Aira (Japan) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
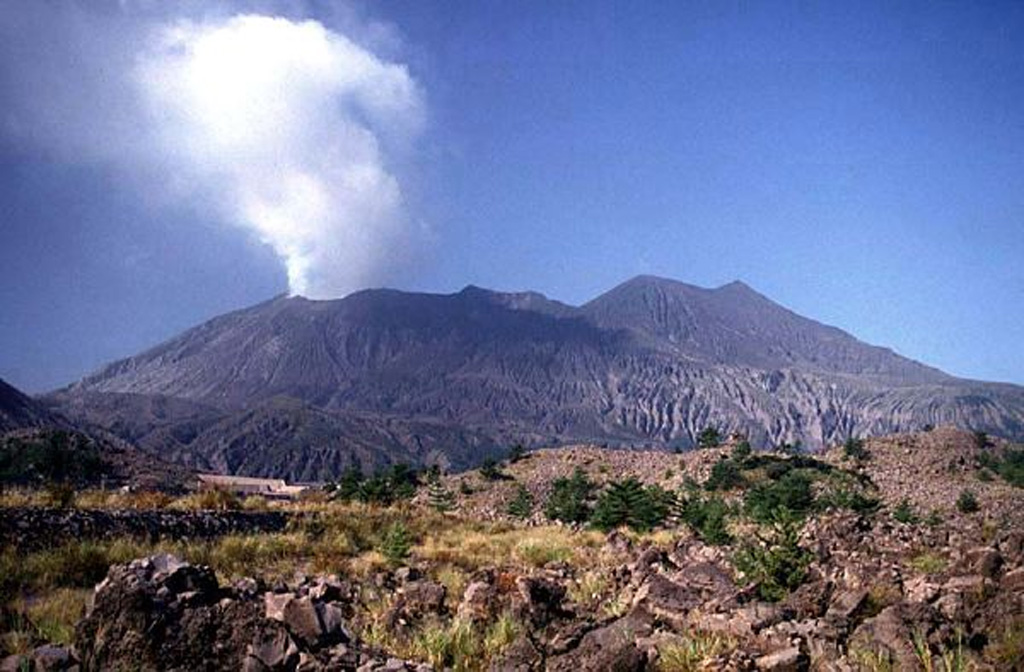 Aira Aira
Ryukyu Volcanic Arc
|
JMA reported ongoing eruptive activity at Minamidake Crater (Aira Caldera’s Sakurajima volcano) during 17-26 February with nighttime crater incandescence. Very small eruptive events were recorded during 17-23 February. An explosion at 1734 on 24 February generated an ash plume that rose 400 m above the crater rim before entering weather clouds, and ejected blocks as far as 1.2 km away from the vent. The Alert Level remained at 3 (on a 5-level scale), and the public was warned to stay 2 km away from both craters.
Source: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)
|
Bezymianny (Russia) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
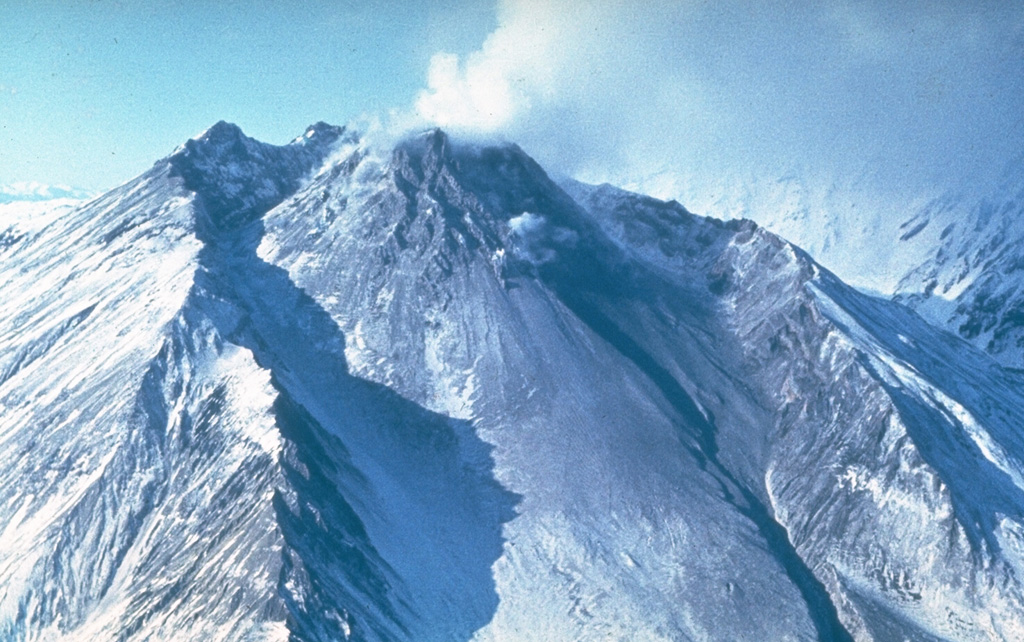 Bezymianny Bezymianny
Eastern Kamchatka Volcanic Arc
|
KVERT reported that a daily thermal anomaly over Bezymianny was identified in satellite images during 15-22 February. Dates are UTC; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
|
Dukono (Indonesia) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
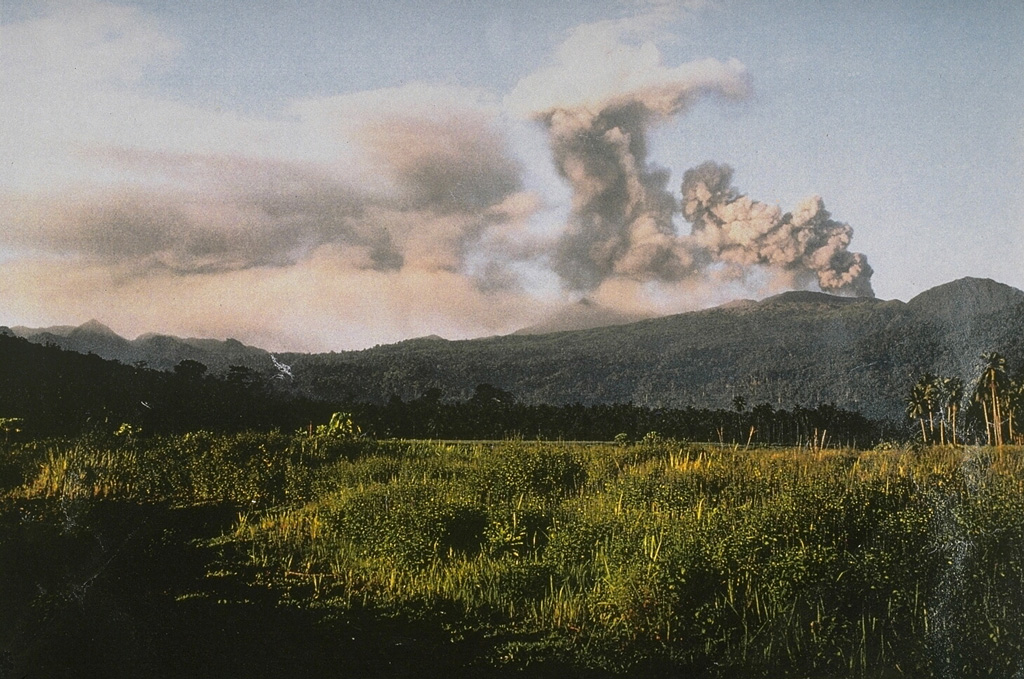 Dukono Dukono
Halmahera Volcanic Arc
|
PVMBG reported that the eruption at Dukono was ongoing during 21-27 February. Daily gray-and-white ash plumes generally rose as high as 1.6 km above the summit and drifted in multiple directions; at 1050 on 24 February ash plumes rose to 2.7 km and drifted N according to a news article. The Alert Level remained at Level 2 (on a scale of 1-4), and the public was warned to remain outside of the 3-km exclusion zone.
