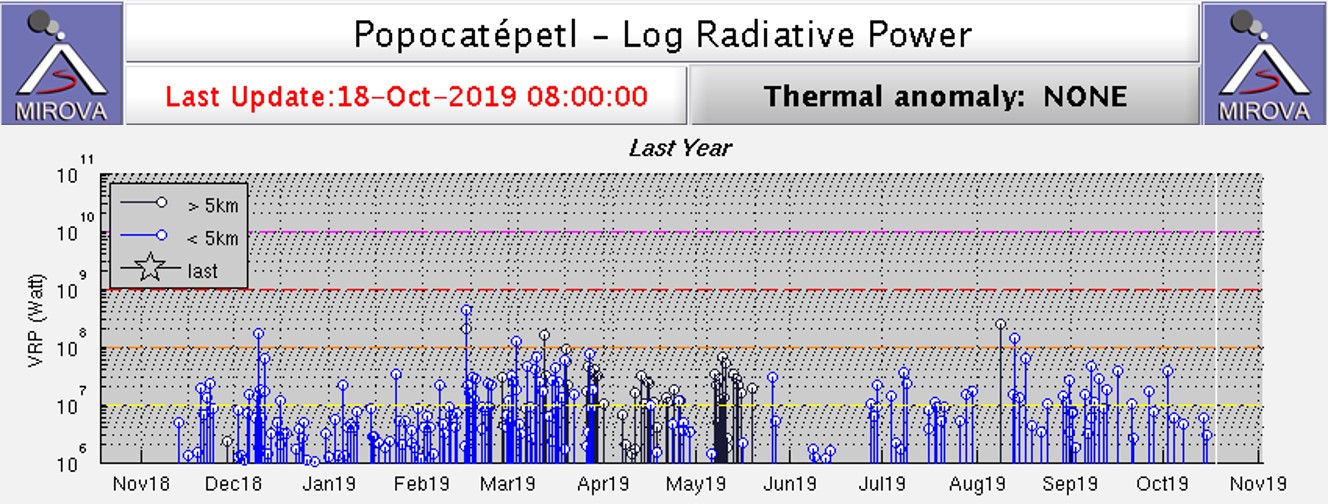
The MODVOLC algorithm for MODIS thermal anomalies registered thermal alerts through this period, with 22 in March, three in May, five in July, and one in August. The MIROVA system showed that the frequency of thermal anomalies at Popocatépetl was higher in March, sporadic in April and May, low in June, and had increased again in July and August (figure 138). Elevated temperatures were frequently visible in Sentinel-2 thermal satellite data when clouds and plumes were not covering the crater (figure 139).
Geological Summary. Volcán Popocatépetl, whose name is the Aztec word for smoking mountain, rises 70 km SE of Mexico City to form North America's 2nd-highest volcano. The glacier-clad stratovolcano contains a steep-walled, 400 x 600 m wide crater. The generally symmetrical volcano is modified by the sharp-peaked Ventorrillo on the NW, a remnant of an earlier volcano. At least three previous major cones were destroyed by gravitational failure during the Pleistocene, producing massive debris-avalanche deposits covering broad areas to the south. The modern volcano was constructed south of the late-Pleistocene to Holocene El Fraile cone. Three major Plinian eruptions, the most recent of which took place about 800 CE, have occurred since the mid-Holocene, accompanied by pyroclastic flows and voluminous lahars that swept basins below the volcano. Frequent historical eruptions, first recorded in Aztec codices, have occurred since Pre-Columbian time.
Information Contacts: Centro Nacional de Prevención de Desastres (CENAPRED), Av. Delfín Madrigal No.665. Coyoacan, México D.F. 04360, México (URL: http://www.cenapred.unam.mx/); Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México (UNAM), University City, 04510 Mexico City, Mexico (URL: https://www.unam.mx/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: https://SO2.gsfc.nasa.gov/); Sentinel Hub Playground (URL: https://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/sentinel-playground); Webcams de Mexico (URL: http://www.webcamsdemexico.com/); Agence France-Presse (URL: http://www.afp.com/).