News Feeds and Google Placemarks
Download Smithsonian / USGS Weekly Volcanic Activity Report Network RSS Feed
The RSS (Really Simple Syndication) feed is identical to the Weekly Volcanic Activity Report minus some features including the header information (latitude and longitude and summit elevation), the Geologic Summary, and a link to the volcano's page from the Global Volcanism Program. At the end of each report is a list of the sources used. Each volcano report includes a link from the volcano's name back to the more complete information in the Weekly Volcanic Activity Report on the Smithsonian website. This feature was first made available on 5 March 2008.
Download Smithsonian / USGS Weekly Volcanic Activity Report Network CAP Feed
The CAP (Common Alerting Protocol) feeds are XML files specifically formatted for disaster management. They are similar in content to the RSS feed, but contain no active links.
 Download Smithsonian / USGS Weekly Volcanic Activity Report Network Link
Download Smithsonian / USGS Weekly Volcanic Activity Report Network Link
A Google Earth network link for the Weekly Volcanic Activity Report can be loaded into the free Google Earth software, and in turn will load placemarks for volcanoes in the current weekly report. Placemark balloons include the volcano name, report date, report text, sources, and links back to the GVP volcano profile page and to the complete Weekly Report for that week. This feature was first made available on 1 April 2009.
Criteria & Disclaimers
The Weekly Volcanic Activity Report does not necessarily include all volcanic activity that occurred on Earth during the week. More than a dozen volcanoes globally have displayed more-or-less continuous eruptive activity for decades or longer, and such routine activity is typically not reported here. Moreover, Earth's sea-floor volcanism is seldom reported even though in theory it represents the single most prolific source of erupted material. The Weekly Volcanic Activity Report summarizes volcanic activity that meets one or more of the following criteria:
- A volcano observatory raises or lowers the alert level at the volcano.
- A volcanic ash advisory has been released by a volcanic ash advisory center (VAAC) stating that an ash cloud has been produced from the volcano.
- A verifiable news report of new activity or a change in activity at the volcano has been issued.
- Observers have reported a significant change in volcanic activity. Such activity can include, but is not restricted to, pyroclastic flows, lahars, lava flows, dome collapse, or increased unrest.
Volcanoes are included in the "New Activity/Unrest" section of the Weekly Volcanic Activity Report if the activity occurs after at least 3 months of quiescence. Once a volcano is included in the "New Activity/Unrest" section, updates will remain in that section unless the activity continues for more than 1 month without escalating, after which time updates will be listed in the "Continuing Activity" section. Volcanoes are also included in the "New Activity/Unrest" section if the volcano is undergoing a period of relatively high unrest, or increasing unrest. This is commonly equal to Alert Level Orange on a scale of Green, Yellow, Orange, Red, where Red is the highest alert. Or alert level 3 on a scale of 1-4 or 1-5.
It is important to note that volcanic activity meeting one or more of these criteria may occur during the week, but may not be included in the Weekly Volcanic Activity Report because we did not receive a report.
1. The Weekly Volcanic Activity Report is intended to provide timely information about global volcanism on a weekly basis. Consequently, the report is generated rapidly by summarizing volcanic reports from various sources, with little time for fact checking. The accuracy of the Weekly Volcanic Activity Report is dependent upon the quality of the volcanic activity reports we receive. Reports published in the Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network are cover longer time periods and are more carefully reviewed, although all of the volcanoes discussed in the Weekly Volcanic Activity Report are not necessarily reported in the Bulletin. Because of our emphasis on rapid reporting