Sources: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as CVGHM), Antara News
|
Ebeko (Russia) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
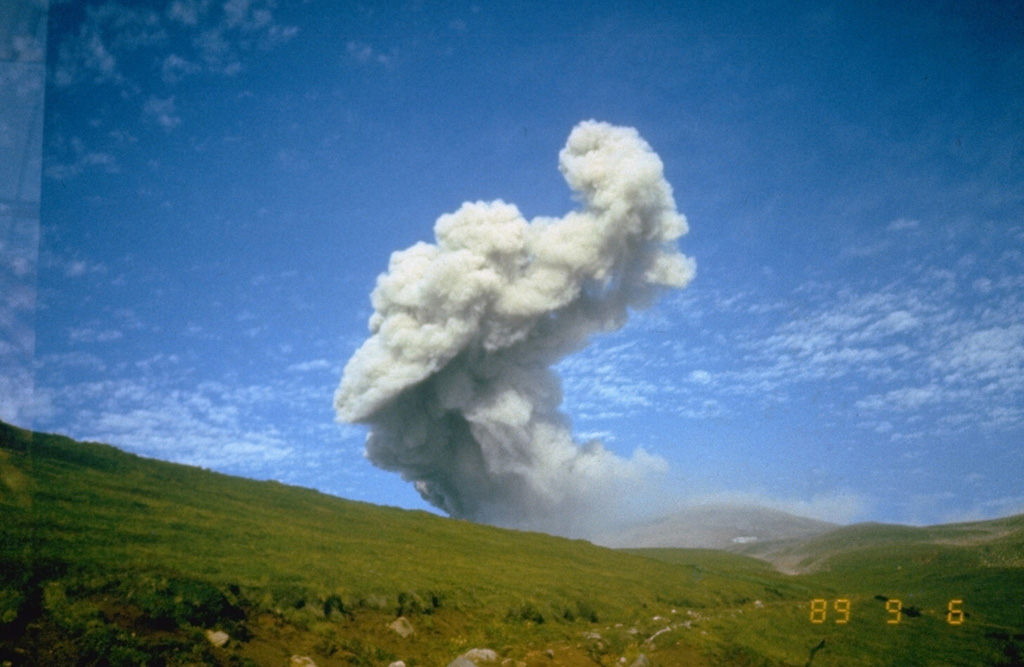 Ebeko Ebeko
Kuril Volcanic Arc
|
KVERT reported that moderate explosive activity was ongoing at Ebeko during 15-22 February. According to volcanologists in Severo-Kurilsk (Paramushir Island, about 7 km E), explosions during 16 and 18-20 February generated ash plumes that rose as high as 2.5 km (8,200 ft) a.s.l and drifted E and NW. Ashfall was reported in Severo-Kurilsk during 18-19 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are UTC; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
|
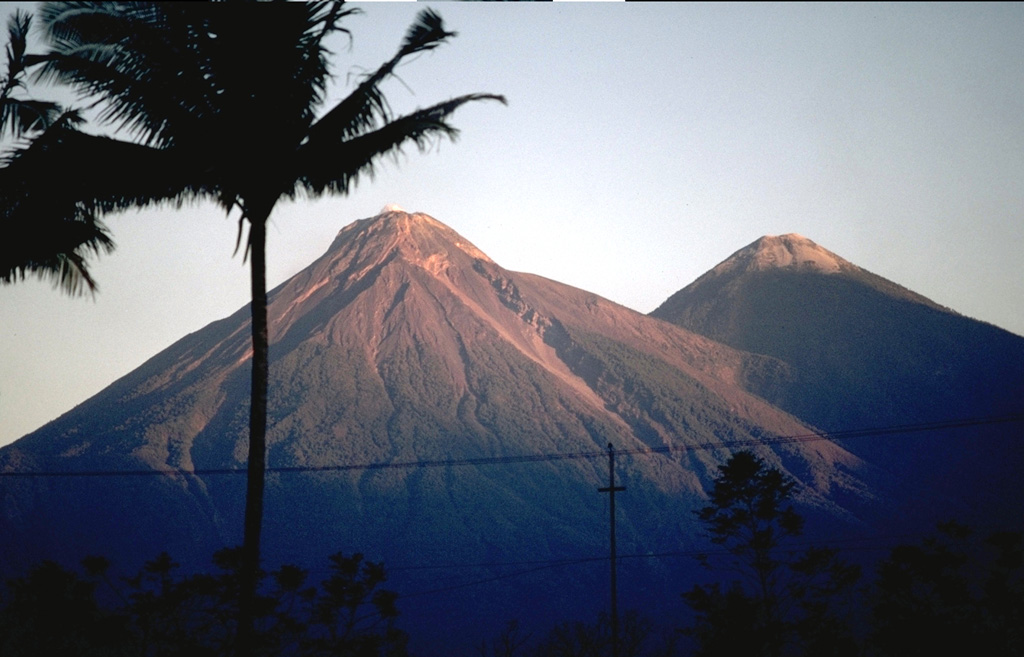
Fuego (Guatemala) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Fuego Fuego
Central America Volcanic Arc
|
INSIVUMEH reported that eruptive activity continued at Fuego during 20-27 February. Explosions were recorded daily, averaging 5-11 per hour on most days, when counts were reported. The explosions generated gas-and-ash plumes that rose as high as 1.1 km above the crater rim and drifted as far as 30 km W, SW, and S. Explosions caused frequent block avalanches that descended various drainages including the Ceniza (SSW), Seca (W), Taniluyá (SW), and Las Lajas (SE), and sometimes reached vegetated areas. The explosions also ejected incandescent material 100-300 m above the summit on most of the days and ejected ballistics as far as 2 km during 20-21 February. Weak rumbling sounds and shock waves were frequently reported. Ashfall was reported on most days in areas downwind including Panimache I and II (8 km SW), Morelia (9 km SW), Santa Sofía (12 km SW), Sangre de Cristo (8 km W), Finca La Asunción (12 km SW), La Rochela (8 km SSW), Finca Ceilán (9 km S), San Andrés Osuna (11 km SSW), Siquinalá (21 km SSW), and Santa Lucía Cotzumalguapa (22 km SW).
