Report on Kusatsu-Shiranesan (Japan) — April 1991
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 16, no. 4 (April 1991)
Managing Editor: Lindsay McClelland.
Kusatsu-Shiranesan (Japan) Continued seismicity
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 1991. Report on Kusatsu-Shiranesan (Japan) (McClelland, L., ed.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 16:4. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.BGVN199104-283120
Kusatsu-Shiranesan
Japan
36.618°N, 138.528°E; summit elev. 2165 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
In April, seismicity remained similar to previous months, with a total of 110 earthquakes and one tremor episode recorded... (figure 5). No surface activity was observed.
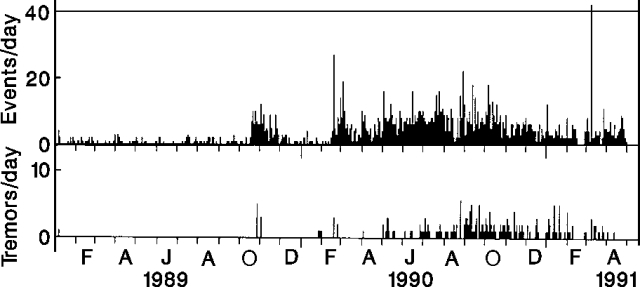 |
Figure 5. Daily number of recorded earthquakes (top) and tremor episodes (bottom) at Kusatsu-Shirane, January 1989-April 1991. Courtesy of JMA. |
Geological Summary. The Kusatsu-Shiranesan complex, located immediately north of Asama volcano, consists of a series of overlapping pyroclastic cones and three crater lakes. The andesitic-to-dacitic volcano was formed in three eruptive stages beginning in the early to mid-Pleistocene. The Pleistocene Oshi pyroclastic flow produced extensive welded tuffs and non-welded pumice that covers much of the E, S, and SW flanks. The latest eruptive stage began about 14,000 years ago. Historical eruptions have consisted of phreatic explosions from the acidic crater lakes or their margins. Fumaroles and hot springs that dot the flanks have strongly acidified many rivers draining from the volcano. The crater was the site of active sulfur mining for many years during the 19th and 20th centuries.
Information Contacts: JMA.

