Report on Kikai (Japan) — November 2020
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 45, no. 11 (November 2020)
Managing Editor: Edward Venzke.
Edited by Kadie L. Bennis. Research and preparation by Paul Berger.
Kikai (Japan) Explosion on 6 October 2020 and thermal anomalies in the crater
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 2020. Report on Kikai (Japan) (Bennis, K.L., and Venzke, E., eds.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 45:11. Smithsonian Institution. https://doi.org/10.5479/si.GVP.BGVN202011-282060
Kikai
Japan
30.793°N, 130.305°E; summit elev. 704 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Kikai is a mostly submarine caldera, 19-km-wide, just S of the Ryukyu Islands of Japan. At the NW rim of the caldera lies the island of Satsuma Iwo Jima (also known as Satsuma-Iojima and Tokara Iojima), and the island’s highest peak, Iodake, a steep stratovolcano. Recent weak ash explosions at Iodake occurred on 2 November 2019 and 29 April 2020 (BGVN 45:02, 45:05). The volcano is monitored by the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) and satellite sensors. This report covers the period May-October 2020. During this time, the Alert Level remained at 2 (on a 5-level scale).
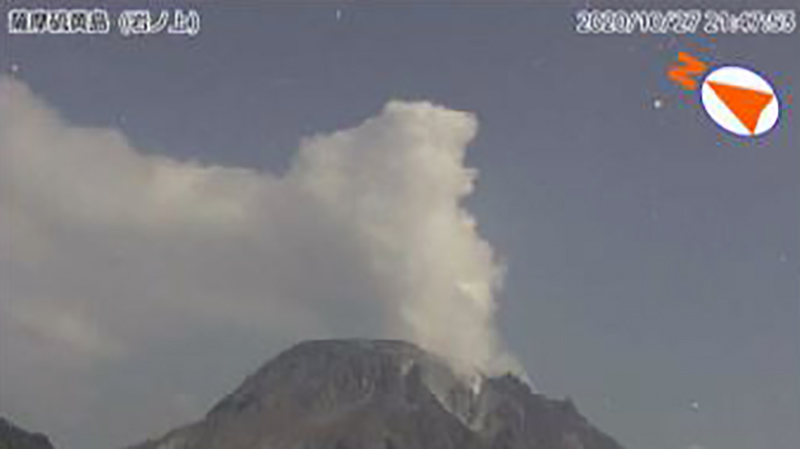
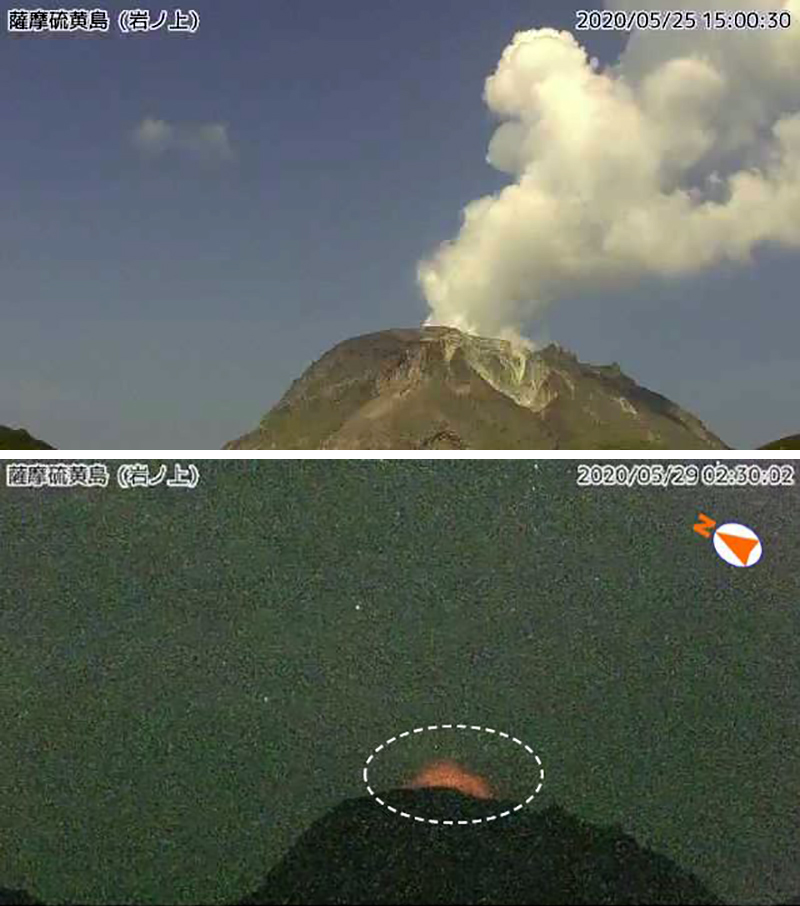
Activity at Kikai has been relatively low since the previous eruption on 29 April 2020. During May through October occasional white gas-and-steam emissions rose 0.8-1.3 km above the Iodake crater, the latter of which was recorded in September. Emissions were intermittently accompanied by weak nighttime incandescence, according to JMA (figure 17).