Source: Instituto Nacional de Sismologia, Vulcanologia, Meteorologia, e Hidrologia (INSIVUMEH)
|
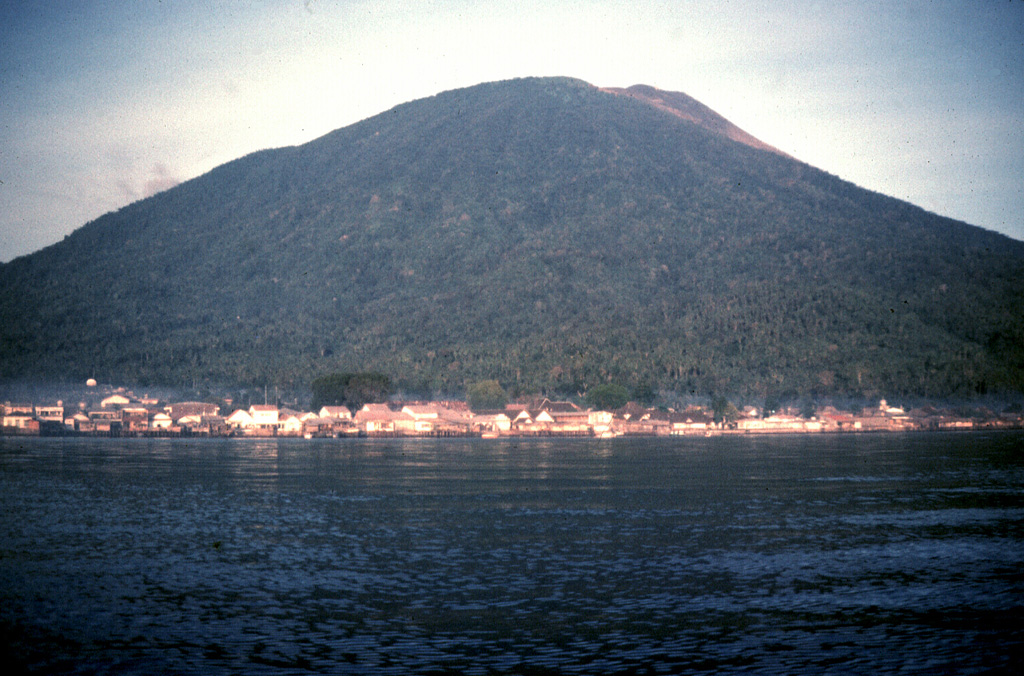
Gamalama (Indonesia) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Gamalama Gamalama
Halmahera Volcanic Arc
|
Although there was no eruptive activity reported at Gamalama, in a 23 February press release PVMBG noted that the number of daily deep volcanic earthquakes had significantly increased. A total of 14 deep volcanic earthquakes were recorded by the seismic network on 22 February, higher than the average of 2-3 events per day that had been recorded since January 2023. At 1623 on 22 February an observer saw a dense white-to-gray ash plume rising 400 m above the summit and drifting W. During 0000-0830 on 23 February the network recorded an additional four deep volcanic earthquakes as well as three events indicating emissions; dense white plumes were visible rising 100-400 m above the summit and drifting N. Seismicity before the increase, during 1-22 February, consisted of one tornillo earthquake, two harmonic earthquakes, one shallow volcanic earthquake, 34 deep volcanic earthquakes, two seismic events indicating floods or lahars, and 26 events indicating emissions. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 1-4); visitors and residents were warned not to approach the crater within a 1.5-km radius.
Source: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as CVGHM)
|
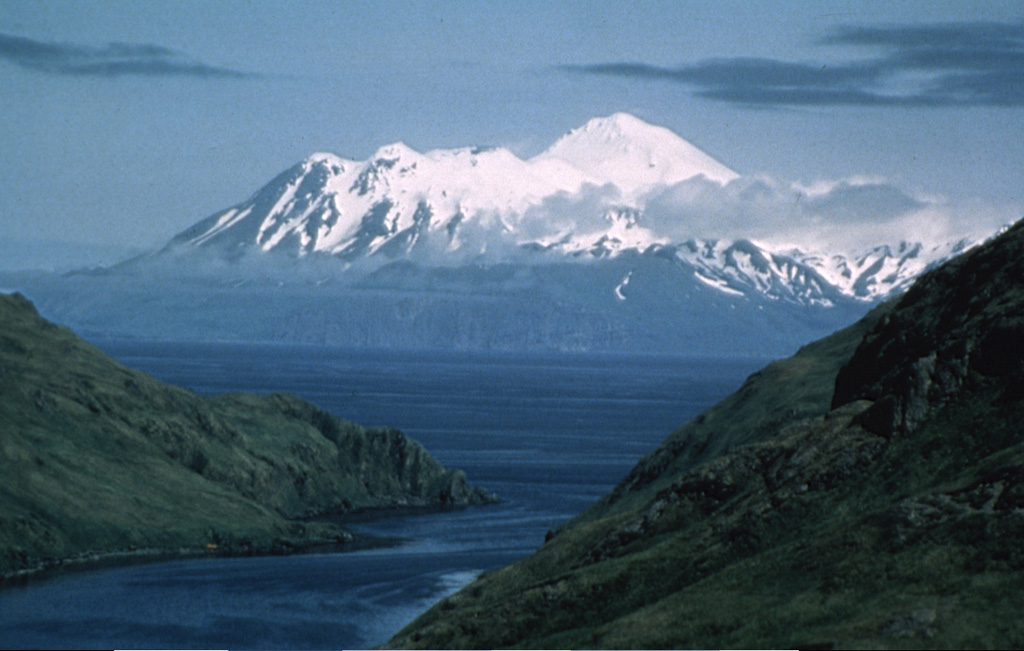
Great Sitkin (United States) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Great Sitkin Great Sitkin
Aleutian Ridge Volcanic Arc
|
AVO reported that slow lava effusion continued in Great Sitkin’s summit crater during 21-27 February, confirmed by a 24 February satellite image. A few small volcanic earthquakes were recorded by the seismic network during 24-26 February. Weather clouds obscured satellite and webcam views during most of the week. The Volcano Alert Level remained at Watch (the third level on a four-level scale) and the Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third color on a four-color scale).
