Report on Agrigan (United States) — July 1990
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 15, no. 7 (July 1990)
Managing Editor: Lindsay McClelland.
Agrigan (United States) Increased fumarolic activity; nine evacuated
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 1990. Report on Agrigan (United States) (McClelland, L., ed.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 15:7. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.BGVN199007-284160
Agrigan
United States
18.77°N, 145.67°E; summit elev. 965 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
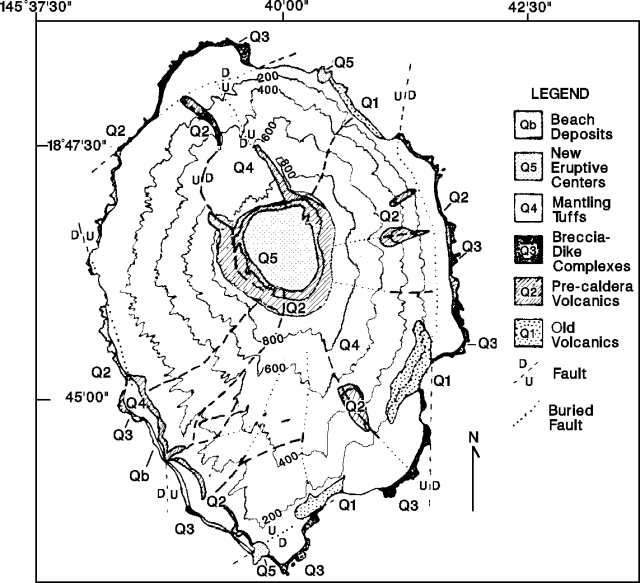
An overflight on 1 August revealed increased fumarolic activity at the volcano [(figure 1)]. Nine residents were evacuated from the island. No felt earthquakes were reported.
Reference. Stern, R.J., 1978, Agrigan: an introduction to the geology of an active volcano in the Northern Mariana Arc: BV, v. 41, p. 43-55.
Geological Summary. The highest of the Marianas arc volcanoes, Agrigan contains a 500-m-deep, flat-floored caldera. The elliptical island is 8 km long; its summit is the top of a massive 4000-m-high submarine volcano. Deep radial valleys dissect the flanks of the thickly vegetated stratovolcano. The elongated caldera is 1 x 2 km wide and is breached to the NW, from where a prominent lava flow extends to the coast and forms a lava delta. The caldera floor is surfaced by fresh-looking lava flows and also contains two cones that may have formed during the only historical eruption in 1917. This eruption deposited large blocks and 3 m of ash and lapilli on a village on the SE coast, prompting its evacuation.
Information Contacts: R. Koyanagi, HVO; F. Sasamoto, Office of Civil Defense, Saipan.