Recently Published Bulletin Reports
Ambrym (Vanuatu) New effusive eruption during January 2024
Popocatepetl (Mexico) Daily gas-and-ash emissions, ashfall, and occasional explosions during August-November 2023
Reventador (Ecuador) Daily explosions, gas-and-ash emissions, and incandescent avalanches during August-November 2023
Erta Ale (Ethiopia) Strong lava lake activity and lava overflows during June-November 2023
Ubinas (Peru) New eruption with explosions and ash plumes during June-December 2023
Kanaga (United States) Small explosion on 18 December 2023
Klyuchevskoy (Russia) New eruption consisting of Strombolian activity, lava flows and fountains, and ash plumes during June-December 2023
Agung (Indonesia) Three eruptive events reported in April, May, and December 2022
Saunders (United Kingdom) Persistent thermal anomalies from the summit crater lava lake during February 2023-January 2024
Tengger Caldera (Indonesia) Minor ash emission in December 2023; persistent weak thermal anomaly in the Bromo crater
Shishaldin (United States) New eruption with significant Strombolian explosions, ash plumes, and ashfall
Ioto (Japan) New eruption with discolored water, ejecta, and floating pumice during October-December 2023
Ambrym (Vanuatu) — February 2024  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Ambrym
Vanuatu
16.25°S, 168.12°E; summit elev. 1334 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
New effusive eruption during January 2024
Ambrym contains a 12-km-wide caldera and is part of the New Hebrides Arc, located in the Vanuatu archipelago. The two currently active craters within the caldera are Benbow and Marum, both of which have produced lava lakes, explosions, lava flows, and gas-and-ash emissions. The previous eruption occurred during late January 2022 and was characterized by ash plumes, sulfur dioxide plumes, and crater incandescence (BGVN 47:05). This report covers a new, short eruption during January 2024, which consisted of a lava effusion and an explosion. Information comes from the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) and satellite data.
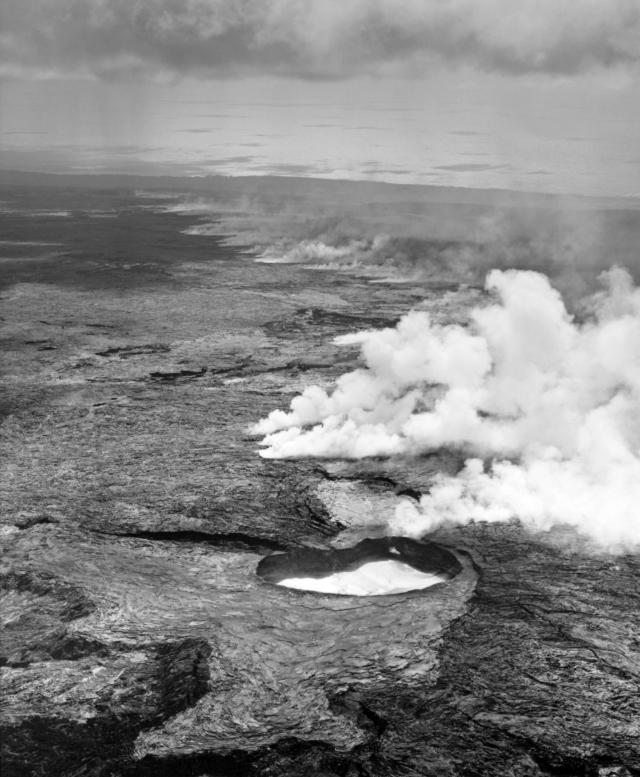
VMGD reported that at 2217 on 13 January an eruption began at Benbow Crater, based on webcam and seismic data. The eruption was characterized by a loud explosion, intense crater incandescence (figure 55), and gas-and-steam emissions. As a result, the Volcano Alert Level (VAL) was raised from 1 to 3 (on a scale of 0-5). A lava flow was reported in Benbow Crater, which lasted for four days. Satellite data showed that 1,116 tons of sulfur dioxide per day (t/d) were emitted on 14 January (figure 56). During the morning of 15 January, ground reports noted loud explosions and minor earthquakes. The sulfur dioxide flux on 15 January was 764 t/d. During 15-17 January activity decreased according to webcam images, seismic data, and field observations. No sulfur dioxide emissions were reported after 15 January. Gas-and-ash emissions also decreased, although they continued to be observed through 31 January, and crater incandescence was less intense (figure 57). The VAL was lowered to 2 on 17 January.
Geologic Background. Ambrym is a large basaltic volcano with a 12-km-wide caldera formed during a major Plinian eruption with dacitic pyroclastic flows about 1,900 years ago. A thick, almost exclusively pyroclastic sequence, initially dacitic then basaltic, overlies lava flows of a pre-caldera shield volcano. Post-caldera eruptions, primarily from Marum and Benbow cones, have partially filled the caldera floor and produced lava flows that ponded on the floor or overflowed through gaps in the caldera rim. Post-caldera eruptions have also formed a series of scoria cones and maars along a fissure system oriented ENE-WSW. Eruptions have been frequently reported since 1774, though mostly limited to extra-caldera eruptions that would have affected local populations. Since 1950 observations of eruptive activity from cones within the caldera or from flank vents have occurred almost yearly.
Information Contacts: Geo-Hazards Division, Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD), Ministry of Climate Change Adaptation, Meteorology, Geo-Hazards, Energy, Environment and Disaster Management, Private Mail Bag 9054, Lini Highway, Port Vila, Vanuatu (URL: http://www.vmgd.gov.vu/, https://www.facebook.com/VanuatuGeohazardsObservatory/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Popocatepetl (Mexico) — January 2024  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Popocatepetl
Mexico
19.023°N, 98.622°W; summit elev. 5393 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Daily gas-and-ash emissions, ashfall, and occasional explosions during August-November 2023
Popocatépetl, located 70 km SE of Mexica City, Mexico, contains a 400 x 600 m-wide summit crater. Records of activity date back to the 14th century; three Plinian eruptions, the most recent of which took place about 800 CE, have occurred since the mid-Holocene, accompanied by pyroclastic flows and voluminous lahars that swept basins below the volcano. The current eruption period began in January 2005, characterized by numerous episodes of lava dome growth and destruction within the summit crater. Recent activity has been characterized by daily gas-and-ash emissions, ashfall, and explosions (BGVN 48:09). This report covers similar activity during August through November 2023, according to daily reports from Mexico's Centro Nacional de Prevención de Desastres (CENAPRED) and various satellite data.
Daily gas-and-steam emissions, containing some amount of ash, continued during August through November 2023. CENAPRED reported the number of low-intensity gas-and-ash emissions or “exhalations” and the minutes of tremor, which sometimes included harmonic tremor in their daily reports (figure 220). A total of 21 volcano-tectonic (VT) tremors were detected throughout the reporting period. The average number of exhalations was 117 per day, with a maximum number of 640 on 25 September. Frequent sulfur dioxide plumes that exceeded two Dobson Units (DU) and drifted in multiple directions were visible in satellite data from the TROPOMI instrument on the Sentinel-5P satellite (figure 221).
Activity during August was relatively low and mainly consisted of occasional explosions, ash emissions, and light ashfall. There were 30 explosions (25 minor explosions and four moderate explosions), and nine VT-type events detected. An average number of 60 exhalations occurred each day, which mostly consisted of water vapor, volcanic gases, and a small amount of ash. On 2 August the National Center for Communications and Civil Protection Operations (CENACOM) reported light ashfall in Ocuituco (22 km SW), Yecapixtla (31 km SW), Cuautla (43 km SW), and Villa de Ayala (47 km SW). On 7 August light ashfall was observed in Atlautla (16 km W). A minor explosion at 0305 on 11 August was accompanied by crater incandescence. Explosions at 0618 on 13 August produced a gas-and-ash plume that rose above the summit, and at 0736 another explosion produced a puff of gas-and-ash (figure 222). Two minor explosions were detected at 0223 and 0230 on 16 August that generated eruptive columns with low ash content rising 800 m and 700 m above the crater, respectively. On 24 August an eruptive event lasted 185 minutes and consisted of light ash emissions that did not exceed 300 m above the crater. According to the Washington VAAC, ash plumes identified in daily satellite images rose to 4.6-7.6 km altitude and drifted in multiple directions, the highest of which occurred on 29 August.
There was an average of 156 exhalations each day during September, a monthly total of seven VT-type events, and 29 explosions, 14 of which were minor and nine of which were moderate. A gas-and-ash plume rose to 2 km above the summit and drifted WSW at 1216 on 1 September. CENACOM reported at 1510 observations of ashfall in Ozumba (18 km W), Atlautla, Tepetlixpa (20 km W), and Ecatzingo (15 km SW), as well as in Morelos in Cuernavaca (65 km WSW), Temixco (67 km WSW), Huitzilac (67 km W), Tepoztlán (49 km W), and Jiutepec (59 km SW). The next day, gas-and-ash plumes rose to 2 km above the summit (figure 223). At 1100 ashfall was reported in Amecameca (15 km NW), Ayapango (24 km WNW), Ozumba, Juchitepec, Tenango del Aire (29 km WNW), Atlautla, and Tlalmanalco (27 km NW). A gas-and-ash plume rose to 1 km above the summit and drifted WNW at 1810. During 5-6, 8-9, 12, 14, 19, and 24-25 September ashfall was reported in Amecameca, Atlautla, Ozumba, Tenango del Aire, Tepetlixpa, Juchitepec, Cuernavaca, Ayala, Valle de Chalco (44 km NW), Ixtapaluca (42 km NW), La Paz (50 km NW), Chimalhuacán, Ecatepec, Nezahualcóyotl (60 km NW), Xochimilco (53 km SE), Huayapan, Tetela del Volcano (20 km SW), Yautepec (50 km WSW), Cuautla (43 km SW), Yecapixtla (30 km SW) and possibly Tlaltizapán (65 km SW), Tlaquiltenango, and Tepalcingo. According to the Washington VAAC, ash plumes identified in daily satellite images rose to 5.8-9.1 km altitude and drifted in multiple directions, the highest of which was identified during 1-2 August.
Activity during October and November was relatively low. An average of 179 exhalations consisting of gas-and-steam and ash emissions were reported during October and 73 during November. Only one VT-type event and two explosions were detected during October and four VT-type events and one explosion during November. A satellite image from 0101 on 14 October showed ash fanning out to the NW at 6.7 km altitude and an image from 0717 showed a continuously emitted ash plume drifting WNW and NW at the same altitude. Ash emissions at 1831 on 14 October were ongoing and visible in webcam images slowly drifting W at an altitude of 6.4 km altitude (figure 224). On 24 October a tremor sequence began at 0310 that generated a gas-and-ash plume that rose 800 m above the summit and drifted W. Another tremor sequence occurred during 1305-1900 on 25 October that consisted of continuous ash emissions. Ash plumes identified in daily satellite images rose to 5.5-8.5 km altitude and drifted in different directions during October, according to the Washington VAAC. The highest ash plume was detected on 23 October. During 10-13 November ash plumes rose to 6.7 km altitude and drifted N, NNW, NE, and NW. On 13 November a M 1.5 VT-type event was detected at 0339 and light ashfall was reported in Amecameca, Cocotitlán (34 km NW), and Tenango del Aire, and Ocuituco. On 14 November ash plumes rose to 6 km altitude and drifted N, NE, and SE and light ashfall was reported in Cuernavaca (64 km W). The Washington VAAC reported frequent ash plumes that rose to 5.8-7.9 km altitude and drifted in several directions; the highest ash plume was recorded on 28 November.
Satellite data. MODIS thermal anomaly data provided through MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) showed frequent low-to-moderate thermal anomalies during the reporting period (figure 225). The intensity of the anomalies was lower compared to previous months. According to data from MODVOLC thermal alerts, a total of ten hotspots were detected at the summit crater on 2 August and 2, 4, 9, 19, and 26 September. Thermal activity in the summit crater was visible in infrared satellite data and was sometimes accompanied by ash plumes, as shown on 17 November (figure 226).
Geologic Background. Volcán Popocatépetl, whose name is the Aztec word for smoking mountain, rises 70 km SE of Mexico City to form North America's 2nd-highest volcano. The glacier-clad stratovolcano contains a steep-walled, 400 x 600 m wide crater. The generally symmetrical volcano is modified by the sharp-peaked Ventorrillo on the NW, a remnant of an earlier volcano. At least three previous major cones were destroyed by gravitational failure during the Pleistocene, producing massive debris-avalanche deposits covering broad areas to the south. The modern volcano was constructed south of the late-Pleistocene to Holocene El Fraile cone. Three major Plinian eruptions, the most recent of which took place about 800 CE, have occurred since the mid-Holocene, accompanied by pyroclastic flows and voluminous lahars that swept basins below the volcano. Frequent historical eruptions, first recorded in Aztec codices, have occurred since Pre-Columbian time.
Information Contacts: Centro Nacional de Prevención de Desastres (CENAPRED), Av. Delfín Madrigal No.665. Coyoacan, México D.F. 04360, México (URL: http://www.cenapred.unam.mx/, Daily Report Archive https://www.gob.mx/cenapred/archivo/articulos); Washington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), Satellite Analysis Branch (SAB), NOAA/NESDIS OSPO, NOAA Science Center Room 401, 5200 Auth Rd, Camp Springs, MD 20746, USA (URL: www.ospo.noaa.gov/Products/atmosphere/vaac, archive at: http://www.ssd.noaa.gov/VAAC/archive.html); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); NASA Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Reventador (Ecuador) — January 2024  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Reventador
Ecuador
0.077°S, 77.656°W; summit elev. 3562 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Daily explosions, gas-and-ash emissions, and incandescent avalanches during August-November 2023
Volcán El Reventador, located in Ecuador, is a stratovolcano with a 4-km-wide avalanche scarp open to the E that was formed by edifice collapse. The largest recorded eruption took place in 2002 producing a 17-km-high eruption column, pyroclastic flows that traveled as far as 8 km, and lava flows from summit and flank vents. Recorded eruptions date back to the 16th century and have been characterized by explosive events, lava flows, ash plumes, and lahars. Frequent lahars have built deposits on the scarp slope. The current eruption period began in July 2008 and has recently been characterized daily explosions, gas-and-ash emissions, and block avalanches (BGVN 48:08). This report covers similar activity during August through November 2023 using daily reports from Ecuador's Instituto Geofisico (IG-EPN) and satellite data.
During August through November 2023, IG-EPN reported daily explosions, gas-and-ash plumes that rose as high as 1.3 km above the crater, and frequent crater incandescence, often accompanied by incandescent block avalanches that affected one or multiple flanks. More daily explosions were detected during November, with an average total of 46 per day.
Table 19. Monthly summary of explosions and plume heights recorded at Reventador from August through November 2023. Data could not be collected for 29-30 September 2023 and 6-23 October 2023. Data courtesy of IG-EPN (August-November 2023 daily reports).
| Month |
Average number of explosions per day |
Max plume height above the crater rim (km) |
| Aug 2023 |
32 |
1.3 |
| Sep 2023 |
30 |
1 |
| Oct 2023 |
31 |
1.3 |
| Nov 2023 |
46 |
1.2 |
Activity during August consisted of 6-75 daily explosions, nighttime crater incandescence, and incandescent avalanches of material. Frequent seismicity was mainly characterized by long-period (LP) events, harmonic tremor (TRARM), tremor-type (TRE), and volcano tectonic (VT)-type events. Daily gas-and-ash emissions rose 200-1,300 m above the summit and drifted W, SW, NW, NE, N, and E, based on webcam and satellite images. The Washington VAAC also reported occasional ash plumes that rose 400-1,600 m above the crater and drifted NW. Avalanches of incandescent material were reported during 1-2, 6-7, 9-14, 16-17, 18-21, and 26-29 August, which traveled 500-900 m below the crater and affected multiple flanks (figure 180). During 24-25 August incandescent material was ejected 300 m above the crater.
Gas-and-ash emissions and seismicity characterized by LP, VT, TRARM, and TRE-type events continued during September; data were not available for 29-30 September. Daily gas-and-ash emissions rose 200-1,000 m above the crater and generally drifted W, NW, and SW (figure 181). Near-daily explosions ranged from 16-53 per day, often accompanied by incandescent avalanches, which affected one or multiple flanks and traveled 100-800 m below the crater. During 2-3 September incandescent material was ejected 200 m above the crater and was accompanied by blocks rolling down the flanks. During 16-17 September incandescent material was ejected 100-200 m above the crater and avalanches descended 600 m below the crater. During 21-22 and 24-26 September incandescent material was ejected 100-300 m above the crater. According to the Washington VAAC, ash plumes rose 700 m above the crater and drifted SW, W, and NW on 3, 16, and 20 September, respectfully.
During October, daily explosions, gas-and-ash plumes, and crater incandescence continued, with 16-40 explosions recorded each day (figure 182); data was not available for 6-23 October. Seismicity consisted of LP, TRE, and TRARM-type events. Gas-and-ash emissions rose 200-1,000 m above the crater and drifted W, SW, NW, SSW, NNW, and NE. The Washington VAAC reported that ash plumes rose 1-1.3 km above the crater and drifted W, SW, and NW during 1-5 October. During 30 September-1 October incandescent avalanches descended 700 m below the crater. Ejected material rose 200 m above the crater during 2-5 October and was accompanied by avalanches of material that traveled 250-600 m below the crater rim; incandescent avalanches were also reported during 23-29 October.
Daily explosions, LP, TRARM, VT, and TRE-type events, crater incandescence, and avalanches of material continued during November. There were 26-62 daily explosions detected throughout the month. Gas-and-ash emissions rose 300-1,200 m above the crater and drifted in different directions (figure 183). The Washington VAAC reported that ash plumes rose 700-1,620 m above the crater and drifted NW, W, WNW, SW, E, SE, and ESE. Frequent incandescent avalanches descended 500-1,000 m below the crater. Explosions ejected material 100-300 m above the crater during 4-7, 11-12, and 19-23 November.
Satellite data. MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) analysis of MODIS satellite data showed intermittent thermal anomalies of low-to-moderate power (figure 184). Thermal activity mainly consisted of incandescent avalanches descending the flanks due to the frequently detected explosions. The MODVOLC hotspot system identified a total of ten hotspots on 3 August, 7, 18, 12, 22, and 28 September, and 7, 9, and 19 November.
