Report on Arenal (Costa Rica) — July 1991
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 16, no. 7 (July 1991)
Managing Editor: Lindsay McClelland.
Arenal (Costa Rica) Increased Strombolian activity; seismicity
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 1991. Report on Arenal (Costa Rica) (McClelland, L., ed.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 16:7. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.BGVN199107-345033
Arenal
Costa Rica
10.463°N, 84.703°W; summit elev. 1670 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Strombolian activity, lava effusion, and seismicity all increased in July . . . . The number of volcanic earthquakes rose to a maximum of 59 recorded events/day on 11 July (figure 39). Seismometers recorded intermittent, vigorous tremor episodes, several hours long (6-hour average duration), especially at the beginning of the month.
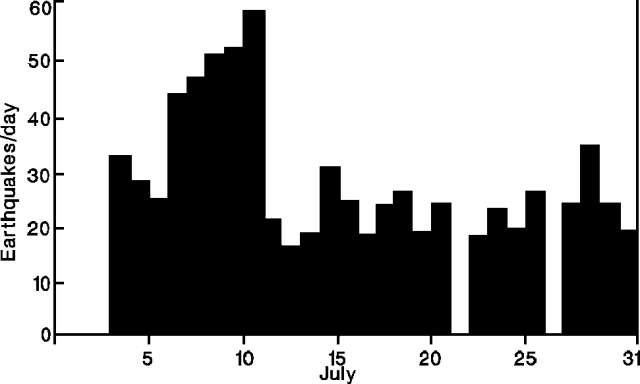 |
Figure 39. Daily number of earthquakes at Arenal, July 1991. Courtesy of the Instituto Costarricense de Electricidad. |
Geological Summary. Conical Volcán Arenal is the youngest stratovolcano in Costa Rica and one of its most active. The 1670-m-high andesitic volcano towers above the eastern shores of Lake Arenal, which has been enlarged by a hydroelectric project. Arenal lies along a volcanic chain that has migrated to the NW from the late-Pleistocene Los Perdidos lava domes through the Pleistocene-to-Holocene Chato volcano, which contains a 500-m-wide, lake-filled summit crater. The earliest known eruptions of Arenal took place about 7000 years ago, and it was active concurrently with Cerro Chato until the activity of Chato ended about 3500 years ago. Growth of Arenal has been characterized by periodic major explosive eruptions at several-hundred-year intervals and periods of lava effusion that armor the cone. An eruptive period that began with a major explosive eruption in 1968 ended in December 2010; continuous explosive activity accompanied by slow lava effusion and the occasional emission of pyroclastic flows characterized the eruption from vents at the summit and on the upper western flank.
Information Contacts: R. Barquero and Guillermo Alvarado, ICE.

