

KVERT reported that thermal anomalies over both the “300 years of RAS” dome and the older lava dome at Sheveluch were identified in satellite images during 12-15 and 18 July. Weather conditions prevented views on the other days during 12-19 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Significant explosions destroyed part of the lava-dome complex during April 2023
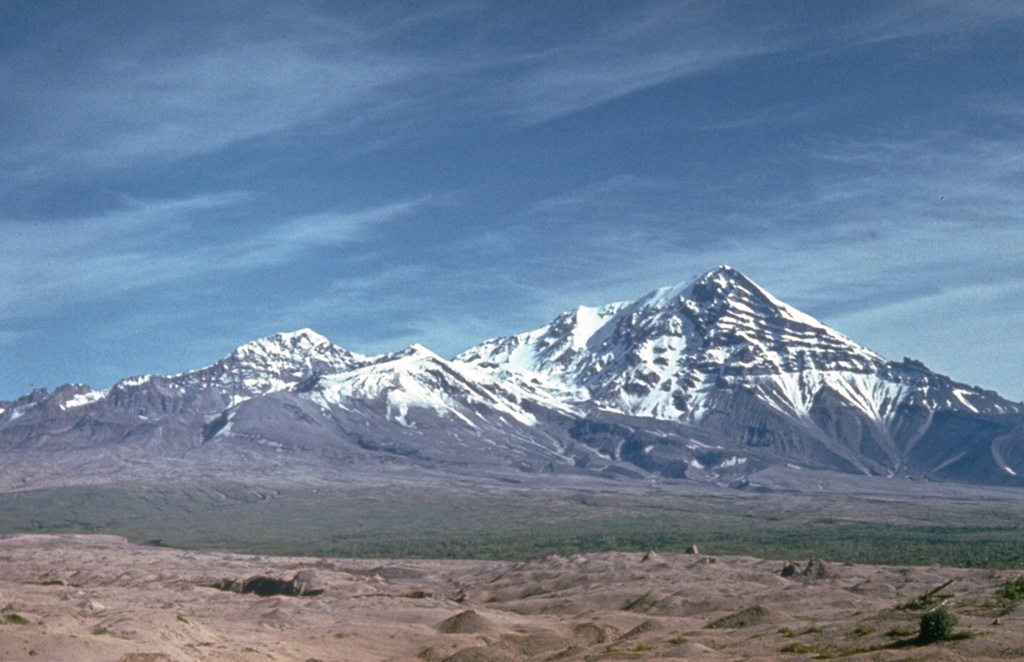
Sheveluch (also spelled Shiveluch) in Kamchatka, has had at least 60 large eruptions during the last 10,000 years. The summit is truncated by a broad 9-km-wide caldera that is breached to the S, and many lava domes occur on the outer flanks. The lava dome complex was constructed within the large open caldera. Frequent collapses of the dome complex have produced debris avalanches; the resulting deposits cover much of the caldera floor. A major south-flank collapse during a 1964 Plinian explosion produced a scarp in which a “Young Sheveluch” dome began to form in 1980. Repeated episodes of dome formation and destruction since then have produced major and minor ash plumes, pyroclastic flows, block-and-ash flows, and “whaleback domes” of spine-like extrusions in 1993 and 2020 (BGVN 45:11). The current eruption period began in August 1999 and has more recently consisted of lava dome growth, explosions, ash plumes, and avalanches (BGVN 48:01). This report covers a significant explosive eruption during early-to-mid-April 2023 that generated a 20 km altitude ash plume, produced a strong sulfur dioxide plume, and destroyed part of the lava-dome complex; activity described during January through April 2023 use information primarily from the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT) and various satellite data.
Satellite data. Activity during the majority of this reporting period was characterized by continued lava dome growth, strong fumarole activity, explosions, and hot avalanches. According to the MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, 140 hotspots were detected through the reporting period, with 33 recorded in January 2023, 29 in February, 44 in March, and 34 in April. Frequent strong thermal activity was recorded during January 2023 through April, according to the MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) graph and resulted from the continuously growing lava dome (figure 94). A slightly stronger pulse in thermal activity was detected in early-to-mid-April, which represented the significant eruption that destroyed part of the lava-dome complex. Thermal anomalies were also visible in infrared satellite imagery at the summit crater (figure 95).
During January 2023 KVERT reported continued growth of the lava dome, accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, incandescence from the lava dome, explosions, ash plumes, and avalanches. Satellite data showed a daily thermal anomaly over the volcano. Video data showed ash plumes associated with collapses at the dome that generated avalanches that in turn produced ash plumes rising to 3.5 km altitude and drifting 40 km W on 4 January and rising to 7-7.5 km altitude and drifting 15 km SW on 5 January. A gas-and-steam plume containing some ash that was associated with avalanches rose to 5-6 km altitude and extended 52-92 km W on 7 January. Explosions that same day produced ash plumes that rose to 7-7.5 km altitude and drifted 10 km W. According to a Volcano Observatory Notice for Aviation (VONA) issued at 1344 on 19 January, explosions produced an ash cloud that was 15 x 25 km in size and rose to 9.6-10 km altitude, drifting 21-25 km W; as a result, the Aviation Color Code (ACC) was raised to Red (the highest level on a four-color scale). Another VONA issued at 1635 reported that no more ash plumes were observed, and the ACC was lowered to Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). On 22 January an ash plume from collapses and avalanches rose to 5 km altitude and drifted 25 km NE and SW; ash plumes associated with collapses extended 70 km NE on 27 and 31 January.
Lava dome growth, fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and occasional explosions and avalanches continued during February and March. A daily thermal anomaly was visible in satellite data. Explosions on 1 February generated ash plumes that rose to 6.3-6.5 km altitude and extended 15 km NE. Video data showed an ash cloud from avalanches rising to 5.5 km altitude and drifting 5 km SE on 2 February. Satellite data showed gas-and-steam plumes containing some ash rose to 5-5.5 km altitude and drifted 68-110 km ENE and NE on 6 February, to 4.5-5 km altitude and drifted 35 km WNW on 22 February, and to 3.7-4 km altitude and drifted 47 km NE on 28 February. Scientists from the Kamchatka Volcanological Station (KVS) went on a field excursion on 25 February to document the growing lava dome, and although it was cloudy most of the day, nighttime incandescence was visible. Satellite data showed an ash plume extending up to 118 km E during 4-5 March. Video data from 1150 showed an ash cloud from avalanches rose to 3.7-5.5 km altitude and drifted 5-10 km ENE and E on 5 March. On 11 March an ash plume drifted 62 km E. On 27 March ash plumes rose to 3.5 km altitude and drifted 100 km E. Avalanches and constant incandescence at the lava dome was focused on the E and NE slopes on 28 March. A gas-and-steam plume containing some ash rose to 3.5 km altitude and moved 40 km E on 29 March. Ash plumes on 30 March rose to 3.5-3.7 km altitude and drifted 70 km NE.
Similar activity continued during April, with lava dome growth, strong fumarolic activity, incandescence in the dome, occasional explosions, and avalanches. A thermal anomaly persisted throughout the month. During 1-4 April weak ash plumes rose to 2.5-3 km altitude and extended 13-65 km SE and E.
Activity during 11 April 2023. The Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS) reported a significant increase in seismicity around 0054 on 11 April, as reported by strong explosions detected on 11 April beginning at 0110 that sent ash plumes up to 7-10 km altitude and extended 100-435 km W, WNW, NNW, WSW, and SW. According to a Tokyo VAAC report the ash plume rose to 15.8 km altitude. By 0158 the plume extended over a 75 x 100 km area. According to an IVS FEB RAS report, the eruptive column was not vertical: the initial plume at 0120 on 11 April deviated to the NNE, at 0000 on 12 April, it drifted NW, and by 1900 it drifted SW. KVS reported that significant pulses of activity occurred at around 0200, 0320, and then a stronger phase around 0600. Levin Dmitry took a video from near Békés (3 km away) at around 0600 showing a rising plume; he also reported that a pyroclastic flow traveled across the road behind him as he left the area. According to IVS FEB RAS, the pyroclastic flow traveled several kilometers SSE, stopping a few hundred meters from a bridge on the road between Klyuchi and Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky.
Ashfall was first observed in Klyuchi (45 km SW) at 0630, and a large, black ash plume blocked light by 0700. At 0729 KVERT issued a Volcano Observatory Notice for Aviation (VONA) raising the Aviation Color Code to Red (the highest level on a four-color scale). It also stated that a large ash plume had risen to 10 km altitude and drifted 100 km W. Near-constant lightning strikes were reported in the plume and sounds like thunderclaps were heard until about 1000. According to IVS FEB RAS the cloud was 200 km long and 76 km wide by 0830, and was spreading W at altitudes of 6-12 km. In the Klyuchi Village, the layer of both ash and snow reached 8.5 cm (figure 96); ashfall was also reported in Kozyrevsk (112 km SW) at 0930, Mayskoye, Anavgay, Atlasovo, Lazo, and Esso. Residents in Klyuchi reported continued darkness and ashfall at 1100. In some areas, ashfall was 6 cm deep and some residents reported dirty water coming from their plumbing. According to IVS FEB RAS, an ash cloud at 1150 rose to 5-20 km altitude and was 400 km long and 250 km wide, extending W. A VONA issued at 1155 reported that ash had risen to 10 km and drifted 340 km NNW and 240 km WSW. According to Simon Carn (Michigan Technological University), about 0.2 Tg of sulfur dioxide in the plume was measured in a satellite image from the TROPOMI instrument on the Sentinel-5P satellite acquired at 1343 that covered an area of about 189,000 km2 (figure 97). Satellite data at 1748 showed an ash plume that rose to 8 km altitude and drifted 430 km WSW and S, according to a VONA.
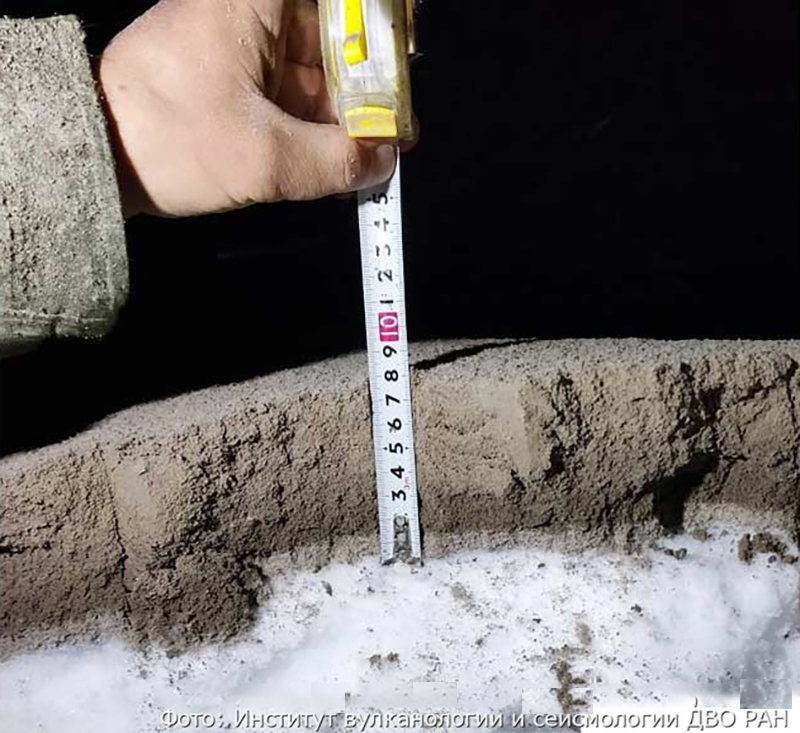 |
Figure 96. Photo of ash deposited in Klyuchi village on 11 April 2023 by the eruption of Sheveluch. About 8.5 cm of ash was measured. Courtesy of Kam 24 News Agency. |
Activity during 12-15 April 2023. On 12 April at 0730 satellite images showed ash plumes rose to 7-8 km altitude and extended 600 km SW, 1,050 km ESE, and 1,300-3,000 km E. By 1710 that day, the explosions weakened. According to news sources, the ash-and-gas plumes drifted E toward the Aleutian Islands and reached the Gulf of Alaska by 13 April, causing flight disruptions. More than 100 flights involving Alaska airspace were cancelled due to the plume. Satellite data showed ash plumes rising to 4-5.5 km altitude and drifted 400-415 km SE and ESE on 13 April. KVS volcanologists observed the pyroclastic flow deposits and noted that steam rose from downed, smoldering trees. They also noted that the deposits were thin with very few large fragments, which differed from previous flows. The ash clouds traveled across the Pacific Ocean. Flight cancellations were also reported in NW Canada (British Columbia) during 13-14 April. During 14-15 April ash plumes rose to 6 km altitude and drifted 700 km NW.
Alaskan flight schedules were mostly back to normal by 15 April, with only minor delays and far less cancellations; a few cancellations continued to be reported in Canada. Clear weather on 15 April showed that most of the previous lava-dome complex was gone and a new crater roughly 1 km in diameter was observed (figure 98); gas-and-steam emissions were rising from this crater. Evidence suggested that there had been a directed blast to the SE, and pyroclastic flows traveled more than 20 km. An ash plume rose to 4.5-5.2 km altitude and drifted 93-870 km NW on 15 April.
Activity during 16-30 April 2023. Resuspended ash was lifted by the wind from the slopes and rose to 4 km altitude and drifted 224 km NW on 17 April. KVERT reported a plume of resuspended ash from the activity during 10-13 April on 19 April that rose to 3.5-4 km altitude and drifted 146-204 km WNW. During 21-22 April a plume stretched over the Scandinavian Peninsula. A gas-and-steam plume containing some ash rose to 3-3.5 km altitude and drifted 60 km SE on 30 April. A possible new lava dome was visible on the W slope of the volcano on 29-30 April (figure 99); satellite data showed two thermal anomalies, a bright one over the existing lava dome and a weaker one over the possible new one.
References. Girina, O., Loupian, E., Horvath, A., Melnikov, D., Manevich, A., Nuzhdaev, A., Bril, A., Ozerov, A., Kramareva, L., Sorokin, A., 2023, Analysis of the development of the paroxysmal eruption of Sheveluch volcano on April 10–13, 2023, based on data from various satellite systems, Modern problems of remote sensing from space, 20(2).
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS), 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/eng/); Kamchatka Volcanological Station, Kamchatka Branch of Geophysical Survey, (KB GS RAS), Klyuchi, Kamchatka Krai, Russia (URL: http://volkstat.ru/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/); Kam 24 News Agency, 683032, Kamchatka Territory, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, Vysotnaya St., 2A (URL: https://kam24.ru/news/main/20230411/96657.html#.Cj5Jrky6.dpuf); Simon Carn, Geological and Mining Engineering and Sciences, Michigan Technological University, 1400 Townsend Drive, Houghton, MI 49931, USA (URL: http://www.volcarno.com/, Twitter: @simoncarn).
2024: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
2023: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2022: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2021: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2020: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2019: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2018: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2017: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2016: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2015: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2014: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2013: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2012: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2011: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2010: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2009: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2008: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2007: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2006: July
| November
| December
2005: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
2004: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2003: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
2002: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2001: January
| February
| March
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
| October
| November
| December
2000: November
| December
KVERT reported that thermal anomalies over both the “300 years of RAS” dome and the older lava dome at Sheveluch were identified in satellite images during 12-15 and 18 July. Weather conditions prevented views on the other days during 12-19 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The Kamchatka Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT) reported that eruptive activity at Sheveluch continued during 4-11 July. Vigorous degassing activity accompanied the effusive eruption in the crater of Young Sheveluch, as well as the growth of the "300 years of RAS" lava dome on the SW flank of Old Sheveluch. Thermal anomalies were observed in both areas on 5-8 and 11 July in satellite images analyzed by KVERT. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are reported in UTC; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that thermal anomalies over both the “300 years of RAS” dome and the older lava dome at Sheveluch were identified in satellite images during 28 June and 3-4 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that thermal anomalies over both the “300 years of RAS” dome and the older lava dome at Sheveluch were identified in satellite images during 21-27 June. Both domes continued to grow. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that thermal anomalies over both the new and older lava domes at Sheveluch were identified in satellite images during 13-21 June. The report noted that the Karan-1 lava dome, located in the SW part of “Old Sheveluch,” was renamed to “300 years of RAS.” The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that thermal anomalies over both the new and older lava domes at Sheveluch were identified in satellite images during 6-7 and 11-13 June; the domes were obscured by weather clouds during 8-10 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that thermal anomalies over both the new and older lava domes at Sheveluch were identified in satellite images during 1-2 and 4-6 June; the domes were obscured by weather clouds on 31 May and 3 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the Karan-1 lava dome on Sheveluch’s SW flank continued to be active during 23-30 May. Thermal anomalies over both the new and older lava domes were identified in satellite images during 23-24 May; the dome was obscured by weather clouds on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the Karan-1 lava dome on Sheveluch’s SW flank continued to grow during 16-23 May. Thermal anomalies over both the new and older lava domes were identified in satellite images during 17, 19-21, and 23 May; the dome was obscured by weather clouds on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the Karan-1 lava dome on Sheveluch’s SW flank continued to grow during 9-16 May. An intense and large thermal anomaly over the dome was identified in satellite images during 9-12 May; the dome was obscured by weather clouds on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the new lava dome at Sheveluch, named Karan-1, continued to grow during 3-9 May. Strong steam-and-gas emissions rose from the active area and incandescence at the dome was visible at night. A daily intense and large thermal anomaly over the dome was identified in satellite images. Kamchatka Volcanological Station volcanologists conducted field work on 8 May, including photos and drone observations of the new dome. At that time the dome was at least 70 m high, actively growing and, spalling rock avalanches down the flanks. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Kamchatka Volcanological Station
The Kamchatka Volcanological Station reported that seismicity at Sheveluch began increasing on 24 April. According to KVERT a new lava dome, named Karan-1, began to grow on the SW flank at around 0200 local time on 27 April based on the intensification of thermal anomalies detected in satellite observations. During 27 April-3 May intense steam-and-gas emissions rose from the active area and on 28 April an ash plume drifted about 25 km NW. Kamchatka Volcanological Station noted that an ash plume rose 2 km on 30 April. Lava-dome incandescence was occasionally visible during the week in webcam images and a daily intense thermal anomaly over the dome complex was identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Sources: Kamchatka Volcanological Station; Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that eruptive activity at Sheveluch continued during 18-26 April with a daily thermal anomaly identified in satellite images. A plume of resuspended ash drifted 195 km S and SE during 22-24 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that eruptive activity at Sheveluch continued during 11-18 April with a daily thermal anomaly identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported continuing eruptive activity at Sheveluch. A thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 6-9 and 11 April. A plume of resuspended ash drifted 140 km ESE on 11 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that eruptive activity at Sheveluch continued during 28 March-4 April with a daily thermal anomaly identified in satellite images. On 29 March a plume of resuspended ash drifted 65 km E. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that eruptive activity at Sheveluch continued during 21-28 March with a daily thermal anomaly identified in satellite images. On 30 March plumes of resuspended ash from the S flank rose as high as 2.5 km (8,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 65 km ESE based on satellite and video data. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that eruptive activity at Sheveluch continued with a thermal anomaly identified in satellite images during 17-21 March. Strong gas and steam emissions were observed at the Karan dome. On 21 March plumes of resuspended ash extended 65 km to the SE [Correction: plumes of resuspended ash from the S flank rose to 2 km (6,560 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 35 km ESE]. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that eruptive activity at Sheveluch continued with a thermal anomaly identified in satellite images on 7, 9, and 13 March. Weather clouds obscured views on the other days during 7-14 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that eruptive activity at Sheveluch continued during 29 February-6 March with a daily thermal anomaly identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that eruptive activity at Sheveluch continued during 22-29 February with a daily thermal anomaly identified in satellite images. On 26 February plumes of resuspended ash drifted 120 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that eruptive activity at Sheveluch continued during 15-22 February with a thermal anomaly identified in satellite images during 16, 18-19, and 22 February. On 19 February plumes of resuspended ash rose to 2.5 km (8,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted about 55 km ESE. Weather clouds sometimes prevented views of the volcano. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 8-15 February with a daily thermal anomaly identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 1-8 February characterized by powerful degassing activity observed from the Karan dome, and thermal anomalies identified in satellite images during 1-3 and 6-7 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 25 January-1 February with a daily thermal anomaly identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 18-25 January. A thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 20-25 January; weather clouds obscured views on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 11-18 January. A thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 11-15 and 17 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 4-11 January with a daily thermal anomaly identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 28 December 2023-4 January 2024 with a daily thermal anomaly identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 21-29 December. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 14-21 December. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 7-14 December. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 1-7 December. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. During 3-6 December plumes of resuspended ash drifted about 230 km E and SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 23-30 November. Thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images on 23, 26, and 28-29 November. Strong steam-and-gas emissions were observed in the area of the Karan Dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 16-23 November. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. On 17 November plumes of resuspended ash drifted about 116 km E. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 10-16 November. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. During 9-10 November plumes of resuspended ash drifted about 275 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 8-14 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 26 October-2 November. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 19-26 October. A thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 20, 23-24, and 26 October; weather clouds obscured views on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 13-20 October and a daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 5-12 October. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images and a plume of resuspended ash drifted 90 km ESE on 11 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 28 September-5 October. Thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images during 28-29 September and 1-2 and 5 October; observations on other days were obscured by weather clouds. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 21-28 September. Thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images during 22 and 27-28 September; observations on other days were obscured by weather clouds. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 14-21 September. Thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images during 17-19 September; observations on other days were obscured by weather clouds. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 7-14 September. Thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images on all days except 14 September (due to weather clouds). Plumes of resuspended ash drifted 160 km SE and E during 9-11 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 31 August-7 September. Intense fumarolic activity was visible at the active dome, and thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images on all days except 7 September (due to weather clouds). Plumes of resuspended ash drifted 650 km SE and E during 31 August and 3-4 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 24-31 August. Intense fumarolic activity was visible at the active dome, and daily thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images. A plume of resuspended ash drifted 650 km SE during 30-31 August. Plumes of resuspended ash drifted 110 km E at altitudes of 2.5-3 (8,200-10,000 ft) a.s.l. on 4 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 17-24 August. Intense fumarolic activity was visible at the active dome, and daily thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 10-17 August. Intense fumarolic activity was visible at the active dome, and daily thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 3-10 August. Intense fumarolic activity was visible at the active dome, and thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images during 5-7 and 9 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 27 July-3 August. Intense fumarolic activity was visible at the active dome, and daily thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images. An ash plume was visible in satellite images drifting 82 km E on 28 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 20-28 July. Intense fumarolic activity was visible at the active dome, and thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images on 22, 25, and 27 July; the volcano was obscured by clouds during the other days of the week. Explosions generated ash plumes to 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. at 0200 UTC on 28 July and 7.7-8 km (25,000-26,000 ft) a.s.l. at 0410 UTC. A resulting ash plume extended NE. Though the Aviation Color Code was briefly raised to Red (the highest on a four-color scale), about an hour later it was lowered back to Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). An ash plume on 28 July rose to 5.5-5.7 km (18,000-18,700 ft) a.s.l. and drifted ENE. Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 13-20 July. Intense fumarolic activity was visible at the active dome, and daily thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch continued during 6-13 July. Intense fumarolic activity was visible at the active dome, and thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images during 9 and 12-13 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the third level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that eruptive activity continued at Sheveluch during 29 June-6 July. Daily thermal anomalies were observed in satellite images and intense fumarolic activity was visible from both the active crater and lava dome. An aviation notice on 2 July described a gas-and-steam plume with some ash that rose 3.5 km a.s.l. and drifted 39 km W. Additional aviation notices caused by resuspended ash were issued on 30 June and 1, 4, and 5 July; plumes rose up to 3 km a.s.l. and drifted as far as 95 km ESE, SE, W, and WNW. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that eruptive activity continued at Sheveluch during 22-29 June. Daily thermal anomalies were observed in satellite images and intense fumarolic activity was visible from both the active crater and the active lava dome. Aviation notices were issued during 26-27 June due to resuspended ash from the SE flank that sent plumes up to 3 km a.s.l. and drifted as far as 277 km ESE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch was ongoing during 15-22 June. Intense fumarolic activity at the active crater was likely associated with growth of the lava dome. A thermal anomaly over the active crater area was identified in satellite images during 16, 18-19, and 22 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch was ongoing during 1-8 June. Intense fumarolic activity at the active crater was likely associated with growth of Karan lava dome. A daily thermal anomaly over the active crater area was identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch was ongoing during 25 May-1 June. Intense fumarolic activity at the active crater was likely associated with growth of Karan lava dome. A thermal anomaly over the active crater and Karan dome area was identified in satellite images during 25-30 May; weather clouds obscured the volcano on the other days. Plumes of ash, originally deposited during the 10-13 April eruption and resuspended by strong winds, were visible in satellite images drifting 120 km ESE during 27-28 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch was ongoing during 18-25 May. A thermal anomaly over the active crater and Karan lava dome area was identified in satellite images all week. Intense fumarolic activity at the active crater was likely associated with dome growth. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the eruption at Sheveluch was ongoing during 11-18 May. A thermal anomaly over the active crater and Karan lava dome area was identified in satellite images all week. Intense fumarolic activity at the active crater was likely associated with dome growth. Plumes of ash, originally deposited during the 10-13 April eruption and resuspended by strong winds, were visible in satellite images drifting 400 km SE during 14-15 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was generally characterized by occasional explosions, continuing lava-dome growth, incandescence, and strong fumarolic activity during 4-11 May. A thermal anomaly over the active crater and Karan lava dome area was identified in satellite images all week. Intense fumarolic activity was likely associated with dome growth. During 8-9 May ash from pyroclastic flow deposits on the SE flank were resuspended by winds and blown 60 km W based on satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was generally characterized by occasional explosions, continuing lava-dome growth, incandescence, and strong fumarolic activity during 27 April-4 May. A thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images all week. Satellite data showed a gas-and-steam plume with some ash drifting 60 km SE at 2350 on 29 April. The Kamchatka Volcanological Station posted pictures and video taken during a 4 May overflight that showed three active fumaroles on the dome. Low weather clouds obscured parts of the dome area. Photos showed tephra-fall on surrounding lakes, rivers, and forests, and it was noted that lahar deposits blocked a road W of the volcano. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Kamchatka Volcanological Station
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was generally characterized by occasional explosions, continuing lava-dome growth, incandescence, and strong fumarolic activity during 20-27 April. Gas-and-steam emissions obscured the volcano during 20-23 April. A thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 24-27 April. A photograph taken on 29 April by the Kamchatka Volcanological Station showed a lava dome which was higher than the crater rim. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Kamchatka Volcanological Station
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 14-20 April. During 14-15 April ash plumes rose to 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 700 km NW. During 17-19 April plumes of unconsolidated ash resuspended from the flanks by wind rose to 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted as far as 224 km NW. The sulfur dioxide gas portion of the eruption cloud produced during the notable 11-12 April activity continued to drift E; by 21 April the leading edge of the plume was over part of Greenland. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
According to KVERT a significant eruption at Sheveluch began at 0110 on 11 April, local time. During the most intense phase of activity ash plumes possibly rose as high as 15.8 km (52,000 ft) a.s.l., a significant sulfur dioxide signature was detected in the plume, pyroclastic flows traveled notable distances, and ash-and-lapilli-fall impacted residents. Strong explosions continued during the morning of 12 April. At 0730 on 12 April satellite images showed ash plumes rising to 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l., though parts of the large ash plume generated earlier extended 600 km SW and 1,050 km ESE. The explosions weakened by 1710 when ash plumes were only rising to 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifting ESE; at 1801 KVERT issued a Volcano Observatory Notice for Aviation (VONA) lowering the Aviation Color Code to Orange. By 2310 ash extended as far as 3,000 km E. KVERT noted that ash deposits in Klyuchi were as deep as 8.5 cm, and ashfall was reported in Kozyrevsk, Maiskoye, Atlasovo, Lazo, and Esso during 10-12 April. According to news sources, the ash-and-gas plumes drifted E toward the Aleutian Islands and reached the Gulf of Alaska by 13 April, causing flight disruptions. More than 100 flights involving Alaska airspace were cancelled due to the plume. Flight cancellations were also reported in NW Canada (British Columbia) during 13-14 April. Alaskan flight schedules were mostly back to normal by 15 April, with only minor delays and far fewer cancellations; a few cancellations continued to be reported in Canada.
On 13 April Kamchatka Volcanological Station (KVS) volcanologists inspected pyroclastic flow deposits that had stopped about 600 m from the Klyuchi-Ust-Kamchatsk federal highway. They walked about 1 km through deep snow (1 m) covered in 6 cm of ash and noted that some parts of the deposits were hot. Steam rose from downed smoldering trees. One picture showed a large block lodged high up in a bare tree. They also noted that the pyroclastic flow deposits were thin with very few large fragments, different from previous flows from Sheveluch. Clearing weather on 15 April revealed that most of the previous lava-dome complex was gone and there was a new crater 1 km in diameter from which voluminous steam-and-gas plumes were rising. Evidence suggested that there had been a directed blast to the SE, and pyroclastic flows traveled more than 20 km.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Kamchatka Volcanological Station; Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (IVS) of the Far Eastern Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (FEB RAS); Anchorage Daily News; Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (CBC); Cabin Radio
On 28 March the Kamchatka Volcanological Station (KVS) reported that activity had increased at Sheveluch during the previous few days. Incandescence at the summit of the lava dome was constant and the focus of activity shifted from the E side to the NE side. KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 30 March-6 April. Satellite images showed an ash plume drifting 250 km E and SE.
Seismic data around 0054 local time on 11 April indicated a significant increase in activity, as reported by the Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS). According to the Tokyo VAAC the ash plume had risen to 15.8 km (52,000 ft) a.s.l. by 0110 and was drifting NW. By 0158 the plume extended over a 75 x 100 km area. KVS reported that significant pulses of activity occurred at around 0200, 0320, and then a stronger phase started around 0600. Video of the rising plume was taken at around 0600 from near Békés (3 km away) by Levin Dmitry, who reported that a pyroclastic flow traveled across the road behind him as he left the area. Ashfall began in Klyuchi (45 km SW) at 0630, and the large black ash plume had blocked the daylight by 0700. At 0729 KVERT issued a Volcano Observatory Notice for Aviation (VONA) raising the Aviation Color Code to Red (the highest level on a four-color scale). They stated that a large ash plume had risen to 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 100 km W. According to IVS FEB RAS the cloud was 200 km long and 76 km wide by 0830, and was spreading W at altitudes of 6-12 km (19,700-39,400 ft) a.s.l.
KVS reported that at about 0930 the plume drifted over Kozyrevsk (112 km SW) and turned the day to night. Almost constant lightning strikes in the plume were visible and sounds like thunderclaps were heard until about 1000. The sky lightened up in Kozyrevsk at about 1030; residents in Klyuchi reported continuing darkness and ashfall at 1100. As the day went on the light had a reddish-brown hue due to the ash in the atmosphere. In some areas ashfall was 6 cm deep and some residents reported dirty water coming from their plumbing. At 1150 an ash cloud 400 km long and 250 km wide was spreading W at altitudes of 5-20 km (16,400-65,600 ft) a.s.l., according to IVS FEB RAS. KVERT issued a VONA at 1155 noting that ash had risen to 10 km and that it had extended 340 km NNW and 240 km WSW. According to Simon Carn about 0.2 Tg of sulfur dioxide in the plume was measured in a satellite image acquired at 1343. A satellite image at 1748 showed ash plumes rising to 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifting 430 km WSW and S, based on a VONA. Residents of Klyuchi measured ashfall as thick as 8.5 cm, according to the Kamchatka Branch of Geophysical Services (KBGS; Russian Academy of Sciences). In a VONA issued at 0748 on 12 April KVERT stated that strong explosions were continuing. Ash plumes from explosions rose to 8 km and drifted ESE. The larger ash cloud continued to drift and had extended 600 km SW and 1,050 km ESE. IVS FEB RAS scientists photographed the terminal part of a pyroclastic flow that had traveled 19 km SSE the day before, which had stopped a few hundred meters from a bridge on the road between Kliuchi and Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Simon Carn; Kamchatka Volcanological Station; Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (IVS) of the Far Eastern Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (FEB RAS); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 23-30 March. Ash plumes drifted 80 km E during 25-26 and 28-30 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 16-23 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 9-16 March. Ash plumes drifted as far as 62 km E on 11 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 2-9 March and ash plumes drifted as far as 118 km E during 4-5 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 23 February-2 March. At 1150 on 5 March local time video images showed an ash plume generated by hot avalanches rising 5.5 km a.s.l. (just over 2.2 km above the summit) and drifting 5 km NE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 16-23 February. During a field visit to the volcano on 25 February Kamchatka Volcano Station scientists observed and photographed the dome and saw incandescent debris avalanches on the originating at the dome’s summit. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Kamchatka Volcanological Station
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 9-16 February was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 2-9 February was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images, and minor ash plumes from lava-dome collapses drifted 110 km NE on 6 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 26 January-2 February was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A persistent thermal anomaly was identified daily in satellite images, and minor ash plumes from explosions and lava-dome collapses drifted 70 km NE on 27 and 31 January and 2 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 19-26 January was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images, and minor ash plumes from explosions and lava-dome collapses drifted 25 km SW on 22 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 12-19 January was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. Explosions on 19 January produced ash plumes that were identified in satellite images rising as high as 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifting W at 1240 local time. KVERT raised the Aviation Color Code to Red (the highest level on a four-color scale). In a Volcano Observatory Notice for Aviation (VONA) posted at 1635 local time KVERT noted that no additional plumes were identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code was lowered to Orange. Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 5-12 January was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images, and minor ash plumes from explosions and lava-dome collapses drifted 92 km W on 7 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 29 December 2022-5 January 2023 was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images, and ash plumes from lava-dome collapses drifted 175 km E, NE, W, and SW during 30-31 December and 4-5 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 22-29 December was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images, and gas-and-steam plumes containing some ash were visible drifting 90 km SW, S, and NE during 26-29 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 15-22 December was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images, and ash plumes were visible drifting 110 km NNE on 16 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 8-15 December was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 2-8 December was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. Collapses generated hot avalanches and ash plumes that drifted 60 km NE and E during the week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 24 November-1 December was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. Collapses generated hot avalanches and ash plumes that drifted 90 km NE on 26 and 29 November, and 1 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 17-24 November was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. Collapses generated hot avalanches and ash plumes that drifted 80 km E during 17-18 and 20 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 11-17 November was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. Collapses generated hot avalanches and ash plumes that drifted 85 km ENE during 13-14, and 16-17 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 3-10 November was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, lava-dome extrusion, and strong fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. Collapses generated hot avalanches and ash plumes that drifted 400 km N, NE, and E during 5-7 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 27 October-3 November was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. Collapses generated hot avalanches and ash plumes that drifted 200 km SE on 31 October and 1 November. The Kamchatka Volcano Station reported that activity notably increased on 5 November. Debris avalanches and small pyroclastic flows were visible throughout the day and incandescent avalanches were seen traveling SE and SW at night. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Kamchatka Volcanological Station
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch during 20-27 October was generally characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. Collapses generated hot avalanches and ash plumes that drifted 80 km SE and NW during 24-25 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion during 14-20 October. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion during 6-14 October. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion during 29 September-6 October. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion during 15-22 September. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. Plumes of re-suspended ash drifted 113 km E on 23 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion during 15-22 September. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. Plumes of re-suspended ash drifted 430 km E during 17-18 and 21-22 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion during 8-15 September. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. Plumes of re-suspended ash drifted 90 km E on 8 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion during 2-8 September. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. Dome collapses produced hot avalanches and ash plumes that drifted 130 km NE and SE during 2 and 5-7 September. Plumes of re-suspended ash drifted 210 km ESE during 4-5 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion during 25 August-1 September. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. Plumes of re-suspended ash drifted 150 km E on 25 August. Hot avalanches generated an ash plume on 1 September that drifted 70 km E. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion during 18-25 August. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 18-19, 21, and 23-25 August. Ash plumes drifted 190 km SE and 150 km E on 19 and 25 August, respectively. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion during 11-18 August. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion during 4-11 August. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images, and gas-and-steam plumes containing some ash were visible drifting 70 km E and SE during 8-9 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion during 29 July-4 August. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images, and ash plumes were visible drifting 24 km SW on 31 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion during 21-28 July. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images, and ash plumes were visible drifting 74 km SSW and SE on 22 and 24 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion during 15-21 July. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images, and ash plumes were visible drifting 125 km E and SE during 16 and 18-19 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the ongoing eruption at Sheveluch was characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion. A thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 7-14 July. Satellite images showed ash plumes drifting 82 km SW and SE during 11-13 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 1-7 July and the eruption was characterized by ongoing explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion. At 1130 local time on 12 July video and satellite images showed an ash plume drifting 12 km S at altitudes of 4-4.5 km (13,100-14,800 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 24 June-1 July and the eruption was characterized by ongoing explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 17-23 June and the eruption characterized by explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion continued. Webcam images recorded explosions on 19 and 21 June that sent ash plumes to 7 and 5 km (23,000 and 16,400 ft) a.s.l., respectively. The ash plumes were visible in satellite images drifting 255 km ENE and 70 km SW during 19-20 and 21 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 10-17 June and explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion continued. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. Webcam images recorded explosions on 10 June that sent ash plumes to 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. The ash plumes were visible in satellite images drifting 130 km SE. At 0847 on 20 June (local time) explosions were recorded in webcam images. Ash plumes rose to 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 10 km E. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 4-9 June and explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion continued. A daily thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 27 May-3 June; explosions, hot avalanches, and lava-dome extrusion continued. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 20-27 May, and lava-dome extrusion continued. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 13-20 May, and lava-dome extrusion continued. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 6-13 May, and lava-dome extrusion continued. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 29 April-6 May, and lava-dome extrusion continued. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 22-29 April, and lava-dome extrusion continued. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 15-22 April, and lava-dome extrusion continued. Explosions during 15-16 April produced ash plumes that rose as high as 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted about 75 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 8-15 April, and lava-dome extrusion continued. Explosions on 9 April produced ash plumes that rose as high as 12 km (39,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted more than 2,000 km NE during 9-10 April. Explosions during 13-14 April generated ash plumes that rose to 6-6.5 km (19,700-21,300 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 80-110 km SW and S. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 2-8 April. The lava dome continued to grow and strong fumarolic activity, incandescence, and avalanches accompanied this activity. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 26 March through 1 April. The lava dome continued to grow and strong fumarolic activity, incandescence, and avalanches accompanied this activity. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 18-25 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 11-18 March. An ash cloud was identified in satellite images drifting 50 km WNW at an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. on 15 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 25 February-4 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 18-25 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 11-18 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 4-11 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 28 January-4 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 21-28 January. Intense steam-and-gas emissions were visible. Gas, steam, and ash plumes drifted 55 km SW on 21 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 14-21 January. Intense steam-and-gas emissions with ash were visible during 15-16 January; plumes rose as high as 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 77 km W. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 8-14 January. Intense steam-and-gas emissions with ash were visible during 6-7 and 9-11 January; plumes rose as high as 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 175 km W. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 1-7 January. Intense steam-and-gas emissions with ash were visible during 3 and 5-6 January; plumes rose as high as 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 180 km N and W. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 24-31 December. Intense steam-and-gas emissions were visible. Ash plumes rose as high as 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 110 km NW and NE during 24-25, 27, and 30 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 17-24 December. At 1210 local time on 23 December explosions produced ash plumes that rose to 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 70 km NE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). Dates are based on UTC times; specific events are in local time where noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 10-17 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 3-10 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 26 November-3 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 19-26 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 12-19 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 5-12 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 29 October-5 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 22-29 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 16-17 and 20-21 October when the volcano was visible through weather clouds. A plume of resuspended ash rose as high as 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. on 21 October and drifted 40 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 8-15 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 1, 4, and 6-7 October. Plumes of resuspended ash drifted 200 km SE during 6-7 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 24 September-1 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 17-24 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 10-17 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a bright thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 3-10 September. The Kamchatka Branch of Geophysical Services (KBGS; Russian Academy of Sciences) Kamchatka volcano station reported that tourists visiting the volcano on 8 September experienced ashfall; weather conditions prevented views of summit. The next day they saw a small pyroclastic flow and that night saw crater incandescence and small incandescent avalanches traveling SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Institute of Volcanology and Geodynamics, Russian Academy of Natural Science
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 27 August-3 September. A gas-and-steam plume with some ash was visible in satellite data drifting 54 km NE and NW on 26 and 28 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the lava dome at Sheveluch continued to grow and produced hot lava avalanches during 20-27 August. A daily bright thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images and gas-and-steam plumes containing some ash drifted 307 km NE, E, and SE. At 1100 on 29 August an ash plume 14x15 km in dimension drifted 30 km W at altitudes of 2.5-3 km (8,200-10,000 ft) a.s.l. On 28 August the Kamchatka Branch of Geophysical Services (KBGS; Russian Academy of Sciences) posted photos of the incandescent dome and avalanches, noting that small landslides and hot avalanches periodically traveled down the S and SE flanks of the dome. Larger landslides were observed 2-4 times per night. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Institute of Volcanology and Geodynamics, Russian Academy of Natural Science
KVERT reported that the growth of the lava dome at Sheveluch continued during 14-24 August, accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches. A thermal anomaly was identified in satellite imagery all week. Gas-and-steam plumes containing some ash drifted 370 km SW, E, and SE. On 21 and 24 August ash plumes rose to 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 86 km SE and 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. and drifted as far as 100 km SE, respectively. The Tokyo VAAC reported ash plumes during 17-25 August that rose to 3.7-5.5 km (12,000-18,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E, S, SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 6-13 August. Gas-and-steam plumes containing some ash drifted 140 km SW during 7 and 9-12 August. On 11 August the Kamchatka Branch of Geophysical Services (KBGS; Russian Academy of Sciences) reported that the spine had crumbled and incandescent material descended the flanks. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Institute of Volcanology and Geodynamics, Russian Academy of Natural Science
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 30 July-6 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 23-30 July. Activity was notable on 26 July with collapses of lava-dome blocks and small explosions. A gas-and-steam plume with some ash was visible in satellite data drifting 45 km E that same day. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 16-23 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 9-16 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 2-9 July. A plume of re-suspended ash drifted 90 km E during 6-7 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 25 June-2 July. An ash plume drifted 18 km SW on 30 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 18-25 June. The newest lava block (named “Dolphin-2”) that had extruded from the top of the lava dome in February was about 200 m tall and 170 m wide at the base on 16 June; the top was slowly crumbling. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 10-18 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 3, 6, and 8-10 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 28 May-4 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 21-28 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 14-21 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 7-14 May. A new lava block (named “Dolphin-2”) that extruded from the top of the lava dome was visible in a 15 May photo. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 30 April-7 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 23-30 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 16-23 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 9-16 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 2-9 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 28 March-2 April. On 3 April a plume of re-suspended ash rose to 2.5 km (8,200 ft) a.sl. and drifted 250 km ESE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that lava dome growth at Sheveluch continued during 20-26 March, accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, incandescence, and block avalanches. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly over the lava dome all week, except on 22 and 25 March due to cloud cover. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 12-19 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 5-12 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 26 February-5 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 19-26 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 12-19 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 5-12 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images on 29 January as well as 2 and 4 February. Weather clouds obscured views of the volcano on the other days during 30 January-5 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 22-29 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 15-22 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 8-15 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 1-8 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 25 December-1 January. A strong explosion on 29 December generated ash plumes that rose as high as 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifting 250 km W. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 18-25 December. Two strong explosive events on 22 and 24 December generated large ash clouds that rose as high as 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 625 km E. The Aviation Color Code was briefly raised to Red (the highest level on a four-color scale) on 22 December, but then was lowered back to Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 11-18 December. On 22 December residents of Ust-Kamchatsk Village, 85 km SE, observed ash plumes rising to 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifting 42 km NE. The Aviation Color Code was raised to Red (the highest level on a four-color scale). Just over an hour later ash plumes rose 6.5-7.5 km (21,300-24,600 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 130 km E; the Aviation Color Code was lowered to Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 4-11 December. The lava block, named “Dolphin,” which had emerged in the E part of the summit lava dome, was absent in an 8 December photo of the volcano. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Volcanoes of Kurile-Kamchatka Island Arc Information System (VOKKIA) Geoportal
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 27 November-4 December. A gas-and-steam plume drifted 60 km NE on 30 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 20-27 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 13-20 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 6-13 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 30 October-6 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 23-30 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 16-23 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 8-16 October. A plume of re-suspended ash drifted 310 km SE during 8-9 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 2-9 October. A plume of re-suspended ash drifted 250 km SE during 7-8 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 25 September-2 October. A new lava block (named “Dolphin”) that extruded from the E part of the lava dome was first visible on 28 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 18-25 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 11, 13-14, and 16-17 September; weather clouds prevented views on other days during 11-18 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 4-5 and 8-10 September; weather clouds prevented views during 6-7 and 11 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images daily during 28 August-4 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified almost daily in satellite images during 14-28 August; weather cloud cover prevented views on 15 and 27 August. A plume of resuspended ash drifted 75 km ESE on 24 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 7-14 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 1-7 August. A moderate explosion produced a small ash plume that rose to 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE and E on 2 August according to the Kamchatka Branch of Geophysical Services (KBGS; Russian Academy of Sciences). The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Institute of Volcanology and Geodynamics, Russian Academy of Natural Science
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 24-31 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 17-24 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 10-17 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 3-10 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 26 June-3 July. A plume of re-suspended ash drifted 140 km E on 28 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 19-26 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 12-19 June. A webcam captured an explosion on 13 June that sent ash up to 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. The ash cloud drifted 120 km NE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 5-12 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 29 May-5 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 22-29 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 15-22 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 8-15 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 1-8 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 24 April-1 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 17-24 April, and a plume of re-suspended ash drifted 140 km NE on 18 and 20 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 10-17 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 3-10 April. Explosions on 8 April generated ash plumes that rose to 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 526 km SE during 8-9 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 27 March-3 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 20-27 March. A gas-and-steam plume containing some ash drifted 45 km N on 25 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 13-20 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 6-13 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 28 February-6 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 21-28 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 15-21 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 7-14 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 1-7 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 23-24 and 27-30 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 17-24 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 10-17 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 3-10 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 27 December-3 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 17-27 December. Ash plumes drifted E on 22 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 13-20 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 6-13 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 29 November-6 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 22-29 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 15-22 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 8-15 November. An ash plume rose to 9-10 km (29,500-32,800 ft) a.s.l. on 11 November; ash plumes drifted as far as 1,300 km ESE during 11-12 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 1-8 November. Ash plumes drifted as far as 640 km NW on 3 and 5 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 25 October-1 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 18-25 October. Resuspended ash drifted 110 km SE during 19-20 October. Explosions recorded on 21 October generated ash plume that rose to 10-11 km (32,800-36,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 1,300 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 11-18 October. Explosions during 11-13 and 15 October produced ash plumes that rose 6.5-7 km (21,300-23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 620 km E and SE. Resuspended ash drifted 125 km E during 16-17 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 4-11 October. Explosions seen in video and satellite images on 6 and 9 October produced ash plumes that rose 6.5-11 km (21,300-36,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 1,100 km E. Resuspended ash drifted 170 km E on 4 and 8 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 29 September and 1-2 October video and satellite images recorded ash plumes from explosions at Sheveluch rising as high as 9 km (29,500 ft) a.s.l., and a notable pyroclastic flow traveled SE on 1 October. Ash plumes from the events drifted 1,400 km SE and E. On 6 October satellite images showed ash plumes rising to 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifting 430 km NE. The Aviation Color Code was raised to Red (the highest level on a four-color scale). Later that day the ash plumes were visible in satellite images drifting 1,080 km ENE. The Alert Level was lowered back to Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 20-27 September. Explosions recorded during 20-21, 23, and 26 September produced ash plumes that rose to 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 580 km ESE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 13-20 September. Ash plumes drifted 200 km SW, SE, and NE during 12-15, 17, and 19 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 6-9 and 12 September. Resuspended ash formed plumes that drifted 250 km ESE during 11-12 September. Satellite and webcam data recorded ash emissions and a gas-and-steam plume with some ash drifting 50 km ESE on 12 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a daily thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified in satellite images during 30 August-6 September. Ash clouds were seen in satellite images drifting 660 km during 29 August, and 2-3 September, and 5 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 22-25 August. Ash plumes on 25 August rose to 4.5-5 km (14,800-16,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted more than 500 km NW. At 1510 on 29 August explosions produced ash plumes that rose to 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. The leading part of the plume drifted W and then curved counterclockwise to the S, then E, and finally drifted 550 km N. Explosions at 1957 on 30 August produced ash plumes that rose to 7-7.5 km (23,000-24,600 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 50 km SSE. Ash plumes drifted SE at an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. on 3 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 17-23 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 9-16 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 2-9 August. A diffuse ash plume rose to 2.5 km (8,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 40 km NW on 5 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 26 July-2 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 19-26 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 13-18 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 6-12 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 28 June-5 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 21-28 June. Explosions on 24 and 27 June generated ash plumes that rose to 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E and SW, respectively. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 14-21 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly at Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified in daily satellite images during 8-14 June. Explosions and hot avalanches of material were captured by video and satellite data during 11-12 June. Ash plumes from the events drifted 60 km WNW. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 1-7 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 24-31 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 17-24 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 10-17 May. Plumes of re-suspended ash were visible drifting 16 km SE on 13 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 3-10 May. Gas-and-steam plumes containing some ash was visible drifting 50 km SE and SW. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 26 April-3 May. Plumes of re-suspended ash were visible drifting 200 km SE during 30 April-2 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 18-26 April. Ash plumes were visible drifting 300 km NE during 22-23 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 12-18 April. Ash plumes were visible on 13 and 15 April drifting 83 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 6-12 April. Explosions on 10 April generated ash plumes that rose to 8-9 km (26,200-29,500 ft) a.s.l. and drifted about 1,300 km SSE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 29 March-6 April. Explosions on 5 April generated ash plumes that rose to 7-7.5 km (23,000-24,600 ft) a.s.l. and drifted about 550 km NW during 5-6 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 22-28 March. An ash plume rose to 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted about 80 km S on 25 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 15-22 March. Strong gas-and-steam emissions containing variable amounts of ash rose 3.5-4 km (11,500-13,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 105 km E during 15-17 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 8-15 March. Explosions on 9 March generated ash plumes that rose to 11 km (36,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 375 km NNW, causing KVERT to temporarily raise the Aviation Color Code to Red. Forceful gas-and-steam emissions containing variable amounts of ash rose to 3.5-4 km (11,500-13,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E during 10-11 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 1-8 March. Strong gas-and-steam emissions containing variable amounts of ash rose to altitudes of 3.5-4 km (11,500-13,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted about 50 km E on 1 March. On 9 March explosions generated ash plumes that rose 10-11.2 km (32,800-36,700 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 70 km NW and N, prompting KVERT to raise the Aviation Color Code to Red (the highest level on a four-color scale). Early on 10 March the Aviation Color Code was lowered to Orange. Ash plumes continued to rise from the crater, to an altitude of 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l., and drift 375 km N. Later that day gas-and-steam plumes with some ash rose as high as 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 15 km NE. On 11 March an ash plume rose as high as 4.7 km (15,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 70 km SE.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch’s lava dome was identified daily in satellite images during 22 February-1 March. Strong gas-and-steam emissions contained variable amounts of ash on 21, 25, and 27 February, and rose 4-5 km (13,100-16,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 100 km SW and E. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 15-22 February Sheveluch’s lava dome continued to grow, extruding blocks on the N side, and producing hot avalanches and fumarolic plumes. A thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images daily. Video and satellite data recorded gas-and-steam plumes with variable ash content rising 4-5 km (13,100-16,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifting W and E. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 8-15 February Sheveluch’s lava dome continued to grow, extruding blocks on the N side, and producing hot avalanches and fumarolic plumes. A thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images daily. Video and satellite data recorded gas-and-steam plumes with variable ash content rising to 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifting in multiple directions. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 2-8 February Sheveluch’s lava dome continued grow, extruding blocks on the N side, and producing hot avalanches and fumarolic plumes. A thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images daily. Video and satellite data recorded gas-and-steam plumes with some ash content rising to 4-5 km (13,100-16,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 105 km E and W. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 25 January-1 February Sheveluch’s lava dome continued grow, extruding blocks on the N side, and producing hot avalanches and fumarolic plumes. Video and satellite data recorded gas-and-steam plumes with some ash content rising to 4-4.5 km (13,100-14,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 415 km E and W. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 7-8 and 11-13 December. A small explosion, recorded at 1222 on 12 December, generated an ash plume that rose 6.5-6.8 km (21,300-22,300 ft) a.s.l. That same day a gas-and-steam plume, containing a small amount of ash and drifting 150 km NE, was visible in satellite data. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images on 30 November, 1 December, and 3-4 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images on 23 November; weather clouds prevented views of the volcano during 24-30 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 16-17 and 19-20 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that explosions at Sheveluch on 9 November generated ash plumes that drifted as far as 460 km E. A weak thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 9-11 and 15 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite data on 2 and 6 November. Explosions at 1510 on 9 November generated ash plumes that rose to 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 5 km NE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite data during 31 October-2 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite data on 20, 22, and 25 October; weather clouds prevented views on the other days during 19-26 October. Moderate levels of gas-and-steam emissions rose from the volcano. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite data during 14-15 October; weather clouds prevented views on the other days during 12-19 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite data during 8-10 October; weather clouds prevented views on the other days during 5-12 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite data during 27-28 and 30 September; weather clouds prevented views on the other days during 29 September-5 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite data during 20, 23, and 27 September; weather clouds prevented views on the other days during 21-28 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite data during 14, 16-17, and 19-20 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite data during 7-8 and 12-13 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite data during 1-7 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite data during 25 and 28-30 August; cloudy weather prevented views of the volcano on the other days during 24-31 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that satellite images showed a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch on 17, 19, and 23 August; cloudy weather prevented views of the volcano on the other days during 17-24 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that satellite images showed a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch during 12-13 August; cloudy weather prevented views of the volcano on the other days during 10-17 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that satellite images showed a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch during 6-7 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that satellite images showed a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch during 27-29 July and 1-2 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that satellite images showed a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch during 19 and 21-22 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that satellite images showed a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch during 13-20 July, and a plume of re-suspended ash drifting 62 km SE on 18 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 6-13 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 4-5 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 23-29 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 16-17 and 19 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 13-14 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 5-6 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images on 31 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images on 19-20 and 23-24 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images on 28 and 11-16 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 10-14 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images on 28 and 30 April and 2 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 21 and 23-25 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 14-18 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 6 and 10-12 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 23-30 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 18-19 and 21-22 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 11-14 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images on 4 and 6-8 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a weak thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images on 26 February and 1 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 16, 18, and 20-21 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 9-11 and 15 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 1-4 and 7 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images on 1 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images on 19 and 23 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 12-19 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 5-12 January. Ash plumes from explosions which began at 1035 on 10 January rose to altitudes of 10-11 km (32,800-36,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted about 900 km E during 10-11 January. KVERT briefly raised the Aviation Color Code to Red on 10 January, and then lowered it back to Orange later that day.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 29 December 2017-5 January 2018. On 10 January satellite images captured an ash cloud, 192x132 km in dimension, from explosions rising to altitudes of 10-11 km (32,800-36,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifting 230 km NE. KVERT raised the Aviation Color Code to Red. Later that day satellite images showed an ash cloud 350x180 km in dimension drifting 400 km E; the Aviation Color Code was lowered back to Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 22-25 December. Explosions on 26 December generated ash plumes that rose as high as 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted about 300 km NE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 19-21 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 8, 11, and 13-14 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 2 and 4-6 December. A strong explosive event on 5 December generated ash plumes that rose as high as 10.5 km (34,500 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE. Ash plumes at 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. drifted E. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 24 November-1 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 17-18, 20, and 22 November; weather clouds prevented observations on the other days during 19-24 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images on 11 November; weather clouds prevented observations on the other days during 12-17 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images on 3, 6, and 8 November; weather clouds prevented observations on the other days during 4-10 November. Explosions on 8 November generated ash plumes that rose 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 990 km NE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 26-30 October and 1-2 November. Explosions on 2 November generated ash plumes that rose 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 20-22 and 25 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a plume comprised of re-suspended ash drifted about 230 km SE from the vicinity of the Sheveluch on 13 October. A thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 15-19 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during 9-11 October. Explosions on 10 October generated ash plumes that rose 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted about 250 km N. A plume comprised of re-suspended ash drifted about 350 km SE from the vicinity of the volcano on 12 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified daily in satellite images on 2 and 5 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified daily in satellite images during 22-29 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified daily in satellite images during 15-22 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified daily in satellite images during 8-15 September. Several explosive events during 8-13 September generated ash plumes that rose 9-10 km (29,500-32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted about 400 km NW, E, and SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified daily in satellite images during 2-3 and 6-7 September. Two explosive events on 7 September generated ash plumes that rose 8-10 km (26,200-32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE, SE, and S. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified daily in satellite images during 25 August-1 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified daily in satellite images during 18-25 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly was identified daily in satellite images over Sheveluch during 11-18 August. Ash plumes drifted about 180 km E, NW, and NE during 12 and 15-16 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly was identified daily in satellite images over Sheveluch during 4-11 August. Strong explosions on 8 August produced a large ash cloud (300 x 400 km in size) that rose as high as 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted more than 550 km SSE during 8-9 August. Ashfall was reported in Klyuchi Village (50 km SW) on 8 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly was identified daily during 28 July-4 August in satellite images over Sheveluch. Strong explosions on 4 August generated ash plumes that rose 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. and drifted ESE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly was identified daily during 21-28 July in satellite images over Sheveluch. Strong explosions on 23 July generated ash plumes that rose 11-12 km (36,100-39,400 ft) a.s.l. and during 23-24 July drifted 1,400 km E. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly was identified daily during 14-21 July in satellite images over Sheveluch. Based on video and satellite data explosive activity lasting about 8 hours on 24 July generated ash plumes that rose 11.5-12 km (37,700-39,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted almost 700 km NE. Strong pyroclastic flows were also observed. The Aviation Color Code was raised to Red (the highest level on a four-color scale). Later that day only steam-and-gas emissions with a small amount of ash were noted; the Aviation Color Code was reduced to Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly was identified daily in satellite images over Sheveluch during 7-11 July; cloud cover prevented views during 12-14 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly was identified daily in satellite images over Sheveluch during 1-7 July. Explosions on 2 July generated ash plumes that rose 10-11 km (32,800-36,100 ft) a.s.l.; one plume drifted 1,050 km SW and another drifted 350 km NE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly was identified daily in satellite images over Sheveluch during 23-30 June. Explosions on 27 June generated ash plumes that rose as high as 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 1,400 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly was identified daily in satellite images over Sheveluch during 16-23 June. Explosions on 17 June generated ash plumes that rose as high as 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 300 km E. Strong explosions the next day produced ash plumes that rose as high as 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 1,500 km ESE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 10-13 June explosions at Sheveluch produced ash plumes that rose as high as 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 1,500 km SE and NW. At 0425 on 15 June powerful explosions generated ash plumes that rose as high as 12 km (39,400 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code was raised to Red (the highest level on a four-color scale), and then back down to Orange at the end of the day. Ash plumes drifted 1,000 km NE and SW during 15-16 June. Ash fell in Klyuchi (50 km SW), Maiskoe, Kozyrevsk (115 km SW), and Atlasovo (160 km SW).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 3, 5, and 7-8 June powerful explosions at Sheveluch generated ash plumes that rose as high as 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 1,554 km SW, S, and SE. Pyroclastic flows traveled 10 km. Ashfall was reported in Klyuchi Village (50 km SW) on 8 June. A thermal anomaly was identified daily in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 26-27 and 31 May powerful explosions at Sheveluch generated ash plumes that rose 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 550 km ESE and about 650 km WSW. A thermal anomaly was identified in satellite images during 26 May-2 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 23-25 May powerful explosions at Sheveluch generated ash plumes that rose 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 715 km in different directions. At 0830 on 25 May explosions generated ash plumes that rose 9-10 km (29,500-32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 16 km NE. The Aviation Color Code (ACC) was raised to Red (the highest color on a four-color scale). Around 30 minutes later the ash plume was identified in satellite images drifting 45 km ENE. Strong steam-and-gas emissions rose from the lava dome. The ACC was lowered to Orange. Within the next hour the ash plume drifted 82 km E.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 13-14 May a series of explosions at Sheveluch generated ash plumes that rose 4.5-5 km (14,800-16,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SW and SE. Powerful explosions on 16 May generated ash plumes that rose as high as 11 km (36,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted about 150 km ENE. Pyroclastic flows descended the S flank. Two explosions were detected on 18 May. Ash plumes during 16-19 May drifted 400 km ENE. The Aviation Color Code (ACC) remained at Orange during 13-19 May, except for a few hours on 16 May when the strong explosions prompted KVERT to raise the ACC to Red.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported continuing lava-dome extrusion at Sheveluch’s N flank during 5-11 May. A daily thermal anomaly over the dome was identified in satellite images, and ash plumes drifted 90 km NNE and NW on 8 and 10 May. Strong explosions on 12 May generated ash plumes identified in satellite images that rose 9-10 km (29,500-32,800 ft) a.s.l., spread 70 km wide, and drifted 115 km NW. The Aviation Color Code was raised to Red. A few hours later satellite images showed a thermal anomaly and no ash emissions; the Aviation Color Code was lowered to Orange. Explosions on 16 May generated ash plumes that rose 8-9 km (26,200-29,500 ft) a.s.l., prompting KVERT to again raise the Aviation Color Code to Red. Pyroclastic flows descended the flanks and produced ash plumes that rose 3.5-4 km (11,500-13,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE. Within a few hours satellite images showed a thermal anomaly and no ash emissions; the Aviation Color Code was lowered to Orange. An ash cloud with the dimensions of 51 x 43 km was still visible in satellite images, moving E.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 28 April-5 May lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. A thermal anomaly at the dome was identified daily in satellite images. Ash plumes drifted more than 730 km SE, SW, and NW during 27 April-3 May; explosions on 30 April generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 9.1 km (30,000 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 21-28 April lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. A thermal anomaly over the dome was identified in satellite images daily. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 15-21 April lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a thermal anomaly over the dome during 13-17 April, and an ash plume that drifted 95 km E on 15 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 7-14 April lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome, and an ash plume that drifted 82 km SW on 10 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 1-6 April lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome, and ash plumes that drifted 20 km SE on 3 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 24-31 March lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome, and ash plumes that drifted 20 km SW on 24 and 26 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 17-24 March lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome, and ash plumes that drifted 126 km WNW on 19 and 21 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 10-17 March lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome, and ash plumes that drifted 100 km NW on 9 and 14 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 3-10 March lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome, and ash plumes that drifted NW 5 and 8-9 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 24 February-3 March lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Explosions on 24 February generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome, and ash plumes that drifted 95 km NE during 25-26 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 17-24 February lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome, and ash plumes that drifted 100 km NE on 18 February. Explosions on 20 February generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NW. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 10-17 February lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 3-10 February lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed an ash plume that drifted 112 km NW on 4 February and a thermal anomaly over the dome during 5 and 7-9 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 27 January-3 February lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 20-27 January lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 13-20 January lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 6-13 January lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 30 December 2016-6 January 2017 lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome, and ash plumes that drifted about 100 km N and NE on 30 and 31 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 23-30 December lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. Explosions recorded by a webcam on 24 December generated ash plumes that rose 6.5-7 km (21,300-23,000 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 10-16 December lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome, and ash plumes that drifted 370 km NNW during 16-20 December. A webcam recorded an explosion on 19 December with an ash plume that rose 7 km a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 10-16 December lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 2-9 December lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a thermal anomaly over the dome on clear days, and ash plumes drifting 60 km NW on 8 December.
