Recently Published Bulletin Reports
Erebus (Antarctica) Lava lake remains active; most thermal alerts recorded since 2019
Rincon de la Vieja (Costa Rica) Frequent phreatic explosions during July-December 2023
Bezymianny (Russia) Explosion on 18 October 2023 sends ash plume 8 km high; lava flows and incandescent avalanches
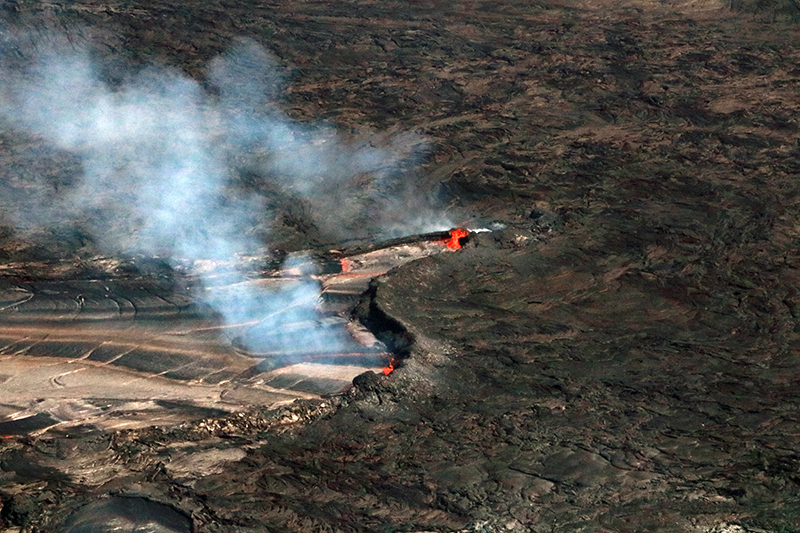
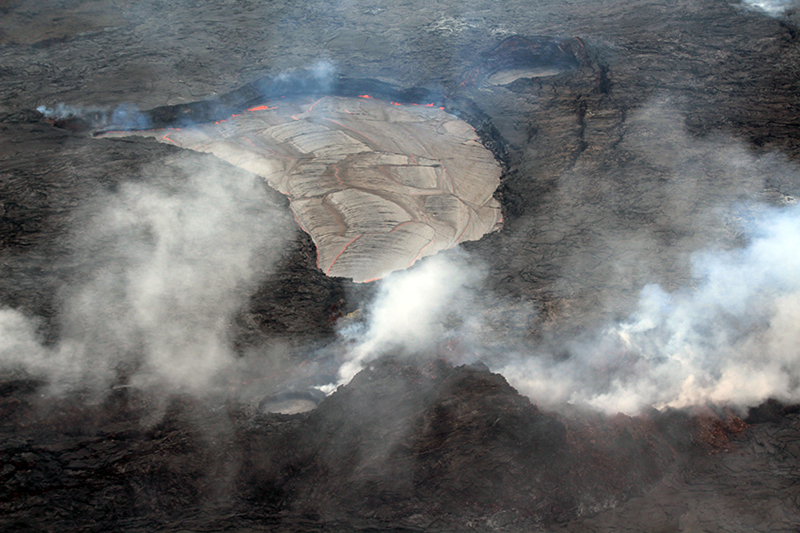
Kilauea (United States) Low-level lava effusions in the lava lake at Halema’uma’u during July-December 2022
Nyamulagira (DR Congo) Lava flows and thermal activity during May-October 2023
Bagana (Papua New Guinea) Explosions, ash plumes, ashfall, and lava flows during April-September 2023
Mayon (Philippines) Lava flows, pyroclastic flows, ash emissions, and seismicity during April-September 2023
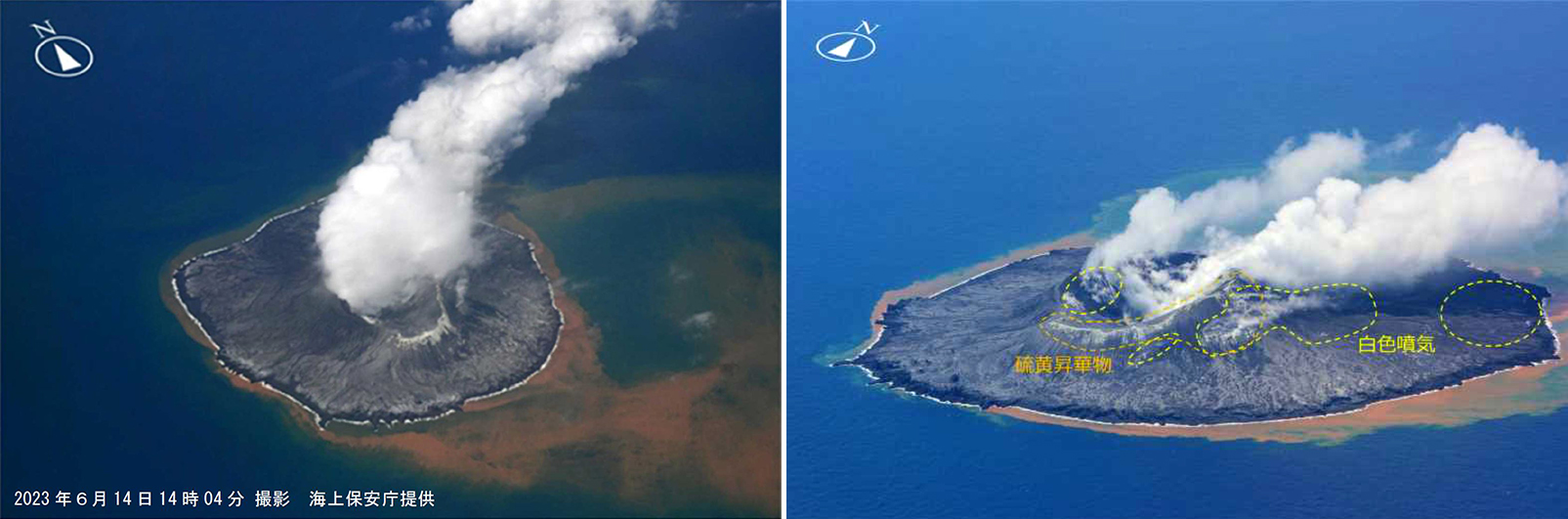
Nishinoshima (Japan) Eruption plumes and gas-and-steam plumes during May-August 2023
Krakatau (Indonesia) White gas-and-steam plumes and occasional ash plumes during May-August 2023
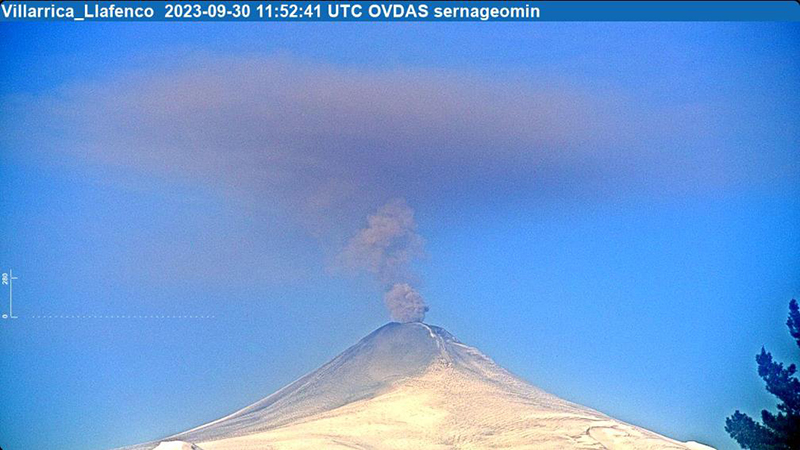
Villarrica (Chile) Strombolian activity, gas-and-ash emissions, and crater incandescence during April-September 2023
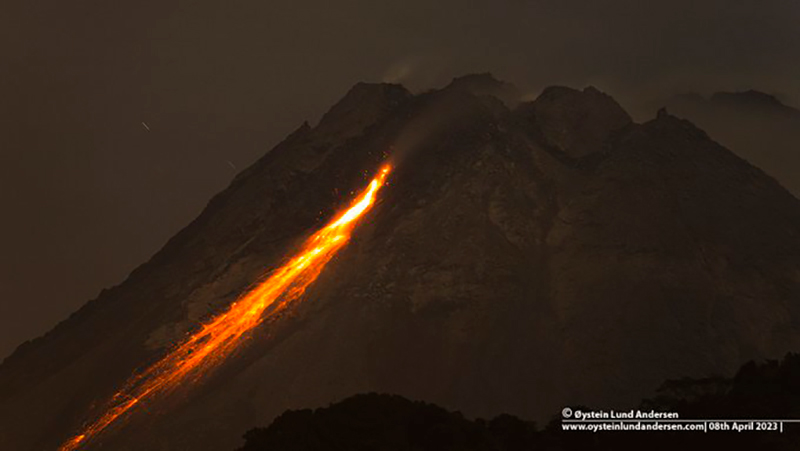
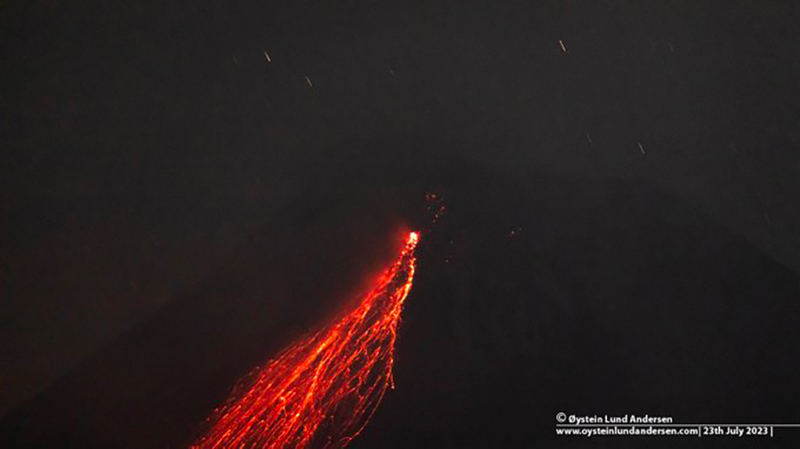
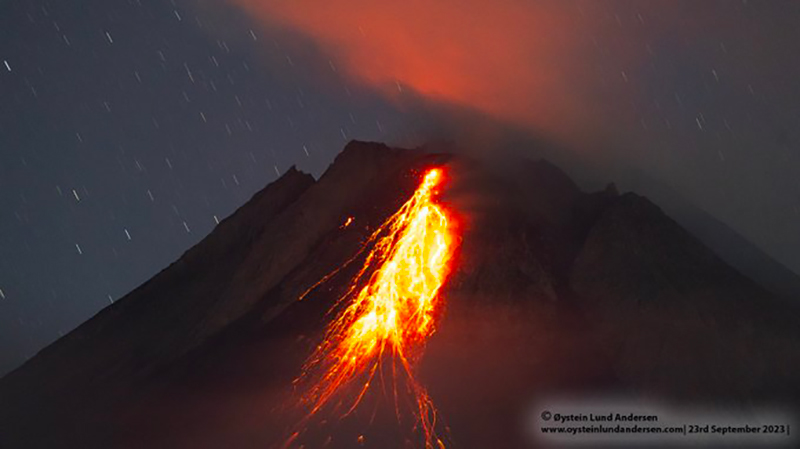
Merapi (Indonesia) Frequent incandescent avalanches during April-September 2023
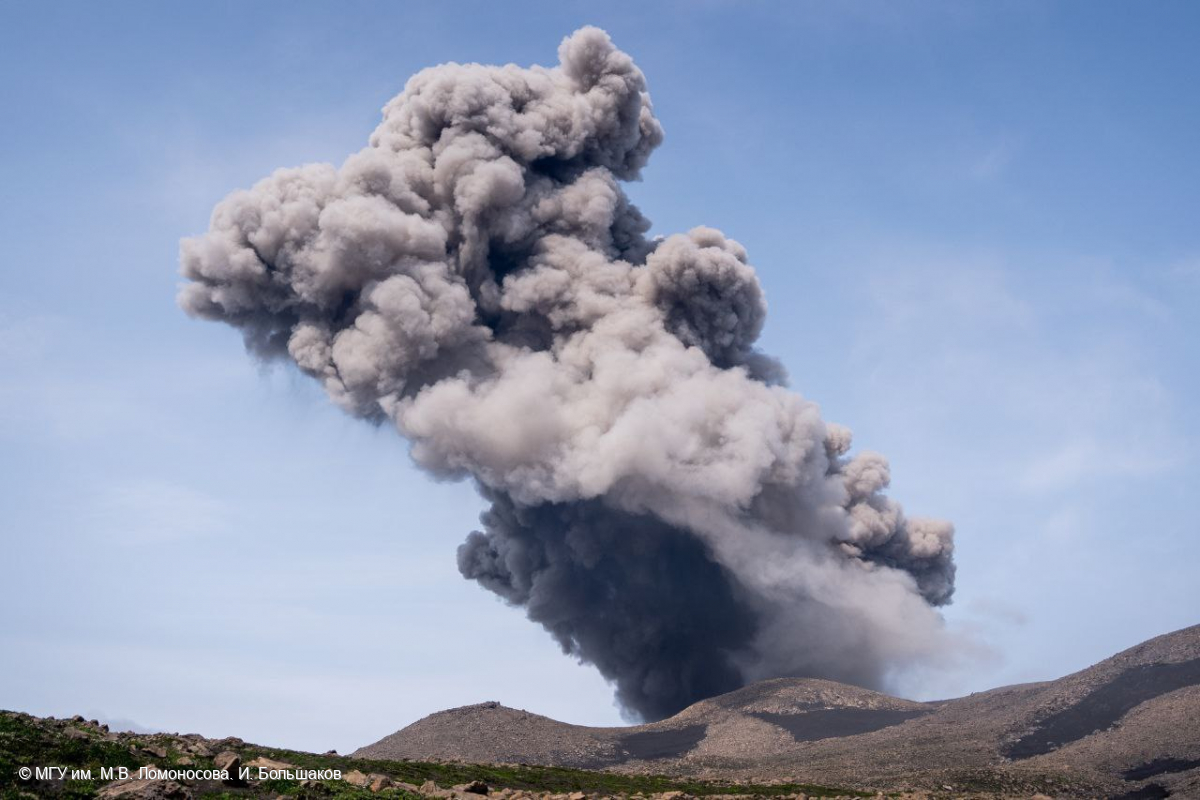
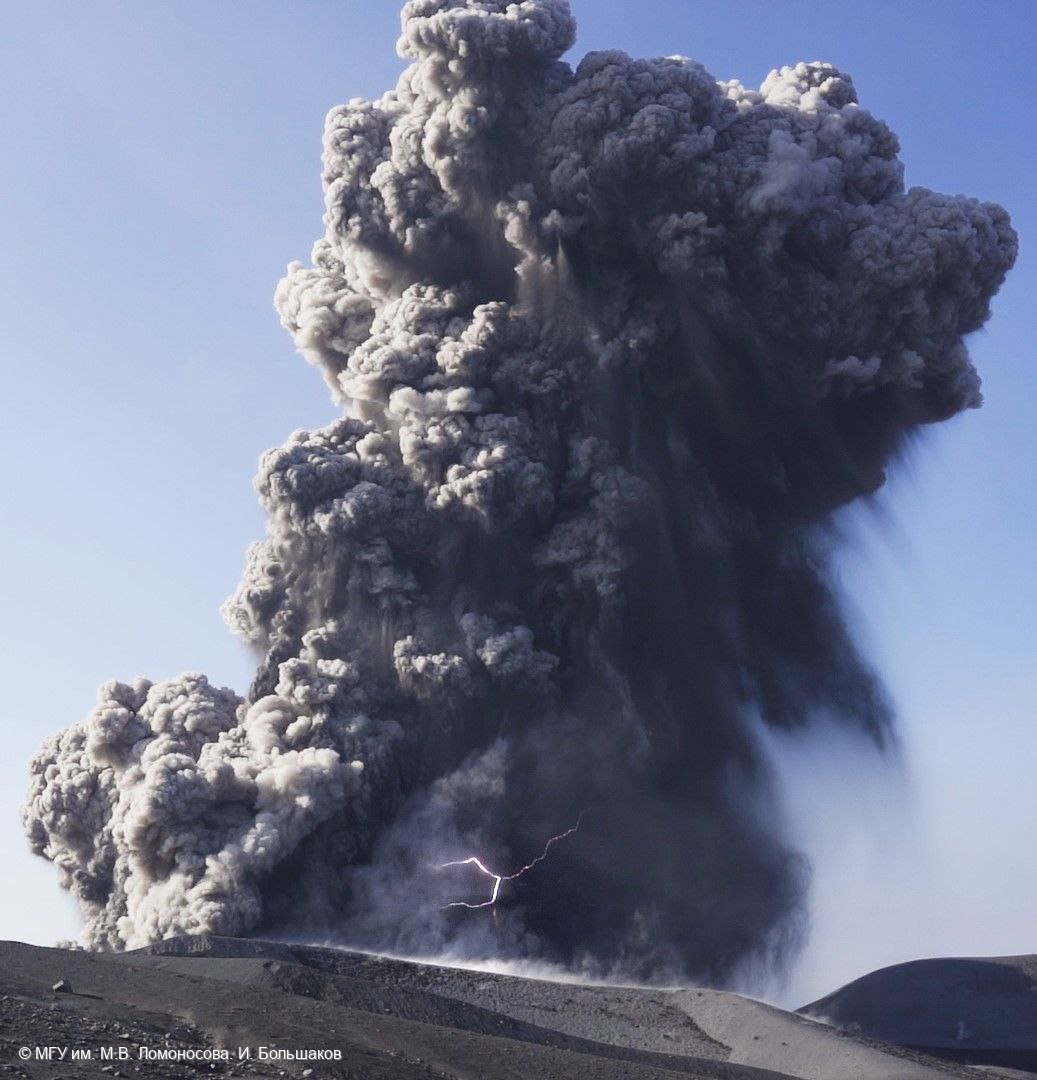
Ebeko (Russia) Moderate explosive activity with ash plumes continued during June-November 2023
Erebus (Antarctica) — January 2024  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Erebus
Antarctica
77.53°S, 167.17°E; summit elev. 3794 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Lava lake remains active; most thermal alerts recorded since 2019
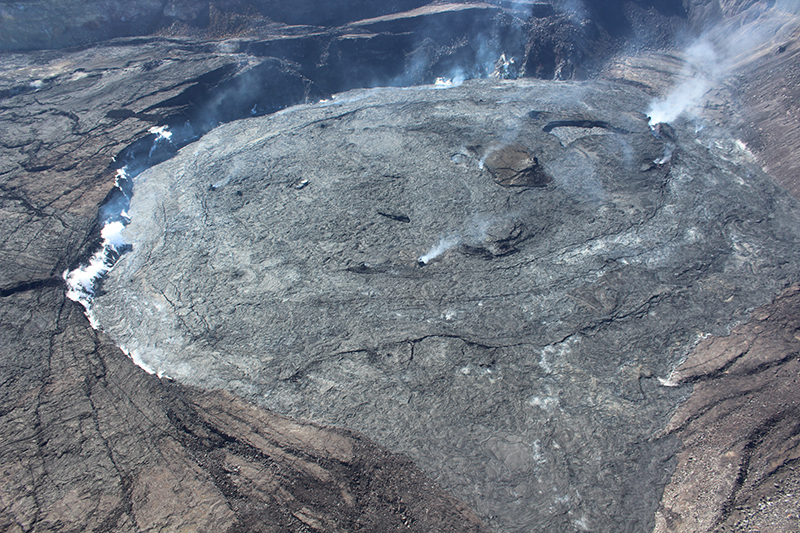
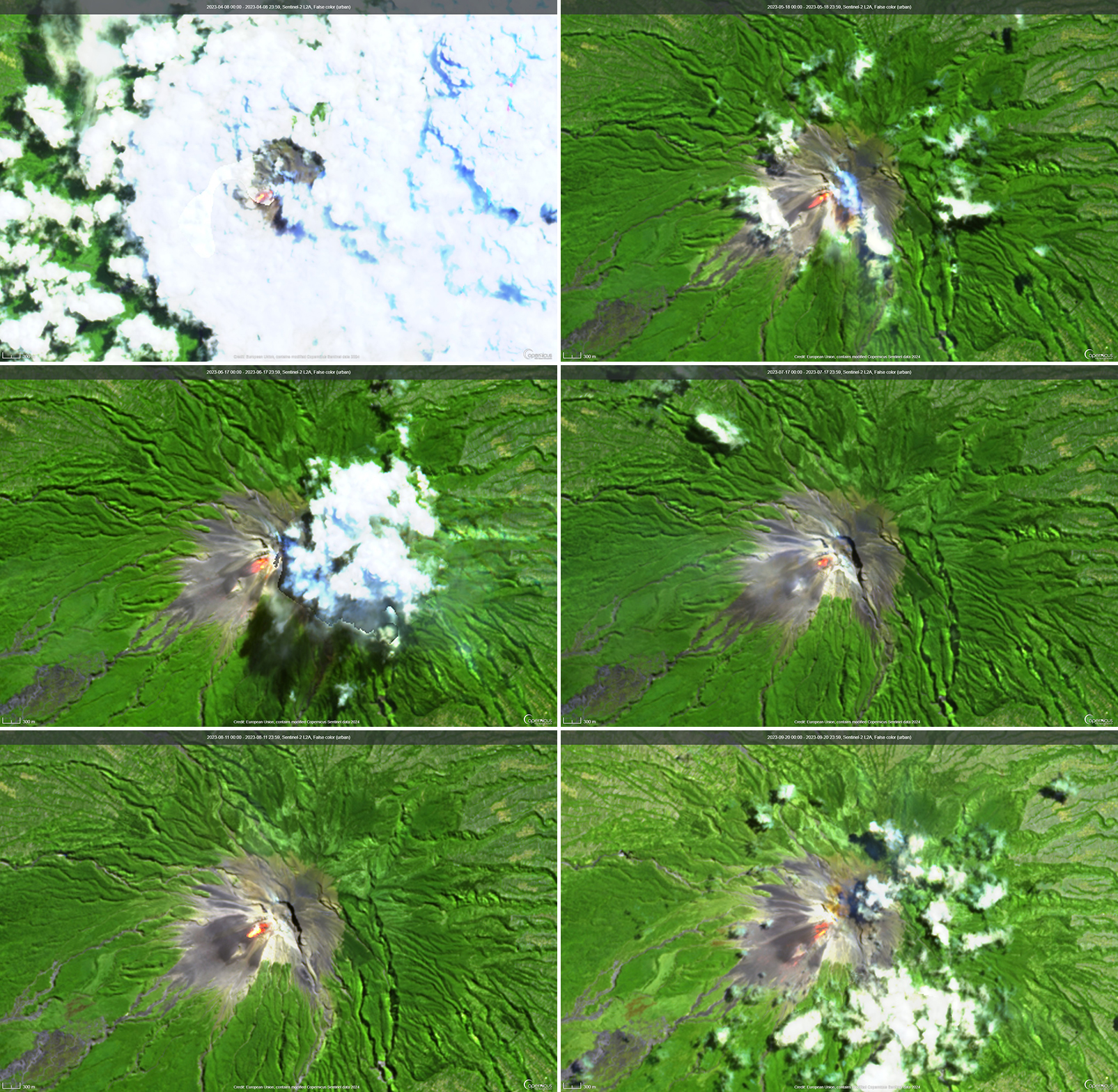
The lava lake in the summit crater of Erebus has been active since at least 1972. Located in Antarctica overlooking the McMurdo Station on Ross Island, it is the southernmost active volcano on the planet. Because of the remote location, activity is primarily monitored by satellites. This report covers activity during 2023.
