Report on Turrialba (Costa Rica) — April 2015
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 40, no. 4 (April 2015)
Managing Editor: Richard Wunderman.
Turrialba (Costa Rica) 29 October 2014 magmatic eruption, the first such event in 150 years
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 2015. Report on Turrialba (Costa Rica) (Wunderman, R., ed.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 40:4. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.BGVN201504-345070
Turrialba
Costa Rica
10.025°N, 83.767°W; summit elev. 3340 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
This report primarily summarizes activity during January 2013 through mid-December 2014 (although a plot of SO2 flux during 1 October 2008-30 November 2013 is also presented). That activity included frequent gas emissions, occasional increases in seismicity, intermittent gas explosions that generated ash plumes and ashfall, and strong gas explosions on 21 May 2013 and 29-31 October 2014. Material here are primarily extracted from a 2013 annual report and the suite of 2014 monthly reports, all prepared by the Observatorio Vulcanologico y Sismologico de Costa Rica-Universidad Nacional (OVSICORI-UNA).
Recent Bulletin reports (BGVN 37:06 and 38:02) indicated that the number of volcanic earthquakes and degassing events at Turrialba's W crater during 2012 were lower than those in 2010 and 2011. The three main fumaroles present in the W crater were as follows: Boca 2010 on the W wall, Boca 2011 on the N wall, and Boca 2012 on the E wall.
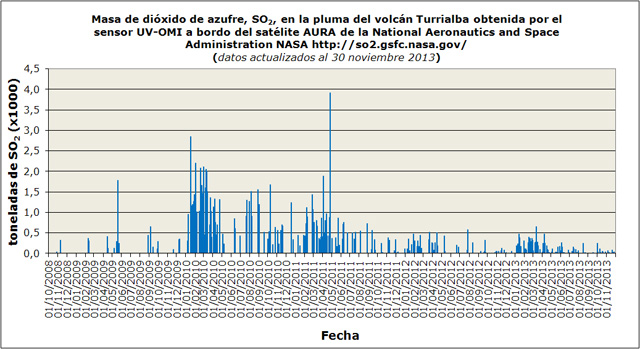
Gas data, 2008-early 2013. Ultraviolet spectral analysis can yield estimates of volcanogenic SO2. The methods to assess and express volcanogenic SO2 vary, with some methods looking at the atmospheric column (total column mass) and others the flux of the gas close to the volcano (mass per unit time, for example, metric tons per day).
The Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) travels in space onboard NASA's Aura satellite and yields estimate of the column SO2 mass. For Turrialba during the 2008-2013 period OMI determined SO2 mass burdens generally below 1,500 metric tons and in a few cases to higher values including two cases in the range 2,500-4,000 metric tons (figure 36).
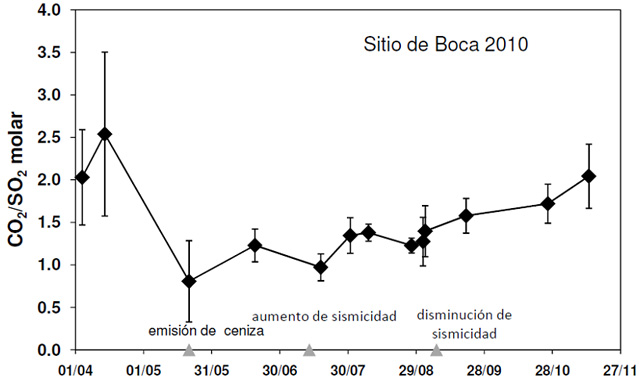
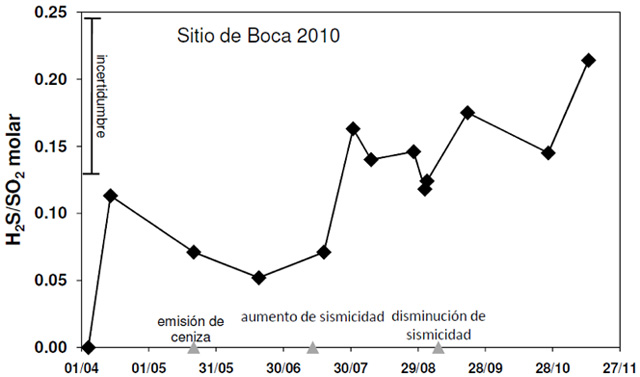
During 1 April 2013 to 27 November 2013, the ground-based differential optical absorption spectroscopy (DOAS) stations near Turrialbal recorded fluxes generally between 500-1,000 metric tons/day. Based on the DOAS observations, OVSICORI-UNA plotted the CO2 / SO2 molar ratio. After an explosion on 21 May 2013, the observatory found this ratio generally increased progressively in available data during the nearly six months that followed (figure 37). In a similar manner, the H2S / SO2 molar ratio also showed a tendancy towards progressive increase in available data (figure 38).