On 10 December explosions generated ash plumes observed in satellite images that rose to altitudes of 10-11 km (32,800-36,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 320 km NNE and N. The Aviation Color Code was raised to Red. Satellite images later that day showed a thermal anomaly over the volcano but no ash emissions; the leading edge of the ash plume released earlier was 910 km NNE, drifting at an altitude of 11 km (36,000 ft). The Aviation Color Code was lowered to Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 25 November-2 December lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome and ash plumes drifting 375 km SE and S on 26 November and 1 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 18-25 November lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions with ash plumes as high as 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l., and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. Satellite and video data recorded ash plumes rising to altitudes of 6-6.5 km (19,700-21,300 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 130 km SW, E, and NE on 18, 20, 22, and 24 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 11-18 November lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions with ash plumes as high as 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l., and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome, and ash plumes that drifted as far as 170 km E on 12 and 15 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 4-11 November lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions with ash plumes as high as 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l., and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. According to video and satellite data, ash plumes drifted as far as 143 km E during 3-4 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 28 October-4 November lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, explosions with ash plumes as high as 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l., and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. According to video and satellite data, ash plumes drifted just over 300 km NE, E, and SE during 30-31 October, and 1 and 3 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 21-28 October lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions with ash plumes as high as 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l., and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. According to video and satellite data, ash plumes drifted just over 300 km E, N, and NW on 20, 22, and 26 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 14-21 October lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. According to video and satellite data, explosions generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 6-7 km (19,700-23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 210 km NW, E, and SE during 14-16, 18, and 20 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 7-14 October lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. According to video and satellite data, explosions generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 65 km N, NE, E, and SE during 10 and 12-13 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 30 September-7 October lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. Video and satellite data showed that during 2-3 and 5-6 October. Re-suspended ash formed a plume that drifted about 280 km E and SE during 3-4 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 23-30 September lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. Re-suspended ash formed a plume that drifted about 100 km SE and E during 28-29 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 16-23 September lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. A moderate explosion on 18 September caused dome collapse and 10-km-long pyroclastic flows. Pyroclastic-flow deposits were noted in the Baydarnaya River valley and in the central part of the S flank. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 9-16 September lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 2-9 September lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 26 August-2 September lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 19-26 August lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 12-19 August lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 5-12 August lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 29 July-5 August lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 22-29 July lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 15-22 July lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 8-15 July lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 1-8 July lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a thermal anomaly over the dome. On 4 July re-suspended ash from the vicinity of Sheveluch drifted 65 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 24 June-1 July lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 17-24 June lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed an intense thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 10-17 June lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed an intense thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 3-10 June lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed an intense thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 27 May-3 June lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed an intense thermal anomaly over the dome during 26-29 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 20-27 May lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed an intense daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 13-20 May lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed an intense daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 6-13 May lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed an intense daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 29 April-6 May lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed an intense daily thermal anomaly over the dome, and ash plumes drifting 36 km SE on 2 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 21-29 April lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed an intense daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 15-21 April lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed an intense daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 8-15 April lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed an intense daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 1-8 April lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed an intense daily thermal anomaly over the dome, and an ash plume that drifted 65 km SE on 2 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 25 March-1 April lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected an intense daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 18-25 March lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected an intense thermal anomaly over the dome almost every day; cloud cover obscured views of the volcano during 20-21 March. An ash plume drifted 38 km N on 23 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 11-18 March lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 4-11 March lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 26 February-4 March lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome. A gas-and-steam plume with minor amounts of ash drifted almost 55 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 19-26 February lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 12-19 February lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Explosions on 18 February generated ash plumes that drifted NE. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 5-12 February lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 29 January-5 February lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome. Ash plumes drifted about 60 km SW on 29 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 22-29 January lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 15-22 January lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 8-15 January lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Explosions on 9 January generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted W. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome, and ash plumes that drifted 200 km W during 9-10 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 1-8 January lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. A collapse from the W flank of the lava dome on 3 January produced a hot avalanche, and an ash plume that rose 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 25 December-1 January lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. A collapse from the W flank of the lava dome produced a hot avalanche, and an ash plume that rose 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 50 km SE. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 18-25 December lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome, and ash plumes from hot avalanches rose up to 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. that drifted SE on 21 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 11-18 December lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome, and ash plumes from hot avalanches that drifted 50 km SE on 15 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 4-11 December lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome, and ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 4-4.5 km (13,100-14,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 130 km on 4, 6, and 10 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 27 November-4 December lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 20-27 November lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily thermal anomaly over the dome and SE-drifting ash plumes during 22 and 25-26 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 13-20 November lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 6-13 November lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected an intense daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 30 October-6 November lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected an intense daily thermal anomaly over the dome. Explosions and hot avalanches generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. and drifted about 30 km SE on 3 and 5 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 23-30 October lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily and intense thermal anomaly over the dome. Explosions and hot avalanches generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 80 km E, NE, and NW during 23-24 and 28-29 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 9-16 October lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. An ash plume drifted 44 km SW on 9 Ocotber. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 2-9 October lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. Explosions and hot avalanches occurring during 2 and 7-8 October generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 2.5-5.5 km (8,200-18,000 km) a.s.l. and drifted 400 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 25 September-2 October lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. On 26 September a 30 x 15 km ash cloud generated by an avalanche rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 130 km SE. A strong explosion at 0959 on 4 October generated an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 18-25 September lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected an almost daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 11-18 September lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. Based on video and satellite data, re-suspended ash from strong winds drifted 185 km SE during 15-16 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 4-11 September lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected an almost daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 28 August-4 September lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected an almost daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 21-28 August lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected an almost daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 14-21 August lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 7-14 August lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 31 July-7 August lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 31 July, and 2-3 and 5-6 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 24-31 July lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 17-24 July lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 10-17 July lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches. Satellite images showed a thermal anomaly over the dome during 10-11, 14, and 16 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 3-10 July lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity. Satellite images showed a thermal anomaly over the dome during 2-4 July. Ash plumes that rose as high as 3.3 km (10,800 ft) a.s.l. were observed during 5-6 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 26 June-3 July lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity. Satellite images showed a thermal anomaly over the volcano during 25-28 and 30 June; weather clouds obscured the volcano on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 19-26 June lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity. Satellite images showed a thermal anomaly over the volcano during 23-24 June; weather clouds obscured the volcano on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 12-19 June lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity. Satellite images showed an ash plume drifting W at an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft ) a.s.l. on 15 June, and a thermal anomaly over the volcano during 15-17 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 5-12 June lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 29 May-5 June lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected in satellite images on 30 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 22-29 May lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected in satellite images on 23 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 15-22 May lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected in satellite images during 15-19 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 8-15 May lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was also detected in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 1-8 May lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was also detected in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 24 April-1 May lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was also detected in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 17-24 April lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected during 16-18 and 23 April; cloud cover obscured views on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 10-17 April lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Several ash plumes rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. Satellite images showed ash plumes drifting as far as 380 km E and SE during 9-11 and 13-16 April. A daily thermal anomaly was also detected. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 3-10 April lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Strong explosions on 3 and 7 April generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 9 and 12 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l., and drifted 100 km SE and more than 450 km NE, respectively. A daily thermal anomaly was also visible in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 27 March-3 April lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A strong explosion on 29 March generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted more than 155 km W. A daily thermal anomaly was also visible in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 20-27 March lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Strong explosions on 20, 22, and 25 March generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 7-10 km (23,000-32,800 ft) a.s.l. Ash plumes visible in satellite images drifted more than 600 km N, E, and SE during 20-22 and 25-26 March. A daily thermal anomaly was also visible in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 13-20 March lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Strong explosions on 16 March generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 9 km (29,500 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 200 km E; ashfall was reported in Ust-Kamchatsk Village, 85 km SE. A daily thermal anomaly was visible in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 6-13 March lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Strong explosions on 8 March generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 7-8 km (23,000-26,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 885 km E. A daily thermal anomaly was visible in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 27 February-6 March lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Strong explosions on 28 February and 3 March generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 9 km (29,500 ft) a.s.l. Ash fell in Ust-Kamchatsk, 85 km SE. Satellite images showed a daily thermal anomaly and ash plumes that drifted 600 km E and NE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 20-27 February lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Strong explosions during 20-21, 24, and 26 February generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 6-7 km (19,700-23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 580 km E and NE during 20-21 and 24-26 February. A thermal anomaly over the dome was detected daily. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. According to a news article ash caused a few flight cancellations in W Alaska on 28 February.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); CNN
KVERT reported that during 13-20 February lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Strong explosions on 16 and 17 February generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 180 km NW. A thermal anomaly over the dome was detected daily. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 6-13 February lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A strong explosion on 8 February generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 9-10 km (29,500-32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 180 km NW. A thermal anomaly over the dome was detected daily. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 30 January-6 February lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Strong explosions on 1 and 4 February generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 10 and 6 km (32,800 and 19,700 ft) a.s.l., respectively. Satellite images detected ash plumes drifting NE and N more than 800 km during 1-2 February and 90 km during 4-5 February. A thermal anomaly over the dome was detected daily. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 23-30 January lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Strong explosions on 21, 26, and 29 January generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 4-7.5 km (13,100-24,600 ft) a.s.l. Satellite images detected ash plumes drifting more than 500 km NW, NE, and E during 21-22, 26-27, and 29 January. A thermal anomaly over the dome was detected daily. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 16-23 January lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Strong explosions during 18-21 January generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 6-7 km (19,700-23,000 ft) a.s.l. Satellite images detected ash plumes drifting more than 118 km ENE on 18 January and more than 530 km NE during 21-22 January. A thermal anomaly over the dome was detected daily. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 9-16 January lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Strong explosions during 10-12 and 15 January generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 6-10 km (19,700-32,800 ft) a.s.l. Ashfall was reported in Klyuchi Village (50 km SW) on 12 January. Satellite images detected ash plumes drifting more than 200 km W and SW during 10-12 and 15-16 January, and a thermal anomaly over the dome daily. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 2-9 January lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A strong explosion on 7 January generated an ash plume that rose to altitudes of 8-9 km (26,200-29,500 ft) a.s.l. A small pyroclastic flow descended the SE flank of the dome. Satellite images detected an ash plume drifting 350 km NW on 7 January, and a thermal anomaly over the dome during 7-8 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 27 December-2 January lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Strong explosions on 26 and 29 December generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 6-9 km (19,700-29,500 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 60 km W and 370 km ENE respectively. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 27-30 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 19-26 December lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A strong explosion on 20 December generated an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 19-21 and 23-25 December, and ash plumes drifting 370 km E during 20-21 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 12-19 December lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A strong explosion on 17 December generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 9-10 km (29,500-32,800 ft) a.s.l. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 12, 14, and 16-18 December, and ash plumes that drifted 109 km SE during 14-15 December and 35 km ESE on 17 December. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 5-12 December lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Two strong explosions on 5 and 11 December generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 8-9 km (26,200-29,500 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 200 km ENE on 5 December and 364 km on 11 December. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 5 and 9-11 December; cloud cover prevented views of the volcano on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 27 November-4 December lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 28-29 November and 2 December; cloud cover prevented views of the volcano on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 21-27 November lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Strong explosions at 1021 on 23 November and 0328 on 26 November generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 8-9 km (26,200-29,500 ft) a.s.l and drifted 400 km NE and 200 km SE, respectively. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 22-23 and 26-27 November; cloud cover prevented views of the volcano on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 14-21 November lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A strong explosion at 2217 on 16 November generated a 30 x 10 km ash cloud that drifted 590 km SW. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 18-20 November; cloud cover prevented views of the volcano on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 7-14 November lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a weak thermal anomaly over the dome on 12 November; cloud cover prevented views of the volcano on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 31 October-7 November lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 1-3 November; cloud cover prevented views of the volcano on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 24-31 October lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 27 and 29-30 October; cloud cover prevented views of the volcano on the other days. Strong explosions on 28 and 30 October generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 11 km (36,000 ft) a.s.l. and 7-8 km (23,000-26,200 ft) a.s.l., respectively. Ash plumes on those two days drifted more than 500 km NE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 17-24 October lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 17, 20, and 22 October; cloud cover prevented views of the volcano on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 10-17 October lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 10-11 and 15 October; cloud cover prevented views of the volcano on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 3-10 October lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 3 and 8-9 October; cloud cover prevented views of the volcano on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 26 September-3 October lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s N flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 27-29 September and 2 October. Two explosions on 2 October generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 220 km WSW. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 19-26 September lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s N flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 18 and 22-25 September. Strong explosions that began at 1238 on 24 September generated ash plumes that rose 11-11.5 km (36,000-37,700 ft) a.s.l. A large ash cloud, 250 by 207 km, drifted NNE. The Aviation Color Code was raised to Red and then lowered back to Orange that same day as the explosive activity subsided.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 12-19 September lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s N flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a daily thermal anomaly over the dome. On 14 September a video camera recorded a short-duration explosion which produced an ash plume that rose 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l.; strong gas-and-steam activity was noted afterwards. On 24 September explosions generated ash plumes that rose 11 km (36,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted N. Ash plumes also drifted E at an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code was raised to Red.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the explosive and effusive eruption of Shiveluch continued and maintained Alert Level Orange during the week of 12 September. Activity was dominated by lava dome growth on the SE flank, moderate ash explosions, fumarolic activity, and hot avalanches. Satellite data showed a persistent thermal anomaly from the dome region during 4-5, 7 and 11 September. Remobilized ash was observed in a dust plume on 11 September that rose 1-2 km (3,280-6,562 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the explosive and effusive eruption of Shiveluch continued and maintained Alert Level Orange during the week of 5 September. Activity was dominated by lava dome growth on the SE flank, moderate ash explosions, fumarolic activity, and hot avalanches. Satellite data showed a persistent thermal anomaly from the dome region.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 22-28 August lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by moderate ash explosions, incandescence of the dome summit, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite data showed a thermal anomaly over the lava dome on 24-28 August. The volcano was obscured by clouds the other days of week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 15-21 August lava-dome extrusion onto Sheveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by moderate ash explosions, incandescence of the dome summit, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite data showed a thermal anomaly over the lava dome on 18-19 August. The volcano was obscured by clouds the other days of week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 8-14 August lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by moderate ash explosions, incandescence of the dome summit, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. On 11-14 August satellite data showed a thermal anomaly over the lava dome, and the volcano was obscured by clouds the other days of week. On 9 August the Tokyo VAAC reported an ash plume rose to 4.6 km (15,000 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 1-7 August lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by moderate ash explosions, incandescence of the dome summit, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite data showed a thermal anomaly over the lava dome on 7 August and the volcano was obscured by clouds in the other days of week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 25 July-1 August lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by moderate ash explosions, incandescence of the dome summit, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images were obscured by clouds over the past week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 19-26 July lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by moderate ash explosions, incandescence of the dome summit, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite data showed a thermal anomaly over the volcano, but satellite images were obscured by clouds or showed the volcano was quiet over the past week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 11-18 July lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by moderate ash explosions, incandescence of the dome summit, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite data showed a thermal anomaly over the volcano on 16-17 July. An eruption was reported to 8.2 km (27,000 ft) a.s.l. on 18 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 3-10 July lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Ash plumes rose to 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. on 30 June and 11 km (36,000 ft) a.s.l. during 5-8 July. During 7-8 July, satellite images detected ash plumes extending 280 km SE of the volcano. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 20-27 June lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome on 22 and 25 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 14-19 June lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly and an ash plume drifting 70 km SW during 15-18 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 6-13 June lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly and an ash plume drifting 70 km SW during 7-8 and 12 June. Ashfall in Klyuchi (50 km SW) was reported on 11 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 30 May-6 June lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome on 31 May and 1 and 3 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 23-30 May lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. An explosion on 26 May generated an ash plume that rose as high as 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 800 km SSE. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome during 23-25 and 27-28 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 16-23 May lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly over the dome on 16 and 19 May. Satellite images on 27 May showed ash plumes rising to altitudes of 3-10 km (9,800-32,800 ft) and drifted as far as 850 km S. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 9-16 May lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images showed a bright thermal anomaly daily. Satellite images detected daily thermal anomalies. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 2-8 May lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images showed a bright thermal anomaly daily. Video images showed ash plumes rising to altitudes of 7-9.5 km (23,000-31,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifting 60 km NW at 1150 on 13 May. Later that day, at 1300, satellite images detected an ash plume that rose to altitudes of 5-8 km (16,400-26,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 90 km NW. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 25 April-2 May lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images showed a bright thermal anomaly daily. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 18-25 April lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images showed a bright thermal anomaly daily. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 4-11 April lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images showed a bright thermal anomaly daily, and ash plumes that drifted SE at an altitude of 4 km (13,000 ft) a.s.l. during 16-17 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 4-11 April lava-dome extrusion onto Shiveluch’s SE flank was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A bright thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 28 March-4 April lava-dome extrusion at Shiveluch was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A bright thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 21-28 March lava-dome extrusion at Shiveluch was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A bright thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 14-21 March lava-dome extrusion at Shiveluch was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A bright thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 7-14 March lava-dome extrusion at Shiveluch was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A bright thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 28 February-7 March lava-dome extrusion at Shiveluch was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A bright thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 21-28 February lava-dome extrusion at Shiveluch was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, hot avalanches, and fumarolic activity. A bright thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images, and a gas-and-steam plume containing small amounts of ash drifted 135 km SE on 25 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 14-21 February lava-dome extrusion at Shiveluch was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. On 19 February a gas-and-steam plume containing small amounts of ash rose to an altitude of 3 km (10,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted about 50 km SSE. On 25 February satellite images detected ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 4-4.5 km (13,100-14,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 7-14 February lava-dome extrusion at Shiveluch was accompanied by ash explosions, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected in satellite images on 9 and 12 February; cloud cover prevented views on the other days. Pyroclastic flow deposits on the SW flank from the 6 February were observed to be 12 km long. On 17 February at 1108 video data showed an ash plume rising to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 31 January-7 February a newer lava dome continued to extrude onto the NW part of Shiveluch's older lava dome. Lava-dome extrusion was accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected in satellite images during 3-4 February. Based on interpretation of seismic data, a large explosion that started at 1245 on 6 February and ended at 0440 on 7 February generated an ash plume that rose to altitudes of 9-10 km (29,500-32,800) a.s.l. A satellite image acquired at 0705 on 7 February showed a large ash cloud (240 x 180 km) over the Sea of Okhotsk 320 km WNW at an altitude of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 24-31 January a newer lava dome continued to extrude onto the NW part of Shiveluch's older lava dome. Lava-dome extrusion was accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images, and ash plumes rose to altitudes of 7-8 km (23,000-26,200 ft) a.s.l. on 23 January and drifted N. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 17-24 January a newer lava dome continued to extrude onto the NW part of Shiveluch's older lava dome. Lava-dome extrusion was accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Moderate ash explosions generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400) a.s.l. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images, and ash plumes rose to altitudes of 7-8 km (23,000-26,200 ft) a.s.l. during 20-21 January and drifted 300 km WNW during 20-22 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 10-17 January a newer lava dome continued to extrude onto the NW part of Shiveluch's older lava dome. Lava-dome extrusion was accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Moderate ash explosions generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400) a.s.l. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images, and ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700) a.s.l. drifted 110 km ENE on 10 January. Explosions on 12 January generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 8-9 km (26,200-29,500 ft) a.s.l., and drifted 400 km SW during 12-13 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 3-10 January a newer lava dome continued to extrude onto the NW part of Shiveluch's older lava dome. Lava-dome extrusion was accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Moderate ash explosions generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400) a.s.l. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images, and ash plumes drifted 360 km SW and 278 km WNW on 7 and 9 January, respectively. On 12 January strong explosions generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 7-8 km (23,000-26,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted ESE. The next day a video camera recorded an ash plume from an explosion that again rose to altitudes of 7-8 km (23,000-26,200 ft) a.s.l. The ash plume drifted 50 km WSW. According to a news report minor amounts of ash fell in Klyuchi Village, 50 km SW. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); RIA Novosti
KVERT reported that during 27 December 2013-2 January 2014 a newer lava dome extruded onto the NW part of Shiveluch's older lava dome. Lava-dome extrusion was accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Moderate ash explosions generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400) a.s.l. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 20-27 December a newer lava dome extruded onto the NW part of Shiveluch's older lava dome. Lava-dome extrusion was accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Moderate ash explosions generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400) a.s.l. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 13-20 December a new lava dome extruded onto the NW part of Shiveluch's older lava dome. Moderate explosions generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400) a.s.l. Lava-dome extrusion was accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. Several strong explosions on 17 December generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 5.5-6 km (18,000-19,700 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 6-13 December a new lava dome extruded onto the NW part of Shiveluch's older lava dome. Moderate ash explosions generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400) a.s.l. Lava-dome extrusion was accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. On 17 December satellite images showed an ash plume drifting 50 km NW at altitudes of 4.5-5 km (14,800-16,400 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 29 November-6 December a new lava dome extruded onto the NW part of Shiveluch's older lava dome. Moderate ash explosions generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400) a.s.l. Lava-dome extrusion was accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 22-29 November a new lava dome extruded onto the NW part of Shiveluch's older lava dome. Moderate ash explosions generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400) a.s.l. Lava-dome extrusion was accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. On 3 December activity increased and hot avalanches occurred continuously. Video data showed ash plumes rising to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400) a.s.l. and drifting 20 km NW. A strong explosive event began at 1325 and generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 8-9 km (26,200-29,500 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NW. Pyroclastic flows descended the SW and NW flanks. The Aviation Color Code was raised to Red. Later that day KVERT noted that the strong explosive phase had ended; the Aviation Color Code was lowered back to Orange. An ash plume observed in satellite images was 200 km long and extended N. Ashfall was reported in Ivashka Village.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 15-22 November a viscous lava flow effused onto the N and NE flanks of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, ash explosions, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. Explosions generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 8-15 November several strong explosions from Shiveluch generated ash plumes that rose to a maximum altitude of 7 km (24,600 ft) a.s.l. Viscous lava continued to effuse onto the N and NE flanks of the lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, ash explosions, and fumarolic activity. A daily thermal anomaly was detected in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 1-8 November several strong explosions from Shiveluch generated ash plumes that rose to an maximum altitude of 7 km (24,600 ft) a.s.l. Ash plumes drifted more than 290 km SE. Viscous lava continued to effuse onto the N and NE flanks of the lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, ash explosions, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the current eruption continued through the week and included several strong ash eruptions that sent plumes to altitudes of 7-10 km (~22,000-33,000 ft) and drifted more than 200 km to the NE. Visual and satellite observations determined that lava extrusion continued on the NE and N flanks of the lava dome. This viscous block lava generated moderate ash explosions; fumarolic activity, hot avalanches, and incandescence at the summit also continued. A thermal anomaly was detected in daily satellite images.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 19-25 October a viscous lava flow effused onto the N and NE flanks of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, ash explosions, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 11-18 October a viscous lava flow effused onto the N and NE flanks of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, ash explosions, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images.
At 1528 on 18 October video data showed ash plumes rising to altitudes of 9-10 km (29,500-32,800 ft) a.s.l. Several explosions during 1506-1528 generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE. The Aviation Color Code was raised to Red. Video images showed ash plumes rising to 6-7 km (19,700-23,000 ft) a.s.l. at 1634, to altitudes of 7-7.5 km (23,000-24,600 ft) a.s.l. at 1708 and 1722, and to altitudes of 9 km (29,500 ft) a.s.l. at 1753 and 1759. KVERT announced that the Aviation Color Code was lowered to Orange at 2038. Continuous ash emissions produced plumes that rose 3-3.5 km (9,800-11.500 ft) a.s.l. and drifted S. The lava dome continued to grow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 13-20 September a viscous lava flow effused onto the N and NW flanks of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, ash explosions, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected in satellite images during 15-16 September; clouds obscured views on the other days. Video data showed that at 1454 on 20 September an ash plume rose to altitudes of 5-5.5 km (16,400-18,000) a.s.l. and drifted 20 km NE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 6-13 September a viscous lava flow effused onto the N and NW flanks of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. At 1128 on 12 September video data showed an ash plume that rose to altitudes of 5-5.5 km (16,400-18,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 30 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 30 August-6 September a viscous lava flow effused onto the N and NW flanks of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 23-30 August a viscous lava flow effused onto the N and NW flanks of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. A thermal anomaly was detected daily in satellite images. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 16-23 August a viscous lava flow effused onto the N and NW flanks of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Explosions generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 3.5-4.5 km (11,500-14,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E and NE. A thermal anomaly was detected in satellite images during 16-18 and 20-23 August; cloud cover obscured views on 19 August. On 27 August video images showed an ash plume rising 3.5-4 km (11,500-13,100 ft) a.sl. and drifting 30 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 9-17 August a viscous lava flow effused onto the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly during 9-12, 14, and 16-17 August; cloud cover prevented observations on the other days. Explosions generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 5-7 km (16,400-23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E and NE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 2-9 August a viscous lava flow effused on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a thermal anomaly during 3-6, 8, and 10-11 August. Explosions during 4-5 August generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 5-7 km (16,400-23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SSE. A video camera recorded ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 7-7.5 km (23,000-24,600 ft) a.s.l. during 10-11 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 26 July-2 August a viscous lava flow effused on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a daily thermal anomaly.
A strong explosion at 2255 on 26 July generated ash plumes that rose as high as 10 km (23,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 520 km SE. Pyroclastic flows traveled 5 km. An ash cloud 15 x 7 km was observed in satellite images about 60 km SE of the volcano on 29 July. At 1707 on 4 August video images showed an ash plume rising to altitudes of 4.5-5 km (14,800-16,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifting 50 km E. The next day the seismic network detected an explosion at 1604; video images showed an ash plume rising to altitudes of 6.5-7 km (21,300-23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifting 50 km ESE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 19-26 July a viscous lava flow effused on the N flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite images detected a daily thermal anomaly. Based on analyses of satellite images, the Tokyo VAAC reported a possible eruption on 27 July. Ash was detected in images the next day. The VAAC also noted that, according to the Kamchatka Branch of Geophysical Services (KBGS; Russian Academy of Sciences), ash plumes rose to altitudes of 6.1-6.4 km (20,000-21,000 ft) a.s.l. on 27 and 29 July. KVERT reported that at 1317 on 29 July an explosion was observed by a web camera. An ash cloud detected in satellite images rose to an altitude of 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 60 km ESE; the cloud was 15 km long and 7 km wide. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 12-19 July a viscous lava flow effused on the N flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Based on notices from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP), the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 15 July an ash plume rose to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E. KVERT noted that satellite images detected a thermal anomaly on 15, 17, and 18 July; cloud cover prevented observations on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 5-12 July a viscous lava flow effused on the N flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Ash plumes as high as 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. were observed during 5-6 July. Satellite images detected a daily thermal anomaly. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 28 June-5 July a viscous lava flow effused on the N flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Ash plumes as high as 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. were observed during 27-28 June and 3 July. Satellite images detected a daily thermal anomaly, and ash plumes that drifted 35 km SE on 3 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 21-28 June a viscous lava flow effused on the N flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity.
The seismic network detected a strong explosive eruption that occurred on 27 June from 0710 to 0800. The Aviation Color Code was raised to Red. Ash plumes drifted SE and SW, likely at altitudes of 10-12 km (33,000-39,400 ft) a.s.l. About 2 mm of red ash fell in Klyuchi Village, 50 km SW; ashfall was also reported in Lazo Village. Later that day the Alert Level was lowered back to Orange. Two ash explosions that occurred on 28 June at 0506 and 1001 produced ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 7 and 6 km (23,000 and 19,700 ft) a.s.l., respectively.
Based on analyses of satellite imagery, notices from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP), and the Kamchatka Branch of Geophysical Services (KBGS; Russian Academy of Sciences), the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 29-30 June an ash plume rose to an altitude of 5.5-6.4 km (18,000-21,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E and SE.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 14-21 June a viscous lava flow effused on the N flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. On 22 June an explosion was detected by the seismic network at 1246 and lasted about four minutes. A second explosion at 1310 produced an ash plume observed with the web camera that rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NW. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 7-14 June a viscous lava flow effused on the N flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. Based on notices from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP), the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 14 and 16 June ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 31 May-7 June a viscous lava flow effused on the N flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. On 10 June the seismic network detected an explosive event at 0902 that lasted 6.5 minutes, and indicated that an ash plume possibly rose to altitudes of 7-8 km (23,000-26,200 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 24-31 May a viscous lava flow effused on the N flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 17-24 May a viscous lava flow effused on the N flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 10-16 May a viscous lava flow effused on the N flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on analyses of satellite imagery and notices from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP), the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 18 May ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 3-10 May a viscous lava flow effused on the NW and NE flanks of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 26 April-3 May a viscous lava flow effused on the NW and NE flanks of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on analyses of satellite imagery and notices from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP), the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 5 May an ash plume rose to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 19-26 April a viscous lava flow effused on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 12-19 April a viscous lava flow effused on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. Based on analyses of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 22 April ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.7 km (12,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE. Subsequent images that day showed that the ash had dissipated. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 5-12 April a viscous lava flow effused on the E flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 29 March-5 April a viscous lava flow effused on the E flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. An explosion on 5 April observed by video generated an ash plume that rose to altitudes of 5.5-6 km (16,400-19,700 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 22-29 March a viscous lava flow effused on the E flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 15-22 March a viscous lava flow effused on the E flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 8-15 March a viscous lava flow effused on the E flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 28 February-7 March a viscous lava flow effused on the E flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. A single explosion on 4 March produced an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. Collapses of hot material on 6 March generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 200 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 22 February-2 March a viscous lava flow effused on the E flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. Based on video images, KVERT reported that explosions produced a gas-and-ash plume that rose to an altitude of 9 km (29,500 ft) a.s.l. on 4 March, and an ash plume rose 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 20 km SE on 6 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 15-22 February a viscous lava flow effused on the E flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 8-15 February a viscous lava flow effused on the E flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 1-8 February a viscous lava flow effused on the E flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 25 January-1 February a viscous lava flow effused on the E flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 18-25 January a viscous lava flow effused on the E flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 11-18 January a viscous lava flow effused on the E flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 4-11 January a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 28 December-4 January a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 21-28 December a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 14-21 December a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 7-14 December a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 30 November-7 December a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 29 November and 3-6 December; cloud cover obscured views on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 23-30 November a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 23-26 and 29 November; cloud cover obscured views on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 16-23 November a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 17-18 and 20-22 November; cloud cover obscured views on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 9-16 November a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 2-9 November a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. During 10-12 November weak seismicity was registered and satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly. Video images recorded gas-and-steam activity, which contained ash on 12 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on analyses of satellite imagery and notices from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP), the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 12 November ash plumes rose to altitudes of 3-4.3 km (10,000-14,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted S.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 26 October-2 November a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 19-26 October a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 20-23 October; clouds prevented views on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 12-19 October a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 12-16 October; clouds prevented views on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 5-12 October a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed ash plumes drifting 360 km SE during 4-6 October, and a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 5-7 October. A plume detected by the seismic network and observed rose to altitudes of 6-7 km (19,700-23,000 ft) a.s.l. on 6 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 28 September-5 October a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome on 28 September and during 1-3 October. Based on analyses of satellite imagery, notices from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP), and information from KVERT, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 5 October ash plumes rose to an altitude of 2.1 km (7,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE. The next day ash plumes rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l and again drifted SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 21-28 September a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome on 21, 23, and 27 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 14-21 September a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, and was accompanied by hot avalanches and fumarolic activity. A strong explosion on 18 September generated an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 8 km (26,300 ft) a.s.l. An ash plume rose to an altitude of 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. on 20 September. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome on 14 and 19 September, and an ash plume drifting 2,000 km SE during 17-20 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 7-14 September a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NW flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, and was accompanied by hot avalanches and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly over the lava dome on 9, 11, and 13 September; cloud cover prevented observations on the other days, and during 15-16 September. Seismicity increased on 18 September. At 1119 observers noted that an ash plume rose to an altitude of 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 137 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that during 31 August-7 September a viscous lava flow continued to effuse on the NE flank of Shiveluch's lava dome, and was accompanied by hot avalanches and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly over the lava dome during 31 August and 4-5 September; cloud cover prevented observations on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 24-31 August a viscous lava flow was active on the NE flank of Shiveluch's lava dome and was accompanied by hot avalanches. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly over the lava dome during 24-26 August; cloud cover prevented observations on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 17-24 August a viscous lava flow was active on the NE flank of Shiveluch's lava dome and was accompanied by hot avalanches. The summit of the dome was incandescent; satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly over the area during 17-24 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 10-18 August weak seismic activity was detected at Shiveluch. Observers noted gas-and-steam activity during 15-17 August; weather conditions prevented observations of the volcano on the other days. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 10, 12-13, and 18-19 August. Seismic activity increased to moderate levels and hot avalanches were observed during 19-20 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 3-10 August weak seismic activity was detected at Shiveluch. Cloud cover prevented ground-based observations; however, a thermal anomaly on the volcano was detected daily in satellite imagery. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 27 July-6 August explosive activity was detected at Shiveluch; a strong explosion detected on 27 July possibly produced an ash plume that rose 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. Observers noted gas-and-steam activity during 28-29 and 21 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 20-29 July explosive activity was detected at Shiveluch and observers noted gas-and-steam activity. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 20, 22-26, and 28-29 July. Based on information from KEMSD and analyses of satellite images, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 27 July an eruption produced an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 10.1 km (33,000 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 13-21 July explosive activity at Shiveluch continued. Observers noted gas-and-steam activity during 12-13, 15-18, 21, and 23 July; weather conditions prevented observations of the volcano on the other days. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 13-20 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 6-13 July explosive activity at Shiveluch continued and seismic data indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,700 ft) a.s.l. Observers noted gas-and-steam activity on 11 and 16 July; weather conditions prevented observations of the volcano on the other days. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 7-12 and 14-16 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 29 June-6 July explosive activity at Shiveluch continued and seismic data indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.7 km (15,400 ft) a.s.l. Observers noted ash plumes rising to an altitude of 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. on 29 June; weather conditions prevented observations of the volcano on the other days. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 28-30 June and 7-10 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 22-29 June explosive activity at Shiveluch continued and seismic data indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 9.5 km (31,100 ft) a.s.l. Observers indicated strong gas-and-steam activity on 22 June and noted ash plumes rising to an altitude of 5.3 km (17,400 ft) a.s.l. during 24-26 June. Weather conditions prevented observations of the volcano on the other days. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome, and gas-and-steam plumes that drifted 152 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 15-22 June explosive activity at Shiveluch continued. Visual observations revealed strong gas-and-steam activity on 15, 17, and 21 June; weather conditions prevented observations on the other days. A thermal anomaly on the lava dome was detected in satellite imagery during 15-17, 21, and 24 June. On 24 June video data showed ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 5.3 km (17,400 ft) a.s.l. Based on information from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP) and KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that ash plumes rose to altitudes of 5.2-9.8 km (17,000-32,000 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 8-15 June explosive activity at Shiveluch continued. During 11-13 June a thermal anomaly on the lava dome was detected in satellite imagery and ground-based observers noted strong gas-and-steam activity. Seismic data indicated that a possible ash plume rose to an altitude of 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. Meteorological cloud cover prevented observations of the volcano on the other days. Based on analyses of seismic data and information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption on 15 June produced an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 8.2 km (27,000 ft) a.s.l. Ash was not detected in satellite images. Based on analysis of seismic data, KVERT reported that on 18 June possible ash plumes rose to altitudes of 3.4-4 km (11,200-13,100 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 1-8 June explosive activity at Shiveluch continued. Ground-based observers and satellite imagery indicated that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the active crater, accompanied by fumarolic activity. Observers noted that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 8.5 km (28,000 ft) a.s.l. on 2 June. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly over the lava dome during 31 May and 1-4 June, and ash plumes drifting 152 km S and 250 km S and ENE during 2-3 June. Seismic data indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. on 5 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on analyses of seismic data, the Tokyo VAAC reported that a possible eruption on 6 June produced an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 8.2 km (27,000 ft) a.s.l. Ash was not detected in satellite images.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 25 May-1 June explosive activity at Shiveluch continued. Ground-based observers and satellite imagery indicated that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the active crater, and was accompanied by fumarolic activity and lava-dome incandescence. Observers noted that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 9 km (29,500 ft) a.s.l. on 25 and 27 May, and to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. during 29-30 May. Satellite imagery showed ash plumes drifting 555 km SW, SE, and E during 25-30 May, and a thermal anomaly over the lava dome during 26-29 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on analyses of satellite images, the Tokyo VAAC reported that a possible eruption on 2 June produced an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 9.1 km (30,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted S. Subsequent images during 2-3 June showed ash.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 18-25 May explosive activity at Shiveluch continued and a thermal anomaly was observed daily in satellite imagery. Ground-based observers and satellite imagery indicated that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the active crater, and was accompanied by fumarolic activity and lava-dome incandescence. On 19 May seismic data indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 9.5 km (31,200 ft) a.s.l. On 20 May observers noted ash plumes rising to altitudes of 8-9 km (26,200-29,500 ft) a.s.l.; satellite images showed ash plumes drifting 410 km SW. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KVERT and KEMSD, and analyses of satellite images, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 26-29 May ash plumes from eruptions and possible eruptions rose to altitudes of 7-9.1 km (23,000-30,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE, W, and SW.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that explosive activity at Shiveluch continued during 11-18 May. Ground-based observers and satellite imagery indicated that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the active crater, and was accompanied by fumarolic activity and lava-dome incandescence. Satellite imagery during 10-12 and 15-16 May showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome. On 12 May observers reported that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. and satellite imagery showed an ash plume drifting more than 800 km E.
Based on information from KVERT and analyses of satellite images, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 20 May an ash plume rose to an altitude of 9.1 km (30,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SW. Images the next day showed that the ash had dissipated.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that explosive activity at Shiveluch continued during 4-11 May. Ground-based observers and satellite imagery indicated that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the active crater and was accompanied by fumarolic activity. Seismic data and visual observations showed that ash plumes rose to altitudes of 10 and 5 km (32,800 and 16,400 ft) a.s.l. on 5 May and during 6-8 May, respectively. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 4-5 and 8-10 May. Ash plumes drifted 800 km SE on 5 May, and an ash cloud 95 km SE of the volcano was observed on 7 May.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that explosive activity at Shiveluch continued during 27 April-4 May. Ground-based observers and satellite imagery indicated that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption and was accompanied by fumarolic activity. Seismic data and visual observations showed that ash plumes rose to altitudes of 4 and 5.4 km (13,200 and 17,800 ft) a.s.l. on 26 April and 1 May, respectively. Satellite imagery showed a weak thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 28-29 April and on 1 and 3 May. Explosions on 1 May produced ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l.; an ash cloud was observed in satellite imagery drifting 270 km NE that same day.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that explosive activity at Shiveluch continued during 20-27 April. Ground-based observers and satellite imagery indicated that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption and was accompanied by fumarolic activity. Seismic data and visual observations showed that ash plumes rose to an altitude greater than 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. on 24 April and were slight on the other days. Satellite imagery showed a weak thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 20-22 April, and ash plumes that drifted 396 km NE on 24 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that explosive activity at Shiveluch continued during 13-20 April. Ground-based observers and satellite imagery indicated that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption and was accompanied by fumarolic activity. Observers reported that ash plumes rose to altitudes of 6.5-7.5 km (21,300-24,600 ft) a.s.l. during 16-17 April and to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400 ft) a.s.l. on the other days. Satellite imagery showed a weak thermal anomaly daily on the lava dome, and ash plumes that drifted 120 km N, NE, and E during 14-15 and 17-18 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that explosive activity at Shiveluch continued during 7-13 April. Ground-based observers and satellite imagery indicated that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption. Satellite imagery showed a weak thermal anomaly daily on the lava dome, and ash plumes that drifted 210 km SW and SE on 6, 8, and 11 April. Seismic data indicated that ash plumes potentially rose to an altitude of 7.7 km (25,000 ft) a.s.l. during 7-8 and 10-12 April, and to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. on the other days. Observers confirmed that an ash plume rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. on 8 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that explosive activity at Shiveluch continued during 29 March-6 April. Ground-based observers and satellite imagery indicated that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption. Visual observations revealed that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. on 30 March and 3 April. Seismic data indicated that ash plumes potentially rose to an altitude of 6.6 km (21,600 ft) a.s.l. every day. Satellite imagery showed a weak thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 29-31 March and 3 April, and ash plumes that drifted 114 km W, E, and NE during 29-30 March and 3 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that explosive activity at Shiveluch continued during 23-30 March. Ground-based observers and satellite imagery indicated that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption. During 25-26 and 28 March ash plumes rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery showed a weak thermal anomaly daily on the volcano and ash plumes that drifted 192 km E and SE during 25-28 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that explosive activity at Shiveluch continued during 16-23 March. Ground-based observers and satellite imagery indicated that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption. During 15-21 March ash plumes rose to altitudes of 5-6 km (16,400-19,700 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery showed plumes drifting 194 km E and SE during 16-18 March and a weak thermal anomaly on the volcano during 16-18 and 20 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that activity at Shiveluch increased on 10 March and during 10-14 March daily explosions produced ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 3-5 km (10,000-16,400 ft) a.s.l. During 10-16 March ground-based observers and satellite imagery indicated that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the volcano and ash plumes that drifted 64 km NE and SE during 10-11 and 13 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP) and satellite images, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an ash plume rose to an altitude of 5.2 km (17,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was low during 2-9 March. Ground-based observers and satellite imagery indicated that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption. Moderate fumarolic activity at the lava dome was observed during 2 and 5-8 March; cloud cover prevented observations on the other days. Satellite imagery showed a weak thermal anomaly over the lava dome during 3, 5, and 7-8 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KVERT, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 10 March an ash plume rose to an altitude of 5.2 km (17,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE. Yelizovo Airport (UHPP) reported that an ash plume rose to an altitude of 2.1 km (7,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SW.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was low during 23 February-2 March. Ground-based observers and satellite imagery indicated that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption. Seismic activity increased on 28 February and hot avalanches likely occurred at the lava dome. Satellite imagery showed a weak thermal anomaly over the lava dome during 23-26 February. Moderate fumarolic activity at the lava dome was observed during 1-2 March; cloud cover prevented observations on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 17-24 February low levels of seismic activity were detected at Shiveluch and satellite imagery showed a weak thermal anomaly. According to visual and satellite observations, a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater that was formed during a 2010 eruption. Moderate fumarolic activity at the lava dome was observed during 19-23 February; clouds prevented observations on the other days of the week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that low levels of seismic activity were detected at Shiveluch during 10-17 February. Satellite imagery showed a weak thermal anomaly during 10-11 and 15-16 February. Ground-based observers noted that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater that was formed during a 2010 eruption. Moderate fumarolic activity at the lava dome was observed on 14 February; clouds prevented observations on the other days of the week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that low levels of seismic activity were detected at Shiveluch 3-10 February. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Ground-based observers noted that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater that was formed during a 2010 eruption. Moderate fumarolic activity at the lava dome and occasional hot avalanches were observed all week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that low levels of seismic activity were detected at Shiveluch during 26 January-3 February. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Ground-based observers noted that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater that was formed during a 2010 eruption. Moderate fumarolic activity at the lava dome and occasional hot avalanches were observed all week. Weak ash explosions from the lava dome were reported from the SE flank on 26 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that mostly low levels of seismic activity were detected at Shiveluch during 20-27 January, though seismicity was higher during 22-23 January. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Ground-based observers noted that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater that was formed during a 2010 eruption. Moderate fumarolic activity at the lava dome and occasional hot avalanches were observed during 25-26 January; clouds prevented observations on the other days of the week. Ash plumes rose to altitudes of 5-6 km (16,400-19,700 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 174 km NE on 23 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that low levels of seismic activity were detected at Shiveluch during 13-20 January, and on 14 January ash plumes were observed. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly over the lava dome every day except on 16 January. Ground-based observers noted that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater that was formed during a 2010 eruption and hot avalanches from the lava flow were occasionally observed at night with a web camera. Moderate fumarolic activity at the lava dome was observed during 13-14 and 17-18 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on satellite observations, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 22 January a possible eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NW; subsequent satellite images showed that ash was present. Based on information from satellite images and KVERT, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.2 km (17,000 ft) a.s.l. on 23 January and dissipated the next day.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that low levels of seismic activity were detected at Shiveluch during 6-13 January. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Ground-based observers noted that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater that was formed during a 2010 eruption and hot avalanches from the lava flow were observed at night with a web camera. Moderate fumarolic activity at the lava dome was observed all week except on 10 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity was detected at Shiveluch during 30 December-6 January. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Ground-based observers noted that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater that was formed during a 2010 eruption. Moderate fumarolic activity at the lava dome was observed during 30-31 December and on 2 and 4 January; clouds prevented observations on the other days of the week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity was detected at Shiveluch during 23-30 December. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome and gas-and-steam plumes drifting 30 km N and SE on 24 and 27 December, respectively. Ground-based observers noted that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption. Moderate fumarolic activity at the lava dome was observed during 22-24 December; clouds prevented observations on the other days of the week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity from Shiveluch was detected during 16-23 December and a large thermal anomaly over the volcano was observed in satellite imagery. Seismic data suggested that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5 km (17,400 ft) a.s.l. Gas-and-steam plumes containing ash drifted 250 km S during 19-20 December. Explosions produced ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. on 19 December. Ground-based observers noted that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption. Moderate fumarolic activity at the lava dome was observed during 18-21 December; cloud cover prevented observations on the other days. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity was detected at Shiveluch during 9-16 December. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Ground-based observers noted that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption. Moderate fumarolic activity at the lava dome was observed during 10-11 and 13-15 December; clouds prevented observations on the other days of the week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP) and satellite images, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 19 December an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 6.1 km (20,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E. On 20 December an ash plume drifted SE at an altitude of 4.3 km (14,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity was detected at Shiveluch during 2-9 December, and satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Ground-based observers noted that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption. Moderate fumarolic activity at the lava dome was observed during 3-6 December; clouds prevented observations on the other days of the week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity was detected at Shiveluch during 25 November-2 December, and satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Ground-based observers noted that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption. A gas-and-steam plume detected in satellite imagery drifted 22 km NW on 26 November. Moderate fumarolic activity at the lava dome was observed during 28-29 November; clouds prevented observations on the other days of the week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity was detected at Shiveluch during 18-25 November, and satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Ground-based observers noted that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption. An ash plume detected in satellite imagery drifted 21 km W on 18 November. Strong fumarolic activity at the lava dome was observed on 18, 21, and 24 November; clouds prevented observations on the other days of the week. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity was detected at Shiveluch during 11-18 November, and indicated that possible ash plumes rose to a maximum altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. Ground-based observers noted that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption. Strong fumarolic activity at the lava dome was observed during 13-14 November; cloud cover prevented observations on the other days. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly over the lava dome during 11-14 and 17 November and gas-and-steam plumes containing ash drifted 100 km E on 14 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity was detected at Shiveluch during 4-11 November, and indicated that possible ash plumes rose to a maximum altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. Ground-based observers noted that a viscous lava flow continued to effuse in the crater formed during a 2010 eruption. Strong fumarolic activity at the lava dome was observed during 2-3 and 5-9 November; cloud cover prevented observations on the other days. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome and gas-and-steam plumes containing small amounts of ash that drifted 25 km E on 5 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KVERT, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 14 November an ash plume drifted E at an altitude of 3 km (10,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported strong seismic activity at Shiveluch during 28 October-4 November, and indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 7.8 km (25,600 ft) a.s.l. on 29 October and to lower altitudes on other days. Ground-based observers noted strong fumarolic activity at the lava dome during 29 October-1 November; cloud cover prevented observations on the other days. Satellite imagery showed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome and gas-and-steam plumes containing small amounts of ash that drifted 150 km E and SE during 31 October and 1-2 November. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported strong seismic activity at Shiveluch during 21-23 October and indicated that possible ash plumes rose to altitudes of 7.1-10.6 km (23,300-34,800 ft) a.s.l. Technical reasons prevented seismic data collection during 24-28 October. Ground-based observers noted hot avalanches in the lava dome area during 23-26 October; cloud cover prevented observations on the other days. Satellite imagery showed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome and gas-and-steam plumes that drifted 170 km SE on 24 and 25 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP), the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 31 October an ash plume rose to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was moderate during 13-18 October and indicated that possible ash plumes rose to altitudes of 8-10.5 km (26,200-34,400 ft) a.s.l. Technical reasons prevented seismic data collection during 19-21 October. Ground-based observers noted hot avalanches in the lava dome area during 13-16 October, and that plumes from those avalanches rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery showed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome and ash plumes that drifted 75 km E on 14 and 16 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 23 October an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 7.3 km (24,000 ft) a.s.l. The altitude was based on seismic analysis. An eruption on 24 October noted by KVERT produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 3 km (10,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was moderate during 7-14 October. Ground-based observers noted hot avalanches from the lava dome and that plumes from those avalanches rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. An ash explosion on 8 October produced an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome and ash plumes that drifted 160 km E on 6 and 8 October. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 15-18 October eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 6.4-10.4 km (21,000-34,000 ft) a.s.l. An eruption on 16 October noted by KVERT produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 3 km (10,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was moderate during 30 September-7 October. Ash plumes rose to altitudes of 6-9 km (19,700-30,000 ft) a.s.l. during 3-5 October, followed by new lava-dome extrusion. Seismicity indicated that possible ash plumes rose to altitudes of 4.5-5 km (14,800-16,400 ft) a.s.l. during 5-6 October; ground-based observers noted that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. on those same days. Satellite imagery showed a large and bright thermal anomaly on the lava dome on 5 October and ash plumes that drifted 100 km NE on 6 October. The Aviation Color Code was lowered to Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 8 October an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E. Subsequent satellite images that day showed that ash was present and then had dissipated. An eruption on 10 October produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 7.3 km (24,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was moderate during 23-30 September, and indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,100 ft) a.s.l. during 23 and 26-27 September. Ground-based observers noted that ash plumes rose to altitudes of 5.5 and 4.5 km (18,000 and 14,800 ft) a.s.l. on 23 and 27 September, respectively. Ash plumes observed in satellite imagery during 23-24 September drifted 45 km E. Seismicity increased on 3 October. Ash plumes rose to altitudes of 6-9 km (19,700-29,500 ft) a.s.l. during 3-5 October. Ground-based observers noted on 5 October a brightly incandescent lava dome, which was also detected as a large and bright thermal anomaly in satellite imagery. The Aviation Color Code was raised to Red.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was moderate during 16-23 September. A thermal anomaly on the volcano was also observed in satellite imagery on 15 and 18 September. Ground-based observers noted fumarolic activity during 18-20 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 24 September an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 6.4 km (21,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E. Subsequent images that day showed that the ash had dissipated.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was moderate during 9-15 September, and indicated that possible ash plumes rose to altitudes of 6.5 km (14,100 ft) and 10.3 km (33,800 ft) a.s.l. on 9 and 11 September, respectively. Ground-based observers noted ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 4.7 km (15,400 ft) a.s.l. on 9 September and fumarolic activity on 9 and 14 September. A thermal anomaly on the volcano was also observed in satellite imagery on 9 and 13 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was moderate during 2-9 September, and indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.3 km (14,100 ft) a.s.l. during 2-3 September. Ground-based observers noted fumarolic activity during the week, and an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 4 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. on 3 September. Also on 3 September an ash cloud 19 by 11 km was observed in satellite imagery drifting 20 km E. A thermal anomaly on the volcano was also observed in satellite imagery on 5 and 7 September. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 10 September an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 6.7 km (22,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was moderate during 26 August-1 September, and indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 8.6 km (28,200 ft) a.s.l. on 28 August. Ground-based observers noted fumarolic activity during 26, 28, and 30-31 August, and an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. on 28 August. A thermal anomaly on the volcano was observed in satellite imagery on 29 and 31 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP) and KVERT, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 3 September an ash plume rose to an altitude of 5.8 km (19,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE. Subsequent images that day showed that the ash had dissipated.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was moderate during 19-26 August, and indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 8.2 km (26,900 ft) a.s.l. on 23 August. A thermal anomaly on the volcano was observed in satellite imagery on 18, 21, and 25 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD and analyses of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 29 August an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 6.1 km (20,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E. Subsequent images that day showed that continuing ash emissions had later dissipated. According to a news article, international flights were re-routed that day due to ash plumes that reportedly rose to an altitude of 8.6 km (28,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: IOL News; Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was moderate during 12-19 August, and indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.8 km (22,300 ft) a.s.l. on 13 August and to an altitude of 7.8 km (25,600 ft) a.s.l. on 15 August. Ash plumes may have risen to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. on the other days. Gas-and-steam plumes containing ash observed in satellite imagery drifted 30 km SW on 12 August. Ground-based observers noted that an ash plume rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. on 16 August. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismicity at Shiveluch was moderate during 5-12 August. Seismic data indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.7 km (22,000 ft) a.s.l. on 8 August, to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. on 10 August, and to altitudes of 4-5.5 km (13,100-18,000 ft) a.s.l. on other days. Ground-based observers indicated that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. on 6 August. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome, and ash plumes that drifted 60 and 20 km SE on 6 and 10 August, respectively. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 13 August a possible eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 4.3 km (14,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted W. Ash was seen in subsequent satellite images that same day. An eruption on 15 August produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 7.9 km (26,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was moderate during 29 July-5 August. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 30 July and 1-3 August. Ground-based observers indicated that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. on 1 August and 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. on 2 August. Satellite images from 1 August showed an ash plume drifting 24 km S. A strong dust storm at the volcano was observed on 3 August; a dust plume detected in satellite imagery drifted 160 km SE. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 6 August an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E. Ash was seen in subsequent satellite images that same day. An eruption on 9 August produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 6.7 km (22,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was moderate during 22-29 July and indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.7 km (15,400 ft) a.s.l. during 23 and 25-27 July. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome on 22 July; cloud cover prevented observations on other days. Ground-based observers noted fumarolic activity on 24 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 1 August an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E. Ash was seen in subsequent satellite images that same day.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was moderate during 15-22 July and indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. during 14-15 and 20 July. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 14-15 and 18-19 July. Ash plumes drifted 13 km SW on 15 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was moderate during 8-15 July and indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 10-11 and 14 July and a gas-and-steam plume that drifted 38 km SE on 10 July. Ground-based observers noted that ash plumes from explosions rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. on 11 and 14 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported moderate seismic activity at Shiveluch during 1-8 July. Seismic data indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. on 4 and 6 July. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 2-5 July and gas-and-ash plumes that drifted 78 km NE during 4-5 July. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported moderate seismic activity at Shiveluch during 24 June-1 July. Ground-based observers noted that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 7.5 km (24,600 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome on 23 and 24 June and ash plumes that drifted 107 km NW on 24 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 5 July a possible eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 3.4 km (11,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E. A subsequent notice that day stated that ash had dissipated.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported moderate seismic activity at Shiveluch during 17-24 June. Seismic data indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. on 19 June and to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. on 18 and 21 June. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome on 18 and 20 June and ash plumes drifting 176 km in multiple directions during 20-21 June. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported moderate seismic activity at Shiveluch during 10-16 June and that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. on 15 June. Satellite imagery showed a gas-and-steam plume drifting 26 km NW on 10 June and a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 10 and 12-13 June. Meteorological clouds prevented observations on the other days. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KVERT and analyses of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruptions on 20 June produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 6.7-10.1 km (22,000-33,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 3-10 June seismic activity at Shiveluch indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 9 km (29,500 ft) a.s.l. on 5 June and to altitudes of 5-7 km (16,400-22,960 ft) a.s.l. during 4-6 and 8 June. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 3-4 June, and ash plumes that drifted 734 km SE on 4 June and 377 km NE during 5-6 June. Based on information from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP), the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 10 June an ash plume rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted W. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 27 May-3 June seismic activity at Shiveluch indicated that possible ash plumes rose to altitudes of 4.7-9 km (15,400-29,500 ft) a.s.l. During 29-30 May satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Those same two days, ground-based observers noted that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted S. Clouds prevented observations on the other days. During 30-31 May long ash clouds drifted 1,000 km SW and approached Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KVERT and analyses of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 4 June an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 5.2 km (17,000 ft) a.s.l. According to KEMSD, eruptions during 5-6 June produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 6.1-9.1 km (20,000-30,000 ft) a.s.l. Plumes drifted E on 5 June.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 20-27 May seismic activity at Shiveluch did not exceed background levels. Strong gas-and-steam activity was observed on 21 May; cloud cover prevented ground-based observations on the other days. Satellite imagery showed ash plumes drifting 58 km SW on 20 May and a thermal anomaly over the lava dome during 19-21 and 24 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 30-31 May eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 7.6-8.2 km (25,000-27,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted S. According to news articles, ash plumes caused authorities to reroute a number of international flights in the region.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); BNO News; Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 15-16 May seismic data at Shiveluch indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.4 km (11,200 ft) a.s.l. According to ground-based observations ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. on 15 May and to 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. on 16 May. Satellite imagery showed ash plumes drifting 58 km SE on 15 May and a thermal anomaly over the lava dome during 15-16 and 19 May. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 5-7 May seismic data at Shiveluch indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.9 km (12,800 ft) a.s.l. According to ground-based observations ash plumes rose to an altitude of 7.5 km (24,600 ft) a.s.l. on 7 May and to altitudes of 3-4 km (9,800-13,100 ft) a.s.l. during 5-6 and 8 May. Satellite imagery showed ash plumes drifting 196 km N during 5-6 May. On 7 May small ash clouds drifted S and SE, and gas-and-steam plumes drifted 230 km E. A thermal anomaly was detected during 7-8 May. KVERT noted that the Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 15 May an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 6.1 km (20,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 29 April-6 May a thermal anomaly on Shiveluch was detected in satellite imagery. According to ground-based observations during 28-29 April ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. On 1 May ash plumes observed in satellite imagery drifted 124 km NE. Seismic data indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. on 29 April and 2 May. KVERT noted that the Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. Based on analyses of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 7 May a possible eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 5.2 km (17,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E. Subsequent notices that day stated that ash had dissipated.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 22-29 April seismic data at Shiveluch indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.7 km (22,000 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly daily on the lava dome. According to ground-based observations during 22 and 25-27 April ash plumes rose to an altitude of 7.5 km (24,600 ft) a.s.l. and drifted N and SE. Satellite imagery showed ash plumes drifting 153 km N on 22 April and as far as 400 km SE during 23-24 and 27 April. KVERT noted that the Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 1 May an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 6.1 km (20,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 15-22 April seismic data at Shiveluch indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.2 km (10,500 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 15-18 and 20 April, and ash plumes that drifted 55 km NE on 17 April. Based on information from KEMSD and information from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP), the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 22 April an eruption produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.3-7.3 km (14,000-24,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted W and NW. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 1-7 April seismic data at Shiveluch indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,100 ft) a.s.l. On 8 April gas-and-steam plumes were observed from the ground and a thermal anomaly over the lava dome was observed in satellite imagery. Ash plumes drifted 33 km NW on 11 April. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 1-7 April seismic data at Shiveluch indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 7.5 km (24,600 ft) a.s.l. Ground-based observations during 1-2 April indicated that gas-and-steam plumes containing ash rose to an altitude of 2.7 km (8,800 ft) a.s.l. A thermal anomaly on the lava dome was observed in satellite imagery those same two days. Ash plumes drifted in different directions as far as 187 km during 1-3 and 5 April. The Tokyo VAAC reported that on 7 April a possible eruption detected in satellite imagery produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 3.7 km (12,000 ft) a.s.l. Subsequent notices that day stated that ash continued to be detected, and then dissipated. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 25 March-1 April seismic data at Shiveluch indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.7 km (12,100 ft) a.s.l. A thermal anomaly on the lava dome was observed in satellite imagery during 25-29 March, and ash plumes drifted 57 km SE on 26 March. Ground-based observers noted that ash-and-gas plumes rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. during 25-30 March.
Based on information from KEMSD and analyses of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 5 April an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 7.6 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted N. A possible eruption detected in satellite imagery the next day produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 3.7 km (12,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 18-25 March seismic data at Shiveluch indicated that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.8 km (19,000 ft) a.s.l. A thermal anomaly on the lava dome was observed daily in satellite imagery, and ash plumes drifted 373 km SE and N during 18-20 March. Ground-based observers noted that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. on 22 March. The Tokyo VAAC reported that on 23 March an eruption detected in satellite imagery and reported by KEMSD produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 6.7 km (22,000 ft) a.s.l. Subsequent notices that day stated that ash then dissipated. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 11-18 March seismic data at Shiveluch indicated that possible ash plumes rose to altitudes of 3.8-8 km (12,500-26,200 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery showed ash plumes drifting 312 km W and NW on 10 and 16 March, and thermal anomalies on the lava dome during 12-13 and 15-16 March. According to ground-based observations, an ash plume rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. on 16 March. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. The Tokyo VAAC reported that on 19 March a possible eruption detected in satellite imagery produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,000 ft) a.s.l. Subsequent notices that day stated that ash continued to be detected, and then dissipated.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 4-11 March seismic data at Shiveluch indicated that possible ash plumes rose to altitudes of 4-7.5 km (13,100-24,600 ft) a.s.l. A thermal anomaly over the lava dome was observed in satellite imagery during 5-7 March.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity was detected at Shiveluch during 25 February-4 March. Gas-and-steam activity was observed during 24-25 February; cloud cover prevented observations on the other days. A thermal anomaly over the lava dome was observed in satellite imagery during 25-26 February, and 2 March. Ash plumes drifted over 140 km N during 26-27 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity was detected at Shiveluch during 18-25 February. A thermal anomaly over the lava dome was observed daily in satellite imagery. Gas and steam activity was observed during 21-24 February and ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. during 22-23 February. Ash plumes observed in satellite imagery drifted more than 220 km SE at altitudes below 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. during 23-24 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity was detected at Shiveluch during 11-18 February. A thermal anomaly over the lava dome was observed daily in satellite imagery. Gas and steam activity was observed on 13 and 16 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. The Tokyo VAAC reported that on 22 February a possible eruption detected in satellite imagery produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 3.4 km (11,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE. Subsequent notices that day stated that ash had dissipated.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity was recorded at Shiveluch during 4-11 February and many volcanic earthquakes were detected. A thermal anomaly over the lava dome was observed in satellite imagery. Ash plumes observed from the ground rose to an altitude of 7.5 km (24,600 ft) a.s.l. on 4 February. That same day ash plumes detected in satellite imagery drifted 120 km E. Gas-and-steam activity was observed during 4 and 6-7 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity was detected at Shiveluch during 28 January-4 February and many volcanic earthquakes were detected. A thermal anomaly over the lava dome was observed in satellite imagery. Gas and steam activity was occasionally observed. Ash plumes were seen rising to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. on 30 January and 3 February. Ash plumes observed in satellite imagery drifted 120 km NE during 31 Janaury-1 February, and rose to altitudes of 6-8 km (19,700-26,200 ft) a.s.l. on 1 February. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
The Tokyo VAAC reported that on 8 February a possible eruption detected in satellite imagery produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E. Subsequent notices that day stated that ash had dissipated.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 21-28 January moderate seismic activity from Shiveluch was recorded, and an intense thermal anomaly over the volcano was detected in satellite imagery. Gas-and-steam emissions were visually observed during 23-26 January and an ash plume was observed rising to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. on 26 January. Satellite imagery showed an ash plume drifting 54 km S on 26 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
The Tokyo VAAC reported that on 31 January and 1 February possible eruptions detected in satellite imagery produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 3.4-3.7 km (11,000-12,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE. Subsequent notices on both days stated that ash had dissipated.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity from Shiveluch was recorded during 14-21 January. Moderate gas-and-steam activity was visually observed during 17-20 January, and on 18 January an ash plume was observed rising to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. A bright thermal anomaly over the volcano was detected in satellite imagery during 13-15 and 18-20 January. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity from Shiveluch was detected during 7-13 January. A bright thermal anomaly over the lava dome was observed in satellite imagery during 7-11 January. Visual observations during 7-9 and 13 January, when the weather did not obscure the volcano, showed steam-and-gas activity. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 18 January an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted W.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity from Shiveluch was detected during 31 December-7 January. A bright thermal anomaly over the volcano was observed daily in satellite imagery. Seismic data showed that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. on 2 January. That same day an explosion generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 8 km (26,000 ft) a.s.l. and were observed in satellite imagery drifting 92 km S. Moderate gas-and-steam activity was visually observed during 2 and 5-6 January. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity from Shiveluch was detected during 24-30 December. Ash explosions on 24 December produced ash plumes that rose to altitudes as high as 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. A bright thermal anomaly over the volcano was observed in satellite imagery during 24 and 27-28 December. Moderate gas-and-steam activity was visually observed on 24 and 28 December. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity from Shiveluch was detected during 17-24 December. A bright thermal anomaly over the volcano was observed in satellite imagery. Moderate gas-and-steam activity was visually observed during 19-20 and 23 December. Ash explosions on 23 December produced ash plumes that rose to altitudes as high as 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity from Shiveluch was detected during 10-17 December and a bright thermal anomaly was observed in satellite imagery. Seismic data analysis suggested that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.2 km (17,100 ft) a.s.l. Strong gas-and-steam activity was observed during 9 and 11-14 December. On 14 December, an ash explosion produced an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. and a 2-km-long pyroclastic flow. Satellite imagery showed an ash plume that drifted 230 km NE. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity from Shiveluch was detected during 3-10 December. A bright thermal anomaly over the volcano was observed in satellite imagery. Plumes composed of either gas and steam or ash were seen in satellite imagery drifting 322 km SE on 3 December. Seismic data analyses on 6 December suggested that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. Gas-and-steam activity was observed visually during 3, 6, and 8-9 December. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Based on analyses of satellite imagery and information from KVERT, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 14 December an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity from Shiveluch was detected during 26 November-3 December. A bright thermal anomaly over the volcano was observed in satellite imagery. Strong gas-and-steam activity was observed on 26 and 29 November. Satellite images showed ash plumes drifting 153 km N and NE during 29-30 November, as well as several ash clouds (as large as 81 by 16 km) at distances as far as 351 km N and NE. Seismic data analysis suggested that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. on 1 December. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity from Shiveluch was detected during 19-26 November, suggesting that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.8 km (12,500 ft) a.s.l. A bright thermal anomaly over the volcano was observed in satellite imagery. Ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 5.8 km (19,000 ft) a.s.l. and strong gas-and-steam activity were observed on 19, 20, 22, and 24 November. Ash plumes observed in satellite imagery drifted 408 km E and S during 19-20 and 23-24 November. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Based on analyses of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 30 November an eruption produced an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity from Shiveluch was detected during 12-19 November, suggesting that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. Two distinct thermal anomalies over the volcano observed in satellite imagery showed the hot lava dome and recent pyroclastic flow deposits from an eruption on 27 October. During 11-14 November, satellite imagery showed ash plumes drifting 100 km N and E, and ash clouds with dimensions as large as 60 by 32 km. Gas-and-steam activity was observed during 16-18 November; cloud cover prevented visual observations the other days. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Based on analyses of satellite imagery and information from KVERT, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 19-21 and 23 November eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.6-5.2 km (15,000-17,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE, E, and SE
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity from Shiveluch was detected during 5-12 November and a large thermal anomaly over the volcano was observed in satellite imagery. Seismic data suggested that possible ash plumes rose to altitudes of 6.5 and 7 km (21,300 and 23,000 ft) a.s.l. on 6 and 8 November, respectively. Ash plumes were detected in satellite imagery during 7-9 November drifting 150 km SE. An ash plume observed on 10 November rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. KVERT noted that growth of the lava dome continued. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
During 13-14 November, the Tokyo VAAC reported that ash plumes from eruptions were observed in satellite imagery drifting E at altitudes of 4.6-5.2 km (15,000-17,000 ft) a.s.l. A possible eruption on 16 November produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 3.7 km (12,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that moderate seismic activity from Shiveluch was detected during 29 October-5 November and a thermal anomaly over the volcano was observed in satellite imagery. Seismic data on 31 October, and 1 and 4 November suggested that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.8 km (19,000 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery showed ash plumes drifting 400 km SE on 31 October and 1 November. Fumarolic activity was seen during 1-2 November. Cloud cover prevented observations the other days.
On 1 November, pyroclastic flow deposits from the large explosive eruption on 27 October were detected in satellite imagery on the ESE flank, and had traveled 15 km. Volcanologists inspected the deposits the next day and found that the pyroclastic flow had annihilated a forest in the Bekesh River valley. More than half of the lava dome edifice was destroyed during the eruption. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
During 4-9 November, the Tokyo VAAC reported that ash plumes from possible eruptions were observed in satellite imagery drifting N, SE, and S at altitudes of km (15,000-25,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity from Shiveluch began to increase on 27 October. The magnitude of volcanic tremor then sharply increased on 28 October, indicating a strong explosive eruption. Cloud cover prevented observations of the volcano, but ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. Ash fell in Ust-Kamchatsk, 85 km SE, a few hours later. The road from Ust-Kamchatsk to Kliuchi, 50 km SW, closed due to poor visibility and darkness. Satellite images indicated that the ash plume rose to an altitude of 12 km (39,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E. The Aviation Color Code level was raised to Red. According to news articles, ash from Shiveluch and Kliuchevskoi caused area flight diversions.