The number of thermal alerts recorded by the Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology’s MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System increased considerably in 2023 compared to the years 2020-2022 (table 9). In contrast to previous years, the MODIS instruments aboard the Aqua and Terra satellites captured data from Erebus every month during 2023. Consistent with previous years, the lowest number of anomalous pixels were recorded in January, November, and December.
Table 9. Number of monthly MODIS-MODVOLC thermal alert pixels recorded at Erebus during 2017-2023. See BGVN 42:06 for data from 2000 through 2016. The table was compiled using data provided by the HIGP – MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System.
| Year |
Jan |
Feb |
Mar |
Apr |
May |
Jun |
Jul |
Aug |
Sep |
Oct |
Nov |
Dec |
SUM |
| 2017 |
0 |
21 |
9 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
11 |
61 |
76 |
52 |
0 |
3 |
234 |
| 2018 |
0 |
21 |
58 |
182 |
55 |
17 |
137 |
172 |
103 |
29 |
0 |
0 |
774 |
| 2019 |
2 |
21 |
162 |
151 |
55 |
56 |
75 |
53 |
29 |
19 |
1 |
0 |
624 |
| 2020 |
0 |
2 |
16 |
18 |
4 |
4 |
1 |
3 |
18 |
3 |
1 |
6 |
76 |
| 2021 |
0 |
9 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
56 |
46 |
47 |
35 |
52 |
5 |
3 |
256 |
| 2022 |
1 |
13 |
55 |
22 |
15 |
32 |
39 |
19 |
31 |
11 |
0 |
0 |
238 |
| 2023 |
2 |
33 |
49 |
82 |
41 |
32 |
70 |
64 |
42 |
17 |
5 |
11 |
448 |
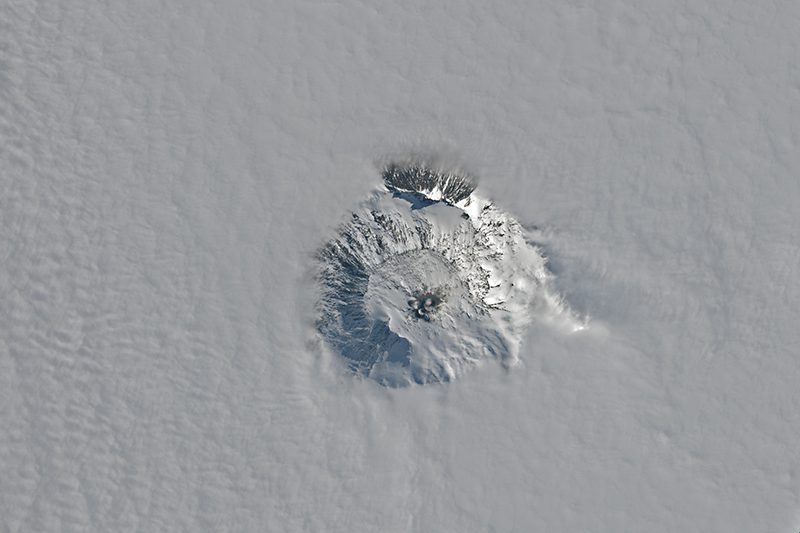
Sentinel-2 infrared images showed one or two prominent heat sources within the summit crater, accompanied by adjacent smaller sources, similar to recent years (see BGVN 46:01, 47:02, and 48:01). A unique image was obtained on 25 November 2023 by the OLI-2 (Operational Land Imager-2) on Landsat 9, showing the upper part of the volcano surrounded by clouds (figure 32).
Geologic Background. Mount Erebus, the world's southernmost historically active volcano, overlooks the McMurdo research station on Ross Island. It is the largest of three major volcanoes forming the crudely triangular Ross Island. The summit of the dominantly phonolitic volcano has been modified by one or two generations of caldera formation. A summit plateau at about 3,200 m elevation marks the rim of the youngest caldera, which formed during the late-Pleistocene and within which the modern cone was constructed. An elliptical 500 x 600 m wide, 110-m-deep crater truncates the summit and contains an active lava lake within a 250-m-wide, 100-m-deep inner crater; other lava lakes are sometimes present. The glacier-covered volcano was erupting when first sighted by Captain James Ross in 1841. Continuous lava-lake activity with minor explosions, punctuated by occasional larger Strombolian explosions that eject bombs onto the crater rim, has been documented since 1972, but has probably been occurring for much of the volcano's recent history.
Information Contacts: Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/); NASA Earth Observatory, EOS Project Science Office, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/152134/erebus-breaks-through).
Rincon de la Vieja (Costa Rica) — January 2024  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Rincon de la Vieja
Costa Rica
10.83°N, 85.324°W; summit elev. 1916 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Frequent phreatic explosions during July-December 2023
Rincón de la Vieja is a volcanic complex in Costa Rica with a hot convecting acid lake that exhibits frequent weak phreatic explosions, gas-and-steam emissions, and occasional elevated sulfur dioxide levels (BGVN 45:10, 46:03, 46:11). The current eruption period began June 2021. This report covers activity during July-December 2023 and is based on weekly bulletins and occasional daily reports from the Observatorio Vulcanologico Sismologica de Costa Rica-Universidad Nacional (OVSICORI-UNA).
Numerous weak phreatic explosions continued during July-December 2023, along with gas-and-steam emissions and plumes that rose as high as 3 km above the crater rim. Many weekly OVSICORI-UNA bulletins included the previous week's number of explosions and emissions (table 9). For many explosions, the time of explosion was given (table 10). Frequent seismic activity (long-period earthquakes, volcano-tectonic earthquakes, and tremor) accompanied the phreatic activity.
Table 9. Number of reported weekly phreatic explosions and gas-and-steam emissions at Rincón de la Vieja, July-December 2023. Counts are reported for the week before the Weekly Bulletin date; not all reports included these data. Courtesy of OVSICORI-UNA.
| OVSICORI Weekly Bulletin |
Number of explosions |
Number of emissions |
| 28 Jul 2023 |
6 |
14 |
| 4 Aug 2023 |
10 |
12 |
| 1 Sep 2023 |
13 |
11 |
| 22 Sep 2023 |
12 |
13 |
| 29 Sep 2023 |
6 |
11 |
| 6 Oct 2023 |
12 |
5 |
| 13 Oct 2023 |
7 |
9 |
| 20 Oct 2023 |
1 |
15 |
| 27 Oct 2023 |
3 |
23 |
| 3 Nov 2023 |
3 |
10 |
| 17 Nov 2023 |
0 |
Some |
| 24 Nov 2023 |
0 |
14 |
| 8 Dec 2023 |
4 |
16 |
| 22 Dec 2023 |
8 |
18 |
Table 10. Summary of activity at Rincón de la Vieja during July-December 2023. Weak phreatic explosions and gas emissions are noted where the time of explosion was indicated in the weekly or daily bulletins. Height of plumes or emissions are distance above the crater rim. Courtesy of OVSICORI-UNA.
| Date |
Time |
Description of Activity |
| 1 Jul 2023 |
0156 |
Explosion. |
| 2 Jul 2023 |
0305 |
Explosion. |
| 4 Jul 2023 |
0229, 0635 |
Event at 0635 produced a gas-and-steam plume that rose 700 m and drifted W; seen by residents in Liberia (21 km SW). |
| 9 Jul 2023 |
1843 |
Explosion. |
| 21 Jul 2023 |
0705 |
Explosion. |
| 26 Jul 2023 |
1807 |
Explosion. |
| 28 Jul 2023 |
0802 |
Explosion generated a gas-and-steam plume that rose 500 m. |
| 30 Jul 2023 |
1250 |
Explosion. |
| 31 Jul 2023 |
2136 |
Explosion. |
| 11 Aug 2023 |
0828 |
Explosion. |
| 18 Aug 2023 |
1304 |
Explosion. |
| 21 Aug 2023 |
1224 |
Explosion generated gas-and-steam plumes rose 500-600 m. |
| 22 Aug 2023 |
0749 |
Explosion generated gas-and-steam plumes rose 500-600 m. |
| 24 Aug 2023 |
1900 |
Explosion. |
| 25 Aug 2023 |
0828 |
Event produced a steam-and-gas plume that rose 3 km and drifted NW. |
| 27-28 Aug 2023 |
0813 |
Four small events; the event at 0813 on 28 August lasted two minutes and generated a steam-and-gas plume that rose 2.5 km. |
| 1 Sep 2023 |
1526 |
Explosion generated plume that rose 2 km and ejected material onto the flanks. |
| 2-3 Sep 2023 |
- |
Small explosions detected in infrasound data. |
| 4 Sep 2023 |
1251 |
Gas-and-steam plume rose 1 km and drifted W. |
| 7 Nov 2023 |
1113 |
Explosion. |
| 8 Nov 2023 |
0722 |
Explosion. |
| 12 Nov 2023 |
0136 |
Small gas emissions. |
| 14 Nov 2023 |
0415 |
Small gas emissions. |
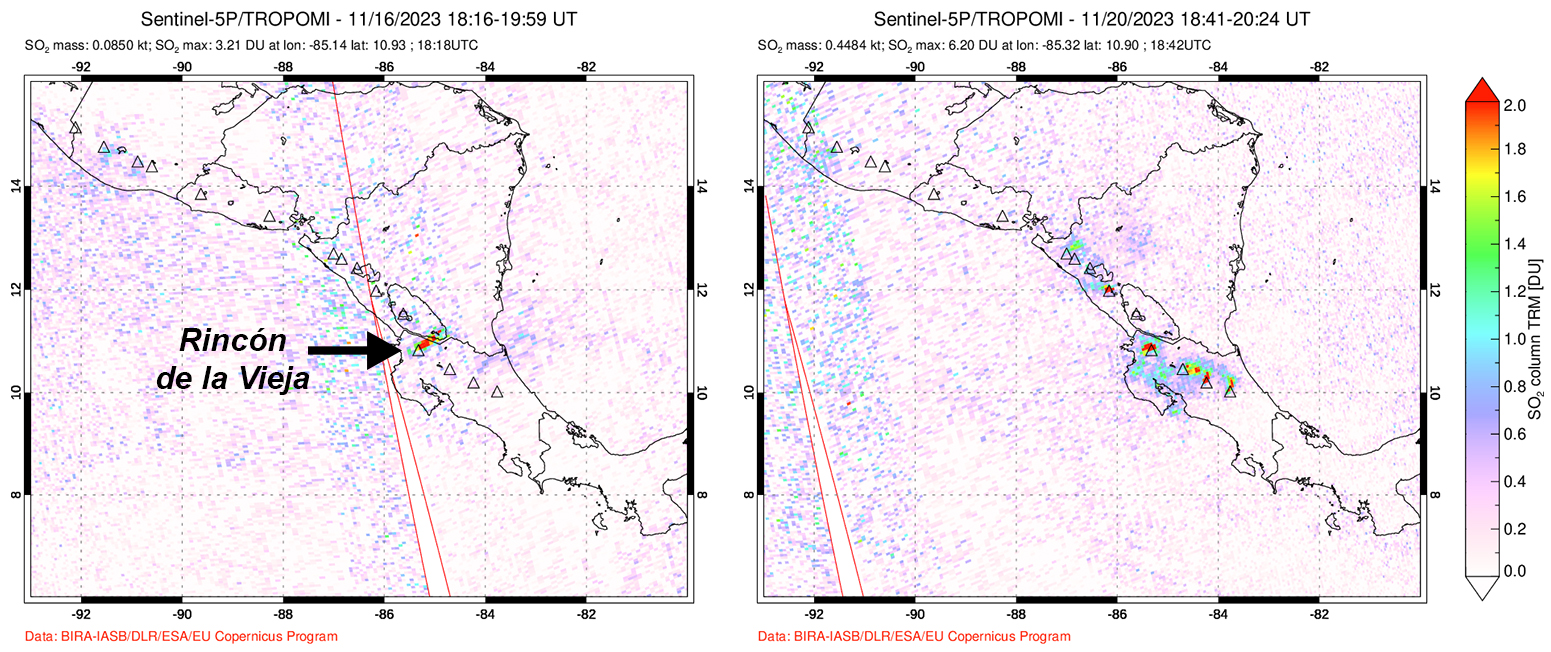
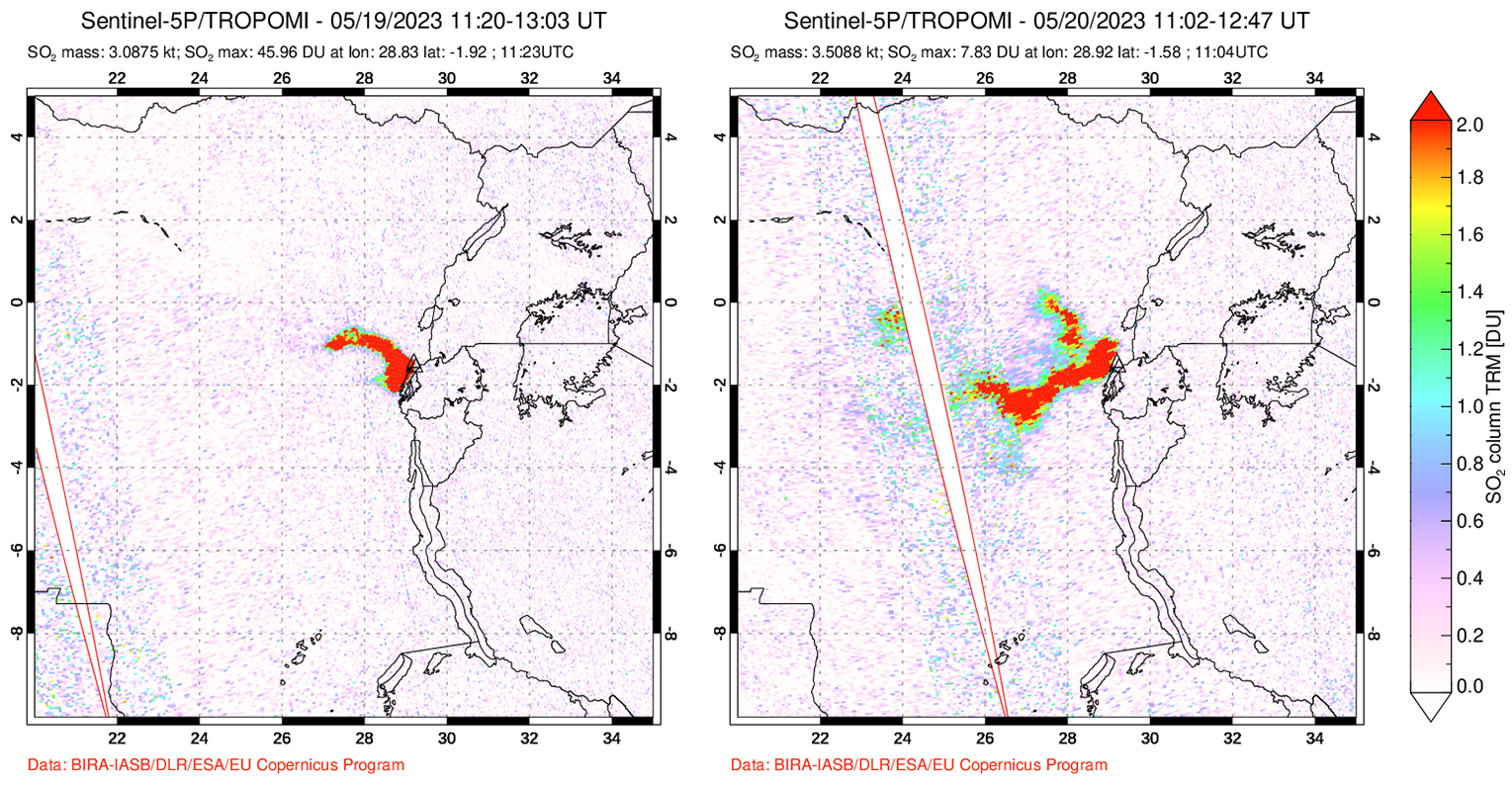
According to OVSICORI-UNA, during July-October the average weekly sulfur dioxide (SO2) flux ranged from 68 to 240 tonnes/day. However, in mid-November the flux increased to as high as 334 tonnes/day, the highest value measured in recent years. The high SO2 flux in mid-November was also detected by the TROPOMI instrument on the Sentinel-5P satellite (figure 43).
Geologic Background. Rincón de la Vieja, the largest volcano in NW Costa Rica, is a remote volcanic complex in the Guanacaste Range. The volcano consists of an elongated, arcuate NW-SE-trending ridge constructed within the 15-km-wide early Pleistocene Guachipelín caldera, whose rim is exposed on the south side. Sometimes known as the "Colossus of Guanacaste," it has an estimated volume of 130 km3 and contains at least nine major eruptive centers. Activity has migrated to the SE, where the youngest-looking craters are located. The twin cone of Santa María volcano, the highest peak of the complex, is located at the eastern end of a smaller, 5-km-wide caldera and has a 500-m-wide crater. A Plinian eruption producing the 0.25 km3 Río Blanca tephra about 3,500 years ago was the last major magmatic eruption. All subsequent eruptions, including numerous historical eruptions possibly dating back to the 16th century, have been from the prominent active crater containing a 500-m-wide acid lake located ENE of Von Seebach crater.
Information Contacts: Observatorio Vulcanológico Sismológica de Costa Rica-Universidad Nacional (OVSICORI-UNA), Apartado 86-3000, Heredia, Costa Rica (URL: http://www.ovsicori.una.ac.cr/); NASA Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard MD 20771, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/).
Bezymianny (Russia) — November 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Bezymianny
Russia
55.972°N, 160.595°E; summit elev. 2882 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Explosion on 18 October 2023 sends ash plume 8 km high; lava flows and incandescent avalanches
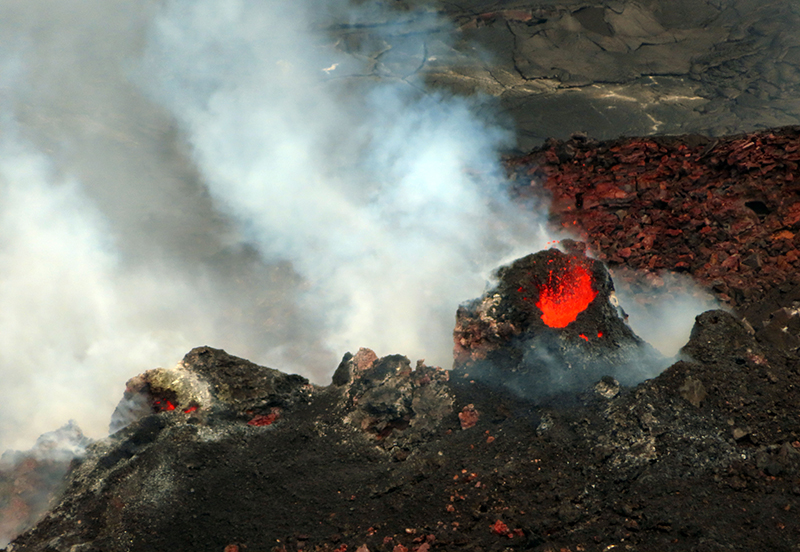
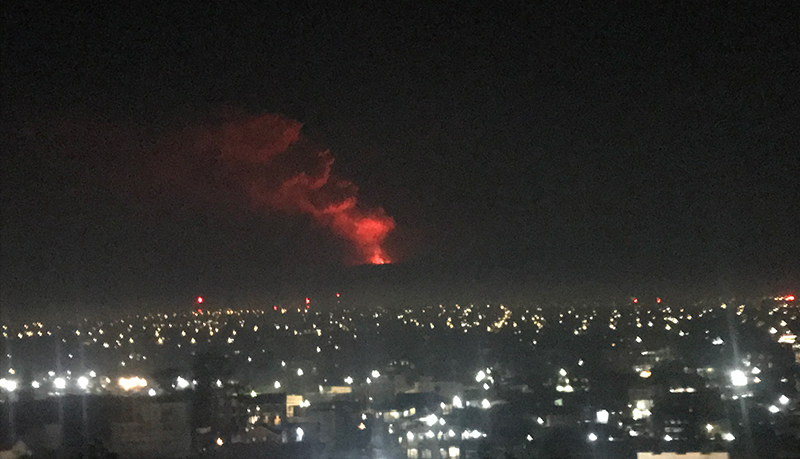
Bezymianny, located on Russia’s Kamchatka Peninsula, has had eruptions since 1955 characterized by dome growth, explosions, pyroclastic flows, ash plumes, and ashfall. Activity during November 2022-April 2023 included gas-and-steam emissions, lava dome collapses generating avalanches, and persistent thermal activity. Similar eruptive activity continued from May through October 2023, described here based on information from weekly and daily reports of the Kamchatka Volcano Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), notices from Tokyo VAAC (Volcanic Ash Advisory Center), and from satellite data.
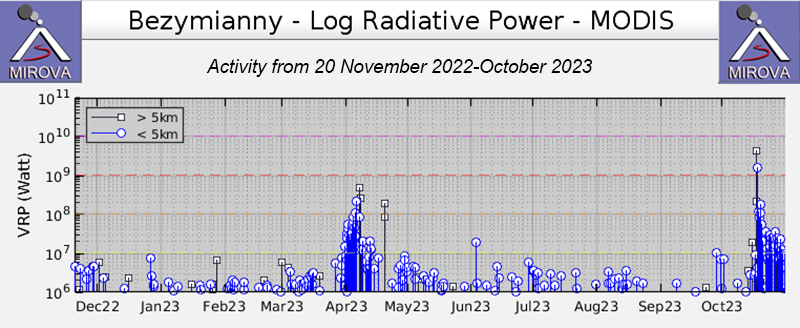
Overall activity decreased after the strong period of activity in late March through April 2023, which included ash explosions during 29 March and 7-8 April 2023 that sent plumes as high as 10-12 km altitude, along with dome growth and lava flows (BGVN 48:05). This reduced activity can be seen in the MIROVA thermal detection system graph (figure 56), which was consistent with data from the MODVOLC thermal detection system and with Sentinel-2 satellite images that showed persistent hotspots in the summit crater when conditions allowed observations. A renewed period of strong activity began in mid-October 2023.
