Kirishimayama (Japan) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | New Activity / Unrest
 Cite this Report Cite this Report
|
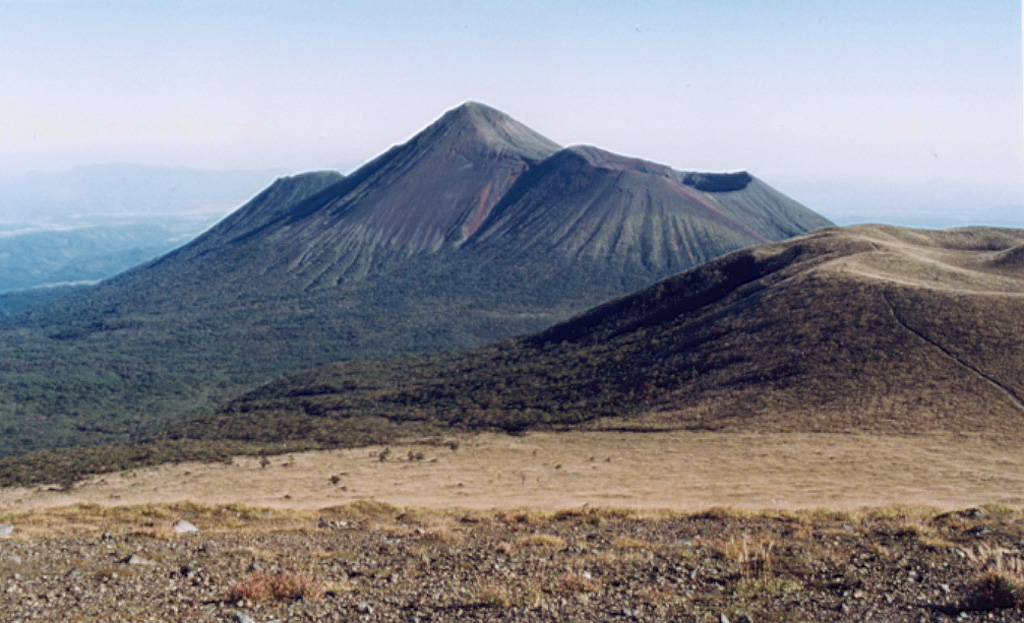 Kirishimayama Kirishimayama
Ryukyu Volcanic Arc
|
The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) reported that an eruption occurred at Shinmoedake (Shinmoe peak, a stratovolcano of the Kirishimayama volcano group) on 22 June, the first eruption since 27 June 2018. The number of volcanic earthquakes with epicenters directly beneath Shinmoedake had been fluctuating since late October 2024 but began to increase starting around 13 June. Another increase occurred at around 2100 on 21 June, and volcanic tremor increased on 22 June. An eruption detected during 1637-1755 on 22 June produced an ash plume that rose 500 m above the crater rim and drifted E. Ashfall was confirmed in a wide area to the NE that included Takaharu Town, Kobayashi City, Miyazaki City, Kunitomi Town, Saito City, and Shintomi Town in Miyazaki Prefecture. A large amount of ashfall in Hirohara, Takaharu-cho, Miyazaki Prefecture obscured the white lines on the roadway. Sulfur dioxide emissions averaged 4,000 tons per day on 23 June; no emissions were detected on 15 May during the last measurement. On 23 June the Alert Level was raised to 3 (on a 5-level scale) and the public was warned to exercise caution within 3 km from Shinmoedake Crater.
Source: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)
|
Kuchinoerabujima (Japan) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | New Activity / Unrest
 Cite this Report Cite this Report
|
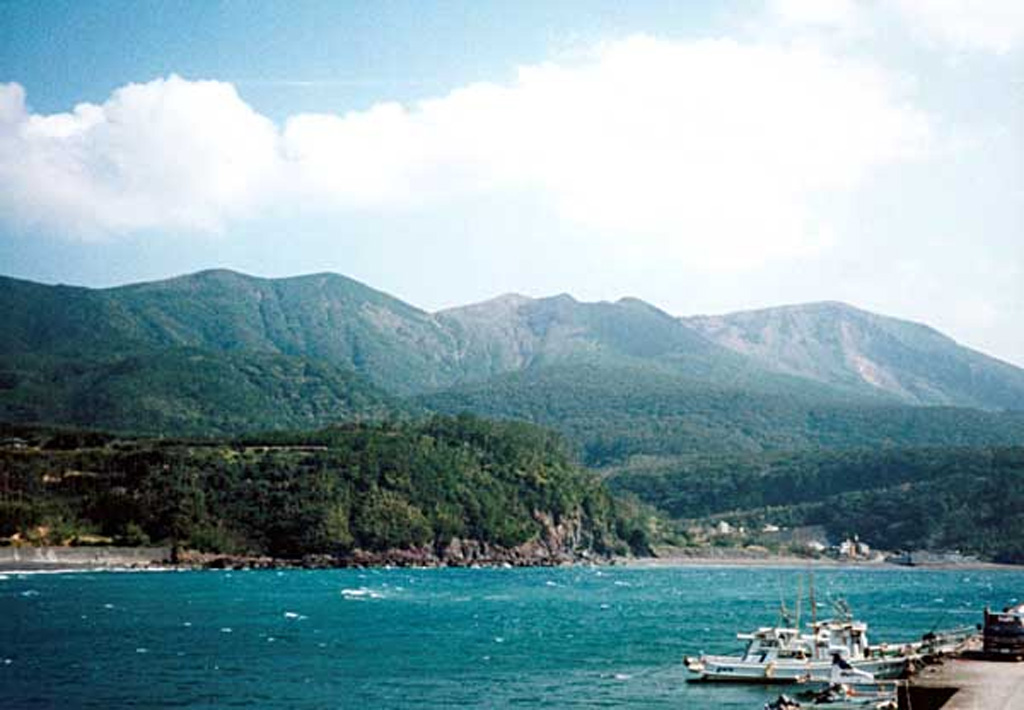 Kuchinoerabujima Kuchinoerabujima
Ryukyu Volcanic Arc
|
The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) reported that the number of shallow volcanic earthquakes increased beneath an area near Kuchinoerabujima’s Furudake Crater in April and continued to increase. Sulfur dioxide emissions were low, averaging 20-80 tons per day since April, and there were days in April where the emissions were below detectable limits. Deformation data indicated ongoing inflation. Volcanic earthquakes with somewhat large amplitudes were occasionally recorded in May by the seismic network. There were many (135) volcanic earthquakes recorded during 2-11 June. No changes to geothermal areas located in and around both Shindake and Furudake craters were observed during a field survey conducted on 11 June. The Alert Level was raised to 3 (on a scale of 1-5) at 2100 on 11 June; the public was warned that ejected blocks may land within 2 km of both craters, and pyroclastic flows may affect areas between Shindake Crater and the coast.
