Global Volcanism Program | Image GVP-08961
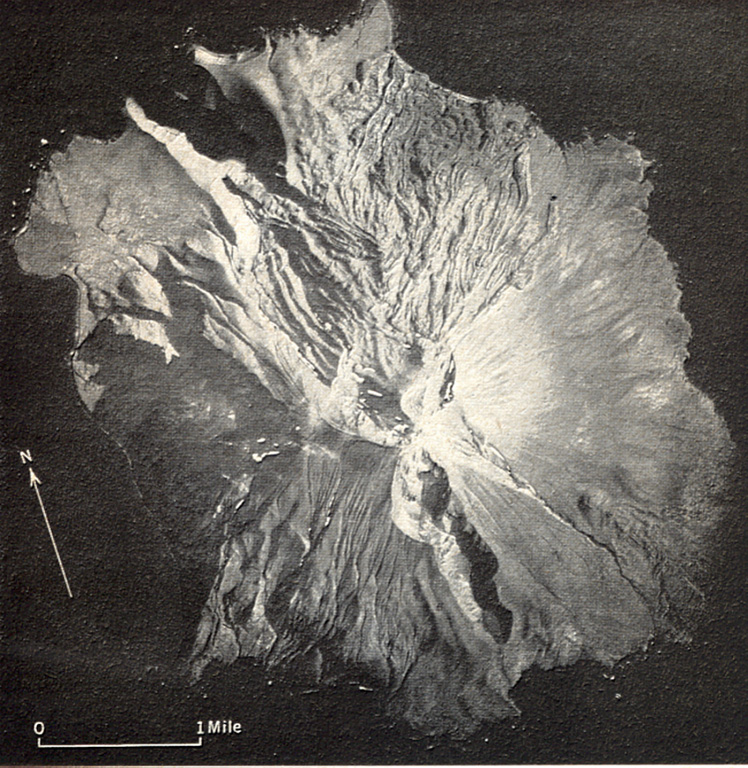
A prominent N-S-trending fissure that extends to sea level at both ends across Segula, located near the western end of the Aleutian Arc. The irregular topography on the N side of the island is an extensive lava field that erupted from the summit crater along the NE flank to the coast. A smaller lava field to the lower right originated from a scoria cone on the lower SE flank. A scoria cone constructed along the S rim of a small caldera forms the high point of the island.
Photo by U.S. Air Force (published in U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 1028-K).
![]() This image is made available as a Public Domain Work, but proper attribution is appreciated.
This image is made available as a Public Domain Work, but proper attribution is appreciated.
Keywords: stratovolcano | fissure | crater | erosion | lava flow

Segula