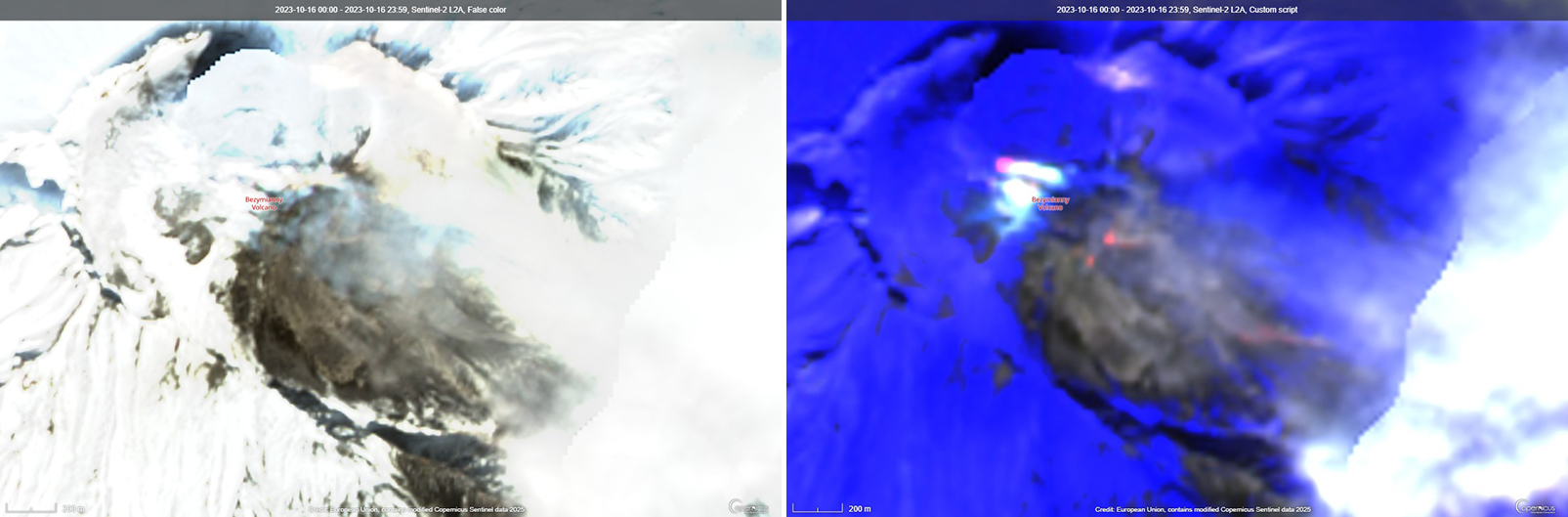
Activity increased significantly on 17 October 2023 when large collapses began during 0700-0830 on the E flanks of the lava dome and continued to after 0930 the next day (figure 57). Ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.5-5 km, extending 220 km NNE by 18 October. A large explosion at 1630 on 18 October produced an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 11 km (8 km above the summit) and drifted NNE and then NW, extending 900 km NW within two days at an altitude of 8 km. Minor ashfall was noted in Kozyrevsk (45 km WNW). At 0820 on 20 October an ash plume was identified in satellite images drifting 100 km ENE at altitudes of 4-4.5 km.
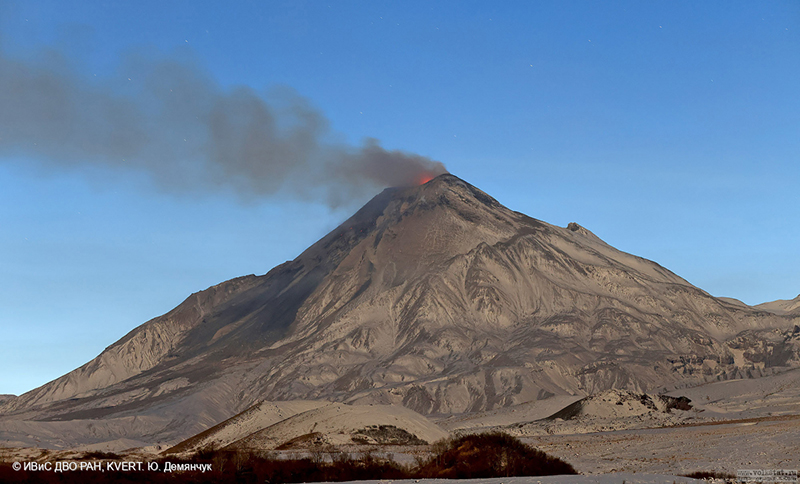
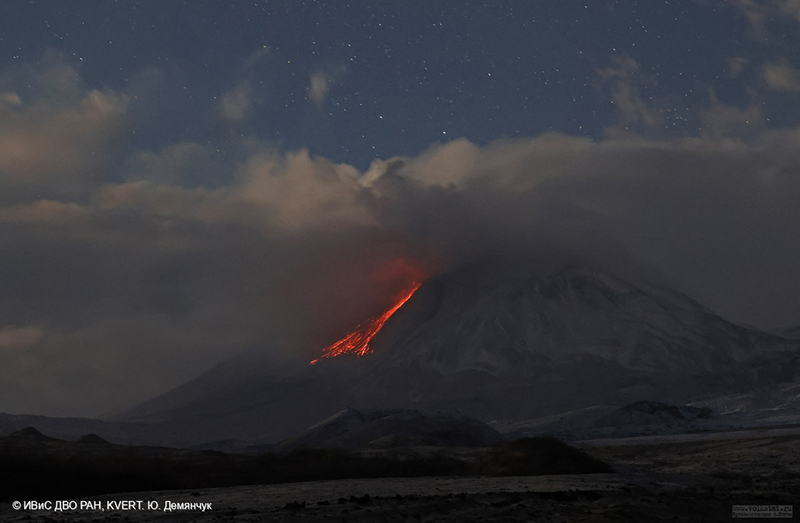
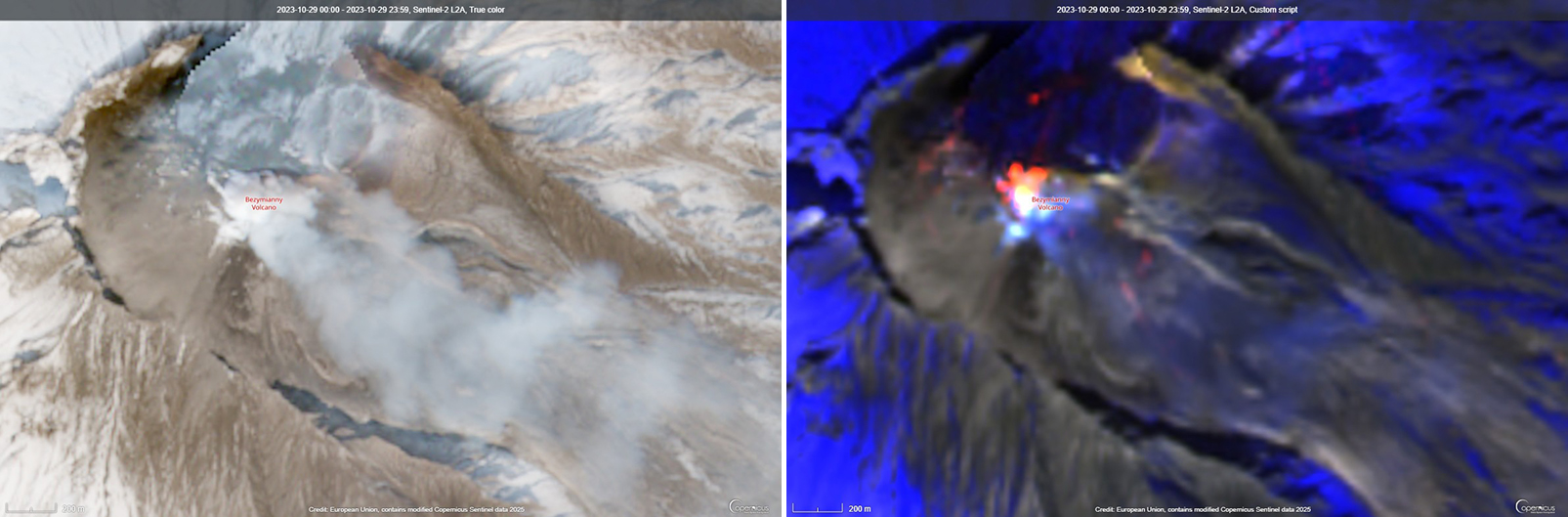
Lava flows and hot avalanches from the dome down the SE flank continued over the next few days, including 23 October when clear conditions allowed good observations (figures 58 and 59). A large thermal anomaly was observed over the volcano through 24 October, and in the summit crater on 30 October (figure 60). Strong fumarolic activity continued, with numerous avalanches and occasional incandescence. By the last week of October, volcanic activity had decreased to a level consistent with that earlier in the reporting period.
Aviation warnings were frequently updated during 17-20 October. KVERT issued a Volcano Observatory Notice for Aviation (VONA) on 17 October at 1419 and 1727 (0219 and 0527 UTC) raising the Aviation Color Code (ACC) from Yellow to Orange (second highest level). The next day, KVERT issued a VONA at 1705 (0505 UTC) raising the ACC to Red (highest level) but lowered it back to Orange at 2117 (0917 UTC). After another decrease to Yellow and back to Orange, the ACC was reduced to Yellow on 20 October at 1204 (0004 UTC). In addition, the Tokyo VAAC issued a series of Volcanic Ash Advisories beginning on 16 October and continuing through 30 October.
Geologic Background. The modern Bezymianny, much smaller than its massive neighbors Kamen and Kliuchevskoi on the Kamchatka Peninsula, was formed about 4,700 years ago over a late-Pleistocene lava-dome complex and an edifice built about 11,000-7,000 years ago. Three periods of intensified activity have occurred during the past 3,000 years. The latest period, which was preceded by a 1,000-year quiescence, began with the dramatic 1955-56 eruption. This eruption, similar to that of St. Helens in 1980, produced a large open crater that was formed by collapse of the summit and an associated lateral blast. Subsequent episodic but ongoing lava-dome growth, accompanied by intermittent explosive activity and pyroclastic flows, has largely filled the 1956 crater.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Kamchatka Volcanological Station, Kamchatka Branch of Geophysical Survey, (KB GS RAS), Klyuchi, Kamchatka Krai, Russia (URL: http://volkstat.ru/); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), 1-3-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8122, Japan (URL: http://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).chr
Kilauea (United States) — January 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Kilauea
United States
19.421°N, 155.287°W; summit elev. 1222 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Low-level lava effusions in the lava lake at Halema’uma’u during July-December 2022
Kīlauea is the southeastern-most volcano in Hawaii and overlaps the E flank of the Mauna Loa volcano. Its East Rift Zone (ERZ) has been intermittently active for at least 2,000 years. An extended eruption period began in January 1983 and was characterized by open lava lakes and lava flows from the summit caldera and the East Rift Zone. During May 2018 magma migrated into the Lower East Rift Zone (LERZ) and opened 24 fissures along a 6-km-long NE-trending fracture zone that produced lava flows traveling in multiple directions. As lava emerged from the fissures, the lava lake at Halema'uma'u drained and explosions sent ash plumes to several kilometers altitude (BGVN 43:10).
The current eruption period started during September 2021 and has recently been characterized by lava effusions, spatter, and sulfur dioxide emissions in the active Halema’uma’u lava lake (BGVN 47:08). Lava effusions, some spatter, and sulfur dioxide emissions have continued during this reporting period of July through December 2022 using daily reports, volcanic activity notices, and abundant photo, map, and video data from the US Geological Survey's (USGS) Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO).
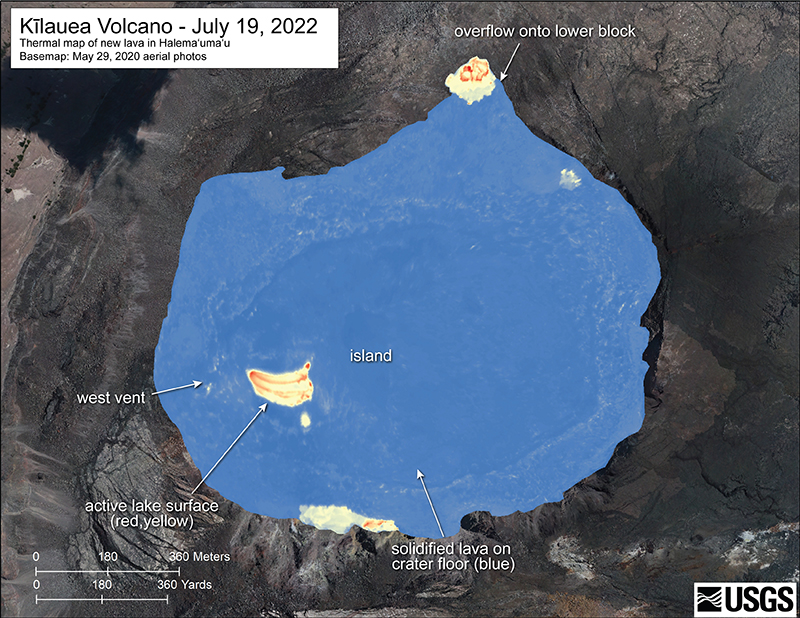
Summary of activity during July-December 2022. Low-level effusions have continued at the western vent of the Halema’uma’u crater during July through early December 2022. Occasional weak ooze-outs (also called lava break outs) would occur along the margins of the crater floor. The overall level of the active lava lake throughout the reporting period gradually increased due to infilling, however it stagnated in mid-September (table 13). During September through November, activity began to decline, though lava effusions persisted at the western vent. By 9 December, the active part of the lava lake had completely crusted over, and incandescence was no longer visible.
Table 13. Summary of measurements taken during overflights at Kīlauea that show a gradual increase in the active lava lake level and the volume of lava effused since 29 September 2021. Lower activity was reported during September-October. Data collected during July-December 2022. Courtesy of HVO.
| Date: |
Level of the active lava lake (m): |
Cumulative volume of lava effused (million cubic meters): |
| 7 Jul 2022 |
130 |
95 |
| 19 Jul 2022 |
133 |
98 |
| 4 Aug 2022 |
136 |
102 |
| 16 Aug 2022 |
137 |
104 |
| 12 Sep 2022 |
143 |
111 |
| 5 Oct 2022 |
143 |
111 |
| 28 Oct 2022 |
143 |
111 |
Activity during July 2022. Lava effusions were reported from the western vent in the Halema’uma’u crater, along with occasional weak ooze-outs along the margins of the crater floor. The height of the lava lake was variable due to deflation-inflation tilt events; for example, the lake level dropped approximately 3-4 m during a summit deflation-inflation event reported on 1 July. Webcam images taken during the night of 6-12 July showed intermittent low-level spattering at the western vent that rose less than 10 m above the vent (figure 519). Measurements made during an overflight on 7 July indicated that the crater floor was infilled about 130 m and that 95 million cubic meters of lava had been effused since 29 September 2021. A single, relatively small lava ooze-out was active to the S of the lava lake. Around midnight on 8 July there were two brief periods of lava overflow onto the lake margins. On 9 July lava ooze-outs were reported near the SE and NE edges of the crater floor and during 10-11 July they occurred near the E, NE, and NW edges. On 16 July crater incandescence was reported, though the ooze-outs and spattering were not visible. On 18 July overnight webcam images showed incandescence in the western vent complex and two ooze-outs were reported around 0000 and 0200 on 19 July. By 0900 there were active ooze-outs along the SW edge of the crater floor. Measurements made from an overflight on 19 July indicated that the crater floor was infilled about 133 m and 98 million cubic meters of lava had erupted since 29 September 2021 (figure 520). On 20 July around 1600 active ooze-outs were visible along the N edge of the crater, which continued through the next day. Extensive ooze-outs occurred along the W margin during 24 July until 1900; on 26 July minor ooze-outs were noted along the N margin. Minor spattering was visible on 29 July along the E margin of the lake. The sulfur dioxide emission rates ranged 650-2,800 tons per day (t/d), the higher of which was measured on 8 July (figure 519).
Activity during August 2022. The eruption continued in the Halema’uma’u crater at the western vent. According to HVO the lava in the active lake remained at the level of the bounding levees. Occasional minor ooze-outs were observed along the margins of the crater floor. Strong nighttime crater incandescence was visible after midnight on 6 August over the western vent cone. During 6-7 August scattered small lava lobes were active along the crater floor and incandescence persisted above the western vent through 9 August. During 7-9 August HVO reported a single lava effusion source was active along the NW margin of the crater floor. Measurements from an overflight on 4 August indicated that the crater floor was infilled about 136 m total and that 102 million cubic meters of lava had been erupted since the start of the eruption. Lava breakouts were reported along the N, NE, E, S, and W margins of the crater during 10-16 August. Another overflight survey conducted on 16 August indicated that the crater floor infilled about 137 m and 104 million cubic meters of lava had been erupted since September 2021. Measured sulfur dioxide emissions rates ranged 1,150-2,450 t/d, the higher of which occurred on 8 August.
Activity during September 2022. During September, lava effusion continued from the western vent into the active lava lake and onto the crater floor. Intermittent minor ooze-outs were reported through the month. A small ooze-out was visible on the W crater floor margin at 0220 on 2 September, which showed decreasing surface activity throughout the day, but remained active through 3 September. On 3 September around 1900 a lava outbreak occurred along the NW margin of the crater floor but had stopped by the evening of 4 September. Field crews monitoring the summit lava lake on 9 September observed spattering on the NE margin of the lake that rose no higher than 10 m, before falling back onto the lava lake crust (figure 521). Overflight measurements on 12 September indicated that the crater floor was infilled a total of 143 m and 111 million cubic meters of lava had been erupted since September 2021. Extensive breakouts in the W and N part of the crater floor were reported at 1600 on 20 September and continued into 26 September. The active part of the lava lake dropped by 10 m while other parts of the crater floor dropped by several meters. Summit tiltmeters recorded a summit seismic swarm of more than 80 earthquakes during 1500-1800 on 21 September, which occurred about 1.5 km below Halema’uma’u; a majority of these were less than Mw 2. By 22 September the active part of the lava lake was infilled about 2 m. On 23 September the western vent areas exhibited several small spatter cones with incandescent openings, along with weak, sporadic spattering (figure 522). The sulfur dioxide emission rate ranged from 930 t/d to 2,000 t/d, the higher of which was measured on 6 September.
Activity during October 2022. Activity during October declined slightly compared to previous months, though lava effusions persisted from the western vent into the active lava lake and onto the crater floor during October (figure 523). Slight variations in the lava lake were noted throughout the month. HVO reported that around 0600 on 3 October the level of the lava lake has lowered slightly. Overflight measurements taken on 5 October indicated that the crater floor was infilled a total of about 143 m and that 111 million cubic meters of lava had been effused since September 2021. During 6-7 October the lake gradually rose 0.5 m. Sulfur dioxide measurements made on 22 October had an emission rate of 700 t/d. Another overflight taken on 28 October showed that there was little to no change in the elevation of the crater floor: the crater floor was infilled a total of 143 m and 111 million cubic meters of lava had erupted since the start of the eruption.
Activity during November 2022. Activity remained low during November, though HVO reported that lava from the western vent continued to effuse into the active lava lake and onto the crater floor throughout the month. The rate of sulfur dioxide emissions during November ranged from 300-600 t/d, the higher amount of which occurred on 9 November.
Activity during December 2022. Similar low activity was reported during December, with lava effusing from the western vent into the active lava lake and onto the crater floor. During 4-5 December the active part of the lava lake was slightly variable in elevation and fluctuated within 1 m. On 9 December HVO reported that lava was no longer erupting from the western vent in the Halema’uma’u crater and that sulfur dioxide emissions had returned to near pre-eruption background levels; during 10-11 December, the lava lake had completely crusted over, and no incandescence was visible (figure 524). Time lapse camera images covering the 4-10 December showed that the crater floor showed weak deflation and no inflation. Some passive events of crustal overturning were reported during 14-15 December, which brought fresh incandescent lava to the lake surface. The sulfur dioxide emission rate was approximately 200 t/d on 14 December. A smaller overturn event on 17 December and another that occurred around 0000 and into the morning of 20 December were also detected. A small seismic swarm was later detected on 30 December.
Geologic Background. Kilauea overlaps the E flank of the massive Mauna Loa shield volcano in the island of Hawaii. Eruptions are prominent in Polynesian legends; written documentation since 1820 records frequent summit and flank lava flow eruptions interspersed with periods of long-term lava lake activity at Halemaumau crater in the summit caldera until 1924. The 3 x 5 km caldera was formed in several stages about 1,500 years ago and during the 18th century; eruptions have also originated from the lengthy East and Southwest rift zones, which extend to the ocean in both directions. About 90% of the surface of the basaltic shield volcano is formed of lava flows less than about 1,100 years old; 70% of the surface is younger than 600 years. The long-term eruption from the East rift zone between 1983 and 2018 produced lava flows covering more than 100 km2, destroyed hundreds of houses, and added new coastline.
Information Contacts: Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO), U.S. Geological Survey, PO Box 51, Hawai'i National Park, HI 96718, USA (URL: http://hvo.wr.usgs.gov/).
Nyamulagira (DR Congo) — November 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Nyamulagira
DR Congo
1.408°S, 29.2°E; summit elev. 3058 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
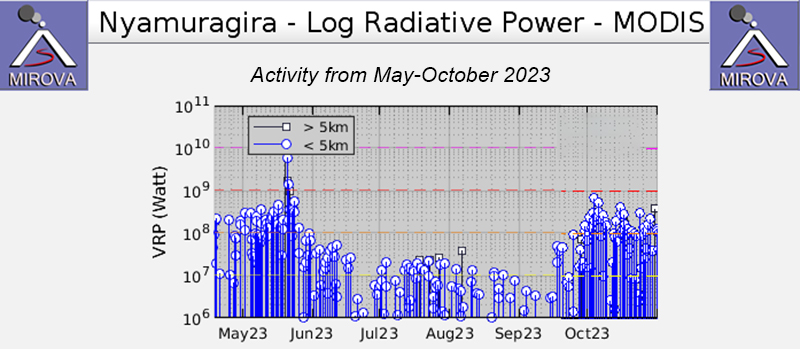
Lava flows and thermal activity during May-October 2023
Nyamulagira (also known as Nyamuragira) is a shield volcano in the Democratic Republic of Congo with the summit truncated by a small 2 x 2.3 km caldera with walls up to about 100 m high. Documented eruptions have occurred within the summit caldera, as well as from numerous flank fissures and cinder cones. The current eruption period began in April 2018 and has more recently been characterized by summit crater lava flows and thermal activity (BGVN 48:05). This report describes lava flows and variable thermal activity during May through October 2023, based on information from the Observatoire Volcanologique de Goma (OVG) and various satellite data.