Source: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)
|
Lewotobi (Indonesia) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | New Activity / Unrest
 Cite this Report Cite this Report
|
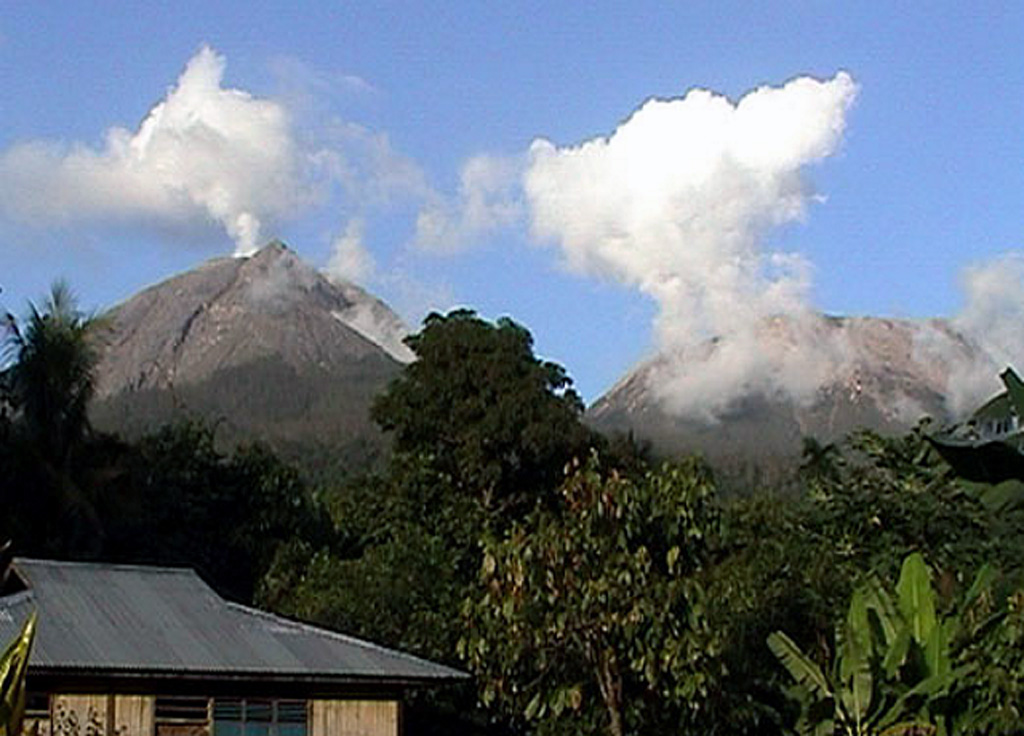 Lewotobi Lewotobi
Sunda Volcanic Arc
|
The Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG) reported that eruptive activity continued at Lewotobi Laki-laki during 18-25 June, after the explosive eruption on 17 June. At 0318 and 0641 on 18 June ash plumes rose 1 km above the summit and drifted N and NE. Visual observations of eruptive events recorded at 1229 and 2212 later that day, and at 0922 and 1008 on 19 June, were obscured by weather conditions; incandescence at the summit was visible in a webcam image at 2223 on 18 June. Dense gray ash plumes rose as high as 2 km above the summit and drifted S and SW at 2213 and 2231 on 20 June and at 0014 and 0024 on 21 June. Webcam images taken near midnight showed incandescent material being ejected above the summit and onto the upper flanks. An eruptive event was recorded at 1440 on 23 June but weather conditions again obscured views. According to news reports the number of evacuees totaled 4,954 on 19 June and 4,007 as of 21 June. The Alert Level remained at 4 (on a scale of 1-4) and the public was warned to stay 7 km away from the center of Laki-laki and 8 km in a semicircle clockwise from the SW to the NE.
Sources: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as CVGHM), Antara News, Antara News
|
Miyakejima (Japan) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | New Activity / Unrest
 Cite this Report Cite this Report
|
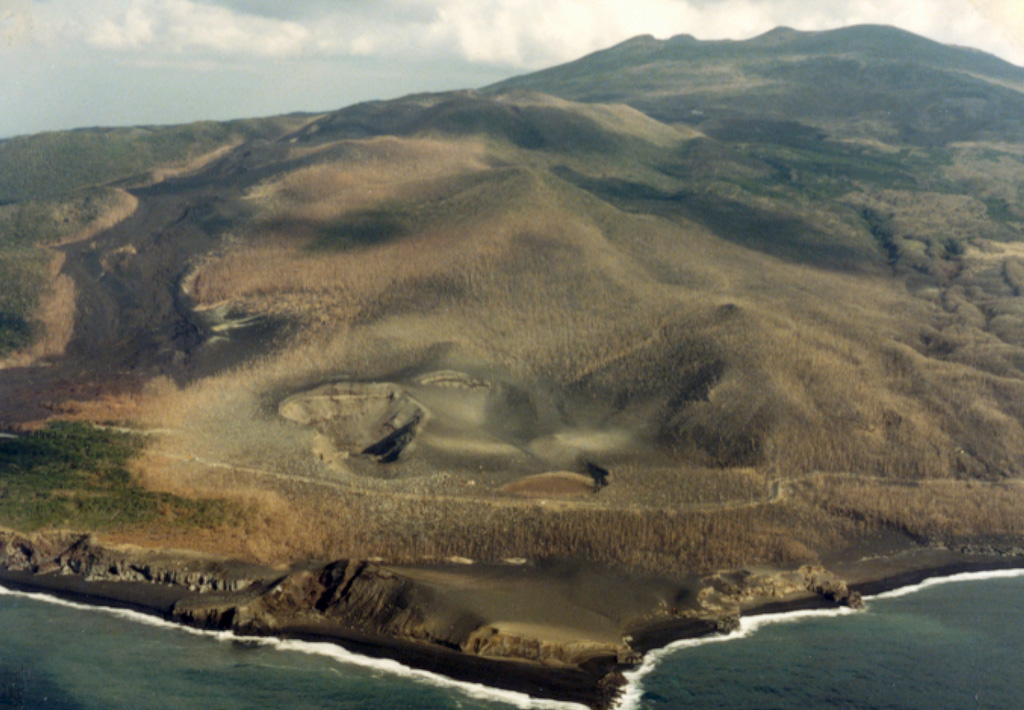 Miyakejima Miyakejima
Izu Volcanic Arc
|
The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) reported that the number of small volcanic earthquakes at Miyakejima decreased after a peak on 17 June that led to an Alert Level change. On 17 June the number of small volcanic earthquakes with epicenters directly below the summit crater totaled 59, and uplift near the summit was detected in tiltmeter data. During 18-23 June the number of daily earthquakes decreased to 0-4 earthquakes per day and no changes in tilt were detected after 18 June. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a 5-level scale) and the public was warned to be cautious in areas inside the Oyama Ring Road.
Source: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)
|
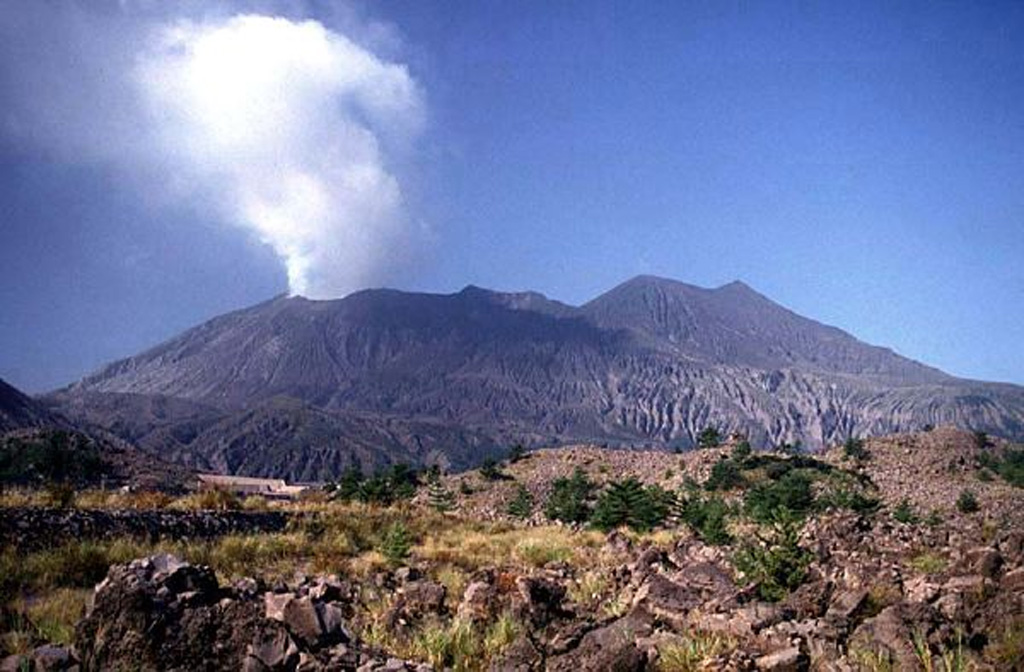
Aira (Japan) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Aira Aira
Ryukyu Volcanic Arc
|
The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) reported ongoing eruptive activity at Minamidake Crater (Aira Caldera’s Sakurajima volcano) during 16-23 June. One small eruptive event was recorded on 20 June. Weather clouds obscured views during 21-23 June. The Alert Level remained at 3 (on a 5-level scale), and the public was warned to be cautious within 2 km of both the Minimadake and Showa craters.
