Report on Kadovar (Papua New Guinea) — January 2021
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 46, no. 1 (January 2021)
Managing Editor: Edward Venzke.
Edited by Kadie L. Bennis.
Kadovar (Papua New Guinea) Occasional ash and gas-and-steam plumes along with summit thermal anomalies
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 2021. Report on Kadovar (Papua New Guinea) (Bennis, K.L., and Venzke, E., eds.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 46:1. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.BGVN202101-251002
Kadovar
Papua New Guinea
3.608°S, 144.588°E; summit elev. 365 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Kadovar is located in the Bismark Sea offshore from the mainland of Papua New Guinea about 25 km NNE from the mouth of the Sepik River. Its first confirmed eruption began in early January 2018, characterized by ash plumes and a lava extrusion that resulted in the evacuation of around 600 residents from the N side of the island (BGVN 43:03). Activity has recently consisted of intermittent ash plumes, gas-and-steam plumes, and thermal anomalies (BGVN 45:07). Similar activity continued during this reporting period of July-December 2020 using information from the Rabaul Volcano Observatory (RVO), the Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), and various satellite data.
RVO issued an information bulletin on 15 July reporting minor eruptive activity during 1-5 July with moderate light-gray ash emissions rising a few hundred meters above the Main Crater. On 5 July activity intensified; explosions recorded at 1652 and 1815 generated a dense dark gray ash plume that rose 1 km above the crater and drifted W. Activity subsided that day, though fluctuating summit crater incandescence was visible at night. Activity increased again during 8-10 July, characterized by explosions detected on 8 July at 2045, on 9 July at 1145 and 1400, and on 10 July at 0950 and 1125, each of which produced a dark gray ash plume that rose 1 km above the crater. According to Darwin VAAC advisories issued on 10, 16, and 30 July ash plumes were observed rising to 1.5-1.8 km altitude and drifting NW.
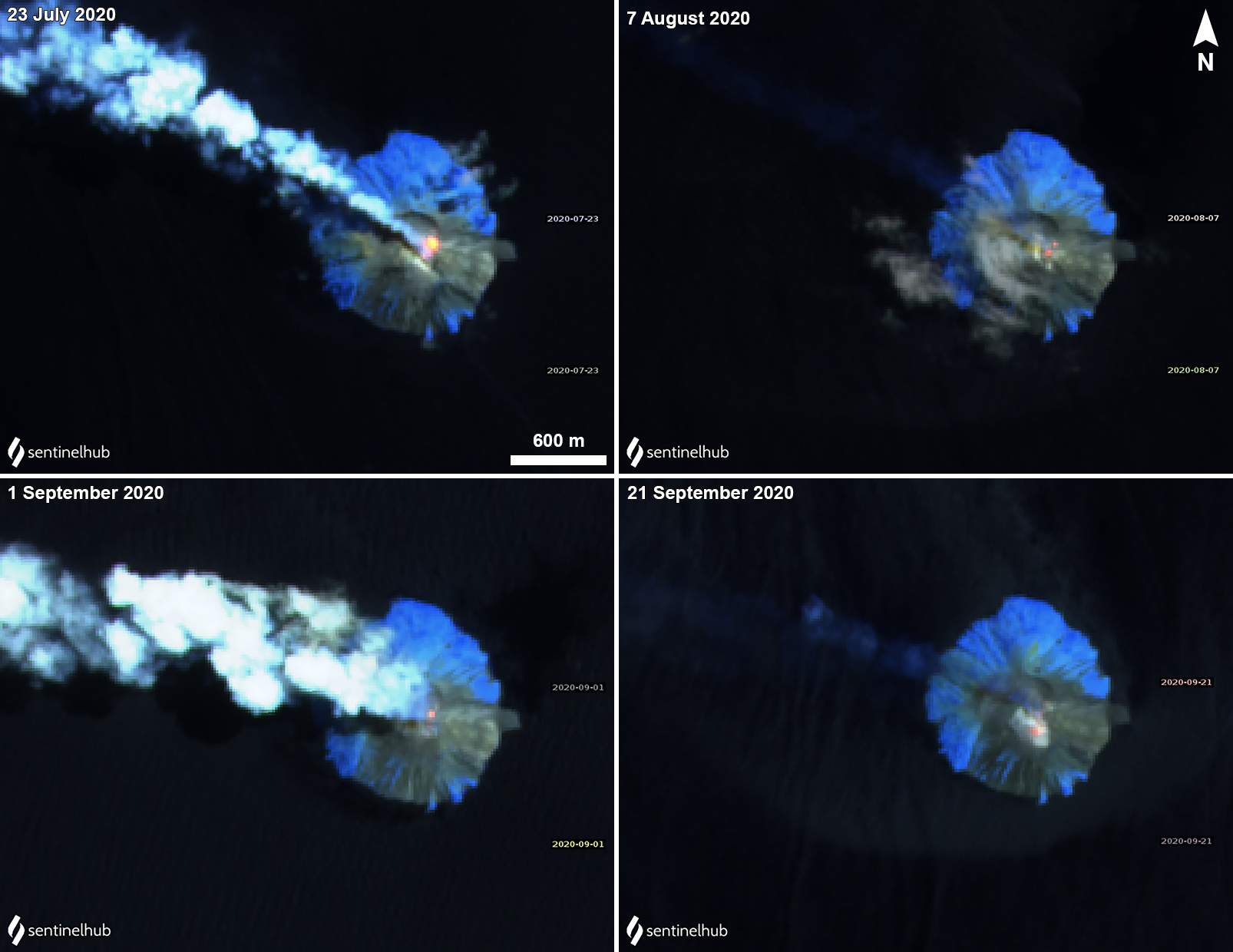