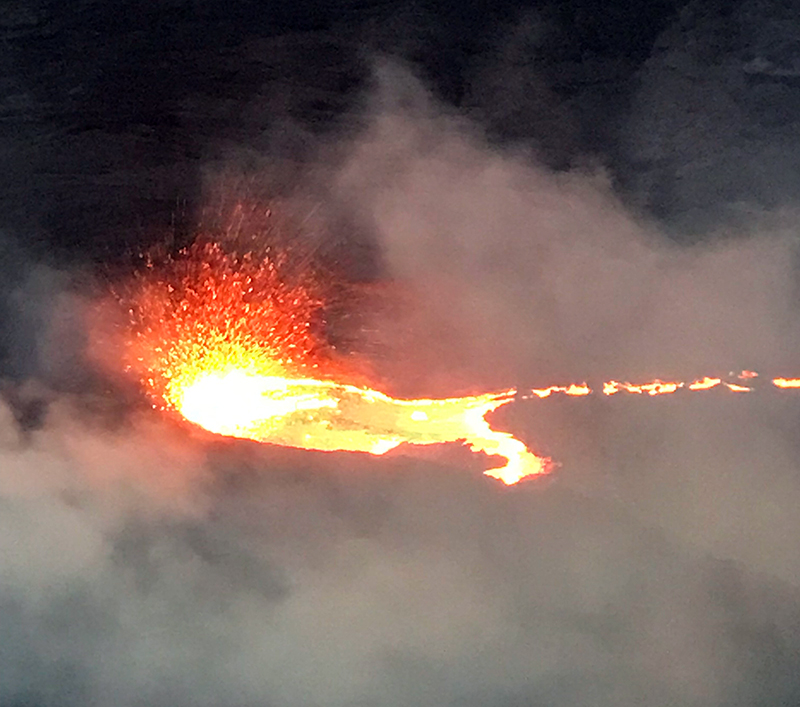
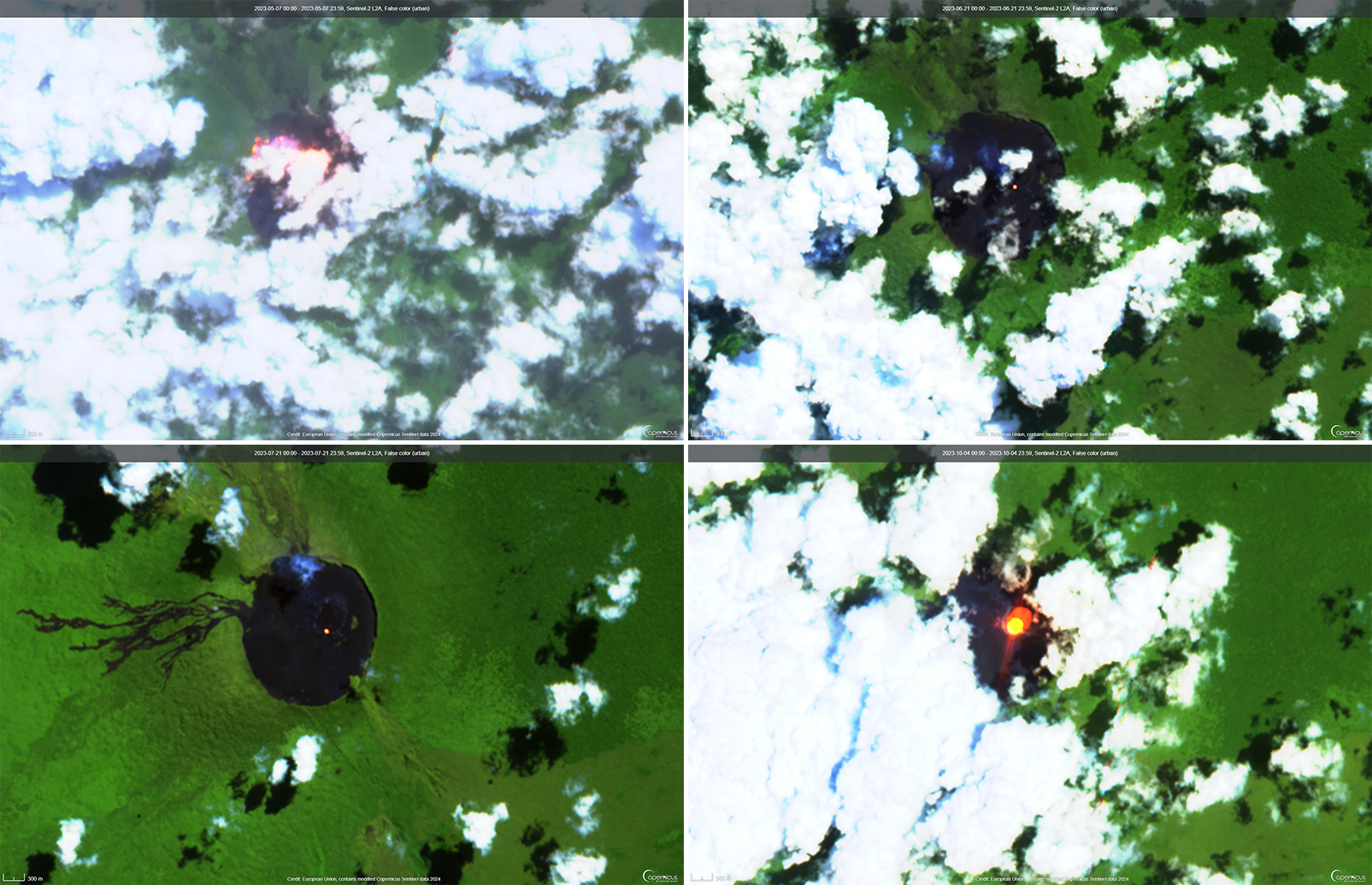
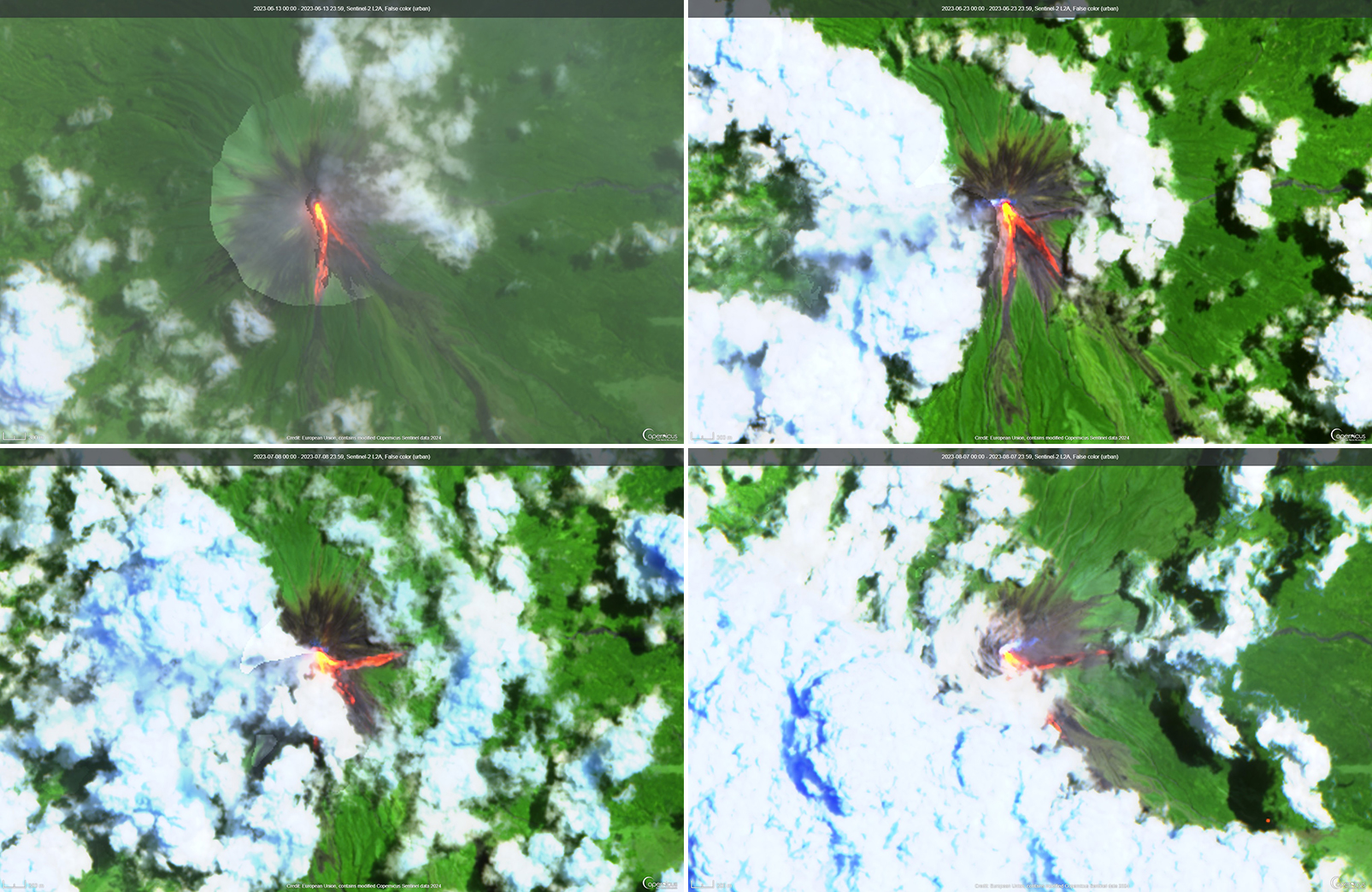
Lava lake activity continued during May. The MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) system recorded moderate-to-strong thermal activity throughout the reporting period; activity was more intense during May and October and relatively weaker from June through September (figure 95). The MODVOLC thermal algorithm, detected a total of 209 thermal alerts. There were 143 hotspots detected during May, eight during June, nine during September, and 49 during October. This activity was also reflected in infrared satellite images, where a lava flow was visible in the NW part of the crater on 7 May and strong activity was seen in the center of the crater on 4 October (figure 96). Another infrared satellite image taken on 12 May showed still active lava flows along the NW margin of the crater. According to OVG lava effusions were active during 7-29 May and moved to the N and NW parts of the crater beginning on 9 May. Strong summit crater incandescence was visible from Goma (27 km S) during the nights of 17, 19, and 20 May (figure 97). On 17 May there was an increase in eruptive activity, which peaked at 0100 on 20 May. Notable sulfur dioxide plumes drifted NW and W during 19-20 May (figure 98). Drone footage acquired in partnership with the USGS (United States Geological Survey) on 20 May captured images of narrow lava flows that traveled about 100 m down the W flank (figure 99). Data from the Rumangabo seismic station indicated a decreasing trend in activity during 17-21 May. Although weather clouds prevented clear views of the summit, a strong thermal signature on the NW flank was visible in an infrared satellite image on 22 May, based on an infrared satellite image. On 28 May the lava flows on the upper W flank began to cool and solidify. By 29 May seismicity returned to levels similar to those recorded before the 17 May increase. Lava effusion continued but was confined to the summit crater; periodic crater incandescence was observed.
Low-level activity was noted during June through October. On 1 June OVG reported that seismicity remained at lower levels and that crater incandescence had been absent for three days, though infrared satellite imagery showed continued lava effusion in the summit crater. The lava flows on the flanks covered an estimated 0.6 km2. Satellite imagery continued to show thermal activity confined to the lava lake through October (figure 96), although no lava flows or significant sulfur dioxide emissions were reported.
Geologic Background. Africa's most active volcano, Nyamulagira (also known as Nyamuragira), is a massive high-potassium basaltic shield about 25 km N of Lake Kivu and 13 km NNW of the steep-sided Nyiragongo volcano. The summit is truncated by a small 2 x 2.3 km caldera that has walls up to about 100 m high. Documented eruptions have occurred within the summit caldera, as well as from the numerous flank fissures and cinder cones. A lava lake in the summit crater, active since at least 1921, drained in 1938, at the time of a major flank eruption. Recent lava flows extend down the flanks more than 30 km from the summit as far as Lake Kivu; extensive lava flows from this volcano have covered 1,500 km2 of the western branch of the East African Rift.
Information Contacts: Observatoire Volcanologique de Goma (OVG), Departement de Geophysique, Centre de Recherche en Sciences Naturelles, Lwiro, D.S. Bukavu, DR Congo; Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); NASA Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/); Charles Balagizi, Goma Volcano Observatory, Departement de Geophysique, Centre de Recherche en Sciences Naturelles, Lwiro, D.S. Bukavu, DR Congo.
Bagana (Papua New Guinea) — October 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Bagana
Papua New Guinea
6.137°S, 155.196°E; summit elev. 1855 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Explosions, ash plumes, ashfall, and lava flows during April-September 2023
The remote volcano of Bagana is located in central Bougainville Island, Papua New Guinea. Recorded eruptions date back to 1842 and activity has consisted of effusive activity that has built a small lava dome in the summit crater and occasional explosions that produced pyroclastic flows. The most recent eruption has been ongoing since February 2000 and has produced occasional explosions, ash plumes, and lava flows. More recently, activity has been characterized by ongoing effusive activity and ash emissions (BGVN 48:04). This report updates activity from April through September 2023 that has consisted of explosions, ash plumes, ashfall, and lava flows, using information from the Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) and satellite data.
An explosive eruption was reported on 7 July that generated a large gas-and-ash plume to high altitudes and caused significant ashfall in local communities; the eruption plume had reached upper tropospheric (16-18 km altitude) altitudes by 2200, according to satellite images. Sulfur dioxide plumes were detected in satellite images on 8 July and indicated that the plume was likely a mixture of gas, ice, and ash. A report issued by the Autonomous Bougainville Government (ABG) (Torokina District, Education Section) on 10 July noted that significant ash began falling during 2000-2100 on 7 July and covered most areas in the Vuakovi, Gotana (9 km SW), Koromaketo, Laruma (25 km W) and Atsilima (27 km NW) villages. Pyroclastic flows also occurred, according to ground-based reports; small deposits confined to one drainage were inspected by RVO during an overflight on 17 July and were confirmed to be from the 7 July event. Ashfall continued until 10 July and covered vegetation, which destroyed bushes and gardens and contaminated rivers and streams.
RVO reported another eruption on 14 July. The Darwin VAAC stated that an explosive event started around 0830 on 15 July and produced an ash plume that rose to 16.5 km altitude by 1000 and drifted N, according to satellite images. The plume continued to drift N and remained visible through 1900, and by 2150 it had dissipated.
Ashfall likely from both the 7 and 15 July events impacted about 8,111 people in Torokina (20 km SW), including Tsito/Vuakovi, Gotana, Koromaketo, Kenaia, Longkogari, Kenbaki, Piva (13 km SW), and Atsinima, and in the Tsitovi district, according to ABG. Significant ashfall was also reported in Ruruvu (22 km N) in the Wakunai District of Central Bougainville, though the thickness of these deposits could not be confirmed. An evacuation was called for the villages in Wakunai, where heavy ashfall had contaminated water sources; the communities of Ruruvu, Togarau, Kakarapaia, Karauturi, Atao, and Kuritaturi were asked to evacuate to a disaster center at the Wakunai District Station, and communities in Torokina were asked to evacuate to the Piva District station. According to a news article, more than 7,000 people needed temporary accommodations, with about 1,000 people in evacuation shelters. Ashfall had deposited over a broad area, contaminating water supplies, affecting crops, and collapsing some roofs and houses in rural areas. Schools were temporarily shut down. Intermittent ash emissions continued through the end of July and drifted NNW, NW, and SW. Fine ashfall was reported on the coast of Torokina, and ash plumes also drifted toward Laruma and Atsilima.
A small explosive eruption occurred at 2130 on 28 July that ejected material from the crater vents, according to reports from Torokina, in addition to a lava flow that contained two lobes. A second explosion was detected at 2157. Incandescence from the lava flow was visible from Piva as it descended the W flank around 2000 on 29 July (figure 47). The Darwin VAAC reported that a strong thermal anomaly was visible in satellite images during 30-31 July and that ash emissions rose to 2.4 km altitude and drifted WSW on 30 July. A ground report from RVO described localized emissions at 0900 on 31 July.
The Darwin VAAC reported that ash plumes were identified in satellite imagery at 0800 and 1220 on 12 August and rose to 2.1 km and 3 km altitude and drifted NW and W, respectively. A news report stated that aid was sent to more than 6,300 people that were adversely affected by the eruption. Photos taken during 17-19 August showed ash emissions rising no higher than 1 km above the summit and drifting SE. A small explosion generated an ash plume during the morning of 19 August. Deposits from small pyroclastic flows were also captured in the photos. Satellite images captured lava flows and pyroclastic flow deposits. Two temporary seismic stations were installed near Bagana on 17 August at distances of 7 km WSW (Vakovi station) and 11 km SW (Kepox station). The Kepox station immediately started to record continuous, low-frequency background seismicity.
Satellite data. Little to no thermal activity was detected during April through mid-July 2023; only one anomaly was recorded during early April and one during early June, according to MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) data (figure 48). Thermal activity increased in both power and frequency during mid-July through September, although there were still some short gaps in detected activity. MODVOLC also detected increased thermal activity during August; thermal hotspots were detected a total of five times on 19, 20, and 27 August. Weak thermal anomalies were also captured in infrared satellite images on clear weather days throughout the reporting period on 7, 12, and 17 April, 27 May, 1, 6, 16, and 31 July, and 19 September (figure 48); a strong thermal anomaly was visible on 31 July. Distinct sulfur dioxide plumes that drifted generally NW were intermittently captured by the TROPOMI instrument on the Sentinel-5P satellite and sometimes exceeded two Dobson Units (DUs) (figure 49).
Geologic Background. Bagana volcano, in a remote portion of central Bougainville Island, is frequently active. This massive symmetrical cone was largely constructed by an accumulation of viscous andesitic lava flows. The entire edifice could have been constructed in about 300 years at its present rate of lava production. Eruptive activity is characterized by non-explosive effusion of viscous lava that maintains a small lava dome in the summit crater, although occasional explosive activity produces pyroclastic flows. Lava flows with tongue-shaped lobes up to 50 m thick and prominent levees descend the flanks on all sides.
Information Contacts: Rabaul Volcano Observatory (RVO), Geohazards Management Division, Department of Mineral Policy and Geohazards Management (DMPGM), PO Box 3386, Kokopo, East New Britain Province, Papua New Guinea; Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Bureau of Meteorology, Northern Territory Regional Office, PO Box 40050, Casuarina, NT 0811, Australia (URL: http://www.bom.gov.au/info/vaac/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); NASA Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/); Autonomous Bougainville Government, P.O Box 322, Buka, AROB, PNG (URL: https://abg.gov.pg/); Andrew Tupper (Twitter: @andrewcraigtupp); Simon Carn, Geological and Mining Engineering and Sciences, Michigan Technological University, 1400 Townsend Drive, Houghton, MI 49931, USA (URL: http://www.volcarno.com/, Twitter: @simoncarn); Radio NZ (URL: https://www.rnz.co.nz/news/pacific/494464/more-than-7-000-people-in-bougainville-need-temporary-accommodation-after-eruption); USAID, 1300 Pennsylvania Ave, NW, Washington DC 20004, USA (URL: https://www.usaid.gov/pacific-islands/press-releases/aug-08-2023-united-states-provides-immediate-emergency-assistance-support-communities-affected-mount-bagana-volcanic-eruptions).
Mayon (Philippines) — October 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Mayon
Philippines
13.257°N, 123.685°E; summit elev. 2462 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Lava flows, pyroclastic flows, ash emissions, and seismicity during April-September 2023
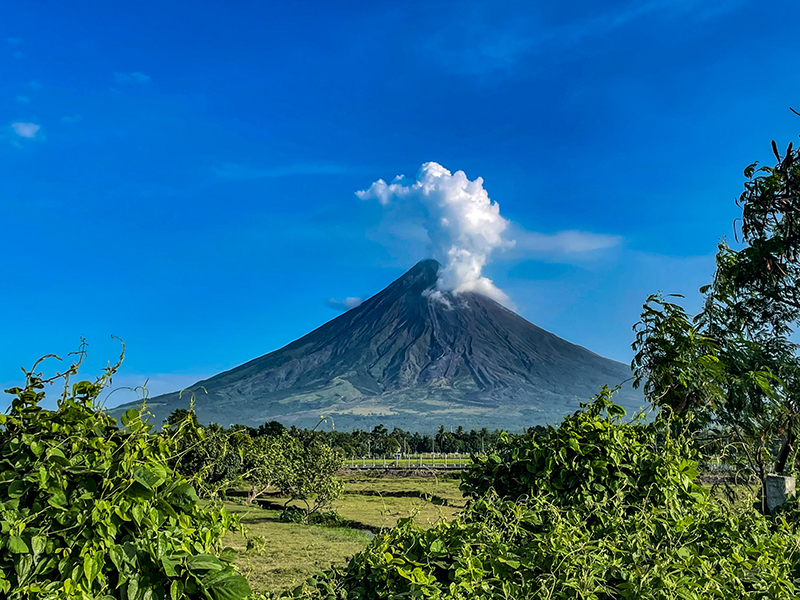
Mayon is located in the Philippines and has steep upper slopes capped by a small summit crater. Historical eruptions date back to 1616 CE that have been characterized by Strombolian eruptions, lava flows, pyroclastic flows, and mudflows. Eruptions mostly originated from a central conduit. Pyroclastic flows and mudflows have commonly descended many of the approximately 40 drainages that surround the volcano. The most recent eruption occurred during June through October 2022 and consisted of lava dome growth and gas-and-steam emissions (BGVN 47:12). A new eruption was reported during late April 2023 and has included lava flows, pyroclastic density currents, ash emissions, and seismicity. This report covers activity during April through September 2023 based on daily bulletins from the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS).
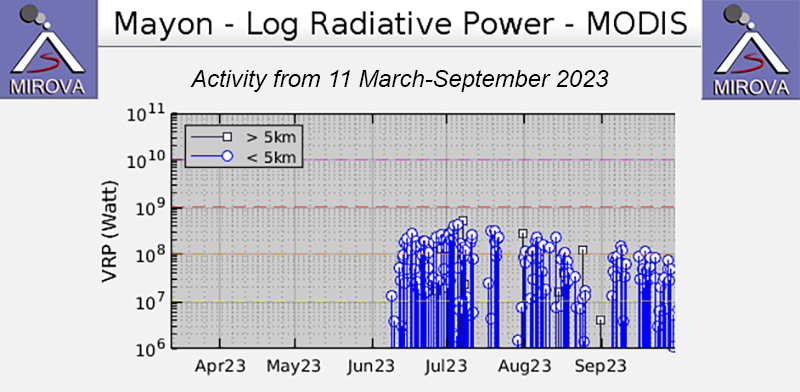
During April through September 2023, PHIVOLCS reported near-daily rockfall events, frequent volcanic earthquakes, and sulfur dioxide measurements. Gas-and-steam emissions rose 100-900 m above the crater and drifted in different directions. Nighttime crater incandescence was often visible during clear weather and was accompanied by incandescent avalanches of material. Activity notably increased during June when lava flows were reported on the S, SE, and E flanks (figure 52). The MIROVA graph (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) showed strong thermal activity coincident with these lava flows, which remained active through September (figure 53). According to the MODVOLC thermal algorithm, a total of 110 thermal alerts were detected during the reporting period: 17 during June, 40 during July, 27 during August, and 26 during September. During early June, pyroclastic density currents (PDCs) started to occur more frequently.
Low activity was reported during much of April and May; gas-and-steam emissions rose 100-900 m above the crater and generally drifted in different directions. A total of 52 rockfall events and 18 volcanic earthquakes were detected during April and 147 rockfall events and 13 volcanic events during May. Sulfur dioxide flux measurements ranged between 400-576 tons per day (t/d) during April, the latter of which was measured on 29 April and between 162-343 t/d during May, the latter of which was measured on 13 May.
Activity during June increased, characterized by lava flows, pyroclastic density currents (PDCs), crater incandescence and incandescent rockfall events, gas-and-steam emissions, and continued seismicity. Weather clouds often prevented clear views of the summit, but during clear days, moderate gas-and-steam emissions rose 100-2,500 m above the crater and drifted in multiple directions. A total of 6,237 rockfall events and 288 volcanic earthquakes were detected. The rockfall events often deposited material on the S and SE flanks within 700-1,500 m of the summit crater and ash from the events drifted SW, S, SE, NE, and E. Sulfur dioxide emissions ranged between 149-1,205 t/d, the latter of which was measured on 10 June. Short-term observations from EDM and electronic tiltmeter monitoring indicated that the upper slopes were inflating since February 2023. Longer-term ground deformation parameters based on EDM, precise leveling, continuous GPS, and electronic tilt monitoring indicated that the volcano remained inflated, especially on the NW and SE flanks. At 1000 on 5 June the Volcano Alert Level (VAL) was raised to 2 (on a 0-5 scale). PHIVOLCS noted that although low-level volcanic earthquakes, ground deformation, and volcanic gas emissions indicated unrest, the steep increase in rockfall frequency may indicate increased dome activity.