Source: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)
|
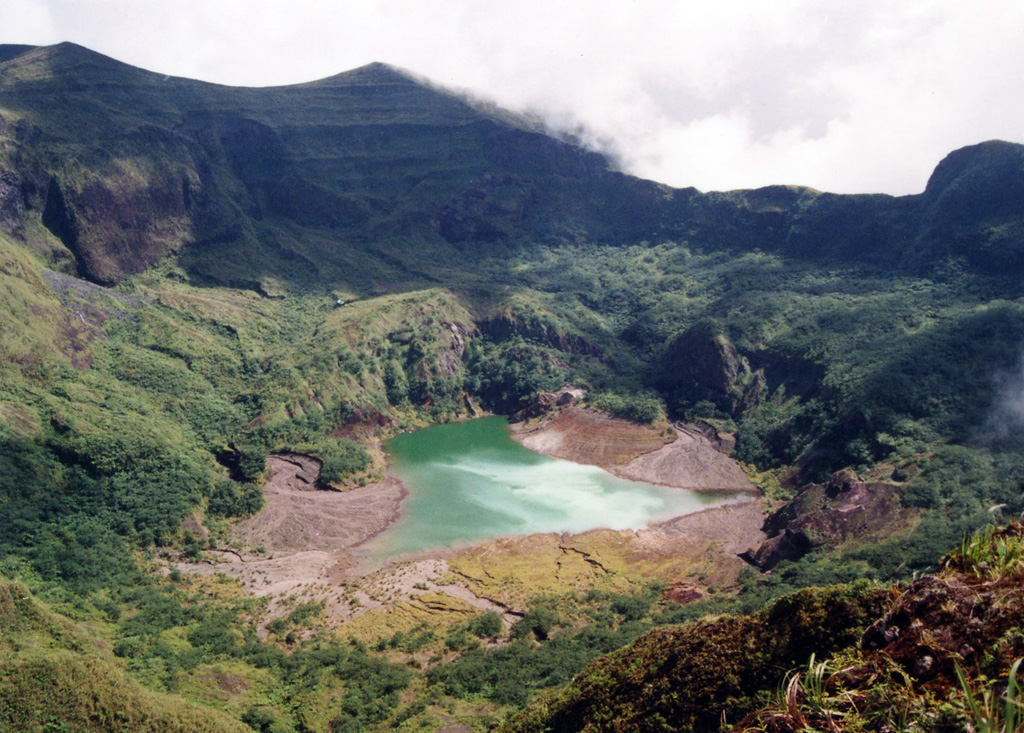
Awu (Indonesia) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Awu Awu
Sangihe Volcanic Arc
|
The Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG) issued a special report for Awu, noting increased seismicity over a two-day period. On 18 June the seismic network recorded 55 shallow volcanic earthquakes and during 0000-1800 on 19 June the network recorded 81 shallow volcanic earthquakes, three deep volcanic earthquakes, and one low-frequency earthquake. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 1-4) and PVMBG reminded the public to stay 3 km away from the crater’s center.
Source: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as CVGHM)
|
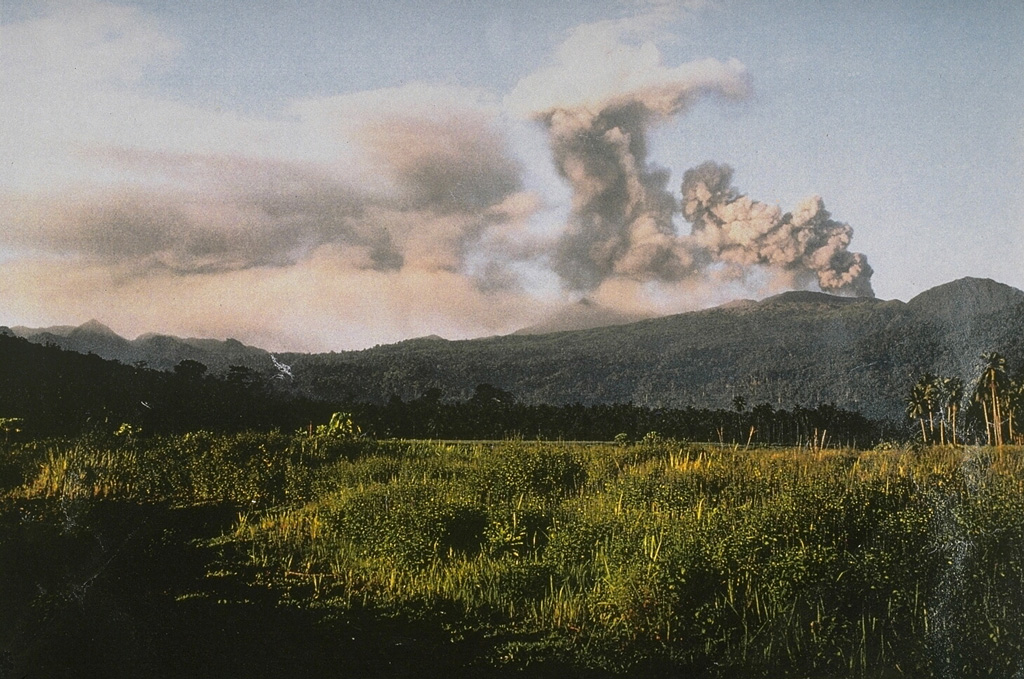
Dukono (Indonesia) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Dukono Dukono
Halmahera Volcanic Arc
|
The Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG) reported that eruptive activity at Dukono continued during 18-24 June. Daily white-and-gray or white, gray, and black gas-and-ash plumes rose 500-2,700 m above the summit and drifted SE, E, and NW. Faint rumbling was heard at the observation post, 11 km N, during 6-7 June. Residents 10-11 km away heard occasional booming and rumbling sounds during 18 and 22-24 June. The Alert Level remained at Level 2 (on a scale of 1-4) and the public was warned to stay 4 km away from the Malupang Warirang Crater.
Source: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as CVGHM)
|
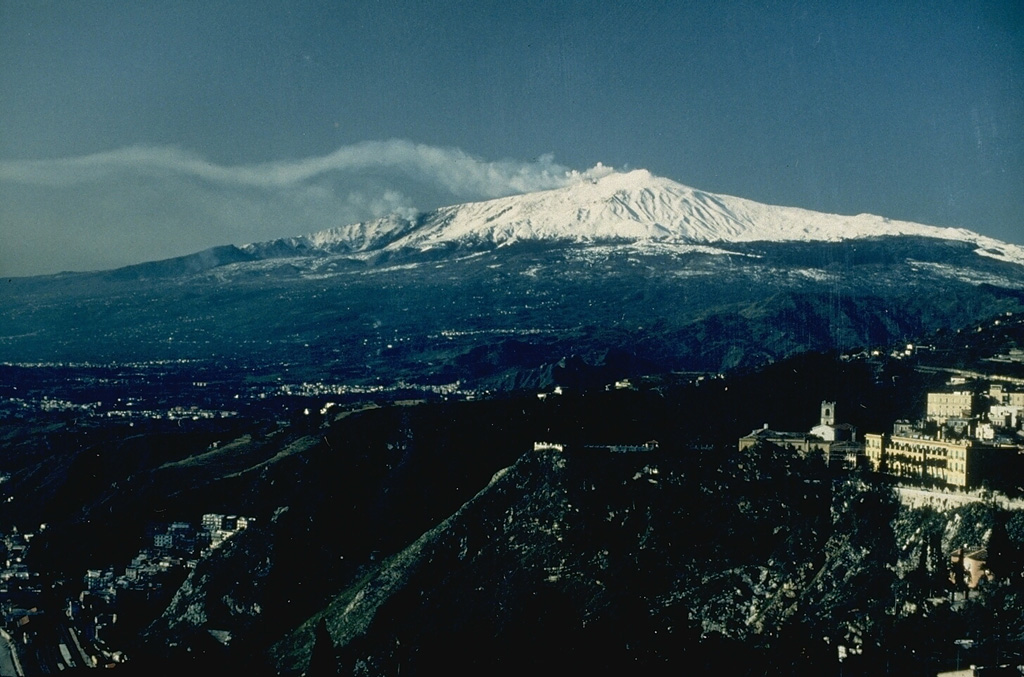
Etna (Italy) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Etna Etna
Sicily Volcanic Province
|
The Sezione di Catania - Osservatorio Etneo (INGV) reported explosive activity and lava flow at Etna during 16-22 June, though poor weather conditions obscured views all week. Explosive activity at SE Crater was first observed in webcam images at 0123 on 19 June and was described as weak and discontinuous. The intensity strengthened over time, though weather conditions often prevented visual observations. At around 0555 lava overflowed the crater and descended the flanks, traveling NE and curving E. Intense Strombolian activity was visible during 1200-1300 and an eruption plume rose 6-7 km a.s.l. and drifted N. Ashfall was reported in Randazzo (15 km NNE) and in the municipality of Gioiosa Marea (46 km N). The lava flow advanced to 1,930 m elevation and was 3.9 km long. Intermittent incandescent flashes at NE Crater were visible in webcam images on 21 June.