Source: US Geological Survey Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO)
|
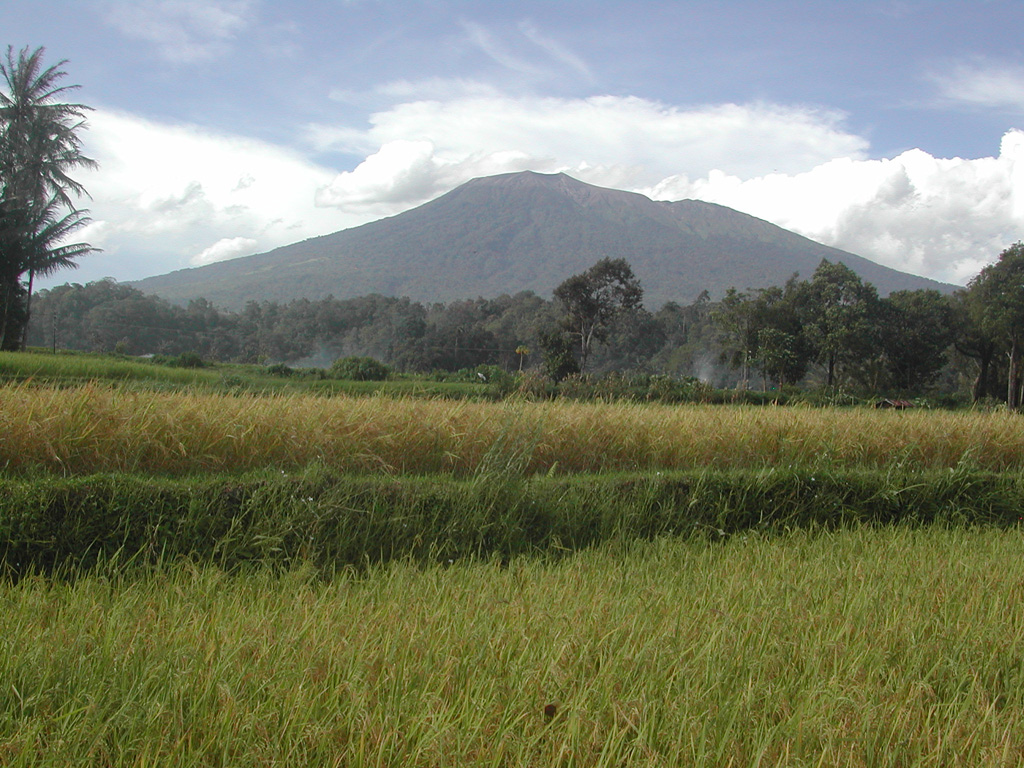
Marapi (Indonesia) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Marapi Marapi
Sunda Volcanic Arc
|
PVMBG reported that eruptive activity at Marapi (on Sumatra) was ongoing during 21-27 February. White-and-gray gas-and-ash plumes rose 200-600 m above the summit and drifted in multiple directions on most days; white plumes rose 250 m and drifted SW, W, and NW on 27 February. The Alert Level remained at 3 (on a scale of 1-4), and the public was warned to stay 4.5 km away from the active crater.
Source: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as CVGHM)
|
Merapi (Indonesia) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
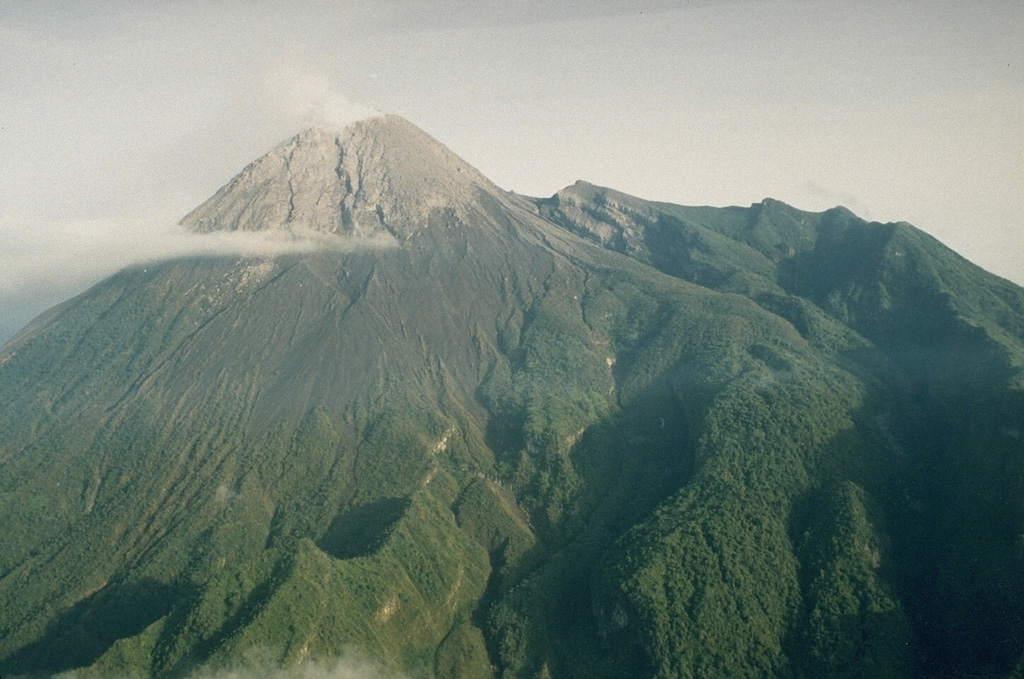 Merapi Merapi
Sunda Volcanic Arc
|
BPPTKG reported that the eruption at Merapi (on Java) continued during 16-22 February. Seismicity remained at high levels. The SW lava dome produced 145 lava avalanches that descended the S and SW flanks; three traveled S as far as 1 km down the upper part of the Boyong drainage and 142 traveled SW as far as 1.7 km down the upper part of the Bebeng drainage. Two pyroclastic flows traveled as far as 1.6 km down the SW flank. Morphological changes to the SW lava dome identified in webcam images were due to continuing effusion and collapses of material. The Alert Level remained at 3 (on a scale of 1-4), and the public was warned to stay 3-7 km away from the summit, based on location.