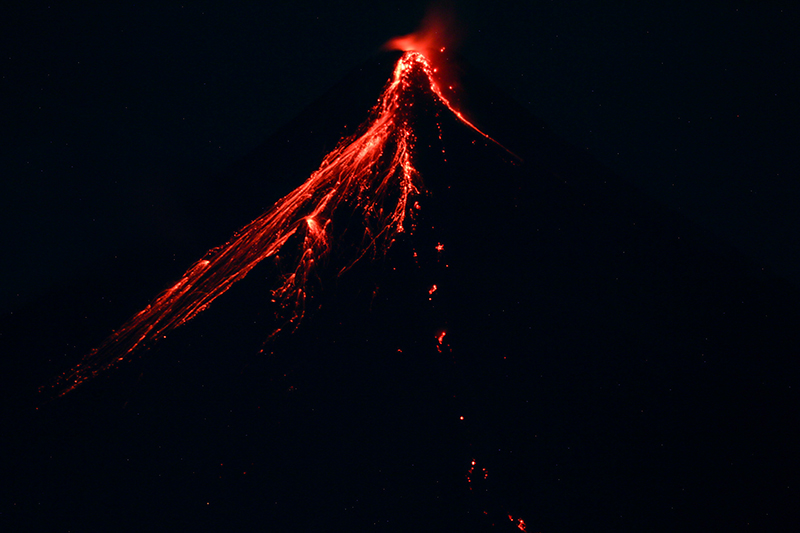
A total of 151 dome-collapse PDCs occurred during 8-9 and 11-30 June, traveled 500-2,000 m, and deposited material on the S flank within 2 km of the summit crater. During 8-9 June the VAL was raised to 3. At approximately 1947 on 11 June lava flow activity was reported; two lobes traveled within 500 m from the crater and deposited material on the S (Mi-isi), SE (Bonga), and E (Basud) flanks. Weak seismicity accompanied the lava flow and slight inflation on the upper flanks. This lava flow remained active through 30 June, moving down the S and SE flank as far as 2.5 km and 1.8 km, respectively and depositing material up to 3.3 km from the crater. During 15-16 June traces of ashfall from the PDCs were reported in Sitio Buga, Nabonton, City of Ligao and Purok, and San Francisco, Municipality of Guinobatan. During 28-29 June there were two PDCs generated by the collapse of the lava flow front, which generated a light-brown ash plume 1 km high. Satellite monitors detected significant concentrations of sulfur dioxide beginning on 29 June. On 30 June PDCs primarily affected the Basud Gully on the E flank, the largest of which occurred at 1301 and lasted eight minutes, based on the seismic record. Four PDCs generated between 1800 and 2000 that lasted approximately four minutes each traveled 3-4 km on the E flank and generated an ash plume that rose 1 km above the crater and drifted N and NW. Ashfall was recorded in Tabaco City.
Similar strong activity continued during July; slow lava effusion remained active on the S and SE flanks and traveled as far as 2.8 km and 2.8 km, respectively and material was deposited as far as 4 km from the crater. There was a total of 6,983 rockfall events and 189 PDCs that affected the S, SE, and E flanks. The volcano network detected a total of 2,124 volcanic earthquakes. Continuous gas-and-steam emissions rose 200-2,000 m above the crater and drifted in multiple directions. Sulfur dioxide emissions averaged 792-4,113 t/d, the latter of which was measured on 28 July. During 2-4 July three PDCs were generated from the collapse of the lava flow and resulting light brown plumes rose 200-300 m above the crater. Continuous tremor pulses were reported beginning at 1547 on 3 July through 7 July at 1200, at 2300 on 8 July and going through 0300 on 10 July, and at 2300 on 16 July, as recorded by the seismic network. During 6-9 July there were 10 lava flow-collapse-related PDCs that generated light brown plumes 300-500 m above the crater. During 10-11 July light ashfall was reported in some areas of Mabinit, Legazpi City, Budiao and Salvacion, Daraga, and Camalig, Albay. By 18 July the lava flow advanced 600 m on the E flank as well.
During 1733 on 18 July and 0434 on 19 July PHIVOLCS reported 30 “ashing” events, which are degassing events accompanied by audible thunder-like sounds and entrained ash at the crater, which produced short, dark plumes that drifted SW. These events each lasted 20-40 seconds, and plume heights ranged from 150-300 m above the crater, as recorded by seismic, infrasound, visual, and thermal monitors. Three more ashing events occurred during 19-20 July. Short-term observations from electronic tilt and GPS monitoring indicate deflation on the E lower flanks in early July and inflation on the NW middle flanks during the third week of July. Longer-term ground deformation parameters from EDM, precise leveling, continuous GPS, and electronic tilt monitoring indicated that the volcano was still generally inflated relative to baseline levels. A short-lived lava pulse lasted 28 seconds at 1956 on 21 July, which was accompanied by seismic and infrasound signals. By 22 July, the only lava flow that remained active was on the SE flank, and continued to extend 3.4 km, while those on the S and E flanks weakened markedly. One ashing event was detected during 30-31 July, whereas there were 57 detected during 31 July-1 August; according to PHIVOLCS beginning at approximately 1800 on 31 July eruptive activity was dominated by phases of intermittent ashing, as well as increased in the apparent rates of lava effusion from the summit crater. The ashing phases consisted of discrete events recorded as low-frequency volcanic earthquakes (LFVQ) typically 30 seconds in duration, based on seismic and infrasound signals. Gray ash plume rose 100 m above the crater and generally drifted NE. Shortly after these ashing events began, new lava began to effuse rapidly from the crater, feeding the established flowed on the SE, E, and E flanks and generating frequent rockfall events.
Intensified unrest persisted during August. There was a total of 4,141 rockfall events, 2,881 volcanic earthquakes, which included volcanic tremor events, 32 ashing events, and 101 PDCs detected throughout the month. On clear weather days, gas-and-steam emissions rose 300-1,500 m above the crater and drifted in different directions (figure 54). Sulfur dioxide emissions averaged 735-4,756 t/d, the higher value of which was measured on 16 August. During 1-2 August the rate of lava effusion decreased, but continued to feed the flows on the SE, S, and E flanks, maintaining their advances to 3.4 km, 2.8 km, and 1.1 km from the crater, respectively (figure 55). Rockfall and PDCs generated by collapses at the lava flow margins and from the summit dome deposited material within 4 km of the crater. During 3-4 August there were 10 tremor events detected that lasted 1-4 minutes. Short-lived lava pulse lasted 35 seconds and was accompanied by seismic and infrasound signals at 0442 on 6 August. Seven collapses were recorded at the front of the lava flow during 12-14 August.
During September, similar activity of slow lava effusion, PDCs, gas-and-steam emissions, and seismicity continued. There was a total of 4,452 rockfall events, 329 volcanic earthquakes, which included volcanic tremor events, two ashing events, and 85 PDCs recorded throughout the month. On clear weather days, gas-and-steam emissions rose 100-1,500 m above the crater and drifted in multiple directions. Sulfur dioxide emissions averaged 609-2,252 t/d, the higher average of which was measured on 6 September. Slow lava effusion continued advancing on the SE, S, and E flanks, maintaining lengths of 3.4 km, 2.8 km, and 1.1 km, respectively. Rockfall and PDC events generated by collapses along the lava flow margins and at the summit dome deposited material within 4 km of the crater.
Geologic Background. Symmetrical Mayon, which rises above the Albay Gulf NW of Legazpi City, is the most active volcano of the Philippines. The steep upper slopes are capped by a small summit crater. Recorded eruptions since 1616 CE range from Strombolian to basaltic Plinian, with cyclical activity beginning with basaltic eruptions, followed by longer periods of andesitic lava flows. Eruptions occur predominately from the central conduit and have also produced lava flows that travel far down the flanks. Pyroclastic density currents and mudflows have commonly swept down many of the approximately 40 ravines that radiate from the summit and have often damaged populated lowland areas. A violent eruption in 1814 killed more than 1,200 people and devastated several towns.
Information Contacts: Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHIVOLCS), Department of Science and Technology, University of the Philippines Campus, Diliman, Quezon City, Philippines (URL: http://www.phivolcs.dost.gov.ph/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/); William Rogers, Legazpi City, Albay Province, Philippines.
Nishinoshima (Japan) — October 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Nishinoshima
Japan
27.247°N, 140.874°E; summit elev. 100 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Eruption plumes and gas-and-steam plumes during May-August 2023
Nishinoshima, located about 1,000 km S of Tokyo, is a small island in the Ogasawara Arc in Japan. The island is the summit of a massive submarine volcano that has prominent submarine peaks to the S, W, and NE. Eruptions date back to 1973 and the current eruption period began in October 2022. Recent activity has consisted of small ash plumes and fumarolic activity (BGVN 48:07). This report covers activity during May through August 2023, using information from monthly reports of the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) monthly reports and satellite data.
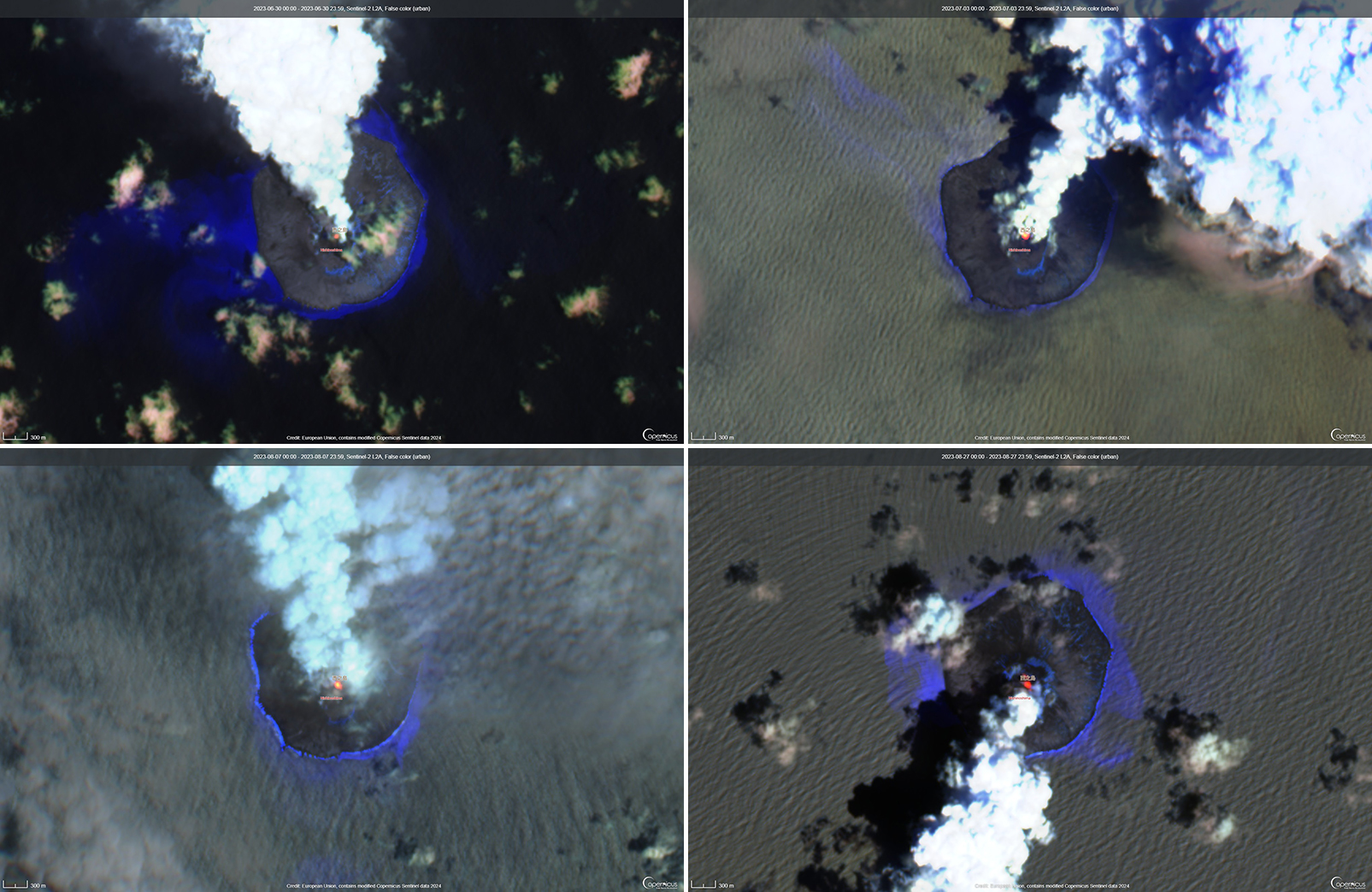
Activity during May through June was relatively low. The Japan Coast Guard (JCG) did overflights on 14 and 22 June and reported white gas-and-steam emissions rising 600 m and 1,200 m from the central crater of the pyroclastic cone, respectively (figure 125). In addition, multiple white gas-and-steam emissions rose from the inner rim of the W side of the crater and from the SE flank of the pyroclastic cone. Discolored brown-to-green water was observed around almost the entire perimeter of the island; on 22 June light green discolored water was observed off the S coast of the island.
Observations from the Himawari meteorological satellite confirmed an eruption on 9 and 10 July. An eruption plume rose 1.6 km above the crater and drifted N around 1300 on 9 July. Satellite images acquired at 1420 and 2020 on 9 July and at 0220 on 10 July showed continuing emissions that rose 1.3-1.6 km above the crater and drifted NE and N. The Tokyo VAAC reported that an ash plume seen by a pilot and identified in a satellite image at 0630 on 21 July rose to 3 km altitude and drifted S.
Aerial observations conducted by JCG on 8 August showed a white-and-gray plume rising from the central crater of the pyroclastic cone, and multiple white gas-and-steam emissions were rising from the inner edge of the western crater and along the NW-SE flanks of the island (figure 126). Brown-to-green discolored water was also noted around the perimeter of the island.
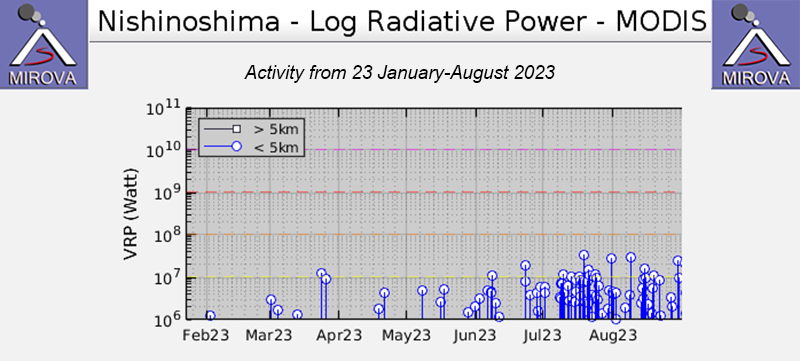
Intermittent low-to-moderate power thermal anomalies were recorded in the MIROVA graph (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), showing an increase in both frequency and power beginning in July (figure 127). This increase in activity coincides with eruptive activity on 9 and 10 July, characterized by eruption plumes. According to the MODVOLC thermal alert algorithm, one thermal hotspot was recorded on 20 July. Weak thermal anomalies were also detected in infrared satellite imagery, accompanied by strong gas-and-steam plumes (figure 128).
Geologic Background. The small island of Nishinoshima was enlarged when several new islands coalesced during an eruption in 1973-74. Multiple eruptions that began in 2013 completely covered the previous exposed surface and continued to enlarge the island. The island is the summit of a massive submarine volcano that has prominent peaks to the S, W, and NE. The summit of the southern cone rises to within 214 m of the ocean surface 9 km SSE.
Information Contacts: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA), 1-3-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8122, Japan (URL: http://www.jma.go.jp/jma/indexe.html); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), 1-3-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8122, Japan (URL: http://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Krakatau (Indonesia) — October 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Krakatau
Indonesia
6.1009°S, 105.4233°E; summit elev. 285 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
White gas-and-steam plumes and occasional ash plumes during May-August 2023
Krakatau is located in the Sunda Strait between Java and Sumatra, Indonesia. Caldera collapse during the catastrophic 1883 eruption destroyed Danan and Perbuwatan cones and left only a remnant of Rakata. The post-collapse cone of Anak Krakatau (Child of Krakatau) was constructed within the 1883 caldera at a point between the former Danan and Perbuwatan cones; it has been the site of frequent eruptions since 1927. The current eruption period began in May 2021 and has recently consisted of Strombolian eruptions and ash plumes (BGVN 48:07). This report describes lower levels of activity consisting of ash and white gas-and-steam plumes during May through August 2023, based on information provided by the Indonesian Center for Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation, referred to as Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG), MAGMA Indonesia, and satellite data.
Activity was relatively low during May and June. Daily white gas-and-steam emissions rose 25-200 m above the crater and drifted in different directions. Five ash plumes were detected at 0519 on 10 May, 1241 on 11 May, 0920 on 12 May, 2320 on 12 May, and at 0710 on 13 May, and rose 1-2.5 km above the crater and drifted SW. A webcam image taken on 12 May showed ejection of incandescent material above the vent. A total of nine ash plumes were detected during 6-11 June: at 1434 and 00220 on 6 and 7 June the ash plumes rose 500 m above the crater and drifted NW, at 1537 on 8 June the ash plume rose 1 km above the crater and drifted SW, at 0746 and at 0846 on 9 June the ash plumes rose 800 m and 3 km above the crater and drifted SW, respectively, at 0423, 1431, and 1750 on 10 June the ash plumes rose 2 km, 1.5 km, and 3.5 km above the crater and drifted NW, respectively, and at 0030 on 11 June an ash plume rose 2 km above the crater and drifted NW. Webcam images taken on 10 and 11 June at 0455 and 0102, respectively, showed incandescent material ejected above the vent. On 19 June an ash plume at 0822 rose 1.5 km above the crater and drifted SE.
Similar low activity of white gas-and-steam emissions and few ash plumes were reported during July and August. Daily white gas-and-steam emissions rose 25-300 m above the crater and drifted in multiple directions. Three ash plumes were reported at 0843, 0851, and 0852 on 20 July that rose 500-2,000 m above the crater and drifted NW.
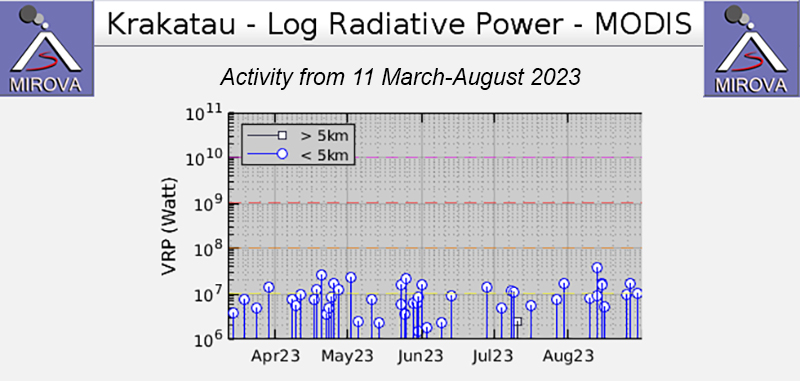
The MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) graph of MODIS thermal anomaly data showed intermittent low-to-moderate power thermal anomalies during May through August 2023 (figure 140). Although activity was often obscured by weather clouds, a thermal anomaly was visible in an infrared satellite image of the crater on 12 May, accompanied by an eruption plume that drifted SW (figure 141).
Geologic Background. The renowned Krakatau (frequently mis-named as Krakatoa) volcano lies in the Sunda Strait between Java and Sumatra. Collapse of an older edifice, perhaps in 416 or 535 CE, formed a 7-km-wide caldera. Remnants of that volcano are preserved in Verlaten and Lang Islands; subsequently the Rakata, Danan, and Perbuwatan cones were formed, coalescing to create the pre-1883 Krakatau Island. Caldera collapse during the catastrophic 1883 eruption destroyed Danan and Perbuwatan, and left only a remnant of Rakata. This eruption caused more than 36,000 fatalities, most as a result of tsunamis that swept the adjacent coastlines of Sumatra and Java. Pyroclastic surges traveled 40 km across the Sunda Strait and reached the Sumatra coast. After a quiescence of less than a half century, the post-collapse cone of Anak Krakatau (Child of Krakatau) was constructed within the 1883 caldera at a point between the former Danan and Perbuwatan cones. Anak Krakatau has been the site of frequent eruptions since 1927.
Information Contacts: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as Indonesian Center for Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation, CVGHM), Jalan Diponegoro 57, Bandung 40122, Indonesia (URL: http://www.vsi.esdm.go.id/); MAGMA Indonesia, Kementerian Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral (URL: https://magma.esdm.go.id/v1); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Villarrica (Chile) — October 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Villarrica
Chile
39.42°S, 71.93°W; summit elev. 2847 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Strombolian activity, gas-and-ash emissions, and crater incandescence during April-September 2023
Villarrica, in central Chile, consists of a 2-km-wide caldera that formed about 3,500 years ago and is located at the base of the presently active cone at the NW margin of a 6-km-wide caldera. Historical eruptions eruptions date back to 1558 and have been characterized by mild-to-moderate explosive activity with occasional lava effusions. The current eruption period began in December 2014 and has recently consisted of nighttime crater incandescence, ash emissions, and seismicity (BGVN 48:04). This report covers activity during April through September 2023 and describes occasional Strombolian activity, gas-and-ash emissions, and nighttime crater incandescence. Information for this report primarily comes from the Southern Andes Volcano Observatory (Observatorio Volcanológico de Los Andes del Sur, OVDAS), part of Chile's National Service of Geology and Mining (Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería, SERNAGEOMIN) and satellite data.
Seismicity during April consisted of long period (LP) events and tremor (TRE); a total of 9,413 LP-type events and 759 TR-type events were detected throughout the month. Nighttime crater incandescence persisted and was visible in the degassing column. Sulfur dioxide data was obtained using Differential Absorption Optical Spectroscopy Equipment (DOAS) that showed an average value of 1,450 ± 198 tons per day (t/d) during 1-15 April and 1,129 ± 201 t/d during 16-30 April, with a maximum daily value of 2,784 t/d on 9 April. Gas-and-steam emissions of variable intensities rose above the active crater as high as 1.3 km above the crater on 13 April. Strombolian explosions were not observed and there was a slight decrease in the lava lake level.
There were 14,123 LP-type events and 727 TR-type events detected during May. According to sulfur dioxide measurements taken with DOAS equipment, the active crater emitted an average value of 1,826 ± 482 t/d during 1-15 May and 912 ± 41 t/d during 16-30 May, with a daily maximum value of 5,155 t/d on 13 May. Surveillance cameras showed continuous white gas-and-steam emissions that rose as high as 430 m above the crater on 27 May. Nighttime incandescence illuminated the gas column less than 300 m above the crater rim was and no pyroclastic emissions were reported. A landslide was identified on 13 May on the E flank of the volcano 50 m from the crater rim and extending 300 m away; SERNAGEOMIN noted that this event may have occurred on 12 May. During the morning of 27 and 28 May minor Strombolian explosions characterized by incandescent ejecta were recorded at the crater rim; the last reported Strombolian explosions had occurred at the end of March.
Seismic activity during June consisted of five volcano-tectonic (VT)-type events, 21,606 LP-type events, and 2,085 TR-type events. The average value of sulfur dioxide flux obtained by DOAS equipment was 1,420 ± 217 t/d during 1-15 June and 2,562 ± 804 t/d, with a maximum daily value of 4,810 t/d on 17 June. White gas-and-steam emissions rose less than 480 m above the crater; frequent nighttime crater incandescence was reflected in the degassing plume. On 12 June an emission rose 100 m above the crater and drifted NNW. On 15 June one or several emissions resulted in ashfall to the NE as far as 5.5 km from the crater, based on a Skysat satellite image. Several Strombolian explosions occurred within the crater; activity on 15 June was higher energy and ejected blocks 200-300 m on the NE slope. Surveillance cameras showed white gas-and-steam emissions rising 480 m above the crater on 16 June. On 19 and 24 June low-intensity Strombolian activity was observed, ejecting material as far as 200 m from the center of the crater to the E.
During July, seismicity included 29,319 LP-type events, 3,736 TR-type events, and two VT-type events. DOAS equipment recorded two days of sulfur dioxide emissions of 4,220 t/d and 1,009 t/d on 1 and 13 July, respectively. Constant nighttime incandescence was also recorded and was particularly noticeable when accompanied by eruptive columns on 12 and 16 July. Minor explosive events were detected in the crater. According to Skysat satellite images taken on 12, 13, and 16 July, ashfall deposits were identified 155 m S of the crater. According to POVI, incandescence was visible from two vents on the crater floor around 0336 on 12 July. Gas-and-ash emissions rose as high as 1.2 km above the crater on 13 July and drifted E and NW. A series of gas-and-steam pulses containing some ash deposited material on the upper E flank around 1551 on 13 July. During 16-31 July, average sulfur dioxide emissions of 1,679 ± 406 t/d were recorded, with a maximum daily value of 2,343 t/d on 28 July. Fine ash emissions were also reported on 16, 17, and 23 July.
