Report on Colima (Mexico) — May 2001
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 26, no. 5 (May 2001)
Managing Editor: Richard Wunderman.
Colima (Mexico) Surficial fractures preceded a light-colored dome emplaced aseismically
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 2001. Report on Colima (Mexico) (Wunderman, R., ed.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 26:5. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.BGVN200105-341040
Colima
Mexico
19.514°N, 103.62°W; summit elev. 3850 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
This report describes two visits to the rim of Colima's main crater (17 March and 26 May 2001) and summarizes collateral data collected around that time. On the earlier visit, observers found an enlarged main crater, they noted the disappearance of an older (1994) crater, and they photographed a recent crater with a sulfur-encrusted, warped, and fractured floor. By the time of the later visit, an unusual new dome had appeared, composed of more fragmentary and lighter color clasts than typical for Colima's lava domes. Effusive activity was previously seen during November 1998-February 1999.
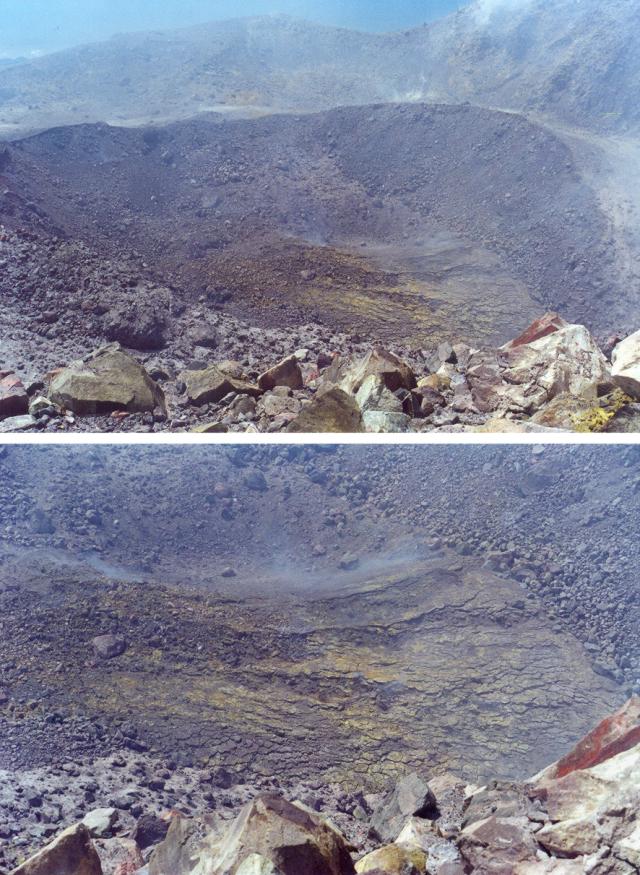
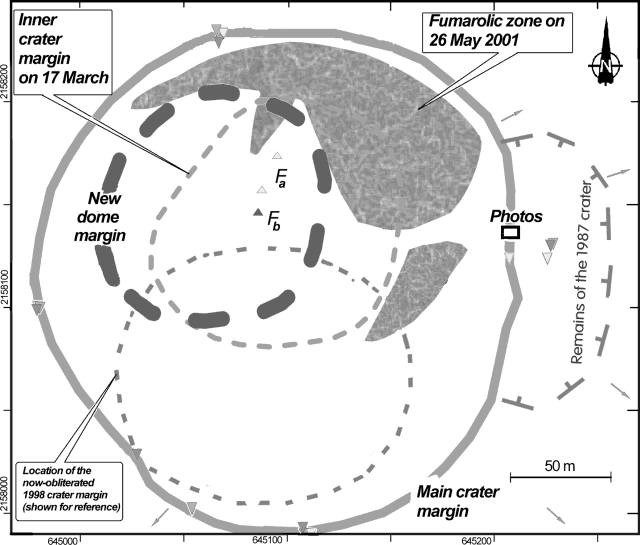
Crater rim observations. On 17 March 2001, Nick Varley and Juan Carlos Gavilanes ascended to Colima's crater rim (figures 40 and 41). It was the first visit there since January 1999. Circumnavigating the main crater, they prepared a map of the current crater and environs (figure 40). The main crater was 230-260 m in diameter, 15-40 m deep, and ~1.4 x 106 m3 in volume. Its diameter had grown two-fold larger than it was before the 1998-99 eruption, reaching its largest size since the early 1960s.
On their 17 March visit Varley and Gavilanes found a smaller crater located inside the main crater's N sector (figure 40). This inner crater was assumed to be formed by the 22 February 2001 explosion. The inner crater was then estimated to be 127 m in diameter, 15 m deep, and ~0.2 x 106 m3 in volume. In the NE sector of the inner crater they observed an inflated, buckled, and fractured surface (figure 41). They inferred that this inflated surface stemmed from an intrusion initiated sometime after the 22 February explosion.
