Report on Reventador (Ecuador) — April 2023
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, vol. 48, no. 4 (April 2023)
Managing Editor: Edward Venzke.
Edited by Kadie L. Bennis.
Reventador (Ecuador) Daily explosions, gas-and-ash emissions, crater incandescence, and block avalanches during December 2022-March 2023
Please cite this report as:
Global Volcanism Program, 2023. Report on Reventador (Ecuador) (Bennis, K.L., and Venzke, E., eds.). Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network, 48:4. Smithsonian Institution.
Reventador
Ecuador
0.077°S, 77.656°W; summit elev. 3562 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Volcán El Reventador, located in Ecuador, includes a 4-km-wide avalanche scarp open to the E. Recorded eruptions date back to the 16th century and have been characterized by explosive events, lava flows, ash plumes, and lahars. Frequent lahars in this region of heavy rainfall have built deposits on the scarp slope. The largest recorded eruption took place in 2002, producing a 17-km-high eruption column, pyroclastic flows that traveled up to 8 km, and lava flows from summit and flank vents. The current eruption began in July 2008 and more recently has consisted of daily explosions, ash plumes, lava flows, and block avalanches (BGVN 48:02). This report covers similar activity during December 2022 through March 2023 using daily reports from Ecuador's Instituto Geofisico (IG-EPN), the Washington Volcano Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), and satellite data.
During December 2022 through March 2023, IG-EPN reported daily explosions, gas-and-steam and ash plumes rising as high as 1,100 m above the crater, and frequent crater incandescence, often accompanied by incandescent block avalanches and lava flows that traveled down each of the flanks and lava flows that generally affected the NE and E flanks. On average, there were more daily explosions detected during December 2022 compared to January through March 2023, with 57 per day (table 17).
Table 17. Monthly summary of explosions and plume heights recorded at Reventador from December 2022 through March 2023. Data courtesy of IG-EPN (December 2022-March 2023 daily reports).
| Month | Average number of explosions per day | Max plume height above the crater rim (m) |
| Dec 2022 | 57 | 1,000 |
| Jan 2023 | 43 | 1,000 |
| Feb 2023 | 30 | 1,000 |
| Mar 2023 | 33 | 1,100 |
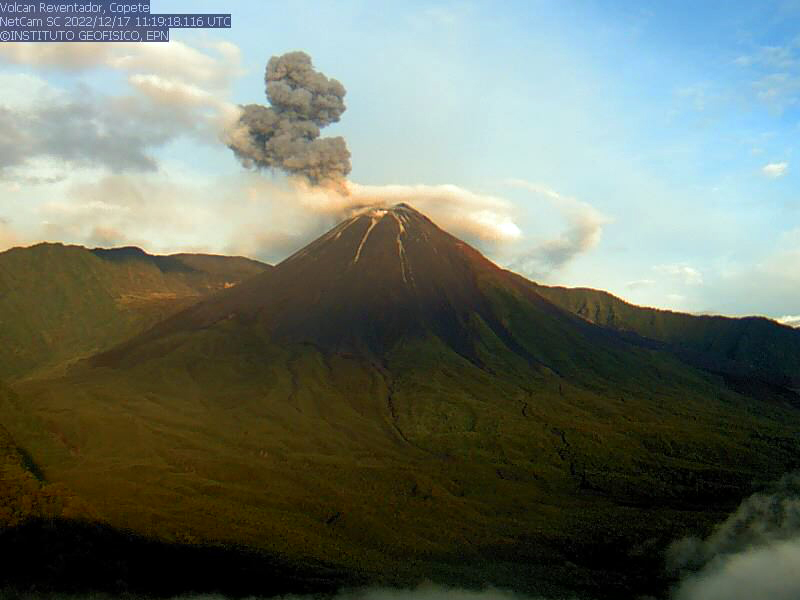
Activity during December 2022 consisted of daily explosions, ash plumes, crater incandescence, a lava flow, and occasional block avalanches, though cloudy weather often obscured clear views of the summit. There were 0-114 explosions recorded each day, in addition to long-period (LP) events and tremor emissions (TREMI). The Washington VAAC reported ash emissions that rose as high as 1.9 km above the crater during 5-6 and 12-13 December and drifted in different directions. IG-EPN also noted that gas-and-ash emissions rose 400-1,000 m above the summit and drifted S, W, NW, W, N, SW (figure 169). A lava flow was observed on the NE flank during 2-6 December and on the E flank during 9-11 December. There were six volcano-tectonic (VT) events detected during 7-8 December. Block avalanches frequently affected one, or multiple flanks, traveling 400-700 m below the crater. During 11-12 December a lava flow was reported on the NE flank.