Seismicity persisted during August, characterized by 27,011 LP-type events, 3,323 TR-type events, and three VT-type events. The average value of sulfur dioxide measurements taken during 1-15 August was 1,642 ± 270 t/d and 2,207 ± 4,549 t/d during 16-31 August, with a maximum daily value of 3,294 t/d on 27 August. Nighttime crater incandescence remained visible in degassing columns. White gas-and-steam emissions rose 480 m above the crater on 6 August. According to a Skysat satellite image from 6 August, ash accumulation was observed proximal to the crater and was mainly distributed toward the E slope. White gas-and-steam emissions rose 320 m above the crater on 26 August. Nighttime incandescence and Strombolian activity that generated ash emissions were reported on 27 August.
Seismicity during September was characterized by five VT-type events, 12,057 LP-type events, and 2,058 TR-type events. Nighttime incandescence persisted. On 2 September an ash emission rose 180 m above the crater and drifted SE at 1643 (figure 125) and a white gas-and-steam plume rose 320 m above the crater. According to the Buenos Aires VAAC, periods of continuous gas-and-ash emissions were visible in webcam images from 1830 on 2 September to 0110 on 3 September. Strombolian activity was observed on 2 September and during the early morning of 3 September, the latter event of which generated an ash emission that rose 60 m above the crater and drifted 100 m from the center of the crater to the NE and SW. Ashfall was reported to the SE and S as far as 750 m from the crater. The lava lake was active during 3-4 September and lava fountaining was visible for the first time since 26 March 2023, according to POVI. Fountains captured in webcam images at 2133 on 3 September and at 0054 on 4 September rose as high as 60 m above the crater rim and ejected material onto the upper W flank. Sulfur dioxide flux of 1,730 t/d and 1,281 t/d was measured on 3 and 4 September, respectively, according to data obtained by DOAS equipment.
Strong Strombolian activity and larger gas-and-ash plumes were reported during 18-20 September. On 18 September activity was also associated with energetic LP-type events and notable sulfur dioxide fluxes (as high as 4,277 t/d). On 19 September Strombolian activity and incandescence were observed. On 20 September at 0914 ash emissions rose 50 m above the crater and drifted SSE, accompanied by Strombolian activity that ejected material less than 100 m SSE, causing fall deposits on that respective flank. SERNAGEOMIN reported that a Planet Scope satellite image taken on 20 September showed the lava lake in the crater, measuring 32 m x 35 m and an area of 0.001 km2. Several ash emissions were recorded at 0841, 0910, 1251, 1306, 1312, 1315, and 1324 on 23 September and rose less than 150 m above the crater. The sulfur dioxide flux value was 698 t/d on 23 September and 1,097 t/d on 24 September. On 24 September the Volcanic Alert Level (VAL) was raised to Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). SENAPRED maintained the Alert Level at Yellow (the middle level on a three-color scale) for the communities of Villarrica, Pucón (16 km N), Curarrehue, and Panguipulli.
During 24-25 September there was an increase in seismic energy (observed at TR-events) and acoustic signals, characterized by 1 VT-type event, 213 LP-type events, and 124 TR-type events. Mainly white gas-and-steam emissions, in addition to occasional fine ash emissions were recorded. During the early morning of 25 September Strombolian explosions were reported and ejected material 250 m in all directions, though dominantly toward the NW. On 25 September the average value of sulfur dioxide flux was 760 t/d. Seismicity during 25-30 September consisted of five VT-type events, 1,937 LP-type events, and 456 TR-type events.
During 25-29 September moderate Strombolian activity was observed and ejected material as far as the crater rim. In addition, ash pulses lasting roughly 50 minutes were observed around 0700 and dispersed ENE. During 26-27 September a TR episode lasted 6.5 hours and was accompanied by discrete acoustic signals. Satellite images from 26 September showed a spatter cone on the crater floor with one vent that measured 10 x 14 m and a smaller vent about 35 m NE of the cone. SERNAGEOMIN reported an abundant number of bomb-sized blocks up to 150 m from the crater, as well as impact marks on the snow, which indicated explosive activity. A low-altitude ash emission was observed drifting NW around 1140 on 28 September, based on webcam images. Between 0620 and 0850 on 29 September an ash emission rose 60 m above the crater and drifted NW. During an overflight taken around 1000 on 29 September scientists observed molten material in the vent, a large accumulation of pyroclasts inside the crater, and energetic degassing, some of which contained a small amount of ash. Block-sized pyroclasts were deposited on the internal walls and near the crater, and a distal ash deposit was also visible. The average sulfur dioxide flux measured on 28 September was 344 t/d. Satellite images taken on 29 September ashfall was deposited roughly 3 km WNW from the crater and nighttime crater incandescence remained visible. The average sulfur dioxide flux value from 29 September was 199 t/d. On 30 September at 0740 a pulsating ash emission rose 1.1 km above the crater and drifted NNW (figure 126). Deposits on the S flank extended as far as 4.5 km from the crater rim, based on satellite images from 30 September.
Infrared MODIS satellite data processed by MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) showed intermittent thermal activity during April through September, with slightly stronger activity detected during late September (figure 127). Small clusters of thermal activity were detected during mid-June, early July, early August, and late September. According to the MODVOLC thermal alert system, a total of four thermal hotspots were detected on 7 July and 3 and 23 September. This activity was also intermittently captured in infrared satellite imagery on clear weather days (figure 128).
Geologic Background. The glacier-covered Villarrica stratovolcano, in the northern Lakes District of central Chile, is ~15 km south of the city of Pucon. A 2-km-wide caldera that formed about 3,500 years ago is located at the base of the presently active, dominantly basaltic to basaltic andesite cone at the NW margin of a 6-km-wide Pleistocene caldera. More than 30 scoria cones and fissure vents are present on the flanks. Plinian eruptions and pyroclastic flows that have extended up to 20 km from the volcano were produced during the Holocene. Lava flows up to 18 km long have issued from summit and flank vents. Eruptions documented since 1558 CE have consisted largely of mild-to-moderate explosive activity with occasional lava effusion. Glaciers cover 40 km2 of the volcano, and lahars have damaged towns on its flanks.
Information Contacts: Servicio Nacional de Geología y Minería (SERNAGEOMIN), Observatorio Volcanológico de Los Andes del Sur (OVDAS), Avda Sta María No. 0104, Santiago, Chile (URL: http://www.sernageomin.cl/); Proyecto Observación Villarrica Internet (POVI) (URL: http://www.povi.cl/); Sistema y Servicio Nacional de Prevención y Repuesta Ante Desastres (SENAPRED), Av. Beauchef 1671, Santiago, Chile (URL: https://web.senapred.cl/); Buenos Aires Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), Servicio Meteorológico Nacional-Fuerza Aérea Argentina, 25 de mayo 658, Buenos Aires, Argentina (URL: http://www.smn.gov.ar/vaac/buenosaires/inicio.php); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/).
Merapi (Indonesia) — October 2023  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Merapi
Indonesia
7.54°S, 110.446°E; summit elev. 2910 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Frequent incandescent avalanches during April-September 2023
Merapi, located just north of the major city of Yogyakarta in central Java, Indonesia, has had activity within the last 20 years characterized by pyroclastic flows and lahars accompanying growth and collapse of the steep-sided active summit lava dome. The current eruption period began in late December 2020 and has more recently consisted of ash plumes, intermittent incandescent avalanches of material, and pyroclastic flows (BGVN 48:04). This report covers activity during April through September 2023, based on information from Balai Penyelidikan dan Pengembangan Teknologi Kebencanaan Geologi (BPPTKG), the Center for Research and Development of Geological Disaster Technology, a branch of PVMBG which specifically monitors Merapi. Additional information comes from the Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as Indonesian Center for Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation, CVGHM), MAGMA Indonesia, the Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), and various satellite data.
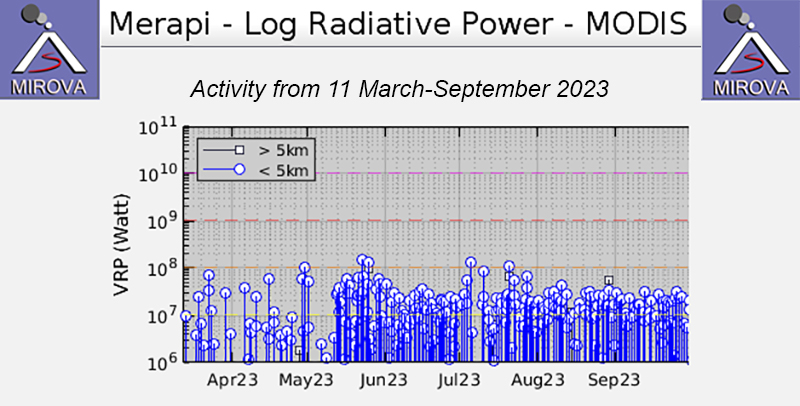
Activity during April through September 2023 primarily consisted of incandescent avalanches of material that mainly affected the SW and W flanks and traveled as far as 2.3 km from the summit (table 25) and white gas-and-steam emissions that rose 10-1,000 m above the crater.
Table 25. Monthly summary of avalanches and avalanche distances recorded at Merapi during April through September 2023. The number of reported avalanches does not include instances where possible avalanches were heard but could not be visually confirmed as a result of inclement weather. Data courtesy of BPPTKG (April-September 2023 daily reports).
| Month |
Average number of avalanches per day |
Distance avalanches traveled (m) |
| Apr 2023 |
19 |
1,200-2,000 |
| May 2023 |
22 |
500-2,000 |
| Jun 2023 |
18 |
1,200-2,000 |
| Jul 2023 |
30 |
300-2,000 |
| Aug 2023 |
25 |
400-2,300 |
| Sep 2023 |
23 |
600-2,000 |
BPPTKG reported that during April and May white gas-and-steam emissions rose 10-750 m above the crater, incandescent avalanches descended 500-2,000 m on the SW and W flanks (figure 135). Cloudy weather often prevented clear views of the summit, and sometimes avalanches could not be confirmed. According to a webcam image, a pyroclastic flow was visible on 17 April at 0531. During the week of 28 April and 4 May a pyroclastic flow was reported on the SW flank, traveling up to 2.5 km. According to a drone overflight taken on 17 May the SW lava dome volume was an estimated 2,372,800 cubic meters and the dome in the main crater was an estimated 2,337,300 cubic meters.
During June and July similar activity persisted with white gas-and-steam emissions rising 10-350 m above the crater and frequent incandescent avalanches that traveled 300-2,000 m down the SW, W, and S flanks (figure 136). Based on an analysis of aerial photos taken on 24 June the volume of the SW lava dome was approximately 2.5 million cubic meters. A pyroclastic flow was observed on 5 July that traveled 2.7 km on the SW flank. According to the Darwin VAAC multiple minor ash plumes were identified in satellite images on 19 July that rose to 3.7 km altitude and drifted S and SW. During 22, 25, and 26 July a total of 17 avalanches descended as far as 1.8 km on the S flank.
Frequent white gas-and-steam emissions continued during August and September, rising 10-450 m above the crater. Incandescent avalanches mainly affected the SW and W flanks and traveled 400-2,300 m from the vent (figure 137). An aerial survey conducted on 10 August was analyzed and reported that estimates of the SW dome volume was 2,764,300 cubic meters and the dome in the main crater was 2,369,800 cubic meters.
Frequent and moderate-power thermal activity continued throughout the reporting period, according to a MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) analysis of MODIS satellite data (figure 138). There was an increase in the number of detected anomalies during mid-May. The MODVOLC thermal algorithm recorded a total of 47 thermal hotspots: six during April, nine during May, eight during June, 15 during July, four during August, and five during September. Some of this activity was captured in infrared satellite imagery on clear weather days, sometimes accompanied by incandescent material on the SW flank (figure 139).
Geologic Background. Merapi, one of Indonesia's most active volcanoes, lies in one of the world's most densely populated areas and dominates the landscape immediately north of the major city of Yogyakarta. It is the youngest and southernmost of a volcanic chain extending NNW to Ungaran volcano. Growth of Old Merapi during the Pleistocene ended with major edifice collapse perhaps about 2,000 years ago, leaving a large arcuate scarp cutting the eroded older Batulawang volcano. Subsequent growth of the steep-sided Young Merapi edifice, its upper part unvegetated due to frequent activity, began SW of the earlier collapse scarp. Pyroclastic flows and lahars accompanying growth and collapse of the steep-sided active summit lava dome have devastated cultivated lands on the western-to-southern flanks and caused many fatalities.
Information Contacts: Balai Penyelidikan dan Pengembangan Teknologi Kebencanaan Geologi (BPPTKG), Center for Research and Development of Geological Disaster Technology (URL: http://merapi.bgl.esdm.go.id/, Twitter: @BPPTKG); MAGMA Indonesia, Kementerian Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral (URL: https://magma.esdm.go.id/v1); Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as Indonesian Center for Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation, CVGHM), Jalan Diponegoro 57, Bandung 40122, Indonesia (URL: http://www.vsi.esdm.go.id/); Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Bureau of Meteorology, Northern Territory Regional Office, PO Box 40050, Casuarina, NT 0811, Australia (URL: http://www.bom.gov.au/info/vaac/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/); Øystein Lund Andersen (URL: https://www.oysteinlundandersen.com/, https://twitter.com/oysteinvolcano).
Ebeko
Russia
50.686°N, 156.014°E; summit elev. 1103 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Moderate explosive activity with ash plumes continued during June-November 2023
Ebeko, located on the N end of Paramushir Island in Russia’s Kuril Islands just S of the Kamchatka Peninsula, consists of three summit craters along a SSW-NNE line at the northern end of a complex of five volcanic cones. Observed eruptions date back to the late 18th century and have been characterized as small-to-moderate explosions from the summit crater, accompanied by intense fumarolic activity. The current eruptive period began in June 2022, consisting of frequent explosions, ash plumes, and thermal activity (BGVN 47:10, 48:06). This report covers similar activity during June-November 2023, based on information from the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT) and satellite data.
Moderate explosive activity continued during June-November 2023 (figures 50 and 51). According to visual data from Severo-Kurilsk, explosions sent ash 2-3.5 km above the summit (3-4.5 km altitude) during most days during June through mid-September. Activity after mid-September was slightly weaker, with ash usually reaching less than 2 km above the summit. According to KVERT the volcano in October and November was, with a few exceptions, either quiet or obscured by clouds that prevented satellite observations. KVERT issued Volcano Observatory Notices for Aviation (VONA) on 8 and 12 June, 13 and 22 July, 3 and 21 August, and 31 October warning of potential aviation hazards from ash plumes drifting 3-15 km from the volcano. Based on satellite data, KVERT reported a persistent thermal anomaly whenever weather clouds permitted viewing.
Geologic Background. The flat-topped summit of the central cone of Ebeko volcano, one of the most active in the Kuril Islands, occupies the northern end of Paramushir Island. Three summit craters located along a SSW-NNE line form Ebeko volcano proper, at the northern end of a complex of five volcanic cones. Blocky lava flows extend west from Ebeko and SE from the neighboring Nezametnyi cone. The eastern part of the southern crater contains strong solfataras and a large boiling spring. The central crater is filled by a lake about 20 m deep whose shores are lined with steaming solfataras; the northern crater lies across a narrow, low barrier from the central crater and contains a small, cold crescentic lake. Historical activity, recorded since the late-18th century, has been restricted to small-to-moderate explosive eruptions from the summit craters. Intense fumarolic activity occurs in the summit craters, on the outer flanks of the cone, and in lateral explosion craters.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/).
Search Bulletin Archive by Publication Date
Select a month and year from the drop-downs and click "Show Issue" to have that issue displayed in this tab.
The default month and year is the latest issue available.
Bulletin of the Global Volcanism Network - Volume 23, Number 05 (May 1998)
Managing Editor: Richard Wunderman
Bezymianny (Russia)
Slowly growing hot spot seen on satellite image
Deception Island (Antarctica)
Stable conditions, 35 hours of tremor
Galeras (Colombia)
Continuing seismicity includes tornillo events
Manam (Papua New Guinea)
Short-lived Vulcanian episode unsettles month of mild activity
Pacaya (Guatemala)
May eruption shrouds capital in ash, harms crops, and spreads NW
Popocatepetl (Mexico)
Moderate activity continues, smoke hinders observation
Rabaul (Papua New Guinea)
Tripling of volcanic events; ash plumes
Sabancaya (Peru)
Summit activity, ice observed on visit in May
Sheveluch (Russia)
Satellite imagery detects large ash plume
Soufriere Hills (United Kingdom)
Low activity; deformation and volume measurements
St. Helens (United States)
Sudden rise in earthquake activity in May
Ukinrek Maars (United States)
Earthquake swarm decreases in rate and intensity
Bezymianny
Russia
55.972°N, 160.595°E; summit elev. 2882 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Slowly growing hot spot seen on satellite image
During 28-30 May, a fumarolic plume was seen rising to 50-300 m above the volcano and moving 5 km E. Visual observations made on 28 May indicated color changes in the fumarolic plume suggesting an increase in gas emission.
Satellite images of Bezymianny made during 1-10 June, when not obscured by clouds, indicated a persistent and slowly growing hot-spot more than 5 km2 in size. This thermal anomaly persisted until late June. It was similar to that observed shortly before the 5 December 1997 eruption (BGVN 22:11), which sent a short-lived eruption plume to over 9 km above sea level. It likely indicates that the summit lava dome is growing again and may be subject to a sudden partial collapse similar to the 5 December event. KVERT changed the level of concern color code to yellow-alert and will monitor the situation closely.
Seismicity during 1-10 June was at background levels. No seismicity was reported during the next three weeks. Fumarolic plumes were seen rising 100 to 800 m and moving up to 10 km to the SE and S during 9-11, 17, and 19-21 June.
Geologic Background. The modern Bezymianny, much smaller than its massive neighbors Kamen and Kliuchevskoi on the Kamchatka Peninsula, was formed about 4,700 years ago over a late-Pleistocene lava-dome complex and an edifice built about 11,000-7,000 years ago. Three periods of intensified activity have occurred during the past 3,000 years. The latest period, which was preceded by a 1,000-year quiescence, began with the dramatic 1955-56 eruption. This eruption, similar to that of St. Helens in 1980, produced a large open crater that was formed by collapse of the summit and an associated lateral blast. Subsequent episodic but ongoing lava-dome growth, accompanied by intermittent explosive activity and pyroclastic flows, has largely filled the 1956 crater.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova and Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Deception Island (Antarctica) — May 1998  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Deception Island
Antarctica
62.9567°S, 60.6367°W; summit elev. 602 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Stable conditions, 35 hours of tremor
A Deception Volcano Observatory team has visited the island every austral summer since 1986. In comparison with measurements made during 1996-1997, the temperatures of fumaroles and hot soils generally remained stable: 96-98°C in Fumarole Bay, 64°C in Whaler's Bay, 43°C in Telefon Bay, and 60°C in Pendulum Cove. At Murature Point an increase of more than 20°C produced greater bubbling under the sea, and a large quantity of dead (boiled) krill at the shoreline.
Fumarolic gases were mainly composed of CO2 and H2S, similar to previous years. SO2 was not detected.
Seismicity was monitored with a digital seismic array having 16-bit dynamic range. The array included 6 vertical-component geophones (Mark L25B) located near the Spanish Antarctic Station Gabriel de Castilla (figure 12). Figure 13 shows seismic data collected from 18 December 1997 to 24 February 1998. A significant component of the seismicity was volcanic tremor of a few minutes to several hours duration totaling 35 hours over the reporting period. Also recorded were 72 hybrid events, 291 long-period events, 12 short-period events, and some regional events generated at 30-100 km distance. Recorded seismicity during this period was greater in both energy and number than in previous years.
Geologic Background. Ring-shaped Deception Island, at the SW end of the South Shetland Islands, NE of Graham Land Peninsula, was constructed along the axis of the Bransfield Rift spreading center. A narrow passageway named Neptunes Bellows provides an entrance to a natural harbor within the 8.5 x 10 km caldera that was utilized as an Antarctic whaling station. Numerous vents along ring fractures circling the low 14-km-wide island have been reported active for more than 200 years. Maars line the shores of 190-m-deep Port Foster caldera bay. Among the largest of these maars is 1-km-wide Whalers Bay, at the entrance to the harbor. Eruptions during the past 8,700 years have been dated from ash layers in lake sediments on the Antarctic Peninsula and neighboring islands.
Information Contacts: C. Risso, Observatorio Volcanológico Decepción, Instituto Antártico Argentino-UBA, Cerrito 1248 (1010) Buenos Aires, Argentina; A. García, R. Abella, and J. Peña, Dpto. Volcanologia, Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales-CSIS, José Guiterrez Abascal 2, 28006 Madrid-Spain; E. Vélez, Instituto de Astronomía y Geodesia-CSIS, Madrid-Spain; F. Navarro, Escuela Superior de Ingenieros de Telecomunicaciones-U.P.M., Madrid, Spain.
Galeras
Colombia
1.22°N, 77.37°W; summit elev. 4276 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Continuing seismicity includes tornillo events
Seismicity continued at low levels around Galeras during March and April. Over this period 92 volcano-tectonic (VT) earthquakes were located; of these, 53 were in the area called the North Source (dashed box in figure 88). On 16 March at 2124 (GMT) a VT event with a coda magnitude of 2.2 was felt in Pasto City and other towns in the area. The event was centered in the North Source 2 km N of the crater at a depth of 5 km below the summit. The most energetic VT event outside of the North Source occurred on 29 April. That event struck SW of the crater with a coda magnitude of 2.1 and a depth of 6.5 km.
Another aspect of seismicity during March and April was the continuation of Long Period (LP) events called Tornillos. Tornillo events characteristically have quasi-monochromatic wave-forms with slowly decaying coda values and hence leave a seismic record that looks like the threads of a screw. A record 38 such events have been recorded since November 1997 (BGVN 22:09 and 22:12). The last Tornillo was recorded 10 April.
On 19 April an event similar to spasmodic tremor was recorded. The cause was mud flow along the Azufral River, which runs west from the summit, resulting from heavy rain on volcanic deposits. The event lasted for about 1 hour.
Two electronic tiltmeters, located at the summit and on the E flank (figure 89), remained stable with minimum fluctuations during the period. Fumarole temperature, hot springs pH, radon, and gas-emission measurements showed no significant changes with respect to previous months. The Galeras Seismological Network monitors the volcano with five short-period and two broad-band telemeters, which are part of a cooperative project between OVP-INGEOMINAS (see below) and the German Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources.
Geologic Background. Galeras, a stratovolcano with a large breached caldera located immediately west of the city of Pasto, is one of Colombia's most frequently active volcanoes. The dominantly andesitic complex has been active for more than 1 million years, and two major caldera collapse eruptions took place during the late Pleistocene. Long-term extensive hydrothermal alteration has contributed to large-scale edifice collapse on at least three occasions, producing debris avalanches that swept to the west and left a large open caldera inside which the modern cone has been constructed. Major explosive eruptions since the mid-Holocene have produced widespread tephra deposits and pyroclastic flows that swept all but the southern flanks. A central cone slightly lower than the caldera rim has been the site of numerous small-to-moderate eruptions since the time of the Spanish conquistadors.
Information Contacts: Pablo Chamorro and Diego Gomez Martinez, Observatorio Vulcanologico y Sismologico de Pasto (OVP), INGEOMINAS, Carrera 31, No. 18-07 Parque Infantil, PO Box 1795, Pasto, Colombia (URL: https://www2.sgc.gov.co/volcanes/index.html).
