Report on Turrialba (Costa Rica) — September 2020
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 45, no. 9 (September 2020)
Managing Editor: Edward Venzke.
Edited by Kadie L. Bennis.
Turrialba (Costa Rica) New eruptive period on 18 June 2020 consisted of ash eruptions
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 2020. Report on Turrialba (Costa Rica) (Bennis, K.L., and Venzke, E., eds.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 45:9. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.BGVN202009-345070
Turrialba
Costa Rica
10.025°N, 83.767°W; summit elev. 3340 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Turrialba is a stratovolcano located in Costa Rica that overlooks the city of Cartago. Three well-defined craters occur at the upper SW end of a broad 800 x 2,200 m summit depression that is breached to the NE. Activity described in the previous report primarily included weak ash explosions and minor ash emissions (BGVN 44:11). This reporting period updates information from November 2019-August 2020; volcanism dominantly consists of ash emissions during June-August, based on information from daily and weekly reports by the Observatorio Vulcanologico Sismologica de Costa Rica-Universidad Nacional (OVSICORI-UNA) and satellite data.
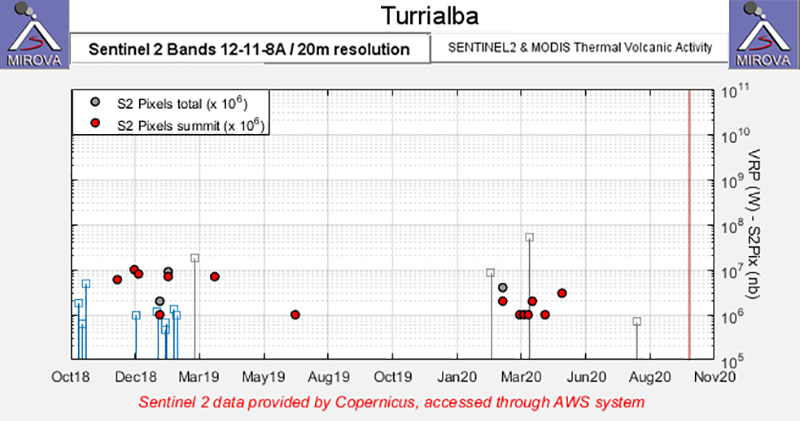
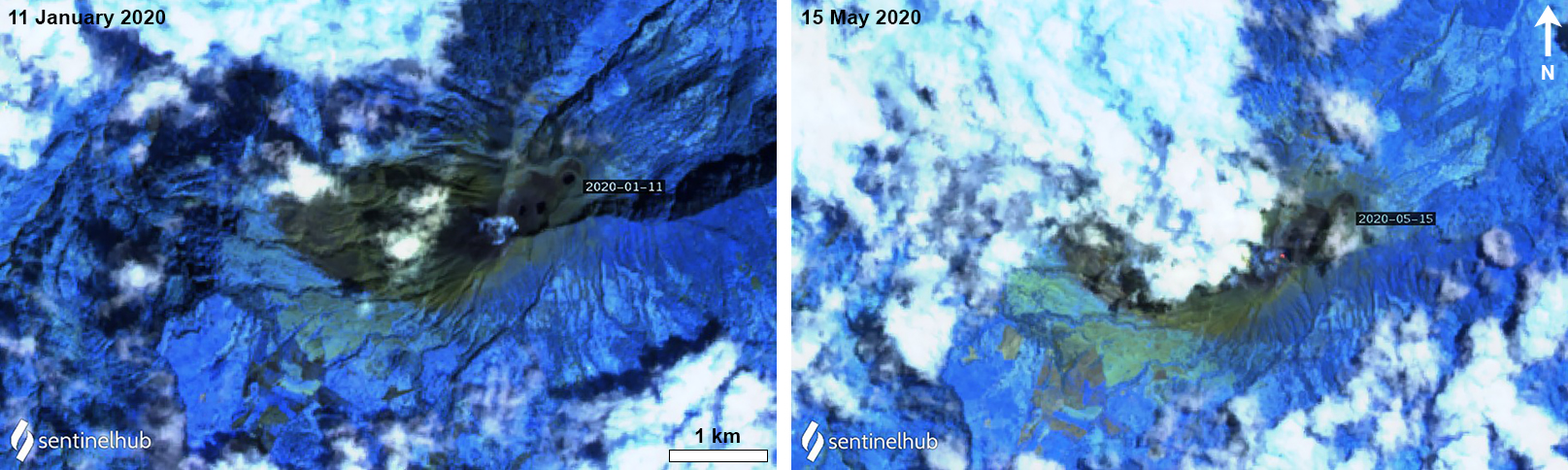
Volcanism during November 2019 through mid-June was relatively low, dominated by low SO2 emissions (100-300 tons/day) and typical low seismic tremors. A single explosion was recorded at 1850 on 7 December 2019, and two gas-and-steam plumes rose 800 m and 300 m above the crater on 25 and 27 December, respectively. An explosion was detected on 29 January 2020 but did not result in any ejecta. An overflight during the week of 10 February measured the depth of the crater (140 m); since the previous measurements made in February 2019 (220 m), the crater has filled with 80 m of debris due to frequent collapses of the NW and SE internal crater walls. Beginning around February and into at least early May 2020 the Sentinel-2 MODIS Thermal Volcanic Activity graph provided by the MIROVA system detected a small cluster of thermal anomalies (figure 52). Some of these anomalies were faintly registered in Sentinel-2 thermal satellite imagery during 10 and 25 April, with a more distinct anomaly occurring on 15 May (figure 53).