Source: Sezione di Catania - Osservatorio Etneo (INGV)
|
Great Sitkin (United States) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Great Sitkin Great Sitkin
Aleutian Ridge Volcanic Arc
|
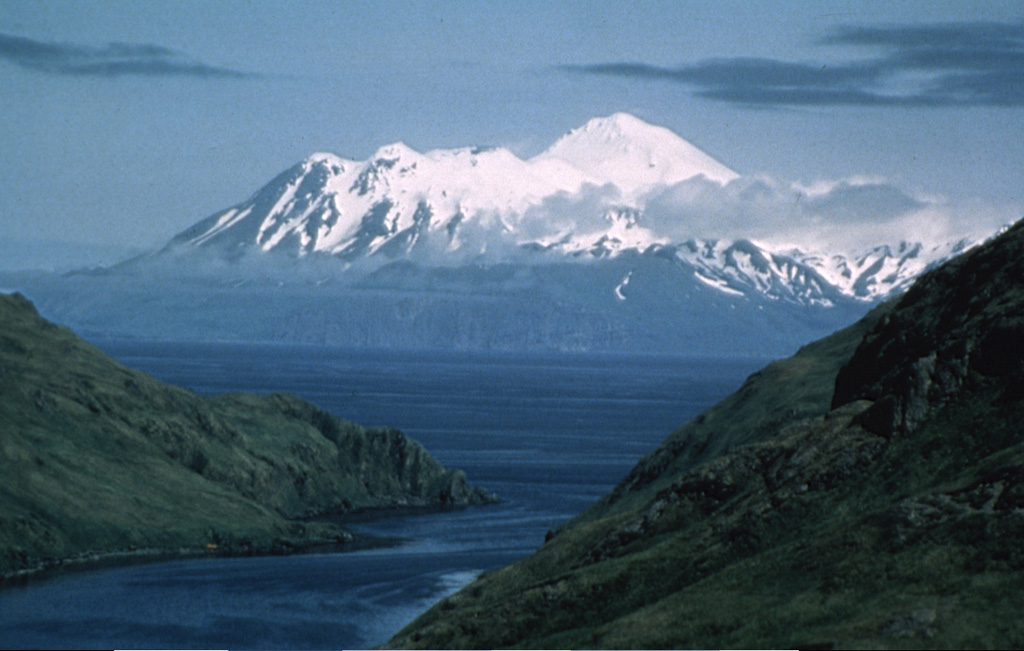
The Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO) reported that slow lava effusion continued to feed a thick flow in Great Sitkin’s summit crater during 18-24 June. Webcam and satellite views showed slight inflation of the dome near the vent area and rockfall deposits on the S and SE sides of the upper part of the dome. Small daily earthquakes were detected by the seismic network, including signals probably caused by small rockfalls from the growing summit lava dome. Minor steaming from the snow-free dome was visible in clear webcam views during 18-19 June. The Volcano Alert Level remained at Watch (the third level on a four-level scale) and the Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third color on a four-color scale).
Source: US Geological Survey Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO)
|
Home Reef (Tonga) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Home Reef Home Reef
Tofua Volcanic Arc
|
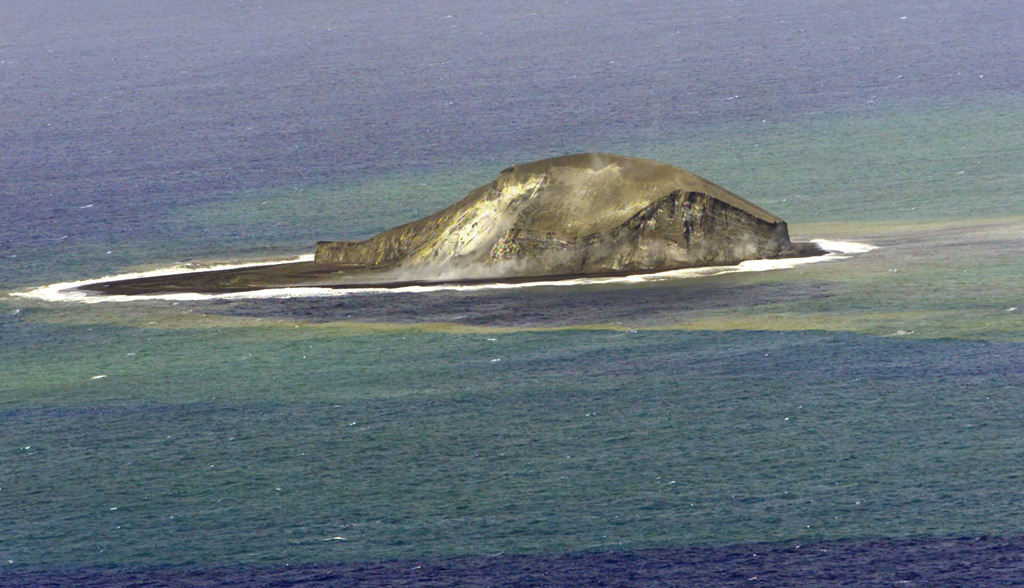
The Tonga Geological Services reported that unrest at Home Reef continued during 7-21 June. Discolored water around the island was visible in both 16 and 21 June clear satellite images. A steam plume was visible in the 16 June image, but no emissions were visible in the 21 June image. No thermal anomalies nor ash emissions were detected in satellite data. The Aviation Color Code remained at Yellow (the second lowest level on a four-level scale, the Maritime Alert Level remained at Orange (the third level on a four-level scale) with advice to stay at least 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) from the island, and the Alert Level for residents of Vava’u and Ha’apai remained at Green (the first level on a four-level scale).
Source: Tonga Geological Services, Government of Tonga
|
Ibu (Indonesia) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Ibu Ibu
Halmahera Volcanic Arc
|
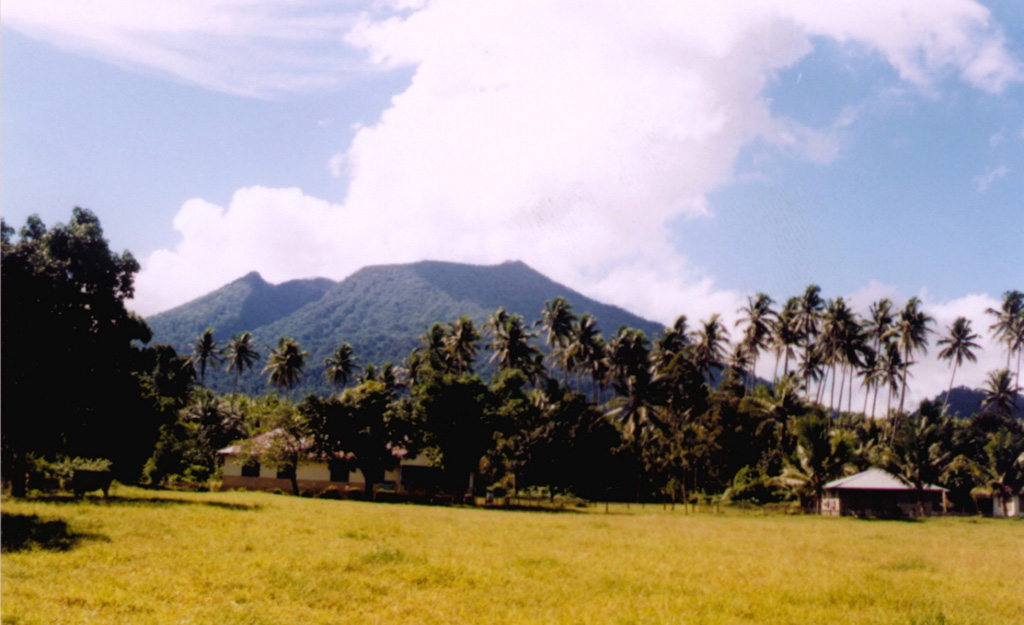
The Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG) reported that the eruption at Ibu continued during 18-24 June. Gray or white-to-gray ash plumes rose 300-800 m above the summit and drifted in multiple directions on most days; eruptive events were recorded on 18 June, but visual observations were obscured by weather clouds. Nighttime crater incandescence was visible in some webcam images. The Alert Level remained at 3 (the second highest level on a four-level scale) and the public was advised to stay 4 km away from the active crater and 5 km away from the N crater wall opening.