Source: Balai Penyelidikan dan Pengembangan Teknologi Kebencanaan Geologi (BPPTKG)
|
Popocatepetl (Mexico) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
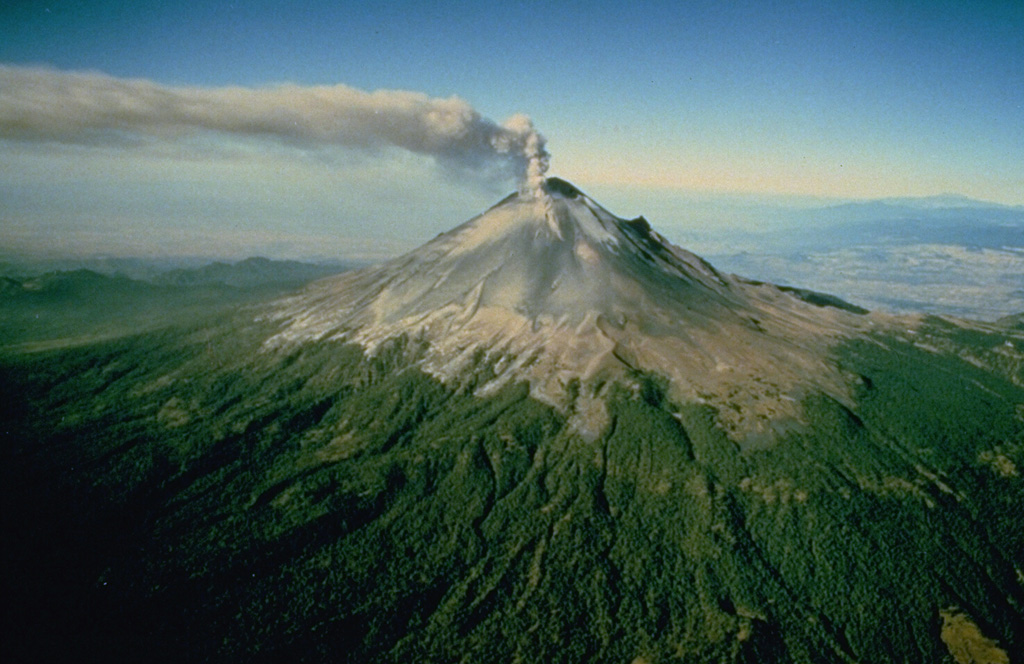 Popocatepetl Popocatepetl
Trans-Mexican Volcanic Arc
|
CENAPRED reported that eruptive activity continued at Popocatépetl during 21-27 February. The seismic network recorded daily periods of high-frequency, low-amplitude tremor that lasted from about 90 minutes to almost 22 hours. The Washington VAAC reported that daily ash plumes visible in webcam and satellite images generally rose to 5.2-6.7 km (17,000-22,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted predominantly E, SE, S, and SW. The ash emissions were continuous for periods of time with remnant ash continuing to be visible in subsequent satellite images, drifting 75-140 km before dissipating. At 1151 on 24 February a dense ash plume rose to 7.6 km (25,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted ENE; the plume was visible in satellite images the next day drifting almost 225 km SE. Several ash emissions lasting 1-2 hours each were visible in webcam and satellite images during 26-27 February.
Based on information from El Centro Nacional de Comunicación y Operación de Protección Civil (CENACOM), CENAPRED noted that minor ashfall was reported in Hueyapan (17 km SSW), Tetela del Volcán (20 km SW), and Jiutepec (59 km SW) in the state of Morelos on 21 February and in the municipalities of Jiutepec (60 km WSW), Atlatlahucán (30 km WSW), Cuautla (43 km SW), Tlaltizapan (65 km SW), and Ciudad Ayala in Morelos, and in Huaquechula (30 km SE) and Tlapanalá (39 km SE), Puebla, on 22 February. Minor ashfall was reported in the municipalities of Hueyapan, Yecapixtla (30 km SW) and Tetela del Volcán, Morelos; in Ixtacuixtla, Panotla, Tepetitla (36 km NE), Nativitas (40 km NE), Zacatelco (45 km NE), Santa Apolonia Teacalco (40 km NE), San Damián Texóloc (45km NE), Tetlahuaca (40 km NE), Zacatelco (45 km NE), Xicohtzingo (40 km ENE), Papalotla (62 km NNW), Tenancingo (47 km ENE), Santa Catarina Ayometla (47 km ENE), Magdalena Tlaltelulco (53 km NE), San Francisco Tetlanohcan (55 km NE), and Teolocholco (51 km ENE), Tlaxcala; in Iztacalco (62 km NW), Iztapalapa (59 km NW), and Coyoacán (65 km WNW), Mexico City; and finally in Atlautla (16 km W), Ayapango (21 km NW), Ecatzingo (15 km SW), Chalco (44 km NW), Tenango del Aire (29 km NW), Temamatla (32 km NW), Ozumba (18 km W), Tepetlixpa (20 km W), Tlalmanalco (30 km NW), and Amecameca (20 km NW), State of Mexico on 27 February. The Alert Level remained at Yellow, Phase Two (the middle level on a three-color scale) and the public was warned to stay 12 km away from the crater.