Daily explosions and ash plumes continued during January 2023, with 12-96 explosions recorded each day. LP and TREMI-type events and crater incandescence were also frequently recorded on clear weather days, cloudy weather often obscured views of the summit. Gas-and-ash emissions rose 500-1,000 m above the crater and drifted W, NW, SW, N, and S. According to the Washington VAAC, ash emissions rose 688-3,750 m above the crater and drifted in multiple directions. During 31 December 2022 through 1 January 2023 nighttime crater incandescence was accompanied by block avalanches 500 m below the crater on all flanks. The lava flow continued to be observed on the NE flank during 31 December 2022 as well as during 1, 5-6, 7-9, 10-11, 16-17, 18-20, and 23-26 January. Block avalanches traveled 500-700 m from the crater throughout the month, affecting one or multiple flanks (figure 170). An ash plume was reported on 15 January that drifted S. A pyroclastic flow occurred during the morning of 29 January on the N flank.
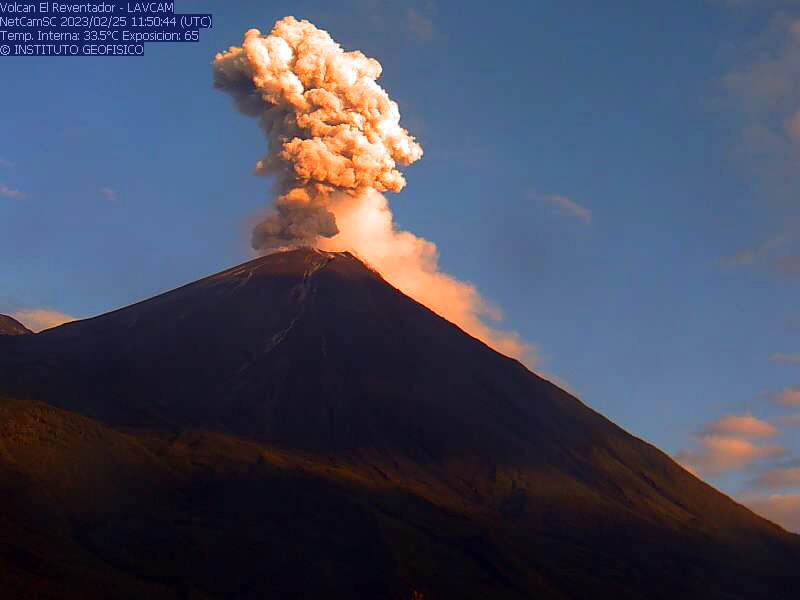
During February there were 12-100 daily explosions detected, along with LP and TREMI-type events. Crater incandescence persisted, in addition to block avalanches. Gas-and-ash emissions rose 200-1,000 m above the crater and drifted W, NW, NE, and N (figure 171). The Washington VAAC reported that ash emissions rose 400-2,200 m above the crater and drifted NE, NW, W, SW, SE, and N. During 1-6, 13-17, and 21-26 February incandescent block avalanches descended all the flanks 600-900 m below the crater. An active lava flow continued down the NE flank during 8-10, 14-15, 18-19, and 20-21 February. Block avalanches descended the E flank 900 m below the crater during 10-11 February. There were three VT-type events that were detected on 24 February.
Daily explosions, LP and TREMI-type events, crater incandescence, and block avalanches continued during March. There were 20-52 daily explosions recorded during the month. Cloudy weather often prevented clear views of the summit. Gas-and-ash emissions rose 600-1,100 m above the crater and drifted NW, W, N, NE, E, S, and SE. According to the Washington VAAC, ash emissions rose 688-1,300 m above the crater and drifted NW, W, NE, E, and SE. Block avalanches traveled down all the flanks 400-700 m below the crater during 2-3, 5-6, 8-12, 14-17, 23-24, and 30-31 March. During 6-7 March block avalanches descended all the flanks as far as 900 m below the crater, accompanied by ash emissions that rose 1,000 m above the summit that drifted W. IG-EPN reported that a lahar was detected on 6 March. During the nights of 12 and 15 March incandescent blocks moved down the S flank 400-500 m below the crater. During 20-21 March ash emissions rose 1 km above the crater and drifted S and SE (figure 172); reports from the Secretaría de Gestión de Riesgos (SGR) reported that light ashfall was observed in San Carlos and San Luis.