Source: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as CVGHM)
|
Karymsky (Russia) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Karymsky Karymsky
Eastern Kamchatka Volcanic Arc
|
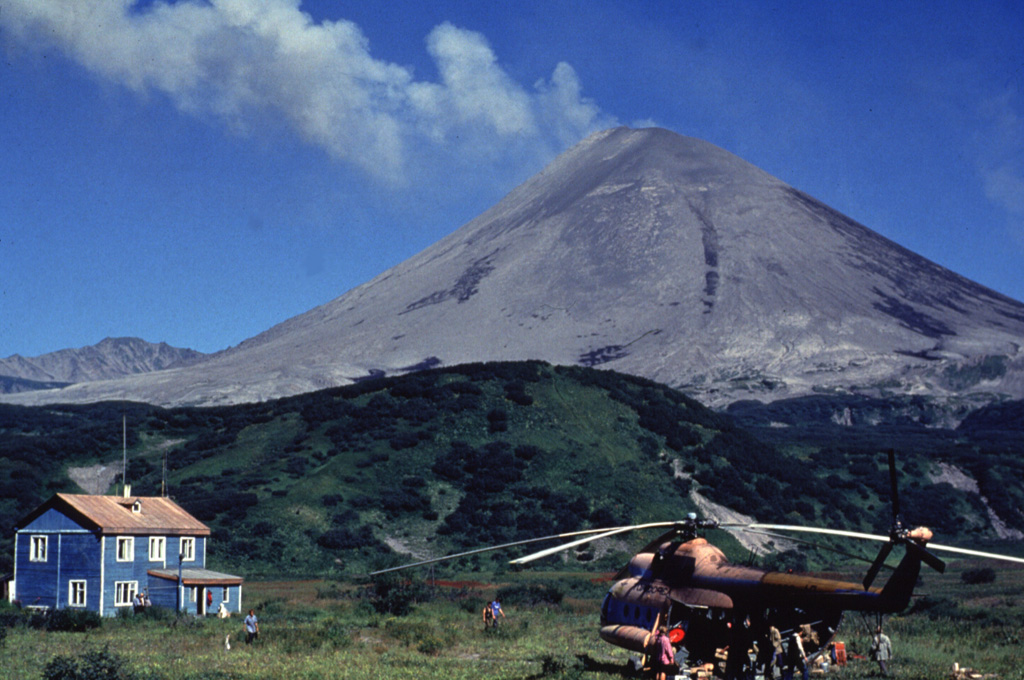
The Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT) reported that moderate activity continued at Karymsky during 13-19 June. A thermal anomaly over the volcano was identified in satellite images during 17-18 June; the volcano was quiet or weather conditions prevented views on the other days of the week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
|
Kilauea (United States) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
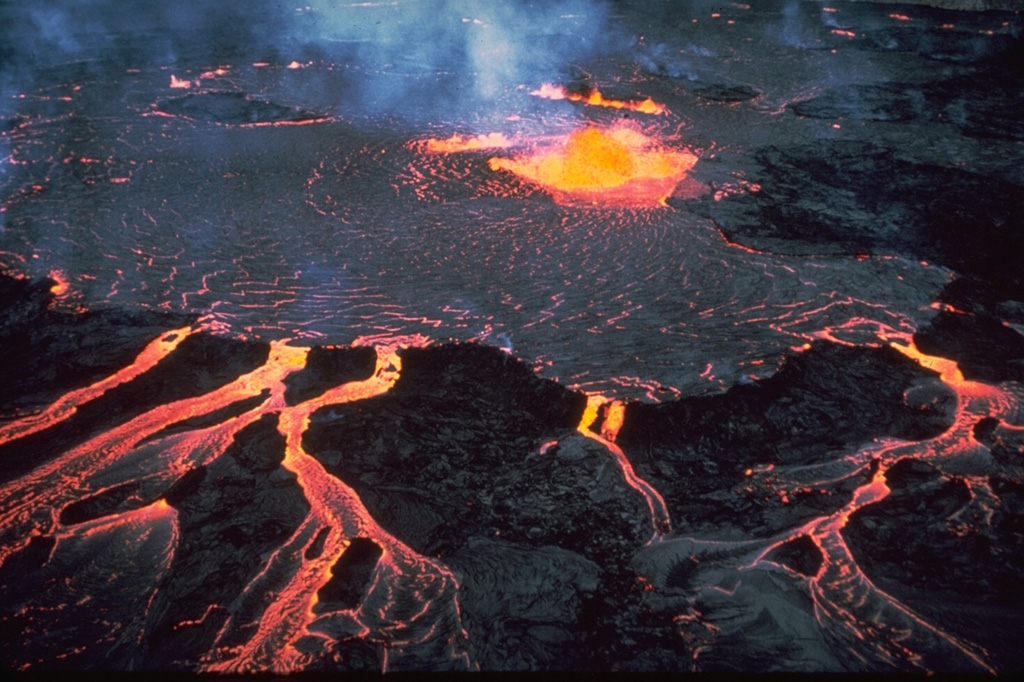 Kilauea Kilauea
Hawaiian-Emperor Hotspot Volcano Group
|
The Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) reported that the eruption within Kilauea’s Kaluapele summit caldera, characterized by episodic fountaining and intermittent spatter at two vents along the SW margin of Halema’uma’u Crater, continued at variable levels during 18-24 June. Nighttime incandescence at both the N and S vents and intermittent lava spattering at the N vent were visible during 18-19 June. Small, sporadic periods of spattering and intermittent overflows of lava began at the N vent at 2326 on 19 June. The activity intensified until 0140 on 20 June when lava fountains became sustained. By 0155 the fountain was 250 m tall, and lava was advancing on the crater floor; by 0210 the fountain was over 300 m tall. Lava fountaining at the S vent began at around 0200. The activity at the N vent continued to intensify and by 0326 the fountain at the N vent rose well over 305 m. The eruptive plume rose at least 6 km (20,000 ft) above ground level. Sulfur dioxide emissions were not directly measured, though typical values observed for past episodes of lava fountaining averaged 50,000-75,000 tonnes per day. Gas and tephra drifted S based on wind data from the National Weather Service. Lava flows from both vents covered parts of the crater floor. After about eight hours of continuous fountaining, the N vent stopped erupting at 1007, and the S vent stopped at 1025. Strong incandescence from both vents was visible overnight during 22-24 June. Data analysis revealed that the fountain from the N vent rose 380 m, a new height record for the current eruption. The Volcano Alert Level remained at Watch (the third level on a four-level scale) and the Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third color on a four-color scale).
Source: US Geological Survey Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO)
|
Klyuchevskoy (Russia) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Klyuchevskoy Klyuchevskoy
Eastern Kamchatka Volcanic Arc
|
The Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT) reported that a bright thermal anomaly at Klyuchevskoy was identified in satellite images during 13-19 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
|
Lascar (Chile) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Lascar Lascar
Central Andean Volcanic Arc
|
The Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería (SERNAGEOMIN) reported declining seismicity, low sulfur dioxide emissions, and no deformation at Láscar in recent weeks. During 1-15 June sulfur dioxide emissions measured at a station 6 km ESE averaged 1,254 tonnes per day (t/d) with a maximum value of 2,572 t/d on 12 June. No anomalous emissions were detected in satellite data. White gas plumes visible in webcam views rose as high as 400 m above the crater rim and drifted ESE. Incandescence from the crater was visible during 6, 9-10, and 15 June, and periodically at night through the first half of June. Satellite data continued to show three zones of elevated temperatures on the crater floor. The seismic network recorded fewer and less intense signals indicative of volcanic processes. The Alert Level was lowered to Green (the lowest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería (SERNAGEOMIN)
|
Lewotolok (Indonesia) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Lewotolok Lewotolok
Sunda Volcanic Arc
|
The Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG) reported that an eruption at Lewotolok was ongoing during 18-24 June. Daily gray, white-to-gray, or gray-to-black ash plumes rose 400-900 m above the summit of the cone and drifted NW, W, and SW. Clear nighttime webcam images showed incandescent material both at the summit cone and being ejected above the cone. Lava flows on the W and SW flanks of the main volcano edifice were also incandescent. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 1-4) and the public was warned to stay 2 km away from the vent and 2.5 km away on the S, SE, and W flanks.