2013 events and monitoring. According to OVSICORI-UNA, the year 2013 began with low seismic activity (shallow hybrid earthquakes) and weak gas emissions similar to those in 2012. In March and April 2013, volcano-tectonic earthquakes originating more than 5 km below the summit began to occur, along with the first tornillo earthquakes of the year. (Tornillo-type earthquakes are long period with wave forms that, at or near the start, contain higher amplitude signals that gradually decrease with time. Their shape on seismograms resembles a woodscrew.) The number of volcanic earthquakes increased from 10/day on 18 April to more than 500/day on 13 July. This high level persisted until the end of August 2013.
On 20 May 2013, increased gas emissions produced a sky-blue plume visible from nearby areas. At 0452 on 21 May, the number of hybrid earthquakes became numerous. Continuous harmonic tremor increased at 0720. At 0830 and after 1100, explosions from both Boca 2010 and Boca 2012 vents generated ash plumes that rose more than 500 m (figure 39). Ashfall was reported in nearby communities to the N, W, and WSW. At noon on 21 May 2013, ash emissions ceased and seismicity decreased. Seismic activity declined sharply after the 21 May explosions, as did the CO2 /SO2 ratio, as measured in situ by a portable Multigas station. As previously noted (figures 37 and 38), for plotted measurements, the CO2/SO2 and H2S/SO2 ratios tended to progressively rise during the months that followed.
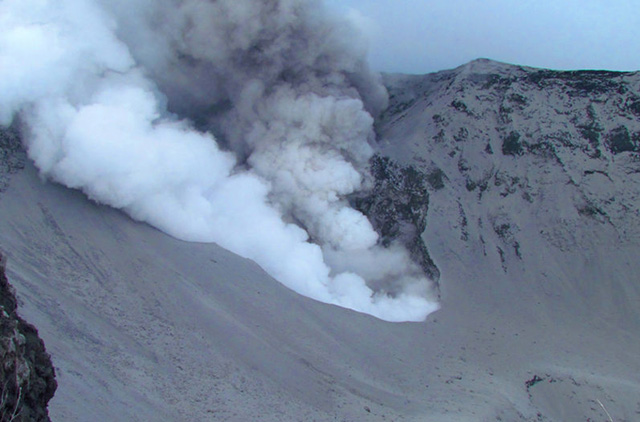
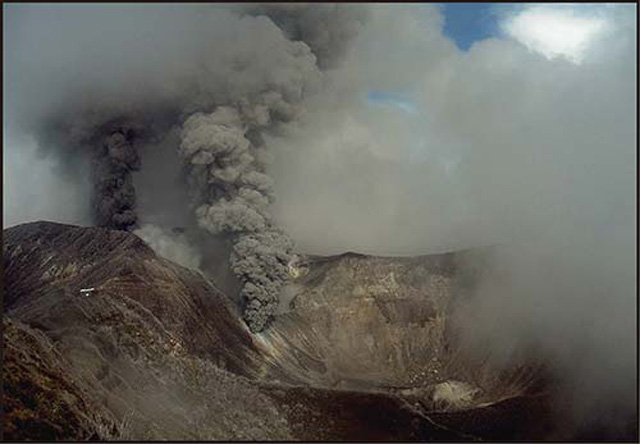 |
Figure 39. Gas explosions on 21 May 2013 at Boca 2010 and Boca 2012 on Turriabla's W crater. Photo taken by the webcam OVSICORI-UNA-A. Courtesy of OVSICORI-UNA. |
OVSICORI-UNA reported that a pilot flying past Turrialba about 40 km away observed a blackish plume on 29 May 2013. Officials from the Parque Nacional Volcán Turrialba observed a gas plume that was slightly darker than usual between 0730 and 0745; however, seismic records showed no abnormal activity at those times or seismic data signifying the discharge of a plume during the previous 48 hours. In addition, web camera images lacked evidence of ash emissions since 23 May. Gas plumes with temperatures more than 750°C were emitted from the two vents. The plume from Boca 2010 was whiter than the plume emitted from Boca 2012.