Geologic Background. Volcán El Reventador is the most frequently active of a chain of Ecuadorian volcanoes in the Cordillera Real, well east of the principal volcanic axis. The forested, dominantly andesitic stratovolcano has 4-km-wide avalanche scarp open to the E formed by edifice collapse. A young, unvegetated, cone rises from the amphitheater floor to a height comparable to the rim. It has been the source of numerous lava flows as well as explosive eruptions visible from Quito, about 90 km ESE. Frequent lahars in this region of heavy rainfall have left extensive deposits on the scarp slope. The largest recorded eruption took place in 2002, producing a 17-km-high eruption column, pyroclastic flows that traveled up to 8 km, and lava flows from summit and flank vents.
Information Contacts: Instituto Geofísico, Escuela Politécnica Nacional (IG-EPN), Casilla 17-01-2759, Quito, Ecuador (URL: http://www.igepn.edu.ec/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/).
Erta Ale (Ethiopia) — January 2024  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Erta Ale
Ethiopia
13.601°N, 40.666°E; summit elev. 585 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Strong lava lake activity and lava overflows during June-November 2023
Erta Ale in Ethiopia has a 50-km-wide edifice that rises more than 600 m from below sea level in the Danakil depression. The summit caldera is 0.7 x 1.6 km and contains at least two pit craters (North and South). Another larger 1.8 x 3.1-km-wide depression is located SE of the summit and is bounded by curvilinear fault scarps on the SE side. Lava flows from fissures have traveled into the caldera and locally overflowed the crater rim. The current eruption has been ongoing since 1967, with at least one long-term active lava lake present in the summit caldera. Recent fissure eruptions from 2017 have occurred on the SE flank (BGVN 42:07). Recent activity has been characterized by minor thermal activity at the S crater and an active lava lake at the N crater (BGVN 48:06). This report covers strong lava lake activity primarily at the N pit crater during June through November 2023 using information from satellite infrared data.
Infrared satellite images generally showed an active lava lake as the N pit crater and variable thermal activity at the S pit crater during the reporting period. On 7 June two strong thermal anomalies were detected at the S pit crater and two weaker anomalies were visible at the N pit crater. Those anomalies persisted throughout the month, although the intensity at each declined. On 2 July a possible lava lake was identified at the S pit crater, filling much of the crater. On 7 July both pit craters contained active lava lakes (figure 120). By 12 July the thermal activity decreased; two smaller anomalies were visible through the rest of the month at the S pit crater while the N pit crater showed evidence of cooling.
Renewed lava lake activity was identified at the N pit crater, based on a satellite image from 11 August, with two smaller anomalies visible at the S pit crater. By 16 August the lava lake in the N pit had begun to cool and only a small thermal anomaly was identified. Activity restarted on 21 August, filling much of the E and SE part of the N pit crater. The thermal activity at the N pit crater intensified on 31 August, particularly in the NW part of the crater. On 5 September lava filled much of the N pit crater, overflowing to the W and SW. During at least 10-20 September thermal activity at both craters were relatively low.
According to a satellite image on 25 September, strong thermal activity resumed when lava overflowed the N pit crater to the S, SW, and NE (figure 120). A satellite image taken on 5 October showed lava flows from the N had spilled into the S and begun to cool, accompanied by two weak thermal anomalies at the S pit crater. On 15 October lava flows again traveled SE and appeared to originate from the S pit crater (figure 120). Following these events, smaller thermal anomalies were visible on the SE rim of the N pit crater and within the S pit crater.
Lava was visible in the NW part of the N pit crater according to a satellite image taken on 4 November. By 9 November the intensity had decreased, and the lava appeared to cool through the rest of the month; young lava flows were visible along the W side of the S pit crater on 24 and 29 November. Lava flows occurred at the N pit crater trending NE-SW and along the E side on 29 November (figure 120).
During the reporting period, the MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) thermal detection system recorded consistent activity during the first half of 2023 (figure 121). Beginning in June 2023, thermal activity increased and remained variable in intensity through the end of the year indicating the presence of an active lava lake and lava flows. The MODVOLC thermal detection system registered a total of 63 anomalies during 7, 8, and 23 July, 10 and 18 August, 3, 5, 16, 23, 24, and 25 September, 15 and 20 October, and 21, 24, 26, 28, and 30 November. Some of these stronger thermal anomalies were also detected in Sentinel-2 infrared satellite images that showed an active lava lake at the N pit crater and subsequent lava overflows from both pit craters (figure 120).
Geologic Background. The Erta Ale basaltic shield volcano in Ethiopia has a 50-km-wide edifice that rises more than 600 m from below sea level in the Danakil depression. The volcano includes a 0.7 x 1.6 km summit crater hosting steep-sided pit craters. Another larger 1.8 x 3.1 km wide depression elongated parallel to the trend of the Erta Ale range is located SE of the summit and is bounded by curvilinear fault scarps on the SE side. Basaltic lava flows from these fissures have poured into the caldera and locally overflowed its rim. The summit caldera usually also holds at least one long-term lava lake that has been active since at least 1967, and possibly since 1906. Recent fissure eruptions have occurred on the N flank.
Information Contacts: MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Ubinas
Peru
16.345°S, 70.8972°W; summit elev. 5608 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
New eruption with explosions and ash plumes during June-December 2023
Ubinas, located in Peru, has had 24 eruptions since 1550, which more recently have been characterized by explosions, ash plumes, and lahars (BGVN 45:03). This report covers a new eruption during June through December 2023 based on reports from Instituto Geofisico del Peru (IGP), Instituto Geológico Minero y Metalúrgico (INGEMMET), and satellite data.
IGP reported that seismic unrest began on 17 May, followed by an increase in seismicity during the second half of the month. There were 168 volcano-tectonic (VT) earthquakes detected, which are associated with rock fracturing processes, and 171 long-period (LP) earthquakes recorded during 16-24 May, which are associated with the movement of volcanic fluid.
Seismicity and fumarolic activity at the crater level continued to increase during June. During 1-18 June there was an average of 631 VT-type earthquakes and 829 LP earthquakes recorded. Webcams showed gas-and-steam emissions rising 500 m above the summit and drifting SE. In addition, the maximum value of emitted sulfur dioxide during this period was 337 tons/day. During 19-22 June an average of 315 VT-type events and 281 LP-type events and tremor were reported. On 20 June the Gobierno Regional de Moquegua raised the Volcano Alert Level (VAL) to Yellow (the second level on a four-color scale), based on recommendations from IGP. Webcam images showed ash emissions rising 1 km above the summit and drifting E at 0011 on 22 June, which IGP reported marked the start of a new eruption. Sporadic and diffuse gas-and-ash emissions continued to rise 800-1,500 m above the summit through the rest of the month and drifted mainly E, N, NW, W, SW, and NE. During 23-25 June there was an average of 402 VT-type earthquakes and 865 LP-type events detected. During 26-28 June the earthquakes associated with ash emissions, which have been observed since 22 June, decreased, indicating the end of the phreatic phase of the eruption, according to IGP. A thermal anomaly was detected in the crater for the first time on 26 June and was periodically visible through 4 July (figure 61). During 29-30 June there was an average of 173 VT-type earthquakes and 351 LP-type events recorded, and sulfur dioxide values ranged between 600 t/d and 1,150 t/d. During this same time, seismicity significantly increased, with 173 VT-type earthquakes, 351 LP-type events, and harmonic tremor which signified rising magma. The Gobierno Regional de Moquegua raised the Alert Level to Orange (the third level on a four-color scale) on 30 June based on the recommendation from IGP and INGEMMET.
Activity during July consisted of continued seismicity and gas-and-ash emissions. Gas-and-ash emissions rose as high as 5 km above the summit and drifted as far as 40 km in different directions during 1, 4-6, 16, 20-23, 26, and 29 July, based on webcam and satellite images. During 1-2 July an average of 72 VT-type earthquakes and 114 LP-type events were detected. In addition, during that time, ashfall was reported in Ubinas (6.5 km SSE) and Querapi (4.5 km SE). During 2-3 July INGEMMET reported gas-and-ash plumes rose 400 m above the summit and drifted SW, causing ashfall in downwind areas as far as 5 km. During 3-4 July there was an average of 69 VT-type earthquakes and 96 LP-type events reported. On 4 July starting around 0316 there were 16 seismic signals associated with explosive activity and ash emissions detected (figure 62). According to INGEMMET an explosion ejected ballistics and generated a gas-and-ash plume that rose 5.5 km above the summit and drifted SW and S. Ashfall was recorded in Querapi, Ubinas, Sacohaya (7 km SSE), Anascapa (11 km SE), San Miguel (10 km SE), Tonohaya (7 km SSE), Huatahua, Huarina, Escacha (9 km SE), and Matalaque (17 km SSE), and was most significant within 5 km of the volcano. IGP noted that ash fell within a radius of 20 km and deposits were 1 mm thick in towns in the district of Ubinas.
During 5-9 July an average of 67 VT-type events and 47 LP-type events were reported. A period of continuous gas-and-ash emissions occurred on 5 July, with plumes drifting more than 10 km SE and E. A total of 11 seismic signals associated with explosions also detected on 6, 16, 17, and 22 July. On 6 July explosions recorded at 0747 and 2330 produced gas-and-ash plumes that rose as high as 3.5 km above the summit and drifted as far as 30 km NW, NE, SE, and S. According to the Washington VAAC the explosion at 0747 produced a gas-and-ash plume that rose to 9.1 km altitude and drifted SW, which gradually dissipated, while a lower-altitude plume rose to 7.6 km altitude and drifted NE. Gobierno Regional de Moquegua declared a state of emergency for districts in the Moquegua region, along with Coalaque Chojata, Icuña, Lloque, Matalaque, Ubinas, and Yunga of the General Sánchez Cerro province, to be in effect for 60 days. On 7 July an ash plume rose to 7.3 km altitude and drifted E at 0320. At 0900 and 1520 gas-and-steam plumes with diffuse ash rose to 6.7 km altitude and drifted SE. Small ash emissions were visible in satellite and webcam images at 0920 and 1520 on 8 July and rose as high as 6.4 km altitude and drifted SE. During 10-16 July there was an average of 80 VT-type earthquakes and 93 LP-type events reported. INGEMMET reported that during 9-11 July sulfur dioxide emissions were low and remained around 300 t/d.
During 17-23 July an average of 46 VT-type events and 122 LP-type events were detected. On 20 July at 0530 an explosion generated an ash plume that rose 3-4.5 km above the crater and drifted 65 km toward Arequipa. An explosion on 21 July at 0922 produced a gas-and-ash plume that rose 5 km above the summit (figure 63). Ashfall was reported in Querapi, Ubinas, Tonohaya, Anascapa, Sacohaya, San Miguel, Escacha, Huatagua (14 km SE), Huarina, Escacha (9 km SE), Matalaque, Logén, Santa Lucía de Salinas, and Salinas de Moche. An explosion on 22 July at 1323 generated an ash plume that rose 5.5 km above the summit and drifted NE, E, and SE. During 24-30 July there were five volcanic explosions detected and an average of 60 VT-type events and 117 LP-type events. An explosion on 29 July at 0957 produced an ash plume that rose 2.5 km above the summit and drifted as far as 40 km NE, E, and SE. As a result, significant ashfall was reported in Ubinas and Matalaque.
During August, explosions, gas-and-ash emissions, and seismic earthquakes persisted. During 31 July to 6 August there was an average of 115 VT-type events and 124 LP-type events reported. Gas-and-ash emissions were observed during 1, 6, 10, 13-14, 17-18, 21, and 23 August and they drifted as far as 20 km in different directions; on 14 and 18 August continuous ash emissions extended as far as 40 km S, SE, and NE. An explosion was detected at 2110 on 1 August, which generated a gas-and-ash plume that rose 5.4 km above the summit and drifted SE and E. The explosion ejected blocks and incandescent material as far as 3 km from the crater onto the SW, S, and SE flanks. Ashfall was reported in Ubinas and Chojata (19 km ESE). Gas-and-ash emissions rose as high as 2 km above the summit and drifted in different directions through 5 August, sometimes causing ashfall within a 15-km-radius. An explosion at 0009 on 6 August ejected blocks and produced a gas-and-ash plume that rose 1.4 km above the summit and drifted SE and E, which caused ashfall in Ubinas and Chojata and other areas within a 30-km radius. During 7-13 August there was an average of 102 VT-type events and 60 LP-type events detected. INGEMMET reported that sulfur dioxide emissions were low on 7 August and averaged 400 t/d.
One volcanic explosion that was recorded on 10 August, producing gas-and-ash emissions that rose 2.4 km above the summit and drifted as far as 25 km SE and E. Ashfall was observed in Ubinas, Matalaque, and Chojata. During 10-11 and 13-14 August sulfur dioxide values increased slightly to moderate levels of 2,400-3,700 t/d. The average number of VT-type events was 104 and the number of LP-type events was 71 during 14-21 August. Two explosions were detected at 0141 and 0918 on 21 August, which produced gas-and-ash emissions that rose 3.5 km above the summit and drifted 50 km N, NE, W, and NW (figure 64). The explosion at 0918 generated an ash plume that caused ashfall in different areas of San Juan de Tarucani. During 22-27 August the average number of VT-type events was 229 and the average number of LP-type events was 54. An explosion was reported at 1757 on 25 August, which generated a gas-and-ash plume that rose 4.2 km above the summit and drifted in multiple directions as far as 25 km. During 28 August through 3 September gas-and-ash emissions rose 600 m above the summit and drifted as far as 5 km E and SE. During this time, there was an average of 78 VT-type events and 42 LP-type events.
Gas-and-steam emissions rose 600-2,600 m above the summit and drifted as far as 15 km in multiple directions during September. During 4-10 and 11-17 September there was an average of 183 VT-type events and 27 LP-type events, and 114 VT-type events and 86 LP-type events occurred, respectively. On 14 September an explosion at 1049 generated a gas-and-ash plume that rose 2.6 km above the summit and drifted as far as 15 km E, NE, SE, and S (figure 65). During 14-16 September an average of three hours of seismic tremor related to ash emissions was recorded each day. During 18-24 September the average number of VT-type events was 187 and the average number of LP-type events was 45. During 25 September and 1 October, there was an average number of 129 VT-type events and 52 LP-type events detected.
Relatively low activity was reported during October; during 2-9 October there was an average number of 155 VT-type events and 27 LP-type events recorded. On 1 October at 1656 seismic signals associated with ash emissions were recorded for an hour and thirty minutes; the ash plumes rose as high as 1 km above the summit and drifted more than 10 km E, S, and SW. On 4 October IGP reported that an ash plume drifted more than 15 km SW and S. Sulfur dioxide emissions were 1,250 t/d on that day. On 7 October a gas-and-ash plume rose 1.9 km above the summit and drifted NE, E, and SE. On 4 October the amount of sulfur dioxide emissions was 1,250 t/d. During 10-15 October there was an average number of 225 VT-type events and 34 LP-type events recorded. On 11 October at 1555 a single seismic signal associated with an ash pulse was recorded; the gas-and-ash emissions rose 700 m above the summit and drifted SW and W. There was an average of 204 VT-type events and 25 LP-type events detected during 16-22 October and 175 VT-type events and 17 LP-type events during 23-29 October. On 27 October at 0043 a gas-and-ash emission rose 500 m above the summit and drifted SE and E. A minor thermal anomaly was visible on the crater floor. During 30 October to 5 November there was an average of 95 VT-type events and 24 LP-type events detected.
Activity remained relatively low during November and December and consisted mainly of gas-and-steam emissions and seismicity. Gas-and-steam emissions rose 900-1,100 m above the summit and drifted mainly E, SE, N, and NE. IGP detected an average of 166 VT-type events and 38 LP-type events during 6-15 November, 151 VT-type events and 17 LP-type events during 16-30 November, 143 VT-type events and 23 LP-type events during 1-15 December, and 129 VT-type events and 21 LP-type events during 16-31 December. No explosions or ash emissions were recorded during November. The VAL was lowered to Yellow (the second level on a four-color scale) during the first week of November. According to the Washington VAAC an ash emission was identified in a satellite image at 0040 on 11 December that rose to 5.5 km altitude and drifted NW. Webcam images at 0620 and 1220 showed continuous gas-and-steam emissions possibly containing some ash rising as high as 7 km altitude. Webcam images during 10-31 December showed continuous gas-and-ash emissions that rose as high as 2.5 km above the summit and drifted up to 5 km NW, W, and SW. On 12 December continuous ash emissions drifted more than 10 km N and NW.
Geologic Background. The truncated appearance of Ubinas, Perú's most active volcano, is a result of a 1.4-km-wide crater at the summit. It is the northernmost of three young volcanoes located along a regional structural lineament about 50 km behind the main volcanic front. The growth and destruction of Ubinas I was followed by construction of Ubinas II beginning in the mid-Pleistocene. The upper slopes of the andesitic-to-rhyolitic Ubinas II stratovolcano are composed primarily of andesitic and trachyandesitic lava flows and steepen to nearly 45°. The steep-walled, 150-m-deep summit crater contains an ash cone with a 500-m-wide funnel-shaped vent that is 200 m deep. Debris-avalanche deposits from the collapse of the SE flank about 3,700 years ago extend 10 km from the volcano. Widespread Plinian pumice-fall deposits include one from about 1,000 years ago. Holocene lava flows are visible on the flanks, but activity documented since the 16th century has consisted of intermittent minor-to-moderate explosive eruptions.