on the web we have avoided diacritical marks. Reports are updated on the Weekly Volcanic Activity Report web page as they are received, therefore information may be included regarding events that occurred before the current report period.
2. Rapidly developing events lead to coverage that is often fragmentary. Volcanoes, their eruptions, and their plumes and associated atmospheric effects are complex phenomena that may require months to years of data analysis in order to create a comprehensive summary and interpretation of events.
3. Preliminary accounts sometimes contain exaggerations and "false alarms," and accordingly, this report may include some events ultimately found to be erroneous or misleading.
4. Many news agencies do not archive the articles they post on the Internet, and therefore the links to some sources may not be active. To obtain information about the cited articles that are no longer available on the Internet contact the source.
5. USGS Disclaimer Statement for this Website:
Information presented on this website is considered public information and may be distributed or copied. Use of appropriate byline/photo/image credit is requested. We strongly recommend that USGS data be acquired directly from a USGS server and not through other sources that may change the data in some way. While USGS makes every effort to provide accurate and complete information, various data such as names, telephone numbers, etc. may change prior to updating. USGS welcomes suggestions on how to improve our home page and correct errors. USGS provides no warranty, expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, reliability or completeness of furnished data.
Some of the documents on this server may contain live references (or pointers) to information created and maintained by other organizations. Please note that USGS does not control and cannot guarantee the relevance, timeliness, or accuracy of these outside materials.
For site security purposes and to ensure that this service remains available to all users, this government computer system employs software programs to monitor