Report on Ebeko (Russia) — June 2020
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 45, no. 6 (June 2020)
Managing Editor: Edward Venzke.
Research and preparation by Paul Berger.
Ebeko (Russia) Frequent moderate explosions, ash plumes, and ashfall continue, December 2019-May 2020
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 2020. Report on Ebeko (Russia) (Venzke, E., ed.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 45:6. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.BGVN202006-290380
Ebeko
Russia
50.686°N, 156.014°E; summit elev. 1103 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
The current moderate explosive eruption of Ebeko has been ongoing since October 2016, with frequent ash explosions that have reached altitudes of 1.3-6 km (BGVN 42:08, 43:03, 43:06, 43:12, 44:12). Ashfall is common in Severo-Kurilsk, a town of about 2,500 residents 7 km ESE, where the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT) monitor the volcano. During the reporting period, December 2019-May 2020, the Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
During December 2019-May 2020, frequent explosions generated ash plumes that reached altitudes of 1.5-4.6 km (table 9); reports of ashfall in Severo-Kurilsk were common. Ash explosions in late April caused ashfall in Severo-Kurilsk during 25-30 April (figure 24), and the plume drifted 180 km SE on the 29th. There was also a higher level of activity during the second half of May (figure 25), when plumes drifted up to 80 km downwind.
Table 9. Summary of activity at Ebeko, December 2019-May 2020. S-K is Severo-Kurilsk (7 km ESE of the volcano). TA is thermal anomaly in satellite images. In the plume distance column, only plumes that drifted more than 10 km are indicated. Dates based on UTC times. Data courtesy of KVERT.
| Date | Plume Altitude (km) | Plume Distance | Plume Directions | Other Observations |
| 30 Nov-05 Dec 2019 | 3 | -- | NE, E | Intermittent explosions. |
| 06-13 Dec 2019 | 4 | -- | E | Explosions all week. Ashfall in S-K on 10-12 Dec. |
| 15-17 Dec 2019 | 3 | -- | E | Explosions. Ashfall in S-K on 16-17 Dec. |
| 22-24 Dec 2019 | 3 | -- | NE | Explosions. |
| 01-02 Jan 2020 | 3 | 30 km N | N | Explosions. TA over dome on 1 Jan. |
| 03, 05, 09 Jan 2020 | 2.9 | -- | NE, SE | Explosions. Ashfall in S-K on 8 Jan. |
| 11, 13-14 Jan 2020 | 3 | -- | E | Explosions. Ashfall in S-K. |
| 19-20 Jan 2020 | 3 | -- | E | Ashfall in S-K on 19 Jan. |
| 24-31 Jan 2020 | 4 | -- | E | Explosions. |
| 01-07 Feb 2020 | 3 | -- | E, S | Explosions all week. |
| 12-13 Feb 2020 | 1.5 | -- | E | Explosions. Ashfall in S-K. |
| 18-19 Feb 2020 | 2.3 | -- | SE | Explosions. |
| 21, 25, 27 Feb 2020 | 2.9 | -- | S, SE, NE | Explosions. Ashfall in S-K on 22 Feb. |