Information Contacts: Instituto Geofisico del Peru (IGP), Calle Badajoz N° 169 Urb. Mayorazgo IV Etapa, Ate, Lima 15012, Perú (URL: https://www.gob.pe/igp); Observatorio Volcanologico del INGEMMET (Instituto Geológical Minero y Metalúrgico), Barrio Magisterial Nro. 2 B-16 Umacollo - Yanahuara Arequipa, Peru (URL: http://ovi.ingemmet.gob.pe); Gobierno Regional Moquegua, Sede Principal De Moquegua, R377+5RR, Los Chirimoyos, Moquegua 18001, Peru (URL: https://www.gob.pe/regionmoquegua); Washington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), Satellite Analysis Branch (SAB), NOAA/NESDIS OSPO, NOAA Science Center Room 401, 5200 Auth Rd, Camp Springs, MD 20746, USA (URL: www.ospo.noaa.gov/Products/atmosphere/vaac, archive at: http://www.ssd.noaa.gov/VAAC/archive.html); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Kanaga (United States) — January 2024  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Kanaga
United States
51.923°N, 177.168°W; summit elev. 1307 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Small explosion on 18 December 2023
Kanaga lies within the Kanaton caldera at the northern tip of Kanaga Island. The caldera rim forms a 760-m-high arcuate ridge south and east of Kanaga; a lake occupies part of the SE caldera floor. Most of its previous recorded eruptions are poorly documented, although they date back to 1763. Fumarolic activity at Kanaga occurs in a circular, 200-m-wide, 60-m-deep summit crater and produces vapor plumes sometimes seen on clear days from Adak, 50 km to the east. Its most recent eruption occurred in February 2012, which consisted of numerous small earthquakes, a possible weak ash cloud, and gas-and-steam emissions (BGVN 38:03). This report covers a new eruption during December 2023, based on information from the Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO).
A small explosion was detected in local infrasound and seismic data at 2231 on 18 December, followed by elevated seismicity. No ash emissions were visible in partly cloudy satellite images. On 19 December the Volcano Alert Level (VAL) was raised to Advisory (the second level on a four-level scale) and the Aviation Color Code (ACC) was raised to Yellow (the second color on a four-color scale). The rate of seismicity significantly declined after the 18th, although it remained elevated through 30 December. Small, daily earthquakes occurred during 19-28 December. Satellite observations following the event showed a debris flow extending 1.5 km down the NW flank. Possible minor gas-and-steam emissions were visible in a webcam image on 20 December. Weakly elevated surface temperatures were identified in satellite data during 23-26 December. A series of cracks extending from the inner crater to the upper SE flank and debris deposits on the upper flanks were observed in satellite images on 27 December. AVO reported that these were likely formed during the 18 December event. Local webcam and seismic data were temporarily offline due to a power failure during 4-28 January.
On 28 January connection to the seismic stations and webcams was restored and webcam images showed gas-and-steam emissions at the summit. Occasional earthquakes were also detected each day. A period of weak seismic tremor was observed on 31 January. During February, the number of earthquakes declined. On 27 February AVO lowered the VAL to Normal (the lowest level on a four-level scale) and the ACC to Green (the lowest color on a four-color scale) due to decreased levels of seismicity and no new surface changes or elevated temperatures based on satellite and webcam data.
Geologic Background. Symmetrical Kanaga stratovolcano is situated within the Kanaton caldera at the northern tip of Kanaga Island. The caldera rim forms a 760-m-high arcuate ridge south and east of Kanaga; a lake occupies part of the SE caldera floor. The volume of subaerial dacitic tuff is smaller than would typically be associated with caldera collapse, and deposits of a massive submarine debris avalanche associated with edifice collapse extend nearly 30 km to the NNW. Several fresh lava flows from historical or late prehistorical time descend the flanks of Kanaga, in some cases to the sea. Historical eruptions, most of which are poorly documented, have been recorded since 1763. Kanaga is also noted petrologically for ultramafic inclusions within an outcrop of alkaline basalt SW of the volcano. Fumarolic activity occurs in a circular, 200-m-wide, 60-m-deep summit crater and produces vapor plumes sometimes seen on clear days from Adak, 50 km to the east.
Information Contacts: Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667 USA (URL: https://avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA (URL: http://dggs.alaska.gov/).
Klyuchevskoy (Russia) — January 2024  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Klyuchevskoy
Russia
56.056°N, 160.642°E; summit elev. 4754 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
New eruption consisting of Strombolian activity, lava flows and fountains, and ash plumes during June-December 2023
Klyuchevskoy, located on the Kamchatka Peninsula, has produced frequent moderate-volume explosive and effusive eruptions and more than 100 flank eruptions have occurred during the past 3,000 years. Eruptions recorded since the late 17th century have resulted in frequent changes to the morphology of the 700-m-wide summit crater. Eruptions over the past 400 years have primarily originated from the summit crater, although numerous major explosive and effusive eruptions have also occurred from flank craters. The previous eruption ended in November 2022 and consisted of Strombolian activity (BGVN 47:12). This report covers a new eruption during June through December 2023, characterized by Strombolian explosions, lava flows, and ash plumes. Information primarily comes from weekly and daily reports from the Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT) and various satellite data.
KVERT reported that a Strombolian eruption began at 2323 on 22 June. A thermal anomaly was visible in satellite data starting on 22 June (figure 75). As a result, the Aviation Color Code (ACC) was raised to Yellow (the second lowest level on a four-color scale). During 4-6 and 13 July small ash clouds were occasionally observed over the crater. On 19 July a new lava flow began to effuse along the Apakhonchich drainage on the SE flank, which continued through 19 August. Lava fountaining was reported on 21 July in addition to the active lava flow, which continued through 23 August and during 27-30 August. During 22-23 and 27-30 August the lava flow was active along the Apakhonchich drainage on the SE flank.
Similar activity was observed during September. Lava fountaining resumed on 2 September and continued through 31 October. In addition, on 2 September a lava flow began to effuse along the Kozyrevsky drainage on the SW flank. During 3-5 September resuspended ash plumes rose to 3-3.5 km altitude and extended as far as 170 km E by 1940 on 4 September. The ACC was raised to Orange (the third level on a four-color scale) at 1240 on 4 September. The ACC was briefly lowered back to Yellow at 1954 that same day before returning to Orange during 1532-1808 on 5 September due to resuspended ash plumes that rose to 3 km altitude and drifted 120 km E at 1500. KVERT reported that Strombolian activity continued, feeding the lava flows advancing down the Apakhonchichsky and Kozyrevsky drainages through most of the month. During 25 September through 16 October the lava flow was only active in the Apakhonchichisky drainage (figure 76). During 9-12 September resuspended ash plumes rose to 1.5-4 km altitude and extended 550 km E and SE. On 22 September resuspended ash plumes rose to 2-2.5 km altitude and drifted 50-90 km E, which prompted KVERT to raise the ACC to Orange; the ACC was lowered back to Yellow on 24 September. On 29 September phreatic explosions generated ash plumes that rose to 5.2-5.3 km altitude.
Activity during October continued with lava fountains, lava flows, and ash plumes. Strombolian activity with lava fountains continued at the crater and active lava flows alternately descended the Apakhonchichisky and Kozyrevsky drainages on the SE and S flanks (figure 77). During 11-12 October gas-and-steam plumes containing some ash rose to 5.5-6 km altitude and extended as far as 65 km NE and SE. The ACC was raised to Orange on 11 October. According to observers at the Kamchatka Volcanological Station, lava effusion was almost continuous, and incandescent material was ejected as high as 300 m above the crater rim. On 13 October at 1420 an ash plume rose to 5-5.5 km altitude and drifted 90-100 km SE. During 14-16 October gas-and-steam plumes containing some ash rose to 4-6 km altitude and drifted 40-145 km ESE and E. On 16 October lava on the SE flank melted the snow and ice, causing phreatic explosions and large collapses of material from the margins of the flow. At 1500 an ash plume rose to 6.5-7 km altitude and drifted 70 km ENE. On 17 October an ash plume was reported extending 360 km NE. Gray-red ashfall was observed in Klyuchi at 0700; this ash was resuspended from older material.
During 22-31 October phreatic explosions generated ash plumes mainly containing ash from collapses of previously deposited pyroclastic material that rose to 7 km altitude and extended as far as 280 km NE, E, SW, and S on 23 and 29 October the ash plumes rose to 8 km altitude. Ash plumes during 27-29 October rose to 8 km altitude and drifted as far as 300 km SE, ESE, and E. Lava fountains rose up to 500 m above the crater during 27-31 October. Scientists from the Kamchatka Volcanological Station visited the volcano on 28 October and reported that the cinder cone at the summit had grown. They also observed advancing lava on the E flank that extended about 2 km from the summit to 2,700 m elevation, incandescent ejecta 500 m above the crater, and avalanches in the Apakhonchichsky drainage. On 31 October activity intensified, and lava flows were reported moving in the Kretovsky, Kozyrevsky, and Apakhonchichisky drainages on the NW, SW, and SE flanks. At 0930 an ash plume rose to 7 km altitude and at first drifted 169 km SW and then 646 km SE. KVERT reported ash plumes rose to 14 km altitude and extended as far as 1,500 km SSE. The ACC was raised to Red (the highest level on a four-color scale). During 31 October to 1 November ash plumes rose as high as 14 km altitude and drifted as far as 2,255 km ESE.
Activity on 1 November intensified. The lava fountains rose as high as 1 km above the summit (figure 78) and fed the lava flows that were active on the Kretovsky, Kozyrevsky, and Apakhonchichsky drainages on the NW, SW, and SE flanks. Ash plumes rose to 10-14 km altitude and drifted as far as 1,500 km SSE (figure 79). According to the Kamchatka Volcanological Station, observers reported pyroclastic flows descending the flanks. Lahars descended the Studenoy River, blocking the Kozyrevsky-Petropavlovsk federal highway and descended the Krutenkaya River, blocking the road E of Klyuchi. According to news articles the ash plumes caused some flight cancellations and disruptions in the Aleutians, British Columbia (Canada), and along flight paths connecting the Unites States to Japan and South Korea. Ash plumes containing old ash from collapses in the Apakhonchichsky drainage due to phreatic explosions rose to 9.5-9.8 km altitude and drifted 192 km SW at 1400 and to 8.7 km altitude and drifted 192 km SW at 1710 on 1 November.
On 2 November ash plumes rose to 6-14 km altitude; the ash plume that rose to 14 km altitude decreased to 6.5 km altitude and drifted NNE by 2000 and continued to drift more than 3,000 km ESE and E. The ACC was lowered to Orange. On 3 November ash plumes rose to 5-8.2 km altitude and drifted 72-538 km ENE, NNE, and ESE; at 0850 an ash plume rose to 6-6.5 km altitude and drifted more than 3,000 km ESE throughout the day. During 4-6 and 8-10 November resuspended ash plumes associated with collapses of old pyroclastic material from the sides of the Apakhonchichsky drainage due to phreatic explosions rose to 4.5-5.5 km altitude and extended 114-258 km NE, ENE, and E. KVERT reported that the eruption stopped on 5 November and the lava flows had begun to cool. Resuspended ash plumes rose to 5-6 km altitude and drifted 60 km E at 0820 on 13 November and to 5 km and 4.5 km altitude at 1110 and 1430 and drifted 140 km E and 150 km ESE, respectively. On 15 November the ACC was lowered to Green.
Activity was relatively low during most of December. On 27 December Strombolian activity resumed based on a thermal anomaly visible in satellite data. On 30 December an ash plume rose to 6 km altitude and extended 195 km NW. The ACC was raised to Orange. On 31 December video and satellite data showed explosions that generated ash plumes that rose to 5-6.5 km altitude and drifted 50-230 km WNW and NW. Though a thermal anomaly persisted through 1 January 2024, no explosions were detected, so the ACC was lowered to Yellow.
Satellite data. Thermal activity was strong throughout the reporting period due to frequent lava fountaining and lava flows. MODIS thermal anomaly data provided through MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) showed strong activity during the entire reporting period, resulting from lava fountaining and lava flows (figure 80). According to data from MODVOLC thermal alerts, a total of 336 hotspots were detected in June (3), July (30), August (11), September (52), October (217), and November (23). Thermal activity was also visible in infrared satellite images, often showing a strong thermal anomaly at the summit crater and a lava flow affecting primarily the SE and SW flanks (figure 81).
Geologic Background. Klyuchevskoy is the highest and most active volcano on the Kamchatka Peninsula. Since its origin about 6,000 years ago, this symmetrical, basaltic stratovolcano has produced frequent moderate-volume explosive and effusive eruptions without major periods of inactivity. It rises above a saddle NE of Kamen volcano and lies SE of the broad Ushkovsky massif. More than 100 flank eruptions have occurred during approximately the past 3,000 years, with most lateral craters and cones occurring along radial fissures between the unconfined NE-to-SE flanks of the conical volcano between 500 and 3,600 m elevation. Eruptions recorded since the late 17th century have resulted in frequent changes to the morphology of the 700-m-wide summit crater. These eruptions over the past 400 years have originated primarily from the summit crater, but have also included numerous major explosive and effusive eruptions from flank craters.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Kamchatka Volcanological Station, Kamchatka Branch of Geophysical Survey, (KB GS RAS), Klyuchi, Kamchatka Krai, Russia (URL: http://volkstat.ru/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Agung (Indonesia) — January 2024  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Agung
Indonesia
8.343°S, 115.508°E; summit elev. 2997 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Three eruptive events reported in April, May, and December 2022
Mount Agung, located on the E end of the island of Bali, Indonesia, rises above the SE rim of the Batur caldera. The summit area extends 1.5 km E-W, with the highest point on the W and a steep-walled 800-m-wide crater on the E. Recorded eruptions date back to the early 19th century. A large and deadly explosive and effusive eruption occurred during 1963-64, which was characterized by voluminous ashfall, pyroclastic flows, and lahars that caused extensive damage and many fatalities. More recent activity was documented during November 2017-June 2019 that consisted of multiple explosions, significant ash plumes, lava flows at the summit crater, and incandescent ejecta. This report covers activity reported during April-May 2022 and December 2022 based on data from the Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC).
Activity during 2022 was relatively low and mainly consisted of a few ash plumes during April-May and December. An ash plume on 3 April rising to 3.7 km altitude (700 m above the summit) and drifting N was reported in a Darwin VAAC notice based on a ground report, with ash seen in HIMAWARI-8 visible imagery. Another ash plume was reported at 1120 on 27 May that rose to 5.5 km altitude (2.5 m above the summit); the plume was not visible in satellite or webcam images due to weather clouds. An eruption was reported based on seismic data at 0840 on 13 December, with an estimated plume altitude of 3.7 km; however, no ash was seen using satellite imagery in clear conditions before weather clouds obscured the summit.
Geologic Background. Symmetrical Agung stratovolcano, Bali's highest and most sacred mountain, towers over the eastern end of the island. The volcano, whose name means "Paramount," rises above the SE rim of the Batur caldera, and the northern and southern flanks extend to the coast. The summit area extends 1.5 km E-W, with the high point on the W and a steep-walled 800-m-wide crater on the E. The Pawon cone is located low on the SE flank. Only a few eruptions dating back to the early 19th century have been recorded in historical time. The 1963-64 eruption, one of the largest in the 20th century, produced voluminous ashfall along with devastating pyroclastic flows and lahars that caused extensive damage and many fatalities.
Information Contacts: Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Bureau of Meteorology, Northern Territory Regional Office, PO Box 40050, Casuarina, NT 0811, Australia (URL: http://www.bom.gov.au/info/vaac/).
Saunders (United Kingdom) — February 2024  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Saunders
United Kingdom
57.8°S, 26.483°W; summit elev. 843 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Persistent thermal anomalies from the summit crater lava lake during February 2023-January 2024
Saunders is one of eleven islands that comprise the South Sandwich Islands in the South Atlantic. The active Mount Michael volcano has been in almost continuous eruption since November 2014 (BGVN 48:02). Recent activity has resulted in intermittent thermal anomalies and gas-and-steam emissions (BGVN 47:03, 48:02). Visits are infrequent due to its remote location, and cloud cover often prevents satellite observations. Satellite thermal imagery and visual observation of incandescence during a research expedition in 2019 (BGVN 28:02 and 44:08) and a finding confirmed by a National Geographic Society research team that summited Michael in November 2022 reported the presence of a lava lake.
Although nearly constant cloud cover during February 2023 through January 2024 greatly limited satellite observations, thermal anomalies from the lava lake in the summit crater were detected on clear days, especially around 20-23 August 2023. Anomalies similar to previous years (eg. BGVN 48:02) were seen in both MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) data from MODIS instruments and in Sentinel 2 infrared imagery. The only notable sulfur dioxide plume detected near Saunders was on 25 September 2023, with the TROPOMI instrument aboard the Sentinel-5P satellite.
Geologic Background. Saunders Island consists of a large central volcanic edifice intersected by two seamount chains, as shown by bathymetric mapping (Leat et al., 2013). The young Mount Michael stratovolcano dominates the glacier-covered island, while two submarine plateaus, Harpers Bank and Saunders Bank, extend north. The symmetrical Michael has a 500-m-wide summit crater and a remnant of a somma rim to the SE. Tephra layers visible in ice cliffs surrounding the island are evidence of recent eruptions. Ash clouds were reported from the summit crater in 1819, and an effusive eruption was inferred to have occurred from a N-flank fissure around the end of the 19th century and beginning of the 20th century. A low ice-free lava platform, Blackstone Plain, is located on the north coast, surrounding a group of former sea stacks. A cluster of cones on the SE flank, the Ashen Hills, appear to have been modified since 1820 (LeMasurier and Thomson, 1990). Analysis of satellite imagery available since 1989 (Gray et al., 2019; MODVOLC) suggests frequent eruptive activity (when weather conditions allow), volcanic clouds, steam plumes, and thermal anomalies indicative of a persistent, or at least frequently active, lava lake in the summit crater. Due to this observational bias, there has been a presumption when defining eruptive periods that activity has been ongoing unless there is no evidence for at least 10 months.
Information Contacts: MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); NASA Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard MD 20771, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/); Copernicus Browser (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser).
Tengger Caldera (Indonesia) — February 2024  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Tengger Caldera
Indonesia
7.942°S, 112.95°E; summit elev. 2329 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Minor ash emission in December 2023; persistent weak thermal anomaly in the Bromo crater
Tengger Caldera, located at the N end of a volcanic massif in Indonesia’s East Java, consists of five overlapping stratovolcanoes. The youngest and only active cone in the 16-km-wide caldera is Bromo, which typically produces gas-and-steam plumes, occasional ash plumes and explosions, and weak thermal signals (BGVN 44:05, 47:01). This report covers activity during January 2022-December 2023, consisting of mostly white gas-and-steam emissions and persistent weak thermal anomalies. Information was provided by the Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as Indonesian Center for Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation, CVGHM) and satellite imagery. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 1-4), and visitors were warned to stay at least 1 km from the crater.
Activity was generally low during the reporting period, similar to that in 2021. According to almost daily images from MAGMA Indonesia (a platform developed by PVMBG), white emissions and plumes rose from 50 to 900 m above the main crater during this period (figure 24). During several days in March and June 2022, white plumes reached heights of 1-1.2 km above the crater.