Source: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as CVGHM)
|
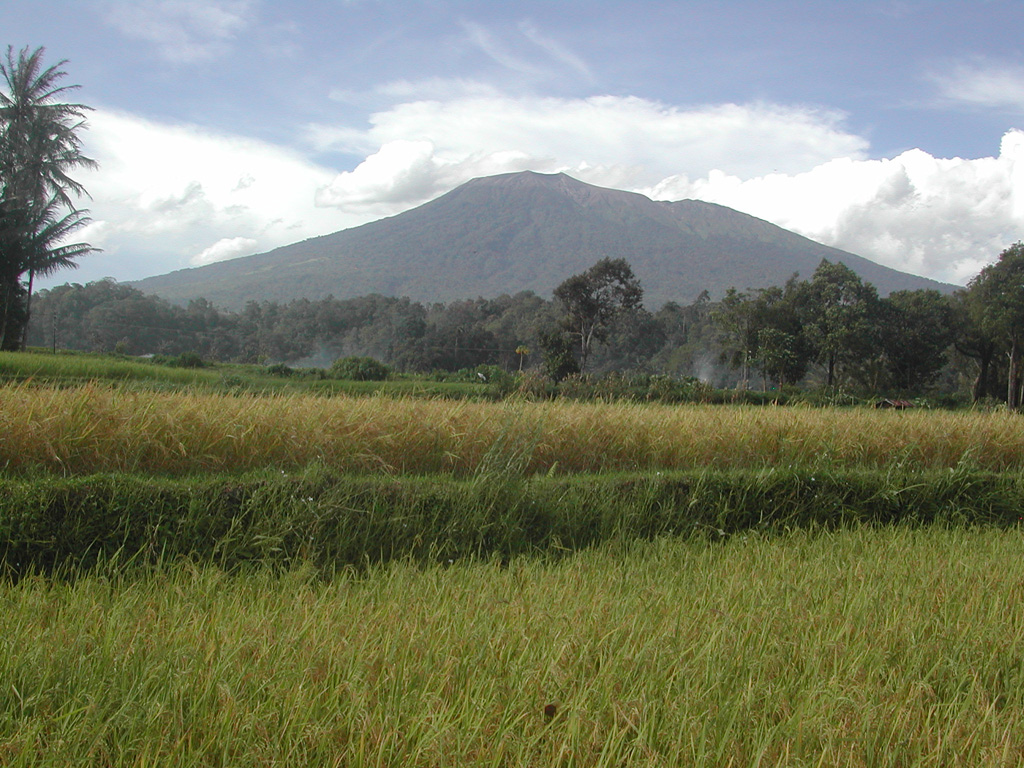
Marapi (Indonesia) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Marapi Marapi
Sunda Volcanic Arc
|
The Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG) reported that eruptive activity at Marapi (on Sumatra) continued during 18-24 June. At 1532 on 18 June a gray ash plume rose to around 450 m above the summit and drifted NE. Later that day, at 2009, a gray ash plume to rose around 700 m above the summit and drifted E. According to a news report the second event was accompanied by loud banging and rumbling noises, felt vibrations, and incandescence visible at the summit. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 1-4) and the public was warned to stay 3 km away from the active crater.
Sources: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as CVGHM), Antara News
|
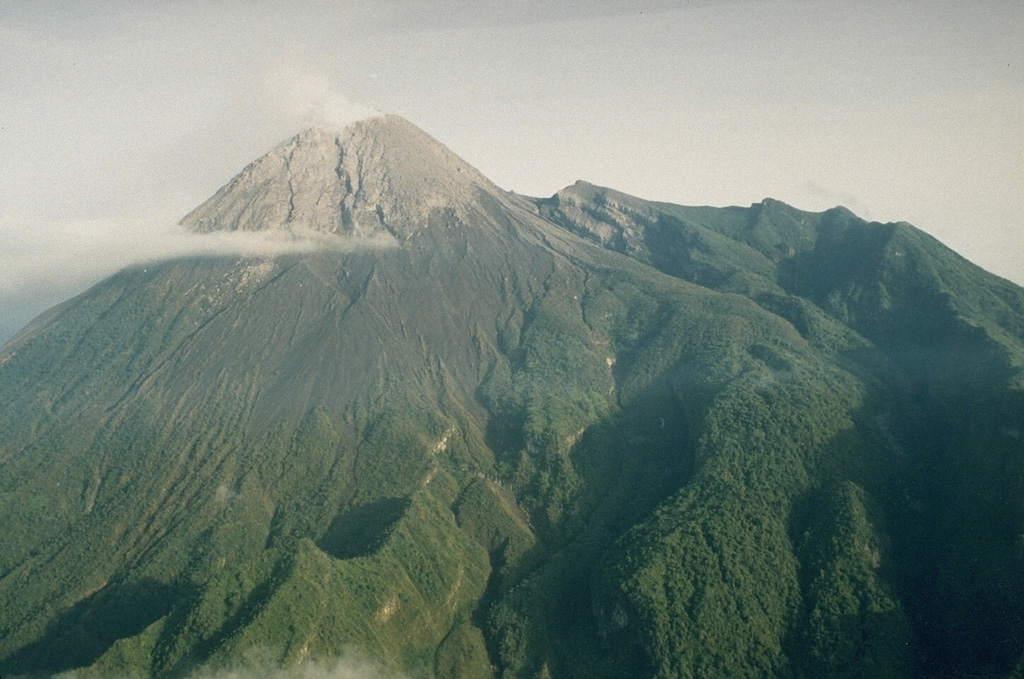
Merapi (Indonesia) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Merapi Merapi
Sunda Volcanic Arc
|
The Balai Penyelidikan dan Pengembangan Teknologi Kebencanaan Geologi (BPPTKG) reported that the eruption at Merapi (on Java) continued during 13-19 June. Seismicity was less intense than the previous week. The SW lava dome produced 26 lava avalanches that traveled as far as 1.9 km SW down the Bebeng drainage, 20 that traveled as far as 2 km SW down the Krasak drainage, and 56 that traveled as far as 1.9 km W down the Sat/Putih drainage. Small morphological changes to the SW lava dome resulted from continuing effusion and minor collapses. The volume of the SW dome increased by 84,500 cubic meters to an estimated 4,133,800 cubic meters, based on webcam images and a 13 June drone survey. The size of the central dome had not changed. The Alert Level remained at 3 (on a scale of 1-4), and the public was warned to stay 3-7 km away from the summit, based on location.
Source: Balai Penyelidikan dan Pengembangan Teknologi Kebencanaan Geologi (BPPTKG)
|
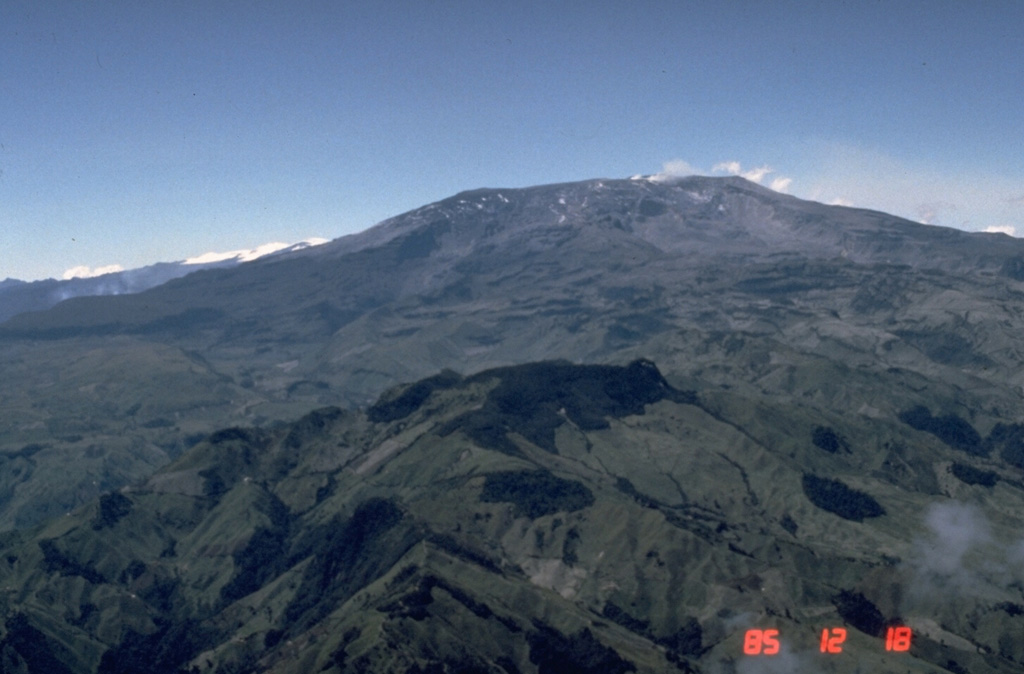
Nevado del Ruiz (Colombia) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Nevado del Ruiz Nevado del Ruiz
Northern Andean Volcanic Arc
|
The Servicio Geológico Colombiano’s (SGC) Observatorio Vulcanológico y Sismológico de Manizales reported that eruptive activity at Nevado del Ruiz continued during 17-23 June, though weather conditions often obscured visual observations. Seismic data indicated that events associated with fluid movement decreased in both number and intensity compared to the previous week. Seismicity associated with rock fracturing decreased in number but increased in intensity compared to the previous week. The earthquakes were mainly located below Arenas Crater and the NE, E, and SE flanks within 5 km at depths of 1-8 km. Low-energy thermal anomalies on the crater floor were identified in satellite data. Daily sulfur dioxide emissions had decreased compared to the previous week. Gas-and-steam plumes rose as high as 900 m above the summit and drifted NW and WNW; ash was not detected in the plumes. The Alert Level remained at Yellow (the second level on a four-level scale).