On 29 October satellite imagery showed the ash plume drifting 2,500 km E; ash continued to fall in Ust-Kamchatsk. Ash explosions continued on 30 October. Seismic data suggested that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE. The Aviation Color Code level was lowered to Orange. Based on analyses of satellite imagery and information from KVERT, the Tokyo VAAC reported that possible eruptions on 31 October and during 1-2 November produced ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 3.7-6.7 km (12,000-22,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE and E. Subsequent notices on 31 October and 1 November stated that ash had dissipated.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Associated Press; Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels during 14-16 October and at background levels during 17-22 October. Seismic data on 14 October suggested that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.8 km (12,500 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery analyses showed a daily thermal anomaly on the volcano and ash plumes that drifted 72 km SE on 15 and 16 October. Gas-and-steam plumes sometimes containing ash were observed during 15-18 October. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 8-15 October seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, suggesting that possible ash plumes rose to altitudes of 5.2-6 km (17,100-19,700 ft) a.s.l. Gas-and-steam plumes sometimes containing ash were periodically observed. Satellite imagery analyses showed a daily thermal anomaly on the volcano and ash plumes that drifted 130 km SE during 9-10 October. Based on analyses of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported a possible eruption on 16 October. Subsequent notices stated that ash was present, but had dissipated. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 1-8 October seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, suggesting that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. during 5-7 October. Satellite imagery analysis showed a thermal anomaly on the volcano and gas-and-steam plumes that drifted 190 km SE on 2 and 3 October. Gas-and-steam plumes sometimes containing ash were visually observed during 3-7 October. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 24 September-1 October seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and suggested that possible ash plumes rose from the volcano. Gas-and-steam plumes were observed during 23, 25, and 28-29 September. Satellite imagery analyses showed a daily thermal anomaly on the volcano and gas-and-steam plumes that drifted 70 km SE on 29 September. Based on analyses of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported a possible eruption on 3 October; a subsequent notice stated that ash had dissipated. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 17-24 September seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and suggested that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery analysis showed a thermal anomaly on the volcano. Gas-and-ash plumes were observed on 21 September, and satellite imagery showed ash plumes drifting 16 km SE the same day. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 10-17 September seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and suggested that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery analysis showed a thermal anomaly on the volcano. Gas-and-ash plumes were observed during 12-15 September; clouds prevented observations on the other days. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 3-10 September seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and suggested that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. during 3-4 September. Gas-and-ash plumes were observed on 6 and 7 September; clouds prevented observations on the other days. Satellite imagery analysis showed a thermal anomaly on the volcano during the week. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 27 August-3 September seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, suggesting that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery analysis showed a thermal anomaly on the volcano. Gas-and-ash plumes were observed during 27-30 August. Based on information from KEMSD and satellite imagery analyses, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 2-3 September eruptions produced plumes that rose to an altitude of 6.7 km (22,000 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 20-27 August seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, suggesting that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 8.5 km (27,900 ft) a.s.l. during 20-24 August. Gas-and-ash plumes were observed on 20 and 21 August. Satellite imagery analysis showed a thermal anomaly on the volcano during 20-22 and 24 August. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 13-20 August seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and gas-and-steam plumes were seen during 14-16 August. A daily thermal anomaly was seen in satellite imagery. Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 22-23 August eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 6.4-8.5 km (21,000-28,000 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 6-13 August seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, suggesting that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. on 9 August and to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. the other days. Cloud cover prevented visual observations. Satellite imagery analysis showed a daily thermal anomaly on the volcano and an ash plume that drifted 55 km NW on 10 August. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 30 July-6 August seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and suggested that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. Gas-and-steam plumes were seen rising to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. during 29-31 July. Cloud cover prevented observations the other days. Satellite imagery analysis showed a large daily thermal anomaly on the volcano. Based on analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption on 9 August produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 6.7 km (22,000 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 23-30 July seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and a daily thermal anomaly was detected in satellite imagery. Possible ash plumes from hot avalanches and explosions on 28 and 29 July rose to altitudes of 4-6.5 km (13,100-21,300 ft) a.s.l. Gas-and-steam plumes were seen rising to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. on 23 and 24 July. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 16-23 July seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating weak ash explosions from the lava dome. According to visual observations, gas-and-steam plumes rose daily to an altitude of 3.7 km (12,100 ft) a.s.l. and ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. on 20 and 21 July. Satellite imagery showed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome and ash plumes that drifted 50 km NE on 21 July. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 9-16 July seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and suggested that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.3 km (12,100 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery showed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Gas-and-steam plumes were seen rising to an altitude of 3.7 km (12,100 ft) a.s.l. during 9 and 11-14 July. Based on analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported a possible eruption on 19 July. Ash was seen in subsequent satellite images and then later dissipated. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 2-9 July seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and suggested that on most days possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 7 km (22,900 ft) a.s.l. On 5 July ash plumes from hot avalanches rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. and strong fumarolic activity was noted. Ashfall was observed around the volcano. Satellite imagery showed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome and an ash plume that drifted 20 km S on 7 July. Tokyo VAAC reported that satellite imagery analyses indicated a possible eruption on 10 July. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 24 June-2 July seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and suggested that possible ash plumes occasionally rose to an altitude of 6.6 km (21,600 ft) a.s.l. On 24 and 29 June ash plumes from hot avalanches rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. Strong fumarolic activity was also noted on these days. On 1 July, seismicity increased and may have indicated ash plumes rose to an altitude of 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. Ashfall was reported in Klyuchi village, 50 km SW. Satellite imagery showed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Based on analysis of satellite imagery and information from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP), the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 3 July an ash plume rose to an altitude of 6.1 km (20,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted N. Satellite imagery showed a possible eruption the next day. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 18-25 June seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and suggested that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.1 km (16,700 ft) a.s.l. Strong fumarolic activity and hot avalanches were observed during 21-23 June. An ash plume was seen rising to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. on 23 June. Satellite imagery showed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome and an ash cloud 5 x 5 km in dimension 30 km SE on 23 June. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 11-18 June seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and suggested that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.9 km (16,100 ft) a.s.l. Strong fumarolic activity and hot avalanches were seen on most days. Satellite imagery showed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome, and a small anomaly near the lava dome on 15 June. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 4-11 June seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and hot avalanches were seen at night. The seismic data suggested that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.1 km (13,400 ft) a.s.l. during 3-4 and 6 June. Ash plumes were seen during 4-6 and 9 June rising to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery showed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome, and ash plumes that drifted 100 km SE on 4 June. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 28 May-4 June seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, suggesting that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.1 km (20,000 ft) a.s.l. Strong fumarolic activity was also noted and, at night, hot avalanches were seen. Ash plumes observed throughout the reporting period rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery showed a large daily thermal anomaly. Gas-and-steam plumes seen in imagery drifted 30 km W on 29 May, and an ash cloud 20 by 6 km in dimension was detected about 15 km N on 31 May. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 21-28 May seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, suggesting that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.7 km (15,400 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery showed a large daily thermal anomaly, and an ash plume that drifted 10 km NE on 23 May. Observations revealed fumarolic activity, and ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. on 24 and 25 May. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 14-21 May seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, suggesting that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.1 km (16,700 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome. An ash plume drifted about 40 km SE on 15 May and gas-and-steam plumes drifted the same distance NE on 18 May. Based on information from KVERT, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 24 May an ash plume rose to an altitude of 3 km (10,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE. Ash was not identified on satellite imagery. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 7-14 May seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and suggested that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 8.3 km (27,200 ft) a.s.l. on most days. Gas-and-steam plumes were sometimes seen rising to an altitude of 3.2 km (10,500 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 30 April-7 May seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and suggested that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome, and ash plumes that drifted about 18 km W on 3 May. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 23-30 April seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and suggested that possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.7 km (18,700 ft) a.s.l. During 22-25 April ash plumes from hot avalanches rose to an altitude of 3 km (10,000 ft) a.s.l. and fumarolic activity from the lava dome was noted. Satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome, and ash plumes that drifted about 60 km SE on 28 April. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 16-23 April seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and ash plumes from hot avalanches rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. Seismic data suggested that ash plumes rose 4-6.9 km (13,100-22,600 ft) a.s.l. during 15-17 and 20-21 April. An ash explosion on 18 April generated an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome, and ash plumes that drifted about 50-220 km SE on 18, 20, and 21 April. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 9-15 April seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Seismic data suggested that ash plumes rose to about 7.5 km (24,600 ft) a.s.l. on 8 April and up to 5.6 km (18,400 ft) a.s.l. the other days of the week. Ash plumes from hot avalanches were seen rising to an altitude of 3.7 km (12,100 ft) a.s.l. during 9-13 April. Satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome and a gas-and-steam plume that drifted about 75 km E on 13 April. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 2-9 April seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Ash plumes from hot avalanches rose to an altitude of 6.1 km (20,000 ft) a.s.l. on 5 and 8 April. Satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome, and ash plumes that drifted about 100 km SE on 5 April. The Tokyo VAAC reported that on 10 April ash plumes were seen in satellite imagery. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 26 March-2 April seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 4.7 km (15,400 ft) a.s.l. Hot avalanches from the lava dome were seen at night. Satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome, and ash plumes that drifted about 40 km SE on 29 March. Based on information from KVERT, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 5 April an ash plume rose to an altitude of 3 km (10,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 19-29 March seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 4.2 km (13,800 ft) a.s.l. Hot avalanches from the lava dome were seen at night. On 22 March, seismic signals detected an explosion that may have produced an ash plume rising to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. Satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the volcano, and ash plumes that drifted over 40 km NE on 21 March. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 12-19 March seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. Hot avalanches were seen at night. Gas-and-steam plumes sometimes containing ash were seen on 12, 13, 15, and 16 March; plumes seen in satellite imagery on 13 and 16 March drifted 90 km E and SE. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome. Based on information from KVERT, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 21 March an ash plume rose to an altitude of 2.7 km (9,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 5-12 March seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 6.4 km (21,000 ft) a.s.l. Gas-and-steam plumes sometimes containing ash were seen daily, rising to altitudes of 2.5-3.5 km (8,200-11,500 ft) a.s.l. and drifting 130 km ESE; an ash plume rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. on 10 March. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 26 February-5 March seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity was occasionally observed. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome, and ash plumes that drifted 30 km NE on 26 February and 130 km SE on 28 February. Ash fell in Klyuchi, 50 km SW, on 26 February. On 3 March, a second thermal anomaly on the S flank was noted. Based on information from KVERT and analyses of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 5 and 8-9 March ash plumes rose to an altitude of 2.7 km (9,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E and SE. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 19-26 February seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity was occasionally observed. Ash and snow fell simultaneously in Klyuchi, 50 km SW, on 21 February. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome, and ash plumes that drifted 30 km to the N and E on 23 and 25 February, respectively. Gas-and-steam plumes drifted 60 km N during 18 and 22-25 February. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange. Based on information from KVERT, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 26 February an ash plume rose to an altitude of 3 km (10,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 12-19 February seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 5.1 km (16,700 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity was occasionally observed. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome and ash plumes that drifted over 70 km in northern directions on 11, 13, and 17 February. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange. Based on information from KVERT, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 23 February an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 3 km (10,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted N.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 5-12 February seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 5.2 km (17,100 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity was occasionally observed. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 29 January-5 February seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 5.7 km (18,700 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity was observed on 1 February; cloud cover prevented observations on other days. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 22-29 January seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,100 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity was occasionally observed. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 29-30 January eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.9-5.8 km (16,000-19,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 15-22 January seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 4.7 km (15,400 ft) a.s.l. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 23-24 and 26 January eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 3-4.6 km (10,000-15,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 8-15 January seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 6.2 km (20,300 ft) a.s.l. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome and an ash plume that drifted 8 km SW on 13 January. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 18 January an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 4.9 km (16,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 1-8 January seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 7.5 km (24,600 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity was occasionally seen when the weather was clear. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome and a gas-and-steam plume that drifted 40 km SW on 6 January. Ashfall was reported in Klyuchi (about 45 km SW) on 4 January. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. Based on information from KEMSD and analyses of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 6-11 January eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.3-6.4 km (14,000-21,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 24-31 December seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 4.9 km (16,000 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity was occasionally seen when the weather was clear. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome and an ash plume that drifted 15 km W on 28 December. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. Based on information from KEMSD and KVERT, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 30 December-3 January eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.3-7.6 km (14,000-25,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 18-25 December seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 4.1 km (13,500 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity was occasionally seen when the weather was clear. A video camera recorded an ash plume on 22 December. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 27-29 December eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.9-5.2 km (16,000-17,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 11-21 December seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 4-11 December seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating ash plumes rising to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity was seen with a video camera. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome and an ash plume drifting 85 km SE on 6 December. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 13 December an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 5.8 km (19,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 27 November-4 December seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity was seen with a video camera. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome and gas-and-steam plumes, possibly with ash, drifting 70 km E on 27, 28, and 30 November. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 4 December an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 5.8 km (19,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 20-27 November seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.3 km (14,100 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity was seen using a video camera. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 13-20 November seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.3 km (17,400 ft) a.s.l. According to video camera data, fumarolic activity and hot avalanches were noted on 14 and 15 November. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 18 November an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 6-13 November seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels, possibly indicating that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. According to video camera data, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.2 km (13,800 ft) a.s.l. on 5 November and hot avalanches were noted during 10-12 November. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome and ash plumes that drifted 320 km E on 11 November. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange. Based on information from KEMSD and analyses of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 14 November an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 4.9 km (16,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 30 October-6 November seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and possibly indicated that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.7 km (15,400 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity was noted and analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large thermal anomaly over the lava dome. According to video camera data, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 8 km (26,400 ft) a.s.l. on 30 October. Ash plumes seen on satellite imagery drifted 130-255 km E on 30 October, and 1 and 5 November. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 23-30 October seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and possibly indicated that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.7 km (12,100 ft) a.s.l. and to an altitude of 6.9 km (22,600 ft) a.s.l. on 29 October. Fumarolic activity was occasionally seen. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large thermal anomaly over the lava dome during 22-27 October and an ash plume that drifted 24 km NE on 26 October. Based on information from KEMSD and analyses of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 30 October an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. A possible eruption plume rose to an altitude of 6.1 km (20,000 ft) a.s.l. later that day. On 1 November, an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 4.9 km (16,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 16-23 October seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and possibly indicated that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large thermal anomaly over the lava dome. According to video camera data and visual observations, multiple hot avalanches traveled down the lava dome. Deposits on the SE flank from a small pyroclastic flow were noted. Fumarolic plumes rose to altitudes of 2.8-5 km (9,200-16,400 ft) a.s.l. during 16, 18-20, and 22 October. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 9-16 October seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels and possibly indicated that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large thermal anomaly over the lava dome during 8-13 and 15 October. Fumarolic plumes containing small amounts of ash rose to an altitude of 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. during 11-13 October. According to video camera data and visual observations, multiple hot avalanches traveled down the lava dome on 12, 13, and 14 October, and deposits from a small pyroclastic flow on the SE flank were noted. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 2-9 October seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. According to video camera data and visual observations, fumarolic plumes containing small amounts of ash rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. during 1-3 October. Based on interpretations of seismic data, possible ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.8 km (22,300 ft) a.s.l. on 6 October and to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. on other days. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 25 September-2 October seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Fumarolic activity was occasionally seen. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. on 27 September and to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. on other days. According to video camera data and visual observations, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. on 28 September. An ash plume was seen on satellite imagery drifting 65 km ESE on 29 September. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 18-25 September seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 5.2 km (17,100 ft) a.s.l. According to video camera data and visual observations, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. on 18, 19, and 22 September, and hot avalanches from the lava dome were noted during 18 and 22-23 September. Ash plumes were occasionally seen drifting 15-70 km N, NW, and SE. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 28 September an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 11-18 September seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 7.1 km (23,300 ft) a.s.l. On 13 September, pyroclastic flow deposits 5 km long were seen on the S part of the lava dome. Fumarolic activity was seen during 13 and 16-17 September, and hot avalanches originated from the lava dome were seen at night on 16 and 17 September. The Level of Aviation Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 19 September eruptions produced plumes that rose to an altitude of 5.2 km (17,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 4-11 September seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 4.2 km (13,800 ft) a.s.l. and hot avalanches occurred at the lava dome. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. during 4-9 September. An ash plume was seen in satellite imagery drifting 80 km E on 8 September.
On 11 September, KVERT reported strong explosions. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes rose to an altitude greater than 15 km (49,200 ft) a.s.l. The seismic network then detected eight minutes of pyroclastic flows from the lava dome; resulting plumes rose to an altitude of approximately 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code level was raised to Red. Ten more events characterized as ash explosions and either pyroclastic flows or avalanches were detected. Cloud cover prevented visual observations. Seismicity decreased during 11-12 September, and indicated that ash plumes rose to altitudes of 4.5-6.5 km (14,800-21,300 ft) a.s.l. The Aviation Color Code level was lowered to Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 28 August-4 September seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 5.2 km (17,100 ft) a.s.l. and hot avalanches occurred at the lava dome. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to an altitude of 3 km (9,800 ft) a.s.l. during 28-29 and 31 August, and1-3 September. The Aviation Color Code level remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 21-27 August seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 4.8 km (15,700 ft) a.s.l. and hot avalanches occurred on the lava dome. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to an altitude of 3.3 km (10,800 ft) a.s.l. during 20-23 and 26-27 August. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 31 August eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.6-5.5 km (15,000-18,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 14-24 August seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 5.9 km (19,400 ft) a.s.l. and hot avalanches occurred at the lava dome. An ash plume drifted 50 km S on 14 August, and gas-and-steam plumes rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. on 16 August. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 7-17 August seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 31 July-7 August seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 7.5 km (24,600 ft) a.s.l. Steam-and-gas plumes with some ash content were also noted. According to video camera data, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. on 2 August; gas-and-steam plumes rose to an altitude of 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. on 2 and 4 August. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on analyses of satellite imagery and information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 6 and 9 August eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.6-5.2 km (15,000-17,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 24-31 July seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. Steam-and-gas plumes with some ash content were also noted. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. According to video camera data, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. on 23 and 27 July; gas-and-steam plumes rose to an altitude of 2.7 km (8,900 ft) a.s.l. on 24 and 27 July. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on analyses of satellite imagery and information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 1-2 August eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 3-5.8 km (10,000-19,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E and NE.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 17-18 and 20-24 July seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. During 17-20 and 22 July, gas-and-steam plumes seen on a video camera rose to an altitude of 3.7 km (12,100 ft) a.s.l. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 5.2 km (17,000 ft) a.s.l. on 20, 21, and 22 July, and steam-and-gas plumes with some ash content were noted on other days. Analyses of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome, and steam plumes that drifted as far away as 40 km on 18 and 20 July. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on analyses of satellite imagery and information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 23-24 and 27-28 July eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.6-6.1 km (15,000-20,000 ft) a.s.l. According to news sources, an ash plume rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. late on 25 July. Increased seismicity, powerful ash bursts, and avalanches were also reported.
Sources: RIA Novosti; Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 10-17 July seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. On 14 July, a gas-and-steam plume seen on a video camera rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. during 10, 13-14, and 16 July, and steam-and-gas plumes with some ash content were emitted during the reporting period. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome, and a steam plume that drifted 19 km SW on 13 July. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange. Based on analyses of satellite imagery and information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 17 July an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 3-10 July seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 5.3 km (13,400 ft) a.s.l. on 2 and 4 July, and steam-and-gas plumes with some ash content were emitted during the reporting period. On 3 July, a gas-and-steam plume seen on a video camera rose to an altitude of 3.3 km (10,800 ft) a.s.l. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 25 June-3 July seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Pyroclastic flows were noted on 25 and 26 June. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 8.1 km (26,600 ft) a.s.l. during 25-30 June, and steam-and-gas plumes with some ash content were emitted during the reporting period. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome and ash plumes that drifted 97 km NE on 26 June. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange. Based on analysis of satellite imagery and information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 3 and 5 July eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.9-5.5 km (16,000-18,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 19-26 June seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Based on interpretations of seismic data, steam-and-gas plumes with some ash content were emitted during the reporting period; ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 6.8 km (20,000 ft) a.s.l. On 20 June, ash plumes seen on a video camera rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. Gas-and-steam activity was observed at other times during the reporting period. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Ash plumes were also seen on satellite imagery drifting 114 km S during 20 and 22-24 June and more than 100 km SW and NE on 25 June. A pyroclastic flow occurred on 25 June. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange. Based on analysis of satellite imagery and information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 27-28 and 30 June eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.9-7 km (16,000-23,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
A new viscous lava flow from the lava dome was reported by KVERT during 11-18 June. Satellite thermal data indicated a large anomaly over the lava dome the entire week. Above-background levels of seismicity persisted throughout that time. Video recordings revealed ash plumes up to an altitude of 6.1 km (20,000 ft) a.s.l on 12-15 and 18 June. Ash plumes extended up to 50 km (31 miles) to the south 11 and 13-14 June. Another ash cloud on 12 June was 40 x 20 km in size at a distance of 140 km (87 miles) SW. Moderate to strong gas-and-steam plumes were observed during other times.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 5-11 June seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Based on interpretations of seismic data, diffuse ash plumes were emitted during the reporting period; ash plumes possibly rose to altitudes of 4.8-7.7 km (16,000-25,300 ft) a.s.l. during 6 and 10-11 June. Video camera images showed steam-and-gas emissions. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome, and ash plumes that drifted 90 km S on 6 and 7 June. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange. Based on analysis of satellite imagery and information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 11-12 and 14-15 June eruptions produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 6.1-7.9 km (20,000-26,000 ft) a.s.l. A possible eruption was seen on satellite imagery on 13 June.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 29 May-5 June seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Based on interpretations of seismic data, diffuse ash plumes were emitted during the reporting period; an ash plume possibly rose to an altitude of 3.8 km (12,500 ft) a.s.l. on 1 June. Video camera images showed steam-and-gas emissions. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange. Based on analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported on 7 June that a possible eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 3.4 km (11,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SW. A report a few hours later stated that ash emissions were continuing.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 22-29 May seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. Steam-and-gas emissions were seen during 21-23 May. Based on video camera views, gas-and-steam plumes containing a small amount of ash rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. on 22 May. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 15-22 May seismic activity from Shiveluch was above background levels. A hot avalanche seen on a video camera on 16 May produced an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. During 17-18 May, observers reported active fumaroles. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes were likely present during the reporting period; a possible ash plume rose to an altitude of 5.3 km (17,400 ft) a.s.l. on 21 May. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 8-15 May. Based on interpretations of seismic data, occasional ash plumes likely rose to an altitude of 5.4 km (17,700 ft) a.s.l. On 13 May, an ash plume generated by a hot avalanche was seen on video and rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 1-8 May. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes likely rose to an altitude of 6.7 km (22,000 ft) a.s.l. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a thermal anomaly from the lava dome every day. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 28 April-1 May. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes likely rose to altitudes of 5-6 km (16,400-19,700 ft) a.s.l. During 29-30 April, observers reported active fumaroles. Ash plumes generated by hot avalanches rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed an intense thermal anomaly on the lava dome every day. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange. Based on information from KEMSD and analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption on 5 May produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 6.7 km (22,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 17-24 April. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes likely rose to altitudes of 4.5-5.3 km (14,800-17,400 ft) a.s.l. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. According to observers, fumaroles were active during 16-22 and 22 April. A hot avalanche produced an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. on 22 April.
On 25 April, increased seismicity indicated that an ash plume rose to an altitude of 7.5 km (24,600 ft) a.s.l. On 26 April, seismicity remained at high levels; continuous spasmodic tremor and a series of weak shallow earthquakes occurred. An ash explosion from the lava dome was seen on video camera. Ash emitted from a large fissure on the S flank of the lava dome produced plumes that rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted ESE. The Level of Concern Color Code was raised to Red. The next day, seismicity decreased slightly but remained elevated and gas-and-steam emissions with some ash content emanated from the fissure. Based on video camera views and analysis of satellite imagery, plumes rose to altitudes of 3.5-5 km (11,500-16,400 ft) a.s.l. during 27-28 April and drifted 250 km NE. On 28 April, pyroclastic flows originated from areas near the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code was lowered to Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 10-17 April. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes likely rose to altitudes of 4.5-7.5 km (14,800-24,600 ft) a.s.l. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome and ash plumes that drifted about 50 km NW on 13 April. According to observers, fumaroles were active on 15 and 16 April. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange. Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruptions on 19 and 22 April produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.6-5.2 km (15,000-17,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 3-10 April. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes likely rose to an altitude of 7.5 km (24,600 ft) a.s.l. during 3-5 and 8-9 April. According to observers, fumaroles were active during 3-7 and 9 April. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruptions during 11-14 April produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.6-5.5 km (15,000-18,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels 27 March-3 April. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes likely rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. According to observers, fumaroles were active daily and explosions produced ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. on 31 March. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome and an ash plume that drifted 80 km S on 1 April. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 20-27 March. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes likely rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. According to observers, fumaroles were active during 23-26 March and explosions produced ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 8 km (26,200 ft) a.s.l. on 24 March. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome and an ash plume that drifted 40 km S on 25 March. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruptions during 27-28 March produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.3-5.5 km (14,000-18,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that during 13-20 March seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes likely rose to an altitude of 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 12-14 and 16-19 March. Strong fumarolic activity was seen on 13, 14, and 18 March and incandescence from the lava dome was seen at night on 14 and 18 March. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that during 6-13 March seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels and strong fumarolic activity was seen. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes likely rose to an altitude of 6.2 km (20,300 ft) a.s.l. Incandescence from the lava dome was seen at night. According to observers, ash plumes from hot avalanches rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE during 9-10 March. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome and ash plumes that drifted about 175 km SE during 7 and 10-11 March. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 27 February-6 March. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes likely rose to an altitude of 5.4 km (17,700 ft) a.s.l. According to observers, fumaroles were active during 28 February and 3-5 March. Ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.7 km (15,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE during 3-4 March. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome and an ash plume that drifted 84 km E on 4 March. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruptions on 8 and 10 March produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 6.1-6.4 km (20,000-21,000 ft) a.s.l. Plumes drifted SE on 10 March.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was at background levels during 21-28 February. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes likely rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. Lava flows continued to be active on the S and N flanks. Fumarolic activity was seen during 20-21 and 23-25 February. During 24-25 February, pilots reported dark plumes near the volcano that rose to altitudes of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome and an ash plume that drifted 40 km NNE on 25 February. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD and analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruptions on 25 February and 4 March produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.9-5.8 km (16,000-19,000 ft) a.s.l. The plumes drifted W on 25 February.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was at background levels during 13-20 February. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes likely rose to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,100 ft) a.s.l. Lava flows continued to be active on the S and N flanks. Fumarolic activity was seen during 12-13 and 19 February. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome and an ash plume that drifted 31 km NW on 17 February. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD and analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption on 18 February produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 4.9 km (16,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 6-13 February. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes likely rose to altitudes of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. Lava flows continued to be active on the S and N flanks. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 6 and 8-10 February; clouds prevented observations on the other days during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption on 12 February produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 30 January-6 February. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes likely rose to altitudes of 5.3 km (17,400 ft) a.s.l. Lava flows continued to be active on the S and N flanks. Weak gas-and-steam activity was noted on 30 January and 1 February. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a large thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 30 January-2 February, and on 5 February. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption on 7 February produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 4.9 km (16,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 22-30 January. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes rose to altitudes of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. on 22 January and to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. on the other days during the reporting period. Weak gas-and-steam activity was noted during 23-24 and 26-27 January. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruptions on 30 January and 1 February produced plumes that rose to altitudes of 4.9-5.5 km (16,000-18,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 16-23 January. Based on interpretations of seismic data, possible ash plumes rose to altitudes of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. on 17 and 21 January and to an altitude of 3 km (9,800 ft) a.s.l. on the other days during the reporting period. Gas-and-steam emissions were noted. On 21 January, an ash plume that was visible on a web camera rose to an altitude of about 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome, gas-and-steam plumes that drifted about 130 km SE, SW, and W during 16-17 and 19-20 January, and an ash plume that drifted 65 km SW on 18 January. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 9-16 January. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes rose to altitudes of 7.3 km (23,900 ft) a.s.l. and 6.9 km (22,600 ft) a.s.l. on 9 and 14 January, respectively, and to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. on the other days during the reporting period. Observers reported that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. on 9 January and noted gas-and-steam activity during 8-10 and 12-14 January. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome and gas-and-steam plumes that drifted about 70 km S, SE, and NE during 9-11 and 13 January. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 18 January an eruption produced a plume that rose to an altitude of 5.8 km (19,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 2-9 January. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 8.8 km (28,900 ft) a.s.l. on 7 January and to an altitude of 5.7 km (18,700 ft) a.s.l. on the other days during the reporting period. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a large daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome and an ash plume that drifted 25 km W on 6 January. Gas-and-steam emissions were seen on 2, 4, and 6 January. Ash deposits were noted in areas about 10 km SW on 7 January. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 25 December-2 January. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 7 km (23,000 ft) a.s.l. on 25 and 26 December, and to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. on the other days during the reporting period. An ash plume was seen on 25 December at an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. and gas-and-steam emissions were noted on 25 and 30 December, and on 1 January. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome and an ash plume that drifted 40 km NW on 30 December. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD and analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 1, 2, 5, and 6 January eruptions produced plumes to altitudes of 4.6-5.8 km (15,000-19,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 19-26 December. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 8.5 km (27,800 ft) a.s.l. on 19 and 20 December and to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. during 21-26 December. An ash plume was seen on 22 December at an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. and gas-and-steam emissions were noted on 23 and 24 December. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD and analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 26-27 and 30 December eruptions produced plumes to altitudes of 5.5-7 km (18,000-23,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 12-19 December. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. Visual observations of weak gas-and-steam emissions were noted during 12-14 and 18 December. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KVERT and analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 21-22 December eruptions produced plumes to altitudes of 5.8-8.5 km (19,000-28,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 5-12 December. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. Visual observations of weak gas-and-steam emissions were noted during 5, 7, and 9-10 December. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD and analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 11 December eruptions produced plumes to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 28 November-5 December. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.8 km (19,000 ft) a.s.l. According to visual observations, gas-and-steam plumes rose to an altitude of 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. during 27 and 29-30 November, and 2 December. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 21-28 November. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.6 km (18,400 ft) a.s.l. Ashfall was reported in the town of Klyuchi, about 30 km SW, on 22 November. Visual observations confirmed that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. on 25 November. Fumarolic activity was visible on the web camera during 26-28 November. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome and a gas-and-steam plume that drifted about 30 km SE on 26 November. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD and analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 1 December eruptions produced plumes to an altitude of 4.9 km (16,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 14-21 November. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity was visible on the web camera on 16 and 17 November. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome and a gas-and-steam plume that drifted about 100 km E on 14 November. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD and analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 22 and 24-25 November eruptions produced plumes to altitudes of 5.2-5.8 km (17,000-19,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 6-14 November. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.8 km (22,300 ft) a.s.l. Hot avalanches descended the lava dome on 6 November and produced ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. On 10 November, an ash plume drifted 30 km E and gas-and-steam plumes drifted 50 km. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange. Fumarolic activity was visible on the web camera on 8, 10, and 12 November.
Based on information from KEMSD and analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 13 and 16 November eruptions produced plumes to altitudes of 4.9-6.1 km (16,000-20,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 31 October-7 November. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.2 km (17,100 ft) a.s.l. A large number of daily hot avalanches were observed descending the lava dome and producing ash plumes on 2, 3, and 5 November that rose to an altitude of 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity was visible on the web camera during 2-3 and 5-6 November. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome on 31 October and 1, 2, 3, and 6 November. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD and analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 8-10 November eruptions produced plumes to altitudes of 4.9-5.8 km (16,000-19,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 24-31 October. Based on interpretations of seismic data, a large number of hot avalanches were inferred to have descended the lava dome and produced ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 5.2 km (17,100 ft) a.s.l. Ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. were seen on 24 October. Fumarolic activity was visible on the web camera during 23-25 and 28-30 October. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD and analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 2 and 4 November eruption plumes rose to altitudes of 5.2 and 4.6 km (17,000 and 15,000 ft) a.s.l., respectively.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 17-24 October. Based on interpretations of seismic data, a large number of hot avalanches were inferred to have descended the lava dome and produced ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 6.7 km (22,000 ft) a.s.l. Significant hot avalanches that produced ash plumes to altitudes of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. were seen on 16 and 20 October. Fumarolic activity was visible on the web camera during 17-20 and 22-23 October. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome, and ash plumes drifted 60 km E on 20 October. Ash plumes about 10 by 11 km and 10 by 5 km in horizontal dimensions drifted about 30-40 km SE on 19 and 22 October, respectively. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 10-17 October. Based on interpretations of seismic data, a large number of hot avalanches descended the lava dome and produced ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. Significant hot avalanches were seen on 13 October. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 10-11 and 13-14 October, and steam-and-ash plumes with a small amount of ash that drifted 30 km NE on 14 October. Fumarolic activity was visible on the web camera during 10-13 and 16-17 October. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD and analysis of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that during 18-20 October eruption plumes rose to altitudes of 4.9-6.7 km (16,000-22,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 3-10 October. Based on interpretations of seismic data, a large number of hot avalanches descended the lava dome and produced ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. Fumarolic activity and gas-and-steam plumes that rose to an approximate altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. were visible on the web camera during 2-5 and 7-9 October. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome and steam-and-ash plumes that drifted 30 km N and E on 6 and 7 October.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 26 September-3 October. A large number of hot avalanches descended the lava dome and produced ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400 ft) a.s.l. On 28 September, an ash plume that was visible on a web camera rose to an altitude of about 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash explosions likely occurred on 28 September and 1 October and generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 7.5 km (24,600 ft) a.s.l. Ashfall was reported in Klyuchi (about 45 km SW) on 1 October. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 28 September and 1-2 October. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 19-26 September. A large number of hot avalanches may have descended the lava dome and produced ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 3.6 km (11,800 ft) a.s.l. Fumaroles on the lava dome were active on 19 September. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. According to a news article, video cameras recorded an eruption that produced an ash plume on 26 September. The ash plume rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Itar-Tass News
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 12-19 September. Video camera data, analysis of seismic data, and visual observations showed that a small hot avalanche descended the SE side of the lava dome, producing an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 100 km NE. Fumaroles were active during 15-18 September; cloud cover prevented visual observations on other days. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 5-12 September. A large number of hot avalanches descended the lava dome; ash produced from one of the events rose to an altitude of 5.1 km (16,700 ft) a.s.l. on 10 September. Fumaroles were active during 10-11 September; cloud cover prevented visual observations on other days. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
According to a news article, a small collapse of the SW part of the lava dome on 13 September generated an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 100 km NE.
Sources: Itar-Tass News; Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 29 August-5 September. Gas-and-steam plumes with a small amount of ash were generated from avalanches on 29 and 30 August and rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 22-29 August. Gas-and-steam plumes with a small amount of ash were generated from avalanches during 22 and 25-28 August. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome and that steam-and-ash plumes drifted 80 km SE on 26 and 27 August. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 15-22 August. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome on 15, 18, and 21 August. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 8-15 August. Analysis of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome. Based on information from KEMSD and observations of satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 15 August an eruption plume rose to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,000 ft) a.s.l. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 1-8 August, and possibly indicated that ash plumes from explosions rose to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,100 ft) a.s.l. on 6 August. Observations of satellite imagery revealed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 1-3 August. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 25 July-1 August. According to visual observations, small hot avalanches occasionally descended the lava dome and fumaroles were active on 18 and 22 July. Observations of satellite imagery revealed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome daily during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 18-25 July. Moderate fumarolic activity was seen on 18 and 22 July. Observations of satellite imagery revealed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 18-22 July; clouds obscured views on other days. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 11-18 July and possibly indicated ash explosions up to 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. on 17 July. Moderate fumarolic activity was seen on 13 and 15 July. Observations of satellite imagery revealed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 10-11 and 13-17 July. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch possibly indicated ash explosions on 26 June and was slightly above background levels during 26 June-4 July. Moderate fumarolic activity was seen on 29 June, and 1 and 3 July. Observations of satellite imagery revealed a strong thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 27-29 June and 1-3 July. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 20-27 June and possibly indicated ash explosions on 21, 22, and 25 June. According to video footage and visual observations, moderate fumarolic activity was noted on 24 and 25 June and an ash plume at an altitude of 4.2 km (13,800 ft) a.s.l. occurred on 25 June. Observations of satellite imagery revealed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 19-20 and 23-25 June. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 13-20 June. According to video footage and visual observations, moderate fumarolic activity was noted on 13 June. Observations of satellite imagery revealed a thermal anomaly on the lava dome during 12-13 June; clouds obscured views on other days. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was at background levels during 6-13 June. According to video footage and visual observations, moderate fumarolic activity was noted during 5-9 June. Observations of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly in the crater. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels on 29 and 30 May and at background levels during 31 May-6 June. Gas-and-ash explosions may have occurred on 29-30 May and 3 June, possibly sending plumes to an altitude of 3.6 km (11,800 ft) a.s.l. According to video footage and visual observations, moderate fumarolic activity was noted during 31 May and 1-5 June. Observations of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly in the crater, and a gas-and-steam plume that drifted 20 km WNW on 31 May. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 27-28 May and at background levels the other days during 23-30 May. Gas-and-ash explosions may have occurred on 22, 27, and 28 May and produced plumes to an altitude of 4.7 km (15,400 ft) a.s.l. According to video footage and visual observations, hot avalanches descended the lava dome and ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.6 km (11,800 ft) a.s.l. during 26-27 May. Fumarolic activity was noted during 23-27 May. Observations of satellite imagery revealed a daily thermal anomaly in the crater, and an ash-and-steam plume that drifted 17 km SW on 28 May. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was at background levels during 15-17 and 21 May and above background levels the other days during 16-23 May; gas-and-ash explosions may have occurred on 18, 19, and 20 May. According to video footage and visual observations, small hot avalanches descended the lava dome every day and fumarolic activity was noted. A large hot avalanche caused an ash plume to rise to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. on 20 May. The plume drifted E. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater daily and an ash-and-steam plume drifted more than 100 km SE on 20 May.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels on 12 and 14 May and at background levels the other days during 9-16 May; gas-and-ash explosions may have occurred on 14 May. During 9 and 11-15 May, hot avalanches descended the lava dome and fumarolic activity was noted. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater daily. During 11-13 May, ash and steam plumes drifted SE, SW, and NW. An ash plume at an altitude of 3.6 km (11,800 ft) a.s.l. was spotted on 14 May. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from the KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that on 20 May an eruption plume rose to an altitude of 5.8 km (19,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels on 5 May and at background levels the other days during 2-9 May. Based on seismic interpretation, hot avalanches possibly descended the growing lava dome. Video footage and visual observations showed fumarolic activity from the lava dome during 5-6 and 8 May. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater during 5-8 May. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was at background levels during 25 April-2 May. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater during 27, 28, and 30 April, and 1 May. On 28 April, ash deposits extending about 10 km NW were observed on satellite imagery and possible gas-and-ash explosions were detected by the seismic network. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 18-25 April. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater during 18 and 20-23 April. According to video footage and visual observations, fumarolic activity from the lava dome occurred during 21-23 April. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 10-15 April and at background levels on 16 April. According to video footage and visual observations, fumarolic activity from the lava dome occurred during 12-15 April. Based on seismic interpretation, a possible ash plume rose to an altitude of 3 km (9,800 ft) a.s.l. on 14 April. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater during 11-14 April. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels and hot avalanches possibly descended the growing lava dome daily during 4-11 April. According to video footage and visual observations, fumarolic activity from the lava dome also occurred every day. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 28 March-4 April and hot avalanches possibly descended the growing lava dome daily. According to video footage and visual observations, fumarolic activity from the lava dome was observed during 28-29 March and 1-3 April. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 21-28 March and hot avalanches possibly descended the dome during 19-22 March. According to video footage and visual observations, fumarolic activity from the lava dome was observed during 20-24 and 27 March. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 14-21 March. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 3.5 km (11,200 ft) a.s.l. on 13 and 17 March. According to video footage and visual observations, an ash plume rose to an altitude of 4 km (12,800 ft) a.s.l. on 17 March and fumarolic activity from the lava dome was observed during 17 and 19-20 March. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a gas plume drifted 17 km SW on 17 March and a thermal anomaly was present in the crater during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 7-14 March. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 4.1 km (13,500 ft) a.s.l. on 6 and 7 March. According to video footage and visual observations, fumarolic activity from the lava dome was observed during 6-8 March. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels and small hot avalanches descended the lava dome during 29 February-7 March. Ash plumes were possibly present. According to video footage and visual observations, fumarolic activity was observed during 29 February and 2-6 March. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels and small hot avalanches descended the lava dome during 22-29 February. According to video footage, fumarolic activity was observed during 21-22 and 24-25 February. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 5.6 km (18,400 ft) a.s.l. during 24-26 February. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 15-22 February. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 3 km (10,000 ft) a.s.l. on 17 and 20 February. During the reporting period strong fumarolic activity was seen daily on video footage and a thermal anomaly was present in the crater on satellite imagery. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 8-11 February and at background levels on 12 and 13 February. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 3.3 km (10,800 ft) a.s.l. on 9 February. Strong fumarolic activity was noted during 8-9 and 11-12 February. According to observations of satellite imagery, a thermal anomaly was present in the crater every day during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 1-8 February. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.8 km (12,200 ft) a.s.l. daily. Strong fumarolic activity was noted on 5 and 6 February. According to observations of satellite imagery, a thermal anomaly was present in the crater on 1, 3, and 6 February. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 25 January-1 February. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.9 km (12,800 ft) a.s.l. daily. Fumarolic activity was noted on 24, 29, and 30 January. According to observations of satellite imagery, a thermal anomaly was present in the crater every day during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 18-25 January. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.3 km (14,100 ft) a.s.l. during 17-18, 20, and 23 January. Fumarolic activity was noted on 19, 20, and 22 January. Based on observations of satellite imagery, a thermal anomaly was present in the crater every day during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 11-18 January. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.1 km (13,500 ft) a.s.l. on 12 and 16 January. Ash plumes at an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. were visible on the Shiveluch web camera on 16 January. Strong fumarolic activity was noted during 15-17 January. Based on observations of satellite imagery, a thermal anomaly was present in the crater every day. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 4-11 January. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.3 km (20,700 ft) a.s.l. during 3-4, 6, and 9 January. Strong fumarolic activity was noted during 7-9 January. Based on observations of satellite imagery, a gas-and-steam plume drifted NW on 3 January and a thermal anomaly was present in the crater every day during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from the KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruption plumes rose to altitudes of 4.9 and 4.6 km (16,000 and 15,000 ft) a.s.l. on 10 and 16 January, respectively.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 28 December-4 January. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.8 km (19,000 ft) a.s.l. during 28-31 December and on 1 and 3 January. Moderate fumarolic activity was noted on 30 December and 2 January. Based on observations of satellite imagery, a thermal anomaly was present in the crater every day. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from the KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruption plumes rose to altitudes of 6.4 and 4.9 km (21,000 and 16,000 ft) a.s.l. on 4 and 6 January, respectively.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 21-28 December. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to an altitude of 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. during 23-24 December. Based on observations of satellite imagery, a thermal anomaly was present in the crater every day. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on observations of satellite imagery and information from the KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruption plumes rose to altitudes of 4.9-5.8 km (16,000-19,000 ft) a.s.l. during 28-29 December.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 14-21 December. Based on seismic interpretation, a series of explosions during 18-19 December produced ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 6.5-8.7 km (21,300-29,000 ft) a.s.l. Ash plumes were observed on satellite imagery and drifted more than 130 km W on 18 December and 300 km to the NW and SW on 19 December. Ashfall was reported in the town of Klyuchi, about 30 km SW on 19 December. Based on visual observations, large pyroclastic flow deposits 8-9 km from the lava dome were noted on the S flank. On 20 December, KVERT reported that the Level of Concern Color Code was raised to Red. On 21 December, the Level of Concern Color Code was lowered back to Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 7-14 December. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. during 7-9 December. Visual observations and video footage analysis indicated that an ash plume rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. on 12 December and gas-and-steam plumes rose to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400 ft) a.s.l. during the reporting period. Based on observations of satellite imagery, a thermal anomaly was present in the crater every day. On 18 December, KVERT reported that the number of shallow earthquakes increased from 70 on 10 December to 390 on 17 December. KVERT warned that the aviation hazard increased. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 30 November-7 December. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.3 km (17,000 ft) a.s.l. and hot avalanches occurred. Visual observations and video footage analysis indicated that gas-and-steam plumes rose to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400 ft) a.s.l. during the reporting period. One ash plume rose to an altitude of 5.7 km (18,700 ft) a.s.l. on 2 December. Based on observations of satellite imagery, a thermal anomaly was present in the crater every day during 30 November-7 December. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from the KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption plume rose to an altitude of 5.2 km (17,000 ft) a.s.l. on 10 December.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 23-30 November. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. and hot avalanches occurred. Visual observations and video footage analysis indicated that gas-and-steam plumes rose to an altitude of 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. on 22 and 26-29 November. Based on observations of satellite imagery, ash plumes drifted SW, NW, N, and SE on 26, 27, and 28 November and a thermal anomaly was present in the crater every day during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from the KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruption plumes rose to altitudes of 5.5 km and 5.8 km (18,000 ft and 19,000 ft) a.s.l. on 30 November and 2 December, respectively.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 2-9 November. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 8.5 km (28,000 ft) a.s.l. and small hot avalanches occurred. Visual observations and video footage analysis indicated that ash and gas-and-steam plumes rose to altitudes of 6-8 km (19,700-26,200 ft) a.s.l. during 4-8 November. Clouds obscured views of the volcano on other days. Based on observations of satellite imagery, ash plumes drifted SW on 7 November and a thermal anomaly was present in the crater every day during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from the KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruption plumes rose to altitudes of 4.9-5.5 km (16,000-18,000 ft) a.s.l. on 11 and 13 November.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 26 October-2 November. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.8 km (22,300 ft) a.s.l. and small hot avalanches occurred. Observations of video footage indicated that ash and gas-and-steam plumes rose to altitudes of 5-5.3 km (16,400-17,400 ft) a.s.l. on 25, 26, and 31 October, and 1 November. Based on observations of satellite imagery, ash plumes drifted SE during 27-31 October and a thermal anomaly was present in the crater every day during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KVERT and KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruption plumes rose to altitudes of 5.2-8.5 km (17,000-28,000 ft) a.s.l. during 4-6 November.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 19-26 October. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.9 km (22,600 ft) a.s.l. and small hot avalanches occurred. Observations of video footage indicated that gas-and-steam plumes rose to altitudes of 3.3 km (10,800 ft) a.s.l. on 21 and 25 October. Based on observations of satellite imagery, ash plumes drifted SE on 19 October and a thermal anomaly was present in the crater every day during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from the KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruption plumes rose to altitudes of 4.6-6.7 km (15,000-22,000 ft) a.s.l. during 27-28 and 30 October.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 12-19 October. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. and small hot avalanches occurred. Observations of video footage indicated that gas and occasionally ash plumes rose to altitudes of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. during 11-12 and 14-15 October. Based on observations of satellite imagery, ash plumes drifted E on 12, 14, and 16 October and a thermal anomaly was present in the crater every day during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from the KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruption plumes rose to altitudes of 4.6-6.7 km (15,000-22,000 ft) a.s.l. on 18, 20, 22, and 23 October.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 5-12 October, KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels and small hot avalanches occurred. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. during 4-6 and 9-11 October. Observations of video footage indicated that gas and occasionally ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. on 4, 6, 7, and 11 October. Fumarolic activity was noted on 8 October. Based on observations of satellite imagery, ash plumes drifted E during 4-8 October and a thermal anomaly was present in the crater every day during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from the KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption plume rose to an altitude of 5.2 km (17,000 ft) a.s.l. on 16 October.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 28 September-5 October, KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.3 km (17,400 ft) a.s.l. and hot avalanches occurred on 27 and 29 September. Ash plumes were visible on satellite imagery drifting WSW and SE. Observations of video footage indicated that gas-and-steam plumes rose up to altitudes of 4.5 km and 3.5 km (14,800 and 11,500 ft) a.s.l. on 27 September and 2 October, respectively. Fumarolic activity was noted on 1 October. A thermal anomaly was present in the crater on satellite imagery during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from the KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption plume rose to an altitude of 5.8 km (19,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 21-28 September, KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels and hot avalanches occurred. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.3 km (14,100 ft) a.s.l. on 20 and 25 September. Observations of video footage indicated that gas-and-ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. on 21, 24, 25, and 26 September. Plumes drifted E during 24-25 September. A thermal anomaly was present in the crater on satellite imagery during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 14-21 September. During 14-15 and 17-20 September, avalanches occurred and ash plumes rose to altitudes of 3.5-5.5 km (11,500-18,000 ft) a.s.l. Observations of video data indicated that gas-and-ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.3 km (10,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE and E on 14 and 15 September. Gas-and-steam plumes were noted on 13, 18, and 19 September. A thermal anomaly was present in the crater on satellite imagery during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 7-14 September. During 6-9 September, avalanches occurred and ash plumes rose to altitudes of 4-6.5 km (13,100-21,300 ft) a.s.l. Observations of video data indicated that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. on 7 September. Gas-and-steam plumes were noted on 7, 10, and 11 September. A thermal anomaly was present in the crater on satellite imagery during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 31 August-7 September. Based on seismic interpretation during this interval, avalanches and ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 5.7 km (18,700 ft) a.s.l. Visual observation and video data indicated that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. on 1 September and drifted SE. Gas-and-steam plumes were noted on the other days. Observations of satellite imagery revealed a thermal anomaly present in the crater during the reporting period. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information reported from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption plume rose to an altitude of 4.9 km (16,000 ft) a.s.l. on 9 September. Ash was not identified on satellite imagery.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 24-31 August. Based on seismic interpretation, avalanches and ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 9 km (29,500 ft) a.s.l. occurred during the reporting period. Based on visual observation and video data, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. on 25 August. Clouds inhibited observations the other days. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater during 24-31 August. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information reported from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption plume rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. on 2 September. Ash was not identified on satellite imagery.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 17-24 August. Based on seismic interpretation, avalanches and ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 8.5 km (27,900 ft) a.s.l. occurred during the reporting period. Based on visual observation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted N and NE during 17-21 August. Incandescence at the lava dome and incandescent avalanches were seen at night on 21 August. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater during 17-24 August. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information reported from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruption plumes rose to altitudes of 4.9-7.6 km (16,000-25,000 ft) a.s.l. during 24-27 August. Ash was not identified on satellite imagery.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 10-17 August. Based on seismic interpretation, avalanches and ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. occurred during the reporting period. Growth of the E part of the lava dome, summit incandescence, and incandescent avalanches were visible from the town of Klyuchi, about 50 km SW, during 11-12 August. A diffuse ash plume was visible on satellite imagery drifting SE on 11 August. On 14 August, two avalanches were accompanied by ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NW. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater during 10-17 August. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information reported from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption plume rose to 5.2 km (17,000 ft) a.s.l. on 21 August. Ash was not identified on satellite imagery.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 3-10 August. Based on seismic interpretation, avalanches and ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. occurred during the reporting period. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater during 2-5 and 8-9 August. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that ash plumes rose to altitudes of 4.6-10.1 km (15,000-33,000 ft) a.s.l. during 12-13 August. Based on seismic interpretation, a high plume occurred again on 13 August. Ash was not identified on satellite imagery.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch was slightly above background levels during 27 July-3 August. Observations of satellite imagery revealed that a thermal anomaly was present in the crater. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes and avalanches occurred during the reporting period. Gas-and-steam plumes were visible drifting S on 31 July; clouds inhibited visual observations on other days. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reports noted that seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 20-27 July. Based on seismic interpretation, during this interval ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. Gas-and-steam plumes with some ash rose to altitudes of 3.0-4.5 km (9,800-14,800 ft) a.s.l. during 20-24 July. Based on satellite imagery, gas-and-steam plumes drifted S on 22 July and a large thermal anomaly was detected in the crater during 20-27 July. Through at least 27 July, the Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 13-20 July. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. during the reporting period. Gas-and-steam plumes with some ash rose to altitudes of 3-4.5 km (9,800-14,800 ft) a.s.l. during 11-15 and 18-19 July. Based on satellite imagery, plumes drifted S and SW during 15-16 July and a large thermal anomaly was detected in the crater during 13-20 July. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information reported from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption plume rose to 5.8 km (19,000 ft) a.s.l. on 24 July. Ash was not identified on satellite imagery.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 6-13 July. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. during the reporting period. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to altitudes of 4-5 km (13,100-16,400 ft) a.s.l. during 9-11 July. A large thermal anomaly was detected in the crater on satellite imagery all days. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 29 June-6 July. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. during the reporting period. A large thermal anomaly was detected in the crater on satellite imagery all days. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption plume rose to 4.6 km (15,000 ft) a.s.l. during 27-28 June. Ash was not identified on satellite imagery.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 22-29 June. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. during the reporting period. A large thermal anomaly was detected in the crater on satellite imagery all days. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption plume rose to 4.6 km (15,000 ft) a.s.l. during 27-28 June. Ash was not identified on satellite imagery.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 15-22 June. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to an altitude of 5.3 km (17,400 ft) a.s.l. during the reporting period. On 15 June, gas-and-steam plumes drifted S. A large thermal anomaly was detected in the crater on satellite imagery during 14-17 and 20 June. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Based on information from KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an eruption plume rose to 5.8 km (19,000 ft) a.s.l. during 25-26 June. Ash was not identified on satellite imagery.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 8-15 June and a thermal anomaly in the crater was detected on satellite imagery. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to altitudes of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. during 8-10 and 13 June. Ash plumes rose to altitudes of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. on 8 and 10 June and were seen on satellite imagery drifting NW on 12 June. Based on seismic interpretation, multiple ash plumes rose to 6.3 km (20,700 ft) a.s.l. during 8-15. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 1-8 June and a thermal anomaly in the crater was detected on satellite imagery. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to altitudes of 4.5 km (14,800 ft) a.s.l. during 1-3 and 5 June. Ash plumes rose to altitudes of 4.5-6 km (14,800-19,700 ft) a.s.l. on 1 and 6 June and were seen on satellite imagery drifting S and SE on 3 and 6 June. Based on seismic interpretation, multiple ash plumes rose to 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. during 1-8. The Tokyo VAAC reported that eruption plumes rose to altitudes of 4.3-9.1 km (14,000-30,000 ft) a.s.l. on 9, 11, and 12 June, based on information from KVERT and KEMSD. Ash was not identified on satellite imagery. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 25 May-1 June. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 9.5 km (31,200 ft) a.s.l. throughout the reporting period. According to visual observation and video data, gas-and-steam and ash plumes rose to altitudes of 5-6 km (16,400-19,700 ft) a.s.l. during 27-28 and 30-31 May. Plumes were seen on satellite imagery drifting SW during 27-28 May. A large thermal anomaly was also visible on satellite imagery. The Tokyo VAAC reported that based on reports from KEMSD, an eruption plume rose to an altitude of 6.4 km (21,000 ft) a.s.l. on 2 June. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 18-25 May. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes possibly rose to altitudes of 4-8 km (13,100-26,200 ft) a.s.l. throughout the reporting period. Plumes were visible on satellite imagery drifting N, NE, and NW during 17-19 May. A large thermal anomaly was also visible on satellite imagery. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 11-18 May. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes possibly rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. throughout the reporting period. A large thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 4-11 May. Based on seismic interpretation, observation, and video data, ash plumes possibly rose to altitudes of 6-7 km (19,700-23,000 ft) a.s.l. throughout the reporting period. Plumes were seen on satellite imagery drifting E on 5 and 7 May and a thermal anomaly was present during 4-11 May. Gas-and-steam activity was noted during 4-7 May. Visual and video data revealed hot avalanches originating from the lava dome during 4 and 6-7 May. Based on information from the KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that ash plumes rose to altitude of 5.8-8.2 km (19,000-27,000 ft) a.s.l. during 9-11 May. An ash plume was possibly seen on satellite imagery to an altitude of 4.9 km (16,000 ft) a.s.l. drifting NW on 15 May. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 27 April-4 May. Based on seismic interpretation, observation, and video data, ash-and-steam plumes possibly rose to altitudes of 4-10 km (13,100-32,800 ft) a.s.l. throughout the reporting period. Plumes were seen on satellite imagery drifting S and SW during 28-29 April and a thermal anomaly was present during 27 April-4 May. Based on visual and video data, hot avalanches originating from the lava dome were observed on 30 April. Based on information from the KEMSD, the Tokyo VAAC reported that an ash plume rose to an altitude of 4.9 km (16,000 ft) a.s.l. on 7 May. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Itar-Tass News; Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 20-27 April. Based on seismic interpretation, observation, and video data, ash-and-steam plumes possibly rose to altitudes of 6.5-9 km (21,300-30,000 ft) a.s.l. throughout the reporting period. Plumes were seen on satellite imagery drifting E and SE, and a thermal anomaly was present. Hot avalanches originated from the dome. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 13-20 April. Based on seismic interpretation, observation, and video data, ash-and-steam plumes possibly rose to altitudes of 5.5-6.5 km (18,000-21,300 ft) a.s.l. throughout the reporting period. Plumes were seen on satellite imagery drifting E, SE, and S and a thermal anomaly was present. Base on pilot reports, satellite imagery, KEMSD, and observations from the Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky Flight Information Region (FIR), the Tokyo VAAC reported that ash plumes rose to altitudes of 4.6-6.1 km (15,000-20,000 ft) a.s.l. during 18-22 April. They drifted E. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 4-10 April. Based on seismic interpretation, observation, and video data, possible ash-and-steam plumes rose to altitudes of 4.5-7 km (14,800-23,000 ft) a.s.l. throughout the reporting period. Based on satellite imagery during 10-12 April, plumes drifted N, NW, SE, and SW and a thermal anomaly was present. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 4-10 April. Based on seismic interpretation, observation, and video data, ash-and-steam plumes rose to altitudes of 4.5-5 km (14,800-16,400 ft) a.s.l. throughout the reporting period. Plumes drifted N on 6 April. A large thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery during 1-10 April. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
An explosive event at Shiveluch on 29 March produced an ash plume that rose to an estimated altitude of 9.8 km (32,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NE. Based on reports from the Yelizovo Meteorological Watch Office and satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that the plume reached an altitude of 11.9 km (39,000 ft) a.s.l. The next day, an explosive event that lasted about 6 minutes produced a plume to altitudes of 10.1-12.2 km (33,000-40,000 ft) a.s.l., based on estimates from AVO, Tokyo VAAC, and the Kamchatkan Branch of Geophysical Services. The plume drifted NE.
According to a news article, a mudflow covered an approximately 900-m-long section of road, about 20 km from Shiveluch on 31 March.
Sources: US Geological Survey Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO); Itar-Tass News
Based on satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that emissions of gas and steam from Shiveluch continued on 22 March. Ash was not identified on satellite imagery.
Source: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
Seismic activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 16-22 February. Based on seismic interpretation, observation, and video data, gas-and-ash plumes rose to altitudes of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. throughout the reporting period. Plumes drifted S, NW, and N. A large thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery. The Tokyo VAAC reported eruption plumes to altitudes of 4.6 km (15,000 ft) a.s.l. on 22 February based on information from KEMSD, KVERT, and satellite imagery. Plumes drifted N. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 9-16 February, with over 180 volcanic earthquakes and tremor occurring daily. Based on seismic interpretation, observation, and video data, gas-and-ash plumes rose to altitudes of 5.5-6 km (18,000-19,700 ft) a.s.l. throughout the reporting period. Plumes drifted W and SW. A large thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery. The Tokyo VAAC reported eruption plumes to altitudes of 5.2-6.1 km (17,000-20,000 ft) a.s.l. on 15 and 19 February based on information from KEMSD, KVERT, and satellite imagery. Plumes drifted NW on 19 February. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 2-9 February, with over 200 shallow earthquakes occurring daily. Based on seismic interpretation, observation, and video data, gas-and-ash plumes rose 4.0-5.5 km (13,100-18,000 ft) a.s.l. throughout the reporting period. Plumes drifted NE and NW. A large thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery. The Tokyo VAAC reported ash plumes to an altitude of 5.2-5.5 km (17,000-18,000 ft) a.s.l. on 10 and 13 February that were visible on satellite imagery. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 26 January-2 February, with over 140 shallow earthquakes occurring daily. Based on seismic interpretation, observation, and video data, gas-and-ash plumes rose 3.5-4.5 km (11,500-14,800 ft) a.s.l. throughout the reporting period. Plumes drifted ESE. A large thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery. The Tokyo VAAC reported ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 4.3 km (14,000 ft) a.s.l. on 1 February were visible on satellite imagery drifting E. An eruption occurred on 6 February that was not visible on satellite imagery. The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 19-26 January, with over 120 shallow earthquakes occurring daily. Based on seismic interpretation and observation and video data, gas-and-ash plumes rose to 5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. and avalanches occurred throughout the reporting period. Plumes drifted W and NW. Fumarolic activity from the SW flank was noted on 25 January. A large thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery. Based on satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 4.6 km (15,000 ft) a.s.l. on 28 and 29 January and drifted SE.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 12-19 January, with over 160 shallow earthquakes occurring daily. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l. and avalanches occurred throughout the reporting period. According to observation and video data, gas-and-ash plumes rose to an altitude of 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. on 16 January. Plumes drifted SW, NW, and NE on 12 and 14-18 January. A large thermal anomaly over the dome was noted. Based on satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6.1 km (20,000 ft) a.s.l. on 22 and 23 January and drifted NW.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
Activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 5-12 January, with over 200 shallow earthquakes occurring daily. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to 7.5 km (24,600 ft) a.s.l. and avalanches occurred throughout the reporting period. According to observation and video data, gas-and-ash plumes rose to an altitude of 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. during 5-7 and 10-11 January. Plumes drifted E and SSW. A large thermal anomaly over the dome was noted.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Activity at Shiveluch continued above background levels during 29 December-5 January, with 200 shallow earthquakes occurring daily. Based on seismic interpretation, ash plumes rose to 13.7 km (45,000 ft) a.s.l. According to visual and video data, a large hot avalanche occurred on the SE flank on 4 January. Fumarolic activity was noted during 29-31 December and 2-4 January. The Tokyo VAAC reported eruption plumes to altitudes of 4.3-7.6 km (14,000-25,000 ft) a.s.l. during 5-7 January based on information from the Kamchatkan Experimental and Methodical Seismological Department (KEMSD) and satellite imagery.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismic activity from Shiveluch decreased on 27 December, but still remained above background levels. Based on video data, a steam-and-gas plume rose to 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. on 27 December. On 28 December, ash plumes rose to 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. and were seen on satellite imagery drifting E. The level of Concern Color Code was lowered to Orange.