After an increase in activity at 2114 on 3 February 2023, a PVMBG team that was sent to observe white emissions rising as high as 300 m during 9-12 February and heard rumbling noises. A sulfur dioxide odor was also strong near the crater and measurements indicated that levels were above the healthy (non-hazardous) threshold of 5 parts per million; differential optical absorption spectroscopy (DOAS) measurements indicated an average flux of 190 metric tons per day on 11 February. Incandescence originating from a large fumarole in the NNW part of the crater was visible at night. The team observed that vegetation on the E caldera wall was yellow and withered. The seismic network recorded continuous tremor and deep and shallow volcanic earthquakes.
According to a PVMBG press release, activity increased on 13 December 2023 with white, gray, and brown emissions rising as high as 900 m above Bromo’s crater rim and drifting in multiple directions (figure 25). The report noted that tremor was continuous and was accompanied in December by three volcanic earthquakes. Deformation data indicated inflation in December. There was no observable difference in the persistent thermal anomaly in the crater between 11 and 16 December 2023.
All clear views of the Bromo crater throughout this time, using Sentinel-2 infrared satellite images, showed a weak persistent thermal anomaly; none of the anomalies were strong enough to cause MODVOLC Thermal Alerts. A fire in the SE part of the caldera in early September 2023 resulted in a brief period of strong thermal anomalies.
Geologic Background. The 16-km-wide Tengger caldera is located at the northern end of a volcanic massif extending from Semeru volcano. The massive volcanic complex dates back to about 820,000 years ago and consists of five overlapping stratovolcanoes, each truncated by a caldera. Lava domes, pyroclastic cones, and a maar occupy the flanks of the massif. The Ngadisari caldera at the NE end of the complex formed about 150,000 years ago and is now drained through the Sapikerep valley. The most recent of the calderas is the 9 x 10 km wide Sandsea caldera at the SW end of the complex, which formed incrementally during the late Pleistocene and early Holocene. An overlapping cluster of post-caldera cones was constructed on the floor of the Sandsea caldera within the past several thousand years. The youngest of these is Bromo, one of Java's most active and most frequently visited volcanoes.
Information Contacts: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as Indonesian Center for Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation, CVGHM), Jalan Diponegoro 57, Bandung 40122, Indonesia (URL: http://www.vsi.esdm.go.id/); MAGMA Indonesia, Kementerian Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral (URL: https://magma.esdm.go.id/v1); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/).
Shishaldin (United States) — December 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Shishaldin
United States
54.756°N, 163.97°W; summit elev. 2857 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
New eruption with significant Strombolian explosions, ash plumes, and ashfall
Shishaldin is located on the eastern half of Unimak Island, one of the Aleutian Islands. Frequent explosive activity, primarily consisting of Strombolian ash eruptions from the small summit crater, but sometimes producing lava flows, has been recorded since the 18th century. The previous eruption ended in May 2020 and was characterized by intermittent thermal activity, increased seismicity and surface temperatures, ash plumes, and ash deposits (BGVN 45:06). This report covers a new eruption during July through November 2023, which consisted of significant explosions, ash plumes, ashfall, and lava fountaining. Information comes from daily, weekly, and special reports from the Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO) and various satellite data. AVO monitors the volcano using local seismic and infrasound sensors, satellite data, web cameras, and remote infrasound and lightning networks.
AVO reported that intermittent tremor and low-frequency earthquakes had gradually become more regular and consistent during 10-13 July. Strongly elevated surface temperatures at the summit were identified in satellite images during 10-13 July. On 11 July AVO raised the Aviation Color Code (ACC) to Yellow (the second color on a four-color scale) and Volcano Alert Level (VAL) to Advisory (the second level on a four-level scale) at 1439. Later in the day on 11 July summit crater incandescence was observed in webcam images. Observations of the summit suggested that lava was likely present at the crater, which prompted AVO to raise the ACC to Orange (the second highest color on a four-color scale) and the VAL to Watch (the second highest level on a four-level scale). The US Coast Guard conducted an overflight on 12 July and confirmed that lava was erupting from the summit. That same day, sulfur dioxide emissions were detected in satellite images.
A significant explosion began at 0109 on 14 July that produced an ash plume that rose to 9-12 km altitude and drifted S over the Pacific Ocean (figure 43). Webcam images and photos taken around 0700 from a ship SW off Unimak Island showed small lahar deposits, which were the result of the interaction of hot pyroclastic material and snow and ice on the flanks. There was also ashfall on the SW and N flanks. A smaller explosion at 0710 generated an ash plume that rose to 4.5 km altitude. Webcam images and pilot reports showed continued low-level ash emissions during the morning, rising to less than 4.6 km altitude; those emissions included a small ash plume near the summit around 1030 resulting from a small explosion.
Seismic tremor amplitude began increasing at around 1700 on 15 July; strongly elevated surface temperatures were also reported. An ash plume rose to 4.6 km altitude and drifted SSE at 2100, based on a satellite image. A continuous ash plume during 2150 through 2330 rose to 5 km altitude and extended 125 km S. At 2357 AVO raised the ACC to Red (the highest color on a four-color scale) and the VAL to Warning (the highest level on a four-level scale), noting that seismicity remained elevated for more than six hours and explosion signals were frequently detected by regional infrasound (pressure sensor) networks. Explosions generated an ash plume that rose to 4.9 km altitude and drifted as far as 500 km SE. Activity throughout the night declined and by 0735 the ACC was lowered to Orange and the VAL to Watch. High-resolution satellite images taken on 16 July showed pyroclastic deposits extending as far as 3 km from the vent; these deposits generated lahars that extended further down the drainages on the flanks. Ash deposits were mainly observed on the SSE flank and extended to the shore of Unimak Island. During 16-17 July lava continued to erupt at the summit, which caused strongly elevated surface temperatures that were visible in satellite imagery.
Lava effusion increased at 0100 on 18 July, as noted in elevated surface temperatures identified in satellite data, increasing seismic tremor, and activity detected on regional infrasound arrays. A significant ash plume at 0700 rose to 7 km altitude and continued until 0830, eventually reaching 9.1 km altitude and drifting SSE (figure 44). As a result, the ACC was raised to Red and the VAL to Warning. By 0930 the main plume detached, but residual low-level ash emissions continued for several hours, remaining below 3 km altitude and drifting S. The eruption gradually declined and by 1208 the ACC was lowered to Orange and the VAL was lowered to Watch. High-resolution satellite images showed ash deposits on the SW flank and pyroclastic deposits on the N, E, and S flanks, extending as far as 3 km from the vent; lahars triggered by the eruption extended farther down the flanks (figure 45). Lava continued to erupt from the summit crater on 19 July.
Elevated surface temperatures were detected in satellite images during 19-25 July, despite occasional weather cloud cover, which was consistent with increased lava effusion. During 22-23 July satellite observations acquired after the eruption from 18 July showed pyroclastic flow and lahar deposits extending as far as 3 km down the N, NW, and NE flanks and as far as 1.5 km down the S and SE flanks. Ash deposits covered the SW and NE flanks. No lava flows were observed outside the crater. On 22 July a sulfur dioxide plume was detected in satellite data midday that had an estimated mass of 10 kt. In a special notice issued at 1653 on 22 July AVO noted that eruptive activity had intensified over the previous six hours, which was characterized by an hours-long steady increase in seismic tremor, intermittent infrasound signals consistent with small explosions, and an increase in surface temperatures that were visible in satellite data. Pilots first reported low-level ash plumes at around 1900. At 2320 an ash plume had risen to 9 km altitude based on additional pilot reports and satellite images. The ACC was increased to Red and the VAL to Warning at 2343. Satellite images indicated growth of a significantly higher ash plume that rose to 11 km altitude continued until 0030 and drifted NE. During the early morning hours of 23 July ash plumes had declined to 4.6 k altitude. Seismic tremor peaked at 0030 on 23 July and began to rapidly decline at 0109; active ash emissions were no longer visible in satellite data by 0130. The ACC was lowered to Orange and the VAL to Watch at 0418; bursts of increased seismicity were recorded throughout the morning, but seismicity generally remained at low levels. Elevated surface temperatures were visible in satellite data until about 0600. On 24 July pilots reported seeing vigorous gas-and-steam plumes rising to about 3 km altitude; the plumes may have contained minor amounts of ash.
During 24-25 July low level seismicity and volcanic tremor were detected at low levels following the previous explosion on 23 July. Strongly elevated surface temperatures were observed at the summit crater in satellite data. Around 2200 on 25 July seismicity began to increase, followed by infrasound signals of explosions after 0200 on 26 July. An ash plume rose to 3 km altitude at 0500 and drifted ENE, along with an associated sulfur dioxide plume that drifted NE and had an estimated mass of 22 kt. Diffuse ash emissions were visible in satellite data and rose to 6.1-7.6 km altitude and extended 125 km from the volcano starting around 1130. These ash events were preceded by about seven hours of seismic tremor, infrasound detections of explosions, and five hours of increased surface temperatures visible in satellite data. Activity began to decline around 1327, which included low-frequency earthquakes and decreased volcanic tremor, and infrasound data no longer detected significant explosions. Surface temperatures remained elevated through the end of the month.
Seismicity, volcanic tremor, and ash emissions remained at low levels during early August. Satellite images on 1 August showed that some slumping had occurred on the E crater wall due to the recent explosive activity. Elevated surface temperatures continued, which was consistent with cooling lava. On 2 August small explosive events were detected, consistent with low-level Strombolian activity. Some episodes of volcanic tremor were reported, which reflected low-level ash emissions. Those ash emissions rose to less than 3 km altitude and drifted as far as 92.6 km N. Pilots that were located N of the volcano observed an ash plume that rose to 2.7 km altitude. Seismicity began to increase in intensity around 0900 on 3 August. Seismicity continued to increase throughout the day and through the night with strongly elevated surface temperatures, which suggested that lava was active at the surface.
An ash cloud that rose to 7.6-7.9 km altitude and drifted 60-75 km NE was visible in a satellite image at 0520 on 4 August. Pilots saw and reported the plume at 0836 (figure 46). By 0900 the plume had risen to 9.1 km altitude and extended over 100 km NE. AVO raised the ACC to Red and the VAL to Warning as a result. Seismic tremor levels peaked at 1400 and then sharply declined at 1500 to slightly elevated levels; the plume was sustained during the period of high tremor and drifted N and NE. The ACC was lowered to Orange and the VAL to Watch at 2055. During 5-14 August seismicity remained low and surface temperatures were elevated based on satellite data due to cooling lava. On 9 August a small lava flow was observed that extended from the crater rim to the upper NE flank. It had advanced to 55 m in length and appeared in satellite imagery on 11 August. Occasional gas-and-steam plumes were noted in webcam images. At 1827 AVO noted that seismic tremor had steadily increased during the afternoon and erupting lava was visible at the summit in satellite images.
Strong explosion signals were detected at 0200 on 15 August. An ash cloud that was visible in satellite data extended 100 km NE and may have risen as high as 11 km altitude around 0240. By 0335 satellite images showed the ash cloud rising to 7.6 km altitude and drifting NE. Significant seismicity and explosions were detected by the local AVO seismic and infrasound networks, and volcanic lightning was detected by the World Wide Lightning Location Network (WWLLN). A sulfur dioxide plume associated with the eruption drifted over the S Bering Sea and parts of Alaska and western Canada. Seismicity was significantly elevated during the eruption but had declined by 1322. A pilot reported that ash emissions continued, rising as high as 4.9 km altitude. Elevated surface temperatures detected in satellite data were caused by hot, eruptive material (pyroclastic debris and lava) that accumulated around the summit. Eruptive activity declined by 16 August and the associated sulfur dioxide plume had mostly dissipated; remnants continued to be identified in satellite images at least through 18 August. Surface temperatures remained elevated based on satellite images, indicating hot material on the upper parts of the volcano. Small explosions were detected in infrasound data on the morning of 19 August and were consistent with pilot reports of small, short-lived ash plumes that rose to about 4.3 km altitude. Low-level explosive activity was reported during 20-24 August, according to seismic and infrasound data, and weather clouds sometimes prevented views. Elevated surface temperatures were observed in satellite images, which indicated continued hot material on the upper parts of the volcano.
Seismic tremor began to increase at around 0300 on 25 August and was followed by elevated surface temperatures identified in satellite images, consistent with erupting lava. Small explosions were recorded in infrasound data. The ACC was raised to Red and the VAL to Warning at 1204 after a pilot reported an ash plume that rose to 9.1 km altitude. Seismicity peaked at 1630 and began to rapidly decline at around 1730. Ash plumes rose as high as 10 km altitude and drifted as far as 400 km NE. By 2020 the ash plumes had declined to 6.4 km altitude and continued to drift NE. Ash emissions were visible in satellite data until 0000 on 26 August and seismicity was at low levels. AVO lowered the ACC to Orange and the VAL to Watch at 0030. Minor explosive activity within the summit crater was detected during 26-28 August and strongly elevated surface temperatures were still visible in satellite imagery through the rest of the month. An AVO field crew working on Unimak Island observed a mass flow that descended the upper flanks beginning around 1720 on 27 August. The flow produced a short-lived ash cloud that rose to 4.5 km altitude and rapidly dissipated. The mass flow was likely caused by the collapse of spatter that accumulated on the summit crater rim.
Similar variable explosive activity was reported in September, although weather observations sometimes prevented observations. A moderate resolution satellite image from the afternoon of 1 September showed gas-and-steam emissions filling the summit crater and obscuring views of the vent. In addition, hot deposits from the previous 25-26 August explosive event were visible on the NE flank near the summit, based on a 1 September satellite image. On 2 and 4 September seismic and infrasound data showed signals of small, repetitive explosions. Variable gas-and-steam emissions from the summit were visible but there was no evidence of ash. Possible summit crater incandescence was visible in nighttime webcam images during 3-4 September.
Seismicity began to gradually increase at around 0300 on 5 September and activity escalated at around 0830. A pilot reported an ash plume that rose to 7.6 km altitude at 0842 and continued to rise as high as possibly 9.7 km altitude and drifted SSE based on satellite images (figure 47). The ACC was raised to Red and the VAL to Warning at 0900. In addition to strong tremor and sustained explosions, the eruption produced volcanic lightning that was detected by the WWLLN. Around 1100 seismicity decreased and satellite data confirmed that the altitude of the ash emissions had declined to 7.6 km altitude. By 1200 the lower-altitude portion of the ash plume had drifted 125 km E. Significant ash emissions ended by 1330 based on webcam images. The ACC was lowered to Orange and the VAL to Watch at 1440. Satellite images showed extensive pyroclastic debris flows on most of the flanks that extended 1.2-3.3 km from the crater rim.
During 6-13 September elevated surface temperatures continued to be observed in satellite data, seismicity remained elevated with weak but steady tremor, and small, low-frequency earthquakes and small explosions were reported, except on 12 September. On 6 September a low-level ash plume rose to 1.5-1.8 km altitude and drifted SSE. Occasional small and diffuse gas-and-steam emissions at the summit were visible in webcam images. Around 1800 on 13 September seismic tremor amplitudes began to increase, and small explosions were detected in seismic and infrasound data. Incandescent lava at the summit was seen in a webcam image taken at 0134 on 14 September during a period of elevated tremor. No ash emissions were reported during the period of elevated seismicity. Lava fountaining began around 0200, based on webcam images. Satellite-based radar observations showed that the lava fountaining activity led to the growth of a cone in the summit crater, which refilled most of the crater. By 0730 seismicity significantly declined and remained at low levels.
Seismic tremor began to increase around 0900 on 15 September and rapidly intensified. An explosive eruption began at around 1710, which prompted AVO to raise the ACC to Red and the VAL to Warning. Within about 30 minutes ash plumes drifted E below a weather cloud at 8.2 km altitude. The National Weather Service estimated that an ash-rich plume rose as high as 12.8 km altitude and produced volcanic lightning. The upper part of the ash plume detached from the vent around 1830 and drifted E, and was observed over the Gulf of Alaska. Around the same time, seismicity dramatically decreased. Trace ashfall was reported in the community of False Pass (38 km ENE) between 1800-2030 and also in King Cove and nearby marine waters. Activity declined at around 1830 although seismicity remained elevated, ash emissions, and ashfall continued until 2100. Lightning was again detected beginning around 1930, which suggested that ash emissions continued. Ongoing explosions were detected in infrasound data, at a lower level than during the most energetic phase of this event. Lightning was last detected at 2048. By 2124 the intensity of the eruption had decreased, and ash emissions were likely rising to less than 6.7 km altitude. Seismicity returned to pre-eruption levels. On 16 September the ACC was lowered to Orange and the VAL to Watch at 1244; the sulfur dioxide plume that was emitted from the previous eruption event was still visible over the northern Pacific Ocean. Elevated surface temperatures, gas-and-steam emissions from the vent, and new, small lahars were reported on the upper flanks based on satellite and webcam images. Minor deposits were reported on the flanks which were likely the result of collapse of previously accumulated lava near the summit crater.
Elevated seismicity with tremor, small earthquakes, and elevated surface temperatures were detected during 17-23 September. Minor gas-and-steam emissions were visible in webcam images. On 20 September small volcanic debris flows were reported on the upper flanks. On 21 September a small ash deposit was observed on the upper flanks extending to the NE based on webcam images. Seismic tremor increased significantly during 22-23 September. Regional infrasound sensors suggested that low-level eruptive activity was occurring within the summit crater by around 1800 on 23 September. Even though seismicity was at high levels, strongly elevated surface temperatures indicating lava at the surface were absent and no ash emissions were detected; weather clouds at 0.6-4.6 km altitude obscured views. At 0025 on 24 September AVO noted that seismicity continued at high levels and nearly continuous small infrasound signals began, likely from low-level eruptive activity. Strongly elevated surface temperatures were identified in satellite images by 0900 and persisted throughout the day; the higher temperatures along with infrasound and seismic data were consistent with lava erupting at the summit. Around 1700 similarly elevated surface temperatures were detected from the summit in satellite data, which suggested that more vigorous lava fountaining had started. Starting around 1800 low-level ash emissions rose to altitudes less than 4.6 km altitude and quickly dissipated.