Source: Servicio Geológico Colombiano (SGC)
|
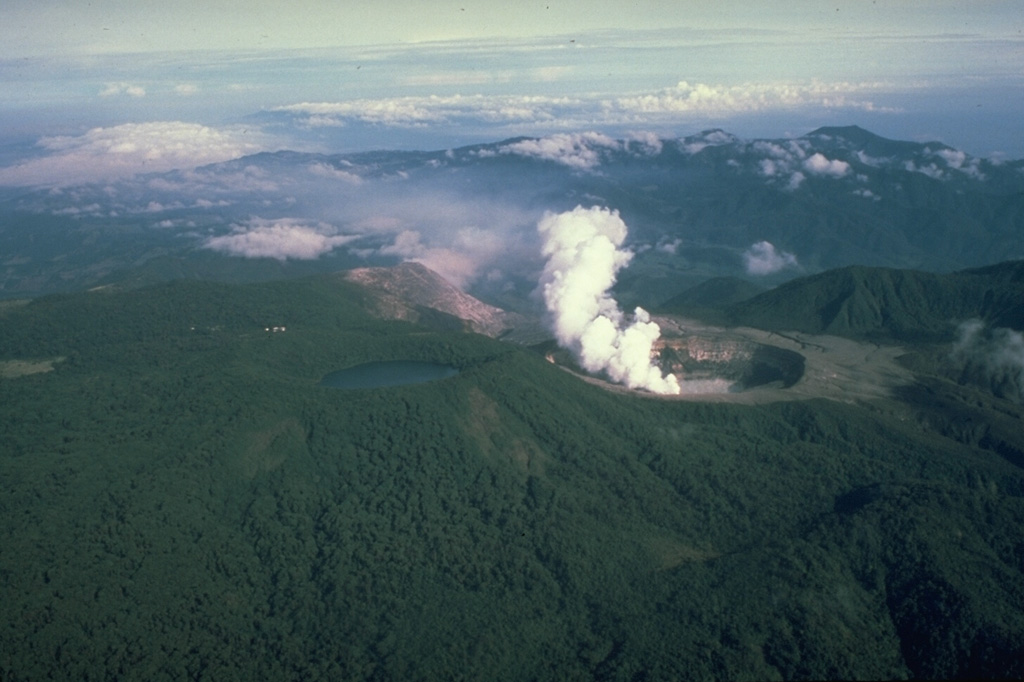
Poas (Costa Rica) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Poas Poas
Central America Volcanic Arc
|
The Observatorio Vulcanológico y Sismológico de Costa Rica-Universidad Nacional (OVSICORI-UNA) reported continuing gas-and-steam emissions with occasional minor amounts of ash at Poás during 18-24 June. Significant amounts of gas-and-steam emissions continued to be emitted, particularly from Boca A. On 18 June sulfur dioxide emissions averaged 273 tons per day (t/d), though they were as high as 1,500 t/d towards the second half of the week; overall, though levels remained high, there has beenwas a decreasing trend in sulfur dioxide emissions during over the previous few weeks, though levels remained high. Gas component ratios indicated less of a magmatic input. Incandescence continued to be visible and detected in infrared webcam views at Boca A vent. The hyperacid lake over Boca C continued to rise, notably on 15 June during a period of heavy rain. Minor amounts of ash in the gas-and-steam plume were visible in webcam images during 1725-1900 on 22 June. The plumes rose 500 m above the crater rim and drifted W. The Comisión Nacional de Emergencias (CNE) lowered the Alert Level to Yellow for Parque Nacional Volcán Poás and district of Toro Amarillo in the Canton of Sarchí (including the Desagüe, Agrio, Anonos, and Gorrión river basins) on 18 June due to decreasing activity. Additionally, the districts of Grecia, Zarcero, Naranjo, Poás, Sabanilla, Sarapiquí, and Rio Cuarto were no longer under “alert.” The Parque Nacional Volcán Poás remained closed. The Alert Level remained at 2 (the second lowest level on a four-level scale) and the Aviation Color Code remained at Yellow (the second lowest color on a four-color scale).
Sources: Observatorio Vulcanologico y Sismologico de Costa Rica-Universidad Nacional (OVSICORI-UNA), Comisión Nacional de Prevención de Riesgos y Atención de Emergencias (CNE)
|
Raung (Indonesia) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
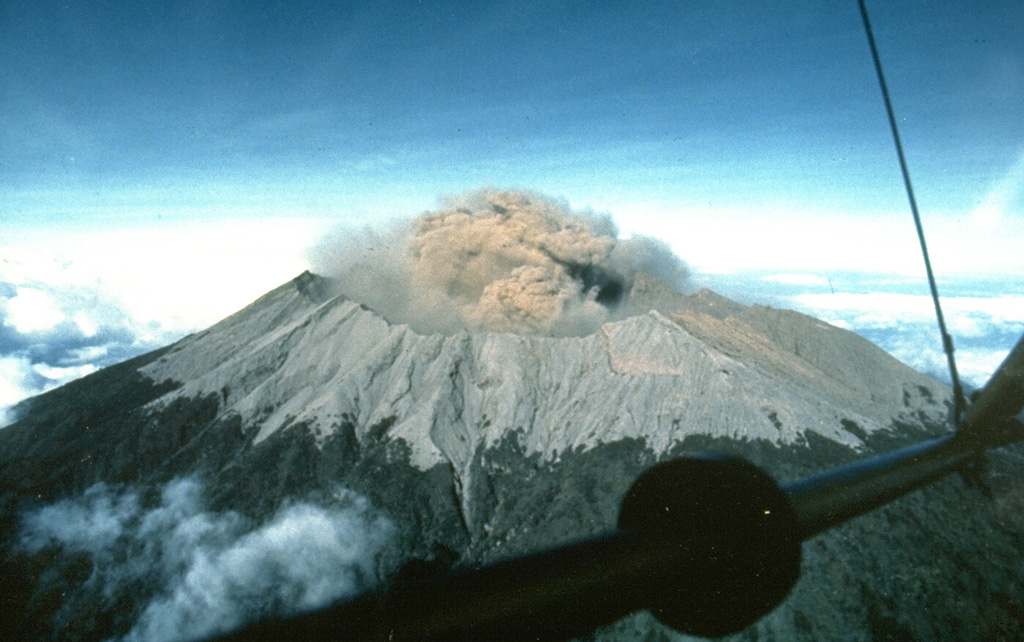 Raung Raung
Sunda Volcanic Arc
|
The Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG) reported that Raung continued to erupt during 18-25 June. Seismicity during 16-18 June fluctuated but increased overall. A thermal anomaly on the crater floor was identified in a satellite image on 18 June. Ash plumes rose 500-1,100 m above the crater rim and drifted in multiple directions. Ash plumes during 19-20 June rose as high has 2 km above the crater rim and drifted SE, S, SW, and W. Incandescent emanated from the summit crater during 0302-0500 on 20 June; seismicity decreased that same day. Ash plumes rose 1-2 km above the crater rim and drifted S, SW, and W. PVMBG noted that eruptive activity during 5-20 June produced ash plumes that mostly deposited ash around the crater area. An ash plume on each day during 21-23 June rose 300-600 m above the crater rim and drifted N, NW, W, and SW. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 1-4) and the public was warned to stay 3 km away from the summit crater.