Manam (Papua New Guinea) — May 1998  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Manam
Papua New Guinea
4.08°S, 145.037°E; summit elev. 1807 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Short-lived Vulcanian episode unsettles month of mild activity
Mild activity from Manam's two summit craters continued throughout May. Emissions at both Southern and Main craters chiefly consisted of white vapors released at weak to moderately high rates.
An hour-long Vulcanian episode occurred on 21 May. At 1300 a single large explosion at Southern crater produced a gray-brown ash cloud that rose ~ 500 m above the crater, followed by occasional gray ash emissions at 3-5 minute intervals. The ash clouds drifted to the SE of the island leaving a fine ashfall in its wake. There was no visible glow at night.
Seismicity remained at low levels. From 1,100 to 1,400 low-frequency events of very low amplitudes were recorded daily. The water-tube tiltmeter at Tabele Observatory, 4 km SW of the summit, showed an inflation of 2 µrad prior to the Vulcanian phase of 21 May, which remained to the end the month.
Geologic Background. The 10-km-wide island of Manam, lying 13 km off the northern coast of mainland Papua New Guinea, is one of the country's most active volcanoes. Four large radial valleys extend from the unvegetated summit of the conical basaltic-andesitic stratovolcano to its lower flanks. These valleys channel lava flows and pyroclastic avalanches that have sometimes reached the coast. Five small satellitic centers are located near the island's shoreline on the northern, southern, and western sides. Two summit craters are present; both are active, although most observed eruptions have originated from the southern crater, concentrating eruptive products during much of the past century into the SE valley. Frequent eruptions, typically of mild-to-moderate scale, have been recorded since 1616. Occasional larger eruptions have produced pyroclastic flows and lava flows that reached flat-lying coastal areas and entered the sea, sometimes impacting populated areas.
Information Contacts: Ben Talai and H. Patia, RVO.
Pacaya
Guatemala
14.382°N, 90.601°W; summit elev. 2569 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
May eruption shrouds capital in ash, harms crops, and spreads NW
Pacaya erupted unusually vigorously on 20 May. As a result, ash falling in the adjacent highlands damaged crops; ash falling to the N choked the capital and its international airport; and ash located at about 10 km altitude entered the Gulf of Mexico and joined smoke from widespread forest fires. An airplane on final approach to landing at the Guatemala City airport hit ejecta, sustaining damage but landing without incident.
The outburst's greatest intensity occurred during the hours 1205-1900. For 30 hours prior to this outburst, relative quiet prevailed with the volcano generally emitting ash-bearing explosions of brown to coffee-brown color and very little incandescent lava. Beginning around 0930, explosions became continuous, and they proceeded to squirt and splatter abundant lava E and N of the active crater (MacKenney Crater).
An initial, higher-intensity phase began before noon, sending a gray ash column 800 m high. Such columns later reached roughly 1.5-2.0 km above the crater. The eruption was described in Spanish in a series of INSIVUMEH reports. Their update at 1400 on 20 May stated that ash with grain sizes up to 3-7 mm fell on Guatemala City (the capital), the center of which lies 30 km N of Pacaya. An update at 1700 told of 2.5 mm of ash at the international airport (La Aurora, ~23 km N of Pacaya) but eruptive plumes at the volcano had dropped to 200-300 m in height. The ash at the airport was described as 0.5-1.5 mm across and dark in color. About 1 mm of ash fell in part of the capital.
Although ash fell in the capital mainly during 1100-1700 on 20 May, the amount falling diminished around 1530, allowing the atmosphere to clear substantially. At 1700, Pacaya sent ash plumes 200-300 m above the summit, more typical of normal behavior at the volcano. At about 2000, the wind carried only very small particles toward the capital. Still, local vegetation tenuously held residual ash that could easily become wind blown. In response to the diminished eruptive vigor, at 2100 on 20 May the alert status was lowered from red to orange.
During the eruption, five lava flows or lobes formed, three oriented towards Cerro Chino. One of these reached 1.5 km in length and ~300-400 m in width. The two other flows proceeded down the N and S flanks for ~600 m. No lavas reached cultivated or populated areas. The eruption disrupted the crater sending blocks 2.5 m in diameter up to 1 km downslope (to "la meseta"). Ash thicknesses of 20-30 cm were reported in villages approximately 2-4 km from the volcano (including San Francisco de Sales, Calderas, Mesillas Altas, and El Bejucal).
Verbal conversations with INSIVUMEH's Eddie Sanchez indicated that ash fell on Guatemala City during 1100-1700 on 20 May. Also, volcanic bombs with masses up to 7 kg landed near Pacaya's summit (on Cerro Chino). They also learned that lapilli fell in a village a few kilometers away on Pacaya's flanks (San Francisco de Sales). Otoniel Mat¡as said the 20 May event prompted 252 people to evacuate local settlements. Authorities had several cautions for people in areas of ash fall: 1) drive at speeds below 30 km/hour; 2) avoid the use of their vehicle's windshield wipers because the ash would scratch glass; and 3) cover cisterns even though the ash was non-toxic.
Seismicity during the event on 20 May left records with amplitudes of 5-17 mm peak-to-peak and maintained RSAM values of 870 counts over 10-minute intervals.
The INSIVUMEH report at 1000 on 21 May described a substantial decrease in eruptive vigor but explosions still sent gray, ash-bearing plumes to ~800 m above the summit. A N wind with speeds of 12-17 km/hour carried ash to El Chupadero and El Caracol, spots located 2-2.5 km from the crater. This same morning, the longest lava flow had reached 1.1 km in length.
Other consequences. The previously mentioned aircraft was a commercial jet that was on final approach to the airport when it entered an ash cloud. A few seconds prior to landing, a Pacaya discharge burst forth propelling rocks into the air. Impact with these rocks damaged the pilot's forward windows (captain and first officer) but the landing was completed without further complications. Repairs and inspection were carried out over a 3-day interval; both the airline's technicians and a manufacturer's representative inspected the plane and found the engines undamaged.
At the airport, ash was removed by mechanical means (and to some extent thanks to rainfall) on 21, 22, and 23 May, returning to full service on Sunday 24 May. Rainfall during 22-24 May was never heavy but it apparently did much to wash the ash away. Not surprisingly, the ash clogged storm drains in the capital forcing crews to clean much of the 3-4 million tons of ash mechanically.
A news report in La Nación stated the National Coffee Association computed that the 20 May eruption caused "some $75 million in losses in the coffee harvest." This was the third time in recent history that Guatemala City had been ash choked: the two previous times, 1932 and 1974 were due to eruptions at Fuego, a stratovolcano that sits along the volcanic front roughly 30 km W of Pacaya.
Later activity. Other outbursts occurred during June. One on 14 June was somewhat weaker than the 20 May event; nevertheless it disrupted the crater's geometry and formed a distinct spatter cone. This outburst took place at 1045, exhaling for 10 minutes in conditions of little or no wind, sending brightly incandescent material to 1 km. The material fell harmlessly back on the crater area.
This type of comparatively short eruptive interval had been rare at Pacaya until recently; previous pulses were typically weaker and continued longer, often for 2-7 hours. The short blasts seen recently were thought to be related to water saturation of the ground associated with a wet rainy season; presumably, more groundwater has been driven toward the magma. The situation became difficult from a civil-defense policy perspective since these short, forceful pulses were typically unpredictable and could create conditions requiring rapid response in flank settlements.
Aviation reports. The NOAA/NESDIS Satellite Analysis Branch (SAB) produced tens of reports on Pacaya's mid-May and early June eruptions. For many of their reports before and well after the 20 May eruption, GOES-8 infrared, and multi spectral imagery did not indicate an ash plume, but channel 2 data often revealed a small hot spot. In accord with the rather sudden emergence of the eruption, no ash was detected during clear weather on GOES-8 visible, infrared, or multi spectral imagery through 1645 GMT on 20 May.
Hours later SAB reported a substantial ash cloud; it appeared in GOES-8 imagery taken at 1900 GMT on 20 May (table 2, first entry). Their same report noted that a sounding from Belize (station 78583) had yielded an estimated plume height of about 9-11 km altitude. The cloud extended 140 km NNE from the summit, reached a width of 46 km, and advanced NNE at about 120 km/hour. Table 2 shows a sample of some noteworthy reports posted during portions of 20-22 May.
Table 2. Several of the reports on Pacaya and its ash clouds during parts of 20-22 May put out by the NOAA/NESDIS Satellite Analysis Branch (SAB). Stated times are GMT. Courtesy of SAB.
| Report Date |
Report Time (GMT) |
Report Number |
Observations |
| 20 May 1998 |
2125 |
98-018 |
Ash cloud of dimensions and velocity discussed in text (extending to the point 16°N, 90°W). |
| 21 May 1998 |
0330 |
98-019 |
The plume extended NE across Central America and into W Gulf of Mexico (from 19°N, 88°W to 21°N, 86°W ) and was 55 km wide. Plume height was about 9-12 km. |
| 21 May 1998 |
0915 |
98-020 |
GOES-8 multi spectral imagery did not show any plume from the earlier eruption at 1900 GMT on May 20. The plume moved NW across Central America into the W Caribbean and dissipated as it approached W Cuba. |
| 21 May 1998 |
1535 |
98-021 |
Surface observations at 1500 GMT indicated Pacaya in eruption. No plume visible on GOES-8. |
| 21 May 1998 |
1745 |
98-022 |
Pacaya erupted through 1700. Although ash moved NE at about 50 knots, newly erupted ash was not discerned on GOES-8 imagery. As best as could be determined, the SIGMET issued earlier by Santo Domingo for ash to 10.4 km spread over large portions of the N Carribean was the result of ash resulting from the 1900 GMT 20 May Pacaya eruption. GOES-8 satellite imagery through 1645 GMT failed to reveal discernible ash in the Caribbean but the presence of thin diffuse ash could not be discounted. |
| 22 May 1998 |
0530 |
98-023 |
Surface observations indicated an eruption from 1500 GMT on 21 May to 0530 GMT on 22 May with uncertain amounts of ash ejecting. Highly different wind velocities at different altitudes. Weather clouds obscured the satellite view of the eruption. |
| 22 May 1998 |
1430 |
98-026 |
Surface observations repeatedly indicated that the eruption continued on 22 May during 0530-1300 GMT but no surface observations were reported during 0900-1200 GMT. Pilot reports around indicated ash near 9.1 km in the central Gulf of Mexico (near 24.3°N, 86.8°W). At some time during 1400-1430 GMT one pilot reported descending to an altitude of 8.2 km from 8.8 km to avoid volcanic ash. Another pilot reported no problem while flying at 10 km in the same area. At some time during 1415-1430 GMT a pilot located over 23.5°N, 86.8 observed a gray layer and smoky smell while flying at 8.8 km altitude. The pilot could not distinguish between volcanic ash and smoke. A velocity for ash moving over the central Gulf of Mexico was estimated based on upper air data from Key West, Florida: 55-65 km/hour directed ENE. |
Fires, El Nino, and smoky atmospheric conditions. During May and early June INSIVUMEH reported intervals of heavy rains and fog around Pacaya. Satellite data, now available on the web (SSEC, 1998 ), also revealed intervals of cloud cover. Despite this rain at Pacaya, thousands of fires remained burning throughout the region, ~40% of them located in the Petén, an area hundreds of kilometers to the N. These fires and associated atmospheric conditions warrant further discussion as they link to both public safety and the interest in understanding the Pacaya's contribution to the atmosphere.
According to news reports, smoke from forest fires burning out of control added to the airborne ash from 300-m-tall eruption columns during 15-18 May had caused breathing problems as far away as Houston, Texas. In addition, at least one news report said that reduced visibility had made airplane landing possible only through the use of instrument guidance in Guatemala City; Honduras was forced to close its two largest airports.
What follows came from a report by the U.S. Agency for International Development (21 May 1998). The report noted that since January, more than 10,650 fires have burned some 1,200 square miles [3,108 km2] in Mexico, an area nearly the size of the state of Rhode Island. As of 21 May, approximately 277 wildfires still raged throughout Guatemala.
"During 1998, Mexico and the entire Central American region have been affected by drought exacerbated by El Nino conditions. The drought has aggravated the effects of slash and burn agricultural practices in forest and grassland areas, leaving thousands of fires burning out of control. Tropical forest, usually too humid to burn, has become extremely vulnerable to fire. In addition to making the land more arid and therefore more flammable, the droughts have eliminated the cleaning effect that rains usually have on the region's air. The ground cover burning may be the driest ever recorded in this century, which has resulted in large quantities of smoke being emitted into the atmosphere. The fires have burned more than one million acres [>4,050 km2] and severely affected visibility and air quality in Mexico, Guatemala, Nicaragua, Honduras, El Salvador, and Costa Rica. In Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua, an estimated 2,146 square miles [5,558 km2] have burned. The smoke from these fires also has entered the southern and Midwestern United States prompting local warnings for residents with respiratory conditions to limit their outdoor activities."
"According to NASA, more than 2,000 fires are currently raging in Guatemala. The U.S. Embassy in Guatemala City reported on May 19 that the fires are intensifying and are threatening human populations. The "red alert" on air quality declared by the Government of Guatemala (GOG) on May 15 remains in effect. Air quality monitors report that total suspended particulate levels in Guatemala City averaged 600 milligrams per cubic meter during the first two weeks of May, three times the World Health Organization maximum level. Since then, air quality has worsened significantly. According to the Embassy, the GOG's Ministry of Health's local health centers have found significant increases in respiratory ailments. The Ministry of Health says that the most heavily affected areas are Petén, Alta Verapaz, Baja Verapaz, and areas of Huehuetenango and Quiche. In Ixcan, 80% of the population are suffering from respiratory-related ailments, eye irritation, vomiting, and headaches, according to local community leaders."
References. SSEC, 1998, Real-time data, Volcano Watch (the world's ten most active volcanoes); Pacaya volcano, Guatemala: Graduate School, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Space Science and Engineering Center (SSEC), 1225 West Dayton Street, Madison, Wisconsin 53706 (URL: http://www.ssec.wisc.edu/data/volcano.html).
U.S. Agency for International Development, 21 May 1998, Fiscal Year (FY) 1998 Situation Report ##2, Mexico and Central America Fires [NAT-DSR:378][OFDA-02]: U.S. Agency for International Development, Bureau for Humanitarian Response (BHR), Office of U.S. Foreign Disaster Assistance (OFDA).
Geologic Background. Eruptions from Pacaya are frequently visible from Guatemala City, the nation's capital. This complex basaltic volcano was constructed just outside the southern topographic rim of the 14 x 16 km Pleistocene Amatitlán caldera. A cluster of dacitic lava domes occupies the southern caldera floor. The post-caldera Pacaya massif includes the older Pacaya Viejo and Cerro Grande stratovolcanoes and the currently active Mackenney stratovolcano. Collapse of Pacaya Viejo between 600 and 1,500 years ago produced a debris-avalanche deposit that extends 25 km onto the Pacific coastal plain and left an arcuate scarp inside which the modern Pacaya volcano (Mackenney cone) grew. The NW-flank Cerro Chino crater was last active in the 19th century. During the past several decades, activity has consisted of frequent Strombolian eruptions with intermittent lava flow extrusion that has partially filled in the caldera moat and covered the flanks of Mackenney cone, punctuated by occasional larger explosive eruptions that partially destroy the summit.
Information Contacts: Eddie Sanchez and Otoniel Matías, Seccion Vulconologia, INSIVUMEH (Instituto Nacional de Sismologia, Vulcanologia, Meteorologia e Hydrologia) of the Ministerio de Communicaciones, Transporte y Obras Publicas, 7A Avenida 14-57, Zona 13, Guatemala City, Guatemala; NOAA/NESDIS Satellite Analysis Branch, Room 401, 5200 Auth Road, Camp Springs, MD 20746, USA; La Nación, San José, Costa Rica; U.S. Agency for International Development, Bureau for Humanitarian Response (BHR), Office of U.S. Foreign Disaster Assistance (OFDA); Tom Fox, Air Navigation Bureau, International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), 999 University St., Montreal H3C 5H7, Canada (URL: https://www.icao.int/safety/airnavigation/); Tom Casadevall, U.S. Geological Survey, National Center, Reston, VA 20192.
Popocatepetl (Mexico) — May 1998  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Popocatepetl
Mexico
19.023°N, 98.622°W; summit elev. 5393 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Moderate activity continues, smoke hinders observation
Activity at the start of April showed an increase over that of late March. Small emissions of gas, steam, and light ash along with rockfalls and short harmonic tremors were typical events at Popocatépetl throughout April and May. Smoke from forest fires, mist, and air pollution made direct observation of the volcano difficult for much of both months.
Although not shown as a located A-type event (table 12), on 1 April a gas-and-steam plume was observed rising 500 m above the crater and dispersing to the NE. At 1653 on 2 April seismometers and flow detectors sensed a disturbance that turned out to be a flow of water and debris traveling down NE-flank ravines. The flow was attributed to glacial runoff after days of intensely hot weather. The flow continued for hours and reached points 8 km downstream from the glacier. For 12 hours after this event seismic activity steadily decreased. Only small, short exhalations occurred until 0522 on 3 April when another A-type event occurred.
Table 12. Located A-type events reported at Popocatépetl, April-May 1998. The columns for distance and direction define epicenters with respect to the summit. Data courtesy of CENAPRED.
| Date |
Local Time |
Magnitude |
Depth (km) |
Distance (km) |
Direction |
| 30 Mar 1998 |
2122 |
2.2 |
4 |
7.1 |
SE |
| 01 Apr 1998 |
0008 |
2.1 |
6.1 |
2 |
E |
| 01 Apr 1998 |
1439 |
2.3 |
3.2 |
1.8 |
NE |
| 02 Apr 1998 |
0522 |
2.8 |
9 |
2 |
N |
| 10 Apr 1998 |
1250 |
2.1 |
5 |
7 |
SE |
| 10 Apr 1998 |
1603 |
2.2 |
4.2 |
-- |
-- |
| 11 Apr 1998 |
1616 |
2.1 |
3.3 |
7 |
SE |
| 12 Apr 1998 |
0322 |
2.4 |
6.6 |
8 |
SE |
| 17 Apr 1998 |
1525 |
2.5 |
4.9 |
6.5 |
SE |
| 23 Apr 1998 |
2116 |
2.1 |
5.2 |
2 |
E |
| 04 May 1998 |
1042 |
2 |
6.4 |
0.5 |
NE |
| 05 May 1998 |
0256 |
2.3 |
4.9 |
7 |
SE |
| 25 May 1998 |
0128 |
2.2 |
6.9 |
6.9 |
NW |
| 25 May 1998 |
0202 |
1.8 |
4.2 |
-- |
-- |
| 28 May 1998 |
0404 |
2.5 |
701 |
10 |
N |
Activity remained low to moderate over the next week. At 0425 of 11 April there occurred a small harmonic tremor of 30-second duration. At 1632 the same day a medium-intensity exhalation was followed by 12 minutes of harmonic tremor. Other exhalations occurred that day at 1912 and 2321, and at 0235 the morning of 12 April, all of which were accompanied by small emissions of gas and steam.
At 1107 on 21 April a large exhalation took place that lasted 5 minutes and produced an ash column 4 km high. Although heavy clouds obstructed visibility, a video image of the ash column showed it clearly (figure 25). Incandescent fragments were ejected producing several grass fires on the upper slopes of the volcano. Vibration of windows in the city of Puebla was reported and some ash fell in both Cholula and La Paz. At 1453 the same day a similar exhalation occurred, but was smaller in magnitude and only 1 minute in duration. The last event possibly emitted ash, but this could not be confirmed because of limited visibility. Activity decreased slightly over the next few days, except for some A-type events. Bad weather engulfed the summit in cloud.
The broad-band seismometer recently installed at the Canario station (BGVN 22:10), located on the N flank at 4,300 m altitude 2 km from the crater, went out of operation 21 April probably because solar panels were damaged by ejected rocks. This is the second station damaged by volcanic activity this year (the first was the Espinera station, PFM2). Because of the danger of future explosions, an area within 4 km of the crater was deemed of high risk and restricted access.
On 24 April a large exhalation was recorded at 1257. It had a duration of three minutes and probably produced a small ash emission, which because of poor visibility could not be confirmed. At 1031 on 27 April another explosive exhalation occurred. The most intense phase lasted three minutes and was followed by high-frequency tremor that lasted an additional five minutes. It produced a 4-km-high ash column over the summit. Immediately afterwards the volcano returned to previous lower levels of activity. Mild ashfall was expected in the towns located to the E and NE of the volcano.
May began with a slight decrease in activity. Mist and clouds with occasional smoke persisted in obstructing visibility of the mountain. Activity increased slightly on 9 May and included seismic events at 0255 of 2.5 minutes duration, and at 0546 of two minutes duration, possibly due to small emissions of gas, steam, and ash. At 1205 an M 5.2 earthquake occurred on the coast of Guerrero and was recorded by all the stations monitoring the volcano. The event did not affect Popocatépetl.
Isolated low- to medium-intensity exhalations were recorded 10 May. The largest events occurred at 0744 (1.5 minutes duration) and at 0842 (one minute). Both events produced small emissions of gas and steam which rose to 1 km above the crater. Rockfalls were recorded on the N flank of the volcano. At 1322 a moderately large exhalation occurred, followed by four similar but smaller events during the next 5 minutes. Immediately after, one minute of low-frequency harmonic tremor of considerable amplitude was recorded followed by five minutes of high-frequency tremor.
Despite the limited visibility of the volcano at that time, an ash column with gas and steam could be observed rising several kilometers above the crater and was directed by low-speed winds to the NE. The appearance of the column was confirmed by observers viewing from a helicopter in the vicinity of the volcano. These events, due to their explosive nature, ejected solid and incandescent material from the crater over an area of 2-3 km radius. After the episode the volcano returned to previous levels of activity and remained stable for the rest of the day. No reports of damage or ashfall were received.
Beginning at 0426 of 11 May, a high-frequency tremor accompanied a gas-and-steam fumarole which ended with a moderate exhalation at 1505. The afternoon of 12 May at 1755 a column of gas and steam rose 2 km above the summit. The following day, emissions of gas and steam with slight amounts of fine ash generated puffs rising 500-1,000 m above the crater. At 1023 on 15 May three small exhalations mixed with harmonic tremors of low frequency occurred. Other tremor episodes lasting up to five minutes were recorded at 1030 and 1035. At 1043 a medium-intensity exhalation occurred which produced a puff of steam, gas and some light ash, dispersing to the NW. During the rest of the day several similar exhalations were recorded.
On 16 May at 1242 another strong M 5.2 earthquake located on the coast of Guerrero was recorded by all seismic stations at the volcano. This event did not produce any changes in the activity of Popocatépetl. At 1308 a small exhalation occurred accompanied by steam and followed by low-amplitude harmonic tremor lasting 6 minutes. Other short tremor episodes were recorded in the afternoon. During the next few weeks forest fires on the N flank of the volcano close to Tlamacas limited visibility.
The measured SO2 value on 30 March was 5,500 tons/day: on 27 April it was 10,600 tons/day. During the Holocene, Popocatépetl produced both effusive and pyroclastic activity. About 30 eruptions are known since 1345, although early documentation is poor. Most historical eruptions were apparently mild-to-moderate Vulcanian steam and ash emissions, with larger explosive eruptions in 1519 and possibly 1663. Activity in 1920-22 produced intermittent explosive eruptions and a small lava plug in the summit crater. Minor ash clouds were also reported in 1923-24, 1933, 1942-43, and 1947.