Beginning at midnight on 25 September, a series of seismic signals consistent with volcanic flows were recorded on the N side of the volcano. A change in seismicity and infrasound signals occurred around 0535 and at 0540 a significant ash cloud formed and quickly reached 14 km altitude and drifted E along the Alaska Peninsula. The cloud generated at least 150 lightning strokes with thunder that could be heard by people in False Pass. Seismicity rapidly declined to near background levels around 0600. AVO increased the ACC to Red and the VAL to Warning at 0602. The ash cloud detached from the volcano at around 0700, rose to 11.6 km altitude, and drifted ESE. Trace to minor amounts of ashfall were reported by the communities of False Pass, King Cove, Cold Bay, and Sand Point around 0700. Ash emissions continued at lower altitudes of 6-7.6 km altitude at 0820. Small explosions at the vent area continued to be detected in infrasound data and likely represented low-level eruptive activity near the vent. Due to the significant decrease in seismicity and ash emissions the ACC was lowered to Orange and the VAL to Watch at 1234. Radar data showed significant collapses of the crater that occurred on 25 September. Satellite data also showed significant hot, degassing pyroclastic and lahar deposits on all flanks, including more extensive flows on the ENE and WSW sections below two new collapse scarps. Following the significant activity during 24-25 September, only low-level activity was observed. Seismicity decreased notably near the end of the strong activity on 25 September and continued to decrease through the end of the month, though tremor and small earthquakes were still reported. No explosive activity was detected in infrasound data through 2 October. Gas-and-steam emissions rose to 3.7 km altitude, as reported by pilots and seen in satellite images. Satellite data from 26 September showed that significant collapses had occurred at the summit crater and hot, steaming deposits from pyroclastic flows and lahars were present on all the flanks, particularly to the ENE and WSW. A small ash cloud was visible in webcam images on 27 September, likely from a collapse at the summit cone. High elevated surface temperatures were observed in satellite imagery during 27-28 September, which were likely the result of hot deposits on the flanks erupted on 25 September. Minor steaming at the summit crater and from an area on the upper flanks was visible in webcam images on 28 September.
During October, explosion events continued between periods of low activity. Seismicity significantly increased starting at around 2100 on 2 October; around the same time satellite images showed an increase in surface temperatures consistent with lava fountaining. Small, hot avalanches of rock and lava descended an unspecified flank. In addition, a distinct increase in infrasound, seismicity, and lightning detections was followed by an ash plume that rose to 12.2 km altitude and drifted S and E at 0520 on 3 October, based on satellite images. Nighttime webcam images showed incandescence due to lava fountaining at the summit and pyroclastic flows descending the NE flank. AVO reported that a notable explosive eruption started at 0547 and lasted until 0900 on 3 October, which prompted a rise in the ACC to Red and the VAL to Warning. Subsequent ash plumes rose to 6-7.6 km altitude by 0931. At 1036 the ACC was lowered back to Orange and the VAL to Watch since both seismic and infrasound data quieted substantially and were slightly above background levels. Gas-and-steam emissions were observed at the summit, based on webcam images. Trace amounts of ashfall were observed in Cold Bay. Resuspended ash was present at several kilometers altitude near the volcano. During the afternoon, low-level ash plumes were visible at the flanks, which appeared to be largely generated by rock avalanches off the summit crater following the explosive activity. These ash plumes rose to 3 km altitude and drifted W. Trace amounts of ashfall were reported by observers in Cold Bay and Unalaska and flights to these communities were disrupted by the ash cloud. Satellite images taken after the eruption showed evidence of pyroclastic flows and lahar deposits in drainages 2 km down the SW flank and about 3.2 km down the NE flank, and continued erosion of the crater rim. Small explosion craters at the end of the pyroclastic flows on the NE flank were noted for the first time, which may have resulted from gas-and-steam explosions when hot deposits interact with underlying ice.
During 4 October seismicity, including frequent small earthquakes, remained elevated, but was gradually declining. Ash plumes were produced for over eight hours until around 1400 that rose to below 3.7 km altitude. These ash plumes were primarily generated off the sides of the volcano where hot rock avalanches from the crater rim had entered drainages to the SW and NE. Two explosion craters were observed at the base of the NE deposits about 3.2 km from the crater rim. Webcam images showed the explosion craters were a source of persistent ash emissions; occasional collapse events also generated ash. Seismicity remained elevated with sulfur dioxide emissions that had a daily average of more than 1,000 tons per day, and frequent small earthquakes through the end of the month. Frequent elevated surface temperatures were identified in satellite images and gas-and-steam plumes were observed in webcam images, although weather conditions occasionally prevented clear views of the summit. Emissions were robust during 14-16 October and were likely generated by the interaction of hot material and snow and ice. During the afternoon of 21 October a strong gas-and-steam plume rose to 3-4.6 km altitude and extended 40 km WSW, based on satellite images and reports from pilots. On 31 October the ACC was lowered to Yellow and the VAL was lowered to Advisory.
Activity in November was characterized by elevated seismicity with ongoing seismic tremor and small, low-frequency earthquakes, elevated surface temperatures, and gas-and-steam emissions. There was an increase in seismic and infrasound tremor amplitudes starting at 1940 on 2 November. As a result, the ACC was again raised to Orange and the VAL was increased to Watch, although ash was not identified in satellite data. An ash cloud rose to 6.1 km altitude and drifted W according to satellite data at 2000. By 0831 on 3 November ash emissions were no longer visible in satellite images. On 6 and 9 November air pressure sensors detected signals consistent with small explosions. Small explosions were detected in infrasound data consistent with weak Strombolian activity on 19 and 21 November. Seismicity started to decrease on 21 November. On 25 November gas-and-steam emissions were emitted from the vent as well as from a scarp on the NE side of the volcano near the summit. A gas-and-steam plume extended about 50 km SSE and was observed in satellite and webcam images on 26 November. On 28 November small explosions were observed in seismic and local infrasound data and gas-and-steam emissions were visible from the summit and from the upper NE collapse scarp based on webcam images. Possible small explosions were observed in infrasound data on 30 November. Weakly elevated surface temperatures and a persistent gas-and-steam plume from the summit and collapse scarps on the upper flanks. A passing aircraft reported the gas-and-steam plume rose to 3-3.4 km altitude on 30 November, but no significant ash emissions were detected.
Satellite data. MODIS thermal anomaly data provided through MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) showed a strong pulse of thermal activity beginning in July 2023 that continued through November 2023 (figure 48). This strong activity was due to Strombolian explosions and lava fountaining events at the summit crater. According to data from MODVOLC thermal alerts, a total of 101 hotspots were detected near the summit crater in July (11-14, 16-19, 23-24 and 26), August (4, 25-26, and 29), September (5, 12, and 17), and October (3, 4, and 8). Infrared satellite data showed large lava flows descending primarily the northern and SE flanks during the reporting period (figure 49). Sulfur dioxide plumes often exceeded two Dobson Units (DUs) and drifted in different directions throughout the reporting period, based on satellite data from the TROPOMI instrument on the Sentinel-5P satellite (figure 50).
Geologic Background. The symmetrical glacier-covered Shishaldin in the Aleutian Islands is the westernmost of three large stratovolcanoes in the eastern half of Unimak Island. The Aleuts named the volcano Sisquk, meaning "mountain which points the way when I am lost." Constructed atop an older glacially dissected edifice, it is largely basaltic in composition. Remnants of an older edifice are exposed on the W and NE sides at 1,500-1,800 m elevation. There are over two dozen pyroclastic cones on its NW flank, which is covered by massive aa lava flows. Frequent explosive activity, primarily consisting of Strombolian ash eruptions from the small summit crater, but sometimes producing lava flows, has been recorded since the 18th century. A steam plume often rises from the summit crater.
Information Contacts: Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667 USA (URL: https://avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA (URL: http://dggs.alaska.gov/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); NASA Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Ioto
Japan
24.751°N, 141.289°E; summit elev. 169 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
New eruption with discolored water, ejecta, and floating pumice during October-December 2023
Ioto (Iwo-jima), located about 1,200 km S of Tokyo, lies within a 9-km-wide submarine caldera along the Izu-Bonin-Mariana volcanic arc. Previous eruptions date back to 1889 and have consisted of dominantly phreatic explosions, pumice deposits during 2001, and discolored water. A submarine eruption during July through December 2022 was characterized by discolored water, pumice deposits, and gas emissions (BGVN 48:01). This report covers a new eruption during October through December 2023, which consisted of explosions, black ejecta, discolored water, and floating pumice, based on information from the Japan Meteorological Association (JMA), the Japan Coast Guard (JCG), and satellite data.
JMA reported that an eruption had been occurring offshore of Okinahama on the SE side of the island since 21 October, which was characterized by volcanic tremor, according to the Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF) Iwo Jima Air Base (figure 22). According to an 18 October satellite image a plume of discolored water at the site of this new eruption extended NE (figure 23). During an overflight conducted on 30 October, a vent was identified about 1 km off the coast of Okinahama. Observers recorded explosions every few minutes that ejected dark material about 20 m above the ocean and as high as 150 m. Ejecta from the vent formed a black-colored island about 100 m in diameter, according to observations conducted from the air by the Earthquake Research Institute of the University of Tokyo in cooperation with the Mainichi newspaper (figure 24). Occasionally, large boulders measuring more than several meters in size were also ejected. Observations from the Advanced Land Observing Satellite Daichi-2 and Sentinel-2 satellite images also confirmed the formation of this island (figure 23). Brown discolored water and floating pumice were present surrounding the island.
The eruption continued during November. During an overflight on 3 November observers photographed the island and noted that material was ejected 169 m high, according to a news source. Explosions gradually became shorter, and, by the 3rd, they occurred every few seconds; dark and incandescent material were ejected about 800 m above the vent. On 4 November eruptions were accompanied by explosive sounds. Floating, brown-colored pumice was present in the water surrounding the island. There was a brief increase in the number of volcanic earthquakes during 8-14 November and 24-25 November. The eruption temporarily paused during 9-11 November and by 12 November eruptions resumed to the W of the island. On 10 November dark brown-to-dark yellow-green discolored water and a small amount of black floating material was observed (figure 25). A small eruption was reported on 18 November off the NE coast of the island, accompanied by white gas-and-steam plumes (figure 23). Another pause was recorded during 17-19 November, which then resumed on 20 November and continued erupting intermittently. According to a field survey conducted by the National Institute for Disaster Prevention Science and Technology on 19 November, a 30-m diameter crater was visible on the NE coast where landslides, hot water, and gray volcanic ash containing clay have occurred and been distributed previously. Erupted blocks about 10 cm in diameter were distributed about 90-120 m from the crater. JCG made observations during an overflight on 23 November and reported a phreatomagmatic eruption. Explosions at the main vent generated dark gas-and-ash plumes that rose to 200 m altitude and ejected large blocks that landed on the island and in the ocean (figure 26). Discolored water also surrounded the island. The size of the new island had grown to 450 m N-S x 200 m E-W by 23 November, according to JCG.
The eruption continued through 11 December, followed by a brief pause in activity, which then resumed on 31 December, according to JMA. Intermittent explosions produced 100-m-high black plumes at intervals of several minutes to 30 minutes during 1-10 December. Overflights were conducted on 4 and 15 December and reported that the water surrounding the new island was discolored to dark brown-to-dark yellow-green (figure 27). No floating material was reported during this time. In comparison to the observations made on 23 November, the new land had extended N and part of it had eroded away. In addition, analysis by the Geospatial Information Authority of Japan using SAR data from Daichi-2 also confirmed that the area of the new island continued to decrease between 4 and 15 December. Ejected material combined with wave erosion transformed the island into a “J” shape, 500-m-long and with the curved part about 200 m offshore of Ioto. The island was covered with brown ash and blocks, and the surrounding water was discolored to greenish-brown and contained an area of floating pumice. JCG reported from an overflight on 4 December that volcanic ash-like material found around the S vent on the NE part of the island was newly deposited since 10 November (figure 28). By 15 December the N part of the “J” shaped island had separated and migrated N, connecting to the Okinahama coast and the curved part of the “J” had eroded into two smaller islands (figure 27).
References. Ukawa, M., Fujita, E., Kobayashi, T., 2002, Recent volcanic activity of Iwo Jima and the 2001 eruption, Monthly Chikyu, Extra No. 39, 157-164.
Geologic Background. Ioto, in the Volcano Islands of Japan, lies within a 9-km-wide submarine caldera. The volcano is also known as Ogasawara-Iojima to distinguish it from several other "Sulfur Island" volcanoes in Japan. The triangular, low-elevation, 8-km-long island narrows toward its SW tip and has produced trachyandesitic and trachytic rocks that are more alkalic than those of other volcanoes in this arc. The island has undergone uplift for at least the past 700 years, accompanying resurgent doming of the caldera; a shoreline landed upon by Captain Cook's surveying crew in 1779 is now 40 m above sea level. The Motoyama plateau on the NE half of the island consists of submarine tuffs overlain by coral deposits and forms the island's high point. Many fumaroles are oriented along a NE-SW zone cutting through Motoyama. Numerous recorded phreatic eruptions, many from vents on the W and NW sides of the island, have accompanied the uplift.
Information Contacts: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA), 1-3-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8122, Japan (URL: http://www.jma.go.jp/jma/indexe.html); Japan Coast Guard (JCG) Volcano Database, Hydrographic and Oceanographic Department, 3-1-1, Kasumigaseki, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8932, Japan (URL: https://www1.kaiho.mlit.go.jp/GIJUTSUKOKUSAI/kaiikiDB/kaiyo22-2.htm); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/); Asahi, 5-3-2, Tsukiji, Chuo Ward, Tokyo, 104-8011, Japan (URL: https://www.asahi.com/ajw/articles/15048458).
Search Bulletin Archive by Publication Date
Select a month and year from the drop-downs and click "Show Issue" to have that issue displayed in this tab.
The default month and year is the latest issue available.
Scientific Event Alert Network Bulletin - Volume 13, Number 02 (February 1988)
Additional Reports (Unknown)
Fiji: Pumice near Lau Island, but no new submarine activity known
Aira (Japan)
More frequent explosions break windows
Akan (Japan)
Two small ash eruptions; seismicity declines
Ambrym (Vanuatu)
Ash cloud reported from aircraft
Atmospheric Effects (1980-1989) (Unknown)
Stratospheric aerosol concentrations continue to decline
Bagana (Papua New Guinea)
Lava flow from summit dome nears base of volcano
Bulusan (Philippines)
Small ash ejections and seismicity
Deception Island (Antarctica)
Strong seismicity but no sign of recent eruption
Erebus (Antarctica)
Lava lakes; Strombolian activity; collapse; SO2 data
Fournaise, Piton de la (France)
Lava production, tremor, and deformation
Gamalama (Indonesia)
Widespread ashfall; evacuations
Kilauea (United States)
Lava continues to enter ocean; littoral cones and tephra
Krakatau (Indonesia)
Ash emission; glow; felt earthquakes
Lamongan (Indonesia)
Increased seismicity but no temperature changes
Langila (Papua New Guinea)
Explosion sounds; glow; minor seismicity
Manam (Papua New Guinea)
Vapor emission and glow
Marapi (Indonesia)
More explosions
Nyamulagira (DR Congo)
Seismic swarm, then lava flow from N flank fissure vent
Okmok (United States)
Ash from new vent
Pacaya (Guatemala)
Frequent Strombolian explosions; lava flow still active
Pagan (United States)
Haze 300 km S attributed to Pagan eruption
Pavlof (United States)
Weak steam and ash emission
Rabaul (Papua New Guinea)
Weak seismicity; no deformation changes
Ranakah (Indonesia)
Continued lava extrusion
Sangeang Api (Indonesia)
Explosions and earthquakes end
Santa Maria (Guatemala)
Lava descends S flank valley; lahars fill channels
Semeru (Indonesia)
Continued Vulcanian activity
Shikotsu (Japan)
Earthquake swarms
Tacana (Mexico-Guatemala)
Steam emission and local seismicity continue
Ulawun (Papua New Guinea)
Frequent earthquakes and tremor; heavy rain
Vulcano (Italy)
New fracture system
Whakaari/White Island (New Zealand)
Minor tephra emission and seismicity
Additional Reports (Unknown) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Additional Reports
Unknown
Unknown, Unknown; summit elev. m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Fiji: Pumice near Lau Island, but no new submarine activity known
The crew of Air Pacific flight FJ 407 (Tonga to Nausori, Fiji) observed a zone of floating pumice ~1.5 km long by 3-4 m wide near 20°S, 178°W (near the S end of the Lau Group, Fiji) on 11 February at 1011. No reports of pumice from ships or island residents [are known to GVN].
Geologic Background. Reports of floating pumice from an unknown source, hydroacoustic signals, or possible eruption plumes seen in satellite imagery.
Information Contacts: J. Latter, DSIR, Wellington.
Aira
Japan
31.5772°N, 130.6589°E; summit elev. 1117 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
More frequent explosions break windows
Explosive activity has become more vigorous in 1988. Explosions occurred at a rate of 1-2/day in February and often ejected large amounts of lapilli that fell on the flanks. The maximum ash cloud height was 2,500 m above the summit crater. A loud explosion at 1252 on 3 February ejected a large ash cloud, and strong air shocks were felt at [KLMO]. Lapilli broke the windshields of two cars and the air shock broke three windowpanes at a hotel and school. An explosion on 9 February at 1852 ejected a large amount of lapilli, breaking a car windshield. Ash accumulation at the observatory was 48 g/m2. February's 35 recorded explosions brought the year's total to 64.
Geologic Background. The Aira caldera in the northern half of Kagoshima Bay contains the post-caldera Sakurajima volcano, one of Japan's most active. Eruption of the voluminous Ito pyroclastic flow accompanied formation of the 17 x 23 km caldera about 22,000 years ago. The smaller Wakamiko caldera was formed during the early Holocene in the NE corner of the caldera, along with several post-caldera cones. The construction of Sakurajima began about 13,000 years ago on the southern rim and built an island that was joined to the Osumi Peninsula during the major explosive and effusive eruption of 1914. Activity at the Kitadake summit cone ended about 4,850 years ago, after which eruptions took place at Minamidake. Frequent eruptions since the 8th century have deposited ash on the city of Kagoshima, located across Kagoshima Bay only 8 km from the summit. The largest recorded eruption took place during 1471-76.
Information Contacts: JMA.