Sources: Centro Nacional de Prevencion de Desastres (CENAPRED), Washington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
|
Reventador (Ecuador) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
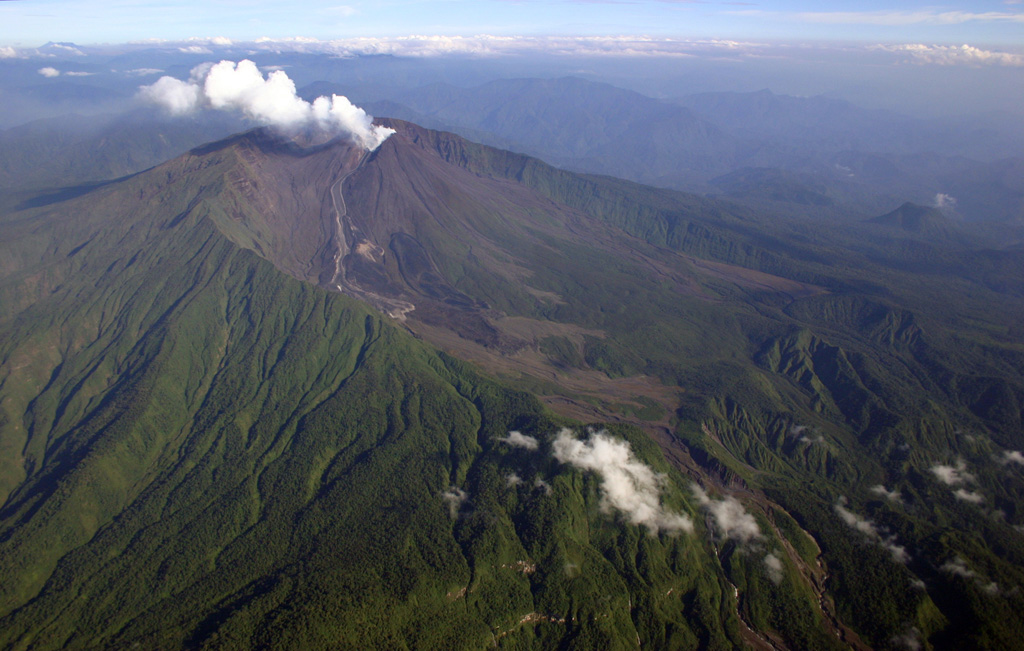 Reventador Reventador
Northern Andean Volcanic Arc
|
IG-EPN reported that a moderate eruption at Reventador was ongoing during 21-27 February. Seismicity was characterized by 28-62 daily explosions, long-period earthquakes, harmonic tremor, and tremor associated with emissions. Daily ash-and-gas plumes rose as high as 1.3 km above the crater rim and drifted in multiple directions, though weather conditions sometimes prevented views. Crater incandescence was occasionally visible during both overnight and morning hours; avalanches of incandescent material descended the flanks as far as 800 m from the summit on a few of the days and incandescent material was ejected 200 m above the crater during 23-24 February. A seismic signal indicating a lahar was recorded at 0015 on 24 February. Secretaría de Gestión de Riesgos maintained the Alert Level at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Sources: Instituto Geofísico-Escuela Politécnica Nacional (IG-EPN), Secretaría de Gestión de Riesgos (SGR)
|
Sangay (Ecuador) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
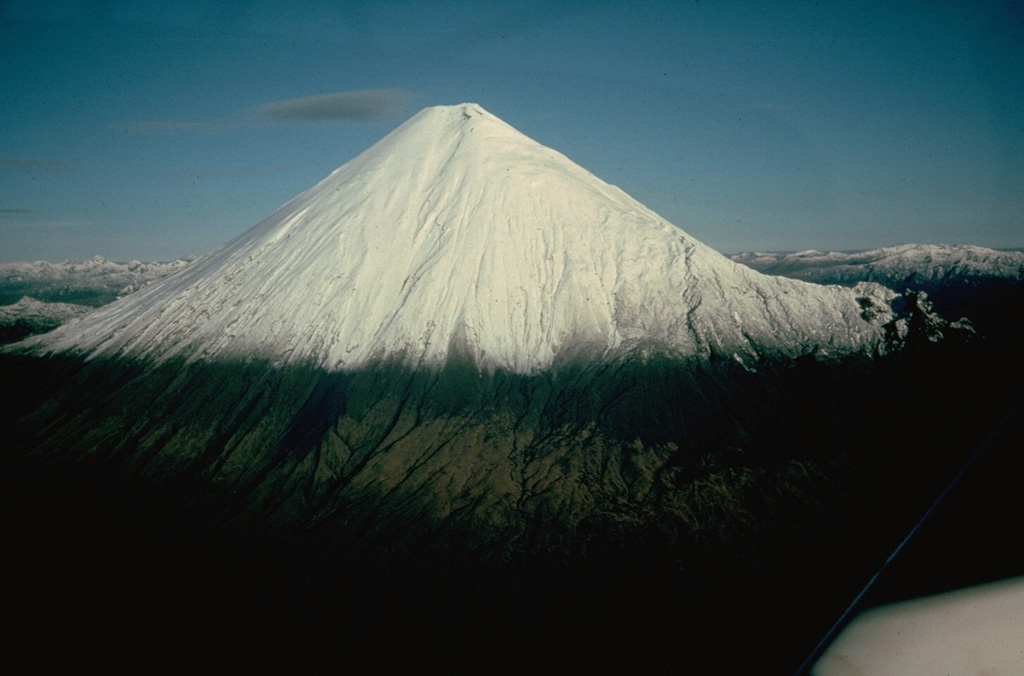 Sangay Sangay
Northern Andean Volcanic Arc
|
IG-EPN reported that high levels of eruptive activity continued at Sangay during 20-27 February. The seismic network recorded 185-465 daily explosions. Gas plumes with low ash content rose 500-1,000 m above the summit and drifted SE during 20-21 February. Crater incandescence was occasionally visible and incandescent material descended the SE flank as far as 1 km during 20-23 February. Weather conditions prevented views during the rest of the week. Secretaría de Gestión de Riesgos (SGR) maintained the Alert Level at Yellow (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Sources: Instituto Geofísico-Escuela Politécnica Nacional (IG-EPN), Secretaría de Gestión de Riesgos (SGR)