| 01-02, 05 Mar 2020 | 2 | -- | S, E | Explosions. |
| 08 Mar 2020 | 2.5 | -- | NE | Explosions. |
| 13, 17 Mar 2020 | 2.5 | -- | NE, SE | Bursts of gas, steam, and small amount of ash. |
| 24-25 Mar 2020 | 2.5 | -- | NE, W | Explosions. |
| 29 Mar-02 Apr 2020 | 2.2 | -- | NE, E | Explosions. Ashfall in S-K on 1 Apr. TA on 30-31 Mar. |
| 04-05, 09 Apr 2020 | 1.5 | -- | NE | Explosions. TA on 5 Apr. |
| 13 Apr 2020 | 2.5 | -- | SE | Explosions. |
| 18, 20 Apr 2020 | -- | -- | -- | TA on 18, 20 Apr. |
| 24 Apr-01 May 2020 | 3.5 | 180 km SE on 29 Apr | E, SE | Explosions all week. Ashfall in S-K on 25-30 Apr. |
| 01-08 May 2020 | 2.6 | -- | E | Explosions all week. Ashfall in S-K on 3-5 May. TA on 3 May. |
| 08-15 May 2020 | 4 | -- | E | Explosions. Ashfall in S-K on 8-12 May. TA during 12-14 May. |
| 14-15, 19-21 May 2020 | 3.6 | 80 km SW, S, SE during 14, 20-21 May | -- | Explosions. TA on same days. |
| 22-29 May 2020 | 4.6 | 60 km SE | E, SE | Explosions all week. Ashfall in S-K on 22, 24 May. |
| 29-31 May 2020 | 4.5 | -- | E, S | Explosions. TA on 30 May. |
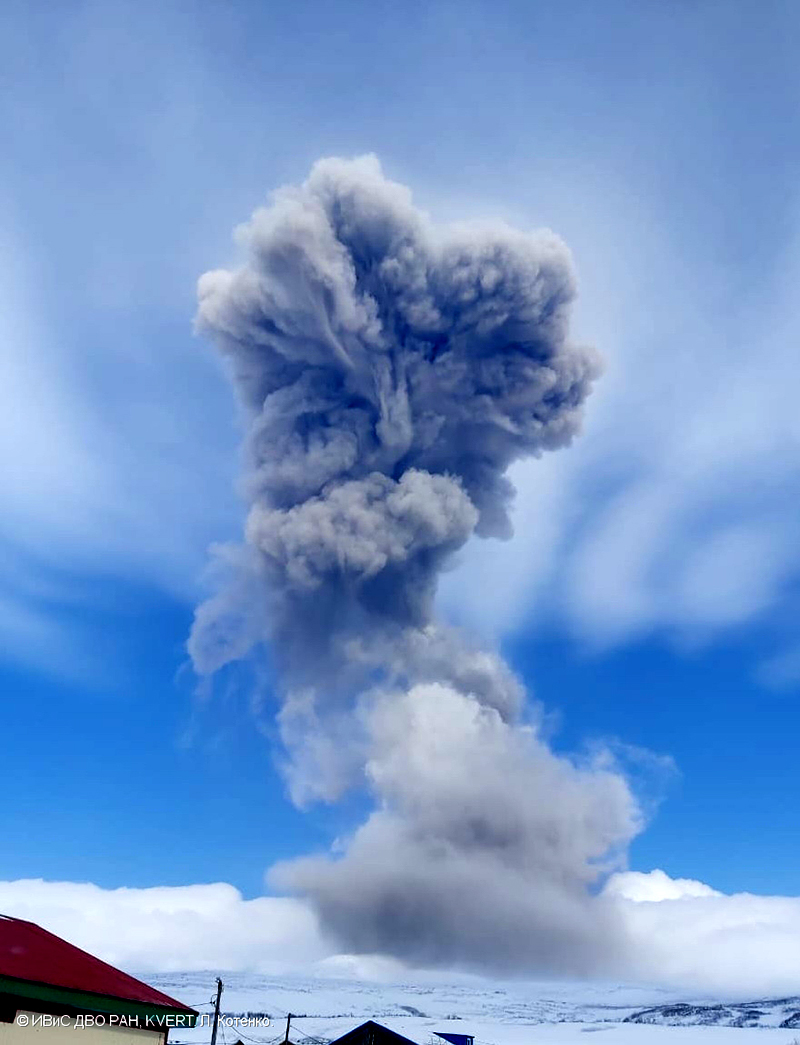 |
Figure 24. Photo of ash explosion at Ebeko at 2110 UTC on 28 April 2020, as viewed from Severo-Kurilsk. Courtesy of KVERT (L. Kotenko). |
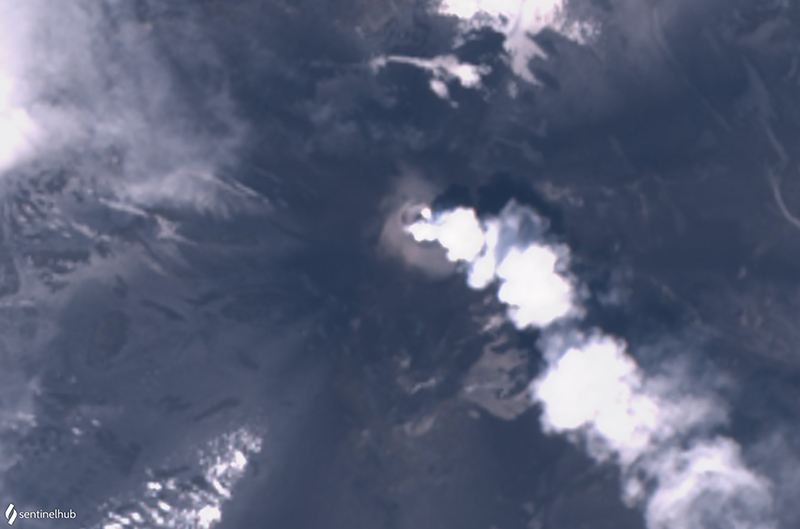 |
Figure 25. Satellite image of Ebeko from Sentinel-2 on 27 May 2020, showing a plume drifting SE. Image using natural color rendering (bands 4, 3, 2) courtesy of Sentinel Hub Playground. |
Geological Summary. The flat-topped summit of the central cone of Ebeko volcano, one of the most active in the Kuril Islands, occupies the northern end of Paramushir Island. Three summit craters located along a SSW-NNE line form Ebeko volcano proper, at the northern end of a complex of five volcanic cones. Blocky lava flows extend west from Ebeko and SE from the neighboring Nezametnyi cone. The eastern part of the southern crater contains strong solfataras and a large boiling spring. The central crater is filled by a lake about 20 m deep whose shores are lined with steaming solfataras; the northern crater lies across a narrow, low barrier from the central crater and contains a small, cold crescentic lake. Historical activity, recorded since the late-18th century, has been restricted to small-to-moderate explosive eruptions from the summit craters. Intense fumarolic activity occurs in the summit craters, on the outer flanks of the cone, and in lateral explosion craters.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS), 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/eng/); Sentinel Hub Playground (URL: https://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/sentinel-playground).