Gas-and-steam emissions and occasional ash plumes were observed in Sentinel-2 satellite imagery on clear weather days during August through December (figure 56). Ash plumes rose to 1.2 and 1.5 km altitude on 3 and 16 August, respectively, and drifted NW, according to Darwin VAAC advisories. On 26 August an ash plume rose to 2.1 km altitude and drifted WNW before dissipating within 1-2 hours. Similar activity was reported during September-November, according to several Darwin VAAC reports; ash plumes rose to 0.9-2.1 km altitude and drifted mainly NW. VAAC notices were issued on 12 and 22 September, 4, 7-8, and 18 October, and 18 November. A single MODVOLC alert was issued on 27 November.
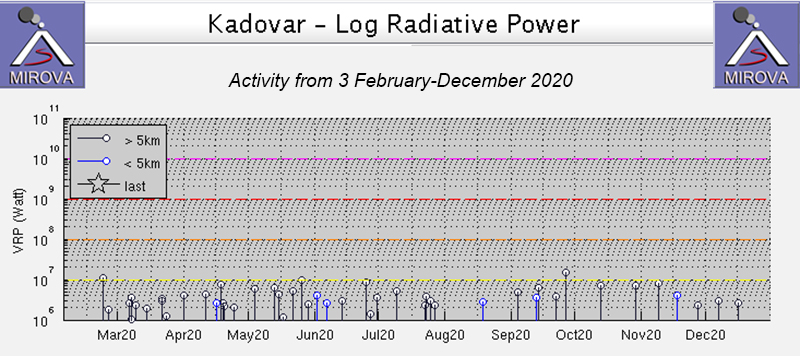
MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) analysis of MODIS satellite data shows intermittent low-power anomalies during July through December 2020 (figure 57). Some of this thermal activity in the summit crater was observed in Sentinel-2 thermal satellite imagery, accompanied by gas-and-steam emissions that drifted primarily NW (figure 58).
Geological Summary. The 2-km-wide island of Kadovar is the emergent summit of a Bismarck Sea stratovolcano of Holocene age. It is part of the Schouten Islands, and lies off the coast of New Guinea, about 25 km N of the mouth of the Sepik River. Prior to an eruption that began in 2018, a lava dome formed the high point of the andesitic volcano, filling an arcuate landslide scarp open to the south; submarine debris-avalanche deposits occur in that direction. Thick lava flows with columnar jointing forms low cliffs along the coast. The youthful island lacks fringing or offshore reefs. A period of heightened thermal phenomena took place in 1976. An eruption began in January 2018 that included lava effusion from vents at the summit and at the E coast.
Information Contacts: Rabaul Volcano Observatory (RVO), Geohazards Management Division, Department of Mineral Policy and Geohazards Management (DMPGM), PO Box 3386, Kokopo, East New Britain Province, Papua New Guinea; Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Bureau of Meteorology, Northern Territory Regional Office, PO Box 40050, Casuarina, NT 0811, Australia (URL: http://www.bom.gov.au/info/vaac/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Sentinel Hub Playground (URL: https://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/sentinel-playground).