On 18 June activity increased, which marked the start of a new eruptive period that produced ash emissions rising 100 m above the crater rim at 1714, 1723, and 1818. The next morning, 19 June, two more events at 1023 and 1039 resulted in ash emissions rising 100 m above the crater. During 23-26 June small ash emissions continued to occur each day, rising no higher than 100 m above the crater. A series of small ash eruptions that rose 100 m above the crater occurred during 28 and 29 June; four events were recorded at 0821, 1348, 1739, and 2303 on 28 June and five more were recorded at 0107, 0232, 0306, 0412, and 0818 on 29 June. The two events at 0107 and 0412 were accompanied by ballistics ejected onto the N wall of the crater, according to OVSICORI-UNA.
Almost daily ash emissions continued during 1-7 July, rising less than 100 m above the crater; no ash emissions were observed on 3 July. On 6 July, gas-and-steam and ash emissions rose hundreds of meters above the crater at 0900, resulting in local ashfall. Passive gas-and-steam emissions with minor amounts of ash were occasionally visible during 9-10 July. On 14 July an eruptive pulse was observed, generating brief incandescence at 2328, which was likely associated with a small ash emission. Dilute ash emissions at 1028 on 16 July preceded an eruption at 1209 that resulted in an ash plume rising 200 m above the crater. Ash emissions of variable densities continued through 20 July rising as high as 200 m above the crater; on 20 July incandescence was observed on the W wall of the crater. An eruptive event at 0946 on 29 July produced an ash plume that rose 200-300 m above the crater rim. During 30-31 July a series of at least ten ash eruptions were detected, rising no higher than 200 m above the crater, each lasting less than ten minutes. Some incandescence was visible on the SW wall of the crater during this time.
On 1 August at 0746 an ash plume rose 500 m above the crater. During 4-5 August a total of 19 minor ash emissions occurred, accompanied by ash plumes that rose no higher than 200 m above the crater. OVSICORI-UNA reported on 21 August that the SW wall of the crater had fractured; some incandescence in the fracture zone had been observed the previous month. Two final eruptions were detected on 22 and 24 August at 1253 and 2023, respectively. The eruption on 24 August resulted in an ash plume that rose to a maximum height of 1 km above the crater.
Geological Summary. Turrialba, the easternmost of Costa Rica's Holocene volcanoes, is a large vegetated basaltic-to-dacitic stratovolcano located across a broad saddle NE of Irazú volcano overlooking the city of Cartago. The massive edifice covers an area of 500 km2. Three well-defined craters occur at the upper SW end of a broad 800 x 2200 m summit depression that is breached to the NE. Most activity originated from the summit vent complex, but two pyroclastic cones are located on the SW flank. Five major explosive eruptions have occurred during the past 3500 years. A series of explosive eruptions during the 19th century were sometimes accompanied by pyroclastic flows. Fumarolic activity continues at the central and SW summit craters.
Information Contacts: Observatorio Vulcanologico Sismologica de Costa Rica-Universidad Nacional (OVSICORI-UNA), Apartado 86-3000, Heredia, Costa Rica (URL: http://www.ovsicori.una.ac.cr/, https://www.facebook.com/OVSICORI/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Sentinel Hub Playground (URL: https://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/sentinel-playground).