Global Volcanism Program | Image GVP-09238
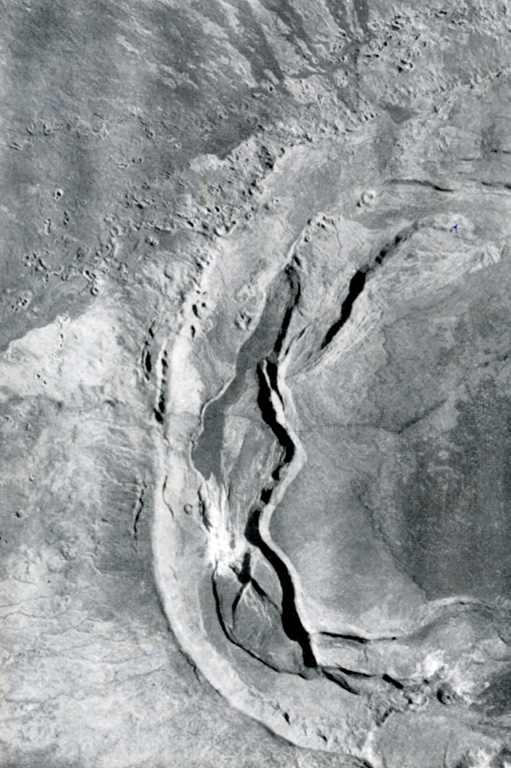
A dramatic sinuous N-S-trending ridge extends across the western side of the summit caldera of Sierra Negra volcano, forming the border of a graben lying between it and the caldera wall to the left. Volcán Azufre, the largest fumarolic area in the Galápagos Islands, is located in this part of the 7 x 10.5 km wide caldera. An arcuate line of small vents parallel to the caldera wall were produced by eruptions from circumferential fissures parallel to the caldera walls and fed lava flows that primarily traveled down the outer flanks of the volcano.
Photo by U.S. Air Force, 1946
![]() This image is made available as a Public Domain Work, but proper attribution is appreciated.
This image is made available as a Public Domain Work, but proper attribution is appreciated.

Sierra Negra
