Report on Bezymianny (Russia) — January 1998
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 23, no. 1 (January 1998)
Managing Editor: Richard Wunderman.
Bezymianny (Russia) Small January steam plumes; correction to 5 December ash plume description
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 1998. Report on Bezymianny (Russia) (Wunderman, R., ed.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 23:1. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.BGVN199801-300250
Bezymianny
Russia
55.972°N, 160.595°E; summit elev. 2882 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
According to the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), activity decreased during January compared to December (BGVN 22:12). During all of January the level of concern was green. Except on many days of bad weather, when observation was impossible, small fumarolic plumes were observed. Typically, plumes rose to 50-100 m above the summit as did those observed on 24, 30, and 31 December, and on 11, 13, 15, 19, and 22 January. The plume of 30 December extended 3-5 km to the E and S. Plumes on 19 and 22 January extended 5 km SE. Observers noted a somewhat larger plume on 18 January, which rose to 300 m and extended 20 km from the summit.
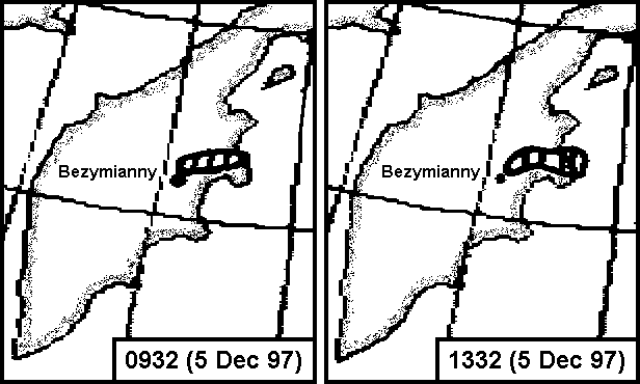
Correction: The ash plume from the eruption on 5 December 1997 was much smaller than previously indicated (BGVN 22:11). The figure in that report was described as showing the advance of an ash plume based on satellite imagery; what it really showed was a series of projected plume locations. The projections were issued in Alaska to provide aviators with an estimate of the plume's dispersal if the eruption continued.
The following gives a more accurate account of the plume during 5 December based on the relevant infrared satellite imagery described in volcanic ash advisories. For example, one 5 December advisory cited a GMS infrared image taken at 0932 showing a plume 55 km wide extending NE (figure 5). Another advisory at 1015 on 5 December reported an ash plume extending 15 km NE at an altitude of ~6 km. Satellite imagery at 1332 showed the plume rising to ~9-10 km; it was 63 km wide and extended 211 km E (figure 5). Pilot reports later in the day placed the ash plume at altitudes of ~12-13 km. Other volcanic ash advisories continued to warn aviators about the ash plume during 6-7 December.
The time conversion to Kamchatkan Standard Time was also misstated; it should be GMT + 12 hours. Our thanks to Nick Heffter (NOAA Air Resources Laboratory) and the NOAA Satellite Analysis Branch for assisting in this correction.
Geological Summary. The modern Bezymianny, much smaller than its massive neighbors Kamen and Kliuchevskoi on the Kamchatka Peninsula, was formed about 4,700 years ago over a late-Pleistocene lava-dome complex and an edifice built about 11,000-7,000 years ago. Three periods of intensified activity have occurred during the past 3,000 years. The latest period, which was preceded by a 1,000-year quiescence, began with the dramatic 1955-56 eruption. This eruption, similar to that of St. Helens in 1980, produced a large open crater that was formed by collapse of the summit and an associated lateral blast. Subsequent episodic but ongoing lava-dome growth, accompanied by intermittent explosive activity and pyroclastic flows, has largely filled the 1956 crater.
Information Contacts: Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA; NOAA/NESDIS Satellite Analysis Branch (SAB), Room 401, 5200 Auth Road, Camp Springs, MD 20746, USA.