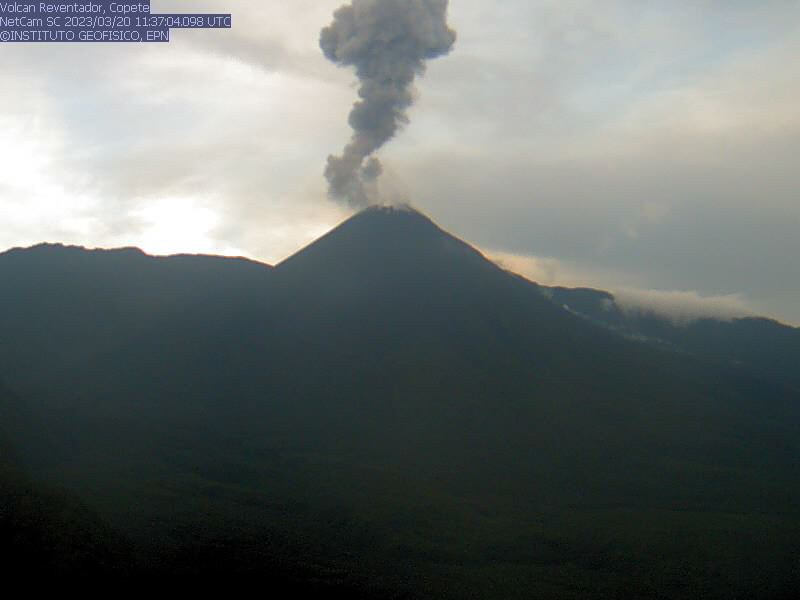 |
Figure 172. Webcam image of a gas-and-ash plume rising Reventador on 20 March 2023. Courtesy of IG-EPN (INFORME DIARIO DEL VOLCAN REVENTADOR No. 2023-079, 20 de marzo de 2023). |
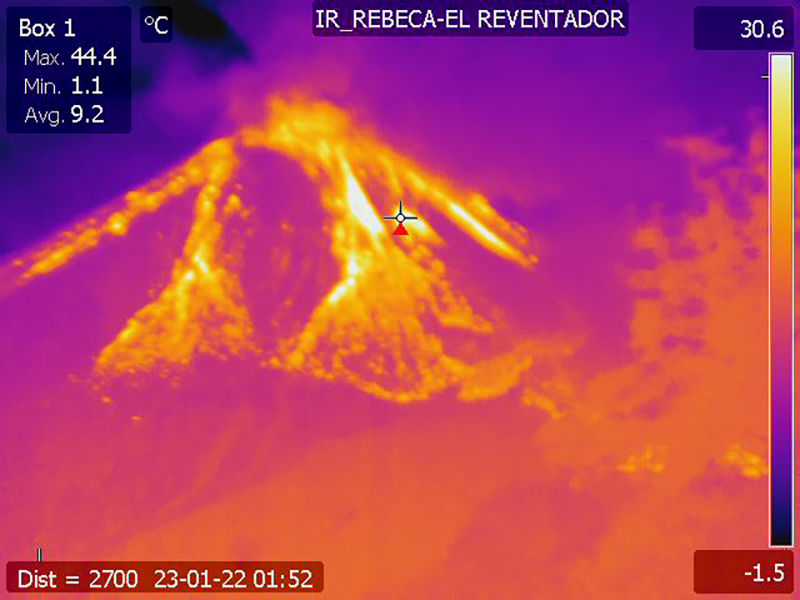
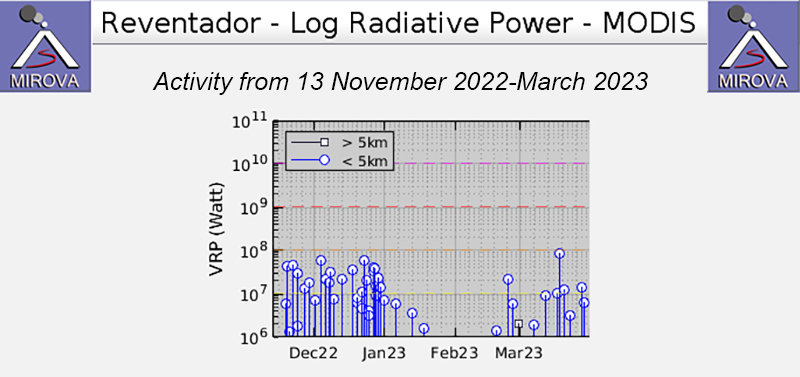
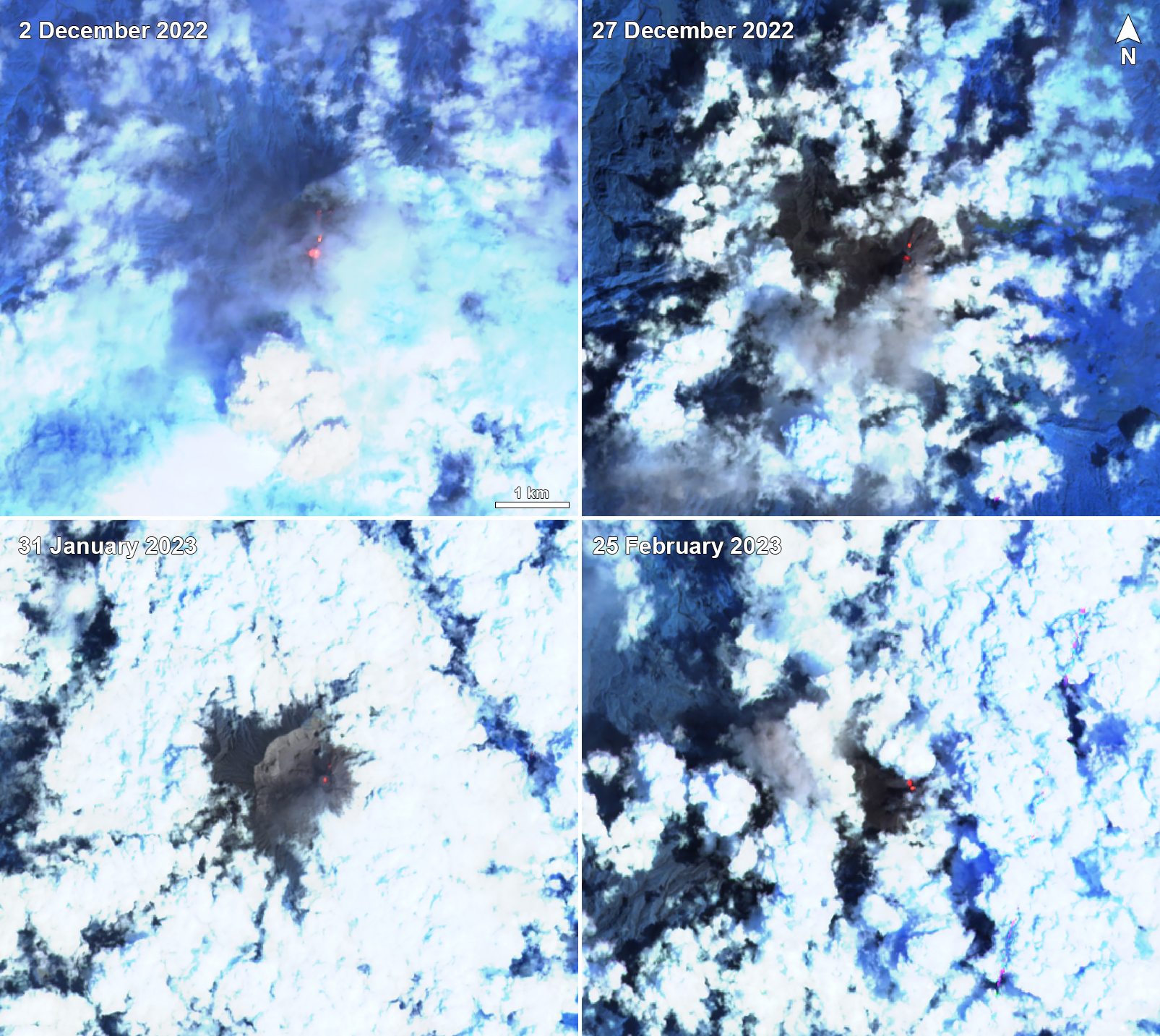
Additional satellite data. MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) analysis of MODIS satellite data showed frequent thermal anomalies of moderate power during December 2022 through mid-January 2023, followed by a break in detected activity through late February (figure 173). During March, eight anomalies were detected intermittently throughout the month. The MODVOLC system identified a total of two thermal hotspots on 6 December 2022 and 20 March 2023. Although the summit was often obscured by weather clouds, Sentinel-2 infrared satellite images sometimes showed thermal activity at the summit crater (figure 174).
Geological Summary. Volcán El Reventador is the most frequently active of a chain of Ecuadorian volcanoes in the Cordillera Real, well east of the principal volcanic axis. The forested, dominantly andesitic stratovolcano has 4-km-wide avalanche scarp open to the E formed by edifice collapse. A young, unvegetated, cone rises from the amphitheater floor to a height comparable to the rim. It has been the source of numerous lava flows as well as explosive eruptions visible from Quito, about 90 km ESE. Frequent lahars in this region of heavy rainfall have left extensive deposits on the scarp slope. The largest recorded eruption took place in 2002, producing a 17-km-high eruption column, pyroclastic flows that traveled up to 8 km, and lava flows from summit and flank vents.
Information Contacts: Instituto Geofísico, Escuela Politécnica Nacional (IG-EPN), Casilla 17-01-2759, Quito, Ecuador (URL: http://www.igepn.edu.ec/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Sentinel Hub Playground (URL: https://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/sentinel-playground).