Akan
Japan
43.384°N, 144.013°E; summit elev. 1499 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Two small ash eruptions; seismicity declines
Me-Akan-dake cone erupted during the nights of 7-8 and 18-19 February. A slight ashfall was observed on fresh snow at the E foot of the volcano during a field survey on 9 February. Ashfall was next observed on snow near Lake Akan, 9 km from the summit, on 19 February. Higher amplitude volcanic tremor was recorded during both eruptive episodes . . . . Only seven discrete earthquakes were detected in February, down from 37 in January. Earthquake swarms had been frequent since December . . . .
Geologic Background. Akan is a 13 x 24 km caldera located immediately SW of Kussharo caldera in eastern Hokkaido. The elongated, irregular outline of the caldera rim reflects its incremental formation during major explosive eruptions from the early to mid-Pleistocene. There are four post-caldera stratovolcanoes, three at the SW end of the caldera and the other on the NE side. Conical Oakandake was frequently active during the Holocene. The 1-km-wide Nakamachineshiri crater of Meakandake was formed during a major pumice-and-scoria eruption about 13,500 years ago. The Meakandake group, composed of nine overlapping cones E of Lake Akan, has produced mild phreatic eruptions since the beginning of the 19th century. The main cone of Meakandake proper has a triple crater at its summit. Although recorded eruptions at Meakandake have consisted of minor phreatic explosions, four major magmatic eruptions with pyroclastic flows have also occurred during the Holocene.
Information Contacts: JMA.
Ambrym (Vanuatu) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Ambrym
Vanuatu
16.25°S, 168.12°E; summit elev. 1334 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Ash cloud reported from aircraft
The crew of a Continental Airlines flight from Australia to Honolulu reported an eruption on 13 February at 0357, with ash clouds below 12 km altitude, moving SW. A NOTAM issued the next day at 2018 said that the eruption was from Benbow Crater, and forecast ash clouds to 10.5 km altitude, spreading ESE. A second NOTAM released 19 February at 0827 stated that volcanic activity had ceased. Geologists in Vanuatu reported that activity from Benbow was slightly stronger than usual for 2-3 days 12-14 February, but had since returned to normal. No damage was reported.
Geologic Background. Ambrym is a large basaltic volcano with a 12-km-wide caldera formed during a major Plinian eruption with dacitic pyroclastic flows about 1,900 years ago. A thick, almost exclusively pyroclastic sequence, initially dacitic then basaltic, overlies lava flows of a pre-caldera shield volcano. Post-caldera eruptions, primarily from Marum and Benbow cones, have partially filled the caldera floor and produced lava flows that ponded on the floor or overflowed through gaps in the caldera rim. Post-caldera eruptions have also formed a series of scoria cones and maars along a fissure system oriented ENE-WSW. Eruptions have been frequently reported since 1774, though mostly limited to extra-caldera eruptions that would have affected local populations. Since 1950 observations of eruptive activity from cones within the caldera or from flank vents have occurred almost yearly.
Information Contacts: J. Latter, DSIR Geophysics, Wellington, New Zealand; C. Clark, Dept of Geology, Mines, and Rural Water Supplies, Port-Vila.
Atmospheric Effects (1980-1989) (Unknown) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Atmospheric Effects (1980-1989)
Unknown
Unknown, Unknown; summit elev. m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Stratospheric aerosol concentrations continue to decline
Stratospheric aerosol concentrations continued to decline in the absence of new large explosive eruptions (figure 54). Lidar profiles from Mauna Loa, Hawaii showed a return to conditions similar to those before the November 1985 Ruiz eruption. A distinct change was evident between the 1 March measurements from Hampton, VA and the previous data set in December, but values had not yet returned to background.
Geologic Background. The enormous aerosol cloud from the March-April 1982 eruption of Mexico's El Chichón persisted for years in the stratosphere, and led to the Atmospheric Effects section becoming a regular feature of the Bulletin. Descriptions of the initial dispersal of major eruption clouds remain with the individual eruption reports, but observations of long-term stratospheric aerosol loading will be found here.
Information Contacts: Thomas DeFoor, Mauna Loa Observatory, P. O. Box 275, Hilo, HI 96720 USA; Horst Jäger, Fraunhofer-Institut für Atmosphärische Umweltforschung, Kreuzeckbahnstrasse 19, D-8100 Garmisch-Partenkirchen, West Germany; William Fuller, NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, VA 23665 USA.
Bagana (Papua New Guinea) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Bagana
Papua New Guinea
6.137°S, 155.196°E; summit elev. 1855 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Lava flow from summit dome nears base of volcano
Activity continued at a low level through February, with the summit area continuously producing moderate to strong white vapor. Glow was noted from the summit on several nights during the month. Seismicity was at a low level with only a few (1-10) events recorded/day. During an aerial inspection on the 25th, the new E-flank lava flow had descended to an elevation of ~1,150 m, close to the foot of the volcano. The flow was ~1.5 km long, and its terminus was ~100 m wide and 20-30 m thick.
The lava dome in the summit crater had a flat top but its sides were very steep, particularly noticeable on its SW flank where the dome stood ~30-40 m above [the SW rim] of the summit crater. The lava flow was being fed from the top of the dome and it appeared that the direction of flow could change quite easily.
Geologic Background. Bagana volcano, in a remote portion of central Bougainville Island, is frequently active. This massive symmetrical cone was largely constructed by an accumulation of viscous andesitic lava flows. The entire edifice could have been constructed in about 300 years at its present rate of lava production. Eruptive activity is characterized by non-explosive effusion of viscous lava that maintains a small lava dome in the summit crater, although occasional explosive activity produces pyroclastic flows. Lava flows with tongue-shaped lobes up to 50 m thick and prominent levees descend the flanks on all sides.
Information Contacts: P. de Saint-Ours and C. McKee, RVO.
Bulusan (Philippines) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Bulusan
Philippines
12.769°N, 124.056°E; summit elev. 1535 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Small ash ejections and seismicity
A mild ash ejection began on 20 February at 1945. Lightning flashes were observed near the summit during the activity, and hissing and rumbling were faintly audible from 2010 until 0600 the next morning on the W side of the volcano. A field investigation revealed traces of ash on W flank villages (Gulanggulang, 7 km SW of the summit; Bolos, 7 km W; and Sangkayon). No clear precursors were observed. Local seismicity had varied from 0 to 3 volcanic events/day, temperatures and chemistry of monitored hot springs showed no anomalous changes, and results of the latest EDM survey, in October, were within background levels.
After the eruption, a white steam plume emerged from the vent under some pressure; during quiescent periods, only a wispy plume is usually emitted. Vapor emission from the upper end of a fissure was about half that of the steaming vent. Temperatures of hot springs remained stable. The single nearby PHIVOLCS seismograph (at San Benon, 5.1 km SW of the crater) recorded an indistinct explosion signal with the onset of ash ejection. An increase in local seismicity followed, as 29 low-frequency volcanic earthquakes (LFVE), 19 tremor episodes, and five explosion shocks were recorded during the remainder of the day. Only one LFVE was detected the next day (21 February), but a sulfurous odor was noted at Gulanggulang. Local seismicity increased again on 22 February, with 6 high-frequency volcanic earthquakes (HFVE) and 12 LFVEs. Amplitudes of the HFVEs were larger, but none were felt.
A magnitude 6.9 regional earthquake was centered 80 km NE of Bulusan on 24 February and felt at Rossi-Forel intensity V in the Bulusan area; several aftershocks were also felt there. At about the time of the regional earthquake, a landslide was observed to have recently occurred on the volcano's middle to lower flank. The number of recorded local earthquakes reached a maximum the same day (80 events), and seismicity remained vigorous through the end of the month. Steaming from the upper end of the fissure varied from weak to moderate. Sulfurous odors and hissing sounds were often evident (at Gulanggulang; Angas, 2 km W; San Benon; and Cogon, 5 km SW).
Small ash emissions occurred on 1 March, at 0502, 0552, 1458, 1510, 1523, 1528, and 1547, accompanied by rumbling sounds, explosion earthquakes, and several minutes of harmonic tremor. The ash plume ejected at 1458 reached 1 km above the crater; summit weather clouds obscured the morning plumes. Ash emitted in the morning was carried west by prevailing winds (to the villages of Gulanggulang, Sangkayon, and Puting Sapa). Afternoon ashfall was more extensive, and included the NW flank (reaching Aniog, 5.5 km NW; Rangas, 7 km NW; Bacolod, 6.5 km WNW; Puting Sapa; Buran-Buran; Sangkayon; Bolos, 7 km W; Guruyan, 9 km WSW; and Cogon). A small mudflow was observed at Cogon at 0700, consisting partly of ash ejected earlier that day. Some low-frequency harmonic tremor was detected after the 1 March explosions.
Ash ejections resumed 6-8 March. On 6 March, a 1,500-m column was emitted at 1504, depositing ash to the W and SW (on the villages of Cogon; San Benon; Mt. Jormajan, 6 km WSW; Puting-Sapa; Gulanggulang; Monbon, 6 km SW; Gabao, 9.5 km WSW; and Tinampo). Additional ejections at 1521, 1525, 1536, 1606, 1649, and 2050 were recorded as explosion earthquakes. On 7 March at 1107, a 1,430-m-high ash cloud was observed from the SE flank village of Salvacion. Ejections continued that evening at 2013 and 2016 and early the next morning at 0030, 0249, and 0414. Ash again fell on the S and SW flanks (at Monbon, Gulang, Cogon, and Tinampo). Rumbling sounds accompanied all of the episodes except those on 7 March at 2013 and 8 March at 0030, when distinct explosions were heard by volcanologists at San Benon. Frequent seismicity continued, with a maximum of 58 tectonic earthquakes and 43 volcanic events on 7 March.
PHIVOLCS noted that Bulusan's 1988 behavior remains similar to the 1980 activity, which lasted for 9 months, and more mild ash ejections are expected.
Geologic Background. Luzon's southernmost volcano, Bulusan, was constructed along the rim of the 11-km-diameter dacitic-to-rhyolitic Irosin caldera, which was formed about 36,000 years ago. It lies at the SE end of the Bicol volcanic arc occupying the peninsula of the same name that forms the elongated SE tip of Luzon. A broad, flat moat is located below the topographically prominent SW rim of Irosin caldera; the NE rim is buried by the andesitic complex. Bulusan is flanked by several other large intracaldera lava domes and cones, including the prominent Mount Jormajan lava dome on the SW flank and Sharp Peak to the NE. The summit is unvegetated and contains a 300-m-wide, 50-m-deep crater. Three small craters are located on the SE flank. Many moderate explosive eruptions have been recorded since the mid-19th century.
Information Contacts: PHIVOLCS.
Deception Island (Antarctica) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Deception Island
Antarctica
62.9567°S, 60.6367°W; summit elev. 602 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Strong seismicity but no sign of recent eruption
International volcanological expeditions organized by the Instituto Antártico Argentino and the Vulcantar Project, Univ Nacional de Salta, visited Deception Island in January-February 1987 and 1988. Local and regional seismicity, thermal activity, and gas emission were monitored, and eruptive mechanisms were investigated, particularly for the 1842, 1967, 1969, and 1970 eruptions. Previous field work by Argentine scientists at Deception Island was during the austral summers of 1971-72, 1972-73, 1973-74, and 1974-75.
The 1988 expedition found no evidence of recent eruptions. Observers from Bellingshausen Base (USSR), 160 km NE, noted the possibility that a shallow submarine eruption could have occurred. Frequent small (mb 0.5) earthquakes were centered ~8 km from the expedition's base camp. These earthquakes were particularly numerous along the 5-km 1969 eruption fissure. Episodes of volcanic tremor with well-defined frequencies and durations of 5-40 minutes were also recorded. Strong regional earthquakes centered 40-80 km from Deception Island and possibly related to the extensive Mar de la Flota (Bransfield Strait) structure seemed to trigger local seismic activity. No significant differences between the 1987 and 1988 seismic data were observed. The distribution of fumarolic activity (90-100°C) was also unchanged. Gas emission was prevalent in the S portions of the main fissure systems on the island, while conductive processes seemed to explain the temperatures of surface water bodies in the N sector.
Geologic Background. Ring-shaped Deception Island, at the SW end of the South Shetland Islands, NE of Graham Land Peninsula, was constructed along the axis of the Bransfield Rift spreading center. A narrow passageway named Neptunes Bellows provides an entrance to a natural harbor within the 8.5 x 10 km caldera that was utilized as an Antarctic whaling station. Numerous vents along ring fractures circling the low 14-km-wide island have been reported active for more than 200 years. Maars line the shores of 190-m-deep Port Foster caldera bay. Among the largest of these maars is 1-km-wide Whalers Bay, at the entrance to the harbor. Eruptions during the past 8,700 years have been dated from ash layers in lake sediments on the Antarctic Peninsula and neighboring islands.
Information Contacts: J. Viramonte, Univ Nacional de Salta, Argentina; R. Ortiz Ramis, Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales, Spain; M. Martini, Univ di Firenze, Italy.
Erebus (Antarctica) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Erebus
Antarctica
77.53°S, 167.17°E; summit elev. 3794 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Lava lakes; Strombolian activity; collapse; SO2 data
"Mt. Erebus was visited by New Zealand and U.S. scientists during November and December 1987. Activity generally remained unchanged from the previous year. The small active anorthoclase phonolite lava lake has increased in size, from about 20 m in diameter a year ago to about 30 m (figure 9). It fluctuated in height by as much as 2-5 m over periods of <1 hour. Such marked fluctuations have not been previously recorded during periods of quiet degassing. Two other small lava lakes, both <10 m in diameter, were observed. One was transient, and only appeared when the lava level was high in the main lake.
"For about a month, from mid-November to mid-December, explosive activity was mild and consisted of small Strombolian eruptions, primarily from the main lava lake. Small eruptions also occurred from two possibly inclined vents at the base of the crater wall, NE of the main lava lake. During this period, no bombs were ejected from the inner crater. In late December, the Strombolian eruptions increased in size, with bombs landing on the main crater floor and rim.
"In early December, a crescent-shaped segment of the main crater floor and inner crater wall, ~60 m long and 10 m wide, collapsed into the southern part of the inner crater. It filled the large steaming collapse site SW of the main lava lake, and covered the S half of the inner crater with talus and debris. Large steaming fissures on the main crater floor suggest that further collapse is imminent.
"COSPEC measurements indicated that the average SO2 emission rate has increased to ~50 t/d. The average flux seemed to be a function of the lava lake surface area. As the lakes have increased in size, so has the SO2 flux. Significant and regular variations in the SO2 emission rates were observed, and may be correlated with changes in the rate of convection within the lava lake."
Geologic Background. Mount Erebus overlooks the McMurdo research station on Ross Island and is the largest of three major volcanoes forming the roughly triangular Ross Island. The summit of the dominantly phonolitic volcano has been modified by one or two generations of caldera formation. A summit plateau at about 3,200 m elevation marks the rim of the youngest caldera, which formed during the late-Pleistocene and within which the modern cone was constructed. An elliptical 500 x 600 m, 110-m-deep crater truncates the summit and contains an active lava lake within a 250-m-wide, 100-m-deep inner crater; other lava lakes are sometimes present. The glacier-covered volcano was erupting when first sighted by Captain James Ross in 1841. A persistent lava-lake, with minor explosions punctuated by occasional larger Strombolian explosions that eject bombs onto the crater rim, has been documented since 1972, but nearly continuous activity has probably been occurring for much longer.
Information Contacts: P. Kyle, Univ. of London.
Piton de la Fournaise (France) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Piton de la Fournaise
France
21.244°S, 55.708°E; summit elev. 2632 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Lava production, tremor, and deformation
The fissure eruption continued through early March, but the rate of lava production was very low. From 7 to 15 February, sizeable lava fountains were erupted, then lava flows were observed, accompanied by limited deflation of the S flank of the central cone. Since 15 February, strong variations in tremor have been well-correlated with fluctuations in the south-lateral tilt stations (Bory), as during the 30 November-1 January eruption. No simultaneous discrete seismic events were recorded. As of 14 March, tremor continued to be recorded at a very low level. No eruptive activity was visible other than a sulfur-rich plume from the new 20-m-high cone.
Geologic Background. Piton de la Fournaise is a massive basaltic shield volcano on the French island of Réunion in the western Indian Ocean. Much of its more than 530,000-year history overlapped with eruptions of the deeply dissected Piton des Neiges shield volcano to the NW. Three scarps formed at about 250,000, 65,000, and less than 5,000 years ago by progressive eastward slumping, leaving caldera-sized embayments open to the E and SE. Numerous pyroclastic cones are present on the floor of the scarps and their outer flanks. Most recorded eruptions have originated from the summit and flanks of Dolomieu, a 400-m-high lava shield that has grown within the youngest scarp, which is about 9 km wide and about 13 km from the western wall to the ocean on the E side. More than 150 eruptions, most of which have produced fluid basaltic lava flows, have occurred since the 17th century. Only six eruptions, in 1708, 1774, 1776, 1800, 1977, and 1986, have originated from fissures outside the scarps.
Information Contacts: H. Delorme, D. Vandamme, and P. Nerbusson, OVPDLF; P. Bachelery, Univ de la Réunion; J. Dubois, J-L. Cheminee, A. Hirn, P. Blum, and J. Zlotnicki, IPGP.
Gamalama (Indonesia) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Gamalama
Indonesia
0.81°N, 127.3322°E; summit elev. 1714 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Widespread ashfall; evacuations
Gamalama erupted on 12 February at 1830, spreading ash over a wide area of Ternate Island. No new lava flow accompanied the activity. VSI issued an aircraft advisory on 13 February, warning of potential hazards from the activity. The press reported that police and soldiers had helped evacuate ~ 1,500 residents of villages near Gamalama, added to ~ 2,000 people from the same area who had previously been evacuated to the neighboring island of Halmahera. Details of premonitory activity are limited, but relatively deep earthquakes had been recorded 18-19 January.
Geologic Background. Gamalama is a near-conical stratovolcano that comprises the entire island of Ternate off the western coast of Halmahera, and is one of Indonesia's most active volcanoes. The island was a major regional center in the Portuguese and Dutch spice trade for several centuries, which contributed to the extensive documentation of activity. Three cones, progressively younger to the north, form the summit. Several maars and vents define a rift zone, parallel to the Halmahera island arc, that cuts the volcano; the S-flank Ngade maar formed after about 14,500–13,000 cal. BP (Faral et al., 2022). Eruptions, recorded frequently since the 16th century, typically originated from the summit craters, although flank eruptions have occurred in 1763, 1770, 1775, and 1962-63.