network traffic to identify unauthorized attempts to upload or change information, or otherwise cause damage. Unauthorized attempts to upload information or change information on this website are strictly prohibited and may be punishable under the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act of 1986 and the National Information Infrastructure Protection Act. Information may also be used for authorized law enforcement investigations. (Last modified September 21, 1999.)
U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey, Reston, VA, USA
URL: https://volcano.si.edu/reports_weekly.cfm
![]() Download Smithsonian / USGS Weekly Volcanic Activity Report Network Link
Download Smithsonian / USGS Weekly Volcanic Activity Report Network Link
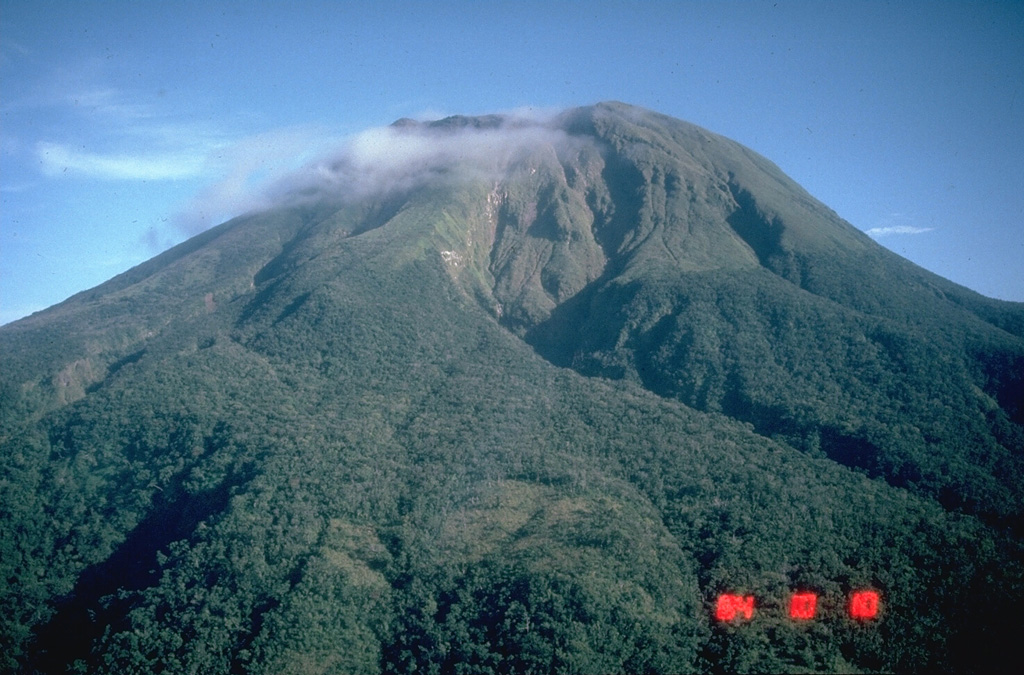
 Bulusan
Bulusan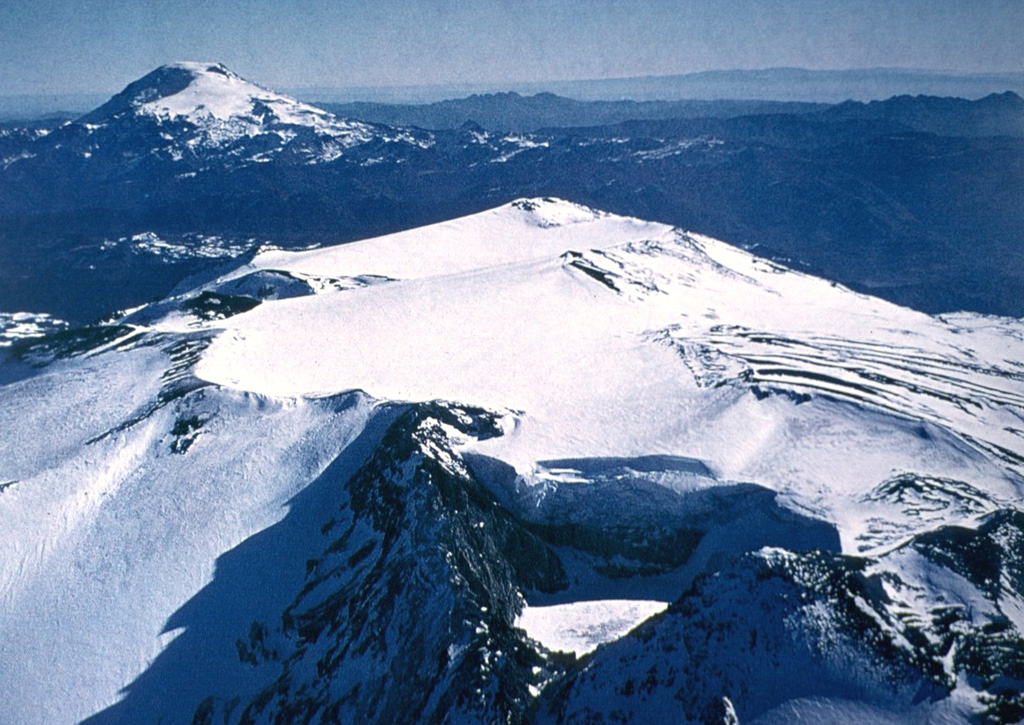 Copahue
Copahue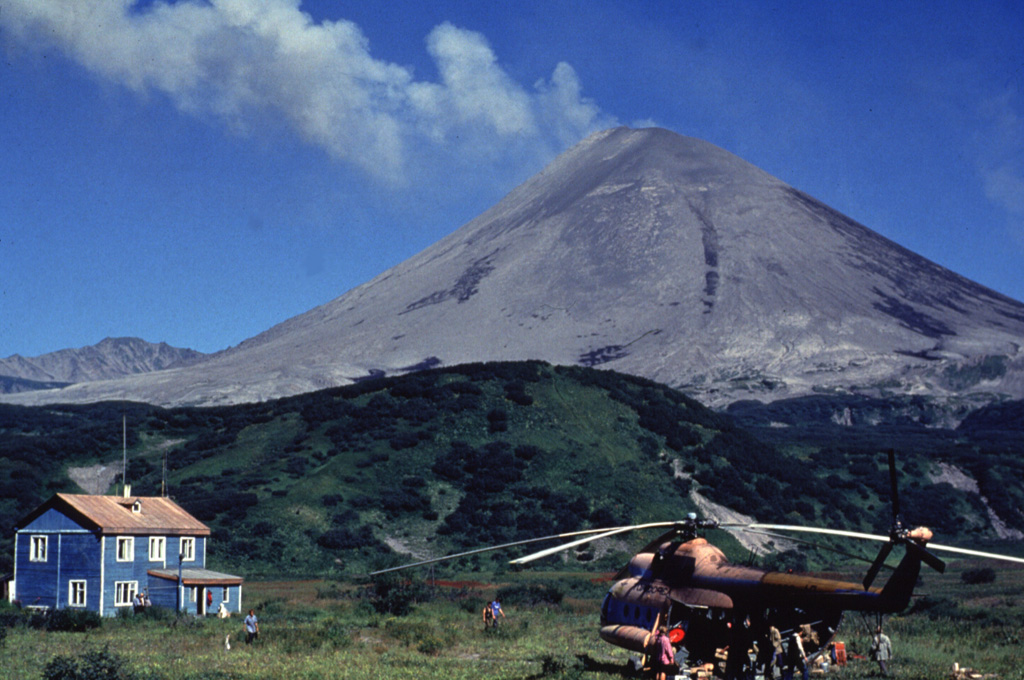 Karymsky
Karymsky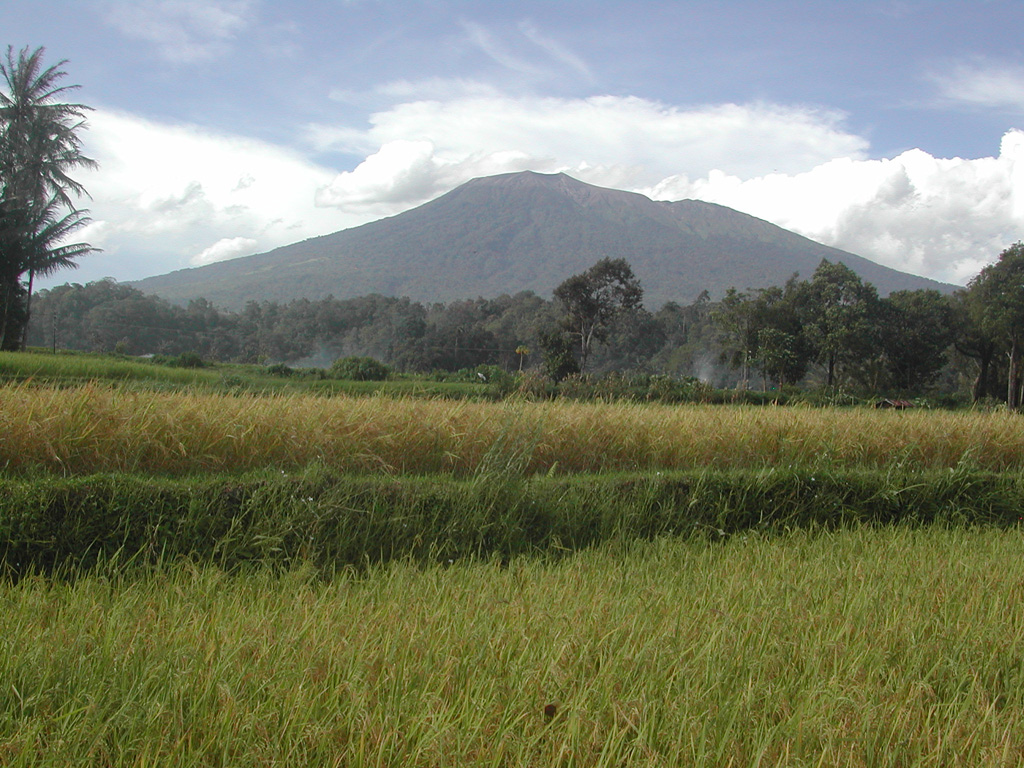 Marapi
Marapi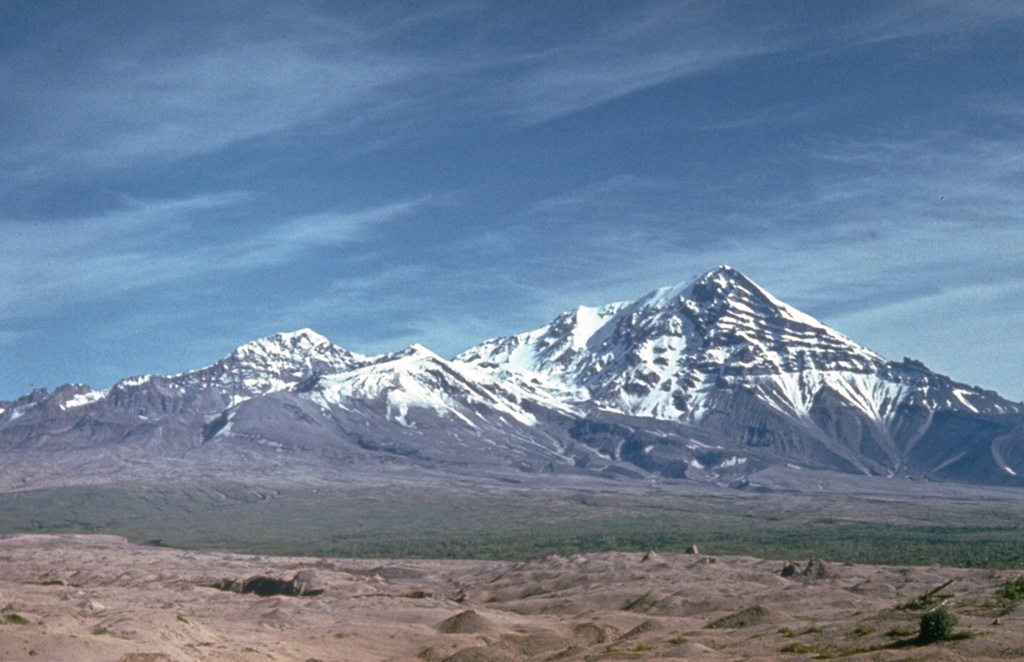 Sheveluch
Sheveluch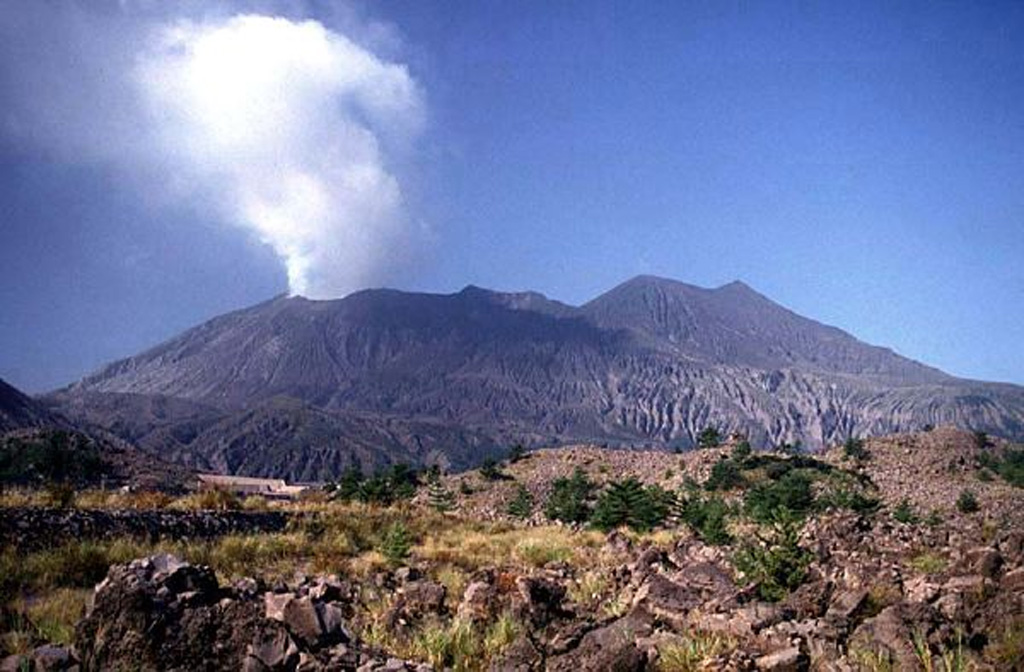 Aira