Based on information from the Kamchatkan Experimental & Methodical Seismological Department (KEMSD) and satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that eruptions produced plumes rising to 4.9-8.2 km (16,000-27,000 ft) a.s.l. on 1 and 2 January.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
According to observations, video data, and satellite imagery KVERT reported that ash plumes from Shiveluch rose to 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E on 16-17 and 20 December. Seismic activity was generally at background levels. Based on satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported that a possible eruption plume rose to an altitude of 9.1 km (30,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E on 24 December. Seismic and video data on 26 December indicated an ash plume above 10 km (32,800 ft.) a.s.l., extending 150 km NE in satellite imagery. The level of Concern Color Code was raised from Orange to Red.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
According to observations and video data, KVERT reported that ash plumes from Shiveluch rose to 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NW and ESE on 8 and 12 December, respectively. Based on satellite imagery, ash plumes rose to altitudes of 6-7.5 km (19,700-24,600 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E and NE during 8-15 December. Seismic activity was generally at background levels. The Tokyo VAAC and KVERT reported that ash plumes rose to altitudes of 7.6-10 km (25,000-32,800 ft) a.s.l. and drifted E and NW on 16 and 17 December.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
According to observations and video data, KVERT reported fumarolic activity from Shiveluch during 2-4 and 6-7 December. Based on satellite imagery, the Tokyo VAAC reported possible eruption plumes on 8 and 11 December that reached altitudes of 5.2 km (17,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SW and NE, respectively. Satellite imagery and a pilot observation reported by the VAAC indicated ash plumes on 12 December to altitudes of 3-5.8 km (10,000-19,000 ft) a.s.l.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that a strong seismic event from Shiveluch was recorded on 4 December at 2100. Prior to the event, seismicity was at background levels and weak fumarolic activity was observed. According to video data from 5 December, explosions produced plumes that rose to an altitude of 4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NW. Strong explosions from the lava dome were possible and avalanches to a distance of 3-5 km down the SW flank were noted. The Level of Concern Color Code was raised from Yellow to Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Eruption plumes from Shiveluch that were visible on satellite imagery on 19 July reached a maximum altitude of 5.2 km (17,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE. Ash was not visible on satellite imagery. A thermal anomaly over the dome was visible on 17 and 18 July.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismic activity and lava-dome growth continued at Shiveluch during 28 October to 4 November. Seismicity decreased gradually during the previous 2 weeks and only weak avalanches were recorded, so KVERT reduced the Concern Color Code at Shiveluch from Orange to Yellow on 4 November.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The growth of Shiveluch's lava dome continued during 21-28 October. Weak shallow earthquakes, hot avalanches, and low-intensity fumarolic activity occurred at the volcano during the week. On 22 and 24 October, incandescence was visible at the lava dome. A weak ash-and-gas plume extending E was observed on 22 October. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The growth of Shiveluch's lava dome continued during 14-21 October. Weak shallow earthquakes, hot avalanches, and low-intensity fumarolic activity occurred at the volcano during the week. On 15 and 17 October, incandescence was visible at the lava dome. A thermal anomaly from the lava dome was seen in satellite imagery during the report week. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Growth of Shiveluch's lava dome and heightened seismicity continued at the volcano during 23-30 September. Weak gas-and-steam plumes, thermal anomalies at the lava dome, and new pyroclastic-flow deposits, were noted during the report week. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT raised the Concern Color Code at Shiveluch from Orange to Red (the highest level) on 22 September. According to interpretations of seismic data, on the 22nd at 1715 a strong eruption began, with ash plumes reaching ~7.5 km (24,600 ft) a.s.l. [corrected by KVERT to 6.5 km (21,300 ft) a.s.l.] and hot avalanches and pyroclastic flows descending the volcano's flanks. The pyroclastic flows extended 10-15 km. The strongest seismic signal of the eruption occurred on 22 September at 2259. Shallower signals recorded between 22 September at 2330 and 23 September at 1200 were possibly associated with ash emissions that rose to 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. An ash plume was visible on satellite imagery at a height of ~3 km (9,850 ft) a.s.l. extending ~20 km SSW. The Concern Color Code was reduced to Orange on 23 September.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Growth of Shiveluch's lava dome continued during 9-16 September. Incandescence was visible at the dome on 13 September. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to 3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. and a large thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 2-9 September, Shiveluch's lava dome continued to grow and viscous lava flowed from it. On 5 September, an ash plume rose to ~4 km (13,100 ft) a.s.l. On 8 September, a hot avalanche was accompanied by an ash plume that rose to a height of ~3.5 km (11,500 ft) a.s.l. A large thermal anomaly was visible at the volcano during the report period. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Growth of Shiveluch's lava dome continued during 26 August to 2 September, and viscous lava continued to flow at the lava dome. Several ash plumes reached ~5.5 km (18,050 ft) a.s.l. The volcano remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Growth of Shiveluch's lava dome continued during 19-26 August. During the report period, about ten shallow earthquakes were recorded, a large thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery, and fumarolic activity occurred. A photo taken by Yu Demyanchuk on 19 August showed a new viscous lava flow emitted from the lava dome. The volcano remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 5-12 August, Shiveluch's lava dome continued to grow, and a persistent thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery. Fumarolic activity and incandescence at the lava dome were visible on 6 August. The volcano remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Shiveluch's lava dome continued to grow during 3-9 August. The volcano remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Shiveluch's lava dome continued to grow during 22-29 July. On 23 July, a persistent thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery, and incandescence was observed at the lava dome. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Growth of Shiveluch's lava dome continued during 15-22 July. A gas-and-steam plume rose to ~3.5 km (~11,500 ft) a.s.l. on 19 July. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Growth of Shiveluch's lava dome continued during 7-15 July. Video footage on 7 July showed ash-and-gas plumes rising to ~5.5 km (18,000 ft) a.s.l. accompanied by hot avalanches. On 9 July, ash-and-gas plumes rose to 3 km (9,800 ft) a.s.l. Ash plumes extended 27 km SW of the volcano during July 11-12. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
On 6 July ash-and-gas plumes from Shiveluch rose to ~7 km (~23,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NW. On 7 July an 11-minute-long seismic event occurred and ash-and-gas plumes may have reached a height of 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. Around 8 July, KVERT raised the Concern Color Code at Shiveluch from Orange to Red, the highest level. On 8 July, video footage showed weak gas-and-steam plumes rising to ~5 km (16,400 ft ) a.s.l. On 9 July, the Concern Color Code was reduced to Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 24 June to 1 July, satellite imagery of Shiveluch showed a persistent thermal anomaly and fumarolic activity producing steam to 4-5 km (13,100-16,400 ft) a.s.l. On 30 June, ash-and-gas plumes rose 3-5 km (9,800-16,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted NW. Hot avalanches of volcanic material were also recorded during the report week. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Shiveluch's lava dome continued to grow as of 24 June. A persistent thermal anomaly and fumarolic activity was also reported during the week of 18-24 June. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Shiveluch's lava dome continued to grow during 10-17 June. A gas-and-steam plume rose ~400 m above the 2.5-km-high lava dome (9,500 ft a.s.l.) on 10 June. A thermal anomaly was visible at the lava dome on satellite imagery on several days. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 3-10 June, two shallow M 1.6-1.7 earthquakes occurred 0-5 km beneath Shiveluch's active lava dome. On 7 June, gas-and-steam plumes rose as high as 100 m above the 2.5-km-high lava dome (8,500 ft a.s.l.). A persistent thermal anomaly was visible at the lava dome all week. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 27 May to 3 June, Shiveluch's lava dome continued to grow and satellite data showed a persistent thermal anomaly at the dome. On 31 May an ash plume rose ~1.5 km above the 2.5-km-high lava dome (13,100 ft. a.s.l.). Gas-and-steam plumes rose to ~400 m above the lava dome (9,500 ft. a.s.l.) during the rest of the report period. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 20-27 May, Shiveluch's lava dome continued to grow. No explosive events were recorded during the week, although gas-and-steam plumes were seen rising as high as 800 m above the 2.5-km-high lava dome (10,800 ft a.s.l.). Satellite data showed a thermal anomaly at the lava dome. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
No explosive events were recorded at Shiveluch during 13-20 May, however, gas-and-steam plumes rose as high as 1.2 km above the lava dome (12,100 ft. a.s.l.). Satellite imagery showed a persistent thermal anomaly at the lava dome. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Growth of the lava dome continued during 6-13 May. A gas-and-steam plume was seen rising up to 400 m above the dome on 6 May. Clouds obscured the volcano at other times. A large thermal anomaly at the dome was detected in satellite imagery all week. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Growth of the lava dome continued during 30 April-6 May with a new extrusion in the W part of the dome. Ash-and-gas plumes, some rising 2 km above the dome, were frequent during this period. A large thermal anomaly was seen in satellite data the entire week. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
On 25 April, a hot avalanche on Shiveluch lava dome's W side produced an ash plume that rose ~2 km above the 2.5-km-high lava dome (14,800 ft a.s.l.). During 22-29 April, gas-and-steam plumes rose to a maximum height of 1 km above the lava dome (11,500 ft a.s.l.). Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 15-22 April, gas-and-steam plumes rose to ~1.2 km above Shiveluch's 2.5-km-high lava dome (~12,100 ft a.s.l.). Satellite imagery showed a large thermal anomaly at the lava dome on 16, and 18-21 April, and a small anomaly associated with a pyroclastic flow on the 19th. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Gas-and-steam plumes rose to ~400 m above Shiveluch's 2.5-km-high lava dome (~9,500 ft a.s.l.) on 8 April and one extended ~50 km SW on the 14th. A thermal anomaly was visible at the lava dome on satellite imagery during the week, except on 10 April. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 1-8 April, intensive growth of the new extrusion at the W part of Shiveluch's lava dome continued. The eastern and western parts of the lava dome had become nearly level. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to ~1 km above the 2.5-km-high lava dome (~11,500 ft a.s.l.).Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The lava dome at Shiveluch continued to grow during 25 March to 1 April. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to 1.5 km above the ~2.5-km-high lava dome (~13,100 ft a.s.l.) on several days. Between 5-28 March a new lava extrusion added ~50 m height to the SW part of the lava dome. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The lava dome at Shiveluch continued to grow during 18-25 March. A lava flow traveled from a portion of the lava dome that was destroyed during an eruption on 28 February. During the report period, gas-and-steam plumes rose to ~1 km above the 2.5-km-high lava dome (~11,500 ft a.s.l.). Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The lava dome at Shiveluch continued to grow during 11-18 March. On 11 March an ash-and-gas plume reached a height of ~2.8 km above the dome (~20,000 ft a.s.l.). During 11-12 March, gas-and-steam plumes rose to 1.2 km above the dome (~14,700 ft. a.s.l.). Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly at the lava dome during the report week, and a large thermal anomaly over the recent pyroclastic-flow deposit during 11-12 March. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Explosions at Shiveluch during 25 February to 4 March deposited ash in Ust'-Hairyuzovo village on 27 and 28 February, and 2 March. The seismic station at Shiveluch stopped working on 27 February. According to visual and video data, part of a large pyroclastic flow was observed on the SW flank of the volcano on 2 March. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Based on interpretations of seismic data, a large eruption occurred at Shiveluch from 1825 on 27 February to 0100 on 28 February, leading KVERT to raise the Concern Color Code from Orange to Red (the highest level). Meteorological clouds obscured the volcano during the eruption. A large thermal anomaly visible near the lava dome on satellite imagery at 0456 on 28 February was probably the signal from a large pyroclastic flow on the volcano's SW flank. At this time a 45-km-long ash cloud was visible on satellite imagery trending NW of the volcano. At 0900 on the 28th, ash deposits were noted in the town of Klyuchi, ~46 km from the volcano. Satellite imagery from 1205 on 28 February showed ash deposits W of Shiveluch covering an area of 24,800 square kilometers. Later that day, an ash cloud extending more than 360 km was centered over the western half of Kamchatka. On 1 March the Concern Color Code was reduced to Orange. Prior to the eruption, during 18-26 February, seismicity was above background levels and ash-and-gas plumes were seen on video rising to ~3 km above the lava dome.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 11-18 February, with weak shallow earthquakes occurring beneath the active lava dome. Ash plumes may have risen to a maximum height of 7.4 km a.s.l. on 17 February. Possible weak ash-and-gas explosions and hot avalanches occurred during the week. Ash deposits were seen on the volcano's snow-covered lava dome extending to the SE and S. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 4-11 February, with weak shallow earthquakes occurring beneath the active dome. On 6 February a pyroclastic flow traveled ~2 km down the volcano's flank. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash-and-gas explosions may have risen to 5.1 km a.s.l. on 6, 7, and 9 February. Weak ash-and-gas explosions and hot avalanches possibly occurred during the week. Ash-and-gas plumes were seen rising to 2.4 km above the lava dome. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 8-14 January, seismicity decreased slightly at Shiveluch but remained above background levels. Seismicity indicated that from 1815 to 1945 on 13 January, several ash explosions up to 5 km a.s.l. and a pyroclastic flow probably occurred. Possible weak ash-and-gas explosions and hot avalanches occurred during 8-14 January. According to visual observations and video data, gas-and-steam plumes rose up to ~2.5-3.4 km a.s.l. during 6-8 January and on 12 January. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
The Tokyo VAAC reported an eruption of Shiveluch on 17 January at 1625 with a plume that rose to a height of ~4.5 km a.s.l.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
During 23-28 December, seismicity decreased slightly at Shiveluch but remained above background levels. Seismicity indicated that possible ash-and-gas explosions occurred on 26 and 27 December and plumes may have risen as high as ~4 km a.s.l. Observed explosions also occurred on 26 and 27 December that produced gas-and-ash explosions to ~2 km above the lava dome. Possible weak gas-and-ash explosions accompanied by hot avalanches occurred throughout the report period. On 28 December a gas-and-steam plume extended as far as 50 km E. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 19-22 December, with weak shallow earthquakes occurring at a depth of ~0.5 km beneath the active lava dome. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash-and-gas explosions may have risen to 3.5 km a.s.l. on 20 December. Hot avalanches may have occurred during 16-19 December. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 12-19 November, with weak shallow earthquakes occurring at a depth of 0.5 km beneath the active lava dome. Based on interpretations of seismic data, possible ash-and-gas explosions up to 6 km a.s.l were registered on 15 November. Ash-and-gas explosions up to 4-5 km a.s.l were noted all week and possible weak ash-and-gas explosions and hot avalanches also occurred. According to visual and video data, ash-and-gas explosions rose up to 4-5 km a.s.l on 11 and 18 November. Gas-and-steam plumes were observed on 11 and 15 November. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 5-12 November, with weak shallow earthquakes occurring beneath the active lava dome. Based on interpretations of seismic data, possible ash-and-gas explosions up to 6.5-7 km a.s.l. were registered on 5, 7, 9, and 11 November. During the week gas-dominated plumes rose to ~4 km a.s.l. and those bearing ash rose to 3.5-6 km. Possible minor ash-and-gas explosions and hot avalanches also occurred. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 29 October-5 November, with weak shallow earthquakes occurring beneath the active lava dome. Based on interpretations of seismic data, possible ash-and-gas explosions up to 6.5 km a.s.l. occurred on 30 October and 2-4 November. Ash-and-gas explosions up to 3.5-5.5 km a.s.l. were noted all week and possible hot avalanches also occurred. According to video data, ash-and-gas explosions rose to 3.5-6 km a.s.l. during 28-30 October, and 1 and 3-4 November. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 15-22 October, seismicity at Shiveluch was above background levels, with shallow earthquakes occurring beneath the active lava dome. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash-and-gas explosions possibly produced plumes to 6.5 km a.s.l. In addition, avalanches of hot material may have occurred during the week. KVERT reported seeing a new lava flow at Shiveluch's lava dome around 26 October. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 8-15 October, with weak shallow earthquakes occurring beneath the active lava dome. Two relatively strong shallow earthquakes, M 1.75 and 2.1, were recorded on 8 and 11 October, respectively. Spasmodic tremor was recorded during 7-12 October. Based on interpretations of seismic data, weak ash-and-gas explosions and hot avalanches may have occurred all week. Visual observations from the town of Klyuchi revealed that ash plumes rose to 3.5 km a.s.l. on 7 and 12 October and extended more than 10 km E. Weak gas-and-steam activity occurred on 11 and 12 October. Clouds obscured the volcano at other times. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 23 September to 1 October, with 26 strong shallow earthquakes up to M 2.3 recorded during 23-29 September. Several explosions were seen that produced ash plumes to a maximum height of 4.5 km a.s.l., while interpretations of seismic data suggested that plumes rose to 6.5 km a.s.l. [Correction: According to interpretations of seismic data there were ~20 ash plumes at heights between 4 and 6.5 km a.s.l. Several explosions were confirmed by video observation at a maximum height of 4.5 km a.s.l. Clouds or night obscured the remainder.] An explosion on 25 September was accompanied by small pyroclastic flows. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Unrest at the volcano continues, with a lava dome growing in the active crater and above-background levels of seismicity. On 12 September a gas-and-steam plume extended > 70 km to the ESE. According to seismic data, during 14-16 September there were four possible ash plumes up to 5-6 km a.s.l.. Video data confirmed an ash plume on the 15th. According to satellite data, 1-12-pixel thermal anomalies were registered over the lava dome on 15-16 September.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 3-10 September, with several weak earthquakes occurring 0-5 km beneath the active lava dome. On 6 September at 2054 an explosion produced small pyroclastic flows and an ash plume that rose to ~5.5 km a.s.l. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 27 August to 3 September, with weak earthquakes occurring 0-5 km beneath the lava dome. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to ~2.6 km a.s.l. on 1 September. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 13-20 August, with weak earthquakes 0-5 km beneath the active lava dome. Gas-and-steam plumes rose ~3 km a.s.l. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 6-13 August, seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch, with weak earthquakes occurring 0-5 km beneath the active dome. On several days gas-and-steam plumes rose to a maximum height of ~2.9 km a.s.l. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 30 July to 6 August, with weak earthquakes occurring 0-5 km beneath the active lava dome. On 4 August at 1705 an ash plume rose ~5 km a.s.l. and drifted E. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 22-30 July, with weak earthquakes occurring 0-5 km below the active lava dome. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to ~2.8 km a.s.l. on 28 and 29 July. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity at Shiveluch remained above background levels during 9-16 July, with earthquakes up to M 1.75. Spasmodic tremor was recorded during the week. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The lava dome continued to grow in Shiveluch's active crater. Gas-and-steam plumes were reported by KVERT on 2-3 July rising as high as 3.3 km a.s.l.; clouds obscured the volcano during 3-8 July. Seismicity was above background levels for 3-9 July. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 25 June to 2 July, with several shallow earthquakes occurring beneath the active lava dome. Gas-and-steam plumes were seen rising to ~3.5 km a.s.l. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 18-25 June. Shallow earthquakes up to M 1.75 were recorded, along with nearly continuous spasmodic tremor. Gas plumes rose to ~4 km a.s.l. On 19 June, a likely ash cloud was seen 10-20 km S of the volcano. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismic activity remained above background levels at Shiveluch during 4-11 June, with several shallow earthquakes occurring beneath the active lava dome. According to visual and video observations from the town of Klyuchi, during 3-5 and 10 June, gas-and-steam plumes rose to 3.3-3.9 km a.s.l. and extended more than 10 km SE, E, W, and NW. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Between 28 May and 4 June, seismic activity at Shiveluch was above background levels with many shallow earthquakes recorded. Continuous spasmodic tremor was recorded during 27-29 May with an increase in volcanic seismicity beginning on 29 May and continuing through 2 June. On 31 May a possible gas-and-ash plume rose to 5.5 km a.s.l. and on 27-28 May gas-and-steam plumes were observed rising up to ~2.5 km a.s.l. and drifting E. A small lava flow on top of the active dome, first observed on 21 May, continued to flow until 28 May. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
On 21 May, observations of Shiveluch from a helicopter revealed pyroclastic flows and partial destruction of the lava dome. Ash deposits were concentrated in the central sector of the southern volcanic slope. During 21-28 May seismicity was above background levels, with a large number of shallow earthquakes occurring. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to ~4 km a.s.l. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
During 7-14 May seismic activity was above background levels at Shiveluch, with a large number of shallow earthquakes occurring. Based on interpretations of seismic data, during 6-7 May there may have been three ash-and-gas explosions that produced plumes to ~ 7 km a.s.l. On 9 May a strong explosion deposited ash in Ust-Kamchatsk, closing the airport. The road and the dam in the area of the Bekesh river were destroyed by mud flows.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
On 10 May around 0200 a strong eruption began at Shiveluch, leading KVERT to raise the Concern Color Code from Orange to Red (the highest level). Video and visual observations revealed ash explosions that rose to ~11 km a.s.l. and drifted ESE. At 1114 pyroclastic and mud flows traveled 7-8 km down the volcano's SE slope. Ash was deposited as far as 100 km from the volcano. On 11 May the Concern Color Code was reduced to Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 16-23 April, with a large number of weak earthquakes occurring 0-5 km beneath the active lava dome and ten M 1.5-2.7 earthquakes. Based on interpretations of seismic data, during 15-18, and 21 April six ash-and-gas explosions may have produced plumes to 4-7 km a.s.l. The highest rising observed plume (8 km a.s.l.) was produced from an ash-and-gas explosion on 18 April. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity at Shiveluch remained above background levels during 9-16 April with many small shallow earthquakes located at depths of 0-5 km and a total of ten M 1.8-2.3 earthquakes recorded on 8, 10, and 14 April. On these days gas-and-ash plumes probably reached ~4.5-5.5 km a.s.l. four times and ~7.5 km a.s.l. at least once. On 18 April, a gas-and-ash plume reached ~9 km a.s.l. and on 19 April a plume rose to ~1 km above the vent. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Pravda News; Anchorage Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
Seismicity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 2-9 April, with 16 earthquakes up to M 2 occurring during 1-3 and 6-7 April. Based on interpretations of seismic data, one ash-and-gas explosion may have produced a plume that reached a height of 9 km a.s.l., and 13 plumes may have reached 7.2 km a.s.l. during several days. During 6-8 April, ash plumes extended 20-50 km SE and E. On 7 April an ash-and-gas explosion produced a plume to a height of 6.2 km a.s.l. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
According to KVERT, during 26 March to 2 April seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch. About 14 shallow earthquakes up to M 2 occurred during 25 and 28-31 March. Based on interpretations of seismic data, 15 ash-and-gas explosions may have produced plumes to 5 km a.s.l. during 25 and 28-31 March. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Sources: RIA Novosti; Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Itar-Tass News
During 19-26 March, seismic activity was above background levels at Shiveluch with many shallow earthquakes up to M 1.75 recorded. Based on interpretations of seismic data, a pyroclastic flow occurred on 19 March and explosions produced gas-and-ash plumes on 19-20 and 25 March that might have reached 6-7 km a.s.l. on two occasions and 3.5-4.5 km a.s.l. on nine other occasions. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 12-19 March, seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch, with a large number of shallow earthquakes up to M 2 occurring beneath the volcano. Spasmodic volcanic tremor was also recorded. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash-and-gas explosions may have produced plumes to a maximum height of 5 km a.s.l. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity at Shiveluch was above background levels during 5-12 March, with a large number of shallow earthquakes up to M 2 occurring beneath the volcano. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash-and-gas explosions rose to a maximum height of ~6 km a.s.l. Video footage shot on 9 March showed an ash plume rising to ~4 km a.s.l. and drifting S. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 27 February to 5 March, seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch. A large number of shallow earthquakes up to M 2 were recorded beneath the volcano, as well as spasmodic volcanic tremor. Based on interpretations of seismic data, ash-and-gas explosions rose to a maximum height of ~5.5 km a.s.l. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 20-27 February, seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch, with a large number of weak shallow earthquakes occurring at depths of 0-5 km beneath the active lava dome. Based on interpretations of seismic data, on 23 February an ash-and-gas explosion produced a plume to ~5 km a.s.l. Gas-and-steam plumes were seen rising to ~4 km a.s.l. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); RIA Novosti
During 13-20 February, seismicity was slightly above background levels at Shiveluch. A large number of weak, shallow earthquakes was recorded daily at depths of 0-5 km beneath the active lava dome. Spasmodic tremor was recorded the entire week. Based on interpretations of seismic data, two ash-and-gas explosions on 12 February, and one on 16 February, produced ash plumes to ~4 km a.s.l. Visual and video observations revealed that two ash plume rose to ~5 km a.s.l. and drifted E on 12 February. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 6-13 February, seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch. A large number of weak shallow earthquakes and one to three M1.5-2.3 earthquakes were recorded daily at depths of 0-5 km beneath the active lava dome. Spasmodic tremor was recorded all week. Based on interpretations of seismic data, one to three ash-and-gas explosions occurred per day, sending ash to 4-6 km a.s.l. Visual and video observations revealed ash plumes rising to ~5 km a.s.l. on 10 February. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 30 January to 6 February, seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch, with 1-4 shallow M 1.25-2.25 earthquakes occurring daily and a large number of weaker earthquakes at depths of 0-5 km beneath the active lava dome. Based on interpretations of seismic data, during 2-4 February three possible ash-and-gas explosion occurred per day, producing plumes to 3.5-5.5 km a.s.l. Video footage on 4 February showed an ash plume rising to ~5 km a.s.l. Gas-and-steam plumes were seen during much of the week. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 23-30 January, seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch, with a large number of weak shallow earthquakes occurring at depths of 0-5 km beneath the lava dome. In addition, 5-7 shallow M 1.75-2.3 earthquakes occurred each day except for 22 January. Intermittent tremor was recorded all week. Based on seismic data, 8 and 9 ash-and-gas explosions occurred on 22 and 23 January, respectively, sending ash to 3.5-4.5 km above the volcano. Video footage on 22 January confirmed that four ash plumes rose to ~3.5 km. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Volcanic activity remained at relatively high levels at Shiveluch during 16-23 January. Several explosions occurred, producing ash plumes that rose to a maximum height of 6 km a.s.l. Ash explosions on 21 January were accompanied by pyroclastic flows with run-out distances of ~ 2 km. During the report period, seismicity was above background levels, with ~200 shallow M 1.75-2.6 earthquakes occurring as well as a large number of weaker events. Intermittent spasmodic volcanic tremor also occurred. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Itar-Tass News
During 11-12 January, explosions at Shiveluch produced ash plumes to 4 km a.s.l. that drifted W. The explosions were accompanied by pyroclastic flows with run-out distances around 1 km. On 16 January at 1125 an eruption produced an ash plume that rose ~5.5 km a.s.l. and drifted W. The same day KVERT raised the Concern Color Code to Orange from Yellow. During 9-16 January, seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch, with the recording of ~70 shallow earthquakes greater than M 1.75 and a large number of weaker earthquakes beneath the active lava dome. In addition, intermittent spasmodic tremor was recorded during 11-16 January.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Itar-Tass News
Seismicity continued to be above background levels at Shiveluch during 16-23 May. Weak, shallow earthquakes were recorded and seismic data indicated that an ash-and-gas explosion reached a height of about 4 km above the lava dome. Incandescent lava avalanches may have occurred on 17 May. Intermittent, spasmodic, volcanic tremor was recorded during 14-22 May. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 9-16 May at Shiveluch seismicity was above background levels, and several small explosions occurred. Weak shallow earthquakes were recorded, and seismic data suggested that 6 ash-and-gas explosions reached heights of 1.5 km above the lava dome and hot avalanches possibly occurred. On 11 May seismic data indicated that two ash-and-gas explosions rose to 6 km a.s.l. and were possibly accompanied by hot avalanches. Video data revealed a series of ash explosions beginning on 14 May at 1550 that produced ash clouds to heights of 4.2 km a.s.l. The explosions were accompanied by several pyroclastic flows. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
A 25 April report on Shiveluch from KVERT stated that, based on seismic data a hot pyroclastic avalanche possibly took place on 23 April. Also, a M 2.25 earthquake occurred this day. Intermittent spasmodic volcanic tremor registered all week. According to visual data from Klyuchi, an ash plume rose 1,500 m above the dome on 24 April; gas and steam plumes rose 50-500 m above the dome on 19-21 and 24 April and the plumes blew 10 km to the E and SE, respectively. Clouds typically obscured the volcano on the other days.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity at Shiveluch remained above background levels during 4-11 April. Seismic data indicated that 8 ash-and-gas explosions reached heights up to 3 km above the lava dome and hot avalanches possibly occurred. Weak shallow earthquakes and intermittent spasmodic volcanic tremor were recorded. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to low levels above the dome. A thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity at Shiveluch remained above background levels during 28 March to 4 April. Seismic data indicated that 10 ash-and-gas explosions reached heights up to 4 km above the lava dome and hot avalanches possibly occurred. Weak shallow earthquakes and intermittent spasmodic volcanic tremor were registered. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to 1.5 km above the dome. Thermal anomalies and ash deposits were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 21-28 March, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. Seismic data indicated that one ash-and-gas explosion reached ~1 km above the lava dome, and hot avalanches possibly occurred. Spasmodic volcanic tremor was recorded and gas-and-steam plumes rose to 900 m above the lava dome. During the report period, thermal anomalies and gas-and-steam plumes were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 14-21 March, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. Seismic data indicated that eight ash-and-gas explosions reached heights of 1 km above the lava dome, and hot avalanches possibly occurred. Spasmodic volcanic tremor was recorded and gas-and-steam plumes rose to 1.2 km above the lava dome. During the report period, thermal anomalies and gas-and-steam plumes were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 7-14 March, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. Seismic data indicated that 13 ash-and-gas explosions reached heights of 2.3 km above the lava dome, and hot avalanches possibly occurred. Spasmodic volcanic tremor was recorded and gas-and-steam plumes rose to 800 m above the lava dome. During the report period, thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery and on 9 March ash deposits were seen extending ~20 km WSW. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 28 February to 7 March, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch and many shallow earthquakes were recorded. Seismic data indicated that 20 ash-and-gas explosions reached heights of 4 km above the lava dome, and hot avalanches possibly occurred. Volcanic spasmodic tremor was recorded and gas-and-steam plumes rose to 1 km a.s.l. Seismic data indicated that ash explosions on 4 March during 1130-1140 produced clouds to 5.5 km a.s.l. At this time a "water flow" washed away the Klyuchi-Ust'-Kamchatsk road in an area 40 km from the town of Klyuchi. The "water flow" was up to 0.7 m deep. On 6 March seismic data indicated that an explosion produced an ash cloud to 8.5 km a.s.l. During the report period, thermal anomalies were visible on satellite data. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 21-28 February, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch and many shallow earthquakes were recorded. Seismic data indicated that 14 ash-and-gas explosions reached heights of 3 km above the lava dome, and hot avalanches possibly occurred. Video footage showed several ash-and-gas clouds, with the highest cloud rising to 4.5 km a.s.l on 25 February. Volcanic spasmodic tremor occurred and gas-and-steam plumes rose to 4 km a.s.l. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 14-21 February, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch and many shallow earthquakes were recorded. Seismic data indicated that 17 ash-and-gas explosions reached heights of 1.5 km above the lava dome, and hot avalanches possibly occurred. Video footage showed several ash-and-gas clouds, with the highest cloud rising to 6.5 km a.s.l on 15 February accompanied by pyroclastic flows. Volcanic spasmodic tremor occurred and gas-and-steam plumes rose to 1 km above the crater. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 7-14 February, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch and many shallow earthquakes were recorded. Seismic data indicated that 10 ash-and-gas explosions reached heights of 1 km above the lava dome, and hot avalanches possibly occurred. Volcanic spasmodic tremor occurred and gas-and-steam plumes rose to 1 km above the crater. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 31 January to 7 February, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch and many shallow earthquakes were recorded. Intermittent volcanic spasmodic tremor occurred and gas-and-steam plumes rose to 1.5 km above the crater. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 24-31 January, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch and many shallow earthquakes were recorded. According to seismic data, on 25 January a short-lived explosion produced an ash-and-gas plume that rose to 3.5 km above the lava dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 17-24 January, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. Seismic data indicated that 11 ash-and-gas explosions reached heights of 2 km above the lava dome, and hot avalanches possibly occurred. Continuous, spasmodic volcanic tremor was recorded on 16-18 January and intermittent volcanic tremor was recorded on 19-23 January. Clouds obscured the volcano all week. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 10-17 January, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. Seismic data indicated that 12 ash-and-gas explosions reached heights of 2 km above the lava dome, and hot avalanches possibly occurred. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to 800 m above the lava dome and drifted E and NW during 10-12 January. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 3-10 January, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. Seismic data indicated that 11 ash-and-gas explosions reached heights of 1.5 km above the lava dome, and hot avalanches possibly occurred. Short-lived explosions produced ash-and-gas clouds to 1.5 km above the lava dome. On 9 January a small, hot avalance was seen on the SW slope of the lava dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 27 December to 3 January, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. Seismic data indicated that 25 ash-and-gas explosions reached heights of 2 km above the lava dome, and hot avalanches possibly occurred. On 28 December a small amount of ash was visible on the volcano's snow-covered flanks. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 20-27 December, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. Seismic data indicated that six ash-and-gas explosions reached heights of 2-3 km above the lava dome, and hot avalanches possibly occurred. Several smaller earthquakes at depths of 0-6 km were recorded. Weak, intermittent, spasmodic tremor was registered during 21-25 December. On 25 December during 1945-2045, the amplitude of volcanic tremor sharply increased. According to visual data from Klyuchi, on 19 December at 1238 and 1514, short-lived explosions sent gas-and-ash plumes to heights of ~5.5 and 5 km a.s.l., respectively. Following the first explosion, pyroclastic flows traveled SE; after the second, they traveled to the S, inside the Baidarnaya River. The runout of both pyroclastic flows was 3 km. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 13-20 December, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. Seismic data indicated that seven ash-and-gas explosions reached heights of 1-2 km above the lava dome, and hot avalanches possibly occurred. A number of smaller earthquakes at depths of 0-6 km and weak intermittent spasmodic tremor was recorded. On 19 December around 0045 a pyroclastic flow traveled ~3 km down Shiveluch's SE slope. The associated plume rose 5.5 km a.sl. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 6-13 December, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch, but it decreased after 8 December. Seismic data indicated that eight ash-and-gas explosions reached heights of 1-2 km above the lava dome, and hot avalanches possibly occurred. A number of smaller earthquakes at depths of 0-6 km and weak intermittent spasmodic tremor was recorded. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to a maximum height of 1.5 km above the lava dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch, but decreased during 29 November to 6 December. Seismic data indicated that nine ash-and-gas explosions reached heights of 1-2 km above the lava dome, and hot avalanches possibly occurred. A number of smaller earthquakes at depths of 0-6 km were recorded. Weak intermittent spasmodic tremor was recorded on 28-30 November. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to a maximum height of 2.5 km above the lava dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 22-29 November, KVERT decreased the Concern Color Code at Shiveluch from Orange to Yellow. Seismicity remained above background levels during the report interval and seismic data indicated that there had been hot avalanches and eight ash-and-gas explosions in which clouds reached 1-2 km above the lava dome (the previous week there were 19 ash-and-gas explosions to 2-3 km above the lava dome). Weak intermittent spasmodic tremor was registered during 24-25 November. Gas-and-steam plumes were seen rising 100-800 m above the lava dome and thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 14-20 November, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. During this interval, seismic data indicated that there had been hot avalanches and 19 ash-and-gas explosions in which clouds reached 2-3 km above the lava dome. Weak intermittent spasmodic tremor was registered during 14-17 November. Ash-and-gas plumes were seen rising to ~2 km a.s.l. and thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 11-14 November, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. During this interval, seismic data indicated that there had been hot avalanches and seven ash-and-gas explosions in which clouds reached 2-3 km above the lava dome. Weak intermittent spasmodic tremor was registered. According to seismic data, possible short-lived explosions sent ash-and-gas plumes to heights of 5.5 km above the dome. Gas-and-steam plumes were seen rising to ~800 m a.s.l. and thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT raised the Concern Color Code at Shiveluch from Yellow to Orange on 11 November. Visual observations revealed that on the 4th at 1020, the 5th at 0830, and the 6th at 1318, short-lived explosions sent ash-and-gas plumes to heights of approximately 3.5, 1.5, and 2 km above the dome, respectively. During 8-11 November, seismicity remained above background levels. Thermal anomalies and a faint ~11-km-long plume (on the 8th) were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not. Seismic data on the 11th indicated possible hot avalanches and several ash-and-gas explosions sending clouds up to 5.5 km above the dome.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 25 October to 1 November, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. During this interval, seismic data indicated that there had been hot avalanches and eight ash-and-gas explosions in which clouds reached 2 km above the lava dome. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to ~2.5 km a.s.l. and thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 18-25 October seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch, but the number of earthquakes decreased. During this interval, seismic data indicated that there had been hot avalanches and 10 ash-and-gas explosions in which clouds reached 1 km above the lava dome. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to ~4.5 km a.s.l. and thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 11-18 October, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. Four earthquakes occurred with magnitudes 2-2.2, as well as many smaller ones. During this interval, seismic data indicated that there had been hot avalanches and 13 ash-and-gas explosions in which clouds reached 1-2.5 km above the lava dome. Intermittent spasmodic tremor was recorded all week. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to 2 km above the lava dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 4-11 October, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. Seven earthquakes with magnitudes 2-2.4 occurred, as well as many smaller ones. During this interval, seismic data suggested there had been hot avalanches and 16 ash-and-gas explosions in which clouds reached 1-2 km above the lava dome. Intermittent spasmodic tremor was recorded. Gas-and-steam plumes were visible rising to 1 km above the lava dome. On the evening of the 6th, incandescence was visible at the lava dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 26 September to 4 October, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. Eleven earthquakes with magnitudes 2-2.7 occurred, as well as many smaller ones. During this interval, seismic data suggested there had been hot avalanches and 38 ash-and-gas explosions in which clouds reached 1-2.5 km above the lava dome. During 30 September to 2 October intermittent spasmodic volcanic tremor was recorded. Video images on 26 September at 1406 and 1759 showed short-lived explosions of ash and gas rising ~2.5 and 0.5 km above the dome, respectively. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 20-27 September, volcanic and seismic activity at Shiveluch were above background levels. There were four earthquakes with magnitudes 2-2.1, and many smaller ones. Seismic data indicated possible avalanches and ash-and-gas explosions that may have sent material to 5.5 km a.s.l. On 25 September continuous spasmodic volcanic tremor was recorded for 27 minutes. Short-lived gas-and-steam plumes were observed rising to 6.5 km a.s.l. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery during several days, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 13-20 September, volcanic and seismic activity at Shiveluch were above background levels. There were eight earthquakes with magnitudes 2-2.3, and many smaller ones. Seismic data indicated possible avalanches and ash-and-gas explosions that may have sent material to 3 km above the lava dome. On 14 September continuous spasmodic volcanic tremor was recorded for about 40 minutes. Short-lived ash-and-gas plumes were observed rising to 3 km above the lava dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery during several days, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 6-13 September, volcanic and seismic activity at Shiveluch were above background levels. There were eight earthquakes with magnitudes 2-2.2, and many smaller ones. Seismic data indicated possible avalanches and ash-and-gas explosions that may have sent material to 3 km above the lava dome. Volcanic tremor continued to slowly decrease. Short-lived ash-and-gas plumes were observed rising to 3.5 km above the lava dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery during several days, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 30 August- 6 September, volcanic and seismic activity at Shiveluch were at similar levels to the previous week. Seismicity remained above background levels, with the occurrence of four earthquakes with magnitudes 2-2.1, and many smaller ones. Seismic data indicated possible avalanches and ash-and-gas explosions that may have sent material 2-2.5 km above the lava dome. Volcanic tremor continued to slowly decrease. On 2 September, a ~15-minute-long episode of strong high-frequency tremor was registered that may have been indicative of an avalanche rolling down the side of the dome. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to 2 km above the lava dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 23-30 August, volcanic and seismic activity at Shiveluch were at similar levels to the previous week. Seismicity remained above background levels, with the occurrence of three earthquakes with magnitudes 1.7-2.1, and many smaller ones. Seismic data indicated possible avalanches and ash-and-gas explosions that may have sent material 1-2.5 km above the lava dome. Volcanic tremor decreased in comparison to the previous week. Gas-and-steam plumes rose 1-1.2 km above the lava dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 16-23 August, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch, although only three earthquakes with magnitudes of 1.7-1.9 occurred. A number of smaller 0- to 6-km-deep earthquakes were registered, as well as many other local shallow seismic signals. The signals were possibly indicative of avalanches and ash-and-gas explosions (one to three per day reached heights of 1-1.5 km above the dome). Volcanic tremor continued at previous levels. Ash-and-gas plumes rose to a maximum height of 4 km above the dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 9-16 August, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch with about 10 earthquakes occurring with magnitudes 1.7-2.4 and a number of smaller earthquakes at depths of 0-6 km. In addition, many other local shallow seismic signals were registered, which possibly indicated ash-and-gas explosions (one to three per day to heights of 1.5-2.5 km above the dome). Avalanches were also registered. Seismicity decreased slightly by the end of the week. On several days thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. The Concern Color Code was reduced from Orange ("explosive eruption is possible within a few days and may occur with little or no warning") to Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 2-9 August, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. More than ten M 1.8-2.5 earthquakes occurred and there were a number of smaller ones at depths of 0-6 km. Other local shallow seismic signals occurred, which possibly indicated ash-poor explosions (one to five per day to heights of 1.5-3 km above the dome). In addition, avalanches were registered and volcanic tremor decreased slightly. Ash-poor plumes rose to a maximum height of 3 km above the lava dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not. KVERT increased the Concern Color Code from Yellow ("volcano is restless") to Orange ("explosive eruption is possible within a few days and may occur with little or no warning").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 27 July-2 August, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch and a lava dome grew in the active crater. Individual earthquakes of M 1.9-2.4, as well as a number of smaller earthquakes at depths of 0-6 km, were recorded. Other local seismic signals indicated that possible weak, ash-poor explosions rose to 1 km above the dome. Avalanches were also registered. Volcanic tremor increased in intensity on 29 July and remained high until 1 August. Tremor gradually decreased in amplitude during 1-2 August. Gas-and-steam emissions, some possibly including small amounts of fine ash, rose to ~1.5 km above the lava dome. On 30 July a short-lived explosion sent ash-and-gas plumes to ~3 km above the dome. Thermal anomalies of 1-4 pixels were visible on satellite images. On 28 July and 1 August, small steam-and-aerosol plumes were visible extending to the S and 35 km to the NW, respectively. KVERT decreased the Concern Color Code from Orange ("explosive eruption is possible within a few days and may occur with little or no warning") to Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 19-26 July, seismicity remained above background levels at Shiveluch. Individual earthquakes up to M 1.9, as well as a number of smaller earthquakes at depths of 0-6 km, were recorded. Other local seismic signals indicated that possible weak, ash-poor explosions rose to 1 km above the dome. Avalanches were also registered. Gas-and-steam emissions, some possibly including small amounts of fine ash, rose to ~1.5 km above the lava dome. A small, likely ash-rich plume was visible on AVHRR satellite imagery on 22 July at 1804. The plume appeared to be centered over the volcano's summit at a height of about 5.3 km. On 29 July at 2000 the intensity of volcanic tremor increased noticeably in comparison with the previous few days. On 30 July at 0946 a short-lived explosion produced a plume to a height of ~3 km above the dome. KVERT raised the Concern Color Code from Yellow ("volcano is restless") to Orange ("explosive eruption is possible within a few days and may occur with little or no warning").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 12-19 July, seismicity slightly increased and remained above background levels. After a nearly 3-week-long hiatus, individual earthquakes with magnitudes between 1.8 and 2.0 began to occur again. In addition, smaller earthquakes were detected at depths of 0-6 km. There were many other local shallow seismic signals, which possibly indicated weak ash-poor explosions up to 1 km above the dome. Avalanches were also registered. During the week the level of volcanic tremor continued to increase constantly and gas-and-steam emissions rose to 2 km above the dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 5-12 July, seismicity generally continued to decline at Shiveluch, but remained above background levels. Earthquakes less than M 1.7 occurred at depths of 0-6 km accompanied by many local shallow seismic signals from possible avalanches or weak gas-and-ash explosions. During the report period the level of volcanic tremor increased; there was a tremor episode on the 9th from 0510 to 0540 in which the amplitude sharply increased to 10 times the previous level. Several short-lived explosions produced ash-and-gas plumes ~1-1.5 km above the lava dome. Some explosions were accompanied by rock avalanches and pyroclastic flows. Gas-and-steam plumes rose 0.2-1.5 km above the dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 28 June to 5 July, seismicity continued to decline at Shiveluch, but remained above background levels. It included earthquakes with magnitudes less than or equal to 1.7 at depths of 0-6 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-and-ash explosions), and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. Gas-and-steam plumes reached to 2 km above the lava dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on AVHRR satellite imagery, but ash was not. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity declined at Shiveluch during 21-28 June, but remained above background levels. It included earthquakes with magnitudes less than or equal to 1.9 at depths of 0-6 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-and-ash explosions), and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. Gas-and-steam plumes reached to 3 km above the lava dome and small avalanches were captured on video rolling down the dome on 23 June. Thermal anomalies were visible on AVHRR satellite imagery, but ash was not. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 14-21 June, seismicity at Shiveluch remained above background levels and included earthquakes at depths of 0-6 km with magnitudes less than or equal to 2.4 on the 14th and less than or equal to 2 during the rest of the week. In addition, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-and-ash explosions) and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor occurred. According to interpretations of seismic data, short-lived explosive eruptions on the 15th and 19th probably sent ash-and-gas plumes ~1 and 1.5 km above the lava dome, respectively. Thermal anomalies were visible on AVHRR satellite imagery, but ash was not. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 7-14 June, seismicity at Shiveluch remained above background levels and included earthquakes with magnitudes less than or equal to 2.3 at depths of 0-6 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-and-ash explosions), and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. According to interpretations of seismic data, from one to three short-lived explosive eruptions per day probably sent ash-and-gas plumes ~1 km above the lava dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on AVHRR satellite imagery, but ash was not. The Concern Color Code was reduced from Orange ("volcano is in eruption or eruption may occur at any time") to Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 2-7 June, several short-lived explosive eruptions per day sent ash-and-gas plumes 0.7-1 km above the lava dome, gas-and-steam plumes rose to 2.5 km above the dome, and seismicity was above background levels. Seismicity included earthquakes with magnitudes less than or equal to 2.3 at depths of 0-6 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-and-ash explosions), and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. Thermal anomalies were visible on AVHRR satellite imagery, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange ("volcano is in eruption or eruption may occur at any time").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Due to an increase in volcanic and seismic activity at Shiveluch, KVERT raised the Concern Color Code from Yellow ("volcano is restless") to Orange ("volcano is in eruption or eruption may occur at any time"). On 1 June at 1616 a short-lived explosive eruption produced an ash-and-gas plume to a height of 3 km above the lava dome. The plume was visible from Klyuchi town, 46 km from Shiveluch. Two ~3-minute-long shallow seismic events were recorded at 1615 and 1626. Prior to the eruption, on 31 May at 1530, a ML (local magnitude) 3.1 earthquake occurred. On 1 June continuous volcanic tremor occurred for about an hour. Small gas-and-steam plumes rose to 1.3 km above the dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery on 31 May and 1 June.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 17-24 May, there were several small emissions of gas, steam, and ash at Shiveluch. Weak earthquakes occurred at depths of 0-6 km, accompanied by many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-and-ash explosions). There were also episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. Thermal anomalies were visible on AVHRR satellite imagery, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 10-17 May, there were several small emissions of gas, steam, and ash at Shiveluch. Seismicity included earthquakes with magnitudes less than or equal to 2.1 at depths of 0-6 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-and-ash explosions), and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. Thermal anomalies were visible on AVHRR satellite imagery, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 3-10 May, there were several small emissions of gas, steam, and ash at Shiveluch. A short-lived eruption on 5 May at 0945 produced an ash-and-gas plume that rose 1.5 km above the lava dome and was accompanied by a 4-minute-long shallow seismic event. Seismicity during the report period included earthquakes with magnitudes less than or equal to 2.1 at depths of 0-6 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-and-ash explosions), and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. Thermal anomalies were visible on AVHRR satellite imagery, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 26 April-3 May, there were several small emissions of gas and steam at Shiveluch. The character of seismicity changed in comparison to the previous week, with more deep earthquakes occuring and no significant events indicating explosions were registered. There were earthquakes with magnitudes less than or equal to 2.0 at depths of 0-9 km, many local shallow seismic signals, and intermittent episodes of weak volcanic tremor. Thermal anomalies were visible on AVHRR satellite imagery. On 5 May at 0945 an ash plume rose 1.5 km above the lava dome. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 19-26 April, there were several emissions of gas, steam, and ash. The highest rising ash cloud reached 800 m above the volcano and visual observations suggested that rockfalls probably accompanied the eruption. Seismicity decreased slightly during the report period; there were earthquakes with magnitudes less than or equal to 2.0 at depths of 0-5 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-and-ash explosions), and intermittent episodes of weak volcanic tremor. Thermal anomalies were visible on AVHRR satellite imagery, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 12-19 April, gas-and-steam and ash-and-gas emissions occurred at Shiveluch and seismicity remained above background levels. A short-lived explosive eruption on 15 April at 1906 produced an ash-and-gas plume that rose 1 km above the volcano. Seismicity during the report period included earthquakes with magnitudes less than or equal to 2.3 at depths of 0-5 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-and-ash explosions), and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. Thermal anomalies were visible on AVHRR satellite imagery, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 29 March-5 April, gas-and-steam and ash-and-gas emissions occurred at Shiveluch and seismicity remained above background levels. A short-lived explosive eruption on 10 April at 0900 produced an ash-and-gas plume that rose 1 km above the volcano. Seismicity during the report period included earthquakes with magnitudes less than or equal to 2.1 at depths of 0-9 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-and-ash explosions), and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. Thermal anomalies were visible on AVHRR satellite imagery, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 29 March-5 April, several gas-and-steam and ash-and-gas emissions occurred at Shiveluch. In addition, seismicity decreased in comparison to previous weeks, but remained above background levels. The highest rising ash-and-gas plume observed was produced from a short-lived explosive eruption on 30 March at 2042. Seismicity during the report period included earthquakes with magnitudes less than or equal to 2.1 at depths of 0-10 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-and-ash explosions), and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 23-29 March, seismicity and volcanism continued at Shiveluch. Ash-and-gas plumes were observed from the town of Klyuchi rising to 2.5 km above the lava dome during 25-27 March. According to seismic data, on 23 March short-lived explosive eruptions sent ash-and-gas plumes to 5 km above the dome. Seismicity included earthquakes with magnitudes less than or equal to 2.4 at depths of 0-5 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-ash explosions), and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Yellow.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
A decrease in the level of activity at Shiveluch during 15-22 March led KVERT to reduce the Concern Color Code from Orange ("eruption may occur at anytime") to Yellow ("volcano is restless"). During the week, several gas-and-steam eruption clouds rose 300-1,500 m above the volcano's lava dome. Seismicity included earthquakes with magnitudes less than or equal to 2.2 at depths of 0-9 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-ash explosions), and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. Thermal anomalies were observed on AVHRR satellite imagery and no ash was detected.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
During 8-15 March, volcanic activity at Shiveluch continued and seismicity decreased, but remained above background levels. The highest rising observed gas-and-steam plume reached a height of 2.5 km above the volcano on the 13th. Seismicity included earthquakes with magnitudes less than or equal to 2.1 at depths of 0-9 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-ash explosions), and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. Thermal anomalies that were 2-4 pixels large were visible on satellite imagery. The volcano remained at Concern Color Code Orange ("volcano is in eruption or eruption may occur at any time").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 1-8 March, volcanic activity remained relatively high at Shiveluch. Four short-lived explosive eruptions visible from the town of Klyuchi, 46 km from the volcano, produced ash-and-gas plumes to heights of 1-3 km above the volcano's lava dome. On 3 March at 1500 a mixture of red ash and snow fell in Klyuchi. The ash may have been produced from an eruption at 1447. Seismicity included earthquakes with magnitudes less than 2.4 at depths of 0-5 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-ash explosions), and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. The volcano remained at Color Concern Code Orange ("volcano is in eruption or eruption may occur at any time").
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Vladivostok News
During 22 February-1 March seismic and volcanic activity remained high at Shiveluch; several steam-and-gas and ash-and-gas eruptions occurred, pyroclastic flows traveled down the volcano's flanks, and seismicity remained above background levels. The highest rising ash-and-gas clouds were produced from eruptions on 27 and 28 February, and 1 March; the clouds reached a height of ~2 km. During the week, pyroclastic flows traveled as far as 2 km down the SE side of the lava dome. Seismicity included earthquakes with magnitudes less than 2.3 at depths of 0-5 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-ash explosions), and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. On the 22nd and the 27th, 1-hour and 45-minute-long series, respectively, of shallow seismic events were registered that may have been associated with pyroclastic flows or gas-and-ash explosions. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. The volcano remained at Color Concern Code Orange ("volcano is in eruption or eruption may occur at any time").
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Volcanic unrest continued at Shiveluch during 15-22 February, with several ash-and-gas explosions occurring and seismicity remaining above background levels. An eruption on 15 February at 1501 produced an ash cloud accompanied by pyroclastic flows that traveled 2.5 km down the SE slope of the dome. The highest rising observed ash cloud was produced by an eruption on 19 February at 0800; it reached a height of 3.5-4 km above the lava dome. Seismicity included earthquakes with magnitudes less than 2.4 at depths of 0-5 km, many local shallow seismic signals (from possible avalanches or weak gas-ash explosions), and episodes of weak intermittent volcanic tremor. Thermal anomalies and ash clouds were visible on satellite imagery. The volcano remained at Color Concern Code Orange ("volcano is in eruption or eruption may occur at any time").
Sources: Anchorage Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 8-15 February volcanism increased at Shiveluch and KVERT raised the Color Concern Code on 15 February from Yellow ("volcano is restless") to Orange ("volcano is in eruption or eruption may occur at any time"). During the report period seismicity was above background levels, thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, and several gas-and-ash eruptions occurred. The highest rising gas-and-ash cloud was produced from an eruption on 14 February at 0835; it reached ~ 3 km above the volcano's dome. A short-lived eruption on 15 February at 1501 produced a gas-and-ash plume that rose to 2 km above the dome and pyroclastic flows that extended 2.5 km to the SE. During 1613-1725 the same day, a dense ash plume continuously rose to 2 km above the dome. The Tokyo VAAC received a report that an eruption on 19 February at 1443 produced an ash cloud that reached a height of ~6.7 km above the volcano and drifted to the ESE.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 1-8 February seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch with many shallow earthquakes occurring within the volcano's edifice. Shallow, weak seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were also registered. Small explosions produced low-rising gas-and-steam plumes throughout the week. On 2 February short-lived explosions produced an ash-and-gas cloud that rose ~1.5 km above the dome. The eruption was accompanied by an increase in shallow seismic events and hot rock avalanches.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was above background levels at Shiveluch during 26-31 January, but on 1 February at 1859 it increased. During the following 2 hours spasmodic tremor occurred and seismic data suggested that an ash-and-gas plume rose to 2.5 km above the lava dome. Afterwards, seismicity returned to levels seen before the increase. During 25 January-2 February several clouds composed of ash, steam, and/or gas were seen, with the highest rising 2 km above the dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. The Color Concern Code remained at Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
A decrease in seismicity over several days led KVERT to reduce the Concern Color Code at Shiveluch on 23 January to Yellow ("volcano is restless") from Orange ("volcano is in eruption or eruption may occur at any time"). During 18-25 January several small steam-and-gas emissions occurred, with the highest plume rising 800 m above the lava dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
On 17 January, increased seismic energy release prompted KVERT to increase the Color Concern Code at Shiveluch to Orange ("volcano is in eruption or eruption may occur at any time") from Yellow ("volcano is restless"). During 11-18 January the total number of earthquakes within Shiveluch's edifice decreased, but the energy of individual earthquakes increased (up to ~M 3). In addition, weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. Seismic data indicated the occurrence of more intense possible gas-and-ash explosions than occurred during previous weeks. During 13-14 and 15-16 January, gas-and-steam plumes rose 1-1.5 km above the lava dome. On 14 January, a plume extended more than 10 km SE, and rock avalanches were visible continuously rolling down the dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 4-11 January, about 40 earthquakes with magnitudes greater than or equal to 1.7 occurred, and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. The total number of earthquakes within the volcano's edifice increased during the week. Several small explosions produced steam-and-gas plumes, with the highest reported plume rising ~1 km above the dome on 5 January. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery, but ash was not. The Color Concern Code remained at Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 28 December-4 January seismicity increased at Shiveluch; about 70 earthquakes with magnitudes greater than or equal to 1.7 occurred in comparison to 20 the previous week. Shallow, weak seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were also registered. Small explosions produced low-rising gas-and-steam plumes, but no ash was visible on satellite imagery. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. The Color Concern Code remained at Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 21-28 December, about 20 earthquakes with magnitudes greater than or equal to 1.7 occurred, and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. Seismicity decreased slightly, but remained above background levels. Small gas-and-steam plumes rose above the lava dome. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. The Color Concern Code remained at Yellow ("volcano is restless").
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 14-21 December, more than 40 earthquakes with magnitudes greater than or equal to 1.7 occurred, and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. The largest earthquake was M 3. Several gas-and-steam plumes were produced from explosions, with the highest reported plume rising 3.5 km above the lava dome on 20 December at 1618 and drifting to the W. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 7-14 December more than 40 earthquakes with magnitudes greater than or equal to 1.7 occurred, and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. On 8, 10, and 13 December gas-and-steam plumes rose 1-2 km above the dome. Thermal anomalies in the active dome area were visible on satellite imagery. The volcano remained at Color Concern Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
A lava dome continued to grow in Shiveluch's active crater, and seismic activity remained above background levels. Many weak, shallow earthquakes occurred within the volcano's edifice, along with about 30 earthquakes with magnitudes greater than or equal to 1.7. Other local shallow seismic events (possible collapses, avalanches, or possible weak gas-ash explosions) and episodes of weak volcanic tremor were registered. During 1 December, a gas-and-steam plume rose 400 m above the dome and extended 5 km to the E and NW. According to visual reports from Klyuchi town, at 0910 a short-lived explosive eruption sent an ash plume to ~2 km above the dome. This explosion was visible by airplane pilots. Several thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery.The volcano remained at Color Concern Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 23-30 November a lava dome continued to grow in Shiveluch's active crater, and small eruptions produced gas-and-steam clouds. The highest reported gas-and-steam cloud rose to 1.3 km above the dome on 27 November. Thermal anomalies in the active dome area were visible on satellite imagery. About 35 earthquakes with magnitudes greater than or equal to 1.7 occurred and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. The volcano remained at Color Concern Code Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 16-23 November a lava dome continued to grow in Shiveluch's active crater, and several eruptions produced ash, steam, and gas clouds. The highest reported ash cloud rose to 1-2 km above the dome on 19 November. Thermal anomalies in the active dome area were visible on satellite imagery. About 60 earthquakes with magnitudes greater than or equal to 1.7 occurred and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. KVERT reduced the Color Concern Code from Orange to Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 9-16 November a lava dome continued to grow in Shiveluch's active crater and several steam, gas, and ash explosions occurred. Seismic data suggested emissions from these explosions rose to a maximum height of ~4 km above the dome. A short-lived explosion on 9 November at 1200 produced an ash plume that was observed from Klyuchi, ~46 km from the volcano, rising ~1 km above the dome. The same day, during 1750-1810 incandescence was visible on the SE flank of the volcano 50 m below the summit. Thermal anomalies in the active dome area and ash clouds were visible on satellite imagery. Spasmodic volcanic tremor and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. The intensity of volcanic tremor noticeably diminished during the week.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 2-9 November a lava dome continued to grow in Shiveluch's active crater, and several eruptions produced ash, steam, and gas clouds. Inclement weather prevented visual observations of several possible gas-and-ash eruptions on 7 November. However, seismic data suggested these eruptions produced clouds that rose to 6.5-7.5 km. During 1630-1720 ash fell in Klyuchi town ~46 km from the volcano. A thermal anomaly in the active dome area was visible on satellite imagery on 2 November. Spasmodic volcanic tremor and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. The intensity of volcanic tremor continued to grow slowly during the report period.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 26 October-2 November, a lava dome continued to grow in Shiveluch's active crater. The evening of 29-30 October incandescent avalanches were observed travelling down the W and SW slopes of the lava dome. Gas-and-steam plumes rose ~1.5 km above the dome on 30 and 31 October. Thermal anomalies in the active dome area were visible on satellite imagery. Spasmodic volcanic tremor and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. The intensity of volcanic tremor was greater than the previous week. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 19-26 October, a lava dome continued to grow in Shiveluch's active crater. An explosion during 22-23 October produced a steam-and-gas plume visible from the town of Klyuchi, 46 km from the volcano, rising 4-4.2 km a.s.l. Thermal anomalies in the active dome area were visible on satellite imagery. Spasmodic volcanic tremor and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. The number of weak shallow seismic events and the intensity of volcanic tremor slowly increased. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 12-19 October, a lava dome continued to grow in Shiveluch's active crater and several gas-and-steam plumes were observed. The highest reported gas-and-steam plume was produced by an explosion on 17 October at 1740; it rose 1.2 km above the dome and extended 3 km to the W. Thermal anomalies in the active dome area were visible on satellite imagery. Spasmodic volcanic tremor and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 6-12 October a lava dome continued to grow in Shiveluch's active crater, and several eruptions produced ash and steam-and-gas clouds. The highest reported steam-and-gas cloud was produced from an eruption on 9 October at 1630 and rose 2 km above the dome. On 10 October at 2250 the reflection from incandescent lava was visible on the dome. Short pyroclastic flows and 400-m-high ash plumes were produced from small explosions on 11 October at 1515 and 1610. Thermal anomalies in the active dome area were visible on satellite imagery. Spasmodic volcanic tremor and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 28 September to 6 October a lava dome continued to grow in Shiveluch's active crater, and several eruptions produced ash and steam-and-gas clouds. The highest reported ash clouds were produced from eruptions on 1 October at 1641 and 1654. The ash plumes rose to 7 and 7.5 km above the volcano, respectively, and deposited a few millimeters of ash in Klyuchi town, 46 km from the volcano. An eruption the same day at 2210 produced a mushroom-shaped ash cloud that rose to ~3 km above the volcano and extended ~10 km SE. On the evening of 3 October incandescence was visible at the dome. Thermal anomalies in the active dome area were visible on satellite imagery. Spasmodic volcanic tremor and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 28-29 September seismic activity was above background levels and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. Several small explosions occurred on 30 September, sending ash clouds to the following heights above the dome: 2.5 km at 1323, 3.5 km at 1719, 2.5 km at 1755, and 4.5 km at 1807. An explosion at 2010 produced an umbrella-shaped ash cloud that rose 9 km above the lava dome and extended ~9 km E to W. Large pyroclastic flows traveled ~5 km to the SE. The same day the Concern Color Code was raised from Orange to Red. During 28-30 September thermal anomalies in the active dome area were visible on satellite imagery. Following the eruption, during 30 September at 2100 to 1 October at 0900, seismic activity decreased and the view of the volcano was obscured by clouds. AVHRR satellite imagery at 0757 showed that the ~25-km-diameter ash cloud remained centered over the volcano. On 1 October the Concern Color Code was reduced back to Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Anchorage Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); China Daily.com
During 14-21 September several steam-and-gas clouds were observed, as were ash clouds produced from explosions at Shiveluch, with the highest ash cloud rising 1.1 km above the lava dome. During the week hot avalanches from the summit of the dome were also noted. Seismic activity was above background levels and spasmodic volcanic tremor and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. Thermal anomalies in the active dome area were visible on satellite imagery. Shiveluch remained at Color Concern Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 7-14 September several gas-and-ash plumes produced from explosions at Shiveluch were observed, with the highest rising 1.2 km above the dome. On 11 September several hot avalanches were observed travelling from the top of the lava dome. On 12 September explosions produced a short pyroclastic flow and an ash plume that rose to 1 km above the dome. During the week, seismic activity was above background levels and spasmodic volcanic tremor and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. The volcano remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismic activity was above background levels during 31 August-7 September. Spasmodic volcanic tremor and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered the entire week. Several gas-and-steam plumes were observed, with the highest rising 1.2 km above the dome. On 4 September an explosion produced an ash plume that rose 1 km above the dome and a 1-km-long pyroclastic flow that traveled to the SE. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. The volcano remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismic activity was above background levels during 24-31 August. Weak shallow earthquakes within the volcano's edifice and signals that may have represented short-lived explosions were recorded. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. The volcano remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismic activity was above background levels during the week. Spasmodic volcanic tremor and weak, shallow seismic signals (possible collapses and avalanches) were registered. Several small explosions produced gas-and-steam plumes that rose to a maximum height of 2 km above the dome. Pyroclastic flows traveled down the flanks of the volcano following an explosion on 23 August. Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery. The volcano remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismic activity remained above background levels during the week and included several small earthquakes. On 15 August volcanic tremor decreased gradually to background levels. Observers in Klyuchi reported that on 11 August gas-and-steam plumes rose 1.2-1.5 km above the dome. Several thermal anomalies were recorded on satellite imagery, as well as a gas-and-steam plume extending 75 km SE. The volcano remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During the week seismic activity remained above background levels, with many small earthquakes occurring within the volcano's edifice and several different seismic signals (explosion, avalanche, collapse) recorded locally. Small gas-and-steam plumes rose to 200 m above the dome. Thermal anomalies were seen in several areas on satellite imagery. The volcano remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During the week seismic activity remained above background levels, with many small earthquakes occurring within the volcano's edifice and several different seismic signals (explosion, avalanche, collapse) recorded locally. The level of continuous spasmodic volcanic tremor increased on 28 July and again on 30 July. Gas-and-steam plumes were observed rising to a maximum height of 1 km above the dome and on the night of 1 August ash fell in the town of Klyuchi, 46 km from the volcano. One- to three-pixel thermal anomalies were occasionally visible in satellite imagery. The volcano remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During the week seismic activity remained above background levels, with many small earthquakes occurring within the volcano's edifice and many different seismic signals (explosion, avalanche, collapse) recorded locally. Gas-and-steam plumes were observed from Klyuchi town and the highest cloud rose to 2 km above the lava dome. One- to three-pixel anomalies were occasionally visible on AVHRR imagery near the SW flank of the volcano. The volcano remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
A moderate-sized eruption at Shiveluch on 19 July prompted KVERT to raise the Concern Color Code from Yellow to Orange the same day. The eruption occurred at 1033 and produced an ash plume that rose 3 km above the lava dome. Prior to the eruption, during 14 through 16 July, spasmodic volcanic tremor increased several times. On 15 July at 1803 a three-pixel thermal anomaly was visible on AVHRR satellite imagery near the SW flank of the volcano. Also, at 2100 a gas-and-steam plume was observed rising 1.5 km above the dome.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismic activity remained above background levels during 6-13 July. Many small earthquakes were recorded within the volcano's edifice, along with weak spasmodic tremor and other local seismic signals, interpreted as related to explosions, avalanches, and collapses. On 6 July explosions sent ash to 0.6-1 km above the volcano. In addition, hot avalanches and pyroclastic flows were observed during clear conditions to be traveling down the flanks of the volcano. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 29 June to 6 July seismic activity remained above background levels, but the level of explosive volcanic activity decreased in comparison to the previous week. On 2 and 3 July a thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery. On 3, 4, and 5 July voluminous gas-and-steam plumes rose 2-2.5 km above the volcano. Due to the decrease in volcanic activity the Concern Color Code at Shiveluch was reduced from Orange to Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Increases in both seismic activity and explosions at Shiveluch led KVERT to raise the Concern Color Code on 2 July from Yellow to Orange. On 26 June, prior to an increase in seismic activity, a possible thermal anomaly was observed on satellite imagery. The volcanic activity increase may have begun on 28 June at 1500 when the level of volcanic tremor and the number of shallow earthquakes increased. According to reports from observers in the town of Klyuchi (46 km from the volcano) on 29 June at 1150 a short-lived explosion sent an ash-and-gas plume to a height of ~4.5 m a.s.l. During the eruption pyroclastic flows traveled 2.5 to 3 km down the slopes of the volcano. Later in the day and during the next day seismic data suggested that six possible gas-and-ash explosions occurred that produced ash to a maximum height of 8.5 km a.s.l. According to the Tokyo VAAC the largest 30 June explosion began at 0300 and produced an ash plume that ascended to 7.3 km a.s.l. Later during 30 June and 1 July, GOES and other satellite's imagery showed a possible ash cloud drifting over the Bering Sea that may have originated in Kamchatka. According to visual observations from the town of Klyuchi, on 1 July explosions produced ash plumes that rose to 1.5 km above the dome, and at 1250 a short-lived explosion produced an ash-and-gas plume that rose to ~8 km a.s.l and drifted to the E. Pyroclastic flows extended 5 km down the Baidarnaya River.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Pravda News; Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
During 15-21 June seismic activity was above background levels. Many small earthquakes occurred within the volcano's edifice and episodes of weak spasmodic volcanic tremor were recorded. Local seismic signals accompanied explosions, avalanches, and collapses. Weak steam, gas, and ash explosions rose to a maximum height of 800 m above the lava dome.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 8-14 June seismic activity was above background level at Shiveluch. Many small earthquakes occurred within the volcano's edifice and local seismic signals accompanied explosions, avalanches, and collapses. There were several ash-and-gas eruptions, with the highest eruption cloud reaching up to 2 km above the lava dome. A thermal anomaly was observed on satellite imagery on 8,9, and 10 June. The level of Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
On 5 June a gas-and-steam plume rose 450-1,200 m above the volcano and extended 3-5 km W. A thermal anomaly observed in satellite images on 5 June at 1809 had two saturated pixels (49°C) in a background of 15-25°C. On 6 June at 0756 the anomaly consisted of one pixel at 49.3°C in a background of near 4°C. According to reports from the town of Klyuchi, on 7 June at 1630 an ash-and-gas plume rose 600 m above the dome and extended to the W. At 1650 a short-lived explosion sent an ash-and-gas plume 1,500 m above the volcano accompanied by 3- and 2-minute-long, shallow seismic events. A thermal anomaly was observed in satellite images on 7 June at 1745. Three pixels near saturation (at 44-45°C) stood out from a background of pixels 15-25°C, in addition to a steam-and-ash plume extending to the NW about 33 km. The level of Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Sources: BBC News; Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Volcanic activity decreased following the 22 May eruption, therefore, on 30 May the Concern Color Code was further reduced from Orange to Yellow. During the week several small eruptions produced gas-and-steam plumes that rose up to 1.2 km above the old lava dome. Seismic activity decreased in comparison to the previous week, but remained above background levels.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
On 22 May at 0209 an explosive eruption produced a mushroom-shaped ash column that rose to a height of more than 10 km a.s.l. (preliminary reports stated ~20 km). The high-pressure system over N Kamchatka caused the plume to remain fairly stationary over the region as it spread out to cover an area of ~50,000 km2. Observations from the town of Klyuchi, 46 km from the volcano, revealed that the new lava dome (first observed on 12 May) and the W part of the old dome were destroyed during the eruption. After the 22 May eruption several small eruptions produced ash-and-gas clouds that rose up to 2 km a.s.l. On 23 May a large thermal anomaly was observed at Shiveluch. In satellite imagery the anomaly consisted of ten pixels ranging in temperature from 30 to 49 °C with two pixels near saturation. The anomaly may have represented a pyroclastic flow that originated from the dome area. Seismic activity remained above background levels. On 24 May the Concern Color Code was reduced from Red to Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Due to the occurrence of several large explosions at Shiveluch, KVERT increased the Concern Color Code to Red on 21 May. An approximately 40-minute-long eruption began at 1556 on 19 May. An ash cloud rose to an altitude of 10 km a.s.l. and drifted to the NE. Short pyroclastic flows and hot avalanches from the lava dome were restricted to areas near the lava dome. At 1802 and 1814 on 20 May a large thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery. At 1925 and 2014 two explosions sent ash columns to heights ranging between 4.7 and 5 km a.s.l. At 0713 on 21 May an explosion sent an ash column to 10-12 km a.s.l. AVO reported that ash was visible on satellite imagery. At 0209 on 22 May an eruption produced a mushroom-shaped ash column to a height of ~20 km a.s.l. that drifted to the SSE. Reflected incandescence was observed above the volcano from the town of Klyuchi, 46 km from the volcano. The Concern Color Code changed several times during the week; on 19 May it was raised from Yellow to Red, on 20 May it was reduced to Yellow, and the following day it was raised again to Red.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Anchorage Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
After a pyroclastic-flow producing eruption occurred at ~0958 on 7 May, seismic activity decreased but it remained above background levels for most of the week, a new extrusive dome formed, and the Concern Color Code was reduced. A noticeable increase in seismic activity occurred between 1820 and 1852 on 7 May, and may have corresponded to an explosion that produced an ash-and-gas plume. The plume was visible in satellite imagery rising up to 4 km a.s.l. and drifting ~40 km to the WNW. A small amount of ash fell in the town of Kliuchi, 46 km from the volcano. During 11-15 May seismic activity continued to decrease, but remained above background levels. Many small earthquakes occurred at the volcano's edifice. At 0900 on 12 May a new extrusive lava dome was observed from Kliuchi that was steaming intensely, 100 m high, 200 m wide at the upper part of the dome, and had a volume of ~10 million m3. Observers in Kliuchi reported that by 2140 on 13 May the dome had grown ~50 m higher. Weak explosions produced ash-and-steam plumes that rose up to 1 km above the new dome. On 16 May the Concern Color Code at Shiveluch was reduced from Orange to Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Volcanic activity continued at high levels at Shiveluch, with an increase in seismic activity, a thermal anomaly visible in satellite imagery, several small explosions, and a small pyroclastic-flow-producing eruption. An increase in seismic activity occurred on 1 May following the initial increase on 22 April and subsequent slight decrease on 28 April. The seismic activity increase on 1 May consisted of many shallow earthquakes and episodes of weak spasmodic tremor. Several small eruptions produced gas-and-steam plumes that rose up to 1.5 km. AVO reported that on 2 May a weak thermal anomaly (3 pixels) that was originally detected on 30 April was visible on satellite imagery. By 3 May the thermal anomaly had increased in intensity, with 2 of the 3-4 pixels at or near saturation on the imagery. At 0958 on 7 May an eruption produced an ash-and-gas plume that rose ~4.5 km a.s.l. and extended to the NW. Small pyroclastic flows were visible traveling down the volcano's SW slope. The Concern Color Code at Shiveluch remained at Orange.