|
Santa Maria (Guatemala) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
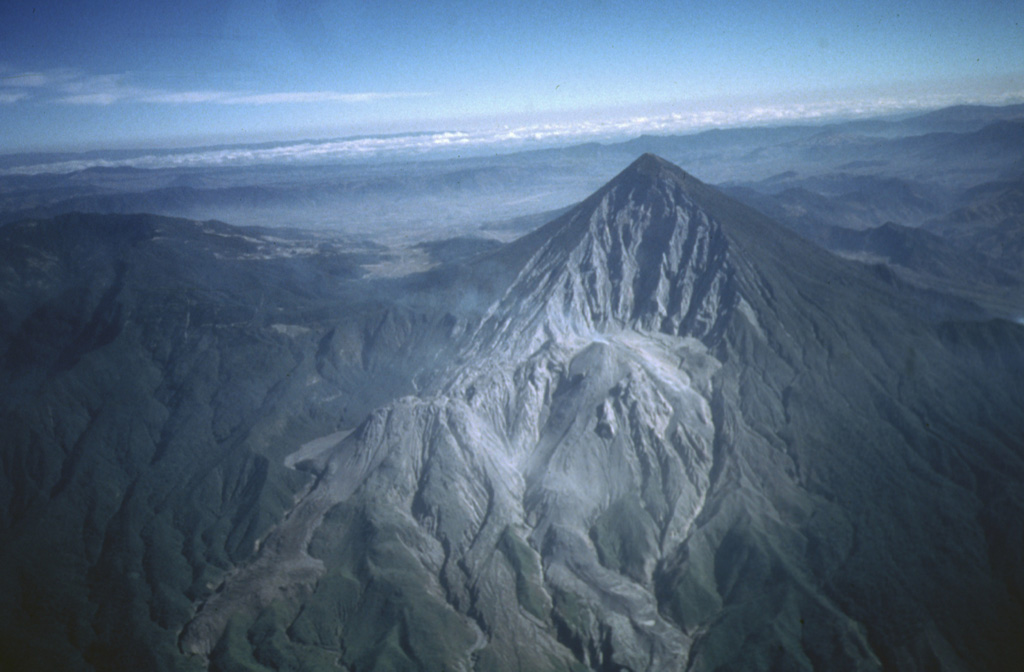 Santa Maria Santa Maria
Central America Volcanic Arc
|
INSIVUMEH reported that eruptive activity continued at Santa Maria’s Santiaguito lava dome complex during 20-27 February with a lava extrusion at the Caliente dome. Incandescence from the dome was visible during most nights and early mornings, and occasional incandescence was also present along the upper part of the SW-flank lava flow. Daily explosions generated gas-and-ash plumes that rose 600-900 m above the summit and drifted W, SW, and S; the explosions occurred at a rate of 1-7 per hour on at least a few of the days. The explosions produced block avalanches on the dome’s W, SW, S, and E flanks and generated occasional, short-range pyroclastic flows that descended multiple flanks. Block avalanches from the margins of the upper part of the lava flow on the WSW flank were also occasionally visible. Ashfall occurred in Loma Linda (7 km W) and San Marcos Palajunoj (8 km SW) during 20-21 February and caused hazy conditions around the volcano during 22-23 February.
Source: Instituto Nacional de Sismologia, Vulcanologia, Meteorologia, e Hidrologia (INSIVUMEH)
|
Semeru (Indonesia) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
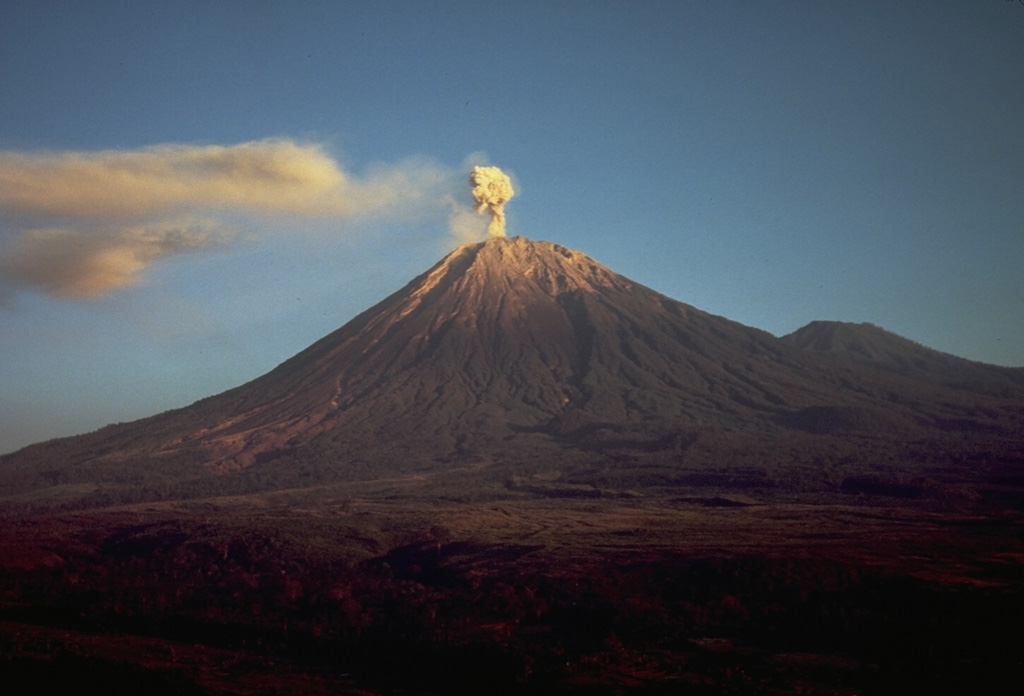 Semeru Semeru
Sunda Volcanic Arc
|
PVMBG reported that eruptive activity continued at Semeru during 21-27 February. Daily gray-and-white ash plumes, often dense, rose 400-1,000 m above the summit and drifted in multiple directions. The Alert Level remained at 3 (the third highest level on a scale of 1-4). The public was warned to stay at least 5 km away from the summit in all directions, 13 km from the summit to the SE, 500 m from the banks of the Kobokan drainage as far as 17 km from the summit, and to avoid other drainages including the Bang, Kembar, and Sat, due to lahar, avalanche, and pyroclastic flow hazards.
