Report on Miyakejima (Japan) — October 2003
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 28, no. 10 (October 2003)
Managing Editor: Edward Venzke.
Miyakejima (Japan) Continued seismicity and regular gas-and-steam plumes
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 2003. Report on Miyakejima (Japan) (Venzke, E., ed.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 28:10. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.BGVN200310-284040
Miyakejima
Japan
34.094°N, 139.526°E; summit elev. 775 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Volcanic activity at Miyake-jima since the eruption during the summer of 2000 (BGVN 25:07) has continued at lower levels through August 2003. The flux of SO2 gas remained high (~ 4, 000-9, 000 tons/day), and has been nearly constant since October 2002 (figure 20). A compilation of seismic data and plume observations through April 2003 (table 3) documents this continuing activity. Plume heights following the June-September 2000 activity have not been greater than 2.2 km above the summit (table 3), and their color has been described as white or grayish white.
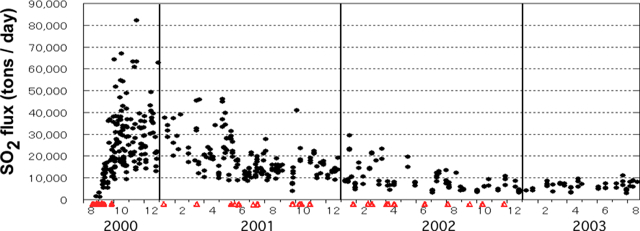 |
Figure 20. SO2 flux at Miyake-jima during August 2000-August 2003. Triangles along the timeline indicate explosions. Courtesy of the Geological Survey of Japan and the Japan Meteorological Agency. |
Table 3. Summary of seismicity and plume observations at Miyake-jima, January 2000-April 2003. All reported plumes originated from the summit crater, and were described as either white (W), light white (LW), grayish white (GW), or gray (G). No months during this time had more than six plumes observed on any single day. Data courtesy of JMA.
| Month | Volcanic earthquakes | Max. Plume Height (km) (date) | Plume Color (date) |
| Jan 2000 | 2 | -- | -- |
| Feb 2000 | 4 | -- | -- |
| Mar 2000 | 1 | -- | -- |
| Apr 2000 | No JMA report received this month | ||
| May 2000 | 3 | -- | -- |
| Jun 2000 | > 13,840 | -- | -- |
| Jul 2000 | > 24,494 | 1.5 (8, 14) | W (8) colored (14, 15) |
| Aug 2000 | > 10,175 | 14 (18) | Mix of white and colored almost daily all after 10th |
| Sep 2000 | 146 | 3.5 (26) frequently above 1 | W (almost daily), C (3, 24, 27) |
| Oct 2000 | 16 | 2.7 (10) | W |
| Nov 2000 | 5 | 2.5 (26) | W |
| Dec 2000 | 6 | 2.0 (22, 27) | W |
| Jan 2001 | 214 | 1.8 (22, 31) | W, GW (11) |
| Feb 2001 | 260 | 2.0 (17) | W |
| Mar 2001 | 299 | 2.0 (2, 16, 24) | W, GW (19) |
| Apr 2001 | 191 | 2.0 (4) | W |
| May 2001 | 707 | 2.2 (6) | W, G (27) |
| Jun 2001 | 192 | 2.2 (10) | W, G (3, 10) |
| Jul 2001 | 249 | 1.6 (16, 21) | W, G (10) |
| Aug 2001 | 306 | 2.0 (24, 25, 27, 28) | W |
| Sep 2001 | 234 | 3.0 (16) | W |
| Oct 2001 | 116 | 1.5 (16, 21, 22, 24, 29, 31) | W, GW |
| Nov 2001 | 124 | 2.0 (20) | W, GW (1) |
| Dec 2001 | 123 | 1.7 (29) | W |
| Jan 2002 | 41 | 2.0 (6) | W, GW |
| Feb 2002 | 88 | 1.7 (14) | W, GW |
| Mar 2002 | 71 | 1.2 (16, 28) | W, GW (31) |
| Apr 2002 | 104 | 1.0 (10) | W, GW (2, 3) |
| May 2002 | 265 | 1.5 (29) | W |
| Jun 2002 | 176 | 0.8 (9) | W, GW (15) |
| Jul 2002 | 78 | 0.8 (27) | W |
| Aug 2002 | 45 | 1.0 (3) | W |
| Sep 2002 | 57 | 1.5 (4) | W |
| Oct 2002 | 47 | 1.0 (6, 30) | W, GW (8) |
| Nov 2002 | 55 | 1.0 (6, 29) | W |
| Dec 2002 | 66 | 0.8 (28) | W |
| Jan 2003 | 202 | 1.0 (25) | W |
| Feb 2003 | 313 | 0.8 (13) | W |
| Mar 2003 | 212 | 1.2 (28) | W |
| Apr 2003 | 450 | 1.0 (28) | W |
The number of monthly earthquakes was very low (1-4/month) until late June through early September 2000. Except for 5 May 2001 when 447 volcanic earthquakes occurred, daily totals have been less than 50. Monthly earthquake totals since August 2000 have been less than 300, except for May 2001 (707) and April 2003 (450). Volcanic tremor also began in July 2000 and became continuous in September 2000. Tremor through April 2003 totaled less than 500 events per month, except for May 2001, when 1, 362 events were recorded (444 on the 22nd). The unusually high seismicity noted in May 2001 corresponded to a period of continuous steam plumes with abundant SO2 content (BGVN 27:03), after which SO2 flux declined (figure 2).
Seismicity at Miyake-jima is recorded by three seismographs maintained by the Japan Meterological Agency (JMA): station "A" is ~ 1.9 km NNE of the summit at 530 m elevation, station "AKOC" is ~ 4.6 km W at 42 m elevation, and station "RST" is ~ 1.9 km SSE at 463 m elevation.
Geological Summary. The circular, 8-km-wide island of Miyakejima forms a low-angle stratovolcano that rises about 1,100 m from the sea floor in the northern Izu Islands about 200 km SSW of Tokyo. The basaltic volcano is truncated by small summit calderas, one of which, 3.5 km wide, was formed during a major eruption about 2,500 years ago. Numerous craters and vents, including maars near the coast and radially oriented fissure vents, are present on the flanks. Frequent eruptions have been recorded since 1085 CE at vents ranging from the summit to below sea level, causing much damage on this small populated island. After a three-century-long hiatus ending in 1469 CE, activity has been dominated by flank fissure eruptions sometimes accompanied by minor summit eruptions. A 1.6-km-wide summit crater was slowly formed by subsidence during an eruption in 2000.
Information Contacts: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA), Volcanological Division, 1-3-4 Ote-machi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100, Japan (URL: http://www.jma.go.jp/); Akihiko Tomiya, Geological Survey of Japan, AIST, 1-1 Higashi, 1-Chome Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8567, Japan (URL: https://staff.aist.go.jp/a.tomiya/tomiyae.html).