Sources: Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Following the sharp increase in seismic activity on 22 April the number and magnitude of seismic events continued to increase at Shiveluch until 27 April. The largest earthquake occurred on 27 April (M 4) and the number and magnitude of earthquakes began to slightly decrease on 28 April. Several gas-and-steam plumes that reached a maximum height of 700 m above the volcano were observed starting on 28 April. As of 1 May seismic activity was still significantly above background levels. KVERT stated that the trend of the seismic activity is similar to the increase that preceded the violent 1993 eruption. The Concern Color Code at Shiveluch remained at Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
During 13-20 April seismic activity was above background levels at Shiveluch before increasing sharply on 22 April. Heavy clouds prevented visual observations of the volcano, but seismic data suggested that no ash explosions occurred. Due to the high seismic activity KVERT raised the Concern Color Code from Yellow to Orange.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Seismicity was at background levels during 6-13 April. Short series of separate, shallow earthquakes and episodes of volcanic tremor were registered during the week. Some of the seismic events may have corresponded to weak ash-and-gas and steam-and-gas explosions. During 6-8 April a gas-and-steam plume rose 500-800 m above the volcano and extended 5-10 km to the E. At 1500 on 7 April a gas-and-steam plume rose up to 1.2 km above the volcano. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The KVERT reported that at 1638 on 5 April a short-lived explosive eruption, with an accompanying increase in seismic activity, produced an ash-poor plume that rose 4.5-5 km above Shiveluch's dome. At 1725 the plume extended more that 50 km to the SSE. According to the Tokyo VAAC the plume was visible on GMS imagery until ~1430 on 6 April. In addition, during the week small gas-and-steam plumes rose 50-400 m above the volcano and four, 2- to 3-minute-long shallow earthquakes were registered on 2, 4, and 5 April. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Sources: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
The KVERT reported that at 0555 on 24 March a 2-minute-long shallow earthquake was followed by weak spasmodic volcanic tremor that lasted ~10 minutes. This burst of activity may have corresponded to weak ash-and-gas explosions that reached a height of ~2 km above the crater. On 27 March a powerful gas-and-steam plume rose 800 m above the volcano. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The KVERT reported that seismicity was mainly at background levels. On 18 March a 12-minute-long series of shallow earthquakes registered. On 22 March a 2-minute-long shallow earthquake swarm was followed by 20 minutes of weak spasmodic volcanic tremor. Another 2-minute earthquake swarm occurred shortly thereafter. These seismic bursts are thought to correspond to weak ash-gas explosions to heights of 2,000-3,000 m above the crater. On 18-19 and 22 March gas-and-steam plumes rose 200 m above the volcano. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The KVERT reported that seismicity was at background levels. On 9 and 11-14 March gas-and-steam plumes rose 400-1,000 m above the volcano. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The KVERT reported that during 2-6 March, several series of shallow earthquakes were registered, with some followed by weak spasmodic volcanic tremor. The bursts of activity may have corresponded to weak ash-and-gas explosions that rose to heights of 2-3 km above the crater. During 3-4 March, visual and satellite-based data revealed that a gas-and-ash plume rose 300-800 m above the crater and drifted more than 50 km to the E. At 1545 on 7 March seismic data indicated the probable occurrence of a short-lived gas-and-ash explosion, accompanied by a series of shallow and high-frequency earthquakes for ~15 minutes. Observers in Klyuchi town reported that at 1600 the same day the ash-and-gas plume rose 1.5 km above the lava dome and extended to the NW. According to a pilot report, at 1620 the ash plume was visible at a height of 10 km above the volcano drifting towards the NE. The AVO reported that satellite imagery at 1715 showed two plumes: one was at a low altitude, composed mostly of steam, and drifted to the E; the other was located 7-8 km a.s.l., composed mostly of ash, and drifted to the N. At 1625 the Tokyo VAAC detected the ash cloud on GMS-5 imagery at a height of ~10 km a.s.l. The ash cloud was no longer visible on satellite imagery by 0342 on 8 March. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The KVERT reported that during 25-27 February there was an increase in seismic activity. Two- and three-minute-long series of shallow earthquakes were registered and followed by weak volcanic tremor. These outbursts may have corresponded to weak ash-and-gas explosions that reached a height of ~2 km above the crater. On 23, 24, and 28 February gas-and-steam plumes rose 250-600 m above the volcano. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The KVERT reported that during 19-20 February there was an increase in seismic activity. Two- and four-minute-long series of shallow earthquakes were registered, possibly corresponding to weak ash-and-gas explosions. On 22 February, a gas-and-steam plume rose 900 m above the volcano. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The KVERT reported that during 9-16 February seismicity was at background levels. On 9-10 February a gas-and-steam plume rose 1-1.2 km above the volcano. On 12-15 February a gas-and-steam plume rose 300-500 m above the volcano. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The KVERT reported that during most of the week seismicity was at background levels. At 1100 on 2 February a powerful gas-and-ash eruption produced a plume that rose 800 m above the volcano and spread ~3 km towards the W. The same day, observations from Klyuchi town revealed that at 1804 a short-lived eruption produced an ash plume that rose up to ~5.3 km a.s.l. The event was accompanied by a 2-minute-long shallow seismic signal that was detected more than 110 km from the volcano. Afterwards, during 1807 to 1824 strong volcanic tremor was registered. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
The KVERT reported that at 1802 and 1820 on 29 January, shallow earthquakes were registered beneath the volcano that were accompanied by short-lived explosions. The ash cloud produced from the first explosion reached ~2.5 km above the volcano, while the second eruption's ash cloud could not be observed. During 26-31 January a gas-and-steam plume rose 50-800 m above the volcano, and on 1 February a gas-and-steam plume rose 2 km above the volcano. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that on 21-24 January seismicity was above background levels and on 20-24 January a gas-and-steam plume rose 50-1,000 m above the volcano. Shallow earthquakes were registered under the volcano along with short-lived explosions at 0444 on 22 January and at 0924 on 24 January. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
On 13 and 18 January seismicity and volcanism rose above background levels. At 0202 on 13 January a shallow earthquake was accompanied by a short-lived explosion, and at 1106 on 18 January similar activity sent an ash cloud to 4.5 km a.s.l. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Volcanic activity was above average on 31 December, and on 2, 4, and 5 January: shallow earthquakes were accompanied by short-lived explosions that sent ash plumes to a maximum height of ~2 km above the volcano. On 2 and 4 January a gas-and-steam plume rose 300 m above the crater. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that seismicity remained at background levels throughout most of the week. Beginning at 0743 on 29 December shallow earthquakes under the volcano were accompanied by short-lived explosions that sent a plume to a height of 2-3 km above the volcano. On 23, 24, and 25 December gas-and-steam plumes were observed rising 300-1,000 m above the crater. KVERT raised the Concern Color Code from Green to Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that much like the previous week, the character of the volcanic activity did not change during 15-22 December. On 15 and 20 December weak seismicity was registered at the volcano and at 2105 on 15 December a seismic event was likely accompanied by a gas-and-ash explosion that sent a cloud to an inferred height of 2 km a.s.l. On 20 December a gas-and-steam plume rose 200-300 m above the crater. KVERT lowered the Concern Color Code from Yellow to Green.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
KVERT reported that the character of volcanic activity at Shiveluch did not change during 9-16 December. Weak seismicity was registered at the volcano during most of the week. Much like the previous week, two seismic events occurred that were above normal levels. First, at 2147 on 9 December a shallow seismic event was likely accompanied by a gas-and-ash explosion that sent a cloud to an inferred 3.5 km a.s.l. The event was followed by volcanic tremor for ~0.5 hour. The second possible gas-and-ash explosion occurred at 0021 on 12 December. The cloud was again inferred from seismic data to have risen to ~4 km a.s.l. These inferred plume heights were determined by comparing the amplitude of the seismic wave caused by the eruption to the heights of ash clouds observed in the past associated with earthquakes with similar amplitudes. After the 12 December event, volcanic tremor was registered for 1 hour. The Concern Color Code at the volcano remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
For most of the period during 1-8 December weak seismicity was registered at the volcano, however two seismic events occurred that were above normal levels. First, at 1853 on 6 December seismic data indicated that a gas-and-ash explosion may have occurred. The possible explosion was registered as a shallow seismic event and was followed by volcanic tremor. Then, at 1556 on 7 December another shallow seismic event and possible gas-and-ash explosion occurred. The height of the cloud was estimated on the basis of seismicity at about 4-4.5 km a.s.l. The Concern Color Code at the volcano remained at Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
On 24 November a gas-and-steam plume rose 400 m above the volcano and extended 5 km to the E. No seismicity was registered at Shiveluch during most of the period during 24 November to 1 December, but at 0935 on 27 November a strong, shallow seismic event occurred. KVERT raised the Concern Color Code from Green to Yellow.
Source: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT)
Reports are organized chronologically and indexed below by Month/Year (Publication Volume:Number), and include a one-line summary. Click on the index link or scroll down to read the reports.
Small ash ejection; no change to lava dome
A single ash ejection to 1 km height occurred 22 May at 2356. No changes to the lava dome were observed. Lava extrusion and explosive activity began in late August 1980.
Information Contacts: B. Ivanov, IVP.
Ash explosions in May, August, September, and October
Explosions ejecting andesitic ash were reported in the BVE (no. 25, 1988) on 26 May, 8 August, 19 September, and 25 October 1985. Rockslides preceded the 19 September explosion, which produced an ash cloud that reached a height of 4 km.
Reference. Volcanological Society of Japan, 1988, Bulletin of Volcanic Eruptions, no. 25.
Information Contacts:
Large ash explosion from lava dome
On 13 January a strong phreatomagmatic explosion that ejected large amounts of ash occurred from the extrusive dome. Intense fumarolic activity at the surface of the dome was noted after the explosion.
Information Contacts: A. Khrenov and G. Bogoyavlenskaya, IV.
Plume on satellite image
A NOAA 10 satellite image showed a plume on 1 May at 0915 extending 100 km SE. On the afternoon of 5 May no plume was visible but by early 6 May a thin plume had formed, drifting 75-80 km NNE. The volcano was obscured by clouds 25-30 April.
Information Contacts: M. Matson and W. Gould, NOAA/NESDIS.
Ash plumes and base surges from extrusive dome
Gas and ash plumes from the extrusive dome were sighted more frequently in 1987. Four or five plumes were seen each month March-June and 6 in July. Seismic activity also intensified and each explosion was accompanied by volcanic tremor. Vertical columnar ash plumes with a maximum height of 5 km were often accompanied by base surges that extended 300 m. Explosion products included ash and andesitic sand-sized tephra with rare blocks as large as 1 m.
Information Contacts: G. Bogoyavlenskaya and V. Beloussov, IV.
More frequent explosions from dome; base surges
"Until 1980, only fumarolic activity was observed in the crater formed during the catastrophic eruption of 12 November 1964. An extrusive andesitic dome grew during 1980-81, but its extrusion was not accompanied by notable explosive activity. The dome volume is estimated at 0.021 km3. Subsequently, until 1984, only fumarolic activity continued on the dome. A period of phreatic explosive activity started in 1984, with 7, 4, and 15 explosions in 1984, 1985, and 1986 respectively. In 1987, the frequency of explosions increased to 2-5/month. The explosions were of differing magnitudes, with the most violent ejecting plumes as much as 5 km high. Annular base surges sometimes formed. The explosions apparently created funnel-shaped craters near the dome's summit, with maximum diameters of a few tens of meters. Several of these features merged to form an 80-m-diameter crater on the top of the dome. Episodes of spasmodic volcanic tremor as much as 1 hour long accompanied the explosions, which were continuing in 1988.
"The products of the explosions were mostly ash and sand-sized tephra of andesitic composition. The morphology of the particles indicates that they were formed by crushing of crystallized magma. Products from the explosions outside of the dome seem to be somewhat more basic and finer grained than those originating from the dome."
Information Contacts: G. Bogoyavlenskaya and A.B. Belousov, IV.
100-m explosion vent in center of lava dome; minor fumarolic activity
During a 2 February overflight, an explosion vent more than 100 m in diameter was observed in the center of the [extrusive] hornblende andesite lava dome (figure 1). Minor fumarolic activity was occurring.
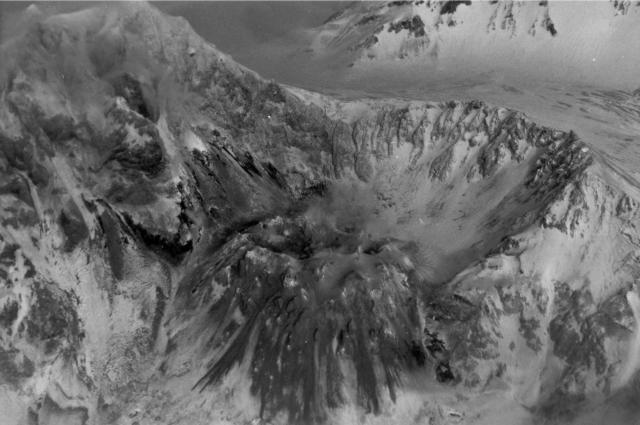 |
Figure 1. Crater and lava dome at Shiveluch, looking roughly N on 2 February 1990, showing explosion vents. Courtesy of B.V. Ivanov. |
Information Contacts: B. Ivanov, IV.
6-8-km-high column; tephra fall to coast
At 1756 on 8 April, an explosive eruption began in the dome area, ejecting an ash cloud 6-8 km high that was visually tracked 40 km to the SE. The eruption, lasting 3-4 minutes, was the volcano's first known explosive activity of 1991. Satellite images at 0950 (NOAA 10) and 1430 (NOAA 11) on 9 April revealed a dark streak (~8-15 km wide, 110 km long, with an azimuth of ~135°) extending from the volcano to the coast (figure 2). Analysts suggested that the streak represented tephra deposited on snow. A thin plume, extending ~50 km SE from Shiveluch, was visible by satellite (NOAA 10) at 0942 on 14 April.
Information Contacts: E. Gordeev, IV; T. Miller, AVO; G. Stephens and O. Karst, NOAA/NESDIS.
Possible new tephra deposit on E flank
After the 8 April explosive eruption, satellite images showed an apparent narrow zone of tephra deposited SE from the summit to the coast. The NOAA 10 polar orbiter showed a second, similar deposit on 9 May at 1000, extending E from the summit then turning SE to parallel the 8 April material. . . .
Information Contacts: W. Gould, NOAA/NESDIS.
Activity increasing; steam and ash explosions
Explosive activity at Shiveluch's active dome and increased seismicity prompted the KVERT to raise the Level of Concern Color Code from yellow to orange on 7 April, stating that an explosive eruption was possible within several hours or days with little warning. A major eruption occurred on 21 April that produced a column to an estimated altitude of 18 km. [But see 18:4.]
Explosive bursts began on 18 March. A gas and ash explosion at 0900 on 20 March sent an eruption cloud ~1 km above the summit. Another eruption cloud rose ~4 km at 2400 on 21 March, and spread to a diameter of 20 km in the absence of any wind. Explosions occurred every day 22-28 March and 3-4 April, with 2/day on 25, 27, and 28 March. Observers in early April saw no unusual activity in the crater, but the normal fumarolic emissions on the SE part of the active dome were continuing.
Shallow earthquake swarms were detected in early April by the seismic network of four stations that monitor Shiveluch. The nearest station is ~8 km from the summit on the slope of Shiveluch. Other stations are in Kliuchi, ~50 km SW of the summit, and on the Sredinny Ridge to the W, with the farthest station ~100 km from the summit. Earthquake counts increased above background (5 earthquakes/day) to 14 on 4 April, 30 in 4 hours on 5 April, and 42 in 20 hours on 6 April. The earthquakes had amplitudes >5 µm and durations of 2-2.5 minutes. There was a continuous swarm with 90 distinct earthquakes registered over constant weak background seismicity on 7 April. Seismicity beneath the active dome continued at similar levels 8-11 April.
A 400-m-high fumarolic plume was visible during clear weather on 11 April. At 1300 the next day, steam and gas explosions with a small amount of ash occurred at 5-minute intervals and produced columns that rose 1 km above the dome and extended 15 km SE. Small mudflows also traveled 1.5 km from the dome. Shallow seismicity beneath the dome decreased following the explosive activity. The number of earthquakes remained high, however, and their magnitudes increased during the period 12-15 April, with a maximum of 124 earthquakes 14 April.
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG.
Eruption sends ash cloud to 20 km altitude
An explosive eruption 22 April followed more than a month of seismic and explosive precursors. Almost daily explosive bursts from 18 March to 4 April sent eruptive clouds to 1-4 km above the summit. Shallow earthquake swarms increased in early April from 14 earthquakes on 4 April to 90 distinct earthquakes in a continuous swarm on 7 April, when the Level of Concern Code was raised to orange by geologists at the IVGG. Magnitudes were estimated to be about M 2 on 6 April. Steam and gas explosions with some ash content continued over the next 3 days with seismicity remaining at high levels. Earthquakes increased in number and magnitude 12-15 April, with a maximum of 124 earthquakes on 14 April.
A snowstorm prevented observations 17-19 April, but explosions from the volcano were heard in Kliuchi (45 km SW) every few seconds on the 19th. Numerous gas and steam bursts occurred from the active dome 19-20 April. The gas-and-ash plume rose 800 m above the crater rim and drifted SW. Two spine-like or obelisk-shaped extrusions, 30-40 m high, were observed on the summit dome 20 April by geologists from IVGG and the IV. Shallow seismicity beneath the dome began to migrate towards the surface that same day. Seismicity began decreasing 19 April, and had declined sharply by the 21st. Gas and steam bursts rose to 600 m above the dome on 21 April.
The climactic eruption began the morning of 22 April. IV scientists reported explosions at the dome and from the crater near the dome beginning at 1030. The eruption cloud was ~7 km high by 1042 and >10 km high at 1313. The cloud obscured the volcano after the explosions until about 1600 when the lower part of the cloud was blown E and the upper part W. The eruption also produced pyroclastic flows and mud flows >10 km long.
The Level of Concern Code was raised to red on 22 April by IVGG geologists, who reported strong explosions at 1205 and 1230. At 1205 the eruptive cloud rose 6 km above the crater rim . . . and then to 15 km by 1330. The lower part of the ash cloud was moving WSW, and the upper portion was moving SE. Lightning was seen within the cloud. At 1340 the height of the eruption column was estimated to be 18 km (~20 km altitude). The ash cloud was detected drifting W by a weather satellite at 1432. By 1545, the ash cloud was moving WSW over the Kamchatka Peninsula. Pyroclastic flows down the flanks of the volcano reached 900 m elev, and mud flows extended 100 m lower.
The next morning, at 0530 on 23 April, another explosive ash eruption sent a column to 9-11 km altitude with the cloud moving in different directions at different altitudes. Bad weather prevented visual helicopter inspections of the crater area that day, but ash had started falling in . . . Kliuchi during the night and continued past 0800, stopping sometime later in the day. Strong winds rapidly redistributed the ash making thickness estimates difficult; however no more than 3 mm of ash appears to have fallen on the town, 45 km SW. Seismic activity decreased in the 24 hours after the eruption, and the Level of Concern Code was lowered to orange. No new pyroclastic flows or mudflows were observed on the lower flanks of the volcano.
IV also reported single explosions continuing on 23 April. The ash column was 3 km high and ashfall also occurred in Ust'-Kamchatsk (100 km SE). Baidarnaya station (8 km from active crater) registered 27 earthquakes on 23 April with amplitudes of 2-4 µm.
The volcano became visible 24 April, and a gas and steam column 4.5 km high was observed by IVGG at 2230, drifting to the N. Shimmering lights inside the crater were observed during the night. Seismicity was twice that recorded 22 April, and 20 earthquakes were detected in addition to constant low-amplitude tremor beneath the crater. An explosive burst was recorded seismically at 0619 on 25 April. A steam-and-ash column to 3.5 km above the crater was observed that day at 0530 and 0730, with a >30-km-long plume directed NNW.
Clouds again prevented visual observations 26-29 April, but the Level of Concern Code was lowered to yellow on 27 April because of the overall decline in volcanic activity. However, seismicity remained above background levels during this period with 36 earthquakes recorded on 27 April. Shallow, low-amplitude tremor was also continuing beneath the active dome.
Separate strong explosions were observed by IV geologists once every few days from 24 April to 3 May. The height of the ash cloud during the last days reached 1.5-2 km.
Thermal capacity and volume of ejected pyroclastics were calculated based on powerful explosions on 21 April at 2242-2258 (plume 6 km above the crater); 22 April at 0013-0026 (>10 km), 1104-1110, 1630 (7 km), and 2030, and 24 April at 1719 (3.5 km). Tremor amplitude was as much as 35 microns, with a period 0.6-0.9s (7.5 km from the active dome). Based on the height of the eruptive cloud and tremor, calculations indicate that the thermal capacity of the plume was about 1-50 x 109 MJ, with about 1-50 x 106 tons of ejected pyroclastics. Calculations were made by V. V. Ivanov (IV) using the methods of Fedotov (1985) and Firstov and others (1977).
References. Fedotov, S. A., 1985, Estimates of heat and pyroclast discharge by volcanic eruptions based upon the eruption cloud and steady plume observations: Journal of Geodynamics, v. 3, p. 275-302.
Firstov, P. P., Lemzikov, V. K., and Rulenko, O. P., 1977, Seismic regime of Karymsky volcano (1970-1973): Volcanism and Geodynamics, p. 161-179 (in Russian).
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG; S. Fedotov, V. Ivanov, G. Bogoyavlenskaya, V. Gavrilov, and N. Zharinov, IV; J. Lynch, SAB.
Persistent gas-and-steam column; growth of extrusive dome
A gas-and-steam column 1-5 km high has been observed every day that the volcano has been visible since the 22 April eruption. A small amount of ash was occasionally present in the plume, which varied in direction and distance with local wind conditions. The plume typically extended up to 40 km or more downwind. The extrusive dome inside the crater (figure 3) has continued to grow throughout May and early June.
During the week of 30 April to 6 May the gas-and-steam column was 3-5 km high with a plume that extended >30 km to the N. Shimmering lights were observed the night of 5 May on the surface of the extrusive dome inside the crater. At 2030 on 10 May a pyroclastic flow from the extrusive dome was seen inside the active crater. Numerous debris avalanches also formed that day on the SW slope of the growing dome. Several gas-and-steam bursts took place at 1200 on 7 May, sending material to a height of 2.5 km before drifting SSW. A gas-and-steam plume rose 2-2.5 km above the crater rim on 17 May, with the plume extending S for about 40 km. Poor weather conditions 11-21 May prevented frequent observations.
The steam-and-ash column from the crater rose to a height of 2-4 km from 21-27 May, and the plume extended up to 40 km N. By 27 May, the extrusive dome in the crater was ~800 m wide and 400 m high; it was 200 m high before the start of the eruption. From 27 May to 2 June, the height of the gas-and-steam column was ~2.5 km above the rim. A large number of avalanches off the extrusive dome indicated continued growth. Shimmering lights were observed on the dome at night. About 3-5 small explosions/day were occurring on the dome in early June, and the plume, carrying a small amount of ash, rose 1-3 km and extended up to 40 km S.
The level of seismicity increased 11 May and remained high through the 29th, when 8 tectonic earthquakes occurred beneath the volcano from 1600-2400. Volcanic tremor disappeared after the earthquakes, and had not returned by 2 June. Seismicity was continuing to decrease on 10 June, but was still above background levels.
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG.
Persistent gas-and-steam column with occasional ash; dome growth continues
The gas-and-steam column rising 1-6 km above the crater rim has persisted through 15 July . . . . A small amount of ash was occasionally present in the plume, which usually extended 30-40 km downwind. After decreasing in early June, seismicity increased again after 10 June. Seismic activity remained above background level 17-24 June, with at least 30 shallow earthquakes detected every day beneath the extrusive dome. On 29 June, rockfalls were observed on the growing dome at intervals of 3 minutes. Seven gas-and-steam bursts within one hour on 5 July produced a column up to 5 km high that extended >60 km S. Seismicity increased by a factor of 4.5 from 29 June to 5 July. Volcanic tremor was slightly above background on the night of 9 July. On 14 July, explosion sounds were heard in Kliuchi, 8 km S, but weather conditions prevented observations. The increase in seismic activity had only been detected by local stations as of 14 July. There were 42 seismic events recorded on 13 July, and 57 on 14 July by stations as far as 8 km from the volcano.
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov and S. Zharinov, IVGG.
Gas-and-steam plume continues
A gas-and-steam plume was observed on the afternoon of 29 July rising to 3 km above the crater and extending >50 km S. Similar activity, with a gas-and-steam column rising 1-6 km above the rim, has persisted since the 22 April eruption. The volcano has also remained seismically active. Seismicity registered at a station 8 km from the volcano increased 23-24 and 28-29 July, then decreased after 1 August. Weather conditions prevented visual observations of the summit in early August.
Information Contacts: S. Zharinov, IVGG.
Extrusive dome growth and gas-and-steam plume continue
Following a week of cloudiness, the gas-and-steam plume . . . was seen on 13 August rising . . . 800 m above the crater. The volcano was again obscured by clouds 14-19 August. When observed on 20 August, the gas-and-steam plume was as high as 1.5 km above the crater and was carried S about 5 km. On 9 September, the plume reached a height of 800 m above the crater and drifted S to a distance of 40 km.
The SE part of the extrusive dome continued to grow from 2-9 September. During that time, the relative height of the dome increased from 370-380 m to 450-470 m, while the upper diameter increased from 300 to 400 m, and the lower diameter increased from 500 to 600 m. Extrusive spines also appeared on the SE sector of the dome, and the frequency of explosions increased to one every 10-15 minutes. Explosive activity was not restricted to any one area of the dome.
Seismicity decreased throughout August before increasing in September to a level similar to 6 April, two weeks before the last eruption. Continuous volcanic tremor was recorded in both periods. Based on previous eruption patterns, an increase in seismicity above the current levels may precede an explosive eruption that could destroy the upper section of the active dome.
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG.
Seismicity remains high; gas-and-ash plume persists
Activity similar to previous months continued through early November, with high seismicity and a plume visible during clear weather. A gas-and-ash plume rose as high as 2-3 km above the crater on 10-19 September, with very high seismicity. Tectonic earthquakes centered 6-8 km under the volcano (40-50/day) registered on seismometers at distances of 8-70 km from the dome; volcanic tremor was continuous. Rock avalanches from the extrusive dome also occurred in mid-September. During 20-24 September, a gas-and-steam plume rose up to 300 m above the crater. Tectonic earthquakes on 21 September (67) and 23 September (17) were centered less than 2 km below the volcano. The level of seismicity had decreased by 24 September, but volcanic tremor remained continuous. By 30 September, more than 20 tectonic earthquakes/day were occurring at depths of less than 1 km. The gas-and-ash plume also increased in the last week of September to a height of 1 km.
During the first week of October, 2-5 tectonic earthquakes/day occurred at depths of less than 1 km beneath the volcano. Seismicity increased slightly during 7-14 October to 3-7 tectonic earthquakes/day at the same depth. Weak volcanic tremor was generally present 7-10 hours/day, although on 12 October tremor occurred for about 18 hours. The gas-and-ash plume rose ~1 km through mid-October, with weak volcanic tremor continuing. From 14-21 October, the gas-and-steam plume reached as high as 1.5 km above the crater; cloud cover prevented observations in late October. During that same period, seismicity increased from 10 to 41 tectonic earthquakes/day at a depth of less than 1 km beneath the volcano, with weak volcanic tremor 24 hours/day. Seismicity remained very high through 26 October, with almost continuous strong tremor recorded. Weak continuous tremor was registered at all seismic stations in the area on 28 October.
After four days of clouds obscuring the volcano, a gas-and-steam plume was observed on 2 November rising 2-3 km above the crater rim. Weak volcanic tremor was continuing 24 hours/day and registering on all of the seismic stations. A steam-and-gas plume rising ~2-2.5 km above the crater rim on 6 November extended ~50 km S. By that time, all the snow had melted off the SE slope of the dome. As of 6 November, continuous volcanic tremor was still being recorded, and the overall level of seismicity was above background.
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG.
Duration of tremor drops; 40-km-long plume persists
During the interval from mid-November to mid-December gas-and-steam plumes rose 0.3-1.5 km above the crater rim; these blew toward the S or SE and remained conspicuous for over 40 km. . . . tremor peaked in the week ending 18 November (21-24 hours/day) and dropped steadily for the subsequent weeks. By the weeks ending on 15 and 22 December, tremor registered for less than 1 hour/day.
For late-November to mid-December, 2-8 earthquakes/day were recorded near the volcano. This level of seismicity is similar to that in the first half of October. The second half of October and some periods in September saw sharp increases in earthquakes to over 40 events/day.
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG.
Tremor and number of shallow earthquakes increase; 40-km-long plume
In December the plume typically rose up to 1 km above the crater, and was mainly composed of gas and steam shed off the extrusive dome. In some cases (for example in late December), it remained conspicuous for over 40 km downwind. In comparison, when visible in early to mid-November, the plume was slightly higher (2-2.5 km), and conspicuous only slightly farther downwind (50 km). These plume observations in early November were coincident with nearly continuous tremor; minor explosions were observed, although a clear eruption was not, possibly due to poor visibility. The strong 22 April eruption was preceded by explosions and clear increases in both tremor and earthquakes.
. . . during the week ending on 3 January, tremor progressively increased; on 3 January it prevailed for 6 hours/day. For the interval 4-12 January tremor durations were in the range of 9-16 hours/day.
For the first half of October, and the interval from late-November to mid-December, 2-8 earthquakes/day were typically recorded near the volcano. Earthquakes in the second half of October, and some periods in September, increased sharply and reached >40 events/day; in early January they varied from 7 to 23 events/day.
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG.
Continued fumarolic activity and plume; variable seismicity
Fumarolic activity from the extrusive dome was observed throughout January and into mid-February. The SE part of the extrusive dome continued to grow in mid-February. The persistent gas-and-steam plume rose 400-1,000 m above the crater rim in January. Weak volcanic tremor was recorded for ~0.3 hours/day in late January, a significant decrease from earlier in the month when tremor was recorded for 7-9 hours/day (18:12). Late January temperatures in Kliuchi, 8 km S, were as low as -40°C.
The height of the gas-and-steam plume above the crater rim was estimated to be 800-2,000 m in the first half of February, but only 400 m at mid-month. Weak volcanic tremor (1-5 hours/day) was recorded in late January to early February, and some shallow volcanic earthquakes (average of 1 event/day) were registered. Weak volcanic tremor increased to 3-5.5 hours/day in the second week of February when 1-2 shallow volcanic earthquakes/day were detected. Seismicity increased the following week to 8-12 hours/day of tremor and 1-3 earthquakes/day.
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG.
Fumarolic activity from extrusive dome continues
Fumarolic activity from the extrusive dome was observed through mid-March. Growth of the SE part of the dome was observed in mid-February. The height of the gas-and-steam plume in late February through mid-March was usually 300-500 m above the crater rim. However, it was as high as 1.5 km in early March. The amount of weak volcanic tremor varied from 3 to 12 hours/day in late February and early March before dropping to 1.5-6 hours/day at mid-month. During this period, shallow volcanic earthquakes registered at rates of 1-5 events/day.
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG.
Gas-and-steam plume persists; avalanches from the extrusive dome
During March a gas-and-steam plume was observed above the extrusive dome. The height of the plume varied from 800 to 2,500 m above the crater rim and extended 40-60 km downwind to the S, SW, and W. Weak volcanic tremor occurred for ~2-4 hours/day, and shallow volcanic earthquakes were registered at a rate of 2-5 events/day. Avalanches from the N part of the dome occurred on 17 March. Fumarolic activity from the extrusive dome was observed during the last week of March. Small explosive events may have occurred on 25 and 31 March based on interpretation of seismic activity. Weak volcanic tremor decreased during the last week of March (0.2-1.5 hours/day), but shallow volcanic earthquakes (1-5 events/day) occurred at a similar rate.
In early April, weak shallow seismic activity (3-8 earthquakes/day) accompanied the continued growth of the extrusive crater dome. Seismicity increased during the second week of April (7-23 events/day), with volcanic tremor registered for 1-3 hours/day. A gas-and-steam plume reached as high as 3 km above the crater rim on 2 April.
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG.
Shallow seismicity and volcanic tremor continue; fumarolic activity
Weak shallow seismicity that accompanies growth of the crater dome and associated small explosions decreased in the second half of April from an average of 21 events/day to 4 events/day. This seismic activity continued through mid-May at a rate of 2-8 weak earthquakes/day. Average duration of volcanic tremor decreased from 4 hours/day in mid-April to less than 1 hour/day in early May. Fumarolic activity was observed on 25 April, and in May consisted of steam-and-gas plumes rising to 300-1,000 m above the extrusive dome. Seismic data indicated a small explosion on 8 May when the volcano was obscured by clouds.
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG.
Brief increases in seismicity, tremor, and fumarolic activity
Weak shallow seismicity and tremor increased during late May and early June. For the week ending 27 May, 4-6 earthquakes/day were registered beneath the volcano and the average duration of volcanic tremor was less than 1 hour/day. By 1 June, the range had increased to 3-11 earthquakes/day with 0.4-1.5 hours of tremor/day; 47 events were registered on 30 May. As of 9 June, weak shallow seismicity had reached a rate of 6-29 events/day and tremor was being registered for 2 hours/day. During 2-25 June, weak shallow seismic activity was fairly consistent at 5-30 events/day, with an average volcanic tremor duration of less than 1-2 hours/day. Seismicity decreased in late June to 1-5 events/day with less than 0.5 hours/day of volcanic tremor. In early July, seismicity decreased to 2-3 events/day; tremor was unchanged.
Weak fumarolic activity generated steam-and-gas plumes 300-400 m above the extrusive dome. This activity increased significantly after a tectonic earthquake at 0530 on 8 June, with a plume rising up to 2 km. The plume rose 1-1.5 km above the extrusive dome from 10 June to 7 July, and originated from two different vents during at least part of this period. On 7 July two gas-and-ash bursts were observed, one at 0955 rising up to 5 km above the crater, and the other at 1550 rising up to 3 km; both clouds drifted NW.
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG.
Normal fumarolic activity and seismicity
Weak shallow seismic activity (1-4 events/day) continued to be registered beneath the volcano throughout July and August. Average duration of volcanic tremor was less than 30 minutes/day. The gas-and-steam plume (up to 500 m above the extrusive dome) observed during 7-14 July was blown E for about 30 km. Clouds frequently prevented observations in July and early August. Normal fumarolic activity was observed above the extrusive dome during mid-August. In late August and early September a gas-and-steam plume was observed up to ~3 km above the extrusive dome. Shallow seismicity remained at normal levels (1-5 events/day) through 12 September, with an average of 0.3 hours of tremor/day.
A strong eruption in April 1993 has been followed by a plume visible during clear weather (18:4-8 & 10-12, and 19:1-4 & 6). Prior to that eruption, the most recent explosive activity was in April 1991 (16:3). The largest historical eruptions from Shiveluch occurred in 1854 and 1964.
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG.
Persistent steam plume and variable seismicity
Seismicity remained at normal levels (1-4 events/day) through the second half of September and early October. A gas-and-steam plume rose ~800 m above the extrusive dome during 18-24 September. Starting on 4 October, daily seismicity rose to 9 events, followed by 21 events the next day and 14 events on 6 October. By 9 October the gas-and-steam plume was rising up to 1,000 m above the crater rim and was directed NE for ~1 km. Seismicity at or near the active dome remained above normal (5-15 events/day), and weak tremor was recorded for ~30 minutes/day during 8-26 October. A gas-and-steam plume rising 1,000-2,500 m above the crater was observed from Kliuchi (8 km S) on 8-15 October. The plume rose 400 m above the crater on the 23rd and 200 m on the 27th; the volcano was obscured by clouds the remainder of the time through 3 November. Seismic activity in late October-early November remained above normal levels, with 7-19 events/day occurring at or near the active dome, and weak volcanic tremor lasting for 24-84 minutes/day.
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG; AVO.
Seismic station closed
[Following notice in early December that seismic stations at Shiveluch and Tolbachik had closed, on 22 December the following message was sent from the Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO): "KVERT [Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team] has informed AVO that, because of a long delay in promised funding from the Ministry of Transportation in Moscow, KVERT must suspend transmittal of information on volcanic activity in Kamchatka. The length of the suspension is unknown at this time.]
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG; T. Miller, AVO.
Low-level fumarolic and seismic activity
Although frequently obscured by weather clouds, low-level fumarolic activity was noticed on 10 November. Seismicity at or near the active dome was above normal in early November (9-16 events/day), with weak tremor (18-36 minutes/day). Seismicity remained above normal on 11 November, with 8 events at the active dome between 10 November and noon the next day; continuous tremor for 2.6 hours was recorded before 1230. Weak fumarolic activity continued on the 12th with a gas-and-steam plume to 1 km above volcano being blown SE. During 12-18 November, 10 shallow earthquakes were recorded near the active dome; weak tremor (0.1 µm) lasted for ~54 minutes on 18th. Seismicity on the 23rd consisted of two shallow earthquakes beneath the active dome. On 24 November, ground observers noted fumarolic activity at the summit dome with a gas-and-steam plume rising 800 m. Weak volcanic tremor on 23 and 24 November had a duration of ~18 minutes each day with a maximum amplitude of 0.1 µm. Other earthquake activity remained slightly above normal. Slight fumarolic activity on 28 November from the summit dome was seen from Kliuchi; weak tremor and six shallow earthquakes were detected. The seismic station closed indefinitely as of December 7. The volcano was obscured by clouds 8-14 December, and no information was available for late December because of the suspension of communications from KVERT.
Information Contacts: V. Kirianov, IVGG; AVO.
Normal seismic activity, but degassing continues
During the period of 26 May-22 July, seismicity remained at normal background levels. Gas and steam plumes were observed above the volcano, rising to heights of 50-300 m above the crater and extending 2-8 km downwind. Regular reports from KVERT (via AVO) resumed in June after funding problems in Russia halted communications in December 1994 (BGVN 19:11).
Information Contacts: Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (URL: https://www.avo.alaska.edu/); Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia.
200-m-tall plumes and normal seismicity
Seismicity remained at normal background levels in late July and August. The usual fumarolic activity was observed, and the plumes rose to 200 m above the crater.
Information Contacts: Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA; Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia.
Normal seismic activity; fumarolic plumes up to 1 km high
Seismicity remained at normal background levels during September, October, and through 10 November. During late November seismic activity increased to above background levels. The usual fumarolic activity was observed, and the plumes rose as high as 1,000 m above the crater.
Information Contacts: Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA; Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia.
Typical fumarolic plumes
On 5-6 December, and on 7 and 14-15 January, the usual fumarolic emissions were observed above the volcano.
Information Contacts: Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA; Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia.
Dome growth; eruption plume rises 4 km above crater
On 8-9 March, dome growth occurred within the active crater. Intermittent ash and gas explosions were also observed and the largest plume rose ~ 4,000 m above the volcano and extended 80 km to the N. During 10- 20 March, steam and gas plumes reached 300-5,000 m above the crater and extended ~15-70 km from the vent. During 21-24 March, activity was limited to fumarole emissions that rose 50-100 m above the volcano.
Information Contacts: Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA; Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia.
Steam and ash plume rises 1.5 km above the crater
On 25 March, a steam-and-ash plume rose ~1,500 m above the volcano and extended 30 km to the NW. During 26-31 March the usual fumarolic activity was observed above the crater. A steam-and-ash plume at 100- 200 m above the crater was also reported during 1-4 April.
Information Contacts: Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA; Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia.
July gas-and-steam plumes to 1.5 km height
On 13 July a steam-and-gas plume rose 100 m above the crater and drifted 5 km W; another rose to 800 m and drifted 10 km SE. One the next day rose up to 1,000 m above the crater and drifted 10 km W. On 15-20 July, more gas-and-steam plumes rose 100-400 m above the crater and drifted 5-10 km to the E and SE. On 21 and 27 July, incandescent gas emissions with temperatures of 200-500°C rose 300-400 m above the extrusive dome inside the crater. Gas explosions rose 1-1.5 km and drifted 15-50 km W-SW. During 22-26 July, gas explosions (on 23 July these included minor ash) sent plumes 700-1,500 m above the crater and moved 20-60 km N and NE.
Information Contacts: Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Normal seismicity and small steam plumes
Seismicity remained normal throughout August and September. Gas and steam plumes to heights of 100-200 m were observed on 5-6 August, 7-9, 16, and 20 September, and 1-2 October. On 27 September a plume rose 300 m above the crater and moved SE.
Information Contacts: Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Normal seismicity and fumarolic activity
Background seismicity prevailed during 13 October-29 December. Normal fumarolic activity was seen during 30 October-2 November and 6-7 November. No fumarolic activity was observed during 10 November-14 December. For the period 15-29 December, Shiveluch was usually obscured by clouds; however, on 22 December, a gas-and-steam plume rising 100 m above the volcano was seen.
Information Contacts: Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk- Kamchatskiy 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Slight increase in seismic activity
Following December activity (BGVN 22:11) only background seismicity was reported at Shiveluch until 13 January when a gas-and-steam plume rose to 300 m and a slight increase in seismicity was reported. This increased level of seismicity continued until the end of January. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to 50 m during 19-21 January and a larger plume was seen on the 25th that rose to 800 m.
Information Contacts: Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Frequent gas-and-steam plumes
During February seismicity remained near or slightly above background level. No volcanic activity was observed during 27 January-1 February. Gas-and-steam plumes rose 50-1,000 m above the volcano on 3, 4, 8, 11-12, 12-14, 17-18, 20, 24, 28 February, and 1 March.
Information Contacts: Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Several gas-and-steam plumes seen during March
Seismicity was about at background level during 2 March-5 April. Gas-and-steam plumes rose 100 m above the volcano on 7 and 13-15 March. On 16-18, 22, and 30-31 March, and 1 and 3 April, gas-and-steam plumes rose 100-500 m above the volcano. Clouds obscured observations of the volcano on several days in early April.
Information Contacts: Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Gas-and-steam plumes throughout April and May
Seismicity was generally at background levels during 5 April-18 May. Some high-frequency volcanic tremor was recorded 22-23 April. High-frequency tremor and shallow earthquakes were recorded in the first week of May. Gas-and-steam plumes rose 50-300 m above the volcano on 9 and 11-19 April. No plume was seen 25 April, but a plume rose 100 m above the summit on 27 April. Clouds obscured observations of the volcano throughout much of late April and most of May. No plume was seen 17 May. Plumes 100-200 m above the summit were seen 21-24 May. During 19-20, and 22-23 May, plumes rising to 700-1000 m moved to the SE 2-5 km from Shiveluch.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA
Satellite imagery detects large ash plume
A report of an ash plume 4 km above sea level extending 35 km from Shiveluch was received by the Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO) via the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) and Anchorage VAAC early on 30 May. AVO analysis of various satellite images determined that the eruption began about 1739 on 29 May. A JMA satellite image taken at 1930 that day showed a small, narrow, well-defined ash plume detached from the vent, extending about 100 km downwind to the SSE. Satellite imagery analysis by AVO on the morning of 30 May showed the Shiveluch area clear with no volcanic activity. There was no ash detected in the area SSE of the volcano where the cloud diffused. Three pilot's reports from flights 9 km above sea level over the Shiveluch area on 30 May confirmed there was no ash cloud remaining in the region.
The ash plume did not act like an energetic, high-level eruption plume but rather a low-level short-lived eruption burst from the volcano. These types of eruption bursts are not uncommon from Shiveluch and are connected with the growing extrusive dome inside the crater. The level-of-concern color code was changed to yellow, but reverted to green on 1 June.
Seismicity was at background levels through most of June. During 11-15 June the system registered increased seismicity and volcanic tremor. On June 15 at 0247 it registered about 2 minutes of explosive activity. It was dark and the volcano was obscured by clouds when this explosive activity took place leaving researchers without visual information; they estimated plume height at 5 km.
On 31 May a gas-and-steam plume without ash rose 2 km above the volcano. During 9-11 June a fumarolic plume rose 100-500 m above the volcano, and during 17-19 a plume rose to 200-800 m. Clouds limited visibility throughout much of May.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova and Vladimir Kirianov, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Series of shallow earthquakes in late July
Seismicity was generally at background levels during 25 July-1 September. On 25 July a fumarolic plume rose 300 m above the summit and extended more than 15 km SE. The following day the plume varied between 200 and 400 m in height and extended 5 km to the SE. During a period of just over 3 hours on 26 July, a series of strong, shallow earthquakes accompanied by volcanic tremor was recorded. Tremor was also recorded on 9 August. On 15 August a plume rising to 250 m extended 5 km E. Clouds obscured the volcano throughout much of the reporting period.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Ash explosions and pyroclastic flow during 3 September
Seismicity remained generally at background levels during 2-28 September. A plume on 2-3 September was seen rising 200 m above the volcano. At 1622 on 3 September, ash explosions produced a cloud that rose 5 km above the summit, and extended 100 km NNE. Pyroclastic flows moving SW were observed at this time. The explosion was also accompanied by a 9-minute series of shallow earthquakes and tremor. The level-of-concern color code remained Green. Observation was restricted by cloud during much of the month.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
A few minor gas-and-steam plumes in October
Seismicity remained generally at background levels during October. During 1, 16, and 23 October plumes were seen rising 200 m above the volcano. On 19 and 24 October, gas-and-steam plumes rose 100 m above the volcano. No plumes were seen on 2, 3, and 9 October. During other days the summit was obscured by cloud. The level-of-concern color code remained green.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Steam-and-gas plumes, tremor episodes
Seismicity was generally at background levels during 1 November-7 December. Clouds obscured the volcano throughout much of the reporting period. On 1, 2, and 6 November steam-and-gas plumes were seen to rise 300 m above the summit before dispersing. High-frequency tremor increased over six hours on both 13 and 15 November. Periods of high-frequency tremor lasted 0.7 hours on 17 November and 3.5 hours on 22 November. Two hours of high-frequency tremor and 3 hours of low-frequency spasmodic tremor were recorded on 2 December. On 5-6 December a plume rose 150 m above the summit.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Low-level seismicity and fumarolic plumes
Seismicity under the volcano was about at background levels from December 1998 through February 1999. On 2 February a M 2 earthquake was located at 23 km depth. Weak volcanic tremor and small earthquakes were registered during the first half of February, and on 21 February a 6-minutes series of shallow earthquakes was detected. The Level of Concern Color Code remained Green.
The volcano was frequently obscured by clouds, making observations only intermittently possible. Fumarolic plumes rising 50-400 m were noted on 10 December, 8, 13-14, and 20 January, 6-7, 13, 16-18, and 22 February. Higher plumes, in the range of 700-800 m above the summit, were observed on 21 and 23 January, and 5 February. On 10 and 15 February fumarolic plumes rose 1,000 m.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Large ash explosions on 3 and 12 April
On 2 April a fumarolic plume rose 800-1,000 m above the crater and extended more than 10 km E. At 1100 on 3 April an ash explosion created a plume that rose 2,000 m above the dome. Coincident with this explosion, a shallow seismic event was registered under the volcano beginning at 1056. The ash cloud dissipated by 1130. That evening and the next day, a gas-and-steam plume rose 600 m above the dome. Fumarolic plumes were observed during most of the following week, including a gas-and-steam plume on 6 April that rose 1,000 m above the dome.
At 1900 on 12 April an ash explosion was observed and a plume rose 1,000 m above the dome. Shallow seismicity under the volcano had started at 1855. Explosions sent ash up to 200 m above the dome every 2-3 minutes during the hour following the initial blast. The ash plume extended 10 km to the E. Satellite imagery taken at 2052 on 12 April showed a 30-km-long, ash-poor, low-altitude plume extending SE. Another satellite image on 13 April, taken at 0750, indicated a possible thermal anomaly at the volcano. A series of shallow seismic events continued to be recorded during 14-15 April. Gas-and-steam plumes were seen on 13, 17-18, and 20 April.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
May-August gas plumes rise less than 1 km above summit
From the period of 24 May to 9 August 1999, seismicity under the volcano generally was about at background levels. Hypocenters clustered under the summit crater. When not obscured by clouds, steam plumes were repeatedly noted. In general, they rose less than 900 m above the volcano and occasionally extended nearly 10 km before dispersing. Observations included a fumarolic plume that rose 300 m above the volcano on 3 June. On 17 June, a gas-and-steam plume rose 100 m above the crater, extending 7 km to the W. On 28-29 June, a gas-and-steam plume rose 800 m above the crater. On 30 June, another gas-and-steam plume rose 200 m above the crater and extended 10 km to the E. On 11 July, a gas-and-steam plume rose 100 m above the crater and extended 5 km to the E. On 3 and 7 August, a gas-and-steam plume rose 350 m above the crater. On 6 August, a gas-and-steam plume rose 200 m above the summit, extending 3 km to the E.
The high, isolated massif of Shiveluch volcano (also spelled Sheveluch) rises above the lowlands NNE of the Kliuchevskaya volcano group. The 1,100 km3 Shiveluch is one of Kamchatka's largest and most active volcanic structures. The summit of roughly 65,000-year-old Strary Shiveluch is truncated by a broad 9-km-wide late-Pleistocene caldera breached to the south. Many lava domes dot its outer flanks. The Molodoy Shiveluch lava dome complex was constructed during the Holocene within the large breached caldera; Holocene lava dome extrusion also took place on the flanks of Strary Shiveluch. At least 60 large eruptions of Shiveluch have occurred during the Holocene, making it the most vigorous andesitic volcano of the Kuril-Kamchatka arc. Widespread tephra layers from these eruptions have provided valuable time markers for dating volcanic events in Kamchatka. Frequent collapses of dome complexes, most recently in 1964, have produced debris avalanches whose deposits cover much of the floor of the breached caldera.
During the 1990s, intermittent explosive eruptions took place at Shiveluch in 1990, 1991, 1992-94, 1997, and 1998, and lava-dome growth occurred in 1993-94 and 1997. The largest historical eruptions from Shiveluch occurred in 1854 and 1964.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Intermittent explosions from the dome; fumarolic plumes
The volcano was frequently obscured by clouds during August-December 1999, but small fumarolic gas-and-steam plumes rising 50-200 m were often observed during clear weather. Higher fumarolic plumes were seen on three days in late November-early December. Four short explosions generated ash-bearing plumes during August-December that were confirmed visually. As many as five additional dome explosions were identified seismically.
On 11 and 13-14 August, fumarolic plumes rose 50-200 m above the crater. On 15 August a 5-minute ash explosion sent a plume to 800 m above the crater. On 17 and 23 August, fumarolic plumes rose 200-600 m; on the 30th a similar plume rose 1,200 m. On 4-5, 12, and 23-25 September, fumarolic plumes rose 50-200 m, extending 5 km E or SE. Similar plumes were seen on 7, 11, 23, and 25-26 October. On the morning of 27 October a short-lived ash explosion was observed, with an accompanying 20-minute burst of seismic activity. According to a Japanese satellite image taken about 3.5 hours later, an ash plume extended NE at an altitude of 6,900 m. Overall seismicity remained about at background levels until the end of October.
Seismicity was above background levels in late October through mid-November, when the hazard status was increased to "Yellow." On the morning of 31 October a 20-minute series of shallow earthquakes and tremor may have been associated with explosions on the dome; however, at daylight only a small fumarolic plume was seen. According to visual reports from Klyuchi town, on the late morning of 1 November a short explosive eruption sent an ash plume to an altitude of 5.5-6.0 km and extended S; an accompanying increase in seismicity occurred. On 2 November a fumarolic plume rose 50 m. On 8 and 10 November, three 20-50-minute-long series of shallow earthquakes and tremor were recorded that may have been associated with dome explosions. On 11 November a fumarolic plume rose 200 m.
A 5-minute-long series of shallow earthquakes and tremor was recorded on the morning of 17 November that may have been associated with an explosion on the dome. On 12, 16, 19, and 22 November fumarolic plumes rose 200 m. On the morning of 24 November a gas-and-ash plume rose 3 km above the crater. Plumes rising 1-2 km above the crater were also observed on the evening of 27 November and the afternoon of 2 December. All three of these larger plumes disappeared within one hour. Smaller fumarolic plumes, to 50-200 m above the crater, were seen again on 26 and 29-30 November, and 1-2, 10, 17, and 20-21 December. On the morning of 27 December a possible gas-and-ash plume was registered.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Intermittent ash explosions from January through March
This report covers the period January-April 2000. As of 28 April 2000, KVERT (Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team) temporarily suspended operations because of a lack of funding. Seismic activity was at or near background level throughout this period. Occasional weak fumarolic activity occurred, accompanied by fumarolic plumes that rose from 50 m to several hundred meters above the volcano and extended to 10 km in various directions. The volcano frequently was obscured by clouds, which prevented both visual and satellite observations. The hazard level was Green throughout most of the period except for a few days in late January and a period in March when seismic events caused the level to be raised to Yellow.
At 0329 on 9 January, seismic data indicated that a short-lived ash explosion may have occurred. An 81-minute-long series of shallow events was recorded. However, no ash plume was seen on the satellite images at 0513. At 0100 on 23 January, and again at 0428 on 26 January, 20-minute episodes of shallow earthquakes and tremor indicated that brief gas-and-ash explosions may have occurred. The hazard level was raised to Yellow. The volcano was obscured by clouds on 23-26 January; however, on the morning of the 27th the volcano was quiet but its W flanks were covered with gray ash, perhaps from dome explosions. The hazard level was returned to Green.
During the first week of February, seismicity under the volcano was mainly at background levels with occasional fumarolic plumes. At 1653 on 7 February, visual sightings from Klyuchi town reported short-lived, explosive eruptions that sent an ash-poor plume to heights of 1,500 m above the dome. An accompanying increase in seismic activity occurred. At 1800 a plume rose 700 m above the dome and extended 5 km to the NW.
On 9 March, there was a possible ash-gas plume and the nature of the seismicity suggested that this plume may have risen 3-4 km above the crater, but the volcano was obscured by clouds. Again during the week ending on 17 March, seismic data suggested a short-lived explosive eruption sending a plume to 3-4 km above the dome. On 11-13 March, shallow earthquakes and volcanic tremor were registered, but the volcano was obscured by clouds the entire week. During 17-23 March, a steam-and-gas plume rose 500-1,000 m above the volcano, spreading up to 10 km to the NE and E. Visual sightings from Klyuchi at 1752 on 17 March revealed that a short-lived explosive eruption sent an ash-poor plume to about 1,000 m above the dome; it drifted 7 km to the W. This event was accompanied by increased seismicity. At 1345 on 18 March, seismic data indicated another short-lived weak explosive eruption. At 0249 on 24 March, in contrast, seismic data indicated a short-lived but vigorous explosive eruption. The hazard level was raised to Yellow during most of this two-week period but was returned to Green after the seismicity returned to background levels, where it remained throughout April.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Short-lived explosive eruptions 30 June-3 July
During June-July 2000 seismicity was generally at background levels with occasional weak fumarolic activity; the hazard level was Green. However at 0447 on 30 June, visual reports indicated a short-lived explosive eruption and an ash-gas plume that rose to about 8 km altitude; in response, the hazard status was raised to Yellow. Similar reports indicated that a short-lived explosive eruption at 1644 on 1 July sent and an ash-gas plume to ~6 km altitude. The mushroom-shaped plume extended to the W and at 2034, satellite imagery showed the arched plume extending 70 km NW. At 1728 on 1 July seismic data indicated a less intensive short-lived explosion, and on 2 July several weak explosions occurred and a gas-steam plume rose 300-700 m extending 3-5 km to the W and E. On 3 July seismicity under the volcano returned to background levels and the hazard status was reduced to Green.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/).
Fumarolic plume, multiple gas-ash explosions, and partial dome collapses
On 29 July, a fumarolic plume rose 100-600 m above the volcano. At the end of July, clouds largely obscured Shiveluch. Low seismic activity occurred during the following week, so the Level of Concern Color Code was Yellow. Seismicity under Shiveluch increased sharply at 0344 on 6 August. Consequently, the hazard status changed to Orange, indicating an eruption or imminent eruption. The volcano itself continued to be concealed by heavy clouds preventing visual observations. Satellite imagery detected no ash or thermal anomaly.
Beginning at 1300 on 6 August, the level of high-frequency volcanic tremor gradually decreased, reaching background levels by 1600. At 1740 seismic data indicated a possible short-lived gas-ash explosion. Based on seismicity, the cloud was estimated to have risen to ~6,000-8,000 m, although this could not be confirmed because the volcano remained obscured by clouds. An increase in tremor level occurred from 2010 to 2120. Seismicity decreased to near background levels, although shallow events continued to occur, and the hazard status was decreased to Yellow. Seismic activity gradually built in the following days as small earthquakes trembled beneath the volcano, but became quiet on 16-17 August.
An increase in seismic activity took place on the morning of 23 August. At 1343, gas-ash explosions rose from Shiveluch to altitudes of 8,000 m and moved to the SE. The following day, gas-ash explosions reached 3,000-4,000 m in altitude, and were accompanied by shallow seismic events. By 25 August, seismicity was close to background levels, and the hazard status was downgraded to Yellow.
A short-lived explosive eruption was observed at 1135 on 29 August sending an ash-rich plume to an estimated altitude of 10 km. The ash cloud drifted SE, and was recorded by geostationary weather-satellite imagery moving E across the Bering Sea. Increased seismicity ensued at 2231-2237 followed by volcanic tremor. Seismicity decreased significantly after this, and denoted the end of this explosion. Since Shiveluch had several short-lived explosive eruptions in the past weeks during partial dome collapses, the hazard status was upgraded to Orange. The status was again downgraded to Yellow at the end of the month, although future unrest seems likely as seismicity continues above background levels.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Thomas Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/).
Low-frequency tremor; gas-and-ash explosions cause ash advisories
Volcanic ash advisory statements were issued to aviators for the 23 and 28 August eruptions at Shiveluch (BGVN 25:08), indicating that aircraft needed to ascend to a higher altitude or to navigate around the potentially dangerous ash clouds. The ash clouds on both dates were carried E or SE from the volcano at speeds of up to 93 km/hour, and drifted up to an altitude of ~10 km.
Volcanic unrest continued throughout September 2000, and a hazard status of Yellow was maintained. At 1417 on 2 September, seismic data indicated a possible short-lived gas-and-ash explosion. Estimates of cloud height based on seismicity suggested that the plume reached ~1,500 m. After this explosion, activity ceased until 6 September, when a fumarolic plume rose 200 m above the volcano.
The volcano remained quiet until 0715 on 13 September when seismic data indicated another gas-and-ash explosion. Following the explosion, strong spasmodic low-frequency tremor was recorded. Visual reports at 0800 from the residents of Kliuchi, 50 km SW of the summit crater, indicated that the ash plume rose 3,000 m above the dome and extended more than 10 km E. By 1000 the plume became ash-poor and decreased in height to 2,000 m. By 1130 the plume had diminished to only 200 m above the dome. Satellite imagery showed the ash cloud extending ~300 km E of Shiveluch by 1242. As a result of this activity, a volcanic ash advisory was issued. At 1530 the summit was obscured, but a fumarolic plume emerged from the E foot of the dome to a height of 100 m. The low-frequency tremor gradually decreased to background level by 1100 on 14 September.
On 17-18 and 20-21 September, gas-and-steam plumes with heights of 200-400 m were observed at the E end of the dome. Seismic activity was close to background levels, with some low-frequency tremor until 0249 on 18 September, when seismic data evidenced another gas-and-ash explosion. Plume height was estimated at ~1,700 m based on seismic data. On September 22-23 and 25-28, gas-and-steam plumes emanated from the E portion of the dome. Seismicity then decreased to background levels.
On 8 and 10 October, gas-and-steam plumes rose 200-400 m from the summit and extended 3-5 km to the east. On 9 October, weak fumarolic activity was observed. Weak continuous volcanic tremor was registered during 5-12 October. A gas-and-ash explosion was indicated by seismicity at 0318 on 10 October; cloud height based on seismic data was ~1,700 m. Intensive spasmodic low-frequency tremor was recorded until about 0400 following the explosive event. On 15 October, weak fumarolic activity was observed. The following day, a gas-and-steam plume rose 250 m above the dome. An episode of strong shallow seismic events during 0512-0532 on 14 October suggested a gas-and-ash explosion with a plume height of 4,200 m. Continuous weak volcanic tremor was recorded from 13-19 October. Shiveluch's hazard status remained at Yellow.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA; Anchorage VAAC (Volcanic Ash Advisory Center), NOAA Alaska Aviation Weather Unit, 6930 Sand Lake Road, Anchorage, AK 99502-1845, USA (URL: http://www.alaska.net/ ~aawu/vaac.html); Tokyo VAAC, Tokyo, Japan (URL: http://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/).
Frequent steam plumes, weak tremor, and possible gas-and-ash explosions
This report covers 20 October-15 November 2000. At the end of October, the hazard status was Yellow. During 22-23 October, seismographs recorded weak continuous tremor and small shallow earthquakes. On 24, 26, and 28 October, shallow seismic events indicated possible explosions. Plume height was estimated at 700-1,200 m above the summit; heights were inferred by correlating previous observed ash-clouds with magnitudes of associated explosions. On 25 October, a gas-and-steam plume rose 200 m above the summit dome. A gas-and-steam plume on the 29th rose 700 m and extended more than 5 km E and NW.
During the first week of November, gas-and-steam plumes ranged from 100 to 300 m above the summit, with one on the 7th rising 1.5 km. Seismicity was at background levels during 10-16 November, although a gas-and-steam plume rose 600 m on 16 November. The hazard status was downgraded to Green the following day. Late on 20 November, however, frequent shallow seismic events suggested that gas-and-ash explosions rose to heights of 3.2 km. Gas-and-steam plumes on 19, 20, 21, and 23 November to respective heights of ~2 km, 1 km, 350 m, and 350 m. By the end of November, little seismicity was registered; only three deep M < 1 earthquakes were recorded. On 24 November, a gas-and-steam plume rose 400 m above the dome and drifted 5 km to the E. At 0935 on 27 November, seismographs detected a strong shallow seismic event.
Shiveluch's hazard status was elevated to Yellow on 1 December. A possible explosion the evening of 6 December was followed by tremor. A similar event the following afternoon produced a cloud estimated from seismic data to have risen 700-1,200 m. Weak seismicity was recorded for most of the second week in December. Possible explosions on 9 and 12 December were again suggested by shallow seismic events. Seismographs recorded tremor for 30 minutes after the 9 December explosion, and for 1 hour after the 12 December event; workers estimated plume heights of 700 m for both. On 13 December a gas-and-steam plume rose 200 m. Shiveluch's extrusive dome and W summit crater wall were observed to be coated with ash, likely from the 12 December explosion.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Hazard status reaches Red; new dome formation during May 2001
At Shiveluch (figures 4, 5, and 6) elevated volcanic activity occurred during 15 December 2000-22 May 2001. The character of the activity had not changed significantly since the previous report (BGVN 25:11). On 15 December 2000 at 2105 seismicity indicated a possible gas-and-ash explosion. On 20 December gas-and-steam plumes rose 200-300 m above the volcano.
Late December 2000: Hazard Status Yellow. The Level of Concern Color Code was raised from Green to Yellow during late December 2000. On 29 December at 0743 seismographs registered shallow earthquakes and a short-lived explosion was inferred to send ash and gas ~2,000-3,000 m above the summit. Gas-and-steam plumes continued to rise through the end of the month.
During 31 December 2000-1 February 2001 similar activity continued, featuring shallow seismicity, small gas-and-ash explosions, and fumarolic emissions. A Yellow hazard status remained in effect. On 2 February at 1100 a powerful gas-and-ash plume rose 800 m above the volcano and extended 3 km W. Visual reports from the nearby community of Kliuchi, 50 km SW of the summit, suggested that another short-lived explosive eruption the same day at 1804 sent an ash plume to a height of 2,000 m; a coeval shallow two-minute-duration event was recorded by seismographs more than 110 km from the volcano. From 1807 to 1825 strong volcanic tremor was registered.
Gas-and-steam plumes that rose up to 1,200 m predominated until 19-20 February when seismographs recorded a series of two-and-four-minute-long shallow earthquakes that may have indicated weak explosions. Two-and-three-minute-long series of shallow earthquakes were recorded on 25 and 27 February, again possibly indicating weak gas-and-ash explosions; minor volcanic tremor followed.
Similar shallow earthquakes and explosions (?) took place during 2-6 March. On 7 March seismic data and visual observations from Kliuchi indicated a 1,500-m-high ash-and-gas plume that extended NW. Ash reports were issued by the Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC). According to information from Elizovo airport (~ 450 km SSW of Shiveluch), at 1620 pilots aboard flight #74052 flying at 8,100 m altitude observed an ash plume ~10 km above Shiveluch that extended 30 km NE. Satellite images processed by the Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO) from 1715 showed bifurcations of the plume. One composed mostly of steam extended E from the volcano at a low altitude while the other stretched 50 km N at an altitude of 7-8 km. Short series of shallow earthquakes and spasmodic volcanic tremor continued to be recorded.
24 April 2001: Hazard Status Orange. Fumarolic emissions, series of seismic events, and inferred explosions occurred through mid-April. The Tokyo VAAC issued an ash advisory to aviators on 6 April. On 22 April seismicity increased sharply. Earthquakes of MBGVN 18:03 and 18:04); KVERT raised the hazard status from Yellow to Orange on 24 April. Cloudy conditions prevented direct observation of Shiveluch's status through 28 April. The energy of individual events increased (up to M ~3.4) through 25 April, and further increased in number and energy the following day. On the morning of 27 April a M ~ 4 event occurred. Beginning on 28 April the quantity and intensity of the events began to decrease slightly. Gas-and-steam plumes were visible up to 700 m above the crater and extended 5 km W. A satellite image processed by AVO taken on 30 April at 0739 showed a four-pixel thermal anomaly at the volcano.
Seismicity began to increase again on 1 May with continued shallow earthquakes and weak spasmodic tremor episodes. A satellite image captured on 2 May at 0652 showed a very weak three-pixel thermal anomaly. By 1757 the following day a satellite image showed a three-to-four-pixel thermal anomaly with two pixels at or near saturation. On 4 May the anomaly had temperatures of 16-25°C against a background of -5-0°C. An ash advisory was issued by the Tokyo VAAC on 6 May.
7 May 2001: New Dome Formation. According to seismicity, eruptive activity initiated on 7 May at 0958 when strong spasmodic volcanic tremor began to occur. Visual reports from Kliuchi at 1015 indicated that a gas-and-ash plume rose ~1,200 m and extended NW; ash fell on the town. AVO satellite imagery showed the plume extending ~40 km WNW by 2026. Small pyroclastic flows were visible on the SW slopes of the dome. On 12 May at 0900 Kliuchi residents observed a new, intensely steaming extrusive dome located between the NW wall of the 1964 eruption crater and the older dome that began forming in 1980 (figure 6). The new dome was ~100 m high with a ~200-m-wide base and a volume of ~107 m3.
On 12 May at 1100 a weak explosion sent a column of ash 1,000 m above the new dome. By 13 May at 2140 Kliuchi observers reported that the dome had grown ~50 m higher. Two days later the height of the new dome had reached that of the old one. No thermal anomalies were observed at Shiveluch on 14-15 May. KVERT decreased the hazard status from Orange to Yellow. A gas-and-steam column rose 400-500 m above the domes on 16 May; weak explosions sent an ash-poor plume to a height of 100-500 m. Satellite images from 17 May at 1710 and 1734 showed a 2-3-pixel thermal anomaly with a temperature of 35°C against a background of ~7.5-11°C. The anomaly likely corresponded to the new growing dome. The Anchorage VAAC issued an ash advisory on 18 May due to a reported short-lived explosive eruption observed from the ground. An ash cloud from the eruption drifted slowly N and dissipated quickly.
19 May 2001: Hazard Status Red. On 19 May at 1756 Shiveluch erupted explosively for about 40 minutes and produced an ash cloud to an altitude of 10 km. The National Weather Service reported the plume moving NE. Short pyroclastic flows and hot avalanches were observed in the dome area. Seismic activity continued, although at a decreased rate, with many earthquakes occurring within the volcano's edifice. The following day KVERT reduced the hazard status to Yellow.
The Anchorage VAAC issued an ash advisory on 20 May at 1500. GOES-10 imagery detected a narrow band of ash at 1400 about 110 km wide moving SE at over 50 km/hour. The ash cloud appeared to be becoming more diffuse with time; the cloud had dissipated by 1800 according to a subsequent ash report.
A large thermal anomaly was detected in satellite images on 20 May from 1802 and 1814. Background temperatures for both images were 15°C. The former image had 10 pixels with temperatures ranging from 30° to 49°C, of which 6 were at or near saturation. The latter image had 8 pixels between 30° and 40°C, of which 5 were at or near saturation. Two explosions at 1925 and 2014 sent ash to altitudes of ~4.7-5.0 km.
On 21 May KVERT again raised the hazard level to Red. At 0713 an explosion caused an ash column to rise 10-12 km. Satellite imagery from AVO captured at 0750 showed a small plume ~15 km long situated above the volcano. A subsequent image from 1032 revealed the plume beginning to move N or NE. Seismic activity remained above background levels.
Shiveluch erupted on 22 May at 0209 and produced a mushroom-shaped ash column to an estimated altitude of ~20 km. The ash cloud moved S-SE toward the Pacific Ocean (figure 7). Residents of Kliuchi observed incandescent illumination from the eruption although the ash column covered all of the volcano edifice. Shiveluch's Level of Concern Color Code remained at Red as of 22 May. More recent information is available on the AVO website and will be covered in future issues of the Bulletin.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller and Dave Schneider, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA; Philip Kyle, Department of Earth & Environmental Science, New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology, Socorro, NM 87801-4796, USA (URL: https://nmtearth.com/); Anchorage Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), NOAA Alaska Aviation Weather Unit, 6930 Sand Lake Road, Anchorage, AK 99502-1845, USA (URL: http://vaac.arh.noaa.gov/); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center, Tokyo, Japan (URL: https://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/).
Eruptions in late June sent plumes to ~8 km altitude
Shiveluch erupted at 0209 on 22 May (BGVN 26:04) and produced a mushroom-shaped ash column to an estimated altitude of ~20 km. According to reports from Klyuchi, the event destroyed both the new dome (first observed on 12 May) and the W part of the old dome. GMS satellite imagery at 1432 on 22 May showed the eruption cloud as it continued to diffuse over the Kliuchevskoi volcanoes; at that time the estimated plume area reached ~50,000 km2. The hazard status remained at Red as of 22 May.
On May 23, an approximately 10-pixel anomaly with temperatures at 30-49°C was observed on satellite images. The anomaly was large and elongated to the S. It may signify a new pyroclastic-flow deposit.