Information Contacts: VSI; ANS; UPI.
Kilauea (United States) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Kilauea
United States
19.421°N, 155.287°W; summit elev. 1222 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Lava continues to enter ocean; littoral cones and tephra
Lava . . . continued . . . building deltas near Kupapau Point and farther E near the old Damien church site (figure 53). The W lobe had several active fronts and more volume than the E lobe. Near the end of February, the volume of lava feeding the E lobe began to decrease slowly, and by 1 March growth of the eastern delta had ceased. During the same period, the W lobe began to increase in volume along all the fronts that were entering the ocean, causing explosions and forming small littoral cones. A small spatter rampart was formed by one flow. Sand-sized tephra was produced by some of the explosions, and flakes of basaltic glass > 5 cm long, formed by steam bubbles rising through lava and exploding at the water's surface, were found as far as 1-2 km downwind of the steam columns.
The flow that . . . destroyed three more houses on the 11th reached the bottom of the steep slope and stopped on 14 February. The lava pond . . . overflowed intermittently 31 January-2 February, raising the N rim of the lava shield 6-8 m. The lava level dropped to 5-10 m below the rim for the rest of the month, at times exposing the top 2-3 m of the outlet to the tube system (figure 54). Lava fountaining and gas piston activity . . . at Pu`u `O`o continued. Strombolian activity and fountaining deposited spatter and reticulite pumice on the rim.
Harmonic tremor continued at a low level . . . beneath Pu`u `O`o and the shield vent. The generally constant tremor amplitude was occasionally interrupted by many hours of gas piston activity, characterized by 1-minute tremor bursts repeating at intervals of ~3-15 minutes. In the summit region, the number of shallow microearthquakes peaked at nearly 400/day then gradually decreased to < 100/day by the end of February. However, there were intermittent swarms of long-period events and weak tremor at shallow and intermediate depths beneath the summit region. Of the thousands of recorded earthquakes during February, 16 of the strongest had magnitudes ranging from 2.5 to 4.6. The M 4.6 event, at 1847 on 19 February, was centered on the S flank of Kīlauea at 9 km depth. It was widely felt on the E half of the island, but no structural damage was reported.
Geologic Background. Kilauea overlaps the E flank of the massive Mauna Loa shield volcano in the island of Hawaii. Eruptions are prominent in Polynesian legends; written documentation since 1820 records frequent summit and flank lava flow eruptions interspersed with periods of long-term lava lake activity at Halemaumau crater in the summit caldera until 1924. The 3 x 5 km caldera was formed in several stages about 1,500 years ago and during the 18th century; eruptions have also originated from the lengthy East and Southwest rift zones, which extend to the ocean in both directions. About 90% of the surface of the basaltic shield volcano is formed of lava flows less than about 1,100 years old; 70% of the surface is younger than 600 years. The long-term eruption from the East rift zone between 1983 and 2018 produced lava flows covering more than 100 km2, destroyed hundreds of houses, and added new coastline.
Information Contacts: C. Heliker and R. Koyanagi, HVO.
Krakatau (Indonesia) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Krakatau
Indonesia
6.1009°S, 105.4233°E; summit elev. 285 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Ash emission; glow; felt earthquakes
An increase in the volume of white fume from the summit crater was observed beginning 11 February. Similar activity, stronger than it had been for several years, continued intermittently until 28 February, when plume color darkened and emissions became more frequent. Plumes apparently rose a few hundred meters above the crater. On 1 March, glow was visible from the Java coast, . . . suggesting the presence of new lava. Earthquakes were felt 5-6 March from Anyer, 55 km E of the volcano.
Geologic Background. The renowned Krakatau (frequently mis-named as Krakatoa) volcano lies in the Sunda Strait between Java and Sumatra. Collapse of an older edifice, perhaps in 416 or 535 CE, formed a 7-km-wide caldera. Remnants of that volcano are preserved in Verlaten and Lang Islands; subsequently the Rakata, Danan, and Perbuwatan cones were formed, coalescing to create the pre-1883 Krakatau Island. Caldera collapse during the catastrophic 1883 eruption destroyed Danan and Perbuwatan, and left only a remnant of Rakata. This eruption caused more than 36,000 fatalities, most as a result of tsunamis that swept the adjacent coastlines of Sumatra and Java. Pyroclastic surges traveled 40 km across the Sunda Strait and reached the Sumatra coast. After a quiescence of less than a half century, the post-collapse cone of Anak Krakatau (Child of Krakatau) was constructed within the 1883 caldera at a point between the former Danan and Perbuwatan cones. Anak Krakatau has been the site of frequent eruptions since 1927.
Information Contacts: VSI; A. Ritter, Carita Beach Hotel, Java.
Lamongan (Indonesia) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Lamongan
Indonesia
7.981°S, 113.341°E; summit elev. 1641 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Increased seismicity but no temperature changes
A brief seismic swarm centered immediately W of Lamongan cone began on 8 February at 0445. Additional seismicity was recorded through February. No changes have been noted in the temperature or behavior of the maar lakes within the epicentral region. The earthquakes occurred in virtually the same epicentral area as those from the 1978 and 1985 swarms.
Geologic Background. Lamongan, a small stratovolcano located between the massive Tengger and Iyang-Argapura volcanic complexes, is surrounded by numerous maars and cinder cones. The currently active cone has been constructed 650 m SW of Gunung Tarub, the volcano's high point. As many as 27 maars with diameters from 150 to 700 m, some containing crater lakes, surround the volcano, along with about 60 cinder cones and spatter cones. Lake-filled maars, including Ranu Pakis, Ranu Klakah, and Ranu Bedali, are located on the E and W flanks; dry maars are predominately located on the N flanks. None of the maars has erupted during historical time, although several of the youthful maars cut drainage channels from Gunung Tarub. The volcano was very active from the time of its first historical eruption in 1799 through the end of the 19th century, producing frequent explosive eruptions and lava flows from vents on the western side ranging from the summit to about 450 m elevation.
Information Contacts: VSI.
Langila (Papua New Guinea) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Langila
Papua New Guinea
5.525°S, 148.42°E; summit elev. 1330 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Explosion sounds; glow; minor seismicity
Low-level activity continued during February. Emissions consisted of weak white vapors from Crater 2 for most of the month. Weak explosion sounds were heard on 8 and 21 February, then more frequently between the 25th and 27th. Weak, deep, roaring noises were heard starting on the 13th and a weak night glow was observed 27-28 February. Crater 3 was inactive. Microseismicity remained at a very low, non-eruptive level.
Geologic Background. Langila, one of the most active volcanoes of New Britain, consists of a group of four small overlapping composite basaltic-andesitic cones on the lower E flank of the extinct Talawe volcano in the Cape Gloucester area of NW New Britain. A rectangular, 2.5-km-long crater is breached widely to the SE; Langila was constructed NE of the breached crater of Talawe. An extensive lava field reaches the coast on the N and NE sides of Langila. Frequent mild-to-moderate explosive eruptions, sometimes accompanied by lava flows, have been recorded since the 19th century from three active craters at the summit. The youngest and smallest crater (no. 3 crater) was formed in 1960 and has a diameter of 150 m.
Information Contacts: P. de Saint-Ours and C. McKee, RVO.
Manam (Papua New Guinea) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Manam
Papua New Guinea
4.08°S, 145.037°E; summit elev. 1807 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Vapor emission and glow
Activity continued at a low level during February. Weak to moderate white vapors were observed from both Southern and Main Craters throughout the month. Deep roaring sounds from the summit area (probably Southern Crater) were heard on most days. Blue vapors were released from Southern Crater on 13-14 February, and a dull, fluctuating glow was seen over Main Crater on the 14th. Amplitudes of low-frequency earthquakes continued at the same steady level as in the past 3 months. No significant tilt changes were observed.
Geologic Background. The 10-km-wide island of Manam, lying 13 km off the northern coast of mainland Papua New Guinea, is one of the country's most active volcanoes. Four large radial valleys extend from the unvegetated summit of the conical basaltic-andesitic stratovolcano to its lower flanks. These valleys channel lava flows and pyroclastic avalanches that have sometimes reached the coast. Five small satellitic centers are located near the island's shoreline on the northern, southern, and western sides. Two summit craters are present; both are active, although most observed eruptions have originated from the southern crater, concentrating eruptive products during much of the past century into the SE valley. Frequent eruptions, typically of mild-to-moderate scale, have been recorded since 1616. Occasional larger eruptions have produced pyroclastic flows and lava flows that reached flat-lying coastal areas and entered the sea, sometimes impacting populated areas.
Information Contacts: P. de Saint-Ours and C. McKee, RVO.
Marapi (Indonesia) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Marapi
Indonesia
0.38°S, 100.474°E; summit elev. 2885 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
More explosions
Marapi erupted again on 19, 20, and 24 February, and 1 March. Fresh, unaltered rock has been found in the tephra from the 1988 explosions.
Geologic Background. Gunung Marapi, not to be confused with the better-known Merapi volcano on Java, is Sumatra's most active volcano. This massive complex stratovolcano rises 2,000 m above the Bukittinggi Plain in the Padang Highlands. A broad summit contains multiple partially overlapping summit craters constructed within the small 1.4-km-wide Bancah caldera. The summit craters are located along an ENE-WSW line, with volcanism migrating to the west. More than 50 eruptions, typically consisting of small-to-moderate explosive activity, have been recorded since the end of the 18th century; no lava flows outside the summit craters have been reported in historical time.
Information Contacts: VSI.
Nyamulagira (DR Congo) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Nyamulagira
DR Congo
1.408°S, 29.2°E; summit elev. 3058 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Seismic swarm, then lava flow from N flank fissure vent
Seismic data from the [CRSN] indicated that N-flank lava production began at about [2200] on [30] December and continued until 4 January at about 1400. The new vent[s], named [Gafuranindi], were about [1700 and] 800 m N of the 1980 cone, along a fissure that trended N20°E. New lava, mostly pahoehoe as in 1980, covered an area 2.5 km long and 500-600 m wide (figure 6). The activity built [two small cones] to ~60 m above the lava field. The eruption was preceded by an earthquake swarm on 10-11 October. Seismic activity had then gradually increased until the onset of lava production.
Further Reference. Zana, N., Tanaka, K., Janssen, T., and Mukeng, K., 1988, Seismic behaviour of volcanoes Nyiragongo and Nyamuragira prior and during eruptive episodes: Proceedings, Kagoshima International Conference on Volcanoes, p. 547-550.
Geologic Background. Africa's most active volcano, Nyamulagira (also known as Nyamuragira), is a massive high-potassium basaltic shield about 25 km N of Lake Kivu and 13 km NNW of the steep-sided Nyiragongo volcano. The summit is truncated by a small 2 x 2.3 km caldera that has walls up to about 100 m high. Documented eruptions have occurred within the summit caldera, as well as from the numerous flank fissures and cinder cones. A lava lake in the summit crater, active since at least 1921, drained in 1938, at the time of a major flank eruption. Recent lava flows extend down the flanks more than 30 km from the summit as far as Lake Kivu; extensive lava flows from this volcano have covered 1,500 km2 of the western branch of the East African Rift.
Information Contacts: N. Zana, CRSN, Bukavu; H-L. Hody, Kigali, Rwanda.
Okmok (United States) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Okmok
United States
53.43°N, 168.13°W; summit elev. 1073 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Ash from new vent
On 26 February, ash emerged from a new vent at the SW base of the cone, while the cone's previously active vent was limited to steaming (table 1).
Table 1. Reports of activity at Okmok, January-February 1987, compiled by John Reeder from James Dickson and Tom Madsen, Aleutian Air Ltd.
| Date |
Time |
Observer |
Activity |
| 08 Jan 1987 |
0900 |
Dickson |
600-m billowing white steam plume seen from boat just N of Unmak Island. |
| 14 Feb 1987 |
1600 |
Madsen |
Continuous steam and ash emission; cloud to 1,400 m altitude (about 500 m above the caldera rim), drifting 70 km NW in a 55 km/hour wind. |
| 26 Feb 1987 |
1730 |
Madsen |
Onset of black plume emission, from a new vent at the SW base of the cone; plume dirfted about 35 km SSW at 1,350 m altitude; only white steam emerged from the cone's previously active vent. |
Geologic Background. The basaltic Okmok shield volcano forms the NE end of Umnak Island in the Aleutian Islands. The summit of the low, 35-km-wide volcano is cut by two overlapping 10-km-wide calderas formed during eruptions about 12,000 and 2,050 years ago when dacitic pyroclastic flows reached the coast. More than 60 tephra layers from Okmok have been found overlying the 12,000-year-old caldera-forming tephra layer. Numerous cones and lava domes are present on the flanks down to the coast, including the SE-flank Mount Tulik, which is almost 200 m higher than the caldera rim. Some of the post-caldera cones show evidence of wave-cut lake terraces; more recent cones were formed after the caldera lake, once 150 m deep, disappeared. Eruptions have been reported since 1805 from cinder cones within the caldera, where there are also hot springs and fumaroles.
Information Contacts: J. Reeder, Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys (ADGGS).
Pacaya (Guatemala) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Pacaya
Guatemala
14.382°N, 90.601°W; summit elev. 2569 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Frequent Strombolian explosions; lava flow still active
The geologic team that visited Tacaná on 27-28 January climbed Pacaya on 31 January. From the summit of Cerro Chino at 1330, they saw frequent ejections of steam and ash, and, less frequently, bluish gas plumes emerging from MacKenney Crater.
Periodic observations of Pacaya's activity were made during February by scientists listed below. Strombolian explosions ejected blocks and incandescent bombs from MacKenney Crater every few minutes, accompanied by detonations. During the evening of 13 February, detonations were audible from Guatemala City, 25 km NNE. Although the SW flank lava flow was not visible from Pacaya's summit, observation of nighttime incandescence on 22 February (from the road below San Vicente Pacaya) indicated that it remained active.
Geologic Background. Eruptions from Pacaya are frequently visible from Guatemala City, the nation's capital. This complex basaltic volcano was constructed just outside the southern topographic rim of the 14 x 16 km Pleistocene Amatitlán caldera. A cluster of dacitic lava domes occupies the southern caldera floor. The post-caldera Pacaya massif includes the older Pacaya Viejo and Cerro Grande stratovolcanoes and the currently active Mackenney stratovolcano. Collapse of Pacaya Viejo between 600 and 1,500 years ago produced a debris-avalanche deposit that extends 25 km onto the Pacific coastal plain and left an arcuate scarp inside which the modern Pacaya volcano (Mackenney cone) grew. The NW-flank Cerro Chino crater was last active in the 19th century. During the past several decades, activity has consisted of frequent Strombolian eruptions with intermittent lava flow extrusion that has partially filled in the caldera moat and covered the flanks of Mackenney cone, punctuated by occasional larger explosive eruptions that partially destroy the summit.
Information Contacts: James Vallance, Jorge Girón, Francisco Alvarez, Lee Siebert, and Gerardo Sánchez Rubio, Estación Regional del Centro, Instituto de Geología, UNAM, Guanajuato, México; A. MacKenney, Guatemala City.
Pagan (United States) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Pagan
United States
18.13°N, 145.8°E; summit elev. 570 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Haze 300 km S attributed to Pagan eruption
Mid-February eruptive activity at Pagan may have been the source of an unusual haze that affected Saipan Island, 300 km to the S, but little information is yet available. A weather bulletin released 16 February at 2000 had reported an eruption on nearby Agrigan Island. However, a Civil Defense overflight detected no signs that an eruption had occurred there, and newspapers attributed the activity to Pagan. Satellite images on 16 February revealed no plume, despite clear weather. Seismographs that usually monitor Pagan's activity were being repaired.
Geologic Background. Pagan Island, the largest and one of the most active of the Mariana Islands volcanoes, consists of two stratovolcanoes connected by a narrow isthmus. Both North and South Pagan stratovolcanoes were constructed within calderas, 7 and 4 km in diameter, respectively. North Pagan at the NE end of the island rises above the flat floor of the northern caldera, which may have formed less than 1,000 years ago. South Pagan is a stratovolcano with an elongated summit containing four distinct craters. Almost all of the recorded eruptions, which date back to the 17th century, have originated from North Pagan. The largest eruption during historical time took place in 1981 and prompted the evacuation of the sparsely populated island.
Information Contacts: R. Walter, NOAA/NESDIS; J. Eldredge, Guam.
Pavlof (United States) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Pavlof
United States
55.417°N, 161.894°W; summit elev. 2493 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Weak steam and ash emission
During observations that were limited by poor weather December-February, only weak steam and ash emission was reported (table 5).
Table 5. Reports of activity at Pavlof, 9 January-2 March 1988, compiled by John Reeder from the following observers: Theresa Dubber, James Yakal, and Marsha Brown (FAA, Cold Bay); Guy Morgan (Peninsula Airways).
| Date |
Time |
Activity Reported |
Observers |
| 09 Jan 1988 |
1530 |
150-m steam plume with some ash from NE summit vent. |
TD |
| 28 Feb 1988 |
0845 |
Black plume several hundred meters high from NE summit vent; 15 minutes later, a steam-and-ash plume was rising 600 m and drifting a short distance E. |
JY, MB |
| 02 Mar 1988 |
1200 |
Gray steam-and-ash plume rising 300-450 m from NE summit vent and drifting E. Only white steam was visible by 1630 and there were no emissions by 1819. The volcano was snow-covered except for snow-free areas around the summit and NE vents. |
GM, MB |
Geologic Background. The most active volcano of the Aleutian arc, Pavlof is a Holocene stratovolcano that was constructed along a line of vents extending NE from the Emmons Lake caldera. Pavlof and Pavlof Sister to the NE form a dramatic pair of symmetrical, glacier-covered stratovolcanoes that overlook Pavlof and Volcano bays. Little Pavlof is a smaller cone on the SW flank of Pavlof volcano, near the rim of Emmons Lake caldera. Unlike Pavlof Sister, eruptions have frequently been reported from Pavlof, typically Strombolian to Vulcanian explosive eruptions from the summit vents and occasional lava flows. The active vents lie near the summit on the north and east sides. The largest recorded eruption took place in 1911, at the end of a 5-year-long eruptive episode, when a fissure opened on the N flank, ejecting large blocks and issuing lava flows.