Source: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as CVGHM)
|
Sheveluch (Russia) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
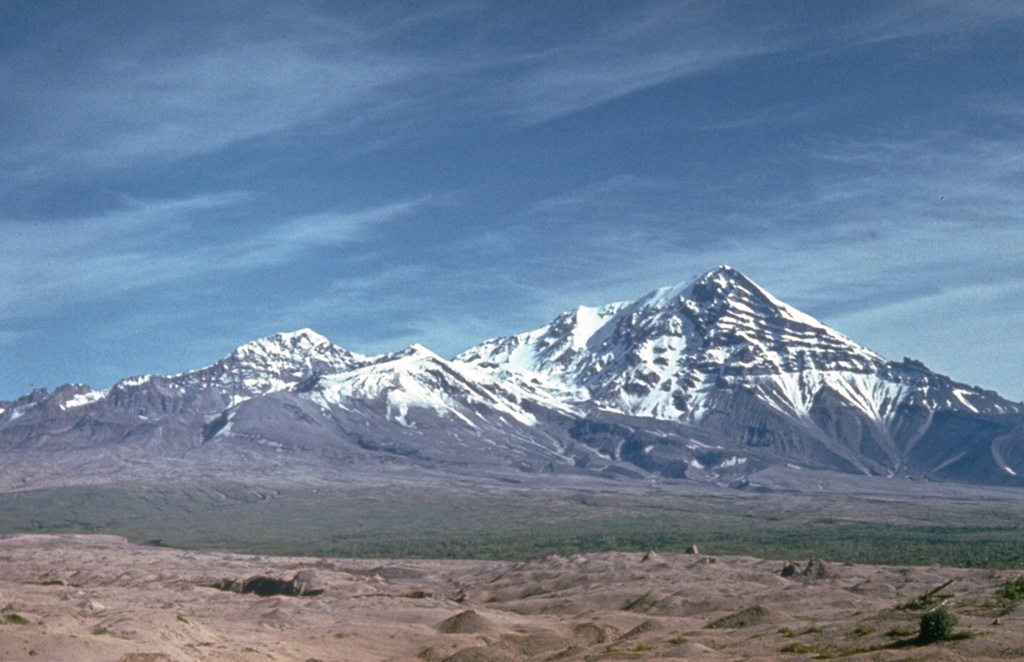 Sheveluch Sheveluch
Eastern Kamchatka Volcanic Arc
|
KVERT reported that eruptive activity at Sheveluch continued during 15-22 February with a thermal anomaly identified in satellite images during 16, 18-19, and 22 February. On 19 February plumes of resuspended ash rose to 2.5 km (8,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted about 55 km ESE. Weather clouds sometimes prevented views of the volcano. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
|
Suwanosejima (Japan) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
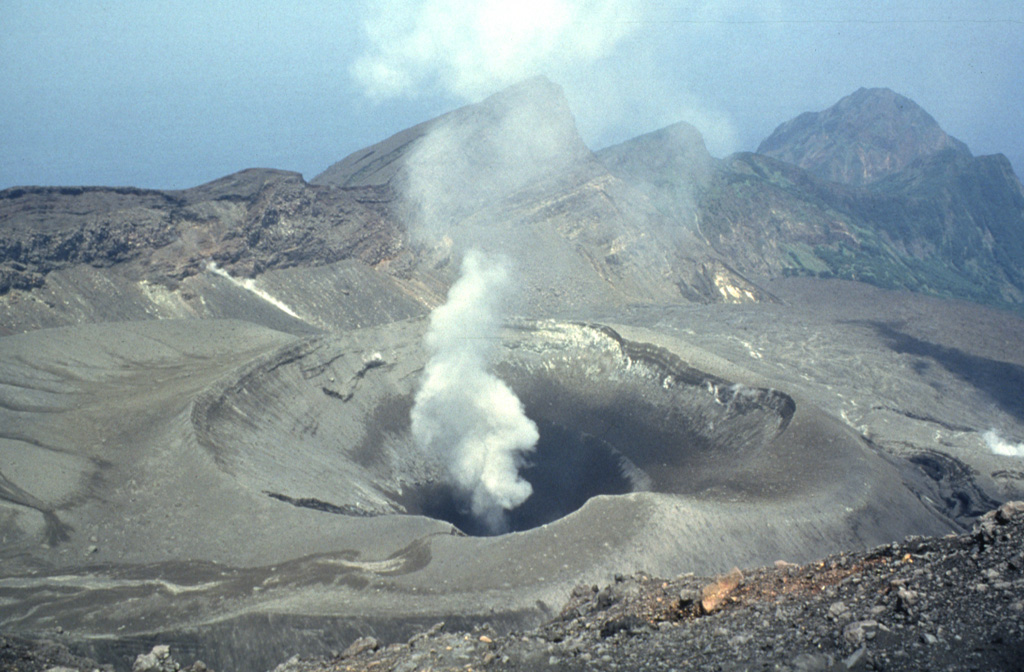 Suwanosejima Suwanosejima
Ryukyu Volcanic Arc
|
JMA reported that the eruption at Suwanosejima's Ontake Crater continued during 19-26
February. Crater incandescence was observed in webcam images nightly. Large blocks were sometimes ejected up to 400 m from the vent. Explosions were recorded at 0616 on 19 February, at 0604 and 2157 on 24 February, and at 1149 on 25 February; details of emissions were unknown. Eruptive events at 1702 and 2056 on 23 February produced ash plumes that rose at least 1 km above the crater rim and drifted S. Explosions at 2343 on 25 February and at 0431, 1402, 1910, and 1918 on 26 February produced ash plumes that rose 400-800 m above the crater rim and drifted S. The plume from the explosion at 1918 on 26 February rose to 800 m before entering into weather clouds. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a 5-level scale) and the public was warned to stay at least 1 km away from the crater.
Source: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)
|
Ubinas (Peru) | 21 February-27 February 2024 | Continuing Activity Cite this Report Cite this Report |
 Ubinas Ubinas
Central Andean Volcanic Arc
|
Instituto Geofísico del Perú (IGP) reported that a lahar descended the Volcánmayo drainage on the SE flank at Ubinas at 1745 on 25 February and traveled towards the Ubinas River. The public was warned to stay away from the drainage and to avoid driving on the Querapi-Ubinas-Huarina highway.
Source: Instituto Geofísico del Perú (IGP)
|
![]() Download Smithsonian / USGS Weekly Volcanic Activity Report Network Link
Download Smithsonian / USGS Weekly Volcanic Activity Report Network Link
 Lewotolok
Lewotolok Aira
Aira Bezymianny
Bezymianny Dukono
Dukono Ebeko
Ebeko Fuego
Fuego Gamalama
Gamalama Great Sitkin
Great Sitkin Marapi
Marapi Merapi
Merapi Popocatepetl
Popocatepetl Reventador
Reventador Sangay
Sangay Santa Maria
Santa Maria Semeru
Semeru Sheveluch
Sheveluch Suwanosejima
Suwanosejima Ubinas
Ubinas