By 24 May the hazard status had been lowered to Orange and, by 31 May, to Yellow. The hazard status was unchanged until 29 June, when a short-lived explosion sent an ash plume to a height of 1,200 m above the dome; associated pyroclastic flows had runouts of ~2.5-3.0 km. During the period from the end of May to the end of June, gas-and-steam plumes were observed rising 500-1,200 m above the dome. Seismic activity remained above background with earthquakes of M 2-3, and many small earthquakes within the edifice. On 8 June a short-lived explosion sent an ash plume 2,000 m above the dome accompanied by 2- and 3-minute-long, shallow seismic events.
During the week of 22-28 June, instruments registered seven M 2 earthquakes, many small earthquakes within the volcano's edifice, local seismic signals (explosions, avalanches, collapses), and episodes of weak spasmodic volcanic tremor. Based on seismicity, a possible increase in eruptive vigor occurred at 1500 on 28 June, a time when tremor and the number of shallow earthquakes increased.
At 1150 on 29 June, the aforementioned short-lived explosion occurred. The hazard status was again raised to Orange. Seismic data recorded on 29 June suggested possible explosion plumes that ascended to ~6 km above the dome (~8.5 km altitude). According to a Tokyo VAAC report, at 0300 on 30 June the ash plume attained 7.3 km altitude.
At 1250 on June 30 another short-lived explosion sent an ash plume to ~8.0 km altitude. The top part of a mushroom-like plume slowly extended to the E. Pyroclastic flows passed 5 km down the Baidarnaya River. Weak volcanic tremor and local seismic signals (avalanches) continued. Starting at 0100 on 2 July, earthquakes occurred in greater number, larger magnitudes, and at greater depth (~5 km). By 6 July the hazard status was returned to Yellow.
Subsequently, seismic activity continued above background levels. A magnitude 2 earthquake accompanied many smaller ones within the edifice, some 3-minute-long shallow seismic events, a variety of local seismic signals, and episodes of weak tremor. In mid-July this spasmodic tremor increased. At 1900 on 14 July it reached velocity-characterized amplitudes of 1.7 x 10-6 m/s; at 2020 that day it reached 2.0 x 10-6 m/s; at 0300 on 16 July it increased to 2.5 x 10-6 m/s and finally, after 2300 on July 15, it attained 4.0 x 10-6 m/s. Accordingly, the hazard status was set to Orange and visual observations from Klyuchi at 2100 on 15 July indicated that a gas plume rose 1,500 m above the dome. Seismic data suggested the plume was accompanied by explosions.
An AVHRR image (number 12.01196.05:03) at 1803 on 15 July revealed a 3-pixel thermal anomaly near the SW flank of Shiveluch. The maximum band-3 temperature was 44°C within a background near 22°C. No associated ash was observed in the imagery.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA; Anchorage Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), NOAA Alaska Aviation Weather Unit, 6930 Sand Lake Road, Anchorage, AK 99502-1845, USA (URL: http://vaac.arh.noaa.gov/); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center, Tokyo, Japan (URL: http://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/).
Eruption on 15 July, pyroclastic flows and explosion on 23 August 2001
During 14-16 July 2001, spasmodic volcanic tremor increased several times. On 15 July at 1803 a three-pixel anomaly was visible on AVHRR satellite imagery near the SW flank of the volcano and at 2100 a gas-and-steam plume was observed rising to 1.5 km above the dome. A moderate-sized eruption took place on 19 July at 1033. KVERT raised the level of concern from Yellow (volcano is restless; eruption may occur) to Orange (volcano is in eruption or eruption may occur at any time). The eruption produced an ash plume that rose 3 km above the lava dome.
After the eruption through 15 August, seismic activity remained above background levels, with many small earthquakes occurring within the volcano's edifice and many different seismic signals (explosion, avalanche, collapse) recorded locally. Gas-and-steam plumes rose from the summit level to ~2 km above the dome. One- to three-pixel anomalies were occasionally visible on AVHRR imagery near the SW flank of the volcano. The level of continuous spasmodic volcanic tremor increased on 28 and 30 July. On the night of 1 August ash fell in the town of Klyuchi, 46 km S of the volcano. On 11 August several thermal anomalies were recorded on satellite imagery, as well as a gas-and-steam plume that extended 75 km SE. On 15 August volcanic tremor decreased gradually to background levels, but increased again soon after. Pyroclastic flows traveled down the flanks of the volcano following an explosion on 23 August. The volcano remained at concern level Orange throughout August.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT); Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA; Anchorage Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), NOAA Alaska Aviation Weather Unit, 6930 Sand Lake Road, Anchorage, AK 99502-1845, USA (URL: http://vaac.arh.noaa.gov/); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center, Tokyo, Japan (URL: http://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/).
Through January 2002, elevated seismicity, and an unstable, growing lava dome
In mid-July 2001, the level of concern for Shiveluch was raised from Yellow to Orange (BGVN 26:08) and remained at that level until the end of November 2001 when it was returned to Yellow. During a very active period, 30 September through 1 October, the level of concern was set to Red. The level of concern remained at Yellow through early January 2002, rising briefly to Orange in mid-January and returning to Yellow at the end of the report period, 25 January 2002.
During mid-July through at least 25 January 2002, seismicity was above background levels. The lava dome, now with a summit at ~2,500 m, continued to grow. Typical activities throughout the period included explosions, some producing pyroclastic flows, ash and/or gas-and-steam plumes typically rising 1-2 km (3,500-4,500 m altitude) above the dome, and localized ash falls. Plumes drifted in various directions depending upon local wind conditions and extended from several to as much as 80 km from the volcano. As many as 60 or more earthquakes over M 1.7 (including some over M 2.0) occurred weekly, with many other weak, shallow earthquakes occurring within the volcano's edifice. Other local, shallow seismic events (possible collapses, avalanches, weak gas-ash explosions), and episodes of weak, volcanic tremor also were registered. In mid-January the earthquake rate decreased but the energy of individual events increased (maximum magnitude, 2.7).
The AVHRR satellite images of the active dome area showed thermal anomalies almost daily throughout the period. Anomalies ranged from 1 to 10 pixels in size with maximum temperatures from a few degrees C to 49°C on numerous occasions. Background temperatures typically ranged from -14 to -29° C.
Activities from the end of August to late-January 2002 include visual reports on 4 September of a gas-and-steam plume rising 1,200 m above the dome and extending 10 km E, and a pyroclastic flow ~1 km long later that day. On 11 September, several hot avalanches from the summit of the dome were observed. An explosive eruption began at 1323 on 30 September and, at 2010, another explosion sent an ash plume 9,000 m above the dome. A small circular cloud ~25 km in diameter located directly over the volcano was reported later. On 1 October, ash plumes were observed to be as high as 7,500 m above the dome with localized ashfall thicknesses in the millimeter range. This eruption was the beginning of a very active period that extended into the first week of October, e.g., eleven M 2 and nine M 1.7 earthquakes were registered during 1-4 October. On 19 November a 10-pixel thermal anomaly was observed with temperatures ranging from 0 to 49°C. A steam plume observed on 7 January extended ~100 km SE. On 14 January, continuous rock avalanches were reported by observers in Klyuchi town. Gas-and-steam plumes that week rose 1,000-1,500 m above the dome and extended 10 km SE. Seismicity decreased during 19-25 January compared to the previous week. Several gas-and-steam plumes were observed, one extending 75 km to the SE on 21 January. Thermal anomalies continued but no ash was detected in any image.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Growing dome, greater seismicity, and plumes to 10 km in early 2002
During late January to early April 2002, seismic activity at Shiveluch remained above background levels and the lava dome in the active crater continued to grow. Explosions, avalanches, pyroclastic flows, and plumes from combinations of steam, gas, and ash, all occurred without warning and rose as high as 7-10 km altitude. Many shallow earthquakes (ML less than or equal to 2.5) occurred within the volcano's edifice along with other shallow seismic events. The Alert Level was raised from Yellow to Orange during a period of increased activity, 12 February-mid-March. Then the Level was returned to Yellow.
Typical activities from the end of January through the first half of February 2002 included weak seismic events and short-lived explosions, which sent ash-gas plumes to heights of 0.8-1.0 km above the ~2.5 km-high dome (reaching 3.3-3.5 km altitude). Occasional explosions sent plumes to higher altitudes; on 25 January a plume rose to ~4.5 km altitude, while an explosive eruption on 1 February sent ash-gas plumes to heights over 5.0 km.
For the latter eruption, Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) satellite images show thermal anomalies up to 10 pixels. Many of these "hot" pixels were at the detector saturation level of 48°C, and appeared against typical background temperatures as low as -25°C. A satellite image on 2 February revealed a 40-pixel thermal anomaly; however, only 5-7 of the pixels had temperatures above 40°C, indicating that only those pixels were influenced by hot material on the ground. The other pixels with elevated temperatures were associated with a cloud caused by hot avalanches.
On the evening of 12 February, the character of the seismicity changed suggesting the occurrence of more intense gas-ash explosions. During the next 30 days, explosions occurred frequently, producing ash-and-gas plumes that rose over 1 km above the dome and occasionally over 3 km above it. On 22 February, a series of shallow seismic events registered for ~1 hour, possibly related to ash-gas explosions or a hot rock avalanche. A similar series was recorded on the night of 27 February, and the next morning observers from Klyuchi town (46 km S) reported a 2-km-long pyroclastic flow to the SE of the dome.
AVHRR images of the resulting plumes showed that some extended to distances of 100 km in various directions, depending upon local wind conditions. A satellite image on 21 February showed a circular ash cloud, 20 km in diameter, at an altitude of ~7.1 km. By 15 March seismic activity declined but remained above background levels. Short-lived explosions continued to send plumes as high as 7.5 km altitude during the last week of March.
Thermal anomalies and pixel size on AVHRR imagery. Dave Schneider (USGS, AVO) provided an explanation of relevant aspects of pixel size and thermal anomalies. The size of a "raw" AVHRR pixel varies across and along the scan of the sensor. The instrument scans from side to side as the satellite moves in orbit. Along the nadir (the line directly beneath the satellite sensor), the pixel size is ~1.1 km on a side. At the far extreme of the scan (55° from nadir) the pixel size increases to 2.4 x 6.5 km. The raw image looks very distorted due to this change in pixel size, so the raw data are resampled to a resolution of 1 x 1 km when processing the data for display. This resampling can generate artifacts, including duplicate "hot" pixels. Analysts usually recognize and account for this problem, and then accurately report the appropriate number of hot pixels.
Another complication is the cause and significance of hot pixels. An AVHRR pixel will begin to appear anomalously warm, compared to its neighbors, when very hot material (hundred's of degrees) occupy a very small percentage of the total pixel area (much less that 1%). So, when a report mentions four hot pixels, and the pixel is 1 km square, one might be tempted to interpret this as 4 km2 of hot material. However, this is not correct. Typically, only a very small portion of a pixel area is hot, but sufficiently hot to reach the pixel's saturation value of ~50°C. The numbers of hot pixels are not all that relevant in an absolute sense. In a relative sense, however, the number of hot pixels can be important, for example, during episodes where we have seen anomalies grow from 1-4 hot pixels and then reach 10-20 hot pixels after an eruption.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller and Dave Schneider, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Growing lava dome, seismicity, and 3-km ash-and-gas plumes through mid-June
During April through mid-June 2002, mild eruptive activity continued at Shiveluch. A lava dome continued to grow in the active crater, gas-and-steam and ash-and-gas emissions occurred, and seismicity remained above background levels. Plumes reached up to 3 km above the lava dome (table 1). Earthquakes reached magnitudes up to 2.4 at depths of 0-10 km. Many other local shallow seismic signals occurred that possibly indicated weak gas-ash explosions and avalanches. Episodes of weak spasmodic volcanic tremor were also registered. Thermal anomalies were visible on AVHRR satellite imagery throughout the report period (table 2). No ash was detected in any image.
Table 1. Plumes reported at Shiveluch during 30 March through 14 June 2002. Courtesy KVERT.
| Date | Time | Plume type | Height above dome | Comment on plume |
| 30 Mar 2002 | 2042 | ash and gas | 1.5 km | -- |
| 31 Mar 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 300-700 m | -- |
| 31 Mar 2002 | 1310 | ash | -- | view obscured by clouds |
| 02 Apr 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 300-700 m | -- |
| 10 Apr 2002 | 0900 | ash and gas | 1 km | -- |
| 15 Apr 2002 | 1906 | ash and gas | 1 km | -- |
| 19 Apr 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 1.0-1.5 km | -- |
| 20 Apr 2002 | ~1240 | ash clouds | 800 m | -- |
| 21 Apr 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 1.0-1.5 km | -- |
| 21 Apr-23 Apr 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 200-500 m | -- |
| 25 Apr 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 200-500 m | -- |
| 26 Apr 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 100 m | -- |
| 29 Apr 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 800 m | extended 10 km E |
| 30 Apr-01 May 2002 | -- | gas | 200-600 m | -- |
| 01 May 2002 | morning | transparent gray, dark blue | -- | extended 40 km S |
| 01 May 2002 | evening | transparent gray, dark blue | -- | extended 5 km NW |
| 05 May 2002 | 0800 | gas; transparent gray-blue | 100 m; 5 km SE | -- |
| 05 May 2002 | 0945 | ash and gas | 1.5 km | -- |
| 05 May 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 200-800 m | -- |
| 08 May-09 May 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 200-800 m | -- |
| 08 May 2002 | -- | gas, steam, and ash | 200-800 m | -- |
| 10 May 2002 | -- | gas, steam, and ash | 300-500 m | -- |
| 11 May 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 1.0-1.6 km | -- |
| 12 May 2002 | morning | gas, little ash | 50 m | -- |
| 13 May-15 May 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 1.0-1.6 km | -- |
| 16 May 2002 | -- | gas, steam, and ash | 300-500 m | -- |
| 17 May 2002 | 2100 | gas and steam, little ash | 800 m | extended 10 km SE |
| 21 May 2002 | 1707 | ash and gas | 800 m | -- |
| 21 May 2002 | evening | gas and steam, possible little ash | 600-800 m | -- |
| 23 May 2002 | evening | gas and steam, possible little ash | 600-800 m | -- |
| 24 May 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 1.2-1.5 km | extended 5 km W |
| 25 May 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 300 m | -- |
| 27 May 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 1.2-1.5 km | extended 5 km W |
| 31 May 2002 | evening | gas and steam | 1.3 km | extended 5 km E |
| 31 May 2002 | -- | steam | -- | extended 50 km SW |
| 31 May 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 900-2,500 m | extended 5 km E |
| 01 Jun 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 200 m | -- |
| 01 Jun 2002 | 1616 | ash and gas | 3 km | -- |
| 01 Jun 2002 | -- | small gas and steam | 1.3 km | -- |
| 03 Jun 2002 | -- | gas and steam | 900-2,500 m | extended 5 km E |
| 02 Jun-07 Jun 2002 | -- | ash and gas | 0.7-1 km | -- |
| 02 Jun-07 Jun 2002 | -- | gas | 2.5 km | -- |
| 07 Jun-14 Jun 2002 | -- | ash and gas | ~1 km | -- |
Table 2. Thermal anomalies visible in AVHRR satellite imagery at Shiveluch during 30 March through 13 June. On some days, clouds obscured the view. Courtesy KVERT.
| Date | Number of pixels | Maximum band-3 temperature | Background | Comment |
| 30 Mar 2002 | 5 | 20°C | -15 to -20°C | -- |
| 31 Mar-02 Apr 2002 | -- | -- | -- | Weak thermal anomalies visible through cloud cover. |
| 19 Apr 2002 | -- | -- | -- | Thermal anomalies visible. |
| 22 Apr-23 Apr 2002 | -- | -- | -- | Thermal anomalies visible. |
| 23 Apr 2002 | 6 | 49°C | -5 to -10°C | Three pixels at max. band-3 temp. (near saturation). |
| 30 Apr 2002 | 1-4 | 49°C | 5 to -10°C | -- |
| 01 May 2002 | -- | -- | -- | Small possible steam/aerosol cloud visible over the summit. |
| 02 May 2002 | 1-4 | 49°C | 5 to -10°C | -- |
| 04 May 2002 | 2 | 35.4°C | -4°C | -- |
| 04 May 2002 | -- | -- | -- | Possible steam/aerosol plume visible extending ~100 km S. |
| 05 May 2002 | 2 | 23.4°C | -6°C | -- |
| 17 May 2002 | 2-6 | 24°C | -4 to 5°C | -- |
| 19 May 2002 | 3-4 | 33-38°C | 3-7°C | Gas-and-steam plume visible extending 50 km to the SW. |
| 23 May 2002 | 3-4 | 33-38°C | 3-7°C | Gas-and-steam plume visible extending 50 km to the SW. |
| 28 May 2002 | 2 | 29.5°C | -- | -- |
| 31 May 2002 | 4 | 49.5°C | -3°C | Steam plume visible extending 50 km to the SW. |
| 31 May 2002 | 5-9 | ~49°C | -5 to 4°C | -- |
| 01 Jun 2002 | 9 | 47-49°C | 0-5°C | "Sensor" recovery pixel also observed. |
| 01 Jun-04 Jun 2002 | 5-9 | ~49°C | -5 to 4°C | -- |
| 09 Jun 2002 | 6 | ~49°C | ~0°C | -- |
| 13 Jun 2002 | 6 | ~49°C | ~0°C | -- |
At 1238 on 20 April a 15-minute-long series of shallow events was registered, and at 1240 an increase in eruptive activity was noticed from Klyuchi town (46 km S). Ash clouds rose 800 m along the entire dome. At the same time, a pilot reported an ash cloud 600 m wide and 800 m high above the dome. The character of the ash cloud, as well as photos and visual observations from Klyuchi town suggested that a rockfall had occurred at the dome.
Continuous volcanic tremor was recorded beginning on 3 May. On 5 May a short-lived eruption at 0945 produced an ash-and-gas plume that rose 1.5 km above the lava dome and was accompanied by a 4-minute-long shallow seismic event. At 0050 on 14 May incandescence was observed at the dome summit from Klyuchi town. During the afternoons of 13, 14, and 15 May the nearest seismic station registered high-frequency seismic signals for 14, 11, and 7 hours, respectively. KVERT suggested that the signals were caused by intense snow thawing and running water near the station, masking the volcanic seismicity.
At 2100 on 17 May a gas-and-steam plume containing a small amount of ash rose 800 m above the dome and extended 10 km to the SE; and at 2320 incandescence at the dome summit was observed from Klyuchi town. At 1707 on 21 May a short-lived explosive eruption sent an ash-gas plume to heights of 800 m above the dome. An accompanying 5-minute-long shallow seismic event was registered.
At 1530 on 31 May a large earthquake (ML 3.1) occurred. At 1616 on 1 June eruptive activity increased. Short-lived explosive eruptions sent an ash-gas plume to heights of 3.0 km above the dome, visible from Klyuchi town at 1616 and 1628. Two ~3-minute-long shallow seismic events were registered at 1615 and 1626. During the week, several short-lived explosive eruptions per day sent ash-gas plumes to heights of 700-1000 m above the dome. On 1 and 2 June two 11- and 100-minute-long episodes of strong high-frequency volcanic tremor were registered. The Concern Color Code was increased from Yellow ("volcano is restless") to Orange ("volcano is in eruption or eruption may occur at any time").
Shallow seismic events 4-5 minutes long registered during early June, and there were 1-3 short-lived explosive eruptions per day that probably sent ash-gas plumes to heights of ~1.0 km above the dome. Seismic data did not reveal any strong explosions. As of 14 June the Concern Color Code was returned to Yellow.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller and Dave Schneider, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA, b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Growing lava dome, seismicity, and plumes up to 7 km high
Last discussed through May 2002 (BGVN 27:05), Shiveluch went on to display mostly mild eruptive activity, punctuated by occasional larger outbursts, during the interval from mid-June through early October 2002. During this reporting period, a lava dome continued to grow in the active crater, both ash-bearing and dominantly gas emissions occurred, and seismicity remained above background levels. Plumes reached up to 7 km above the lava dome (table 3). Earthquakes reached up to M 2.7 at depths of 0-10 km. Other local shallow seismic signals occurred that indicated possible weak gas-and-ash explosions and avalanches. Episodes of weak spasmodic tremor were registered. Thermal anomalies were visible on AVHRR satellite imagery throughout the report period (table 4) but no ash was detected in any image.
Table 3. Plumes reported at Shiveluch during 14 June-11 October 2002. All visual observations and recordings were made from Klyuchi town. Cloudy weather prevented observations on some days. Courtesy KVERT.
| Date | Plume type | Height above dome | Comment |
| 15 Jun 2002 | Ash and gas | ~1000 m | Shallow seismic events registered; no strong explosions |
| 16 Jun 2002 | Gas and steam | 300 m | -- |
| 19 Jun 2002 | Ash and gas | ~1500 m | Shallow seismic events registered; no strong explosions |
| 20 Jun 2002 | Gas and steam | 100 m | -- |
| 20 Jun 2002 | Gas and steam | 900 m | Extended 10 km to the SW |
| 22-24, 26-27 Jun 2002 | Gas and steam | 1000-3000 m | Extended 10 km to the SW on 22-23, 26-27 June |
| 30 Jun-02 Jul 2002 | Gas and steam | 800-2000 m | Extended 10 km to the E |
| 06, 08-10 Jul 2002 | Ash and gas | ~1000-1500 m | One to three explosions per day accompanied by rock avalanches/pyroclastic flows (recorded on video) |
| 06-10 Jul 2002 | Gas and steam | 200-1500 m | Extended 10 km to the E on 7-9 July |
| 12-13, 16 Jul 2002 | Gas and steam | 1500-2000 m | -- |
| 13 Jul 2002 | Ash-poor | ~1000 m | Short-lived explosions (recorded on video) |
| 19 Jul 2002 | Gas and steam | 50 m | -- |
| 19-20 Jul 2002 | Gas and steam | 400-500 m | -- |
| 22 Jul 2002 | Likely ash-rich | ~7 km | Small, circular (~10 km in diameter), appeared to be centered over summit; no strong explosive event identified; no ash reported |
| 23-25 Jul 2002 | Steam/aerosol | -- | Possibly a little fine ash; observed in satellite images |
| 24-25 and early 26 Jul 2002 | Gas and steam | 1500 m | Extended 10 km to the SSE, SSW, and SW; visual observation revealed no ash plumes |
| 30 Jul 2002 | -- | ~3000 m | Visual observation; accompanied by short-lived explosion; possible small amount of ash |
| 26-27 Jul 2002 | Gas and steam | 1500 m | Extended 10 km to the SE on 28 July |
| 27 Jul 2002 | Ash and gas | 1500 m | Short-lived explosive eruption |
| 28 Jul 2002 | Gas and steam | 200 m | -- |
| 29 Jul 2002 | Ash and gas | ~3000 m | Short-lived explosive eruption; possible small amount of ash observed above low clouds |
| 06-07 Aug 2002 | Ash and steam | 1500-3000 m | Four short-lived explosive eruptions sent ash-poor plumes to 1500-3000 m above dome (recorded on video) |
| 14 Aug 2002 | Gas and steam | 1500 m | -- |
| 15 Aug 2002 | Ash and gas | ~2000 m | -- |
| 16-17 Aug 2002 | Gas and steam | 300-400 m | -- |
| 17 Aug 2002 | Ash and gas | ~1000 m | Short-lived explosion observed |
| 18, 22 Aug 2002 | Gas and steam | 1200-4000 m | Extended 10 km to the W and SW on 17-18, 22 August |
| 23, 28 Aug 2002 | Gas and steam | 1000-1500 m | -- |
| 25 Aug 2002 | Gas and steam | 200 m | -- |
| 25 Aug 2002 | Ash and gas | ~1500 m | Short-lived explosion |
| 31 Aug 2002 | Gas and steam | 100 m | -- |
| 03 Sep 2002 | Gas and steam | 400 m | -- |
| 05 Sep 2002 | Ash and gas | ~2000 m | Short-lived explosion |
| 08 Sep 2002 | Ash and gas | ~1500-~2000 m | Short-lived explosions; plumes extended to the E |
| 08-09 Sep 2002 | Gas and steam | 300-1500 m | -- |
| 09 Sep 2002 | Ash and gas | ~1000-~3500 m | Short lived explosions |
| 11 Sep 2002 | Ash and gas | ~1500 m | Short-lived explosions |
| 15 Sep 2002 | Ash and gas | ~1000 m | Short-lived explosions |
| 16-17 Sep 2002 | Gas and steam | 100 m | -- |
| 17 Sep 2002 | Ash and gas | ~3000 m | Short-lived explosion |
| 17-18 Sep 2002 | Ash and gas | ~2000 m | -- |
| 24 Sep 2002 | Gas and steam | ~5000 m | Short-lived explosions |
| 26 Sep 2002 | Ash and gas | 100-700 m | -- |
| 06 Oct 2002 | Ash and gas | ~1000 m | At 2100 a glow from hot lava was observed at the dome area (recorded on video) |
Table 4. Thermal anomalies recognized in AVHRR satellite imagery at Shiveluch during 14 June-11 October 2002. On some days, clouds obscured the view or there were no passes over the volcano. Unless noted, all images came from the AVHRR satellite. Courtesy KVERT.
| Date | Number of pixels | Max band-3 temp. (°C) | Background (°C) | Comment |
| 15 Jun 2002 | 4 | -- | -- | Faint plumes to SE for 53-130 km observed 15-16 June; no ash detected |
| 16 Jun 2002 | 4 | 49.5 | 0 | Most intense 15-20 June; no ash detected |
| 20 Jun 2002 | 4 | -- | -- | -- |
| 22-26 Jun 2002 | 2-5 | 38-43 | 0 to 17 | Steam plumes trailed 40-75 km observed 22, 25, 27 June (no direction given); no ash detected |
| 29 Jun; 01, 04 Jul 2002 | 1-4 | 1-2 pixels at 49 | -5 to 26 | No ash detected |
| 06-11 Jul 2002 | 1-4 | 2 pixels at 49 | 1 to 10 | Plumes extended 30-200 km to the E observed 8-9 July; no ash detected |
| 13, 16 Jul 2002 | 5-7 | 36.9-45 | 5 to 10 | No ash detected |
| 19-20, 24-early 26 Jul 2002 | 1-7 | 18.5-49.5 | -5 to 22 | No ash detected |
| 26, 28 Jul; 01 Aug 2002 | 1-4 | 38-49 | 5 to 10 | On 28 July and 1 August small steam plumes extended to the sincerely and 35 km to the NW, respectively |
| 06-07 Aug 2002 | 5 | 20-21 | 0 to 4 | Small steam plumes extended 30 km to the SW and 55 km to the NW (observed in satellite images); no ash detected |
| 10, 12-13, 15 Aug 2002 | 1-4 | ~30 | -- | No ash or steam-and-gas plumes detected |
| 16-17, 19, 22 Aug 2002 | Two 6 | 46-49 | -- | On 22 August at 0718 a steam-and-gas plume extended 35 km to the SW |
| 23-24, 28 Aug 2002 | 2-4 | 20-44 | -- | -- |
| 29 Aug 2002 | 5 | 2 pixels at 49.44 | ~15 | Steam-and-gas plume extended ~68 km to the SW; no ash detected |
| 30-31 Aug 2002 | 1-5 | 37-39 | ~3 morning | No ash detected |
| 02-04 Sep 2002 | -- | -- | ~15 afternoon | -- |
| 08, 09, 12, 13 Sep 2002 | 2-5 | 2.8-36.5 | ~-18 to 0 | No ash detected |
| 14-17 Sep 2002 | 2-6 | 39.64-49.5 | ~-3 to 20 | On 16 September a small plume extended ~34 km to the SE; on 17 September a plume extended ~127 km to the ESE; no ash detected |
| 21, 24, 25 Sep 2002 | 3-4 | -- | -- | No ash detected (NOAA12 and NOAA16 satellite images) |
| 24 Sep 2002 | 1-4 | 18-44.8 | ~-10 | No ash detected |
| 27, 30 Sep; 01-03 Oct 2002 | 2-4 | -- | -- | On 2 October a steam-and-gas plume extended 80 km to the SE (NOAA12 and NOAA16 satellite images) |
| 02 Oct 2002 | 2-3 | 40.46 to 45-48 | ~-10 to -3 | Faint plume extended 15 km to the SE; no ash detected |
| 05-07 Oct 2002 | 2-8 | 36.81-49.35 | ?14 to 0 | On 6 October a plume extended 111 km to the SE; no ash detected |
The Level of Concern Code was Yellow ("volcano is restless") throughout the reporting period, except for a few days starting 30 July and again early in August when Code Orange ("volcano is in eruption or eruption may occur at any time") was declared.
Summary of recent activity. Except when the summit was obscured by clouds, ash-and-gas or gas-and-steam plumes were seen visually almost daily (table 3). These plumes, frequently accompanied by short-lived explosions and avalanches, typically rose 1-3 km above the summit with occasional plumes rising as high as 7-10 km.
Similarly, satellite imagery (principally AVHRR) reported significant thermal anomalies on an almost daily basis with an extent of several (1-6) pixels, reaching maximum, band-3 temperatures of 20-49°C and frequently associated with steam or aerosol plumes, some extending over 100 km from the volcano.
From mid-June to late-July, numerous earthquakes were recorded, typically M 1.7 to 2.4 and several reaching M 2.7. At 2000 on 29 July, four earthquakes (M 2.1-2.3) occurred and the intensity of volcanic tremor increased noticeably in comparison with the previous days. The following day (30 July), the Level of Concern was raised from Yellow to Orange, but it returned to Yellow when the tremor amplitude decreased over the following two days. However, the activity level increased again during subsequent days and the level was raised again to Orange.
During 12-16 August, about 10 earthquakes of magnitude 1.7-2.4 occurred. Along with smaller earthquakes and many other local seismic signals, these probably indicated ash and gas explosions (at a rate of 1-3 a day, to heights of 1500-2500 m above the dome). However, the Level of Concern was returned to Yellow by the end of the week.
Through the remainder of the period, many earthquakes up to M 2.7 occurred, frequent gas-and-steam plumes rose as high as 5 km above the dome, and thermal anomalies of 6-8 pixels were observed as were gas/steam plumes that extended 80-120 km. On 25 September, continuous spasmodic tremor prevailed for 27 minutes.
Information Contacts: Olga Chubarova, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Tom Miller and Dave Schneider, Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA, b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/).
Continued lava dome growth, short-lived explosions, and seismicity
During mid-September 2002 through February 2003 at Shiveluch, a lava dome continued to grow in the active crater. Short-lived explosions generally sent gas-steam plumes tens of meters to ~3 km above the dome. Seismicity remained above background levels. Earthquakes with magnitudes of ~2-2.7, as well as many smaller ones, occurred at depths of 0-6 km (table 5). Thermal anomalies were visible on satellite imagery (table 6). Intermittent spasmodic tremor with amplitudes of 0.3-1.3 x 106 mps occurred throughout the report period.
Table 5. Earthquakes, explosions, and plumes at Shiveluch during 26 September 2002 through February 2003. Courtesy KVERT.
| Date | Earthquakes | Magnitude | Explosions | Plume height above dome |
| 26 Sep-04 Oct 2002 | 11 | 2-2.7 | 38 | 1-2.5 km |
| 04 Oct-11 Oct 2002 | 7 | 2-2.4 | 16 | 1-2 km |
| 11 Oct-18 Oct 2002 | 4 | 2-2.2 | 13 | 1-2.5 km |
| 18 Oct-25 Oct 2002 | -- | -- | 10 | 1.0 km |
| 25 Oct-01 Nov 2002 | -- | -- | 8 | 2 km |
| 01 Nov-08 Nov 2002 | -- | -- | 7 | 2-3 km |
| 11 Nov 2002 | 6 | 2.0-2.4 | -- | -- |
| 11 Nov-14 Nov 2002 | 5 | 2.0-2.4 | 7 | 2-3 km |
| 14 Nov-20 Nov 2002 | 6 | 2.0 | 19 | 2-3 km |
| 22 Nov-29 Nov 2002 | 2 | 1.9 | 8 | 1-2 km |
| 29 Nov-06 Dec 2002 | -- | -- | 9 | 1-2 km |
| 06 Dec-13 Dec 2002 | 3 | 1.7-2.3 | 8 | 1-2 km |
| 13 Dec-20 Dec 2002 | 1 | 1.8 | 7 | 1-2 km |
| 20 Dec-27 Dec 2002 | -- | -- | 6 | 2-3 km |
| 27 Dec-03 Jan 2003 | -- | -- | 25 | 2 km |
| 03 Jan-10 Jan 2003 | -- | -- | 11 | 1.5 km |
| 10 Jan-17 Jan 2003 | -- | -- | 12 | 2 km |
| 17 Jan-24 Jan 2003 | -- | -- | 11 | 2 km |
| 31 Jan-07 Feb 2003 | 6 | 1.6-2.5 | -- | 1.5 km |
| 07 Feb-14 Feb 2003 | -- | -- | 10 | 1.0 km |
| 14 Feb-21 Feb 2003 | -- | -- | 17 | 1.5 km |
| 21 Feb-28 Feb 2003 | 1 | 2.1 | 14 | 3.0 km |
Table 6. Plumes at Shiveluch visible on satellite imagery during October 2002 through February 2003. Courtesy KVERT.
| Date | Number of pixels | Max band-3 temp. (°C) | Background (°C) | Comment |
| 02 Oct 2002 | 2-3 | 40.46-45.48 | ~-10 to -3 | A 15 km faint plume extended to the SE |
| 27 and 30 Sep, 01-03 Oct 2002 | 2-4 | -- | -- | On 2 October, an 80-km plume extending to the SE was observed in a NOAA16 image |
| 05 Oct-07 Oct 2002 | 2-8 | 36.81-49.35 | ?-14-0 | On 6 October, a 111-km plume extended to the SE |
| 09 Oct-10 Oct 2002 | 2-8 | -- | -- | -- |
| 11 Oct-13 Oct 2002 | 2 | 15-49 | -19 to -6 | -- |
| 12 Oct-14 Oct 2002 | 2-3 | -- | -- | -- |
| 21-22, 24-25 Oct 2002 | 1-8 | 33-49 | -20 to -1 | On 22 October a faint plume extended 125 km to the SE |
| 21 Oct-24 Oct 2002 | 1-5 | -- | -- | NOAA12, NOAA16, and MODIS imagery |
| 27 Oct-30 Oct 2002 | 2-6 | 17-36 | -22 to -6 | AVHRR |
| 27 Oct-30 Oct 2002 | 2-6 | -- | -- | NOAA12, NOAA16, MODIS |
| 08 Nov-09 Nov 2002 | 2-4 | 34-49 | -20 to -4 | AVHRR; On 8 November a faint ~11-km-long plume extended to the SE, visible on band-3 |
| 08 Nov and 09 Nov 2002 | 4, 9 | -- | -- | MODIS |
| 08 Nov-11 Nov 2002 | 2-4 | -- | -- | NOAA12 and NOAA16 |
| 11 and 13 Nov 2002 | 4-5 | 40-49 | -18 to -10 | AVHRR |
| 11-13 Nov 2002 | 2-5 | -- | -- | NOAA12 and NOAA16 |
| 13 Nov 2002 | 4 | -- | -- | MODIS from Sakhalin |
| 16-19, 22 Nov 2002 | 2-6 | 2-49 | -26 to -20 | AVHRR and MODIS; On 17-18 November, 20-km and 70-km-long gas-steam plumes extended to the WNW and SSE, respectively |
| 23, 25-27 Nov 2002 | 1-5 | 1-49 | -27 to -20 | AVHRR and MODIS; on 27 November a 150-km-long gas-steam plume extended to the NE |
| 29 Nov-05 Dec 2002 | 2-5 | -1 to 49 | -31 to -20 | AVHRR and MODIS; on 29 November, a possible steam-gas plume extended 80 km to the SSE |
| 01 and 05 Dec 2002 | -- | -- | -- | Gas-and-steam plumes extended 40 km and 45 km to the ENE and NNW |
| 09 Dec-12 Dec 2002 | 2-6 | 3-39 | -29 to -20 | AVHRR and MODIS |
| 13-17 and 19-20 Dec 2002 | 1-6 | -15 to 49 | -34 to -25 | AVHRR and MODIS |
| 19-20 and 23-25 Dec 2002 | 1-6 | 10-40 | -27 to -23 | -- |
| 27, 29, 31 Dec and 01-02 Jan 2003 | 2-4 | -7 to 34 | -38 to -30 | On 1 January, a 10+ km plume extending ESE was visible on MODIS imagery |
| 03 Jan-10 Jan 2003 | 1-6 | -8 to 47.5 | -30 to -13 | -- |
| 10-13 and 15 Jan 2003 | 1-7 | 12-47.5 | -33 to -20 | -- |
| 17-22 and 24 Jan 2003 | 1-4 | -2 to 19 | -27 to -20 | -- |
| 25-29 Jan 2003 | 2-7 | -2 to 46 | -25 to -15 | -- |
| 01-06 Feb 2003 | 2-6 | 3-49 | -24 to -9 | Gas-steam plumes extended ~40 km to the W and NNE from the dome on 1 and 3 Feb, respectively |
| 07-13 Feb 2003 | 1-7 | -12 to 49 | -30 to -12 | Gas-steam plume extended ~35 km NNW from the dome on 9 Feb |
| 14-20 Feb 2003 | 1-6 | 26-49 | -33 to 5 | On 15 Feb a wide gas-steam plume extended > 25 km E; on 16 Feb a narrow plume extended 110 km N; during 16-17 Feb ash and pyroclastic deposits were noted from the S to E slopes; a gas-steam plume extended 30 km W on 19 Feb; a gas-steam plume extended up to 96 km SSW on 20 Feb |
| 21-28 Feb 2003 | 2-6 | 21-49 | -30 to -8 | Gas-steam plumes extended up to 50 km to the SSW, SE, and NE during 24-27 Feb |
Incandescence was observed at the lava dome on 6 October. On 11 November, seismic data indicated possible hot avalanches sending clouds up to 5.5 km above the dome.
During late November and early December, gas-and-steam plumes extended >10 km to the E and W. On 19 December, short-lived explosions at 1238 and 1514 sent gas-ash plumes to ~5.5 km and 5.0 km altitude, respectively. In the first case, pyroclastic flows moved to the SE; in the second, to the S, inside the Baidarnaya river. The runout of both pyroclastic flows was 3 km.
On 28 December 2002, a small amount of light-gray ash was observed on the surface of snow. During early January 2003, plumes extended >5-10 km to the W and NW. During late February, plumes extended 10-40 km to the SW, S, and SE. Ash was noted in plumes on 24 October, 1, 11, 15, 19, and 20 November, 1, 19, and 24 December, 4 and 25 January, and 15, 17, 25, and 26 February. The Concern Color Code remained at Yellow.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of a) U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), b) Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and c) Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Lava dome growth and ash-and-gas plumes to 5 km high
Eruptive activity continued during May-August 2003, including growth of a lava dome in the active crater. Seismic activity continued to remain above background levels, and shallow earthquakes at a depth of 5 km were recorded with magnitudes in the range of 1.8-2.8. Several short-lived explosive eruptions each week sent ash-gas plumes to heights of 2,500-5,000 m above the dome. Intermittent spasmodic volcanic tremor was registered. Satellite data on thermal anomalies are shown in table 7.
Table 7. US and Russian satellite data summarizing thermal anomalies associated with Sheveluch from late May to early August 2003. Courtesy of Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT).
| Date(s) | Thermal Anomaly (pixels) | Comments |
| 30 May 2003 | 1-4 | No ash plumes observed. |
| 06-09 Jun 2003 | 1-6 | Gas/steam plumes rose 100-700 m above dome and extended E. |
| 13-14, 16-17 Jun 2003 | 1-6 | Gas/steam plume rose 100 m above dome and extended 5 km NE. |
| 21-22 Jun 2003 | 1-4 | Gas/steam plumes rose 100 m above dome. |
| 28-30 Jun, 02 Jul 2003 | 1-5 | Gas/steam plumes rose 100 m above dome. |
| 05-06, 10 Jul 2003 | 1-2 | Gas/steam plumes rose 500 m above dome. |
| 11, 13-16 Jul 2003 | 1-2 | Gas/steam plumes rose 200-800 m above dome. |
| 19-22, 24 Jul 2003 | 1-2 | Gas/steam plumes rose 500-600 m above dome. |
| 27, 31 Jul, 01 Aug 2003 | 1-3 | Temperatures of 10-19°C in background of 0-5°C; gas/steam plumes rose 100 m above dome. |
| 08-10 Aug 2003 | 2-3 | -- |
Information Contacts: Olga Girina, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), a cooperative program of the Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia, the Kamchatka Experimental and Methodical Seismological Department (KEMSD), GS RAS (Russia), and the Alaska Volcano Observatory (USA); Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), the Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Ash eruptions, lava dome growth, steam plumes, and thermal anomalies
Eruptive activity continued during August-October 2003, including growth of a lava dome in the active crater. Seismicity remained above background levels, and weak, shallow earthquakes were recorded throughout the period. Slightly higher seismic activity was recorded on 30 October with magnitudes in the range of 2.0-2.4. Short-lived eruptions each week sent ash-and-gas plumes to heights of 100-1,500 m above the dome. Thermal anomalies were often recorded by US and Russian satellites.
Weak volcanic tremor was detected during 22-31 August. Tremor was accompanied by gas-and-steam plumes as high as 800 m during 26-27 August, and 2-4-pixel thermal anomalies on 26-30 August. Small thermal anomalies (1-4 pixels) and 500-800-m-high steam plumes were common through 19 September, with an 11-pixel anomaly on the 18th. Similar small thermal anomalies and plumes appeared again during 25-30 September. Thermal anomalies continued to be detected during 1-4, 7-8, 10-12, 16-20, 26, and 29-30 October. Steam plumes were also common, with varying heights of 100-800 m. Small steam plumes and a 1-pixel anomaly occurred 2-3 November.
Information Contacts: Olga Girina, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), a cooperative program of the Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia, the Kamchatka Experimental and Methodical Seismological Department (KEMSD), GS RAS (Russia), and the Alaska Volcano Observatory (USA); Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), the Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Lava dome continues growing in the active crater
A lava dome continued to grow in the active crater at Shiveluch (also called Sheveluch). In accord with the hazard associated with lava dome growth, the level of concern from 7 November 2003 to 2 January 2004 was yellow. During this ~ 2-month interval, US and Russian satellites recorded thermal anomalies averaging 1-3 pixels.
Increasing seismicity in December was accompanied by gas-steam plumes with varying heights of 50-800 m. Sometimes the plumes extended over 10-30 km to the E, as was noted on 30 November and 2-3 December.
Seismicity was at background levels during most of November. On 29-30 November instruments detected a series of shallow events lasting 3-4 minutes. On November 29-30 and December 1-4, weak shallow earthquakes were registered. Similar earthquakes also occurred at depths of 0-5 km beneath the active dome during 19 December 2003 to 2 January 2004.
On 13 December geophysicists noted a series of weak, local, and continuous seismic events interpreted as possibly resulting from the descent of hot avalanches, but visual observations revealed only weak fumarolic activity. Later, on 11, 12, 15, and 16 December, people in the town of Klyuchi saw gas-steam plumes rise up to 100-400 m above the dome.
Eight strong earthquakes registered in December. Two occurred on 14 and 16 December; ;they were of ML over 2.25 in the depth range 0-5 km. Three occurred on 20 December; they were of ML 1.9-2.0 in the depth range 0-10 km. Three total earthquakes occurred in the two days 28 December and 1 January; they were of ML 1.7-2.5 in the depth range 2-5 km.
Information Contacts: Olga Girina, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), a cooperative program of the Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia, the Kamchatka Experimental and Methodical Seismological Department (KEMSD), GS RAS (Russia), and the Alaska Volcano Observatory (USA); Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), the Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Lava dome growth and associated unrest
Unrest at Shiveluch continued from 1 January through 9 April 2004, including above-background seismicity and lava-dome growth with associated pyroclastic flows. Gas-and-steam plumes rising as high as 4.5 km altitude and ash plumes rising to 4-6 km altitude were frequent. Plumes were noted as far as 175 km from the volcano. During the period, US and Russian satellites repeatedly detected thermal anomalies. For viewers on the ground the volcano was obscured by clouds throughout much of the period.
Earthquakes occurred at depths of 0-5 km with local magnitudes (Ml) of 1.25-2.6. About 70 shallow earthquakes with Ml over 1.75 occurred during the week ending 16 January. These were exceeded the following week by 206 earthquakes with Ml of 1.75-2.6 and about 40 ash explosions. Intermittent spasmodic volcanic tremors of 0.5-1.0 µm/s were also recorded that week. These events caused the level of concern to raise from Yellow to Orange, where it remained throughout the remainder of the report period.
Accompanying these events were pyroclastic flows with run-out distances of 1-2 km. Ash plumes rose as high as 6 km, extending in various directions for several kilometers. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to 3.5-4.5 km. One extended 50 km to the SE on 22 January while another, on 26 January, extended over 75 km to the SW.
Events and activities similar to those described above were noted throughout the report period. Shallow earthquakes were recorded almost daily through February, >10/week was typical except for the period in late January noted earlier. However, during late February and through March and April, strong earthquakes occurred, numbering 14-24 per week. Spasmodic volcanic tremor was registered throughout this latter period, attaining a maximum velocity of 0.8 µm/s during 4-6 March.
Gas-and-steam plumes, some containing ash and extending as far as 175 km, were noted throughout the period. During the beginning of April, one ash-gas explosion delivered ash up to 9.0 km while 13 other explosions sent plumes up to 4.0-7.2 km and spasmodic tremor with velocities of 0.2-0.7 µm/s was recorded.
Information Contacts: Olga Girina, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), a cooperative program of the Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia, the Kamchatka Experimental and Methodical Seismological Department (KEMSD), GS RAS (Russia), and the Alaska Volcano Observatory (USA); Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), the Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Continued elevated seismicity with strong explosions in mid-May
With the exception of strong ash explosions and related seismic activity on 9-10 May (described below), unrest at Shiveluch during 9 April-27 May 2004 was similar to that described in our last report (BGVN 29:03).
In effect, observers noted above-background seismicity, lava dome growth, and associated pyroclastic flows. Steam plumes rising as high as 3.5 km altitude, and ash plumes rising 4-7 km altitude, were seen frequently. Earthquakes occurred at depths of 0-5 km and had local magnitudes (Ml) of 1.25 - 2.25 while spasmodic tremor varied between 0.1-0.9 µm/sec.
During the period, U.S. and Russian satellites repeatedly detected 1- to 9-pixel thermal anomalies. Accordng to ground-based observers, the volcano was obscured by clouds throughout much of the report period.
Less than ten strong earthquakes were recorded each week in April. However, activity increased during the week ending 6 May when 35 strong earthquakes were recorded. According to seismic data, from 0210 to 0730 on 10 May, a series of strong ash explosions occurred at the lava dome. Continuous tremor at 14.8 µm/sec occurred during that time, decreasing to 0.3 µm/sec by 0940. Seismic activity increased again during 2150-2325, and tremor was 5-6 µm/sec. According to video and visual observation, explosions sent ash to altitudes of 8-11 km. American and Russian satellite data recorded a 9-pixel thermal anomaly over the lava dome at 2336 on 9 May and a 6-pixel anomaly at 0642 on 10 May. Around this time, authorities temporarily raised the level of concern from orange to red.
From 0725 through 1502 on 10 May an ash plume extended over 450 km to the SE and ash deposits were observed on 11 May over a wide sector to the SE at distances over 100 km. At 0914, pyroclastic- and mud-flow deposits were observed on the SE slopes of the volcano extending to distances of ~7-8 km.
At Ust-Kamchatsk (coastal settlements ~100 km ENE of Bezymianny), the thickness of orange-brown ash deposits on 10-11 May was ~1-2 mm. On 10 May, the airport at Ust-Kamchatsk was closed and the road and the dam in the area of the Bekesh River were destroyed by mud flows.
On 10 May seismic activity continued with 27 and 21 strong earthquakes recorded, respectively, during the subsequent two weeks. The number of thermal anomalies reported from satellite observations also increased to as many as 36 during the week ending 13 May.
By 27 May, activity had returned to levels typical of April (and earlier). On 21 May, the lava dome and pyroclastic-flow deposits were observed from a helicopter and from the ground. A part of the dome had been destroyed. Deposits were gas-rich, high-temperature juvenile pyroclastic flows in the central sector of the S slope of the volcano. The temperature of the main flow was ~ 300°C at a depth of 15 cm. According to satellite data, 1-20 pixel thermal anomalies were observed over the lava dome during the week.
Information Contacts: Olga A. Girina, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), a cooperative program of the Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia, the Kamchatka Experimental and Methodical Seismological Department (KEMSD), GS RAS (Russia), and the Alaska Volcano Observatory (USA); Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), the Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
27 February eruption left deposits covering 24,800 km2 to W of volcano
The previous report on Shiveluch (BGVN 29:05) covered activity until 27 May 2004. From May 2004 until September 2004, seismicity at Shiveluch was above background, with many shallow earthquakes recorded 0-5 km beneath the active lava dome, and Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange. Periods of continuous spasmodic tremor were recorded in May, June, July, and October 2004. Gas-and-steam plumes rising to 3-6 km altitude were frequent, sometimes drifting up to 10 km or more. A small lava flow on top of the active dome, first observed on 21 May, continued to flow until 28 May. On 19 June, a likely ash cloud was seen 10-20 km S of the volcano. The lava dome continued to grow in Shiveluch's active crater.
On 6 September at 2054 an explosion produced small pyroclastic flows and an ash plume that rose to ~ 5.5 km altitude. According to satellite data, 1- to 12-pixel thermal anomalies were registered over the lava dome on 15-16 September 2004. During 23-29 September, 26 strong shallow earthquakes up to M 2.3 were recorded. An explosion on 25 September was accompanied by small pyroclastic flows. The Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT),again reported seeing a new lava flow at Shiveluch's lava dome around 26 October.
Based on interpretations of seismic data, possible ash-and-gas explosions up to 7 km altitude occurred throughout October (figure 8), November, and December 2004. Possible minor ash-and-gas explosions and hot avalanches also occurred. On 28 December a gas-and-steam plume extended as far as 50 km E.
During January and February 2005, seismicity decreased slightly at Shiveluch but remained above background levels, with weak shallow earthquakes occurring beneath the active dome. Possible weak ash-and-gas explosions and hot avalanches occurred throughout January and February, and gas-and-steam plumes rose up to 2-7 km altitude.
On 13 January, several ash explosions up to 5 km altitude and a pyroclastic flow probably occurred. The Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) reported an eruption of Shiveluch on 17 January at 1625 with a plume that rose to a height of ~ 4.5 km altitude. On 6 February a pyroclastic flow traveled ~ 2 km down the volcano's flank. On 17 February ash deposits were seen on the volcano's snow-covered lava dome extending to the SE and S.
A large eruption occurred at Shiveluch from 1825 on 27 February to 0100 on 28 February, leading KVERT to raise the Concern Color Code from Orange to Red (the highest level). Meteorological clouds obscured the volcano during the eruption. According to satellite data (NOAA 16 at 1656 UTC on 27 February), a 45-pixel thermal anomaly was registered near the dome (band 3). This anomaly was probably related to a large pyroclastic flow on the SW flank. At this time analysts detected a 45-km-long ash cloud on satellite imagery trending NW of the volcano. At 0900 on the 28th, ash deposits were noted in the town of Klyuchi, ~ 46 km from the volcano. Satellite imagery from 1205 on 28 February showed ash deposits W of Shiveluch covering an area of 24,800 km2. Later that day, an ash cloud extending more than 360 km was centered over the western half of Kamchatka. On 1 March the Concern Color Code was reduced to Orange. Prior to the 27 February eruption, seismicity was above background levels and ash-and-gas plumes were seen on video rising to ~ 3 km above the lava dome.
Explosions deposited ash in Ust'-Hairyuzovo village, about 250 km to the W, on 27 and 28 February, and on 2 March. The seismic station at Shiveluch stopped working on 27 February. According to visual and video data on 2 March, part of a large pyroclastic flow was observed on the SW flank of the volcano. According to satellite data from the USA and Russia, a 2- to 23-pixel thermal anomaly was registered at the dome on 1-3 March. Clouds obscured the volcano at other times. Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange.
Information Contacts: Olga A. Girina, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), a cooperative program of the Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia, the Kamchatka Experimental and Methodical Seismological Department (KEMSD), GS RAS (Russia), and the Alaska Volcano Observatory (USA); Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), the Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA; Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center, Tokyo Aviation Weather Service Center, Haneda Airport 3-3-1, Ota-ku, Tokyo 144-0041, Japan (URL: https://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/).
Lava dome growth, ash falls, pyroclastic flows during early to mid-2005
Following explosions from Shiveluch during 25 February to 4 March 2005 ash fell in Ust'-Hairyuzovo, about 250 km W (BGVN 30:02). From March 2005 until July 2005, Shiveluch remained at Concern Color Code Orange. Throughout March 2005 the lava dome at Shiveluch continued to grow and on several days ash-and-gas plumes and gas-and-steam plumes rose to a maximum of ~ 2.8 km above the dome. Satellite imagery showed a thermal anomaly at the dome during the first week of March and a large thermal anomaly over the recent pyroclastic-flow deposit during 11-12 March. Between 5-28 March a new lava extrusion added ~ 50 m height to the SW part of the dome.
During April 2005, intensive growth of the new extrusion at the W part of the dome continued, and the E and W parts of the lava dome became nearly level. Gas-and-steam plumes rose to a maximum of ~ 1.2 km above the dome during April 2005. Satellite imagery showed a large thermal anomaly at the dome during mid-April and a small anomaly associated with a pyroclastic flow on 19 April. On 25 April, a hot avalanche on the dome's W side produced an ash plume that rose ~ 2 km above the 2.5-km-high lava dome. Growth of the dome continued during May 2005 with a new extrusion to the W. Ash-and-gas plumes, some rising 2 km above the dome, were frequent. Satellite imagery showed a persistent thermal anomaly at the lava dome throughout May.
The dome continued to grow during June 2005. During 3-10 June, two shallow M 1.6-1.7 earthquakes occurred 0-5 km beneath the active dome. Gas-and-steam plumes rose as high as 400 m above the dome during June. A persistent thermal anomaly was visible throughout June. Fumarolic activity was reported during the week of 18-24 June. During the last week of June, satellite imagery showed a persistent thermal anomaly, and fumarolic activity produced steam to 4-5 km altitude. On 30 June, ash-and-gas plumes rose 3-5 km altitude. and drifted NW. Hot avalanches of volcanic material were also recorded. On 6 July ash-and-gas plumes rose to ~ 7 km altitude and drifted NW. On 7 July an 11-minute-long seismic event occurred, and ash-and-gas plumes may have reached a height of 10 km altitude. Around 8 July, KVERT raised the Concern Color Code from Orange to Red, the highest level. On 8 July 2005, video footage showed weak gas-and-steam plumes rising to ~ 5 km altitude. On 9 July 2005, the Concern Color Code was reduced to Orange.
Information Contacts: Olga A. Girina, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), a cooperative program of the Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia, the Kamchatka Experimental and Methodical Seismological Department (KEMSD), GS RAS (Russia), and the Alaska Volcano Observatory (USA); Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), the Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
22 September eruption generated a substantial pyroclastic flow
From March 2005 until July 2005, the lava dome at Shiveluch continued to grow and ash-and-gas plumes and gas-and-steam plumes were frequent (BGVN 30:06). The alert level was at Orange.
On 7 July, the Russian News and Information Agency (RIA Novosti) reported that Shiveluch was producing pyroclastic flows and ash plumes rising to 5 km altitude. On 8 July, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT) raised the alert level from Orange to Red, the highest level. Video footage taken the same day showed weak gas-and-steam plumes rising to ~ 5 km altitude. On 9 July, ash-and-gas plumes rose to 3 km altitude and the alert level was reduced to Orange. Ash plumes extended 27 km SW of the volcano during July 11-12.
Through July and August, the lava dome continued to grow and Shiveluch remained at alert level Orange. On 15 July, RIA Novosti reported that "[m]assive ash emissions from Shiveluch...are posing danger to nearby towns and villages. The Federal Earthquake Prediction Center's Kamchatka branch said ash storms, as well as mudflows from Shiveluch's slopes, could be dangerous for nearby settlements . . .. [T]he volcano began emitting massive ash clouds. Gas, ash, and magmatic material . . . are barreling down the slope . . .. The ash cloud has spread more than 700 kilometers to the [W] of the volcano, covering the peninsula and the nearby Sea of Okhotsk with a nearly 150-kilometer-wide strip."
On 19 July KVERT reported that a gas-steam plume extended 30 km SW from the volcano on 18 July and a gas-steam plume up to 3.5 km altitude was observed on 19 July. On 19 July, 23 July, and during 5-12 August, satellite data from the USA and Russia indicated a persistent 1 to 7 pixel thermal anomaly at the dome. On 23 July and 6 August, incandescence was observed at the lava dome. Fumarolic activity was visible on 6 August.
During 19-26 August, about ten shallow earthquakes were recorded, and a larger thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery. On 19 August a new viscous lava flow was emitted from the lava dome and continued to flow during 26 August to 9 September. Several ash plumes reached ~ 5.5 km altitude.
On 5 September, an ash plume rose to ~ 4 km altitude. On 8 September, a hot avalanche was accompanied by an ash plume that rose to a height of ~ 3.5 km altitude. The large thermal anomaly continued during the first week of September. On 7 September RIA Novosti reported that Shiveluch "is spewing gas and ash to heights of up to 5,000 feet [1.5 km]". On 16 September KVERT reported that the dome was continuing to grow and that viscous lava continued to flow from the dome. Incandescence at the lava dome was observed on 13 September. Gas-steam plumes up to 3.5 km altitude and a large thermal anomaly were registered all week.
On 22 September KVERT raised the alert level to Red, the highest level, and reported that according to seismic data, at 05:15 UTC on 22 September, a paroxysmal eruption began. Ash plumes reached a height about 7.5 km altitude, and ash fall was noted from 06:00 until 08:00 UTC on 22 September by seismologists working about 9 km SW of the volcano.
KVERT reported, based on US and Russian satellite data, an ash cloud with a diameter of ~ 20 km located ~ 90 km to the NW of the volcano and, based on Russian satellite data, an ash cloud with a diameter of ~ 15 km located ~ 20 km to the SSE at about 3 km altitude. Ash fall was observed in Klyuchi on the night of 22 September. According to visual data, a new pyroclastic flow extended 10-15 km.
Information Contacts: Olga A. Girina, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), a cooperative program of the Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia, the Kamchatka Experimental and Methodical Seismological Department (KEMSD), GS RAS (Russia), and the Alaska Volcano Observatory (USA); Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), the Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Ash plumes rising to ~ 10 km in December
In December 2006 Shiveluch underwent heightened seismic and volcanic activity of an intensity not seen since 22 September 2005. During the latter episode, plumes reached ~ 7.5 km altitude (BGVN 30:08). This report covers from September 2005 to December 2006.
Activity during 2005. Seismic levels declined in the weeks subsequent to the previously described 22 September eruption. The Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT) had raised the Concern Color Code level to orange due to the 22 September 2005 eruption and then lowered it to yellow at the start of November. During October, KVERT noted that weak shallow earthquakes, hot avalanches, and small fumarolic activity persisted. Incandescence at the dome was reported on 13, 15, 17, 22, and 29 October, and thermal anomalies over the lava dome were frequently registered.
On 22 October a weak ash-gas plume extended to the E. Seismic activity decreased further and did not exceed background levels in October and November, and remained at low levels in December. Weak avalanches were reported at the start of November. Weak seismicity and fumarolic activity was registered in December. Numerous thermal anomalies over the lava dome and incandescence at the dome were widely reported (specifically, on 1, 7, 8-11, 15, 17-18, 25, and 27-29 December).
Activity during 2006. The lava dome continued to grow in 2006; overall volcanism and seismicity remained low during January to May 2006. Visual and satellite observations of weak fumarolic activity and thermal anomalies were noted during periods of visibility early in 2006 (13-14, 16-17, 22, and 30-31 January and 1 February). One shallow earthquake was registered on 30 January. On 23 May a thermal anomaly was reported, and on 21, and 27-31 May moderate gas-and-steam plumes were observed.
Three deep earthquakes were recorded, one each day, on 1-2 and 5 June, and a shallow earthquakes was recorded on both 2 and 4 June. On 5 and 8 June gas-and-steam plumes rose over the volcano. A thermal anomaly from the volcanic crater was noted on 2-5 and 7-8 June. Fumarolic activity of the lava dome was observed on 23 and 29-30 June. On 16 and 19 June, gas-and-steam plumes rose to ~ 3-3.5 km altitude from the lava dome summit. A steam plume extending 9.5 km NE from the volcano was observed on a 24 July satellite image. Observers noted frequent fumarolic emissions from the dome (on 1-2, 8, 10, 17-20, 22, and 24-26 July). Frequent thermal anomalies over the dome also were noted (on 4, 7-8, 17-18, and 23-26 July).
In August and September, activity remained the same with periods of fumarolic activity and reports of thermal anomalies. Seismicity remained low except for five earthquakes in the middle of August. Several weak earthquakes were registered throughout October and November, as well as fumarolic activity of the lava dome in periods of good visibility. Sporadic thermal anomalies were recorded (on 6, 8, 14-15, 22, and 27-31 October and 1-2, 6-7, 13-15, and 19-22 November). According to visual and video data, gas-and-steam plumes rose to ~ 3.5 km altitude and extended NW on 23 October. A weak continuous spasmodic volcanic tremor was registered on 29-30 October and 2 November.
Heightened volcanic activity during December began with a strong seismic event on 4 December from 1906-1940. According to satellite data, an ash plume raising up ~ 6 km altitude and extending NW was observed at 2100, and during 2130-2400 gas-and-steam plumes containing ash extended NW at ~ 3.0 km altitude. On 4 December ashfall extended ~ 150 km. Several tens of shallow earthquakes were registered in the following days. On 5 December the level of Concern Color Code was raised from yellow to orange. On 8 December another eruption occurred with ash plumes to ~ 4 km altitude that extended NW.
On 12 December, ash explosions to a height ~ 4 km produced a plume that extended E-SE from 25-460 km, according to satellite data from various sources. According to visual and video data, two separate ash plumes rose to ~ 10 km altitude and extended NW on 16, 17, and 20 December. On subsequent days, satellite data showed ash clouds extended primarily ~ 570 km to the E, as well as to the NE.
On 26 December 2006 the Concern Color Code level was raised to red. At 2130 on 27 December, video data recorded a gas-and-steam plume rising to ~ 3.5 km altitude. An ash plume rose to ~ 10 km altitude and extended E on 25-27 December (figure 9) and N on the 28th. The Concern Color Code level lowered to orange on 28 December 2006, where it remained in early January 2007.
Information Contacts: Olga A. Girina, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), a cooperative program of the Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia, GS RAS (Russia), and the Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), the Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA; Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Land Rapid Response Team, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (URL: http://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/); National Aeronautics and Space Administration Earth Observatory (URL: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards).
Ash plumes continued through at least April 2007
In December 2006 Shiveluch underwent heightened seismic and volcanic activity after more than a year of lesser activity (BGVN 31:11). After significant explosive activity during 26-27 December 2006 that caused the Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT) to briefly raise the hazard status, activity remained above background levels into January 2007.
The seismic network recorded 200 shallow earthquakes daily between 29 December and 12 January 2007, accompanied by fumarolic activity, avalanches, and gas-and-ash plumes that rose from 4.3 km to 13.7 km altitude, drifting E and SSW. A large thermal anomaly over the dome was noted.
Between 12 January to 16 February, this activity continued. The number of earthquakes dipped to as low as 120 per day before increasing to 200 again during 2-9 February. Plumes during this time rose to an altitude of 3.5-6.5 km and drifted in a variety of directions. The large thermal anomaly over the dome remained. An eruption occurred on 6 February that was not visible on satellite imagery.
Astronauts aboard the Space Shuttle noted a plume around 21 March (figure 10). On 29 March, an explosive event at Shiveluch produced an ash plume (figure 11) that, according to the Tokyo VAAC, reached an altitude of 11.9 km and drifted NE. The next day, an explosive event that lasted about 6 minutes produced a plume that reached altitudes of 10.1-12.2 km, and drifted NE. According to a news article, on 31 March, a mudflow covered an approximately 900-m-long section of road, in an area ~ 20 km from Shiveluch.
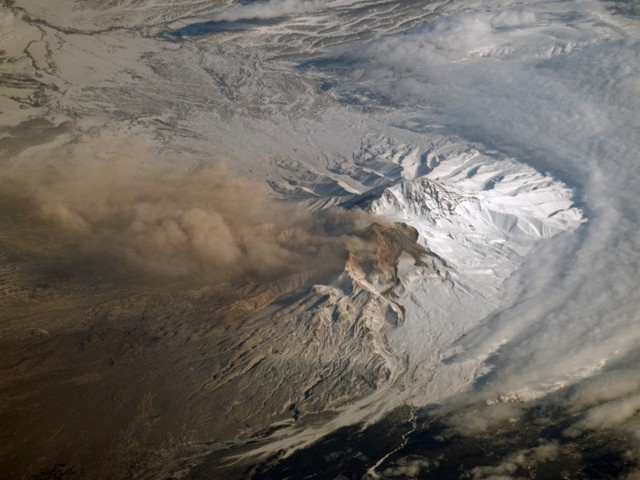 |
Figure 10. Plume from Shiveluch taken by astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) around mid-morning on or around 21 March 2007. Photograph ISS014-E-17165. Courtesy of NASA. |
In subsequent reports, KVERT indicated that seismic activity continued above background levels during 4-12 April. Based on seismic interpretation, observation, and video data, ash-and-steam plumes rose to altitudes of 4.5-7 km throughout this period. The large thermal anomaly was visible on satellite imagery during 1-10 April. As of 10 April, the Color Code at Shiveluch remained at Orange.
Information Contacts: Olga A. Girina, Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), a cooperative program of the Institute of Volcanic Geology and Geochemistry, Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia; Kamchatka Experimental and Methodical Seismological Department (KEMSD), Geophysical service of the Russian Academy of Science (Russia) (URL: http://kbgs.kscnet.ru/information-e.html); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center, Tokyo Aviation Weather Service Center, Haneda Airport 3-3-1, Ota-ku, Tokyo 144-0041, Japan (URL: https://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/); Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA; Yelizovo Meteorological Watch Office, Yelizovo Airport Aviation Meteorology Center, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, Russian Federation, 684010 Kamchatka; Itar-Tass (URL: http://tass.ru/eng/); US National Aeronautics and Space Administration, NASA.
Lava-dome growth and block-and-ash flows continue April-December 2007
Shiveluch (also spelled Sheveluch), the scene of lava-dome growth, is one of the most active volcanoes on Kamchatka. It was last reported here discussing events through early April 2007 (BGVN 32:03). The following report covering the interval early April-December 2007 came from multiple sources.
Shiveluch's eruptions are of an explosive nature and the volcano has been in a state of heightened activity since 5 December 2006. Vigorous activity continued to the time of this report (March 2008). Small lava-dome collapse events produced ash plumes and short block-and-ash flows, which in turn generated mudflows when snow was present. This activity was recorded in shallow volcanic earthquakes and tremor and a large, ever-present thermal anomaly on satellite imagery.
The Level of Concern Color Code remained at Orange throughout this report period (early April through December 2007). The Kamchatka Branch of the Geophysical Service of the Russian Academy of Sciences (KB GS RAS) is monitoring the volcano and believes that it poses little danger for nearby populated localities.
During April 2007 growth of the lava dome continued, and hot lava extruded at the top of the dome. Hot avalanches from the top of the dome occurred daily. Ash and ash-and-steam plumes rose to altitudes of ~ 4.6-6.5 km. Some plumes were seen on satellite imagery drifting E, SE, and S. According to satellite data, ash plumes extended ~ 60 km on 28-29 April, mainly to the S and SW, and ~ 50 km to the E on 5 and 7 May. During 27-28 May, plumes were seen on satellite imagery drifting SW.
A large thermal anomaly was conspicious during the last week of April 2007, and hot avalanches originating from the dome were noted on 30 April, 4 May, and 6-7 May. Gas-steam emissions occurred repeatedly. On 7 May a mudflow traveled down Shiveluch's slope, reaching ~ 20 km beyond the lava dome and blocking ~ 30 m of a road, isolating the district center Ust-Kamchatsk on the E of the peninsula. There were no vehicles on this portion of the road when the mudflow descended, and no casualties occurred. Figure 12 contrasts the dome in 2006 and 2007.
During July, gas-steam plumes frequently reached 4.0-6.1 km altitude. Ash was not always identified on satellite imagery because clouds obscured visibility; however, on 16 July satellite imagery detected gas-steam and ash plumes that extended for about 7-40 km to the S and SW of the volcano. Seismic data suggested that gas-and-ash emissions were concurrent with hot avalanches (figure 13).
