Global Volcanism Program | Image GVP-10435
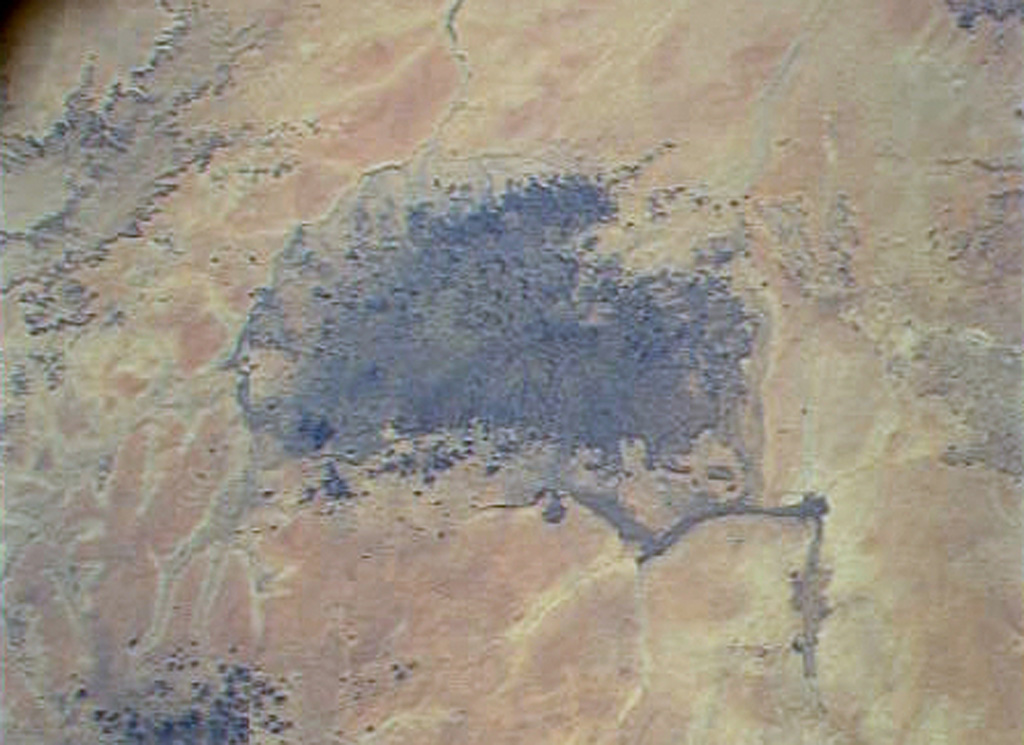
The dark-colored area in the center of this Space Shuttle view is the alkaline Meidob volcanic field in western Sudan. This broad volcanic field covers an area of 5,000 km2 with nearly 700 Pliocene-to-Holocene vents. The margins of the field are dominated by basaltic scoria cones and associated lava flows, but the lava domes, tuff rings, and maars that are concentrated along the central E-W-trending axis of the volcanic field are among the youngest features. The latest dated eruptions took place about 5,000 years ago.
NASA Space Shuttle image STS073-713-87, 1995 (http://eol.jsc.nasa.gov/).
![]() This image is made available as a Public Domain Work, but proper attribution is appreciated.
This image is made available as a Public Domain Work, but proper attribution is appreciated.
Galleries: Volcanic Fields
Keywords: remote sensing | volcanic field
Meidob Volcanic Field