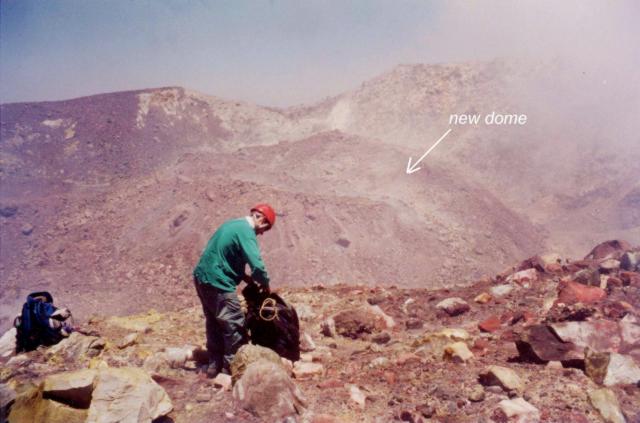
Figure 42 records the scene Varley and Gavilanes found when they ascended to the crater rim on 26 May 2001. Close to the inflated surface observed on 17 March they found a new lava dome. It stood ~115 m across its base, ~57 m across its top, ~30 m high, and was ~0.15 x 106 m3 in volume. The two observers also noted that in comparison to conditions witnessed during the previous crater ascent, new and stronger fumarolic zones surrounded the new dome, mainly to its N, NE, and E (figure 40).
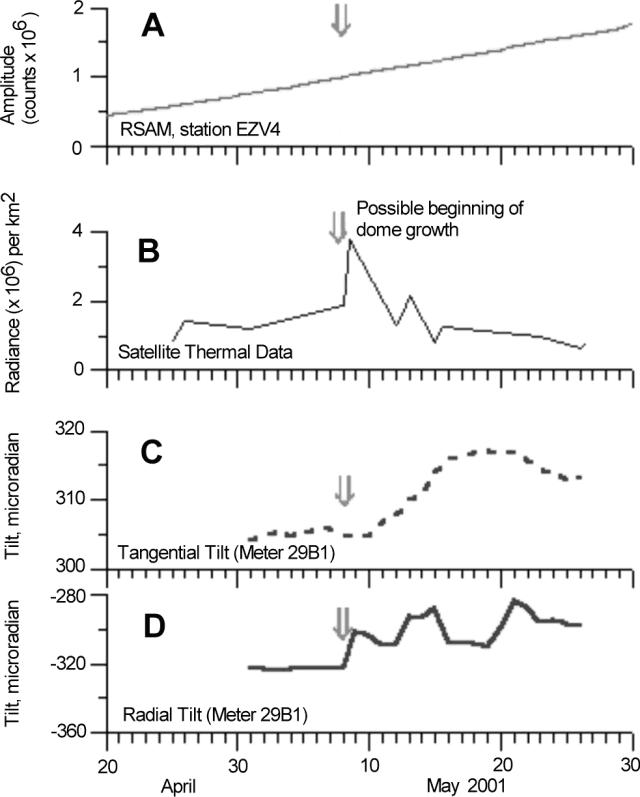
Collateral observations. Later review of seismic, deformation, and GOES radiation data (figure 43) showed that dome extrusion may have started on 8 May, a day with distinct increases in both thermal radiation and tilt. No increase in seismic activity was observed; the proposed explanation for this is that the lava was plastic enough to avoid the shear fracturing of surrounding structures. Assuming that the extrusion started on 8 May 2001, the resulting growth rate (for 8-26 May, 19 days) was ~0.1 m3 s-1. Fieldwork in the crater's vicinity took place over a 3-hour interval and included gas sampling. Only a small rockfall was heard.
The new dome appeared anomalous in certain ways. It was not composed of large dark-colored blocks (as observed for the effusive events that occurred during the last 40 years), but instead consisted mainly of smaller-sized blocks with a light-gray color. The new dome could be an example of endogenous dome growth, where no new molten material reaches the surface.
On 1 May 2001 the measured SO2 flux was 200 t/d, and on March 16 it was 145 t/d. These are only slightly higher than mean values recorded during the calm period of 1997, which were less than 100 t/d.
Geological Summary. The Colima complex is the most prominent volcanic center of the western Mexican Volcanic Belt. It consists of two southward-younging volcanoes, Nevado de Colima (the high point of the complex) on the north and the historically active Volcán de Colima at the south. A group of late-Pleistocene cinder cones is located on the floor of the Colima graben west and east of the complex. Volcán de Colima (also known as Volcán Fuego) is a youthful stratovolcano constructed within a 5-km-wide scarp, breached to the south, that has been the source of large debris avalanches. Major slope failures have occurred repeatedly from both the Nevado and Colima cones, producing thick debris-avalanche deposits on three sides of the complex. Frequent recorded eruptions date back to the 16th century. Occasional major explosive eruptions have destroyed the summit (most recently in 1913) and left a deep, steep-sided crater that was slowly refilled and then overtopped by lava dome growth.
Information Contacts: Observatorio Vulcanológico de la Universidad de Colima, Colima, Col., 28045, México; Facultad de Ciencias de la Universidad de Colima, Colima, Col., 28045, México (URL: http://www.ucol.mx/).