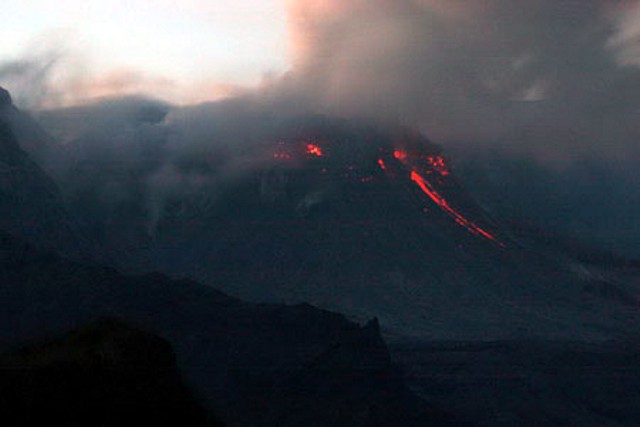 |
Figure 13. The lava dome of Shiveluch volcano as seen from the SW on 11 July 2007. The dark dome contrasts with glowing zones where hot avalanches descended. Photo by Y. Demyanchuk. |
On 25 September 2007, video observations indicated ash plumes rising to 6 km altitude and drifting E. According to video for 27 September and 2 October 2007, gas-steam plumes rose up to 4.5 and 3.5 km altitude, respectively. Weak fumarolic activity was noted on both 1 and 8 October. KB GS RAS noted that there was no significant variation in the previous ongoing activity through December 2007 that might indicate any impending activity of greater significance. Frequent MODIS thermal alerts continued throughout 2007 into 2008.
Reference. Gorbach, N., 31 July 2007, Bulletin of activity at Sheveluch volcano, issued 31 July 2007 [title approximate (translated from Russian); available in Russian at URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/volcanoes/inform_messages/2007/Sheveluch_072007/Sheveluch_072007.html).
Information Contacts: Yuri Demyanchuk, Natasha Gorbsch, and theKamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/); Kamchatka Branch of the Geophysical Service of the Russian Academy of Sciences (KB GS RAS), Russia (URL: http://www.emsd.ru/); Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Emissions continue since January 2008 as lava dome grows; morphology
From the January to May 2008, dome growth at Shiveluch has consistently been accompanied by shallow, low-amplitude earthquakes, satellite thermal anomalies, and tremor. According to the Kamchatka Branch of the Geophysical Service of the Russian Academy of Sciences (KB GS RAS), several cases of elevated magnitude seismic signals occurred (figure 14). In some cases, these signals took place during times of zero visibility and the signals were interpreted to suggest a plume above to 4 km altitude.
On 3 March a plume of gas stretched 31 km to the SW of the volcano, and ash clouds rose up to ~ 4.5 km altitude. During the last two weeks of March, reports noted gas-and-ash emissions to ~ 3.5-4.5 km altitude; hot avalanches occurred each day (figure 15).
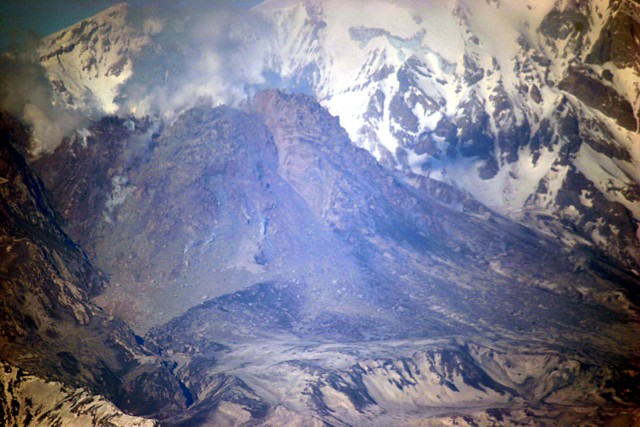 |
Figure 15. The lava dome of Young Shiveluch as seen from the SE on 18 March 2008. A thick lava flow had recently extruded from the left (SW) side. Photo by Yuri Demyanchuk. |
Background on the edifice and deposits. Shiveluch is the northern-most active volcano of the Kamchatka peninsula, Russian Far East (figure 16a). The volcano forms a large isolated edifice surrounded by lowlands of the northern part of the Central Kamchatka depression. Two basic structural elements of the volcano are clear on figure 16b where Young Shiveluch is seen located inside the caldera of Old Shiveluch.
 |
Figure 16. Photo of the Shiveluch volcano complex in a view from the S. The dotted line divides the two structures of Old Shiveluch and the growing dome of Young Shiveluch. From Gorbach (2007). |
Old Shiveluch includes a thick sequence of basaltic and andesitic pyroclastic layers exposed in the base of the caldera wall; the NE and SW parts of the complex contain a folded sequence of pyroclastic deposits overlapped by basaltic-basaltic andesite flows and broken through by numerous radial dikes. The lava flows and domes of Young Shiveluch are richer in silica (59.5-62.5%) than those of Old Shiveluch (54.5-56.5%). Young Shiveluch (figures 16 and 17) has produced numerous Plinian tephras.
References. Belousov, A., Belousova, M., and Voight, B., 1999, Multiple edifice failures, debris avalanches and associated eruptions in the Holocene history of Shiveluch volcano, Kamchatka, Russia: Bulletin of Volcanology, v. 61, p. 324-342.
Gorbach, N., 2007, Bulletin of activity at Shiveluch volcano, (title approximate translated from Russian issued 31 July 2007) available (in Russian) at URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/volcanoes/inform_messages/2007/Shiveluch_072007/Shiveluch_072007.html).
Information Contacts: Yuri Demyanchuk, Natasha Gorbsch, and theKamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/); Kamchatka Branch of the Geophysical Service of the Russian Academy of Sciences (KB GS RAS), Russia (URL: http://www.emsd.ru/); Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), the Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Near-constant dome growth during May 2008 through March 2010
Volcanism at Shiveluch that has been almost continuous since 1980 remained so from May 2008 through March 2010. During that time the lava dome was active and frequently growing, and produced moderate and weak explosions (figure 18). The most active phases took place during July-October 2008, March-April 2009, and November-December 2009 (figure 19).
During the two years discussed, there were many short-lived ash plumes (1-3 km above the dome), ash clouds produced by rockfalls and avalanches, and strong explosions that generated long-distance plumes (those with 'ash cloud' symbols above the arrows, figure 19). The large explosive eruptions of 26 April and 23 June 2009 sent respective ash plumes to 510 km and 754 km distances (table 8). The day after the earlier event, there was clear visibility on 27 April (figure 20).
Table 8. Significant explosions and ash plumes recorded at Shiveluch from May 2008 to March 2010. Plumes lower than ~1.2 km above the dome and seen for less than 10 km from the vent were omitted. Data courtesy of KVERT.
| Date | Plume altitude (m) | Plume extension (km) |
| 14 May 2008 | 5800 | -- |
| 20 May 2008 | 5500 | -- |
| 27 May 2008 | 3600 | -- |
| 25 Jun 2008 | 4200 | -- |
| 13 Sep 2008 | 6500 | 100 km NE |
| 28 Sep 2008 | 5000 | -- |
| 01 Oct 2008 | -- | 70 km S, W |
| 14 Oct 2008 | 6000 | -- |
| 16 Oct 2008 | 4500 | -- |
| 19 Oct 2008 | -- | 30 km E |
| 20 Oct 2008 | -- | 62 km E |
| 05-06 Nov 2008 | 4000 | -- |
| 04 Dec 2008 | -- | 25 km NE |
| 17 Jan 2009 | -- | 10 km E |
| 20 Jan 2009 | 4500 | -- |
| 25 Feb 2009 | 5500 | -- |
| 04 Mar 2009 | 4700 | -- |
| 10 Mar 2009 | 6000 | -- |
| 24 Mar 2009 | 7500 | -- |
| 27-29 Mar 2009 | -- | 10 km SE |
| 04 Apr 2009 | 4500 | -- |
| 05 Apr 2009 | -- | 10 km E |
| 15, 22 Apr 2009 | 4000 | -- |
| 25 Apr 2009 | 6700 | 50 km SE |
| 26 Apr 2009 | 5000 | 510 km SE |
| 27-29 Apr 2009 | 5000 | 107-120 km NE |
| 13 May 2009 | 5000 | -- |
| 22 May 2009 | 4000 | -- |
| 10 Jun 2009 | 7700 | -- |
| 11 Jun 2009 | 4500 | 140 km SW |
| 13-14 Jun 2009 | 5500-6100 | -- |
| 18 Jun 2009 | 5700 | -- |
| 20 Jun 2009 | 5000 | -- |
| 23 Jun 2009 | -- | 754 km S |
| 24 Jun 2009 | -- | 28 km NW |
| 25 Jun 2009 | -- | 95 km |
| 03 Jul 2009 | -- | 20 km SE |
| 18 Jul 2009 | -- | 34 km E |
| 24 Jul 2009 | 5000 | -- |
| 27 Jul 2009 | 5000 | 10 km E |
| 02 Aug 2009 | -- | 23 km E |
| 15 Aug 2009 | 4500 | -- |
| 31 Aug 2009 | -- | 107 km E |
| 02 Sep 2009 | -- | 20 km S |
| 11 Sep 2009 | 15000 | -- |
| 18-19 Sep 2009 | 5000-5500 | -- |
| 20 Sep 2009 | -- | 30 km NW |
| 22 Sep 2009 | 4500 | 70 km SW |
| 29 Sep 2009 | -- | 45 km E |
| 02-03 Oct 2009 | -- | 30-60 km SE |
| 30 Oct 2009 | -- | 255 km E |
| 04-05 Nov 2009 | 4200-4500 | -- |
| 10 Mar 2010 | 5500 | -- |
| 11 Mar 2010 | -- | 10 km E |
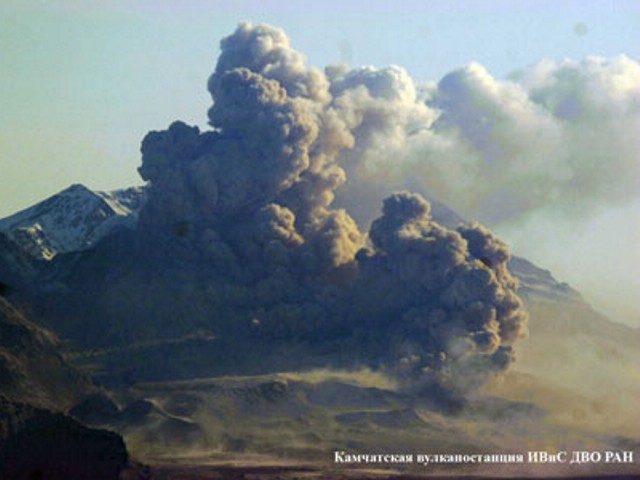 |
Figure 20. Strong explosion on 26 April 2009 at Shiveluch produced a pyroclastic flow on the S slope and a resulting ash plume that extended 120 km to the NE. Photo by Yuri Demyanchuk, IVS RAS. |
KVERT noted that on 11 September 2009 there were strong explosions. Based on interpretations of seismic data, the inferred ash plumes that day rose to an altitude greater than 15 km above sea level. The seismic network then detected 8 minutes of signals interpreted as pyroclastic flows from the lava dome; resulting plumes rose to an altitude of ~ 15 km. Cloud cover prevented visual observations. Ten more events characterized as ash explosions and either pyroclastic flows or avalanches were detected. Seismicity then decreased during 11-12 September. A visit during clear visibility on 13 September revealed fresh pyroclastic-flow deposits (figure 21).
Seismicity. Extended intervals of low-level seismicity were detected at the dome in May and June 2008, during May to October 2009, and to some extent from January through March 2010 (figure 19, bottom). A plot of regional seismicity during December 2009-5 April 2010 in a 70-km-diameter circle around Shiveluch (figure 22) indicates SW-dipping epicenters that rise to shallow depths under Shiveluch (and similarly for other volcanoes in the Kliuchevskoi group).
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (IV&S) Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences (FED RAS), Kamchatka Branch of the Geophysical Service of the Russian Academy of Sciences (KB GS RAS), Piip Ave. 9, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs, http://www.emsd.ru/~ssl/monitoring/main.htm); Yuri Demyanchuk, IV&S FED RAS; Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/), the Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, PO Box 757320, Fairbanks, AK 99775-7320, USA, and the Alaska Division of Geological and Geophysical Surveys, 794 University Ave., Suite 200, Fairbanks, AK 99709, USA.
Unrest continued during 2010; strong eruption on 28 October 2010
Our last report (BGVN 35:03) described activity at Shiveluch during from May 2008 through March 2010. This report describes unrest that continued from April through December 2010, characterized by above-background or moderate seismicity, a large daily thermal anomaly from the lava dome detected in satellite imagery, and ash plumes observed throughout the reporting period (figure 23). During this time period, an explosive eruption from the growing lava dome started on 28 October 2010 at about 0200, based on seismic data (local time and date). The eruption generated significant ash plumes as well as pyroclastic flows. A table below delineates the thermal anomalies and summarizes behavior during October through December 2010, approximately from the eruption onwards (table 9).
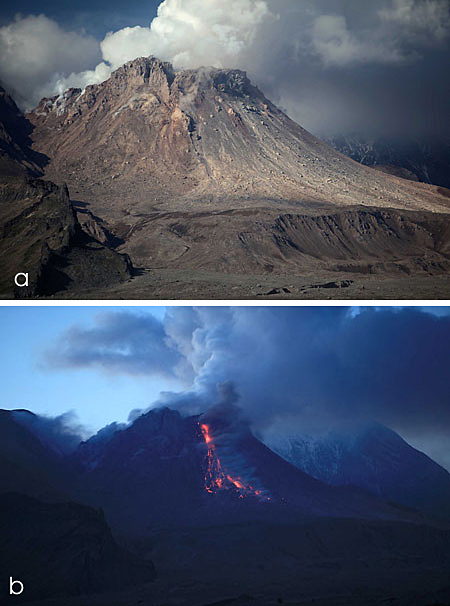 |
Figure 23. Images of Shiveluch taken 23 June 2010 both (a) during the day and (b) at night. Photo by Yuri Demyanchuk. |
Table 9. The activity of Shiveluch during 28 October-15 November 2010. Courtesy of the Kamchatka Branch of the Geophysical Service, Russian Academy of Sciences (KB GS RAS).
| Date | Thermal anomaly, number of pixels | Ash clouds, plume (from AVO) |
| 27 Oct 2010 | -- | Ash cloud 10 km above see level and 20 km in length; A dense plume extending 360 km to SE. |
| 28 Oct 2010 | 7 | Ash plume extending 1 500 km SE. |
| 29 Oct 2010 | -- | A dense ash plume extending 165 km E and a more diffuse plume extending 1 132 km to E. |
| 30 Oct 2010 | 5 | A dense plume extending 361 km to SE and a more diffuse plume extending 404 km to SE. |
| 31 Oct 2010 | -- | A dense plume extending 270 km to SE and more diffuse plume extending 390 km to SE. |
| 01 Nov 2010 | 10 | A dense plume extending 300 km to SE. |
| 03 Nov 2010 | 3 | -- |
| 04 Nov 2010 | 9 | A dense plume extending 260 km to SW and two diffuse plumes extending 260 km SE and 160 km SE. |
| 06 Nov 2010 | 19 | -- |
| 07 Nov 2010 | 10 | A diffuse plume extending 48 km to SE. |
| 08 Nov 2010 | 5 | A dense plume extending 63 km to SW. |
| 09 Nov 2010 | 8 | A dense plume extending 20 km to SE. |
| 10 Nov 2010 | 4 | Ash plume 4.8 km altitude extending 1 km to E. |
| 11 Nov 2010 | 4 | -- |
| 12 Nov 2010 | 2 | -- |
| 13 Nov 2010 | 2 | A dense plume extending 52 km to NW. |
| 14 Nov 2010 | 5 | -- |
| 16 Nov 2010 | 4 | Steam emission 1 km to W. |
| 17 Nov 2010 | 4 | Steam emission 600 m to NW. |
| 18 Nov 2010 | 7 | Steam emission 700 m. |
| 19 Nov 2010 | 10 | Ash plume extending 20 km to E. |
| 20 Nov 2010 | 4 | Ash plume extending 20 km to E. |
| 21 Nov 2010 | 6 | -- |
| 22 Nov 2010 | 8 | Ash plume about 1.5 km altitude. |
| 24 Nov 2010 | 6 | Hot avalanches. |
| 26 Nov 2010 | 7 | Moderate steam emission to NE. |
| 01 Dec 2010 | 7 | -- |
| 03 Dec 2010 | 4 | Ash plume extending 322 km to SE. |
| 05 Dec 2010 | 3 | -- |
| 06 Dec 2010 | 2 | -- |
| 07 Dec 2010 | 4 | -- |
| 10 Dec 2010 | 3 | -- |
| 11 Dec 2010 | 3 | -- |
| 12 Dec 2010 | 2 | -- |
| 13 Dec 2010 | 4 | -- |
| 14 Dec 2010 | 3 | Ash clouds to 4.5 km altitude blowing NE. Avalanche with runout distance of 2 km going SSE. |
| 18 Dec 2010 | 4 | -- |
| 19 Dec 2010 | 3 | -- |
| 20 Dec 2010 | 2 | -- |
| 22 Dec 2010 | 4 | -- |
| 23 Dec 2010 | 4 | Moderate steam emission to W. |
| 24 Dec 2010 | 2 | Ash cloud 4.5 km altitude. |
| 27 Dec 2010 | 7 | -- |
| 28 Dec 2010 | 2 | -- |
| 29 Dec 2010 | 3 | -- |
| 30 Dec 2010 | 3 | -- |
| 31 Dec 2010 | 2 | Moderate steam emission. |
Prior to the large explosion of 28 October, behavior was characterized by the growing lava dome generating strong or weak gas-steam emissions, and explosions of different intensity that sometimes produced hot avalanches. Notably, on 1 July 2010 seismicity increased. Not long afterwards in Klyuchi village (50 km SW from volcano) residents saw ash falling, material they described as reddish in color.
During July to September 2010, KVERT reported that analyses of satellite imagery showed a large daily thermal anomaly over the lava dome. Seismic activity remained above background levels suggesting that on most days there were possible ash plumes. Ash and gas plumes, or the combination of the two, rose to altitudes between 3.5 and 8.5 km and drifted in multiple directions as far as 190 km from the volcano. Ash plumes that were possibly generated by hot avalanches rose to altitudes up to 4.5 km the latest being observed July 5.
Both Shiveluch and Kliuchevskoi volcanoes often produce ash plumes and this was the case both before and during the 28 October eruption at Shiveluch. Prior to the eruption a 29 September 2010 image of Shiveluch and neighboring Kliuchevskoi showed SE-trending plumes from each. The plume from Shiveluch was described on the NASA Earth Observatory website and as "thin"; the one for Kliuchevskoi was described as "wider and more diffuse." In a later (post-eruption) report, Earth Observatory discussed Shiveluch's 28 October plume, which appeared moderately dense and light brown on a natural color satellite image. Visible on the same image, Kliuchevskoi also discharged a small dense plume.
Seismicity increased on 27 October, then the number of local earthquakes and the tremor magnitude both increased sharply starting about 0200 on 28 October. This seismicity disclosed a strong explosive eruption that was soon confirmed by other observations. The NOAA-16 satellite data collected at 0809 on the 28th indicated a dark E-trending ash plume that obscured Ust-Kamchatsk village (population, 5,000) located 85 km SE of Shiveluch. In that village, the local visibility went down to ~5 m and several centimeters of ash ultimately fell. Conditions closed roads and drove residents indoors where they waited out the event with tightly closed doors and windows.
Figure 2 shows processed satellite imagery of an extensive ash cloud E of Shiveluch late on 27 October (local time and date). Relevant to figure 24, the GOES-R algorithm uses spectral channels that are available on both MODIS and GOES-R satellites. Thus, in the sense of a volcanic ash retrieval algorithm, MODIS satellites are a good proxy for GOES-R (figure 24).
Figure 3 shows a photo of the resultant brownish-gray ash-fall deposit on the ash-capped snow.
By the end of the 28th, satellite images showed ash clouds near and over the volcano that had a width of ~20 km and a cloud-top altitude of about 10-15 km (the 15 km estimate, higher than most, was from experimental work by Mike Pavolinis, figure 24). Satellite imagery followed the plume as it drifted across the North Pacific visible for at least 1,500 km SE.
Volcanic Ash Graphics such as the one on figure 4 were sent to the aviation community to help aviators respond to the threat of ash at high altitudes and along airways (flight routes).
According to a KVERT report, ash plumes rose up to 7 km at 0600 on 29 October. Ash continued to fall in Ust-Kamchatsk that same day.
Explosions continued on 30 October. Weather conditions prevented initial visible and satellite observations of the eruption, but seismic data suggested that ash plumes rose to an altitude of ~10 km and drifted NE. Based on analyses of satellite imagery and information from KVERT, the Tokyo VAAC reported that possible eruptions on 31 October and during 1-2 November produced ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 3.7-6.7 km and drifted SE and E. Subsequent notices on 31 October and 1 November stated that ash had dissipated.
News reported by The Boston Globe noted the eruptions had complicated air travel in the area of the Kamchatkan Peninsula. According to this news source, several pilots reported seeing ash clouds in the Alaskan region, but it was below 25,000 ft (7.6 km), too low to present problems to aircraft at cruising altitudes. The Aviation Hazard Status reached Red, the highest level, during 28-31 October 2010.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/); Yuri Demyanchuk, IVIS FED RAS; NASA Earth Observatory; Michael J. Pavolonis, US National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration, Satellites and Information, National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service (NOAA/NESDIS); Center for Satellite Applications and Research (STAR)], 1225 W. Dayton St., Madison, WI 53706; Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Tokyo, Japan (URL: http://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/)
Ongoing dome growth into early 2011; and pyroclastic flows of 27 October 2010
This report first describes activity seen at Shiveluch during December 2010-March 2011. Data from that interval included several ash plumes visible as they blew to over 100 km from the volcano. Thermal imagery analysis showed the character of the dome and the path of pyroclastic-flow deposits during that interval. After that, we provide a follow-up to the 27 October 2010 eruption (BGVN 35:11), adding some previously unmentioned details. That eruption destroyed the dome's SE sector and generated pyroclastic flows.
During December 2010-March 2011, KVERT reported that Shiveluch both underwent moderate seismicity and emitted bright thermal anomalies conspicuous in satellite imagery (figure 27). Details of significant explosions and ash plumes during that time appear on table 10. Figure 28 shows a photo with the distant skyline dominated by a long Shiveluch ash plume.
Table 10. An inexhaustive synopsis of significant plumes at Shiveluch visible on satellite imagery from December 2010 through 26 March 2011 (times and dates are UTC). Courtesy KVERT.
| Date | Comments |
| 03 Dec 2010 | Ash plumes drifted 322 km SE. |
| 14 Dec 2010 | Ash plume drifted 230 km NE, 2-km-long pyroclastic flow. |
| 23-24 Dec 2010 | Ash plumes rose to altitudes as high as 4.5 km |
| 02 Jan 2011 | Ash plumes rose to altitudes as high as 8 km and drifted 92 km S. |
| 18 Jan 2011 | Ash plumes rose to altitudes as high as 7 km and drifted W. |
| 26 Jan 2011 | Ash plume drifted 54 km S. |
| 31 Jan-1 Feb, 4 Feb 2011 | Ash plume drifted 120 km NE, E. Ash plumes rose 7.5 km |
| 23-24 Feb 2011 | Ash plumes altitudes below 6 km and drifted 220 km SE (figure 28). |
| 26-27 Feb 2011 | Ash plumes drifted over 140 km N. |
| 10, 16 Mar 2011 | Ash plumes drifted 312 km W, NW. |
| 18-20 Mar 2011 | Ash plumes drifted 373 km SE, N. |
| 26 Mar 2011 | Ash plumes drifted 57 km SE. |
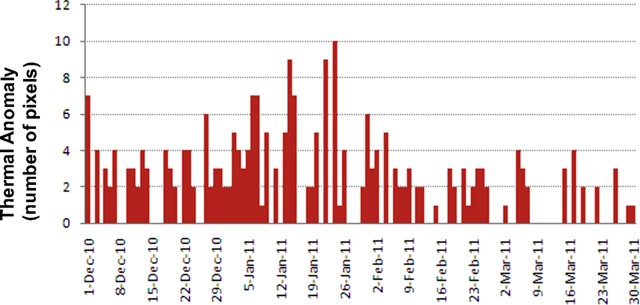 |
Figure 27. Satellite thermal anomalies recorded at Shiveluch during December 2010-March 2011. Data from KB GS RAS, with cooperation from Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO). |
More on the 27 October 2010PFs. As previously reported, an explosive eruption on 27 October 2010 (BGVN 35:11) vented at the dome and destroyed its SE portion, generating pyroclastic flows laden with many fragments of dome material (figure 29). The associated eruptive plume extended more than 1,500 km from the volcano. The pyroclastic flows traveled SSE in a radial direction, as far as 20 km from the source.
Near the dome, visiting scientists found agglomerate deposits of fragmental dome material spread widely down the SE slope. The character of the deposits was similar to debris avalanches, since so much dome material suddenly traveled down slope. The pyroclastic flow deposits retraced numerous upslope tributaries along the Kabeku River. The deposits filled small valleys and other low-lying areas, leveling landscapes that had prior to the eruption been rough (figure 30).
Figures 31a and b, satellite images, illustrate the trail of hot material descending to the S. They formed a large, complex, and widely distributed deposit following the recent collapse of the lava dome. A sub-circular area about ~4 km in diameter at about 9-14 km distance from the dome may reflect denser deposition (figure 31a). The images make clear that pyroclastic flow deposits descended yet farther, leaving dense, thermally radiant tracks over narrower valleys trending to the SE. The images are from ASTER (Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer). Figure 31b shows the flow's heat signature as measured in thermal infrared energy. The white area at the lava dome was very hot, while the red areas on the edge of the flow were merely warmer than the surrounding snow.
Fieldwork in the distal area revealed that the most powerful pyroclastic flow went into the headwaters of two narrow valleys, then merged into a single stream down into the Kabeku Valley river almost to its confluence with the Bekesh river (5 km N of the Kluchi-Ust'-Kamchatsk road, figures 32 and 33).
Water in the bed of the Bekesh river ran down the same path as thick pyroclastic flows and continued to be fed by melting snow on the upper slopes. Water also seeped through the loose pyroclastic flow deposit, resulting in large amounts of steam escaping at the surface in the form of fumaroles, degassing pipes, and zones of jetting emissions. This created the impression that the river water was boiling; on its surface rose a wall of steam (figure 34). Walking over the pyroclastic flow deposit was difficult and potentially dangerous, since the deposit's upper portion remained hot and gas saturated (figure 34b).
Reference. Ovsyannikov, A., Manevich, A., 2010, Eruption Shiveluch in October 2010, Bulletin of Kamchatka Regional Association (Educational-Scientific Center); Earth Sciences (in Russian), IV&S FEB RAS, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 2010, vol. 2, no. 16, ISSN 1816-5532 (Online).
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Institute Volcanolohy and Seismology Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FED RAS), Kamchatka Branch of the Geophysical Service, Russian Academy of Sciences (KB GS RAS) (URL: http://www.emsd.iks.ru/index-e.php). 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/); Y. Demyanchuk, A. Ovsyannikov, A. Manevich (IVS FED RAS); Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO), a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, 4200 University Drive, Anchorage, AK 99508-4667, USA (URL: http://www.avo.alaska.edu/); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Tokyo, Japan (URL: http://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/); NASA Earth Observatory (URL: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/).
Dome growth and volcanic activity continues
Background. A summary of Shiveluch volcano was included in a paper by Van Manen and others (2012). It noted that the activity of Shiveluch was predominantly characterized by dome formation accompanied by strong explosions (as described by Belousov and others, 1999). After 14 years of intense fumarolic activity, Shiveluch fed a Plinian eruption accompanied by large-scale edifice failure on 11 November 1964 (Gorshkov and Dubik, 1970). Since 1964, at least 0.27 km3 of magma had been discharged from Shiveluch during three main phases: (1) 1980-1981, (2) 1993-1995 and (3) 2001-2004 (Dirksen and others, 2006). An additional phase of dome extrusion, accompanied by minor explosive activity that commenced in 2006, continued at least to January 2012. Each of these phases was associated with andesite dome growth punctuated by explosions.
A website by KVERT (Kamchatka Volcanic Eruption Response Team) (2013) shows several years of primarily ground-based photographs of plumes from Shiveluch volcano.
The Institute of Volcanology and Seismology website (2013) reported that Shiveluch is noted for its unusual rocks, close to adakites, likely indicating its position over the northern edge of the subducting Pacific plate, warmed by mantle flow (Volynets et al. 2000; Yogodzinski et al. 2001). It is one of the most prolific explosive centers of Kamchatka, with a magma discharge of ˜36x106 tons per year, an order of magnitude higher than that typical of island arc volcanoes (Melekestsev et al. 1991).
March 2011-May 2013. Our last issue on Shiveluch covered up to March 2011 (BGVN 36:04). Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, KVERT reported that from March 2011 through at least May 2013, explosive-extrusive-effusive eruption of the volcano continued. A viscous lava flow effused on the NW to E flanks of the lava dome, accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Satellite imagery showed a daily thermal anomaly on the lava dome when not obscured by clouds. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange except for a few days in October 2011.
In Table 11 we include several representative cases where possible plumes (steam and/or ash) of larger sizes were documented during the last 2 years. Measurements were made by ground observers or from satellite images; in many cases, cloud cover over several weeks or months presumably excluded observations. In addition, the KVERT reports contain many unexplained time gaps for description of the plume.
Table 11. Representative cases of occurrence of reported possible plume altitude in excess of 8 km and/or plume drift greater than 100 km during the period March 2011-June 2013; "nr" = not reported. It should be noted that the distances based on observations are probably accurate to no more than ˜1-2 km. International flights were rerouted on 28-31 August 2011. The Aviation Color code was raised to Red, then lowered to Orange during 3-8 October 2011. Courtesy of KVERT and Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC).
| Date(s) | Plume altitude | Plume drift (km)/direction | Comments |
| 11-18 Mar 11 | 3.8-8 km | 312 km/W and NW | -- |
| 18-20 Mar 11 | 5.8 km | 373 km/SE and N | -- |
| 1-5 Apr 11 | 7.5 km | 187 km | -- |
| 22-27 Apr 11 | 6.7 km | 153 km/N; 400 km/SE | -- |
| 1 May 11 | 4.5 km | 124 km/NE | -- |
| 5-7 May 11 | 3-7.5 km | 196 km/N | -- |
| 29-31 May 11 | 7.6-10 km | 1,000 km/S-SW | -- |
| 4-6 Jun 11 | 6.1-9.1 km | 734 km/SE | -- |
| 15 Jun 11 | 10 km | 26 km/NW | -- |
| 19-21 Jun 11 | 10 km | 176 km/nr | -- |
| 23 Aug 11 | 8.2 km | nr/nr | -- |
| 28-31 Aug 11 | 6.1-8.6 km | nr/E and NE | International flights rerouted |
| 11 Sep 11 | 10.3 km | nr/nr | -- |
| 3-8 Oct 11 | 6-9 km | 160 km/NE | Aviation Color Code raised to Red, then lowered to Orange |
| 13-18 Oct 11 | 8-10.5 km | 75 km/E | -- |
| 21-25 Oct 11 | 7.1-10.6 km | 170 km/SE | -- |
| 25-28 Mar 12 | 7 km | 192 km/E and SE | -- |
| 29 Mar-3 Apr 12 | 6.6 km | 114 km/W,E, and NE | -- |
| 14-18 Apr 12 | 4-7.5 km | 120 km/N, NE, and E | -- |
| 24 Apr 12 | 10 km | 396 km/NE | -- |
| 1 May 12 | 5 km | 270 km/NE | -- |
| 5 May 12 | 10 km | 800 km/SE | -- |
| 12 May 12 | 8 km | 800 km/E | -- |
| 19-20 May 12 | 9.1-9.5 km | 410 km/SW | -- |
| 25-30 May 12 | 9 km | 555 km/SW, SE, and E | -- |
| 2 Jun 12 | 9.1 km | 250 km/S | -- |
| 5-6 Jun 12 | 8-8.2 km | nr/nr | -- |
| 15 Jun 12 | 8.2 km | nr/nr | -- |
| 24 Jun 12 | 5.2-9.8 km | nr/nr | -- |
| 27 Jul 12 | 10.1 km | nr/nr | -- |
| 6-11 Apr 12 | 7.7 km | 210 km/SW and SE | -- |
| 18-20 Sep 12 | 8 km | 2,000 km/SE | -- |
| 4-6 Oct 12 | 6-7 km | 360 km/SE | -- |
| 4-6 Mar 13 | 7-9 km | 200 km/SE | -- |
| 10 Jun 13 | 7-8 km | nr/nr | -- |
As shown on the table, on 5 October 2011, KVERT reported that the current Aviation Color Code for Shiveluch was Red. Activity of the volcano began to increase from 3 October. Ash plumes rose up to 6.0-9.0 km on 3-5 October. According to visual data, a bright incandesce of the lava dome was observed over several hours. Satellite data showed a large thermal anomaly over the lava dome, and strong explosive events could occur in near time. On 6 October 2011, the Aviation Color Code was reduced to Orange. Explosive-extrusive eruption of the volcano continued. New lava extruded at the lava dome after strong explosions on 3-5 October, and moderate seismic activity of the volcano continued. On 5-6 October, ash plumes rose up to 4.5-5.0 km. Ash plumes drifted to the NE from the volcano. Satellite images showed that the large thermal anomaly continued over the lava dome.
A rather interesting pair of satellite images were collected on 6 October 2012 (figure 35). The first image image captured Shiveluch just before an exuption; the second, 2 hours later, showed an eruption plume drifting away from the volcano. The MODVOLC Hot Spots web site showing Modis satellite thermal alerts measured no alert during this 6 October event.
On 4 March 2013, a single explosion ejected an ash plume up to 7 km. Strong collapses of hot avalanches from the lava dome occurred on 6 March, and resulting ash plumes rose up to 5 km and extended about 200 km SE of the volcano. An explosion on 5 April observed by video generated an ash plume that rose to altitudes of 5.5-6 km (figure 36).
References: Belousov, A.B., 1995, The Shiveluch volcanic eruption of 12 November 1964-explosive eruption provoked by failure of the edifice, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 66, pp. 357-365.
Belousov, A., Belousova, M., and Voight, B., 1999, Multiple edifice failures, debris avalanches and associated eruptions in the Holocene history of Shiveluch volcano, Kamchatka, Russia, Bulletin of Volcanology, v. 61, no. 5, pp. 324-342.
Dirksen, O., Humphreys, M.C.S., Pletchov, P., Melnik, O., Demyanchuk, Y., Sparks, R.S.J., and Mahony, S., 2006, The 2001-2004 dome-forming eruption of Shiveluch volcano, Kamchatka: observation, petrological investigation and numerical modelling, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, v. 155, issue 3-4, pp. 201-226.
Gorshkov, G.S. and Dubik, Y.M., 1970, Gigantic directed blast as Shiveluch volcano (Kamchatka), Bulletin of Volcanology, v. 34, no. 1, pp. 261-288.
Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, 2013, Holocene Kamchatka volcanoes - Shiveluch, Global Volcanism Program number 1000-27, Kamchatka, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/volcanoes/holocene/main/textpage/shiveluch.htm ).
KVERT, 2013, Current activity of the volcanoes, (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/current_eng.php?pageNum_img=1&name=Sheveluch ).
Melekestsev, I.V., Volynets, O.N., Ermakov, V.A., Kirsanova, T.P., and Masurenkov, Yu.P., 1991, Shiveluch volcano. In: Fedotov, S.A., and Masurenkov, Yu.P. (eds) Active volcanoes of Kamchatka. V. 1. Nauka, Moscow, pp 84-92 [in Russian, summary in English].
Ponomareva, V.V., Pevzne,r M.M., and Melekestsev, I.V., 1998, Large debris avalanches and associated eruptions in the Holocene eruptive history of Shiveluch volcano, Kamchatka, Russia. Bulletin of Volcanology, v. 59, no. 7, pp. 490-505.
van Manen, S.M., Blake, S., and Dehn, J., 2012, Satellite thermal infrared data of Shiveluch, Kliuchevskoi, and Karymsky, 1993-2008: effusion, explosions and the potential to forecast ash plumes, Bulletin of Volcanology, v. 74, pp. 1313-1335 (DOI 10.1007/s00445-012-0599-8).
Volynets, O.N., Babanskii, A.D., and Gol'tsman, Y.V., 2000, Variations in isotopic and trace-element composition of lavas from volcanoes of the Northern group, Kamchatka, in relation to specific features of subduction, Geochemistry International. v. 38, no. 10, pp. 974-989.
Yogodzinski, G.M., Lees, J.M., Churikova, T.G., Dorendorf, F., Woerner, G., and Volynets, O.N., 2001, Geochemical evidence for the melting of subducting oceanic lithosphere at plate edges, Nature, v. 409, 25 January, pp. 500-504.
Information Contacts: Kamchatkan Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT) (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/index_eng.php); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC); NASA Earth Observatory (URL: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=80830).
Ongoing eruption with ash plumes to 11 km through August 2014
Sheveluch has been frequently active since 1980, remaining so through at least August 2014. Activity has included strong explosions that have ejected ash plumes high into the atmosphere, hot avalanches, lava flows, incandescence, fumarolic activity, and cycles of lava dome growth and destruction. Our previous report (BGVN 38:04) described activity through May 2013; this report summarizes subsequent activity through August 2014.
Based on visual observations and analyses of satellite data, the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT) reported that from 31 May 2013 through August 2014, viscous lava continued to contribute to lava-dome growth which was accompanied by hot avalanches, incandescence, and fumarolic activity. Most weeks a thermal anomaly was detected on the lava dome. The lava flow direction varied between the NW, N, and NE flanks during May-mid-November 2013. During 22-29 November the flow from a new lava dome shifted to the NW flank of the older dome and continued through February 2014. During 4-11 April, the flow moved to the SE flank of the new dome. Ashfall and pyroclastic flows near the summit could be seen in satellite imagery on 31 January 2014 (figure 37). Some of the tallest reported plumes ejected ash to altitudes as high as 10-12 km (table 12).
Table 12. Notable explosive activity at Sheveluch compiled from KVERT and Tokyo VAAC reports, June 2013-August 2014. VAAC data were based on analyses of satellite imagery, notices from Yelizovo Airport (UHPP) and the Kamchatka Branch of Geophysical Services (KBGS; Russian Academy of Sciences). Explosions that ejected plumes to under 4 km altitude or were unverified (i.e., possible or uncertain cases) were omitted.
| Dates | Event | Ash plume altitude (km)/ drift distance and direction | Remarks |
| 10 Jun 2013 | Explosion (6.5 min) | 8 | -- |
| 22 Jun 2013 | Two explosions; first (4 min) | 6 / NW | -- |
| 27 Jun 2013 | Strong explosions 0710-0800 | 10-12 / SE, SW | Aviation Color Code raised to Red, lowered to Orange later that day. ~2 mm ash deposits in Klyuchi, 50 km SW; ashfall also in Lazo village to the SW. |
| 28 Jun 2013 | Two explosions | 6-7 | -- |
| 29-30 Jun 2013 | -- | 5.5-6.4 / E, SE | -- |
| 26 Jul 2013 | Strong explosion | 10 / 520 km SE | -- |
| 29 Jul 2013 | Explosions | 6.1-6.4 | -- |
| 05 Aug 2013 | Explosion | 6.5-7 / 50 km ESE | -- |
| 10-11 Aug 2013 | -- | 7-7.5 | -- |
| 09-17 Aug 2013 | -- | 5-7 / E, NE | -- |
| 18 Oct 2013 | Several explosions and plumes during 1506-1759 | 9-10 / SE | Aviation Color Code raised to Red for a few hours. Lava dome continued to grow. |
| 30 Oct-05 Nov 2013 | Several strong explosions | 7-10 / 200 km NE | -- |
| 01-08 Nov 2013 | Several strong explosions | 7 / 290 km SE | -- |
| 08-15 Nov 2013 | Several strong explosions | 7 | -- |
| 22-29 Nov 2013 | Moderate explosions | -- | New lava dome extruded onto NW part of older lava dome. |
| 03 Dec 2013 | Strong explosion | 8-9 / NW, 200 km N | Continuous hot avalanches, pyroclastic flows on SW and NW flanks. Color Code raised to Red for a few hours. Ashfall in Ivashka village. |
| 29 Nov-31 Dec 2013 | Moderate explosions | -- | New lava-dome extrusion continued. |
| 10 Jan 2014 | Moderate explosions | 6 / 110 km ENE | -- |
| 12-13 Jan 2014 | Strong explosions | 7-9 / ESE, 50 km WSW, 400 km SW | New lava dome extrusion continued. Minor ashfall in Klyuchi village, 50 km SW. |
| 20-22 Jan 2014 | -- | 7-8/300 km WNW | -- |
| 23 Jan 2014 | -- | 7-8/N | -- |
| 06-07 Feb 2014 | Large explosion | 9-10 | Satellite image showed large ash cloud (240 x 180 km) over Sea of Okhotsk, 320 km WNW, at 4-5 km altitude. Pyroclastic flow on SW flank, 12 km long. |
| 13 May 2014 | -- | 7-9.5 / 60-90 km NW | -- |
| 26-27 May 2014 | Explosion | 3-10 / 850 km S; 800 km SSE | -- |
| 30 Jun 2014 | -- | 7 | -- |
| 05-08 Jul 2014 | -- | 11 | -- |
| 18 Jul 2014 | Explosion | 8.2 | -- |
| 09 Aug 2014 | -- | 4.6 | -- |
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), Tokyo, Japan (URL: http://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/); NASA Earth Observatory (URL: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=8303).
Ongoing strong explosions and ash plumes during September 2014-February 2015
An eruption at Sheveluch has been ongoing since 1999, and the activity there was previously described through August 2014 (BGVN 39:08). During 1 September 2014-28 February 2015 the same type of activity prevailed, with periods of strong explosions producing ash plumes as high as 11 km altitude. Most of the following data comes from Kamchatka Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT) reports. Views of the volcano are often obscured by clouds.
KVERT reported that the explosive and effusive eruption continued into September 2014 through at least the end of February 2015. Activity was dominated by lava dome growth on the SE flank (N flank after mid-September), moderate ash explosions, fumarolic activity, and hot avalanches. According to KVERT, satellite data showed a thermal anomaly over the dome most days, when weather permitted observation. However, few MODVOLC alerts about MODIS thermal anomalies were recorded during the reporting period: two in September 2014, one in November, one in December, three in January 2015, and two in February.
Occasional strong explosions were reported by KVERT that produced ash plumes that rose as high as 11.5 km and drifted mostly in a northerly and easterly direction (NW to E). Strong explosions were recorded 2-3 times per month during September-November 2014, and about seven times per month during December 2014-February 2015. The Alert Level remained Orange (second highest) throughout the reporting period, except on 24 September, when it was briefly raised to Red due to strong explosions at 1238 that generated a large ash plume (207 x 250 km) that rose 11-11.5 km (figure 38); the Alert Level was lowered back to Orange that same day as the explosive activity subsided.
In addition to the above activity, KVERT recorded a small pyroclastic flow on 7 January 2015 that descended the SE flank of the dome. Ashfall was reported in Klyuchi Village (50 km SW) on 12 January and in in Ust-Kamchatsk (85 km SE) on 4 March.
According to a news article (CNN), strong explosions on 28 February 2015 blew ash plumes across the Bering Sea into western Alaska and caused Alaska Airlines to cancel several flights. The article also indicated that an airlines spokesman mentioned that a similar cancellation had occurred in January.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, (IVS FEB RAS), 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/eng/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP), MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Cable News Network (CNN), Turner Broadcasting System, Inc. (URL: http://www.cnn.com/).
Dome extrusion, hot block avalanches, and strong explosions continue through August 2015
An eruption at Sheveluch has been ongoing since 1999, and the activity there was previously described through February 2015 (BGVN 42:01). During March-August 2015, the same type of activity prevailed, with lava dome extrusion, incandescence, hot block avalanches, fumarolic activity, and occasional strong explosions that generated ash plumes. Most of the following data comes from Kamchatka Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT) reports. During this period the Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
KVERT reported that during 27 February-15 May 2015, lava-dome extrusion onto the N flank continued to be accompanied by incandescence, hot block avalanches, and fumarolic activity. This activity diminished somewhat during 22 May-14 July, when lava-dome extrusion was accompanied only by fumarolic activity. However, heightened activity resumed during 15 July-31 August, when KVERT reported that lava-dome extrusion was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and hot avalanches.
Between 28 February and the middle of April 2015, strong explosions generated ash plumes that rose to 7-12 km altitude. Ash drifted as much as 885 km in various directions, and ash fell in Ust-Kamchatsk (85 km SE) at least twice in March. Based on KVERT reports, ash plumes on 15 June and 5-6 July only rose as high as 3.3-5 km in altitude.
A daily thermal anomaly was detected 27 February-15 May, except when cloud cover obscured views. During 16-30 May, thermal anomalies were only detected occasionally in satellite images, but became more frequent thereafter, depending on cloud cover. KVERT reported that during 10 July-31 August, satellite images again detected an almost daily thermal anomaly over the dome.
Thermal anomalies based on MODIS satellite instruments analyzed using the MODVOLC algorithm were infrequent during the reporting period, in contrast to the almost daily hotspots reported by KVERT. One hotspot was detected in March, April, and June, none in May, four in July, and eight in August.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP), MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/).
Lava dome extrusion continues with occasional explosions and ash plumes through February 2016
An eruption at Sheveluch has been ongoing since 1999, and recent activity there was previously described through August 2015 (BGVN 42:02). During September 2015-February 2016, the same type of activity prevailed, with lava dome extrusion, incandescence, hot block avalanches, fumarolic activity, and occasional strong explosions that generated ash plumes. The following data comes from Kamchatka Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT) reports. During this period the Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
KVERT reported that during 1 September 2015-28 February 2016, lava-dome extrusion onto the N flank was accompanied by fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, hot avalanches, and ash explosions. Satellite images detected an almost daily, and sometimes intense, thermal anomaly over the dome. Ash plumes generated by occasional explosions, hot avalanches, and sometimes strong winds rose to altitudes of 2.5-7 km and drifted primarily SE during September-December 2015 (up to 185 km) and in more variable directions (up to 200 km) during January-March 2016. A series of photos taken in late 2015 shows characteristic types of activity, including small explosions and hot avalanches on 28 October (figure 39), an explosion and pyroclastic flow on 22 November (figure 40), and incandescence on 25 November (figure 41).
Thermal anomalies based on MODIS satellite instruments analyzed using the MODVOLC algorithm were frequent during the current reporting period, in contrast to March-August 2015 (BGVN 42:02). From September 2015-February 2016, thermal anomalies were detected 10-15 days each month. On 22 November, seven pixels were recorded.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS), 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/eng/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP), MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/).
Ash explosions, pyroclastic flows, and lava dome growth continues through July 2017
An eruption at Sheveluch has been ongoing since 1999, and recent activity there was previously described through February 2016 (BGVN 42:03). During March 2016-July 2017, the same type of activity prevailed as before, consisting of lava dome growth, explosions, and pyroclastic flows. The following data comes from Kamchatka Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT) reports. During this period the Aviation Color Code (ACC) remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale), except for a brief period on 10 December 2016 and brief periods during May-July 2017 when it was Red (highest level).
Activity during March 2016-April 2017. According to KVERT, ongoing activity during March 2016-April 2017 consisted of lava-dome extrusion onto the N flank accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, ash explosions, and hot avalanches. Satellite images detected an intense daily thermal anomaly over the dome.
On 18 September 2016, a moderate explosion caused dome collapse and 10-km-long pyroclastic flows. Pyroclastic-flow deposits were noted in the Baydarnaya (also spelled Baidarnaya) River valley to the SSW and in the central part of the S flank.
Ash plumes generated by explosions and re-suspended ash usually occurred several times per month, and generally reached altitudes of 4.5-7 km. On 10 December 2016, explosions generated ash plumes observed in satellite images that rose to altitudes of 10-11 km and drifted 910 km NNE. The ACC was raised to Red. By the following day, no further ash emissions were observed, and the ACC was lowered back to Orange. However, explosions continued in December that sent ash plumes as high as 7 km altitude (figure 42). Typical activity continued through the first few months of 2017, including ash explosions sending plumes to as high as 5-6 km altitude (figure 43) that remained visible in satellite imagery 100 km downwind.
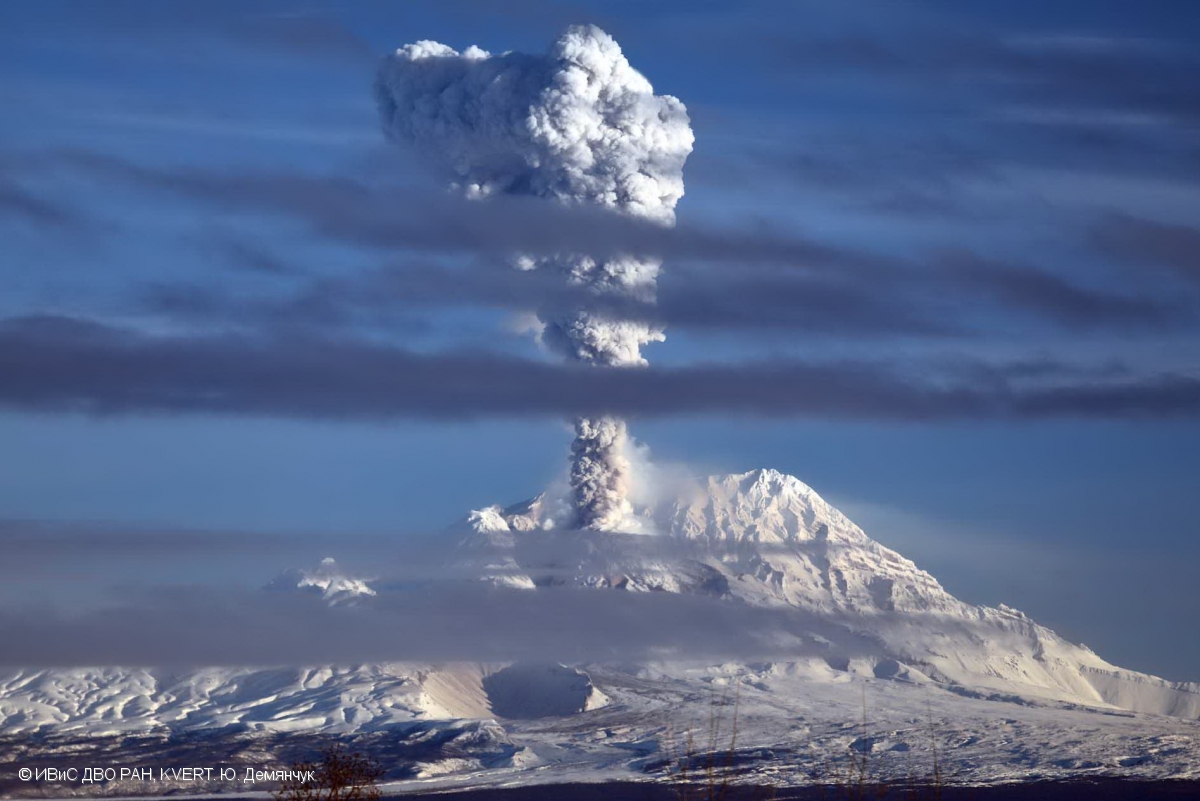 |
Figure 42. Explosions from Sheveluch sent ash up to 7 km altitude at 2314 UTC on 19 December 2016. Photo by Yu. Demyanchuk; courtesy of Institute of Volcanology and Seismology FEB RAS, KVERT. |
Activity during May-July 2017. Beginning In May 2017, explosive activity appeared to intensify. Strong explosions on 12 May 2017 generated ash plumes identified in satellite images that rose to altitudes of 9-10 km, spread 70 km wide, and drifted 115 km NW. The ACC was raised to Red. Pyroclastic flows descended the flanks and produced ash plumes that rose 3.5-4 km and drifted NE. A few hours later, satellite images showed a thermal anomaly but no ash emissions, and the ACC was lowered back to Orange.
According to KVERT, after a series of explosions during 13-14 May (figure 44), powerful explosions on 16 May generated ash plumes that rose 8-11 km in altitude, prompting an increase of the ACC to Red. Pyroclastic flows descended the S flank, producing ash plumes that rose 3.5-4 km in altitude (figure 43) and drifted NE; within a few hours, satellite images did not show any ash emissions; the ACC was lowered to Orange.
Additional explosions occurred 18 May. During 23-25 May 2017 powerful explosions generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 8 km and drifted 715 km in different directions. On 25 May, at 0830, explosions generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 9-10 km and drifted 16 km NE. The ACC was raised briefly to Red. Within the next 90 minutes, the ash plume was identified in satellite images drifting 82 km ENE. Strong steam-and-gas emissions rose from the lava dome. The ACC was lowered back to Orange.
KVERT reported that during the last week of May and first half of June, powerful explosions generated ash plumes that rose 8 km in altitude and drifted 550-1,554 km in various directions. Pyroclastic flows traveled 10 km. Ashfall was reported in Klyuchi Village (50 km SW) on 8 June.
On 15 June, at 0425, powerful explosions generated ash plumes that rose as high as 12 km altitude (figure 45). The ACC was raised to Red, and then back down to Orange by the end of the day. Ash plumes drifted 1,000 km NE and SW during 15-16 June. Ash fell in Klyuchi (50 km SW), Maiskoe, Kozyrevsk (115 km SW), and Atlasovo (160 km SW).
According to KVERT, explosions on 17, 18, and 27 June generated ash plumes that rose as high as 7-10 km altitude and drifted as far as 1,500 km. Explosions on 2 July sent ash plumes to 10-11 km; one plume drifted 1,050 km SW and another drifted 350 km NE. On 23 July, strong explosions generated ash plumes that sailed up to 11-12 km and drifted 1,400 km E. Explosive activity the next day lasted about 8 hours and generated ash plumes that rose 11.5-12 km in altitude and drifted almost 700 km NE and 1,400 km E. Strong pyroclastic flows were also noted. The ACC was raised to Red. Later that day, only steam-and-gas emissions with a small amount of ash was observed, and the ACC was lowered to Orange.
Thermal anomalies. Thermal anomalies based on MODIS satellite instruments analyzed using the MODVOLC algorithm were frequent during the current reporting period. From 1 March to 31 August 2016 thermal anomalies were detected 11-20 days each month. The number of days each month with anomalies was lower during 1 September 2016 to 30 July 2017 (except for October with 13 days), ranging from 3 days in April and May 2017 to 10 days in March. Only one hotspot was recorded in July 2017. The MIROVA system detected numerous hotspots every month during August 2016-July 2017, most of which were about 5 km or less from the summit with very low power signatures.
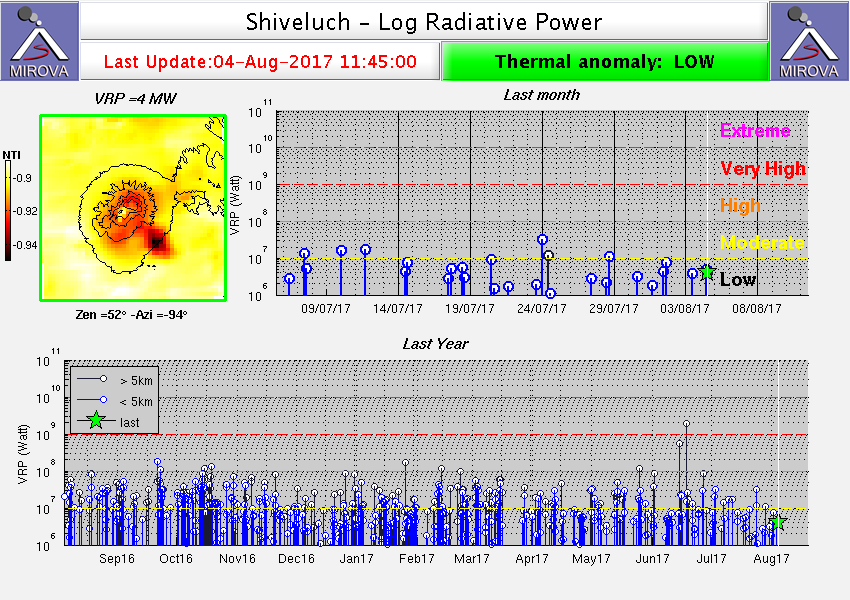 |
Figure 46. Thermal anomalies at Sheveluch identified on MODIS data by the MIROVA system (log radiative power) for the year ending 4 August 2017. Courtesy of MIROVA. |
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS), 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/eng/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/).
Ash explosions, pyroclastic flows, and lava dome growth continue through January 2018
An eruption at Sheveluch has been ongoing since 1999, and volcanic activity was previously described through August 2017 (BGVN 42:08). Ongoing activity consists of pyroclastic flows, explosions, and lava dome growth with a viscous lava flow in the N. Strong fumarole activity, ash explosions, hot avalanches and incandescence from the dome accompany this process. Explosions and ash flows were reported by Kamchatka Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT) during the August 2017 through January 2018 period.
During this report period the Aviation Color Code (ACC) remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale), except for 10 January 2018 when it was briefly elevated to Red (highest level) and lowered back to Orange later the same day. Satellite infrared data also showed increased activity on this day. Ash plume altitudes ranged from a low of 5 km to a high of 11 km on 10 January 2018. The farthest lateral extent of the ash plume was reported at 990 km to the NE on 8 November 2017.
On 4 and 8 August 2017 large ash clouds reached altitudes of 6.5 km and approximately 10 km, respectively. Ashfall was reported in Klyuchi Village (50 km SW) on 8 August and drifted about 180 km E, NW, and NE during 12 and 15-16 August. On 7 September ash plumes rose to 8-10 km altitude and drifted NE, SE, and S; another ash plume was photographed on 8 September (figure 47). On 15-22 September ash plumes rose to 9-10 km altitude and drifted about 400 km NW, E, and SE. Explosions on 10 October generated ash plumes to 10 km altitude and drifted about 250 km N (figure 48). Plumes comprised of re-suspended ash drifted about 350 km SE on 12 October and about 230 km SE on 13 October.
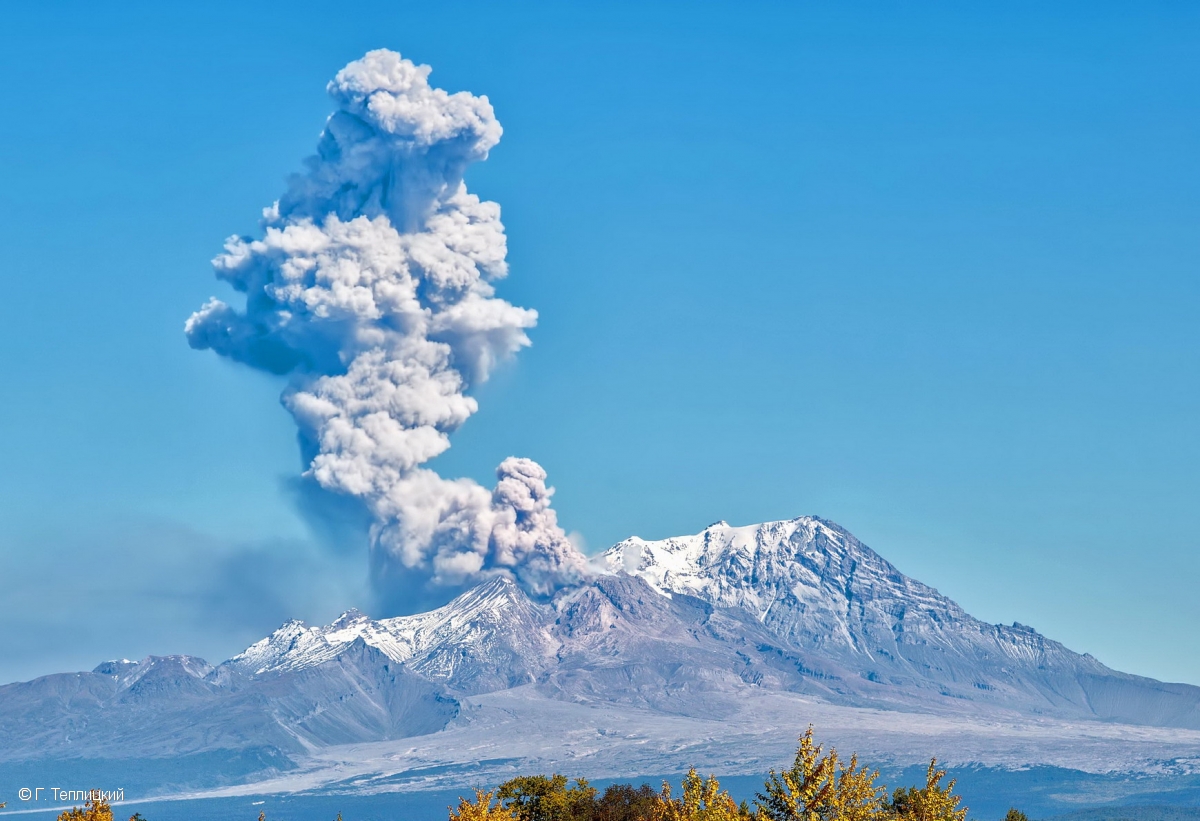 |
Figure 47. Photo of an ash cloud from Sheveluch generated by an explosion on 8 September 2017. Photo by G. Teplitsky; courtesy of the Institute of Volcanology and Seismology FEB RAS, KVERT. |
 |
Figure 48. Explosions from Sheveluch sent ash up to 10 km altitude on 10 October 2017. Photo from a webcam, courtesy of the Institute of Volcanology and Seismology FEB RAS, KVERT. |
Explosions on 2 and 8 November generated ash plumes that rose to an altitude of 8 km and drifted approximately 990 km NE. Weather prevented observations on the other days from 4-10, 12-17, and 19-24 November. A strong explosive event on 5 December generated ash plumes that rose to altitudes of 10.5 km and 5 km and drifted NE and E, respectively. Explosions on 26 December generated an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 8 km and drifted about 300 km NE.
On 10 January 2018 satellite images captured an ash cloud with a dimension of 192 x 132 km drifting 230 km NE from explosions rising to altitudes of 10-11 km. In response, KVERT raised the ACC to Red. Later that same day, satellite images showed the ash cloud expanded to 350 x 180 km in dimension and had drifted 400 km E; the ACC was lowered back to Orange. The 10 January explosions began at 1035 with resulting ash that drifted about 900 km E during 10-11 January.
Thermal anomalies. As reported by KVERT, satellite imagery continue to detect the existence of a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch. The anomaly was reported on 10-30 days every month from August 2017 through January 2018. Detections of the thermal anomaly were lower in certain months because cloudy conditions obscured satellite imagery. The MIROVA system detected numerous hotspots every month during August 2017-January 2018, most of which were about 5 km or less from the summit with mainly low to a few high power signatures in August, September 2017 and January 2018. Thermal anomalies based on MODIS satellite instruments analyzed using the MODVOLC algorithm were detected in 11-12 August 2017 and 10 January 2018 corresponding to the explosive eruptions on those days.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS), 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/eng/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/).
Intermittent thermal anomalies along with gas and steam emissions continue through April 2018
An eruption at Sheveluch has been ongoing since 1999, and volcanic activity was previously described through January 2018 (BGVN 43:02). Ongoing activity has consisted of pyroclastic flows, explosions, and lava dome growth with a viscous lava flow in the N. According to the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT), moderate emissions of gas-and-steam have continued, and ash explosions up to 10-15 km in altitude could occur at any time. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale) throughout this reporting period from February through April 2018.
KVERT reported continuous moderate gas-and-steam plumes from Sheveluch during February-April 2018 (figure 49). Satellite imagery interpreted by KVERT showed a thermal anomaly over the volcano on 13 days during February, 21 days in March, and 15 days in April. Cloud cover obscured satellite imagery the remainder of the time during this reporting period.
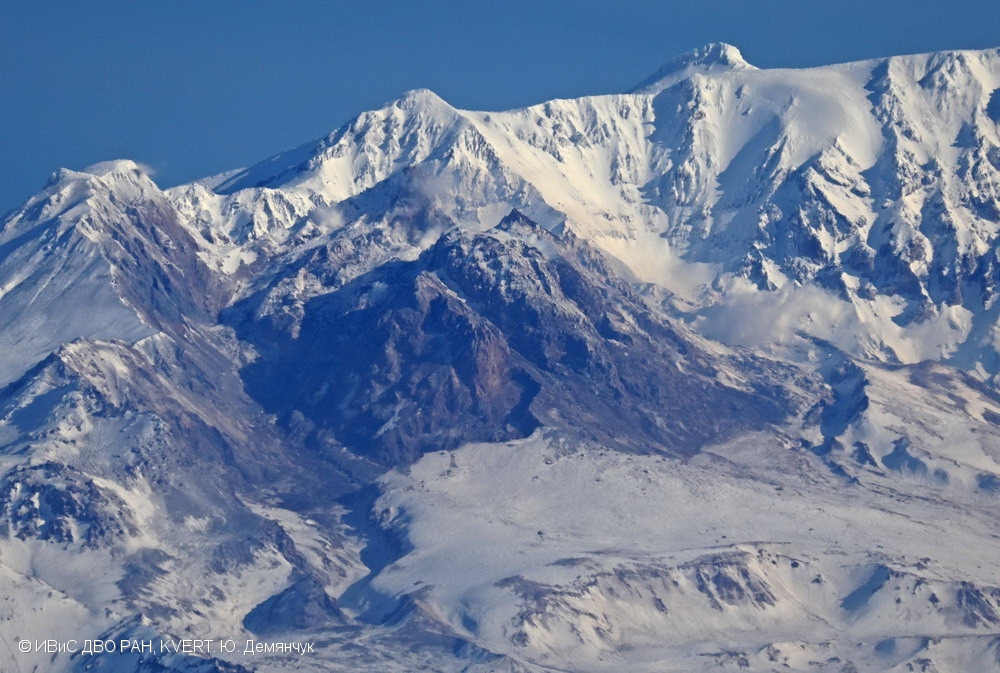 |
Figure 49. Photo of the lava dome at Sheveluch on 25 March 2018. Courtesy of Yu. Demyanchuk (IVS FEB RAS, KVERT). |
The MIROVA system detected intermittent low-power thermal anomalies from February through April 2018. Thermal anomalies, based on MODIS satellite instruments analyzed using the MODVOLC algorithm, were not detected during this period.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS), 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/eng/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/).
Thermal anomalies along with minor gas and steam emissions continue through October 2018
Volcanic activity at Sheveluch declined during the period of May through October 2018. This decline followed a lengthy cycle of eruptive activities which began in 1999, including pyroclastic flows, explosions, and lava dome growth, as previously reported through April 2018 (BGVN 43:05). According to the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruption Response Team (KVERT), during this time a thermal anomaly was detected in satellite imagery and two gas-and-steam events were reported in July and October 2018. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale).
KVERT reported that satellite data showed a plume of re-suspended ash up to 62 km to the SE of the volcano on 18 July 2018. Moderate gas and steam emissions rose from the volcano on 19-26 October 2018. Thermal anomalies were frequently reported by KVERT during May through October 2018. The MIROVA system detected intermittent low-power thermal anomalies during this time.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far East Division, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/).
Renewed activity with lava dome growth and ash explosions starting in late December 2018
Volcanism at Sheveluch has been ongoing for the past 20 years. Previous activity consisted of pyroclastic flows, explosions, moderate gas-and-steam emissions, and lava dome growth, according to the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT). Between May 2018 and mid-December 2018 activity levels were low, with intermittent low-power thermal anomalies and gas-and-steam emissions. Activity increased in the second half of December 2018, remaining high through at least April 2019.
Activity intensified beginning in late December through April 2019, which included increased and more frequent thermal anomalies, according to KVERT and the MIROVA system (figure 50). On 30 December 2018, video data from KVERT showed explosions producing an ash cloud that rose up to 11 km altitude and drifted 244 km WSW and 35 km NE. Eruptive activity included incandescent lava flows and hot avalanches. The ash cloud that drifted WSW resulted in ashfall over Klyuchi Village (50 km SW) and Kozyrevsk (100 km SW).