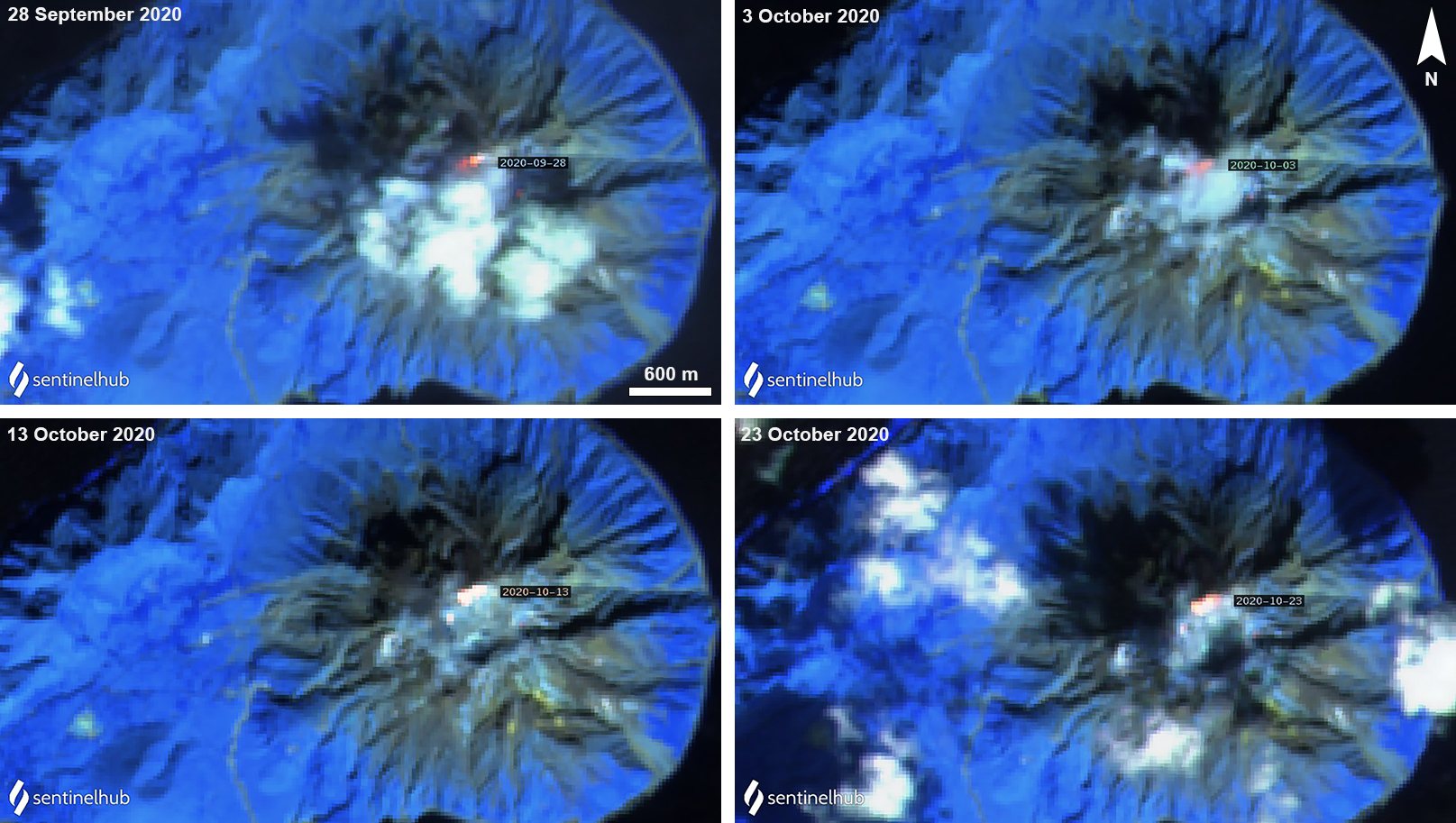
A small eruption at 0757 on 6 October occurred in the NW part of the Iodake crater, which produced a grayish white plume rising 200 m above the crater (figure 18). Faint thermal anomalies were detected in Sentinel-2 thermal satellite imagery in the days just before this eruption (28 September and 3 October) and then after (13 and 23 October), accompanied by gas-and-steam emissions (figures 19 and 20). Nighttime crater incandescence continued to be observed. JMA reported that sulfur dioxide emissions measured 700 tons per day during October, compared to the previous eruption (400-2,000 tons per day in April 2020).
Geological Summary. Multiple eruption centers have exhibited recent activity at Kikai, a mostly submerged, 19-km-wide caldera near the northern end of the Ryukyu Islands south of Kyushu. It was the source of one of the world's largest Holocene eruptions about 6,300 years ago when rhyolitic pyroclastic flows traveled across the sea for a total distance of 100 km to southern Kyushu, and ashfall reached the northern Japanese island of Hokkaido. The eruption devastated southern and central Kyushu, which remained uninhabited for several centuries. Post-caldera eruptions formed Iodake (or Iwo-dake) lava dome and Inamuradake scoria cone, as well as submarine lava domes. Recorded eruptions have occurred at or near Satsuma-Iojima (also known as Tokara-Iojima), a small 3 x 6 km island forming part of the NW caldera rim. Showa-Iojima lava dome (also known as Iojima-Shinto), a small island 2 km E of Satsuma-Iojima, was formed during submarine eruptions in 1934 and 1935. Mild-to-moderate explosive eruptions have occurred during the past few decades from Iodake, a rhyolitic lava dome at the eastern end of Satsuma-Iojima.
Information Contacts: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA), Otemachi, 1-3-4, Chiyoda-ku Tokyo 100-8122, Japan (URL: http://www.jma.go.jp/jma/indexe.html); Sentinel Hub Playground (URL: https://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/sentinel-playground).