Source: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as CVGHM)
|
Semeru (Indonesia) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
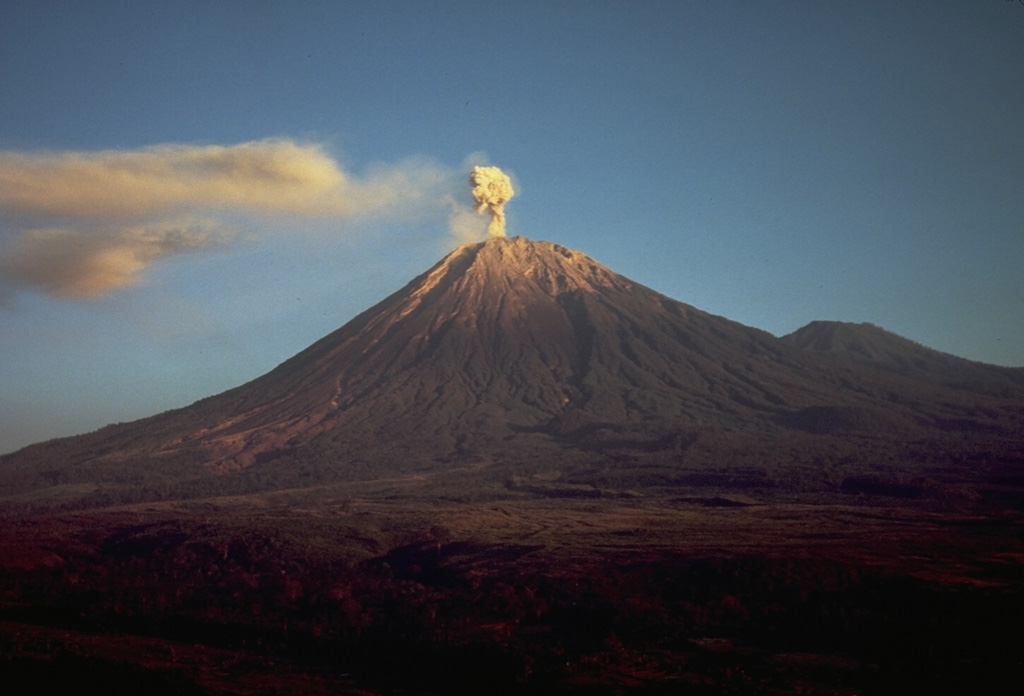 Semeru Semeru
Sunda Volcanic Arc
|
The Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG) reported that activity continued at Semeru during 18-24 June, often with multiple daily eruptive events recorded by the seismic network. White-and-gray ash plumes rose 400-1,200 m above the summit and drifted SW, N, and W; no plumes were visible on 22 and 24 June due to weather conditions. The Alert Level remained at 2 (the second lowest level on a scale of 1-4). The public was warned to stay at least 3 km away from the summit in all directions, 8 km from the summit to the SE, 500 m from the banks of the Kobokan drainage as far as 13 km from the summit, and to avoid other drainages including the Bang, Kembar, and Sat, due to lahar, avalanche, and pyroclastic flow hazards.
Source: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as CVGHM)
|
Sheveluch (Russia) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
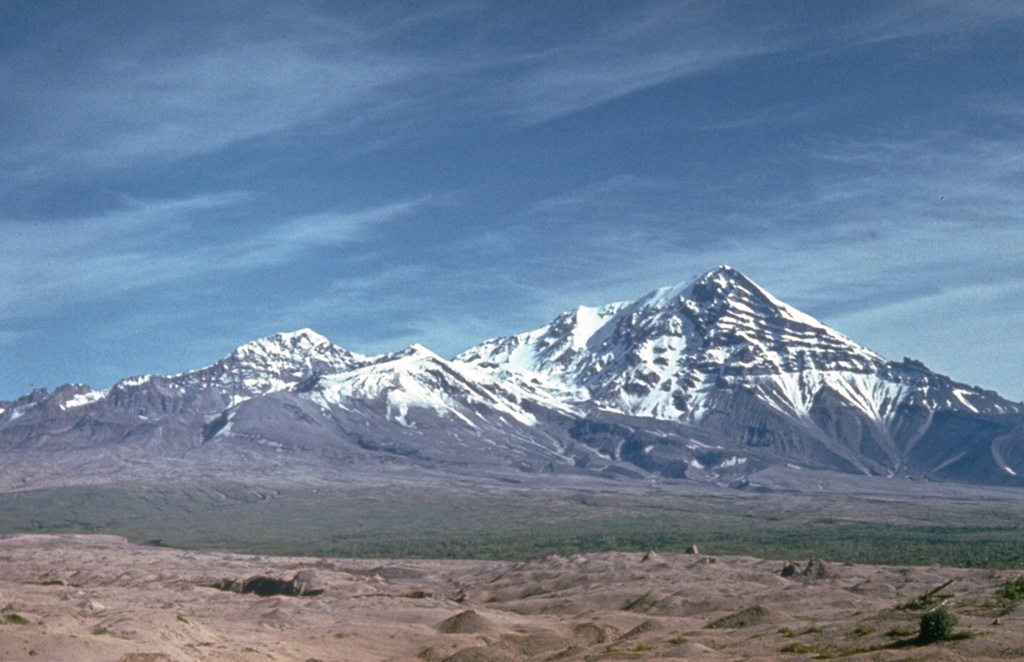 Sheveluch Sheveluch
Eastern Kamchatka Volcanic Arc
|
The Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT) reported that lava extrusion may have continued at Sheveluch’s “300 years of RAS” dome on the SW flank of Old Sheveluch and at the Young Sheveluch dome during 13-19 June. Thermal anomalies over the domes were identified in satellite images on 13, 15, and 18 June. The Far Eastern Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (FEB RAS) reported that minor steam, gas, and ash plumes rose as high as 4.3 km (14,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted mainly E and SE during 13-14 and 18 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC; specific events are in local time where noted.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (IVS) of the Far Eastern Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (FEB RAS)
|
Suwanosejima (Japan) | 18 June-24 June 2025 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
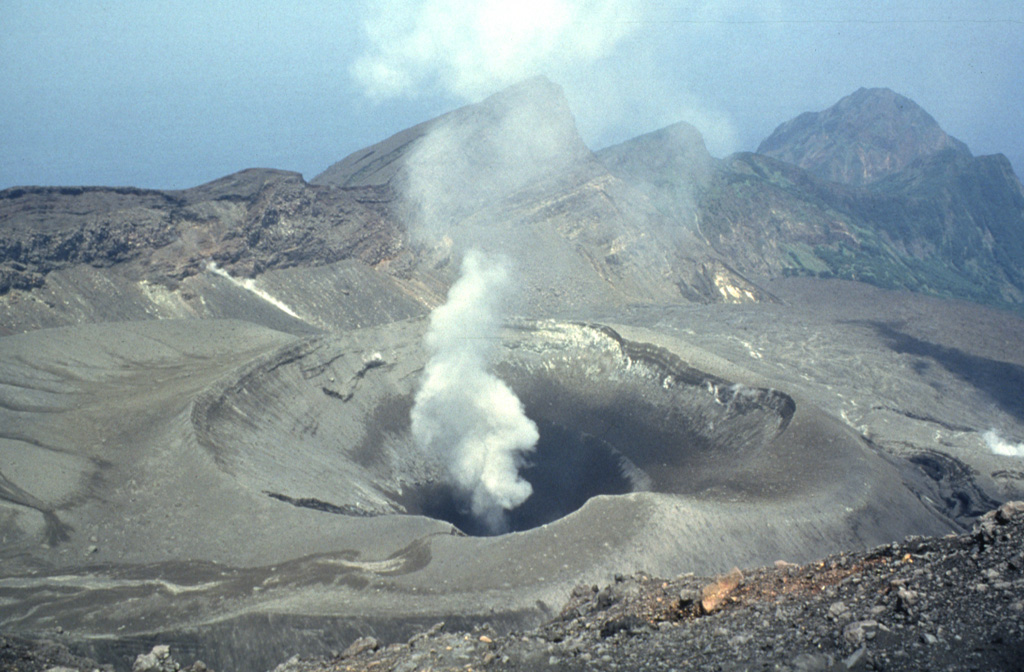 Suwanosejima Suwanosejima
Ryukyu Volcanic Arc
|
The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) reported that eruptive activity at Suwanosejima's Ontake Crater continued during 16-23 June. Incandescence was observed nightly in webcam images. Eruptive events at 0730 and at 0823 on 19 June and at 0331 on 21 June produced ash plumes that rose 1.3-1.6 km above the crater rim and drifted E, straight up, and NW, respectively. Another explosion at 1041 on 23 June generated an ash plume that rose 2.3 km above the crater rim and drifted NE. The Alert Level remained at 2 (the second level on a five-level scale) and the public was warned to be cautious within 1.5 km of the crater.
Source: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)
|
![]() Download Smithsonian / USGS Weekly Volcanic Activity Report Network Link
Download Smithsonian / USGS Weekly Volcanic Activity Report Network Link
 Kirishimayama
Kirishimayama Kuchinoerabujima
Kuchinoerabujima Lewotobi
Lewotobi Miyakejima
Miyakejima Aira
Aira Awu
Awu Dukono
Dukono Etna
Etna Great Sitkin
Great Sitkin Home Reef
Home Reef Ibu
Ibu Karymsky
Karymsky Kilauea
Kilauea Klyuchevskoy
Klyuchevskoy Lascar
Lascar Lewotolok
Lewotolok Marapi
Marapi Merapi
Merapi Nevado del Ruiz
Nevado del Ruiz Poas
Poas Raung
Raung Semeru
Semeru Sheveluch
Sheveluch Suwanosejima
Suwanosejima