Aira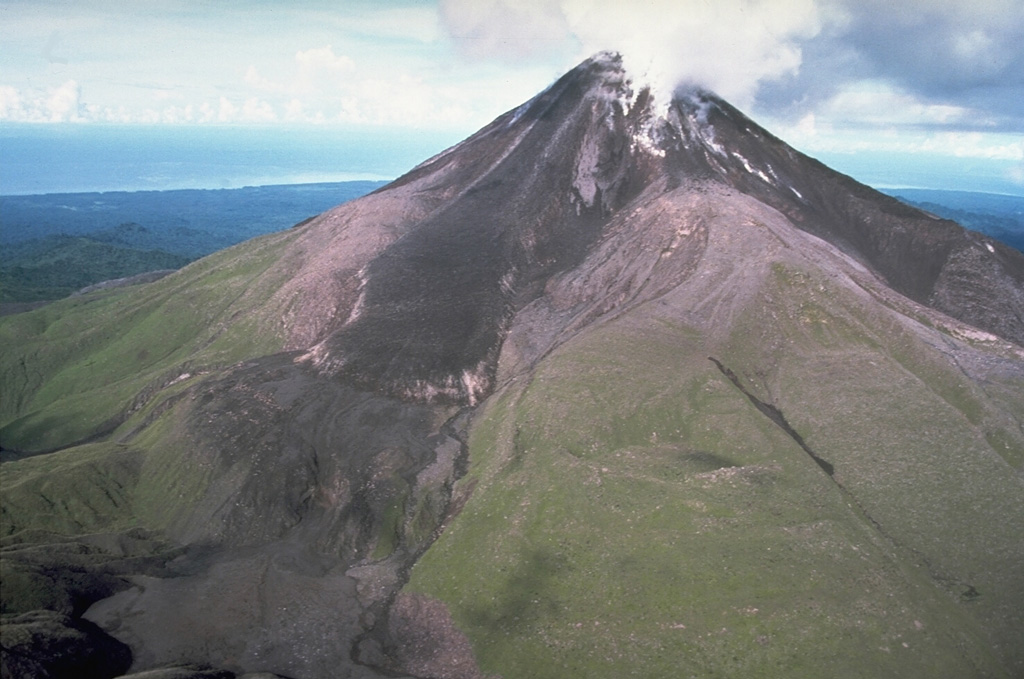 Bagana
Bagana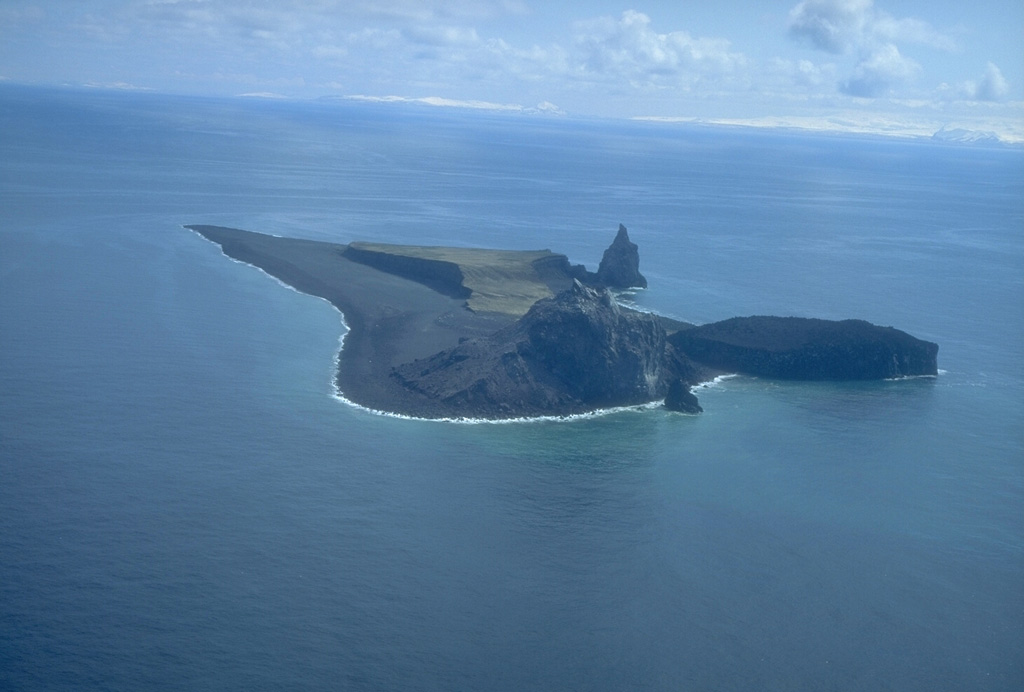 Bogoslof
Bogoslof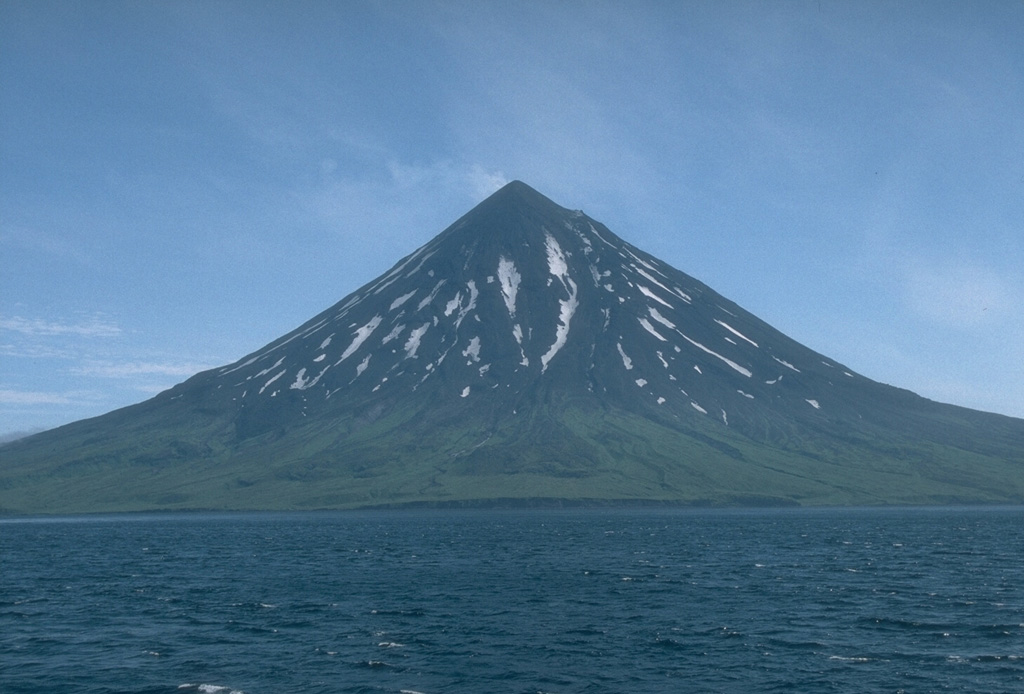 Cleveland
Cleveland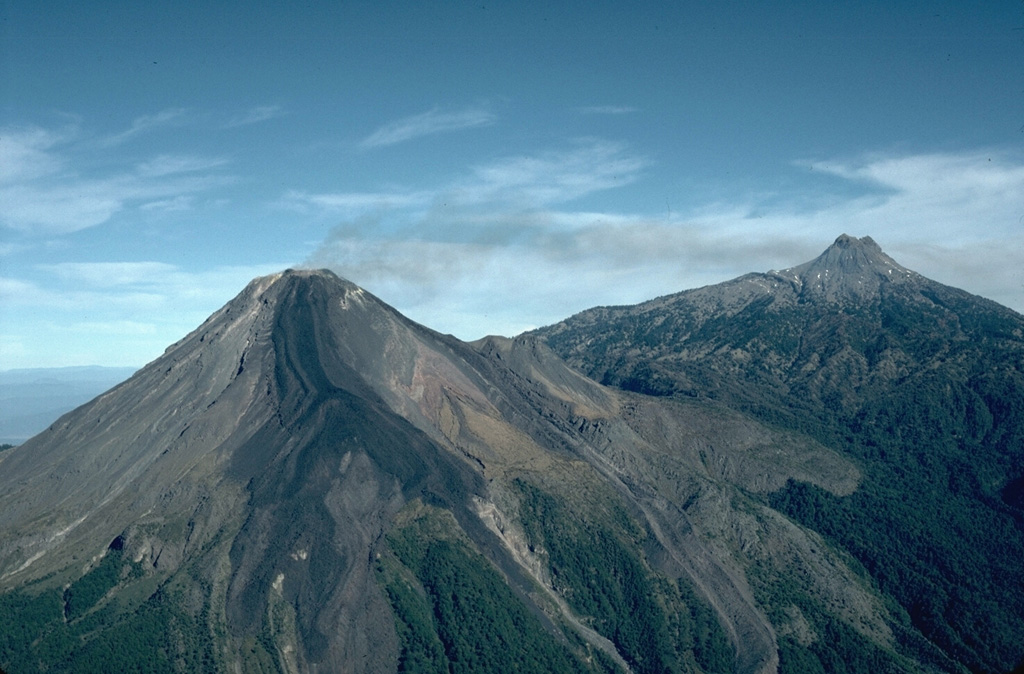 Colima
Colima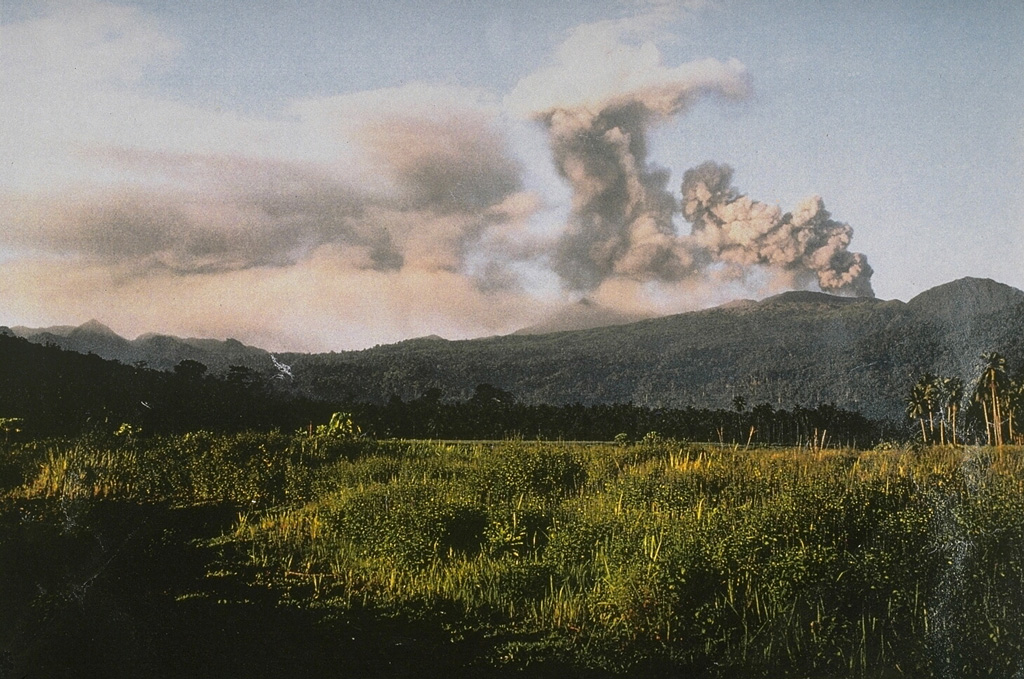 Dukono
Dukono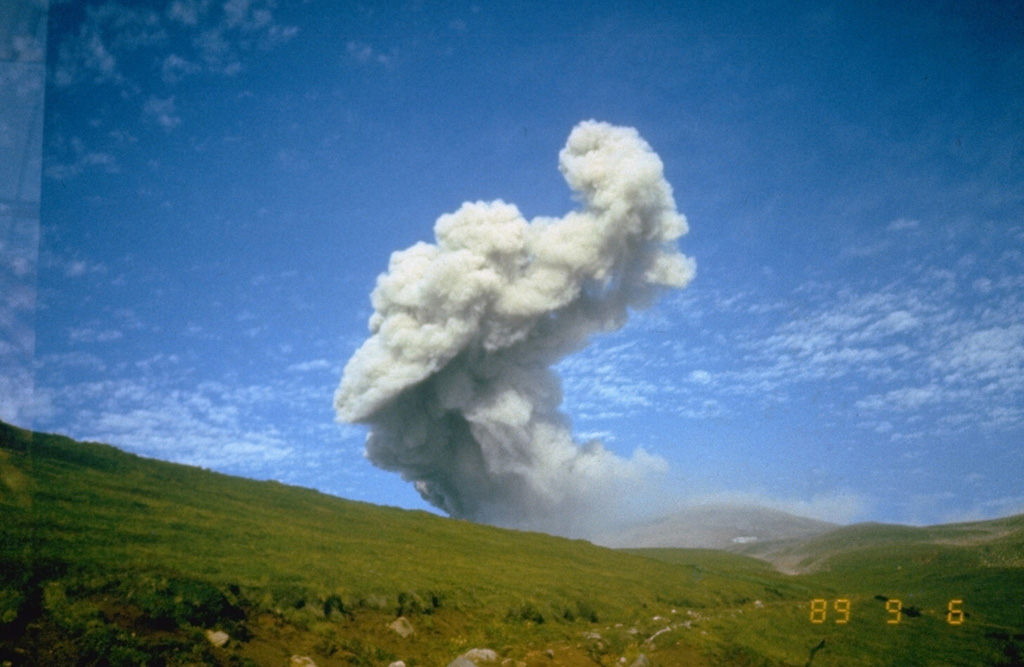 Ebeko
Ebeko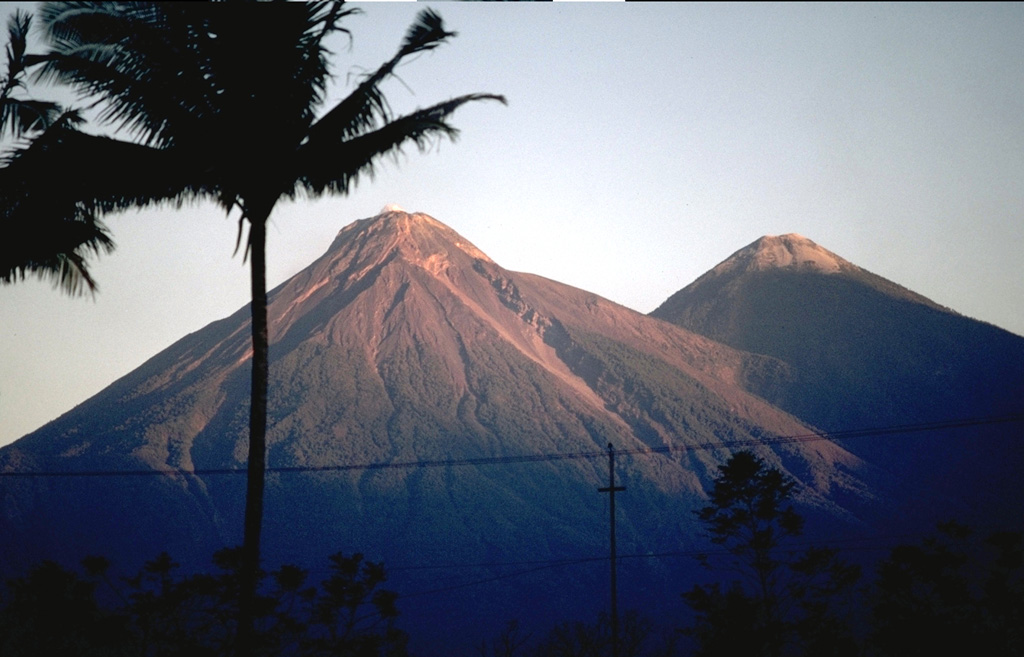 Fuego
Fuego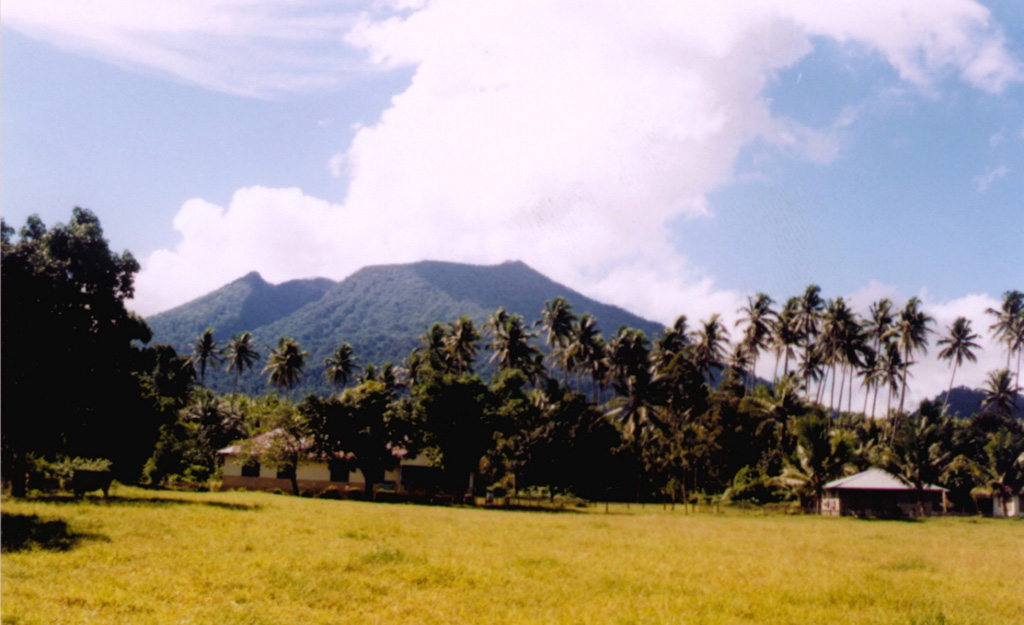 Ibu
Ibu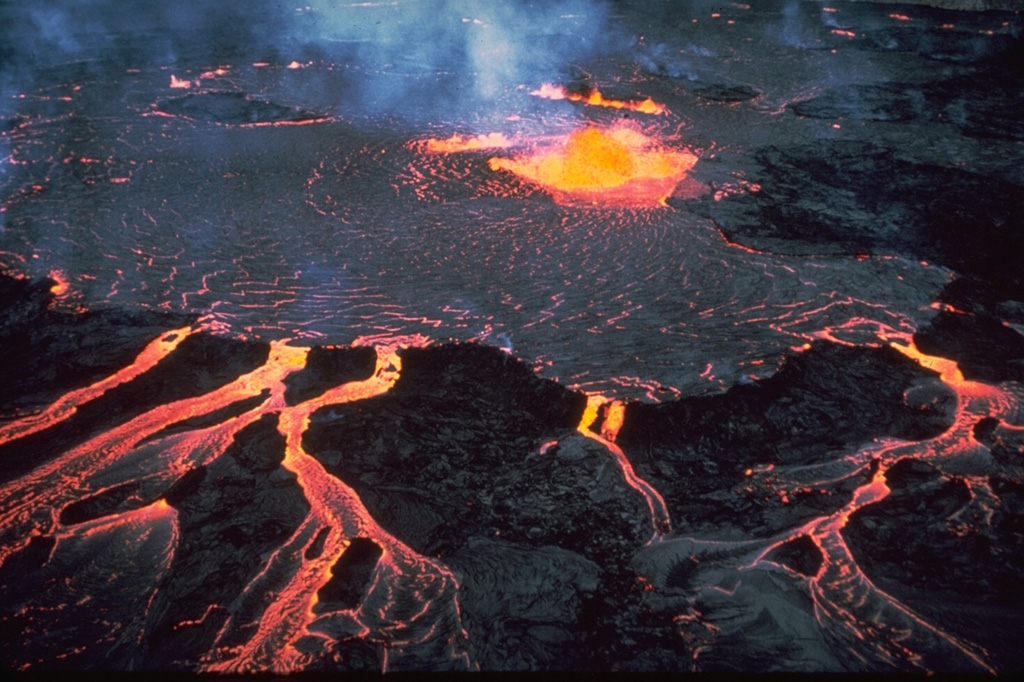 Kilauea
Kilauea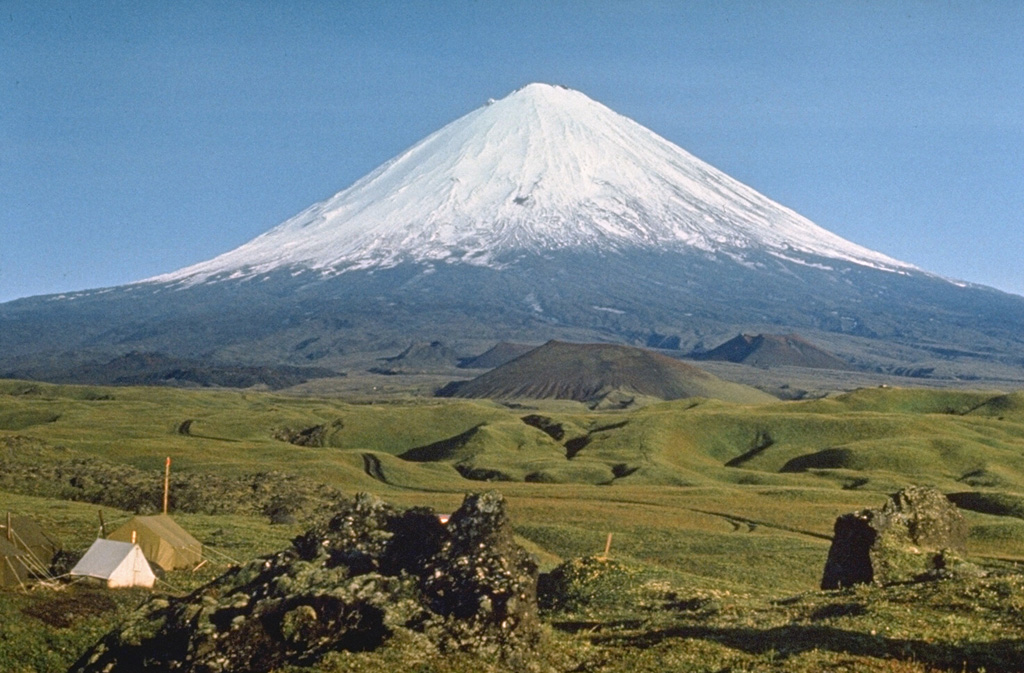 Klyuchevskoy
Klyuchevskoy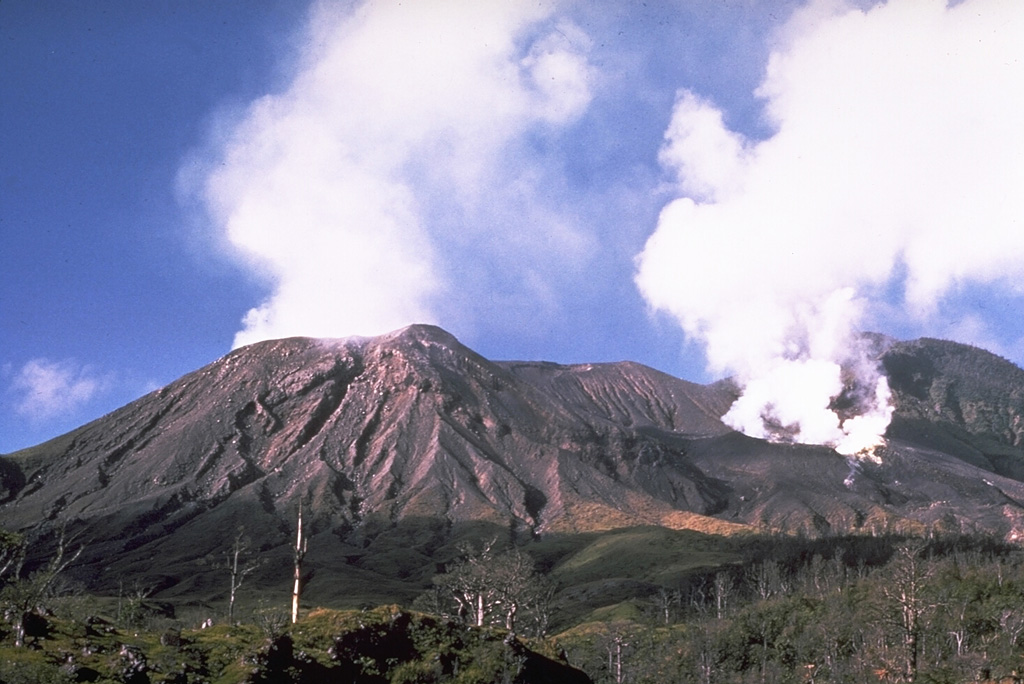 Langila
Langila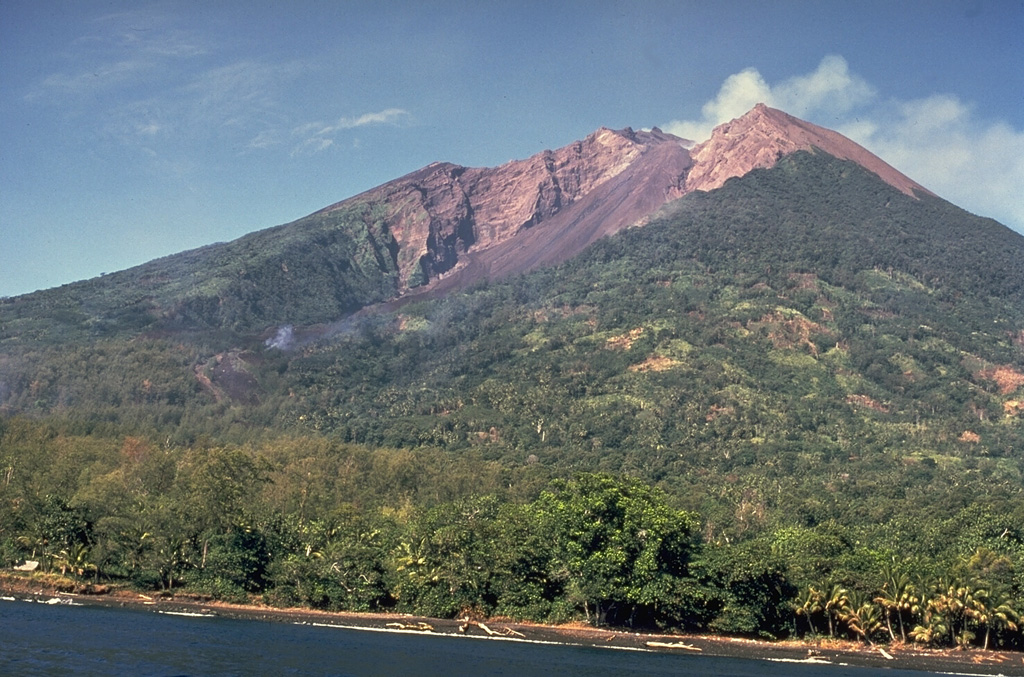 Manam
Manam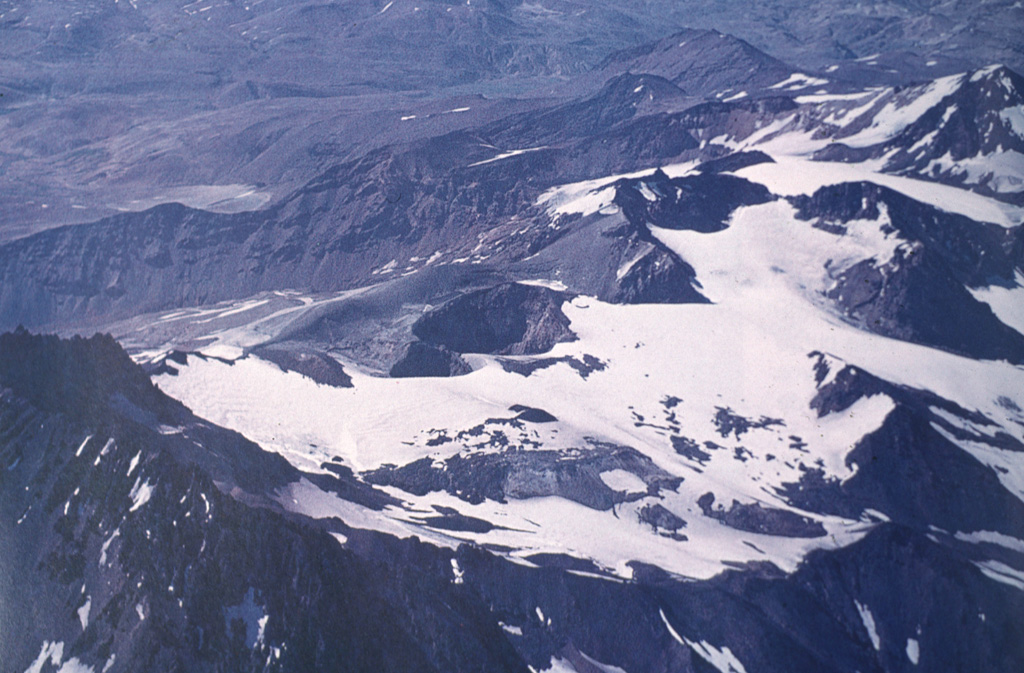 Planchon-Peteroa
Planchon-Peteroa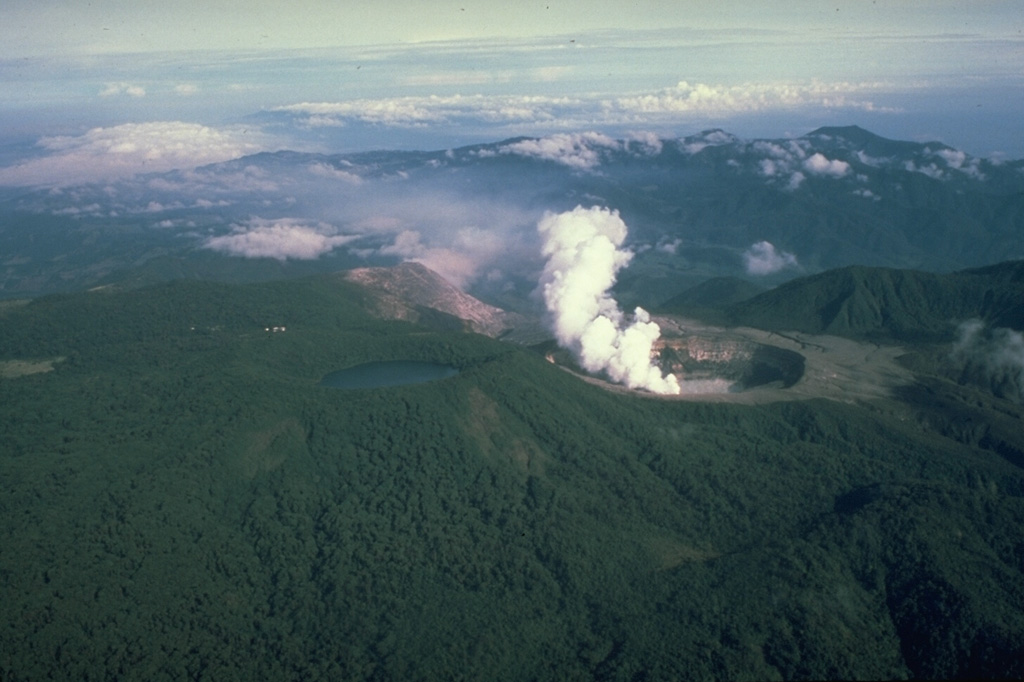 Poas
Poas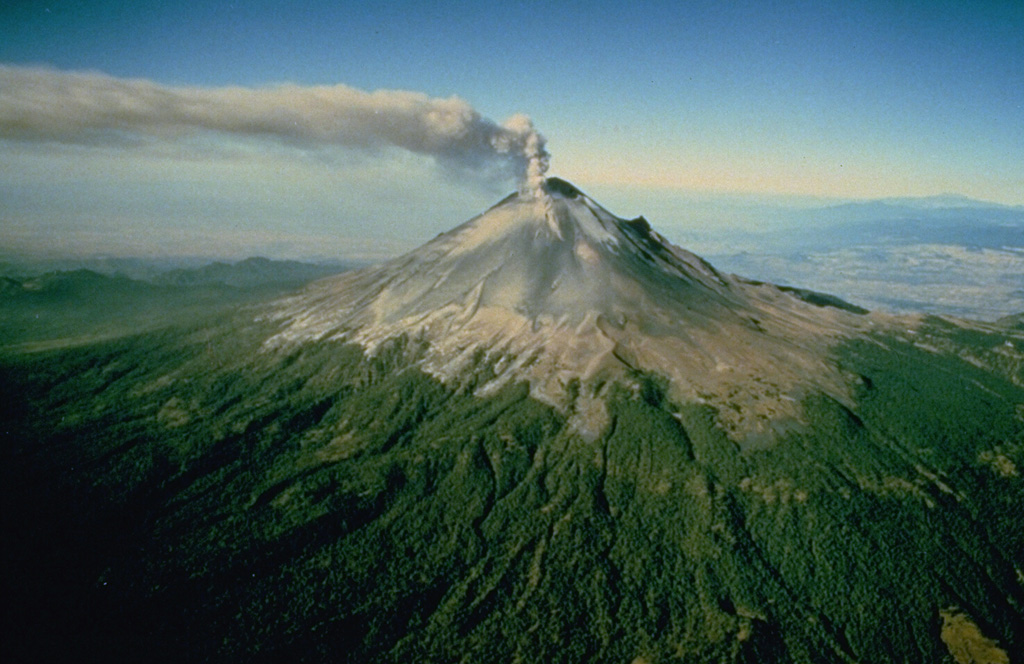 Popocatepetl
Popocatepetl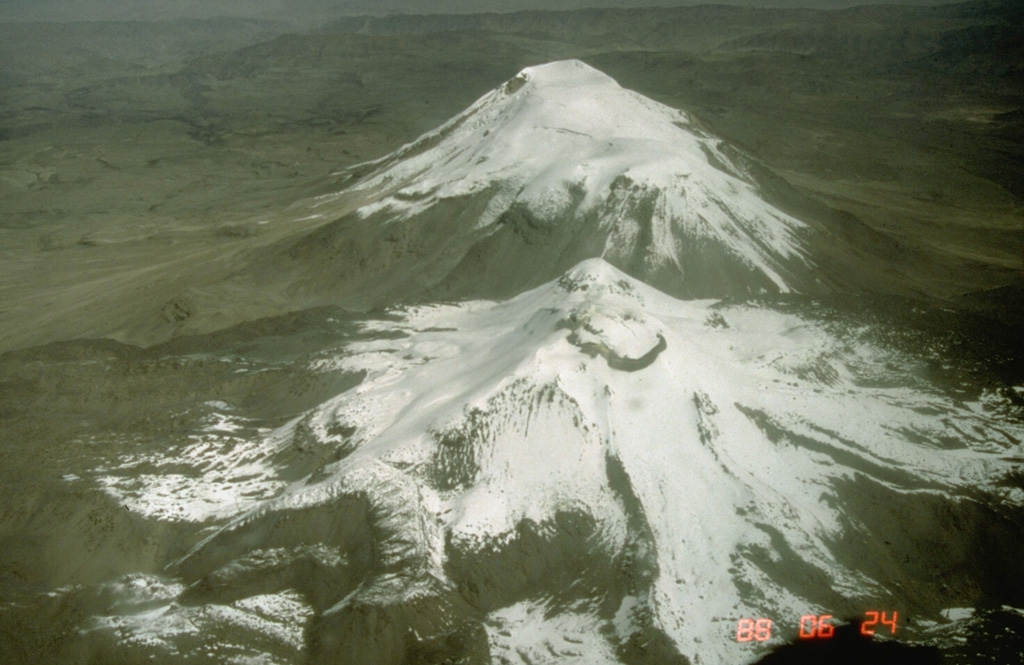 Sabancaya
Sabancaya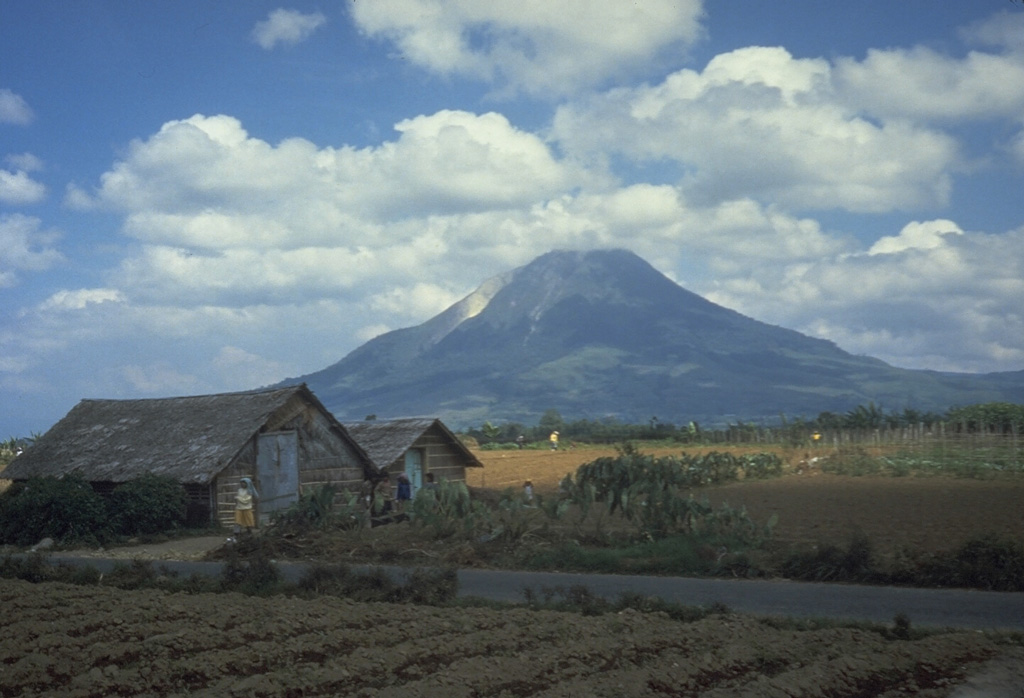 Sinabung
Sinabung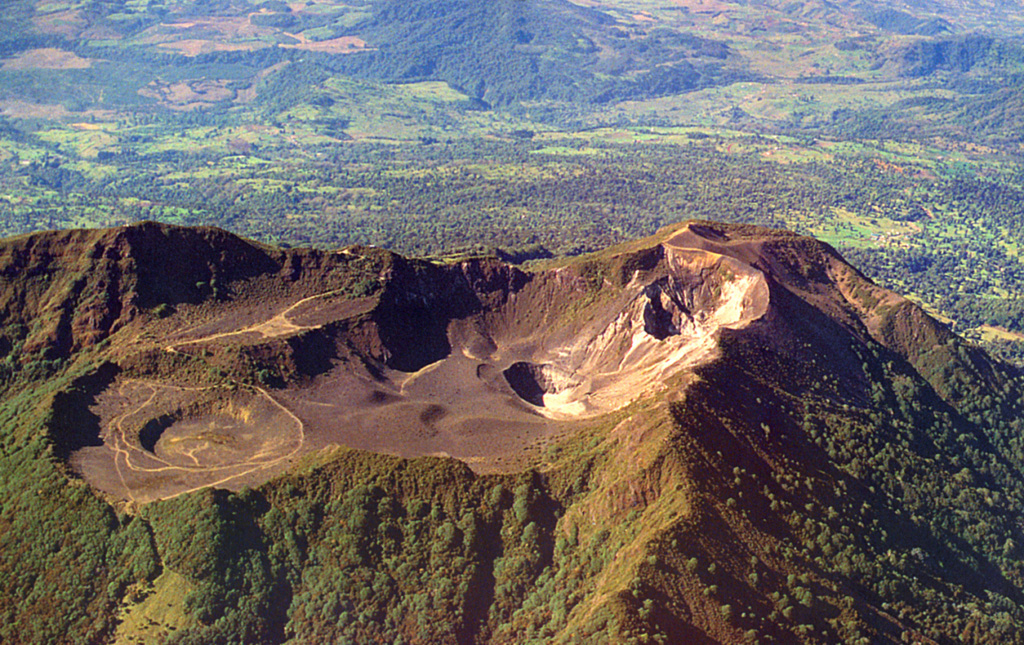 Turrialba
Turrialba