Report on Aira (Japan) — January 1983
Scientific Event Alert Network Bulletin, vol. 8, no. 1 (January 1983)
Managing Editor: Lindsay McClelland.
Aira (Japan) Increased explosive activity, ash ejection
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 1983. Report on Aira (Japan) (McClelland, L., ed.). Scientific Event Alert Network Bulletin, 8:1. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.SEAN198301-282080
Aira
Japan
31.5772°N, 130.6589°E; summit elev. 1117 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Activity at the summit crater of Minami-dake intensified in January; 54 explosions (figure 9) and 35 ash ejections not accompanied by instrument-recorded explosions were observed. In the second half of January, explosions were accompanied by larger amounts of lapilli. An explosion at 1059 on 26 January (table 4) ejected an eruption column that rose 3.8 km above the summit, the highest observed in the past 9 years. This cloud was large enough to be observed from JMA's Asosan Weather Station, 150 km to the NNE; aircraft crews reported that it rose 7.8 km above sea level. Lapilli from this explosion broke the windshield of a car passing near Arimura, 3 km S of the summit. Incandescent columns were observed during two of the explosions on 31 January. A 300-m-high column accompanied the explosion at 0228 and lasted 40 seconds; a column 200 m high lasted 30 seconds during the 0545 explosion.
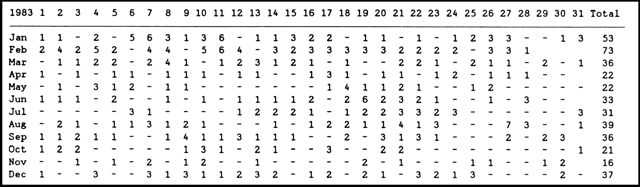 |
Figure 9. Summary table of explosions from Minami-dake crater at Sakura-jima, 1983. Data courtesy of JMA. |
Table 4. Notable eruptive activity of Sakura-jima, 1983. Courtesy of JMA.
| Date | Event | Comment |
| 26 Jan 1983 | Explosion at 1059 | Windshields broken on 4-5 cars at SE foot. |
| 02 Feb 1983 | Debris flows | One flow damaged nine houses and a hotel at S foot after pushing away part of a sand trap wall. |
| 18 Feb 1983 | Explosion at 1326 | Ejected blocks as large as 0.5-1 m; one hut at SE foot burned. |
| 21 Feb 1983 | Explosion at 1043 | Windshields broken on four cars at SE foot. |
| 02 Mar 1983 | Debris flows | Road at S foot temporarily covered. |
| 22 May 1983 | Explosion at 1237 | Eruption column at 4 km above the summit, 2 hours of continuous ash ejection; electric supply interrupted, equipment damaged at Kurokami, 5 km E. |
| 26 May 1983 | Explosion | Five hours of continuous ash ejection; windshields broken on 23 cars, gymnasium roof cracked. |
| 24 Jul 1983 | Three explosions | Strong SW wind carried ash to Miyazaki City, 80 km NE, reducing visibility to 4 km. |
| 02 Aug 1983 | Explosion at 1401 | Large amount of lapilli fell near Karutayama Volcano Observatory, about 3 km NW, and at site of sand trap construction, 2 km SE, where four workers were slightly burned. |
| 14 Aug 1983 | Explosion at 1614 | Windshields on 16 cars, windows in two houses, and a hut roof broken at Nojiri (SW foot); windshields on three cars broken in Kamoike (S part of Kagoshima City, 10 km WSW). |
| 27 Aug 1983 | Explosion at 1401 | Car windshields broken at Arimura, 3 km S. |
| 01 Sep 1983 | Debris flows | Roads temporarily closed. Total of five flows (on 1, 10, 20, and 21 September). |
| 17-18 Sep 1983 | Continuous ash ejection | Ash on track derailed streetcar in N Kagoshima City, 10 km WNW |
| 20 Sep 1983 | Explosion at 1518 | A few windows in a temple damaged at Kamoike. Debris flows (see 1 Sep comment). |
| 10 Oct 1983 | Explosion at 1351 | Windshields broken on two cars at SW foot. |
| 07 Dec 1983 | Explosion at 1702 | Car windshield broken in Tarumizu City, 10 km SSE. |
| 13 Dec 1983 | Explosion at 1028 | Large air shock broke windows in hotel and house. |
Geological Summary. The Aira caldera in the northern half of Kagoshima Bay contains the post-caldera Sakurajima volcano, one of Japan's most active. Eruption of the voluminous Ito pyroclastic flow accompanied formation of the 17 x 23 km caldera about 22,000 years ago. The smaller Wakamiko caldera was formed during the early Holocene in the NE corner of the caldera, along with several post-caldera cones. The construction of Sakurajima began about 13,000 years ago on the southern rim and built an island that was joined to the Osumi Peninsula during the major explosive and effusive eruption of 1914. Activity at the Kitadake summit cone ended about 4,850 years ago, after which eruptions took place at Minamidake. Frequent eruptions since the 8th century have deposited ash on the city of Kagoshima, located across Kagoshima Bay only 8 km from the summit. The largest recorded eruption took place during 1471-76.
Information Contacts: JMA, Tokyo.