On 4 June 2013, light ashfall was reported in Pacayas (about 13 km W) and San Pablo in Oreamuno de Cartago (25 km SW). An observer in the previously closed National Park engulfing Turrialba noted that gas emissions that day were slightly stronger and more grayish than usual.
According to OVSICORI-UNA, seismic activity increased significantly again on 13 July 2013 with low-frequency signals (figure 40). On that day, the number of seismic events increased to more than 500/day. Seismicity remained at this level until late August when it decreased. During this period the gas temperature from Boca 2012 decreased from ~800°C to ~600°C. During 18-19 July, low-frequency tremor was detected. No morphological changes at the surface were observed.
Volcanic earthquakes with very long periods ceased in November 2013. Tornillos also became less frequent.
2014. The 29 October magmatic eruption discussed below culminated years of high gas emissions at Turrialba. The eruption was sudden and impulsive, termed an explosion by OVSICORI-UNA, but was led by ongoing ash-bearing emission and a clear multihour escalation in tremor. No human injuries were reported. Costa Rica has bolstered its hazard infrastructure in recent years. According to GFDRR (2012) the legislation called the "Emergencies and Risk Prevention Law (No. 8488) requires Government agencies and municipalities to allocate resources for disaster risk reduction activities in their programs and budgets. Presidential Decree (No.36721-MP-PLAN) enhanced the risk management competencies of the CNE [the National Risk Prevention and Emergencies Management Commission] and provides a model to assess vulnerability (compulsory in governmental planning processes)."
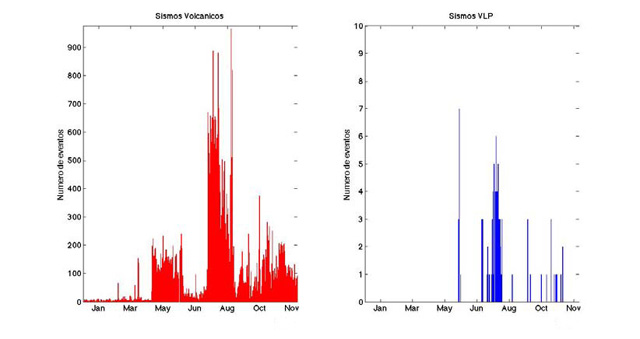
During January-September 2014, the number of volcanic earthquakes often remained relatively low (under 100, figure 41, left plot). Occasionally the number approached 200. The low seismicity was broadly similar to that in the last half of 2013; the majority of earthquakes were of low magnitude, including those of tornillo, volcanic-tectonic, and hybrid affinities. During January-September 2014, volcano-tectonic (VT) seismicity was generally stable (at 3 or fewer events per day)(figure 41, right plot).
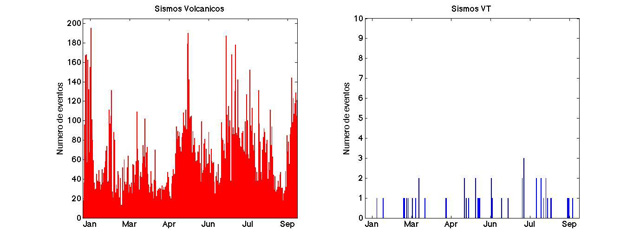 |
Figure 41. The number of daily seismic events at Turrialba during 1 January 2014-30 September 2014. Courtesy of OVSICORI-UNA. |
On 28 July 2014, a swarm of small, low-amplitude, short-duration, and high-frequency events lasted two hours. OVSICORI-UNA attributed the swarm to movement of fluids through cracks.