Information Contacts: J. Reeder, ADGGS.
Rabaul (Papua New Guinea) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Rabaul
Papua New Guinea
4.2459°S, 152.1937°E; summit elev. 688 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Weak seismicity; no deformation changes
Seismicity continued at a very low level, with 33 earthquakes recorded in February. There were only two locatable events in February, both in the Greet Harbour area. There were no significant changes in tilt and horizontal distance measurements.
Geologic Background. The low-lying Rabaul caldera on the tip of the Gazelle Peninsula at the NE end of New Britain forms a broad sheltered harbor utilized by what was the island's largest city prior to a major eruption in 1994. The outer flanks of the asymmetrical shield volcano are formed by thick pyroclastic-flow deposits. The 8 x 14 km caldera is widely breached on the east, where its floor is flooded by Blanche Bay and was formed about 1,400 years ago. An earlier caldera-forming eruption about 7,100 years ago is thought to have originated from Tavui caldera, offshore to the north. Three small stratovolcanoes lie outside the N and NE caldera rims. Post-caldera eruptions built basaltic-to-dacitic pyroclastic cones on the caldera floor near the NE and W caldera walls. Several of these, including Vulcan cone, which was formed during a large eruption in 1878, have produced major explosive activity during historical time. A powerful explosive eruption in 1994 occurred simultaneously from Vulcan and Tavurvur volcanoes and forced the temporary abandonment of Rabaul city.
Information Contacts: P. de Saint-Ours and C. McKee, RVO.
Ranakah (Indonesia) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Ranakah
Indonesia
8.637°S, 120.5302°E; summit elev. 2288 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Continued lava extrusion
The eruption continued through February. No explosions have been reported since 9 January, and seismicity since then has been limited to rockfall events from the growing lava extrusion. Photographs taken in late February indicate that the summit of the steep-sided lava dome was considerably higher than it had been during field work by VSI personnel a month earlier. Lava flows extending N and E from the dome had advanced further, and a new flow had emerged from the dome and moved S. Eruption rates appeared to slow during February to an average of roughly 200,000 m3/day.
Geologic Background. The Anak Ranakah (Child of Ranakah) lava dome was formed in 1987 in an area without previous recorded eruptions at the base of the large older lava dome of Gunung Ranakah. An arcuate group of lava domes extending about 12 km west from Gunung Ranakah to Poco Mandosawa occurs on the outer N flanks of the poorly known Poco Leok caldera on western Flores Island.
Information Contacts: VSI.
Sangeang Api (Indonesia) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Sangeang Api
Indonesia
8.2°S, 119.07°E; summit elev. 1912 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Explosions and earthquakes end
The number of explosions . . . declined steadily from 50-70/day in early 1987 to ~15/day at the end of the year. By February, explosions had stopped, although fuming continued from the summit crater, producing a whitish plume. No earthquakes were reported during February.
Geologic Background. Sangeang Api volcano, one of the most active in the Lesser Sunda Islands, forms a small 13-km-wide island off the NE coast of Sumbawa Island. Two large trachybasaltic-to-tranchyandesitic volcanic cones, Doro Api and Doro Mantoi, were constructed in the center and on the eastern rim, respectively, of an older, largely obscured caldera. Flank vents occur on the south side of Doro Mantoi and near the northern coast. Intermittent eruptions have been recorded since 1512, most of them during in the 20th century.
Information Contacts: VSI.
Santa Maria (Guatemala) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Santa Maria
Guatemala
14.757°N, 91.552°W; summit elev. 3745 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Lava descends S flank valley; lahars fill channels
The quoted material is a report from William Rose.
"Santiaguito was observed by scientists from INSIVUMEH, Michigan Tech and Arizona State Universities, and the Smithsonian Institution 10-16 February, the initial days of an intensive volcanic hazard study that will continue until April.
"Caliente vent was the focus of activity, as it has been for every observation since 1977. A dacite lava flow 3.5 km long was being extruded and was advancing SSW, filling the steep valley of a tributary of the Río Nimá II (figure 4). The flow is the result of continuous extrusion from Caliente vent since 1975. During the first 9 years, the extrusion fed a lava flow that extended only a few hundreds of meters from the vent, where it oversteepened, generating incandescent avalanches and small block and ash flows (Rose, 1987). Lava began to descend the southern slopes of Caliente vent in June 1986, but the flow was much more extensive in May and June 1987. Its movement is now generating incandescent rockfalls and small block and ash flows. These affect the upper, steeper parts of the lava flow and an oversteepened mound downslope (over a constricted part of the former river drainage into which the flow is channeled). The present flow is the longest yet observed in Santiaguito's 66 years of continuous activity and represents an increase in the extrusion rate since 1985. This is the seventh period of rapid extrusion at Santiaguito. Previous episodes have recurred about every 10-12 years and lasted about 3-5 years.
"Caliente vent is also the source of vertical, possibly phreatomagmatic eruptions of fine-grained dacite ash, very similar to those described 1975-84. They occur as often as 1 or 2 times an hour and consist of very brief (1-2-minute) emissions, some of which reached altitudes of 4,000 m (about 1,500 m above the vent). Light ashfalls (<0.1 mm thick) affect areas as much as 6 km from Santiaguito." The geologists who visited Tacaná on 27-28 January also made observations from about 2 km W of Santiaguito on 30 January. Steam and ash were ejected at 0930 and 1000. A local observer, Alejandro Chávez, reported some roaring, whistling noises, and very minor seismicity.
"An important result of the current activity has been the accelerating sedimentary load (chiefly laharic) into river systems downslope (figure 5). Most now enters the Río Nimá II, which has aggraded by at least several tens of meters for its entire length. The formerly incised channels are now filled and in many places the riverbed is far above the elevation of former confluences with tributaries, resulting in their damming and redirection. The situation has caused increasingly difficult problems for residents of villages and plantations in the area. The most serious affect the town of El Palmar, which has been frequently flooded by the Río Nimá I.
"Blocked from its former confluence with the Río Nimá II by mudflow accumulations, it now flows through El Palmar into the Río Samalá (figure 5). At El Palmar, the Río Nimá II flows less than 100 m from the Río Nimá I, with no remaining topographic barriers other than mudflow levees. Erratic mudflow deposition in the coming rainy season could divert the entire Río Nimá II, including its mudflow load, via the Río Nimá I into the Río Samalá over a waterfall more than 100 m high, at a point 3 km N of the present confluence. Near San Felipe (14 km SSW of Santiaguito), the Río Nimá II aggraded by more than 20 m during the last rainy season (May-November 1987). Similar aggradations occurred as far south as San Sebastián (22 km SSW of Santiaguito) in the Río Samalá, which receives the Río Nimá II just W of San Felipe. Because of strongly parallel drainage systems, filling of the Río Nimá II and the Río Samalá must eventually result in overflow into nearby rivers, which are at significantly lower levels. The consequences of such stream diversions are complex and hard to rigorously forecast, but such problems occupy much of the current hazard study because the area S of El Palmar is densely populated."
Reference. Rose, W.I., 1987, Volcanic activity at Santiaguito Volcano, 1976-1984 in Fink, J., ed., The Emplacement of Silicic Domes and Lava Flows: GSA Special Paper 212, p. 17-27.
Geologic Background. Symmetrical, forest-covered Santa María volcano is part of a chain of large stratovolcanoes that rise above the Pacific coastal plain of Guatemala. The sharp-topped, conical profile is cut on the SW flank by a 1.5-km-wide crater. The oval-shaped crater extends from just below the summit to the lower flank, and was formed during a catastrophic eruption in 1902. The renowned Plinian eruption of 1902 that devastated much of SW Guatemala followed a long repose period after construction of the large basaltic andesite stratovolcano. The massive dacitic Santiaguito lava-dome complex has been growing at the base of the 1902 crater since 1922. Compound dome growth at Santiaguito has occurred episodically from four vents, with activity progressing E towards the most recent, Caliente. Dome growth has been accompanied by almost continuous minor explosions, with periodic lava extrusion, larger explosions, pyroclastic flows, and lahars.
Information Contacts: W.I. Rose, Reinaldo Mercado, and James Vallance, Michigan Tech UniversityOtoniel Matías, Jorge Girón, and Francisco Alvarez, INSIVUMEH; J. Fink and Steve Anderson, Arizona State University; Lee Siebert, SI; Gerardo Sánchez Rubio, Estación Regional del Centro, Instituto de Geología, UNAM, Guanajuato, México.
Semeru (Indonesia) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Semeru
Indonesia
8.108°S, 112.922°E; summit elev. 3657 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Continued Vulcanian activity
. . . Vulcanian activity during February.
Geologic Background. Semeru, the highest volcano on Java, and one of its most active, lies at the southern end of a volcanic massif extending north to the Tengger caldera. The steep-sided volcano, also referred to as Mahameru (Great Mountain), rises above coastal plains to the south. Gunung Semeru was constructed south of the overlapping Ajek-ajek and Jambangan calderas. A line of lake-filled maars was constructed along a N-S trend cutting through the summit, and cinder cones and lava domes occupy the eastern and NE flanks. Summit topography is complicated by the shifting of craters from NW to SE. Frequent 19th and 20th century eruptions were dominated by small-to-moderate explosions from the summit crater, with occasional lava flows and larger explosive eruptions accompanied by pyroclastic flows that have reached the lower flanks of the volcano.
Information Contacts: VSI.
Shikotsu (Japan) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Shikotsu
Japan
42.688°N, 141.38°E; summit elev. 1320 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Earthquake swarms
Local earthquake swarms occurred 24 January-18 February. The JMA seismometer, 1.1 km NE of the summit cone, recorded 30 events in January and 124 in February. Epicenters were located at the NW somma using data from five Hokkaido University seismometers. A white plume constantly rose ~100 m.
Tarumai's strongest earthquake swarm of the past two decades began in late 1980, peaking in February 1981, when more than 1,200 shocks were recorded. Late that month ~400 m3 of ash was deposited near the crater by a very small eruption. Seismicity then declined, and the number of local events has averaged <10/month in the last few years (figure 4).
Geologic Background. The 13 x 15 km Shikotsu caldera, largely filled by the waters of Lake Shikotsu, was formed during one of Hokkaido's largest Quaternary eruptions about 31-34,000 years ago. The small andesitic Tarumaesan stratovolcano was then constructed on its SE rim and has been frequently active in historical time. Pyroclastic-flow deposits from Tarumaesan extend nearly to the Pacific coast. Two other Holocene post-caldera volcanoes, Fuppushidake (adjacent to Tarumaesan) and Eniwadake (on the opposite side of the caldera), occur on a line trending NW from Tarumaesan, and were constructed just inside the caldera rim. Minor eruptions took place from the summit of Eniwadake as late as the 17th century. The summit of Tarumaesan contains a small 1.5-km-wide caldera formed during two of Hokkaido's largest historical eruptions, in 1667 and 1739. Tarumaesan is now capped by a flat-topped summit lava dome that formed in 1909.
Information Contacts: JMA.
Tacana (Mexico-Guatemala) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Tacana
Mexico-Guatemala
15.132°N, 92.109°W; summit elev. 4064 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Steam emission and local seismicity continue
Geologists (Gerardo Sánchez Rubio, UNAM; Rudy Machorro Sagastume, Univ of Guanajuato; Aroldo López Perdomo, CUNOR, Guatemala; Napoleón Rodríguez and Víctor Danilo Valdez, INTECAP, Guatemala; and Juan Sánchez Márquez, México) visited Tacaná on 27-28 January. A flank steam plume continued to be emitted. Residents of Tacaná and Sibinal, the nearest villages in Guatemala, reported infrequent to occasional seismicity.
Geologic Background. Tacaná is a 4064-m-high composite stratovolcano that straddles the México/Guatemala border at the NW end of the Central American volcanic belt. The volcano rises 1800 m above deeply dissected plutonic and metamorphic terrain. Three large calderas breached to the south, and the elongated summit region is dominated by a series of lava domes intruded along a NE-SW trend. Volcanism has migrated to the SW, and a small adventive lava dome is located in the crater of the youngest volcano, San Antonio, on the upper SW flank. Viscous lava flow complexes are found on the north and south flanks, and lobate lahar deposits fill many valleys. Radial drainages on the Guatemalan side are deflected by surrounding mountains into the Pacific coastal plain on the SW side of the volcano. Historical activity has been restricted to mild phreatic eruptions, but more powerful explosive activity, including the production of pyroclastic flows, has occurred as recently as about 1950 years ago.
Information Contacts: Gerardo Sánchez Rubio, Estación Regional del Centro, Instituto de Geología, UNAM, Guanajuato, México.
Ulawun (Papua New Guinea) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Ulawun
Papua New Guinea
5.05°S, 151.33°E; summit elev. 2334 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Frequent earthquakes and tremor; heavy rain
Conditions for observing Ulawun were poor in February. The mountain was obscured on most days and received very heavy rainfall between the 9th and the end of the month. A maximum of 36 cm of rain was recorded on the 22nd at the base station, 10 km from the summit. In possible association with the rainfall, the recorded seismicity increased markedly, from 10-200 small events/day at the beginning of the month to a maximum of 1400/day on the 27th. In addition, periods of sub-continuous, non-harmonic tremor started on the 11th, becoming continuous for periods of 1-2 hours daily after the 14th. During 26-28 February, the seismic pattern consisted of alternating periods of intense non-harmonic tremor lasting 1-3 hours and periods of seismic quiet. Seismicity was still strong at the end of the month.
There were no dramatic changes in the emissions from the summit crater. Occasional ground and aerial observations indicated emissions were of weak to moderate white vapours.
Geologic Background. The symmetrical basaltic-to-andesitic Ulawun stratovolcano is the highest volcano of the Bismarck arc, and one of Papua New Guinea's most frequently active. The volcano, also known as the Father, rises above the N coast of the island of New Britain across a low saddle NE of Bamus volcano, the South Son. The upper 1,000 m is unvegetated. A prominent E-W escarpment on the south may be the result of large-scale slumping. Satellitic cones occupy the NW and E flanks. A steep-walled valley cuts the NW side, and a flank lava-flow complex lies to the south of this valley. Historical eruptions date back to the beginning of the 18th century. Twentieth-century eruptions were mildly explosive until 1967, but after 1970 several larger eruptions produced lava flows and basaltic pyroclastic flows, greatly modifying the summit crater.
Information Contacts: P. de Saint-Ours and C. McKee, RVO.
Vulcano
Italy
38.404°N, 14.962°E; summit elev. 500 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
New fracture system
"After the last explosive event, in 1888-90, activity has been mainly fumarolic emissions of varying intensity at the crater. A new fracture system, transverse to the main alignment along which the more recent activity had originated, opened during the last few months.
"No important seismic activity was detected at the same time, and the progressive spreading trend beginning in 1985 was not substantially modified. The rate of longitudinal opening (some meters/month), however, along with the well-defined magmatic character of the gaseous species emitted through these fractures, appear as a clear indication of an increasing pressure from beneath."
Geologic Background. The word volcano is derived from Vulcano stratovolcano in Italy's Aeolian Islands. Vulcano was constructed during six stages over the past 136,000 years. Two overlapping calderas, the 2.5-km-wide Caldera del Piano on the SE and the 4-km-wide Caldera della Fossa on the NW, were formed at about 100,000 and 24,000-15,000 years ago, respectively, and volcanism has migrated north over time. La Fossa cone, active throughout the Holocene and the location of most historical eruptions, occupies the 3-km-wide Caldera della Fossa at the NW end of the elongated 3 x 7 km island. The Vulcanello lava platform is a low, roughly circular peninsula on the northern tip of Vulcano that was formed as an island beginning more than 2,000 years ago and was connected to the main island in about 1550 CE. Vulcanello is capped by three pyroclastic cones and was active intermittently until the 16th century. Explosive activity took place at the Fossa cone from 1898 to 1900.
Information Contacts: M. Martini, Univ di Firenze.
Whakaari/White Island (New Zealand) — February 1988  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Whakaari/White Island
New Zealand
37.52°S, 177.18°E; summit elev. 294 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Minor tephra emission and seismicity
Eruptive activity has declined since 1987, accompanied by continuing deflation of the main crater floor. When geologists visited the volcano on 10 February, the small vent that had formed on the W edge of the 1978 Crater floor in November was not active. Gas and a little ash were being emitted at low pressure from Hitchhiker vent. At a site 350 m SE of the vent, 32-38 mm of new tephra had accumulated since 14 January and 310 mm since 30 October 1987. A few small bombs, probably ejected within the previous few days, were found 100 m SE of the vent; the bombs and associated ash were similar to those found on 14 January and 30 October. Temperatures at fumaroles SE and E of the vent (Donald Mound and Blue Duck areas) had increased in the past year, to a maximum measured value of 541°C, but had declined NE of the vent (Noisy Nellie area). Seismicity since 14 January has been characterized by sub-continuous volcanic tremor of low amplitude and medium-low frequency. E-type (eruption) volcanic earthquakes were recorded on 18 January at 1714, 19 January at 1209, and 21 January at 1713.
Geologic Background. The uninhabited Whakaari/White Island is the 2 x 2.4 km emergent summit of a 16 x 18 km submarine volcano in the Bay of Plenty about 50 km offshore of North Island. The island consists of two overlapping andesitic-to-dacitic stratovolcanoes. The SE side of the crater is open at sea level, with the recent activity centered about 1 km from the shore close to the rear crater wall. Volckner Rocks, sea stacks that are remnants of a lava dome, lie 5 km NW. Descriptions of volcanism since 1826 have included intermittent moderate phreatic, phreatomagmatic, and Strombolian eruptions; activity there also forms a prominent part of Maori legends. The formation of many new vents during the 19th and 20th centuries caused rapid changes in crater floor topography. Collapse of the crater wall in 1914 produced a debris avalanche that buried buildings and workers at a sulfur-mining project. Explosive activity in December 2019 took place while tourists were present, resulting in many fatalities. The official government name Whakaari/White Island is a combination of the full Maori name of Te Puia o Whakaari ("The Dramatic Volcano") and White Island (referencing the constant steam plume) given by Captain James Cook in 1769.
Information Contacts: I. Nairn, NZGS Rotorua.