Geologic Background. Volcán Popocatépetl, whose name is the Aztec word for smoking mountain, rises 70 km SE of Mexico City to form North America's 2nd-highest volcano. The glacier-clad stratovolcano contains a steep-walled, 400 x 600 m wide crater. The generally symmetrical volcano is modified by the sharp-peaked Ventorrillo on the NW, a remnant of an earlier volcano. At least three previous major cones were destroyed by gravitational failure during the Pleistocene, producing massive debris-avalanche deposits covering broad areas to the south. The modern volcano was constructed south of the late-Pleistocene to Holocene El Fraile cone. Three major Plinian eruptions, the most recent of which took place about 800 CE, have occurred since the mid-Holocene, accompanied by pyroclastic flows and voluminous lahars that swept basins below the volcano. Frequent historical eruptions, first recorded in Aztec codices, have occurred since Pre-Columbian time.
Information Contacts: Servando de la Cruz-Reyna, Roberto Meli, Roberto Quaas, G. Castelan, F. Castillo-Alanis, J.L. Delgollado, F. Galicia, A. Gómez, A.O. González, G. Juarez M., A. Martínez, A. Montalvo, L. Orozco, and E. Ramos, Centro Nacional de Prevencion de Desastres (CENAPRED), Av. Delfin Madrigal 665, Col. Pedregal de Santo Domingo, Coyoacán, CP 04360, México D.F., México.
Rabaul (Papua New Guinea) — May 1998  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Rabaul
Papua New Guinea
4.2459°S, 152.1937°E; summit elev. 688 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Tripling of volcanic events; ash plumes
During May, the intracaldera cone Tavurvur continued Vulcanian eruptive activity with minor fluctuations. In the first few days of the month there was a sharp increase, from 15 to 200 per day, in the number of low-frequency seismic events related to ash emissions. However, activity soon returned to more normal levels; between the 11th and 18th there were an average 20 events per day.
Most ash plumes contained relatively low to moderate amounts of ash and rose to less than 1,000 m above sea level. Throughout the first week ash plumes were blown to the SE and SW resulting in fine ashfall at the abandoned village of Talwat and in the Kokopo area. For the remainder of the month winds shifted between N and W resulting in ashfall in villages on the W of the caldera and in Rabaul town were it continued to be a nuisance to inhabitants. There were larger explosions with dark-gray ash clouds that rose to 1.5-3.0 km. From 9 May until the end of the month occasional explosions and roaring noises ranging in intensity from weak to loud accompanied the ash emissions. A weak glow was observed above the crater rim throughout the nights of 7 and 8 May, and incandescent lava fragments were ejected during explosions on the 7th.
Activity continued with minor fluctuations from 19 May to the end of the month. The seismic system recorded a total of 3,265 low-frequency volcanic events during May, a significant increase over the 1,064 recorded during April. Five high-frequency events originating outside the caldera were also recorded. Only two of these were located: one W of the caldera on 13 May, and another to the NE on 29 May.
Ground-deformation data showed that the slow on-going inflationary trend associated with the current phase of the eruption temporarily stabilized in early May only to resume again at the end of the month. These data may indicate that Vulcanian activity is likely to continue.
Geologic Background. The low-lying Rabaul caldera on the tip of the Gazelle Peninsula at the NE end of New Britain forms a broad sheltered harbor utilized by what was the island's largest city prior to a major eruption in 1994. The outer flanks of the asymmetrical shield volcano are formed by thick pyroclastic-flow deposits. The 8 x 14 km caldera is widely breached on the east, where its floor is flooded by Blanche Bay and was formed about 1,400 years ago. An earlier caldera-forming eruption about 7,100 years ago is thought to have originated from Tavui caldera, offshore to the north. Three small stratovolcanoes lie outside the N and NE caldera rims. Post-caldera eruptions built basaltic-to-dacitic pyroclastic cones on the caldera floor near the NE and W caldera walls. Several of these, including Vulcan cone, which was formed during a large eruption in 1878, have produced major explosive activity during historical time. A powerful explosive eruption in 1994 occurred simultaneously from Vulcan and Tavurvur volcanoes and forced the temporary abandonment of Rabaul city.
Information Contacts: Ben Talai and H. Patia, Rabaul Volcano Observatory (RVO), P.O. Box 386, Rabaul, Papua New Guinea.
Sabancaya
Peru
15.787°S, 71.857°W; summit elev. 5960 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Summit activity, ice observed on visit in May
Sabancaya was observed by scientists of the National Air and Space Museum's Colca Valley Geohazard Project during a four-day visit (18-21 May) made in preparation for field work later in the year. Continuous fumarolic activity at the E side of the crater rim was observed during this visit. Seasonal snow patches were visible on the SE flank that were not present when the team made an aerial observation in July 1997 (BGVN 22:07).
On 18 May a seismic event was noted by observers traveling in a vehicle on the Pampa Lliullipampa, SE of the volcano. The disturbance produced a dust cloud that spanned the entire Ampato-Sabancaya-Hualca Hualca complex along its E slopes, a distance of 15 kilometers. A video camera recorded the disturbance at 1525 on 18 May. Roughly concurrently, scientists at the Instituto Geofísico in Arequipa detected a deep focus M 6 earthquake centered 250 km to the N near Ayacucho. Tremors occurred at this time in the pueblo of Cabana Conde located 15 kilometers NW of Hualca Hualca.
On 20 May A. Seimon of the University of Colorado ascended Sabancaya's SE flank and recorded a video of the fumarolic activity inside the crater rim, including the steady emission of gas from the crater floor (figure 8). He noticed ice along the route up the E flank. The ice lies beneath a layer of ash 5 to 10 cm thick, a depth that seemed sufficient to insulate it from higher surface temperatures. Ice was also observed filling a breach in the N side of the crater rim.
Sabancaya is the youngest of the three adjacent stratovolcanoes located 75 km NW of Arequipa. The volcano's 29 May 1990 eruption produced a plume reaching a maximum height of 7 km (BGVN 15:05). The plume traveled NE and carried fine ash that fell up to 20 km away. Extensive mudflows (not mudslides) had occurred in the area in the months after the Sabancaya eruptions that began in late May 1990. These mudflows resulted from fallen ash and the subsequent melting of snow and ice on Hualca Hualca (BGVN 16:05; v. 15, no. 5).
Geologic Background. Sabancaya, located in the saddle NE of Ampato and SE of Hualca Hualca volcanoes, is the youngest of these volcanic centers and the only one to have erupted in historical time. The oldest of the three, Nevado Hualca Hualca, is of probable late-Pliocene to early Pleistocene age. The name Sabancaya (meaning "tongue of fire" in the Quechua language) first appeared in records in 1595 CE, suggesting activity prior to that date. Holocene activity has consisted of Plinian eruptions followed by emission of voluminous andesitic and dacitic lava flows, which form an extensive apron around the volcano on all sides but the south. Records of observed eruptions date back to 1750 CE.
Information Contacts: F. Engle, Center for Earth and Planetary Studies (CEPS), National Air and Space Museum, Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C. 20560 USA; A. Seimon, Department of Geography, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309-0260 USA; S.O. Brooks, Department of Geography, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI USA 53706-1491.
Sheveluch
Russia
56.653°N, 161.36°E; summit elev. 3283 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Satellite imagery detects large ash plume
A report of an ash plume 4 km above sea level extending 35 km from Shiveluch was received by the Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO) via the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) and Anchorage VAAC early on 30 May. AVO analysis of various satellite images determined that the eruption began about 1739 on 29 May. A JMA satellite image taken at 1930 that day showed a small, narrow, well-defined ash plume detached from the vent, extending about 100 km downwind to the SSE. Satellite imagery analysis by AVO on the morning of 30 May showed the Shiveluch area clear with no volcanic activity. There was no ash detected in the area SSE of the volcano where the cloud diffused. Three pilot's reports from flights 9 km above sea level over the Shiveluch area on 30 May confirmed there was no ash cloud remaining in the region.
The ash plume did not act like an energetic, high-level eruption plume but rather a low-level short-lived eruption burst from the volcano. These types of eruption bursts are not uncommon from Shiveluch and are connected with the growing extrusive dome inside the crater. The level-of-concern color code was changed to yellow, but reverted to green on 1 June.
Seismicity was at background levels through most of June. During 11-15 June the system registered increased seismicity and volcanic tremor. On June 15 at 0247 it registered about 2 minutes of explosive activity. It was dark and the volcano was obscured by clouds when this explosive activity took place leaving researchers without visual information; they estimated plume height at 5 km.
On 31 May a gas-and-steam plume without ash rose 2 km above the volcano. During 9-11 June a fumarolic plume rose 100-500 m above the volcano, and during 17-19 a plume rose to 200-800 m. Clouds limited visibility throughout much of May.
Geologic Background. The high, isolated massif of Sheveluch volcano (also spelled Shiveluch) rises above the lowlands NNE of the Kliuchevskaya volcano group. The 1,300 km3 andesitic volcano is one of Kamchatka's largest and most active volcanic structures, with at least 60 large eruptions during the Holocene. The summit of roughly 65,000-year-old Stary Shiveluch is truncated by a broad 9-km-wide late-Pleistocene caldera breached to the south. Many lava domes occur on its outer flanks. The Molodoy Shiveluch lava dome complex was constructed during the Holocene within the large open caldera; Holocene lava dome extrusion also took place on the flanks of Stary Shiveluch. Widespread tephra layers from these eruptions have provided valuable time markers for dating volcanic events in Kamchatka. Frequent collapses of dome complexes, most recently in 1964, have produced debris avalanches whose deposits cover much of the floor of the breached caldera.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova and Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Soufriere Hills (United Kingdom) — May 1998  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Soufriere Hills
United Kingdom
16.72°N, 62.18°W; summit elev. 915 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Low activity; deformation and volume measurements
The following condenses scientific reports from Montserrat Volcano Observatory (MVO) for 12 April-10 May 1998.
Summary. Activity during the reporting period continued at low levels: there were no changes in dome morphology and only a few pyroclastic flows occurred. Seismicity was generally low, with occasional volcano-tectonic (VT) earthquakes being the predominant signals recorded by the seismic network. Rockfall activity was particularly low but showed an increase after heavy rains. Several mudflows were generated during the reporting period, most of them moving down Dyers River into the Belham River valley.
Visual observations. Fresh pyroclastic-flow deposits were seen along the N side of the Tar River Valley on 14 April. A small pyroclastic flow occurred during the morning of 19 April and was seen by the remote video camera at MVO as it traveled down the Tar River as far as the site of the Tar River Estate House. Another small pyroclastic flow coursed down the Tar River on the morning of 25 April, but could not be seen from MVO due to low clouds. Three more small pyroclastic flows traveled halfway down the Tar River Valley during 26 April and the morning of 27 April. All of these flows were believed to have originated on the steep upper flanks to the E of the old dome. Each event lasted 2 minutes and generated small ash clouds.
Rockfall activity was minor with small rockfalls occurring down the E and SW flanks. Some of these events are gradually carving deeper chutes on the Tar River side and S flank of the new Galway's dome. Minor rockfall activity also began near the top of the dome over Galway's wall and traveled down a chute on the S flank of Chances Peak.
During a brief clearing in the weather around the dome early on 6 May observers on a reconnaissance flight saw no evidence of new growth, suggesting a lack of significant extrusion since the growth of the summit spine around 10 March (BGVN 23:04). They did see moderate fumarolic activity coming from a point in the main chute on the upper E flank, and in several areas within the trench located between the scar of 26 December (BGVN 22:12) and the fresh growth within it. They also noted that the summit area appeared blanketed by over 5 m of tephra including both fine ash and blocks of glassy dome rock (up to 1 m diameter).
The temperatures of the pyroclastic flows deposited at Trant's during the 21 September collapse (BGVN 22:10) were measured on 28 April. A maximum temperature of 348°C was obtained at a depth of 2 m. They showed only very minor changes since they were last measured 2 weeks ago.
Seismicity. Over the reporting period, seismicity remained low. Volcano-tectonic (VT) earthquake activity continued to be dominate (table 28). VT earthquakes mainly occurred in groups too few in number to constitute swarms, but exceptions to this are shown in table 29, including a swarm of hybrids on 6 May. These were the first hybrids of high amplitude seen for many weeks, but were not followed by others of similar type.
Table 28. Earthquake counts at Soufriere Hills listed by type (based on signal character), 12 April-9 May 1998. These counts were of events that triggered the broadband network's event-recording system between 0000 and 0000 each day. The type "Dome RF" denotes a dome rockfall. The type "Long-period / Rockfall" signifies a Long-period earthquake followed by rockfall signal. "Hybrid / Rockfall" is a hybrid earthquake followed by rockfall signal. Courtesy of MVO.
| Date |
Volcano-tectonic |
Hybrid |
Long-period |
Dome Rockfall |
Long-period / Rockfall |
Hybrid / Rockfall |
| 12 Apr 1998 |
15 |
1 |
-- |
-- |
10 |
-- |
| 13 Apr 1998 |
15 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
6 |
-- |
| 14 Apr 1998 |
1 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
| 15 Apr 1998 |
2 |
1 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
| 16 Apr 1998 |
4 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
| 17 Apr 1998 |
4 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
| 18 Apr 1998 |
1 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
| 19 Apr 1998 |
5 |
-- |
-- |
1 |
4 |
1 |
| 20 Apr 1998 |
14 |
-- |
-- |
2 |
5 |
-- |
| 21 Apr 1998 |
8 |
1 |
-- |
-- |
1 |
-- |
| 22 Apr 1998 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
1 |
-- |
| 23 Apr 1998 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
4 |
-- |
| 24 Apr 1998 |
1 |
-- |
-- |
1 |
4 |
-- |
| 25 Apr 1998 |
3 |
1 |
-- |
-- |
2 |
-- |
| 26 Apr 1998 |
17 |
-- |
-- |
1 |
2 |
-- |
| 27 Apr 1998 |
7 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
2 |
-- |
| 28 Apr 1998 |
8 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
6 |
-- |
| 29 Apr 1998 |
2 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
| 30 Apr 1998 |
3 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
| 01 May 1998 |
7 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
| 02 May 1998 |
10 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
3 |
-- |
| 03 May 1998 |
2 |
2 |
-- |
-- |
7 |
-- |
| 04 May 1998 |
4 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
4 |
-- |
| 05 May 1998 |
6 |
2 |
-- |
-- |
3 |
-- |
| 06 May 1998 |
5 |
12 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
| 07 May 1998 |
6 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
| 08 May 1998 |
25 |
-- |
-- |
-- |
2 |
-- |
Table 29. Swarms registered at Soufriere Hills during 12 April-10 May 1998. Courtesy of MVO.
| Date |
Local Time |
Duration (minutes) |
Hybrid |
Long-period |
Volcano-tectonic |
| 26 Apr 1998 |
2247 |
1.45 |
0 |
0 |
9 |
| 06 May 1998 |
0445 |
1.40 |
11 |
0 |
-- |
| 27 May 1998 |
2257 |
5.75 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| 18 May 1998 |
0841 |
8.32 |
0 |
0 |
15 |
Epicenters were located on the E of the volcano at focal depths tightly clustered from 2.5 to 3.5 km below the summit. Fault-plane solutions were calculated using P-wave first-motions detected by the 7 broadband stations along with first motions from the Lee's Yard and Jack Boy Hill stations of the short-period network. The calculated fault-plane solutions are consistent with a strike-slip fault mechanism. The number of recorded rockfall signals was very low. However, in many cases there was a correlation between occurrence of the rockfalls and periods of heavy rainfall.
Ground deformation. With respect to the Harris GPS measuring station, the stations at Dagenham, Old Towne, Lookout Yard, and Windy Hill showed height increases of 5, 5.5, 6, and 4 cm respectively since December 1996. These values are preliminary, as the height component is the least well constrained by GPS. It was judged more likely that the reference at Harris was actually sinking. Height differences between Harris and sites on the E (Long Ground, Tar River and Perches) all showed continued slow movement to the NE of around 7 cm in the last year; Whites and Roches have moved slightly less and in different directions.
A survey from Windy Hill measured the distance to the N crater wall reflector and found it had shortened by only 1 cm since the middle of March. The line to Windy Hill from Harris is stable, as confirmed by repeated measurements since December 1997 that gave site positions lying within a box 3 mm by 7 mm. In contrast, the survey point at Brodericks had shown accelerated movement: 3 cm to the N between November 1997 and January 1998. This coincided with the period of rapid extrusion in the S area of the dome during December, 1997. Subsequently Brodericks appeared to stabilize in its new position.
A new permanent GPS site was installed in the South Soufriere Hills. Telemetry equipment used by the station was installed by the University of Puerto Rico on Antigua and in the Centre Hills.
Volume measurements. A new theodolite site known as Fergus Ridge was set up on the high ridge of the W flank of South Soufriere Hills, to the N of Fergus Mountain, overlooking the White River Valley. Measurements from this site triangulated with measurements from Perches Mountain were obtained on 16 April. In conjunction with the combined photo and GPS data collected on 6 April, a revised total dome volume was calculated to be 113 x 106 m3. This figure differed from the initial estimate of 120 x 106 m3; however, the revised figure incorporated a greater number of theodolite, photo, and GPS points that improved constraints on both the summit area and the new dome on the SW sector of the complex.
Environmental monitoring. Generally, low volcanic activity and the number of rain showers kept aerosol levels low through the reporting period. Extremely wet weather, 14-15 April, produced the lowest aerosol levels since the heavy ash fall at the beginning of February. Rain also prevented the ash produced by the small pyroclastic flow of 19 April from being transported N by wind to any of the sites that were being monitored.
The volcano's small ash output left inhabited N island areas comparatively ash free. Each disturbance of ash by moving vehicles seemed to help the wind and rain remove more ash.
The three pyroclastic flows that occurred on 26-27 April had no effect on the measured levels of airborne ash and dust. On 1 May observers saw a very small venting of ash escape at the top of the Tar River Valley. Scientists working in the SW of the island over the next few days noticed a strong smell of rotten eggs (hydrogen sulfide). Following the hybrid swarm on 6 May dust levels remained low, but aerosol levels doubled. Heavy rain two days later once more reduced levels. Aerosol levels continued low later in this period despite drier weather, except in Salem, an area likely affected by ash blown W from the pyroclastic flows.
Geologic Background. The complex, dominantly andesitic Soufrière Hills volcano occupies the southern half of the island of Montserrat. The summit area consists primarily of a series of lava domes emplaced along an ESE-trending zone. The volcano is flanked by Pleistocene complexes to the north and south. English's Crater, a 1-km-wide crater breached widely to the east by edifice collapse, was formed about 2000 years ago as a result of the youngest of several collapse events producing submarine debris-avalanche deposits. Block-and-ash flow and surge deposits associated with dome growth predominate in flank deposits, including those from an eruption that likely preceded the 1632 CE settlement of the island, allowing cultivation on recently devegetated land to near the summit. Non-eruptive seismic swarms occurred at 30-year intervals in the 20th century, but no historical eruptions were recorded until 1995. Long-term small-to-moderate ash eruptions beginning in that year were later accompanied by lava-dome growth and pyroclastic flows that forced evacuation of the southern half of the island and ultimately destroyed the capital city of Plymouth, causing major social and economic disruption.
Information Contacts: Montserrat Volcano Observatory (MVO), c/o Chief Minister's Office, PO Box 292, Plymouth, Montserrat (URL: http://www.mvo.ms/).
St. Helens (United States) — May 1998  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
St. Helens
United States
46.2°N, 122.18°W; summit elev. 2549 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Sudden rise in earthquake activity in May
The level of earthquake activity at Mount St. Helens had been gradually increasing over the past several months and accelerated during May. Rates of activity increased from an average of ~60 well-located events per month last winter to 165 events in May. Most of the recent earthquakes were very small with only three events larger than M 2. The largest earthquake was on 1 May with M 2.2. These earthquakes occurred in two clusters directly beneath the lava dome in the crater. One cluster was in the range of 2-5 km and the other 7-9 km below the dome. Very few events were located in the very shallow region of 0-2 km below the dome. None of the earthquakes were low-frequency volcanic events that typically occur as precursors to major eruptions.
This increased activity seems to be similar to that which occurred in 1995, although the activity of May 1998 was more energetic. The 1995 activity lasted for several months, had a maximum earthquake rate of 95 events per month, and resulted in no volcanic activity. A similar increase in earthquake activity in the St. Helens system occurred in 1989-91. However, at that time there were also a number of very shallow earthquakes accompanied by a series of sudden steam explosions. These explosions were small eruptions of steam and gas that ejected rocks and ash from cracks in the dome. Rocks were thrown up to 1 km from the dome, ash clouds reached altitudes up to 6 km, and a dusting of ash was deposited locally downwind. Some explosions melted snow in the crater and generated small lahars that flowed N onto the Pumice Plain.
Because increased earthquake activity within the deep St. Helens system may reflect increased pressure at depth, it is possible that the current seismicity may eventually lead to renewed volcanic activity. However, it is unlikely to do so without significant additional precursors.
Geologic Background. Prior to 1980, Mount St. Helens was a conical volcano sometimes known as the Fujisan of America. During the 1980 eruption the upper 400 m of the summit was removed by slope failure, leaving a 2 x 3.5 km breached crater now partially filled by a lava dome. There have been nine major eruptive periods beginning about 40-50,000 years ago, and it has been the most active volcano in the Cascade Range during the Holocene. Prior to 2,200 years ago, tephra, lava domes, and pyroclastic flows were erupted, forming the older edifice, but few lava flows extended beyond the base of the volcano. The modern edifice consists of basaltic as well as andesitic and dacitic products from summit and flank vents. Eruptions in the 19th century originated from the Goat Rocks area on the N flank, and were witnessed by early settlers.
Information Contacts: Cascades Volcano Observatory, U.S. Geological Survey, 5400 MacArthur Blvd., Vancouver, WA 98661 USA (URL: http://volcanoes.usgs.gov/); Geophysics Program, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195 USA (URL: http://www.geophys.washington.edu/SEIS/PNSN/HELENS/).
Ukinrek Maars (United States) — May 1998  Cite this Report
Cite this Report
Ukinrek Maars
United States
57.8344°N, 156.5203°W; summit elev. 91 m
All times are local (unless otherwise noted)
Earthquake swarm decreases in rate and intensity
During the last week of May, the anomalous seismic activity under SW Lake Becharof (BGVN 23:04) continued but at a decreased rate and intensity; magnitudes of 12 located earthquakes ranged from M 1.7 to 3.3. During 1-5 June, 20 earthquakes were located ranging from M 1.8 to 4.3. Activity decreased significantly during 6-12 June; only four earthquakes were located, all M > 3.0. Several overflights of the location by AVO scientists revealed no signs of volcanic activity or surface breakage. The area of seismicity was not monitored by real-time seismic instrumentation; however, a portable seismic instrument has recently been installed. AVO is in communication with local citizens and land managers who frequently overfly the area. There was no evidence of imminent hazard at the site.
Geologic Background. Ukinrek Maars are two explosion craters that were created in an area without previous volcanic activity during a 10-day phreatomagmatic eruption March-April 1977. The basaltic maars were erupted through glacial deposits in the Bering Sea lowlands 1.5 km S of Becharof Lake and 12 km W of Peulik volcano; their location is related to the regional Bruin Bay fault. The elliptical West Maar, which was the first to form, is 105 x 170 m and 35 m deep. The other maar, 600 m to the east, is 300 m wide and 70 m deep. Both maars are now filled by crater lakes; the eastern lake encircles a 49-m-high lava dome that was emplaced at the end of the eruption. Base surges were directed primarily to the NW. Juvenile material from the Ukinrek eruptions was of mantle-derived olivine basaltic composition. The dacitic Gas Rocks lava domes, of Quaternary age, are located on the shores of Becharof Lake, 3 km N of Ukinrek maars and were the site of a phreatic eruption about 2,300 years ago.
Information Contacts: Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.