Conde and others (2014a) published an article about volcanic SO2 and CO2 fluxes at Turrialba during early 2013. They discussed SO2 and CO2 measurement methodologies used at Turrialba and Telica. OVSICORI-UNA reports during January-March 2014 noted the development of significantly more accurate, continuous ground-based SO2 monitoring. In addition, OVSICORI-UNA acquired and used an additional instrument, a Flyspec (a mini-spectrometer to measure SO2 levels). According to the OVSICORI-UNA September 2014 monthly report, SO2 fluxes in 2014 through September ranged from 400 to 1,500 metric tons/day, well below the maximum ~3,500 t/d they recorded during several days in June-August 2009 (Conde and others, 2014b).
In addition, reported CO2/SO2 ratios were ~8 in May, 2-4 in June, and ~2.5 in July 2014. H2S/SO2 molar ratios were ~1.2 in May and 0.2-0.7 in June 2014. Several authors in the two cited articles by Conde and others are affiliated with the NOVAC project (Network for Observation of Volcanic and Atmospheric Change). According to its website, the main objective of NOVAC is to establish a network for the measurements of volcanic gas and aerosol emissions--in particular SO2 and BrO--and to use the data from this network for risk assessment and volcanological research, both locally and on a regional and global scale. OVSICORI-UNA is part of the NOVAC consortium.
The temperatures at the W crater vents during January-July 2014 were about 600°C or lower, similar to the values of the previous six months as measured 15-20 m from the vents. In August and September, temperatures rose slightly to ~650°C; the composition of the gases were stable and interpreted as primarily magmatic.
Deformation in the August and September 2014 OVSICORI-UNA reports was determined by using interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR), Global Position System (GPS), and electronic distance meter (EDM) surveys. According to the August 2014 report, the InSAR and EDM measurements showed, in the 2013-2014 time interval, a relative contraction of several centimeters around the E and W craters. The September 2014 OVSICORI-UNA reported that a GPS survey on a 4-point transect from the base of the volcano to the summit yielded preliminary results indicating that one of the stations (VTQU, on the S flank) had sunk 2-3 cm/year since 2011. The September 2014 report did not report deformation at other stations.
According to OVSICORI-UNA, seismic activity, which had been low earlier in the year, began to increase in late September 2014. In mid-October instruments recorded a three-day swarm of volcano-tectonic earthquakes. The largest event, M 2.8, occurred at 2035 on 16 October at a depth of 5 km beneath the active crater. SO2 flux remained low to moderate ranging between 400 and 1,500 metric tons per day during through October 2014. Magmatic influenced degassing intensified during 28-29 October; the SO2 flux was ~2,000 t/d, higher than the 1,300 t/d average measured in September 2014 and the highest to date during 2014. (Recalling the previously mentioned interval 1 April-27 November 2013, the recorded fluxes also stood lower, generally in the range 500-1,000 tons/day).
The 30 October report by OVSICORI-UNA, which contains informative graphics omitted here, including photos of the plume, tephra deposited on a car, seismic instrument records and spectral information, a helicorder record for a 24-hour interval bracketing the explosion). OVSICORI-UNA described the eruption on the 29th as a moderate eruption of ash between 2310 and 2335 (25 munutes).
According to that report, tremor began at 0600 on the 29th and continued unbroken into at least early the next day. The tremor and the associated RSAM escalation was sufficiently ominous as to lead OVSICORI to notify locals of the situation (including the CNE, the National Park, as well as a nearby lodge. The same OVSICORI-UNA report added that at unstated time during this episode the lodge's chief Tony Lachner noted the plume was darker than usual, contained a yellowish tinge, and was judged to contain ash. At 1700, OVSICORI-UNA again informed local authorities on the situation. The tremor had increased in amplitude and continuity (duration) during the afternoon. Tremor became strongest around 2310-2320 on the 29th coincident with the strong explosion then. The same report noted that OVSICORI-UNA had alerted aviation authorities of the explosion around midnight.
The explosion, heard by local residents, also left a clear record on instruments in the region including those at Poas and Irazu. The explosion ended what started as an initially small eruption from the West Crater that lasted about 25 minutes. The explosion was heard by nearby villagers. An ash cloud rose to an altitude of 5.8 km and drifted WSW. Ash fell on numerous nearby communities, including parts of the capital of San José (whose outskirts are ~30 km W) and Heredia (centered less than 40 km WNW of the volcano). In more detail, settlements noted by OVSICORI-UNA included San Gerardo de Irazú, San Ramón de Tres Ríos, Coronado, Moravia, Curridabat, Desamparados, Aserrí, Escazú, Santa Ana, Belén, Guácima de Alajuela, Río Segundo de Alajuela, San Pedro Montes de Oca, Guadalupe, areas of Heredia, and the capital of San José (population ~350,000, with central downtown located~ 70 km SW of Turrialbla).
The explosion on the 29th destroyed the wall between the West and Central craters, depositing material around the Central Crater and partially burying it. According to a news report (Agence France-Presse), Turrialba National Park remained closed, and eleven people from Santa Cruz de Turrialba were evacuated to shelters. Some schools were also temporarily closed, affecting over 300 area students. OVSICORI-UNA literature (including the 30 October report discussed above) noted that magma had not previously reached the surface at Turrialba since an eruption in 1866 (~150 years ago).
The magmatic eruption continued during 30-31 October (figure 42) with growing magmatic components seen in samples. Analyses of tephra showed that the proportion of juvenile material increased during 30 and 31 October, respectively, rising from the range of 3-5% by volume to the range of 7-10% by volume. A 30 October OVSICORI-UNA report noted that the ash dispersion modeling assumed a plume height of 1.5 km, consistent with a photo they showed (time unstated), which showed much of the plume remaining comparatively low in the area of view near the volcano. According to the Washington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), the 30-31 October eruption produced a continuous emission of gas and light ash with an occasional burst of heavier ash, generally moving W and SW.
In their 7 November 2014 report, OVSICORI-UNA discussed how named staff collected and ran tests on leachate acidity for material deposited in the explosions during 29-31 October. Leachate reached pH 3.3 (highly acidic). In contrast, ash erupted during 4-5 January 2010 yielded leachate with pH 6.7-7.1 (near neutral). The 2014 report cautioned that such values were of considerable concern to human health, to environmental impacts (native vegetation, aquatic species, etc.), to cultivated plants, and to the well being of livestock and farm animals. The authors attributed the low pH values to the magmatic nature of the eruption and to absorption of those gases on the ash particle surfaces.
An explosion at 0520 on 1 November 2014 generated an ash plume that drifted toward the E and N parts of the Central Valley. A 3 November report stated that during the previous 24 hours seismicity had decreased significantly and no explosions had been detected; seismicity remained elevated. An phone and online (Facebook) public survey allowed residents to record if they had observed ashfall in their localities during the eruptive interval. Responses depicted a W-directed dispersal pattern that covered much of the urban area around San Jose.
OVSICORI-UNA reported a seismic signal indicating a strong emission lasting 50 minutes that started at 2320 on 6 November. The same 7 November report noted that in broad terms seismicity had decreased overall during the previous few days.
An ash-bearing explosion from Turrialba started at 1926 on 13 November and lasted about 10 minutes. Another explosion occurred at 1342 on 14 November and lasted about 15 minutes, although the strongest part was 7-minutes long. The OVSICORI-UNA report issued at 1635 on the 14th emphasized the associated explosive signal of these two emissions in terms of seismicity, for example, noting the dominant frequencies for the respective events were centered at 6.8 and 4.0 Hz. The report also said that of National Park officials reported ashfall at the top of Irazú. Volcanologists observed the 14 November explosion and collected samples at Hacienda La Central, 3 km SE of West Crater.
According to news reports (The Tico Times and crhoy.com), OVSICORI-UNA reported a strong gas emission on 13 November, accompanied by a massive outpouring of ash. A pilot reported ash plume S of the volcano at an altitude of 3.7-4.3 km.
According to OVSICORI-UNA, a strong Strombolian explosion occurred at 2128 on 8 December 2014, considered by them as one of the large explosions in the series that started with the magmatic eruption on 29 October 2014. The explosion lasted about ten minutes and had no precursory activity. The main pulse of ash emissions took place in under 100 seconds. Ashfall, 1 cm thick, and ballistics up to ~5 kg were deposited as far as 300 m W. Ashfall of 0.01 to 2 cm thickness was reported in the Central Valley and in towns to the W and SW, with 23 reports from citizens consistent with ash at distances of 45-80 km from the source. The report also noted constant inflation at Turriabla, ~10-15 mm annually, since the year 2010.
Citizen input to acquire ash thickness data. The Turriabla reporting took advantage of an OVSICORI questionare (Encuesta Alcance de Cenizas, V. Turrialba) to engage citizen observations on ash deposition. The online questionnaire (find link in "Information Contacts" section below) features a scalable map that features a positionable icon to show the location of ash-thickness observation. This position then automatically computes the resulting coordinates (latitude and longitude). The questionare includes several other questions relating to thickness, date and time of observation, rainfall, and weather conditions (which can perturb the original thickness). Entering contact information is optional.
References. Conde V., Robidoux, P., Avard, G., Galle, B. Aiuppa, A.,? Muñoz, A., and Giudice, G., 2014a, Measurements of volcanic SO2 and CO2 fluxes by combined DOAS, Multi.GAS and FTIR observations: a case study from Turrialba and Telica volcanoes, Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch), 103, pp. 2335-2347, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg. (Also Errata November 2014, 103 (8), p 2349.)
Conde, V., Bredemeyer, S., Duarte, E., Pacheco, J., Miranda, S., Galle, B., and Hansteen, T., 2014b, SO2 degassing from Turrialba Volcano linked to seismic signatures during the period 2008–2012, International Journal of Earth Sciences (Geol Rundsch) 103, pp. 1983–1998, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg.
GFDRR, 2012, Costa Rica Country Update – GFDRR, October 2012; Global Facility for Disaster Reduction and Recovery (GFDRR). (URL: http://www.gfdrr.org/sites/gfdrr.org/files/COSTA_RICA.pdf) (Accessed 12 July 2015).
Geological Summary. Turrialba, the easternmost of Costa Rica's Holocene volcanoes, is a large vegetated basaltic-to-dacitic stratovolcano located across a broad saddle NE of Irazú volcano overlooking the city of Cartago. The massive edifice covers an area of 500 km2. Three well-defined craters occur at the upper SW end of a broad 800 x 2200 m summit depression that is breached to the NE. Most activity originated from the summit vent complex, but two pyroclastic cones are located on the SW flank. Five major explosive eruptions have occurred during the past 3500 years. A series of explosive eruptions during the 19th century were sometimes accompanied by pyroclastic flows. Fumarolic activity continues at the central and SW summit craters.
Information Contacts: Observatorio Vulcanologico y Sismologico de Costa Rica-Universidad Nacional (OVSICORI-UNA) (URL: http://www.ovsicori.una.ac.cr/); Washington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), Satellite Analysis Branch (SAB), NOAA/NESDIS E/SP23, NOAA Science Center Room 401, 5200 Auth Rd, Camp Springs, MD 20746, USA (URL: http://www.ospo.noaa.gov/Products/atmosphere/vaac/); Network for Observation of Volcanic and Atmospheric Change (NOVAC) (URL: http://www.novac-project.eu/); The Tico Times (URL: http://www.ticotimes.net/); Agence France-Presse (URL: http://www.afp.com/); The Costa Rica Star (URL: http://news.co.cr/); and crhoy.com (URL: http://www.crhoy.com/).