Beginning in early January and going through April 2019, the lava dome at the northern part of the volcano continued to grow, extruding incandescent, viscous lava blocks (figure 51). Throughout these months, KVERT reported that satellite imagery and video data showed strong fumarolic activity, as well as strong gas-and-steam plumes containing some amount of ash; gas-and-steam plumes rose as high as 7 km. According to the KVERT Daily Reports on 3 and 4 January 2019, a gas-and-steam plume containing ash drifted NE up to about 600 and 400 km, respectively. Gas-and-steam plumes noted in the KVERT Daily Report, Weekly Releases, and Volcano Observatory Notice for Aviation (VONA), drifted 50-263 km in different directions. On 9 November 2018, the KVERT Daily Report recorded an ash plume drifting 461 km E from the volcano and on 26 December 2018, the KVERT Weekly Information Release recorded an ash cloud drifting 300 km NW. The KVERT Weekly Information Release reported that on 10 April 2019 an ash cloud drifted up to 1,300 km SE.
Thermal anomalies based on MODIS satellite instruments analyzed using the MODVOLC algorithm were frequent beginning on 28 December 2018. In just three days in late December (28-31 December 2018) there were 34 thermal alerts. Hotspots were detected 21-27 days each month between January-April 2019. A majority of these hotspot pixels occurred within the summit crater.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS), 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/eng/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/).
Frequent ash explosions and lava dome growth continue through October 2019
After a lull in activity at Sheveluch, levels intensified again in mid-December 2018 and remained high through April 2019, with lava dome growth, strong explosions that produced ash plumes, incandescent lava flows, hot avalanches, numerous thermal anomalies, and strong fumarolic activity (BGVN 44:05). This report summarizes activity between May and October 2019. The volcano is monitored by the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT).
According to KVERT, explosive activity continued to generate ash plumes during May-October 2019 (table 13). Strong fumarolic activity, incandescence and growth of the lava dome, and hot avalanches accompanied this process. There were also reports of plumes caused by re-suspended ash rather than new explosions. Plumes frequently extended a few hundred kilometers downwind, with the longest ones remaining visible in imagery as much as 1,000-1,400 km away. One of the larger explosions, on 1 October (figure 52), also generated a pyroclastic flow. Some of the stronger explosions sent the plume to an altitude of 10-11 km, or more than 7 km above the summit. The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale) throughout the reporting period, except for several hours on 6 October when it was raised to Red (the highest level).
Table 13. Explosions and ash plumes at Sheveluch during May-October 2019. Dates and times are UTC, not local. Data courtesy of KVERT.
| Dates | Plume altitude (km) | Drift Distance and Direction | Remarks |
| 30 Apr-02 May 2019 | -- | 200 km SE | Resuspended ash. |
| 03-10 May 2019 | -- | 50 km SE, SW | Gas-and-steam plumes containing some ash. |
| 13 May 2019 | -- | 16 km SE | Resuspended ash. |
| 11-12 Jun 2019 | -- | 60 km WNW | Explosions and hot avalanches seen in video and satellite images. |
| 24, 27 Jun 2019 | 4.5 E, W | Ash plumes. | |
| 05 Aug 2019 | 2.5 | 40 km NW | Diffuse ash plume. |
| 25 Aug 2019 | 4.5-5 | 500 km NW | Ash plumes. |
| 29 Aug 2019 | 10 | Various; 550 km N | Explosions at 1510 produced ash plumes. |
| 30 Aug 2019 | 7-7.5 | 50 km SSE | Explosions at 1957 produced ash plumes. |
| 03 Sep 2019 | 5.5 | SE | -- |
| 02-03, 05 Sep 2019 | 10 | 660 km SE | Ash plumes seen in satellite images. |
| 05 Sep 2019 | -- | -- | Resuspended ash. |
| 11-12 Sep 2019 | -- | 250 km ESE | Resuspended ash plumes. Satellite and webcam data recorded ash emissions and a gas-and-steam plume with some ash drifting 50 km ESE on 12 Sep. |
| 12-15, 17, 19 Sep 2019 | -- | 200 km SW, SE, NE | Ash plumes. |
| 20-21, 23, 26 Sep 2019 | 7 | 580 km ESE | Explosions produced ash plumes. |
| 29 Sep, 01-02 Oct 2019 | 9 | 1,400 km SE, E | Explosions produced ash plumes. Notable pyroclastic flow traveled SE on 1 Oct. |
| 04 Oct 2019 | -- | 170 km E | Resuspended ash. |
| 06 Oct 2019 | 10 | 430 km NE; 1,080 km ENE | Ash plumes. Aviation Color Code raised to Red for several hours. |
| 08 Oct 2019 | -- | 170 km E | Resuspended ash. |
| 06, 09 Oct 2019 | 6.5-11 | 1,100 km E | -- |
| 11-13, 15 Oct 2019 | 6.5-7 | 620 km E, SE | Explosions produced ash plumes. |
| 16-17 Oct 2019 | -- | 125 km E | Resuspended ash. |
| 19-20 Oct 2019 | -- | 110 km SE | Resuspended ash. |
| 21 Oct 2019 | 10-11 | 1,300 km SE | Explosions produced ash plumes. |
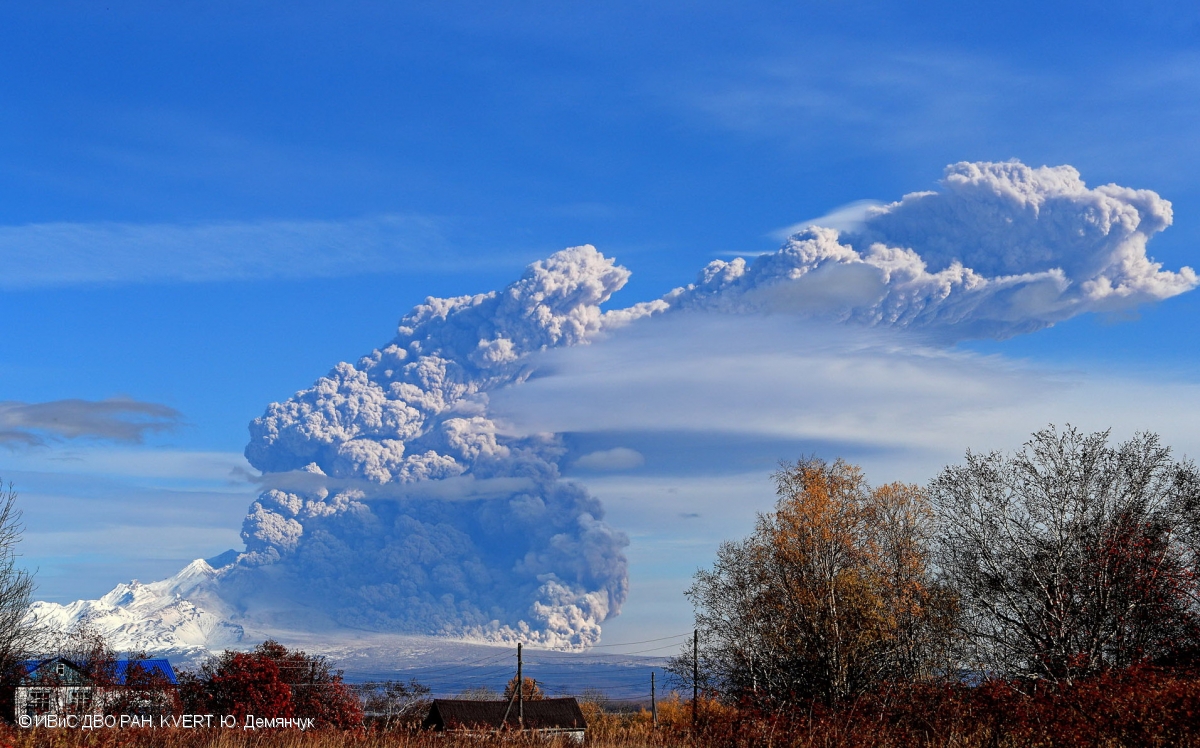 |
Figure 52. An explosion of Sheveluch on 1 October 2019. A pyroclastic flow was also reported by KVERT this day. Courtesy of Yu. Demyanchuk, IVS FEB RAS, KVERT. |
Numerous thermal anomalies, based on MODIS satellite instruments analyzed using the MODVOLC algorithm, were observed every month. Consistent with this, the MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) system recorded thermal anomalies almost daily. According to KVERT, a thermal anomaly over Sheveluch was identified in satellite images during the entire reporting period, although cloudy weather sometimes obscured observations.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS), 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/eng/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/).
Lava dome growth and thermal anomalies continue through April 2020, but few ash explosions
The eruption at Sheveluch has continued for more than 20 years, with strong explosions that have produced ash plumes, lava dome growth, hot avalanches, numerous thermal anomalies, and strong fumarolic activity (BGVN 44:05). During this time, there have been periods of greater or lesser activity. The most recent period of increased activity began in December 2018 and continued through October 2019 (BGVN 44:11). This report covers activity between November 2019 to April 2020, a period during which activity waned. The volcano is monitored by the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT) and Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC).
During the reporting period, KVERT noted that lava dome growth continued, accompanied by incandescence of the dome blocks and hot avalanches. Strong fumarolic activity was also present (figure 53). However, the overall eruption intensity waned. Ash plumes sometimes rose to 10 km altitude and drifted downwind over 600 km (table 14). The Aviation Color Code (ACC) remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale), except for 3 November when it was raised briefly to Red (the highest level).
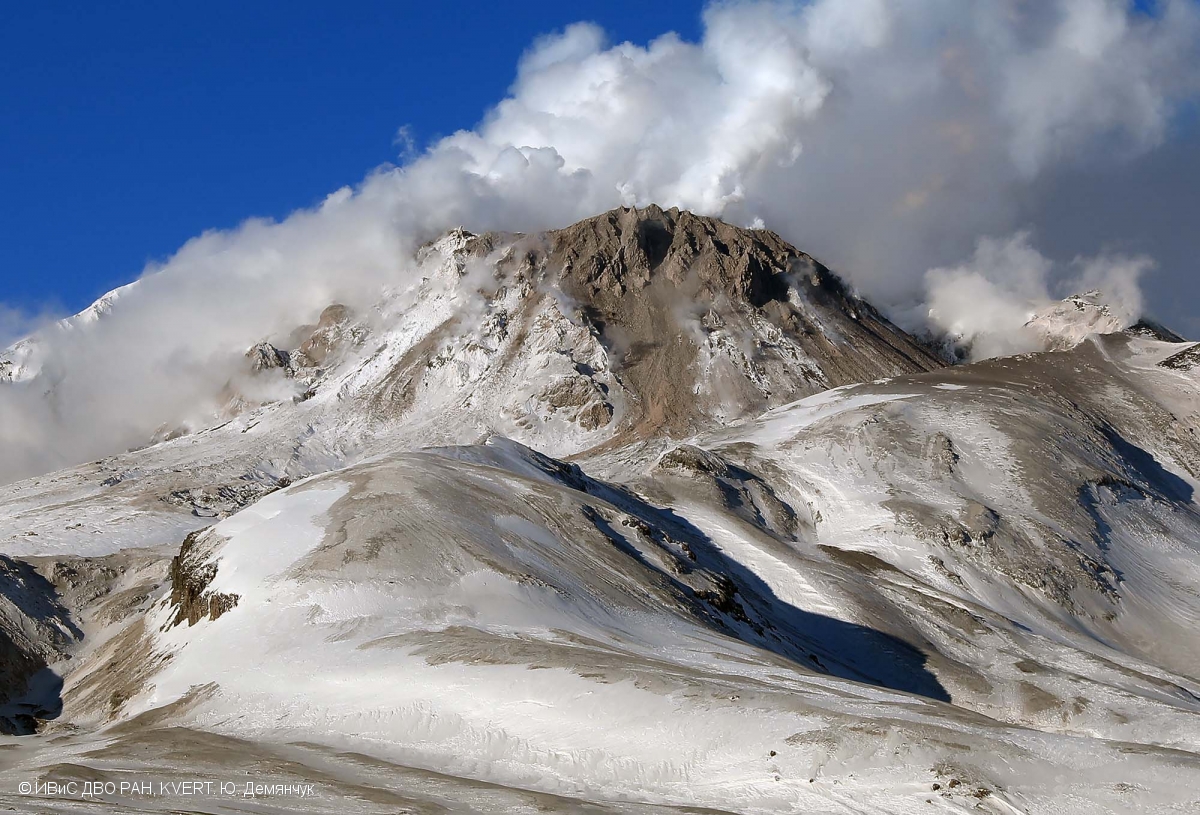 |
Figure 53. Fumarolic activity of Sheveluch’s lava dome on 24 January 2020. Photo by Y. Demyanchuk; courtesy of KVERT. |
Table 14. Explosions and ash plumes at Sheveluch during November 2019-April 2020. Dates and times are UTC, not local. Data courtesy of KVERT and the Tokyo VAAC.
| Dates | Plume Altitude (km) | Drift Distance and Direction | Remarks |
| 01-08 Nov 2019 | -- | 640 km NW | 3 November: ACC raised to Red from 0546-0718 UTC before returning to Orange. |
| 08-15 Nov 2019 | 9-10 | 1,300 km ESE | |
| 17-27 Dec 2019 | 6.0-6.5 | 25 km E | Explosions at about 23:50 UTC on 21 Dec. |
| 20-27 Mar 2020 | -- | 45 km N | 25 March: Gas-and-steam plume containing some ash. |
| 03-10 Apr 2020 | 10 km | 526 km SE | 8 April: Strong explosion at 1910 UTC. |
| 17-24 Apr 2020 | -- | 140 km NE | Re-suspended ash plume. |
KVERT reported thermal anomalies over the volcano every day, except for 25-26 January, when clouds obscured observations. During the reporting period, thermal anomalies, based on MODIS satellite instruments analyzed using the MODVOLC algorithm recorded hotspots on 10 days in November, 13 days in December, nine days in January, eight days in both February and March, and five days in April. The MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) volcano hotspot detection system, also based on analysis of MODIS data, detected numerous hotspots every month, almost all of which were of moderate radiative power (figure 54).
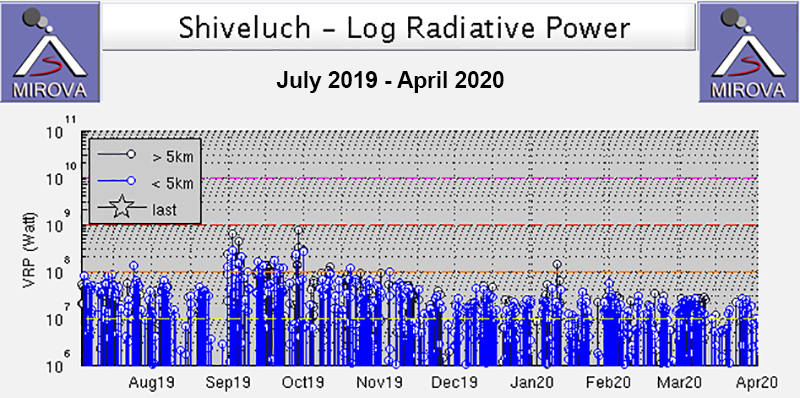 |
Figure 54. Thermal anomalies at Sheveluch continued at elevated levels during November 2019-April 2020, as seen on this MIROVA Log Radiative Power graph for July 2019-April 2020. Courtesy of MIROVA. |
High sulfur dioxide levels were occasionally recorded just above or in the close vicinity of Sheveluch by the TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) aboard the Copernicus Sentinel-5 Precursor satellite, but very little drift was observed.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS), 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/eng/); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), 1-3-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, Japan (URL: http://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Sentinel Hub Playground (URL: https://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/sentinel-playground); Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/).
New whaleback dome extruded in late September 2020; intermittent explosions
The ongoing eruption at Sheveluch continued during May-October 2020, characterized by lava dome growth, strong fumarolic activity, and several explosions that generated plumes of resuspended ash. Activity waned between November 2019 and April 2020 (BGVN 45:05), and this less intense level of activity continued during the reporting period (table 15). The volcano is monitored by the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT). The Aviation Color Code remained at Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale) throughout.
Notable explosions took place on 13 June, 28 June, 2 August, 24 August, and 7-9 October 2020 (table 15), sending ash plumes more than 1 km above the summit that drifted to distances of between 75 and 310 km. Some of the plumes were described by KVERT as being composed of re-suspended ash. On 28 September a large dacitic block of lava, a “whaleback” dome, was first seen being extruded from the eastern part of the larger lava dome in the summit crater (figure 55); it was given the name “Dolphin” by KVERT.
Table 15. Explosions, ash plumes, and extrusive activity at Sheveluch during May-October 2020. Dates and times are UTC, not local. VONA is Volcano Observatory Notice for Aviation. Data courtesy of KVERT and the Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC).
| Dates | Plume altitude | Drift Distance and Direction | Remarks |
| 13 Jun 2020 | 5 km | 120 km NE | Webcam captured an explosion. VONA issued. |
| 28 Jun 2020 | -- | 140 km E | Plume of re-suspended ash. VONA issued. |
| 02 Aug 2020 | 4.5 km | SE, E | Moderate explosion produced a small ash plume. |
| 24 Aug 2020 | -- | 75 km ESE | Plume of resuspended ash. |
| 28 Sep 2020 | -- | -- | A new lava block extruded from the E part of the lava dome was first visible. |
| 07-09 Oct 2020 | -- | 310 km SE | Plume of re-suspended ash. VONAs issued. |
According to KVERT, a thermal anomaly was identified from the lava dome in the summit crater (figure 56) in satellite images every day during the reporting period, except for several days in August and September when weather clouds obscured the view. During the reporting period, thermal anomalies, based on MODIS satellite instruments analyzed using the MODVOLC algorithm, recorded hotspots from 2-13 days per month; after June, the number of days with hotspots gradually diminished every month. The MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) volcano hotspot detection system, also based on analysis of MODIS data, detected frequent anomalies. NASA recorded high levels of sulfur dioxide above or near Sheveluch during several scattered days in May and June by the TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) aboard the Copernicus Sentinel-5 Precursor satellite, but very little drift was observed.
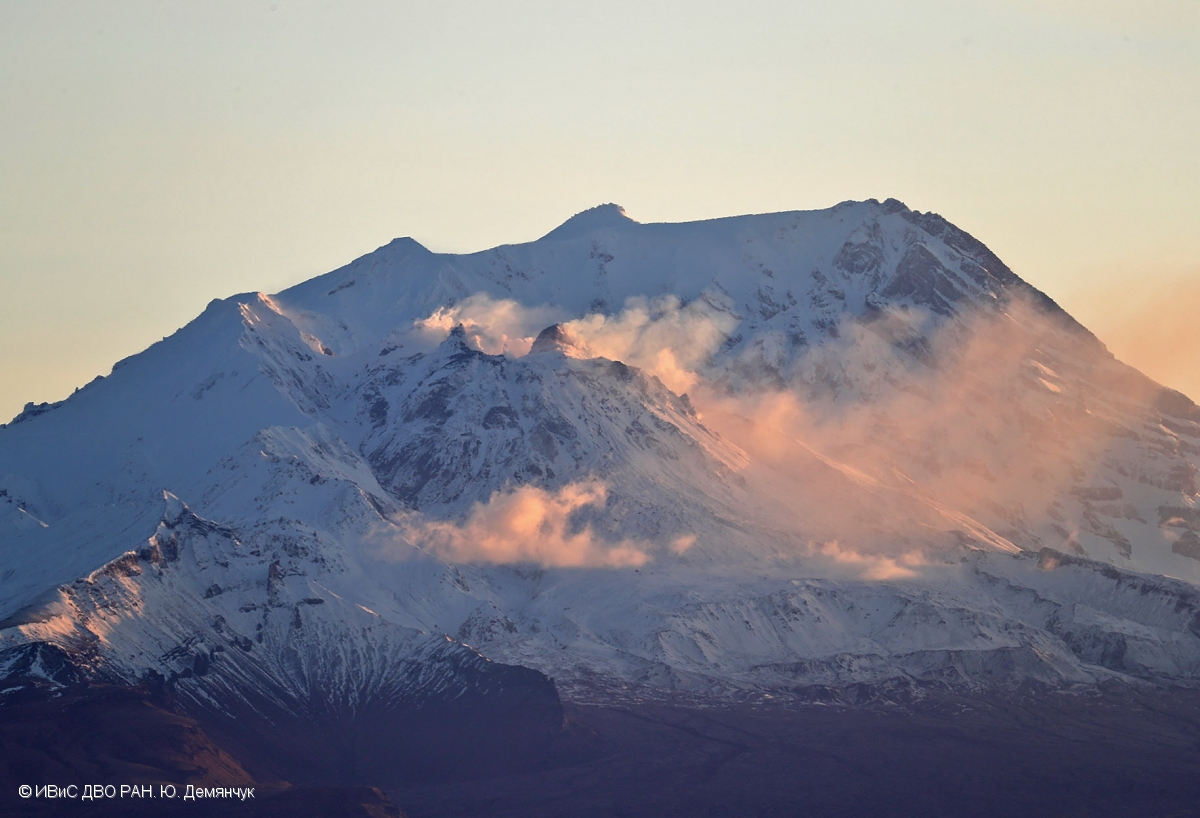 |
Figure 56. Photo showing typical fumarolic activity from the lava dome at Sheveluch on 18 September 2020. Photo by Yu. Demyanchuk; courtesy of IVS FEB RAS, KVERT. |
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS), 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/eng/); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), 1-3-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, Japan (URL: http://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/).
Continued activity during November 2020-June 2021 produced a whaleback dome and occasional ash plumes
Sheveluch (also spelled Shiveluch) is a frequently active volcano consisting of Old Sheveluch and Young Sheveluch, with a large lava dome complex in the open crater that formed during a flank collapse in 1964 (figures 57 and 58). Typical activity consists of lava dome growth with intermittent ash emission and collapse events that produce block-and-ash flows. This report summarizes activity from November 2020 through June 2021 and is based on Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT) and Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS) reports and photographs, and satellite data. During this time activity consisted of lava dome growth, active fumaroles producing gas and steam, and visible incandescence of the eastern dome area when not obscured by clouds. Before this period, on 28 September 2020, a “whaleback” dome or lava spine was seen in the upper eastern part of the large dome that was given the name “Dolphin” by KVERT (BGVN 45:11). An image taken on 31 October showed the dome fracturing with new lava extrusion.
Frequent thermal anomalies were detected throughout November 2020-June 2021, with a decrease in energy output starting in November (figure 60). This was also seen in thermal satellite images when the active dome area was not obscured by clouds (figure 61). A gas-and-steam plume produced on the 30th dispersed 60 km NE. Avalanches of hot material from the growing dome area occurred through the month.
Low-level activity continued in early December, with avalanches of hot material from the dome removing a significant part of the whaleback by the 8th (figure 62). On the 22nd an explosion produced an ash plume up to 8 km altitude that dispersed E (figure 63), and a satellite image acquired the following day showed the ash deposit across the snow (figure 64). Another explosive event on the 24th again sent a plume to 8 km; both plumes reached around 625 km E. A satellite image acquired on 25 December showed fresh material across the dome and a lahar, likely from hot blocks melting snow (figure 65). Slightly lower ash plumes were erupted on the 29th, reaching 7 km altitude, with the latter plume drifting 250 km W.
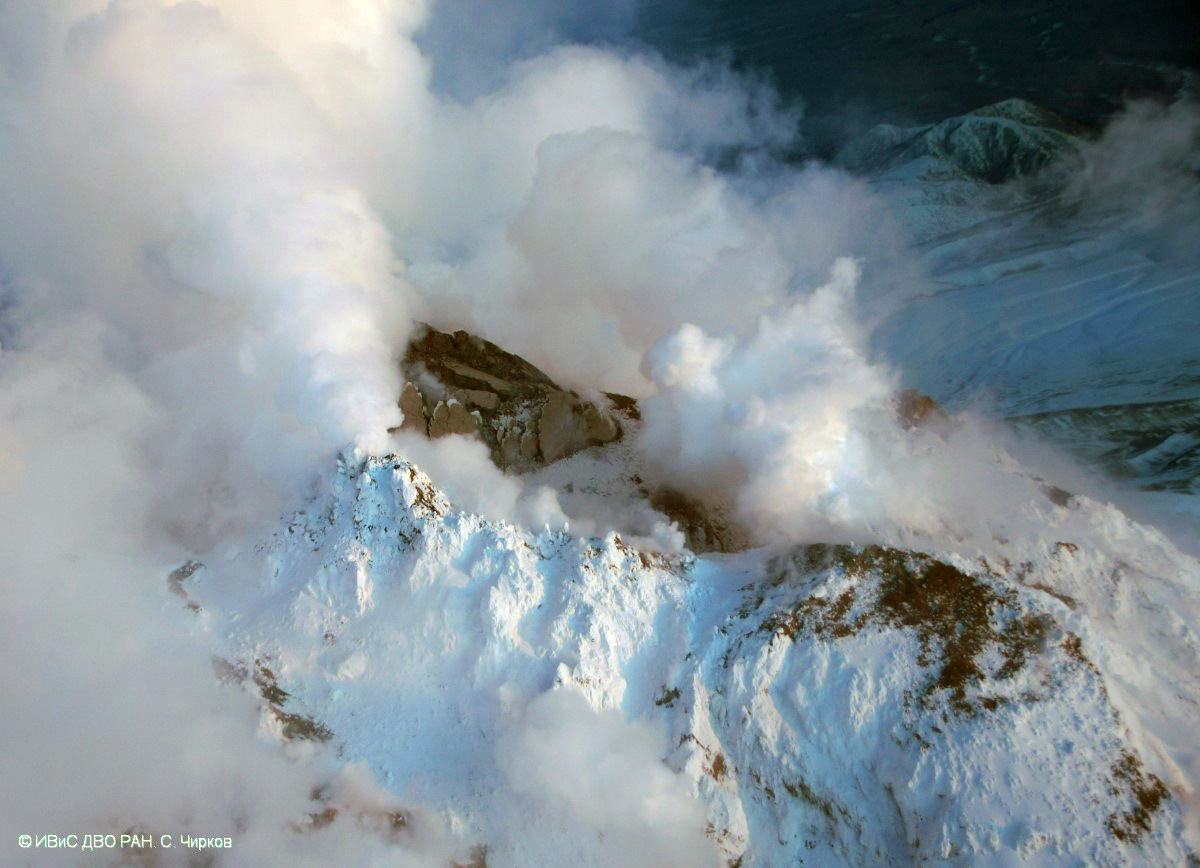 |
Figure 62. The remnants of the “Dolphin” whaleback lava dome in the eastern part of the larger Sheveluch lava dome complex is shown in this 8 December 2020 photo. Courtesy of S. Chirkov, IVS FEB RAS. |
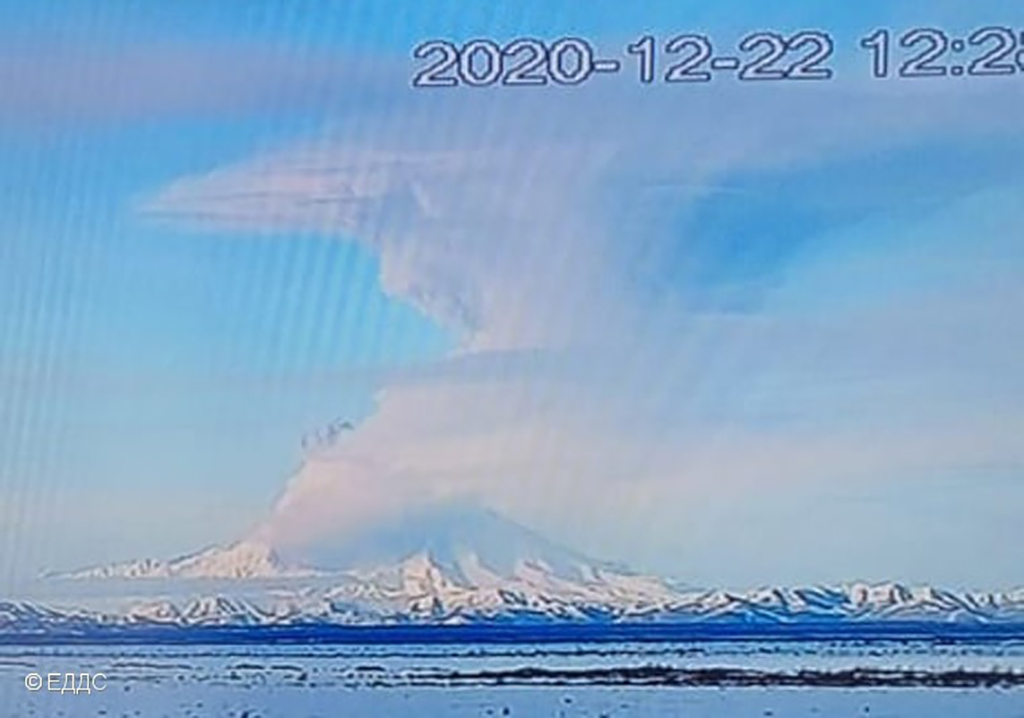 |
Figure 63. An explosive eruption at Sheveluch on 22 December 2020 is seen in this image from the south. Image courtesy of IVS FEB RAS, KVERT. |
Continued dome growth produced hot avalanches, thermal anomalies, and gas-and-steam plumes (figures 66 to 70) during January through May, with no explosive activity reported. The whaleback dome continued to grow vertically, forming a smooth top similar to that seen in November. Ash resuspended by winds on 2 April created an ash plume that reached 2.5 km altitude and extended 400 km ESE.
Throughout June activity remained the same, with dome growth, avalanches, and gas emission (figure 71). By 16 June the whaleback dome was about 200 m high and 170 m wide at the base, and was beginning to crumble, producing avalanches (figures 72 and 73).
Information Contacts: Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS), 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/eng/); Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Kamchatka Volcanological Station, Klyuchi, Kamchatka Krai, Russia (URL: http://volkstat.ru/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Sentinel Hub Playground (URL: https://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/sentinel-playground); Planet Labs, Inc. (URL: https://www.planet.com/).
Explosions destroy most of the whaleback dome; dome growth continues, July-December 2021
Russia’s Sheveluch (Shiveluch) volcano in the northeastern region of the Kamchatka peninsula, has produced numerous major eruptions documented in both reported observations dating back several hundred years and also with tephrochronology dating back 10,000 years. A major south-flank collapse during a 1964 Plinian explosion produced a scarp within which a “Young Sheveluch” dome began to form in 1980. Repeated episodes of dome formation and destruction since then have produced major and minor ash plumes, pyroclastic, and block-and-ash flows, and two “whaleback domes” of spine-like extrusions in 1993 and 2020. The whaleback domes were subsequently destroyed with further dome growth and the ongoing explosive activity. This report summarizes activity from July-December 2021 with information provided by the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), the Kamchatka Volcano Station (part of the Kamchatka Branch of the Geophysical Survey, Russian Academy of Science (KB GS RAS), the Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), and satellite information.
The growth of the lava dome inside the 1964 flank collapse scarp continued throughout July-December 2021. Strong fumarolic activity with gas and steam rising from multiple vents around the dome was recorded in either satellite images or was visible whenever the volcano was not obscured by weather. Incandescence at the dome persisted and incandescent block avalanches were reported on most days. A significant increase in thermal and explosive activity during August coincided with the destruction of part of the “Dolphin” whaleback dome that first appeared in September 2020 (BGVN 45:11, figure 55). Ash emissions were recorded daily for much of August. Activity decreased from September through mid-December, with low levels of thermal activity persisting. A new episode of explosions with ash emissions was recorded in late December. The spike in thermal activity during August is clearly seen in the MIROVA Log Radiative Power graph of activity from 6 April through December 2021 (figure 74).
Lava dome growth continued during July 2021, with observations of strong fumarolic activity and incandescent blocks on the dome. A thermal anomaly was present almost every day, according to KVERT, and multiple anomalies were observed in Sentinel-2 satellite imagery during the month (figure 75). MODVOLC thermal alerts were recorded on 7, 8, 22, 25, 28, and 30 July. During 6-7 July, KVERT satellite data indicated that resuspended ash extended about 90 km E from the volcano at 3.4 km altitude. The Tokyo VAAC reported an ash emission on 17 July that rose to 3.7 km altitude and drifted SE. Activity increased on 26 July with small explosions and collapses of numerous lava dome blocks observed that day and the next. A gas and steam plume containing ash drifted 45 km E. The Tokyo VAAC reported that the ash emission on 26 July rose to 4.3 km altitude and drifted SE. They noted another explosion on 27 July that was estimated at 6.1 km altitude from seismic data. On 28 July two possible ash plumes were observed drifting E and SE at 3.4 km altitude.
Thermal and explosive activity increased significantly during August 2021. The Tokyo VAAC reported a series of ash emissions during 2-4 August that rose to 3.7-3.9 km altitude and drifted S and SE. Multiple MODVOLC thermal alerts were issued on several days including 3, 10, 11, 13, 15-22, 24-25, and 28-29 August(figure 76). In addition to the strong fumarolic activity and incandescence observed daily on the dome, avalanches of incandescent blocks began on 5 August and lasted throughout the month (figure 77). KVERT reported ash emissions extending about 90 km SW from the volcano on 7 August; the Tokyo VAAC reported these emissions at 4.3 km altitude. KVERT noted an increase in dome thermal anomaly brightness from 8 August through the rest of the month. Beginning on 9 August, the Tokyo VAAC issued multiple daily ash alerts through 30 August. Emissions rose to altitudes from 3.7 to 5.5 km that initially drifted SW, switched to SE then back to SW at the end of the month. KVERT reported plumes drifting 50-170 km SW during 10-13 August and reaching as far as 350 km SE during 13-24 August. Steam and gas emissions containing ash were also recorded by Kamchatka Volcano Station researchers during 10-13 August. They also reported small explosions on 10 and 11 August that contributed to the destruction of the ‘Dolphin’ whaleback dome, and noted multiple small collapses and incandescent block avalanches on the S and SE slopes of the dome each night in late August.
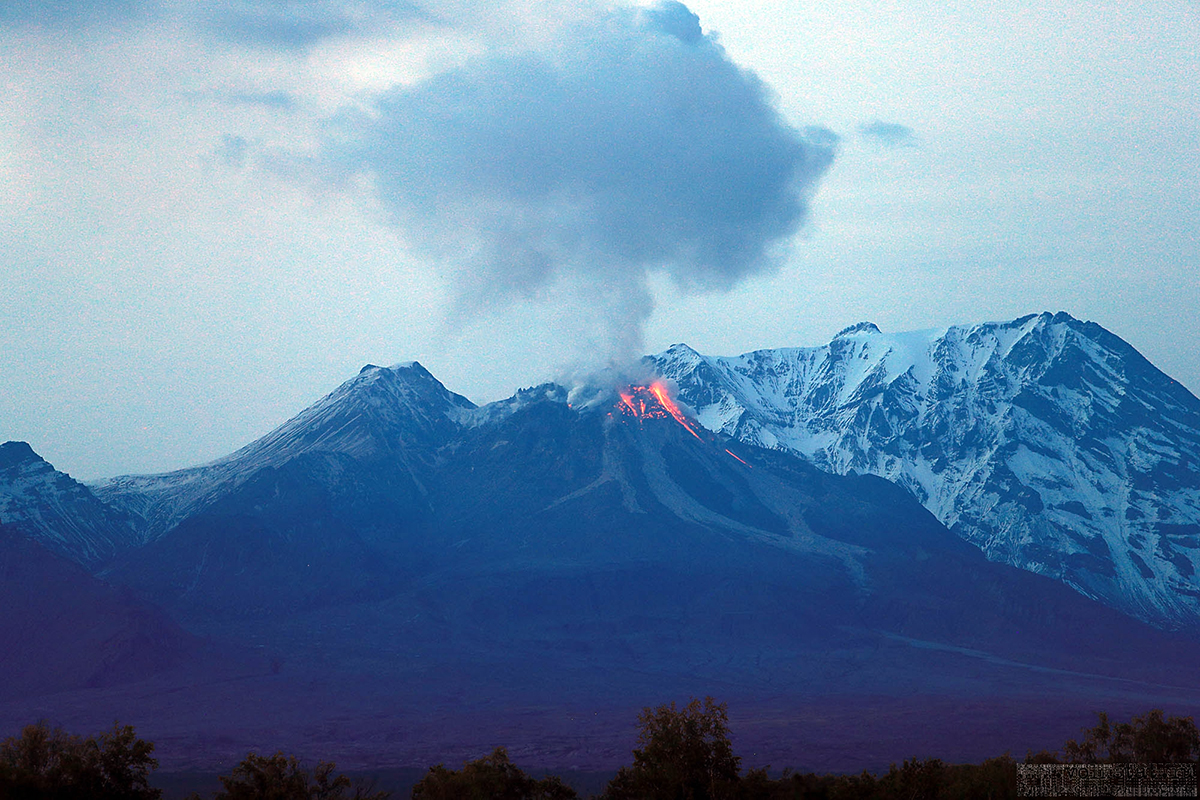 |
Figure 77. Blocks of incandescent ejecta roll down the flanks of the dome at Sheveluch on 10 August 2021. Photo by Alexey Demyanchuk, courtesy of the Kamchatka Volcano Station. |
Both thermal and explosive activity decreased significantly during September 2021, although the lava dome continued to grow. Incandescent blocks were visible on the flank of the dome, and a thermal anomaly was present at the dome throughout the month according to KVERT, decreasing slightly in intensity for the second half of the month. MODVOLC thermal alerts decreased in frequency and intensity compared with August; single or double alerts were recorded on 4, 5, 7, 9, 14-15, and 17-18 September, but no more were reported for the remainder of 2021. Researchers at the Kamchatka Volcano Station reported the noticeable drop in overall activity including far fewer incandescent block avalanches than during August, but continued to report incandescence at the SE edge of the crater at night. Visitors to the volcano experienced ashfall on 8 September; inclement weather prevented views of the summit. The next morning on 9 September a clear view of the volcano revealed a small pyroclastic flow on the flank in the direction of the Baydarnaya River (figure 78). Infrared imagery observed the previous nights had shown an increase in incandescence and small block avalanches on the SE flank. Resuspended ash was reported drifting SE at 3.4 km altitude on 10 September. Dense steam and gas emissions drifted SE from multiple spots around the dome on 13 September (figure 79).
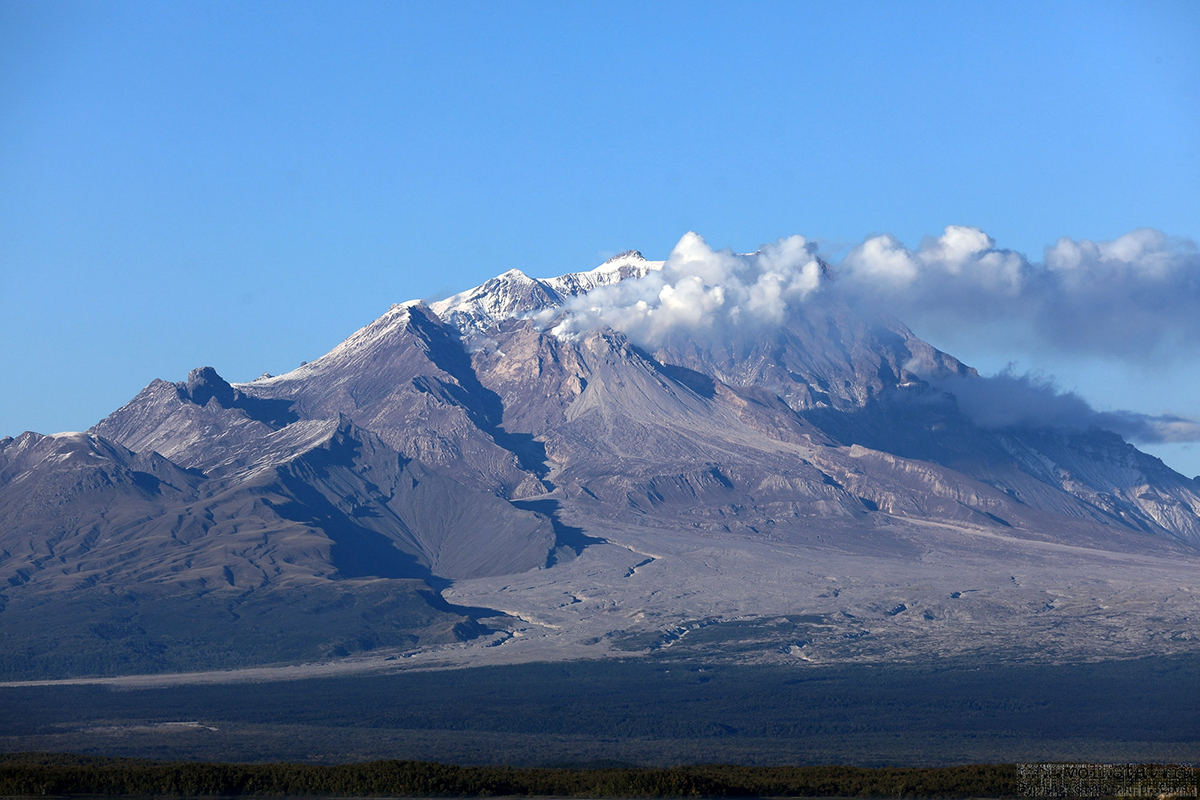 |
Figure 79. Dense steam and gas emissions at Sheveluch drifted SE from multiple spots around the dome on 13 September 2021. Photo by Alexey Demyanchuk, courtesy of the Kamchatka Volcano Station. |
The Tokyo VAAC reported volcanic ash extending W from the volcano on 17 September at 6.1 km altitude. A field team from the KF FRC EGS RAS (Kamchatka Branch of Federal Research Center Unified Geophysical Service of the Russian Academy of Sciences) performed maintenance and repair on the radio telemetered seismic stations in the region on 18 September, and with excellent visibility photographed the larger Sheveluch massif as well as fumarolic activity around the growing dome of “Young Sheveluch” (figures 80 and 81). An eruption on 23 September was reported by the Tokyo VAAC sending ash to 5.2 km altitude and extending SE. KVERT reported the ash cloud visible 22 km E.
The growth of the lava dome continued during October 2021; strong fumarolic activity was accompanied by visible incandescence and incandescent block avalanches descending the flank of the dome. KVERT reported a thermal anomaly over the volcano on all nights that were not obscured by clouds. A strong wind on 6-7 October resuspended ash from the S flank to altitudes of 4-6 km that was observed in satellite images extending 200 km SE. The same thing happened on 21 October with the ash rising to 4 km altitude and drifting 40 km SE. KVERT reported a gas and steam plume containing ash on 24 October extending 33 km NE. Sentinel-2 satellite imagery revealed dark debris flows surrounded by fresh snow on the SE flank of the dome on 24 October (figure 82). The Tokyo VAAC reported resuspended ash at 3.4 km altitude drifting E on 30 October.
Strong fumarolic activity, incandescence, and block avalanches during November 2021 indicated continued growth of the dome. Most clear days revealed a thermal anomaly in satellite imagery according to KVERT. The Tokyo VAAC reported two possible ash emissions on 1 November that rose to 3.7-3.9 km altitude and drifted SE. An eruption on 6 November produced an ash plume that rose to 3.7 km altitude and was visible moving S and W in satellite imagery for about 13 hours before dissipating. On 10 November a team from the Kamchatka Volcano Station was able to make a site visit and observed emissions of gas and steam rising from multiple sites around the edges of the active dome (figure 83). The Tokyo VAAC reported an ash emission on 18 November that rose to 3.4 km altitude and drifted N for about ten hours.
The growth of the lava dome continued throughout December 2021, indicated by strong fumarolic activity, incandescence, block avalanches, and thermal anomalies in satellite data on most days. The Tokyo VAAC reported a possible ash emission on 21 December that rose to 3.7 km altitude and drifted NW. Beginning on 23 December and lasting through the rest of the month, near-daily ash emissions produced ash clouds that rose to 4.5-6 km altitude and drifted up to 100 km NE or NW (figure 84).
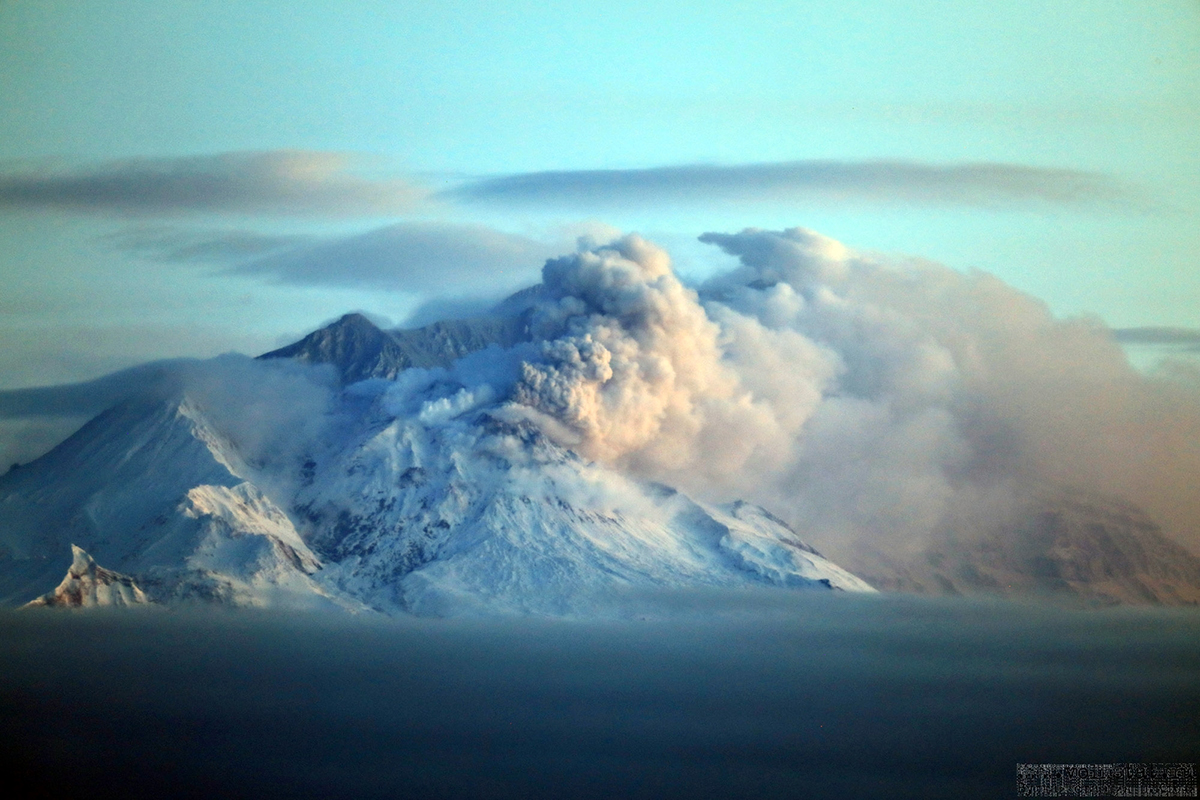 |
Figure 84. A dense ash plume rose from the dome at Sheveluch on 23 December 2021 and drifted NE. Photo by Alexey Demyanchuk, courtesy of the Kamchatka Volcano Station. |
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Kamchatka Volcanological Station, Kamchatka Branch of Geophysical Survey of the Russian Academy of Science, (KB GS RAS), Klyuchi, Kamchatka Krai, Russia (URL: http://volkstat.ru/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Sentinel Hub Playground (URL: https://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/sentinel-playground); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), 1-3-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8122, Japan (URL: http://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/).
Occasional explosions, ash plumes, and lava dome growth during January-June 2022
Sheveluch, in the northeastern region of the Kamchatka peninsula, Russia, has produced at least 60 eruptions during the Holocene, with eruptions known from tephrochronology dating back 10,000 years. Frequent collapses of dome complexes have produced debris avalanches; the resulting deposits cover much of the caldera floor. A major south-flank collapse during a 1964 Plinian explosion produced a scarp within which a “Young Sheveluch” dome began to form in 1980. Repeated episodes of dome formation and destruction since then have produced major and minor ash plumes, pyroclastic flows, block-and-ash flows, and two “whaleback domes” of spine-like extrusions in 1993 and 2020 (BGVN 45:11). The current eruption period began in August 1999 and has more recently consisted of ongoing explosions, frequent ash emissions, incandescent block avalanches, and lava dome growth (BGVN 47:02). This report describes similar activity of intermittent explosions, ash plumes, continued lava dome growth, strong fumarolic activity, and block avalanches during January through June 2022 using information from the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), the Kamchatka Volcano Station (part of the Kamchatka Branch of the Geophysical Survey, Russian Academy of Science (KB GS RAS) and various satellite data.
Activity during this reporting period was relatively low. The growth of the lava dome inside the 1964 flank collapse scarp continued through June 2022 and on clear weather days, a small thermal anomaly was visible in satellite data (figure 85). Strong fumarolic activity with gas-and-steam emissions often accompanied this dome growth from multiple vents. Frequent low-level thermal activity persisted, though there was a gradual decline in power during January through April that remained low through June, as is shown in the MIROVA Log Radiative Power graph (figure 86).
The incandescent lava dome continued to grow during January 2022, in addition to observations of strong fumarolic activity and block avalanches. A thermal anomaly was visible over the dome daily. Satellite data showed a strong gas-and-steam plume containing some amount of ash on 7 January that rose to 4-4.5 km altitude and drifted as far as 24 km W. Explosions during 9-11 January generated gas-and-ash plumes to 3.5-5.5 km altitude and drifted 20-140 km WNW, 175 km W, and 80 km SW, respectively. Continued explosions were detected on 13 and 15-16 January, which produced ash plumes that rose to 5-6.5 km altitude and drifted 10-31 km NNW, W, and WSW.
Low activity persisted during February and March with strong fumaroles, block avalanches, and incandescence from the growing lava dome. A thermal anomaly was frequently visible over the lava dome on clear weather days. An ash cloud detected in satellite imagery on 15 March rose to 4.5 km altitude and drifted 50 km WNW. During April, lava dome growth continued, accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, block avalanches, and frequent thermal anomalies. Satellite data by KVERT on 9 April showed that explosions sent ash plumes to 12 km altitude and extended more than 2,000 km NE. Continued explosions during 14-17 April produced ash plumes that rose to 4-6.5 km altitude and drifted generally 4-45 km SW and SE.
During May and June, activity was relatively low and consisted of lava dome growth, strong fumarolic activity (figure 87), block avalanches, and incandescence. Thermal anomalies continued to be frequently detected in satellite data on clear weather days. According to video data, explosions on 10 June generated an ash plume that rose to 6.5 km altitude and extended 130 km SSE and E over the volcano. On 20 June at 0847 video data from KVERT showed an ash plume rose to 7 km altitude that extended 10 km E (figure 88). The next day on 21 June explosions produced an ash plume that rose to 5 km altitude and drifted 70 km SW.
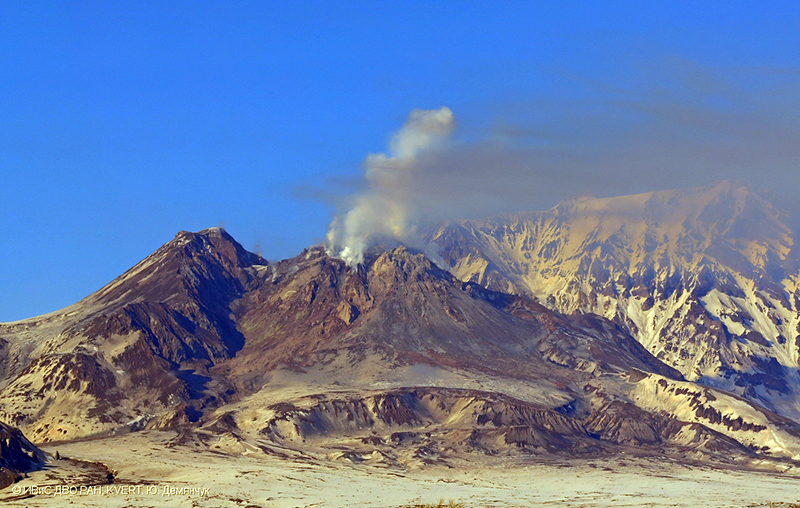 |
Figure 87. Photo of strong fumarolic activity at Sheveluch on 5 May 2022. Photo has been color corrected. Photo by Yu Demyanchuk, courtesy of IVS FEB RAS, KVERT. |
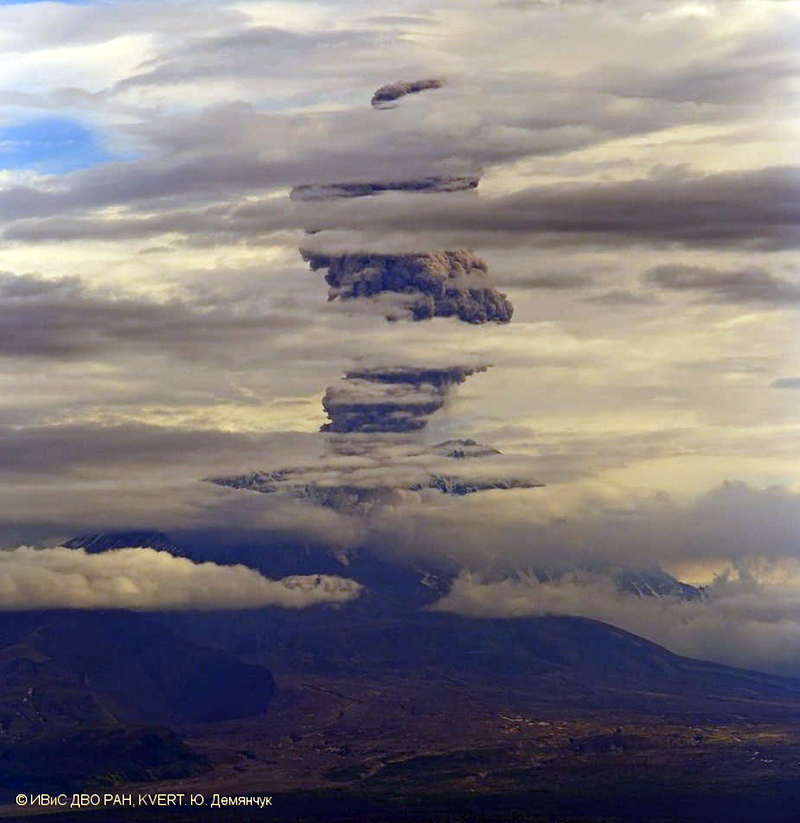 |
Figure 88. A dense ash plume rose to 7 km altitude from Sheveluch on 20 June 2022 and drifted E. Photo has been color corrected. Photo by Yu Demyanchuk, courtesy of IVS FEB RAS, KVERT. |
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Sentinel Hub Playground (URL: https://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/sentinel-playground); Tokyo Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), 1-3-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-8122, Japan (URL: http://ds.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vaac/data/).
Continued lava dome growth, explosions, ash plumes, and avalanches during July-December 2022
Sheveluch (also spelled Shiveluch), located in Kamchatka, has had at least 60 large eruptions during the last 10,000 years. The summit is truncated by a broad 9-km-wide caldera that is breached to the S, and many lava domes occur on the outer flanks. The lava dome complex was constructed within the large open caldera. Frequent collapses of the dome complex have produced debris avalanches; the resulting deposits cover much of the caldera floor. A major south-flank collapse during a 1964 Plinian explosion produced a scarp within which a “Young Sheveluch” dome began to form in 1980. Repeated episodes of dome formation and destruction since then have produced major and minor ash plumes, pyroclastic flows, block-and-ash flows, and “whaleback domes” of spine-like extrusions in 1993 and 2020 (BGVN 45:11). The current eruption period began in August 1999 and has more recently consisted of lava dome growth, occasional explosions, block avalanches, and ash plumes (BGVN 47:07). This report covers activity through July-December 2022 using information from the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT) and various satellite data.
Volcanism during this reporting period was relatively consistent and characterized by lava dome growth and incandescence, explosions accompanied by hot avalanches that resulted from collapses on the lava dome, ash plumes, and strong fumarolic activity. According to the MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, 218 hotspots were detected throughout the reporting period, with 63 recorded in July, 59 in August, 24 in September, 7 in October, 40 in November, and 25 in December. Frequent strong thermal activity was recorded during July through December, according to the MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) graph due to the growing lava dome and hot avalanches (figure 89). These thermal anomalies were also visible in Sentinel-2 infrared satellite images throughout the reporting period, from both the lava dome and flank avalanches (figure 90).
Activity during July consisted of lava dome growth, explosions accompanied by hot avalanches, ash plumes, incandescence from the lava dome, and strong fumarolic activity. Satellite data analyzed by KVERT showed a daily thermal anomaly over the volcano. During 11-13 July satellite and video data showed that ash plumes rose to 4.3-4.5 km altitude and drifted 12-82 km SW and SE. On 16 July an ash plume rose to 4.5 km altitude and extended 50 km E. Video and satellite data from KVERT showed a plume of resuspended ash that rose to 3.5 km altitude and drifted as far as 127 km ESE during 18-19 July. Video data taken on 20 July showed that an ash plume rose to 5 km altitude and drifted 15-65 km E. On 21 July a resuspended ash plume rose to 4.5 km altitude and drifted 65 km SE. During 23-24 July video and satellite data showed that an ash plume rose to 4 km altitude and drifted 25-85 km SSW and SE. On 27 July a gas-and-steam plume containing some amount of ash rose to 5.5 km altitude and drifted 20 km NE. Ash plumes were visible drifting 24 km SW on 31 July.
During August, the lava dome continued to grow, in addition to dome incandescence, explosions, hot avalanches, occasional ash plumes, and strong fumarolic activity (figure 91). A thermal anomaly was visible over the volcano each day during clear weather. During 8-9 August gas-and-steam plumes containing some amount of ash drifted 70 km E and SE. An ash plume drifted 190 km SE on 19 August. A plume of resuspended ash extended 150 km E on 25 August.
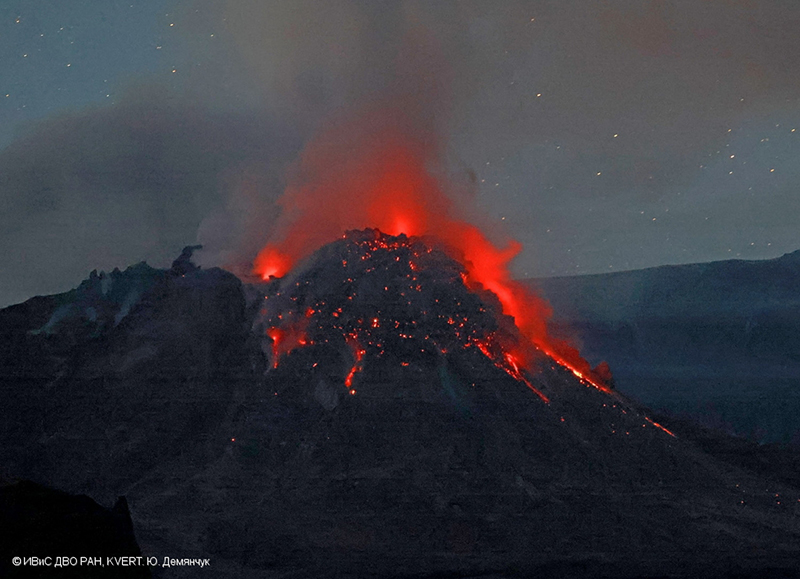 |
Figure 91. Photo of the active lava dome at Sheveluch on 5 August 2022, showing gas-and-steam emissions, dome incandescence, and avalanches. Photo by Yu Demyanchuk, courtesy of IVS FEB RAS, KVERT. |
Dome growth, strong fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, explosions, and associated avalanches were reported during September. A daily thermal anomaly persisted throughout the month. An eruptive plume associated with avalanches drifted 40-70 km E and NE on 1 September. Video and satellite data showed a gas-and-steam plume with some ash that rose to 4.5 km altitude and drifted 42 km NE on 2 September. According to a VONA (Volcano Observatory Notice for Aviation), strong winds during 5 September resuspended ash from the E flank, which rose to 3 km altitude and extended as far as 210 km E and ESE. During 5-7 September ash plumes, caused by avalanches associated with collapses on the lava dome, extended as far as 130 km NE and SE. A gas-and-steam plume containing some ash rose to 4 km altitude on 6 September and drifted 84 km ESE. Video data taken on 6 September showed explosions that generated ash plumes rising 5 km altitude and extending 10 km ESE. On 7 September ash plumes from avalanches on the E flank of the lava dome rose to 4 km altitude and drifted 128 km ESE. A strong wind on 18 September resuspended ash on the E flank that rose to 3 km altitude and drifted 300 km SE. During 21-24 September strong winds lifted ash from the S flank that rose to 3.5 km altitude and drifted as far as 430 km E and 105 km SE.
Activity continued during October with lava dome growth, incandescence in the lava dome, strong fumarolic activity, explosions, and avalanches (figure 92). Satellite data showed a thermal anomaly over the volcano throughout the entire month. Strong winds on 8 October resuspended an ash plume from the S flank which rose to 3 km altitude and extended 105 km E. During 24-25 October ash plumes associated with avalanches extended as far as 80 km SE and NW. On 29 October strong winds generated a resuspended ash plume that rose to 3 km altitude and extended 80 km SE. Collapses of the lava dome on 31 October generated avalanches and ash plumes that drifted 200 km SE.
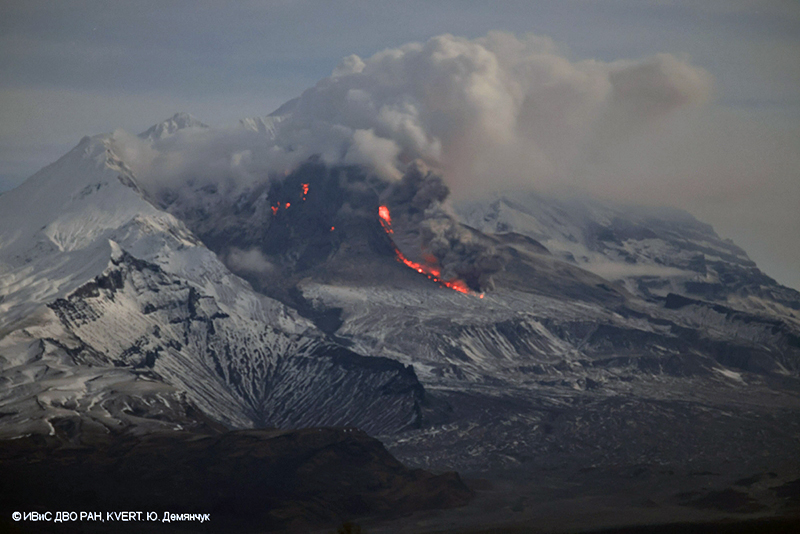 |
Figure 92. Photo of incandescent avalanches descending the growing lava dome at Sheveluch on 11 October 2022 along with associated ash plumes. Photo by Yu Demyanchuk, courtesy of IVS FEB RAS, KVERT. |
Lava dome growth, incandescence, explosions, and strong fumarolic activity were reported during November. Satellite data analyzed by KVERT showed a daily thermal anomaly over the volcano. During 1-2 November hot avalanches on the S and SE flanks generated an ash plume that rose to 3.5 km altitude and drifted 105-210 km ESE. More ash plumes from avalanches during 5-7 November rose to 4 km altitude and drifted as far as 400 km N, NE, and E. The Kamchatka Volcano Station reported that activity notably increased on 5 November; debris avalanches and small pyroclastic flows were visible throughout the day and incandescent avalanches were visible descending SE and SW flanks during the night. On 8 November an ash plume rose to 5.5 km altitude and drifted 25 km ENE. During 13-14, 16-18, 20, 26, and 29 November ash plumes associated with avalanches drifted as far as 90 km NE, ENE, and E (figure 93).
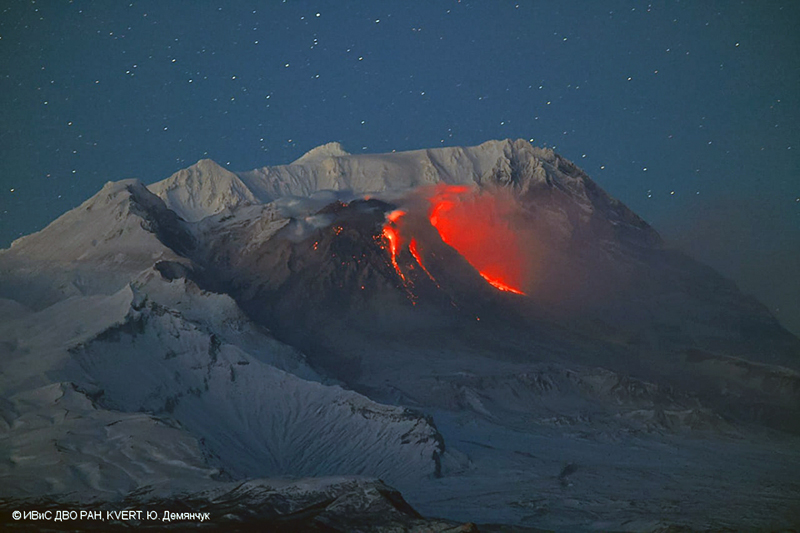 |
Figure 93. Photo of incandescent avalanches originating from the growing lava dome at Sheveluch on 19 November 2022. Photo by Yu Demyanchuk, courtesy of IVS FEB RAS, KVERT. |
During December similar activity was reported, with dome growth, dome incandescence, explosions, strong fumarolic activity, and avalanches. A daily thermal anomaly over the volcano was visible in satellite imagery. An ash plume associated with avalanches on 1 December drifted as far as 90 km NE. During 2-3 and 9 December satellite data from KVERT showed strong gas-and-steam plumes that contained some amount of ash and were associated with avalanches rose to 3-4.5 km altitude and drifted 15-60 km N and NE. Satellite and video data showed that an ash plume rose to 6 km altitude and extended for 90-110 km NE and NNE on 16 December. During 26-29 December gas-and-steam plumes containing some ash rose to 4.5 km altitude and drifted 90 km SW, S, and NE.
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Sentinel Hub Playground (URL: https://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/sentinel-playground).
Significant explosions destroyed part of the lava-dome complex during April 2023
Sheveluch (also spelled Shiveluch) in Kamchatka, has had at least 60 large eruptions during the last 10,000 years. The summit is truncated by a broad 9-km-wide caldera that is breached to the S, and many lava domes occur on the outer flanks. The lava dome complex was constructed within the large open caldera. Frequent collapses of the dome complex have produced debris avalanches; the resulting deposits cover much of the caldera floor. A major south-flank collapse during a 1964 Plinian explosion produced a scarp in which a “Young Sheveluch” dome began to form in 1980. Repeated episodes of dome formation and destruction since then have produced major and minor ash plumes, pyroclastic flows, block-and-ash flows, and “whaleback domes” of spine-like extrusions in 1993 and 2020 (BGVN 45:11). The current eruption period began in August 1999 and has more recently consisted of lava dome growth, explosions, ash plumes, and avalanches (BGVN 48:01). This report covers a significant explosive eruption during early-to-mid-April 2023 that generated a 20 km altitude ash plume, produced a strong sulfur dioxide plume, and destroyed part of the lava-dome complex; activity described during January through April 2023 use information primarily from the Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT) and various satellite data.
Satellite data. Activity during the majority of this reporting period was characterized by continued lava dome growth, strong fumarole activity, explosions, and hot avalanches. According to the MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, 140 hotspots were detected through the reporting period, with 33 recorded in January 2023, 29 in February, 44 in March, and 34 in April. Frequent strong thermal activity was recorded during January 2023 through April, according to the MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) graph and resulted from the continuously growing lava dome (figure 94). A slightly stronger pulse in thermal activity was detected in early-to-mid-April, which represented the significant eruption that destroyed part of the lava-dome complex. Thermal anomalies were also visible in infrared satellite imagery at the summit crater (figure 95).
During January 2023 KVERT reported continued growth of the lava dome, accompanied by strong fumarolic activity, incandescence from the lava dome, explosions, ash plumes, and avalanches. Satellite data showed a daily thermal anomaly over the volcano. Video data showed ash plumes associated with collapses at the dome that generated avalanches that in turn produced ash plumes rising to 3.5 km altitude and drifting 40 km W on 4 January and rising to 7-7.5 km altitude and drifting 15 km SW on 5 January. A gas-and-steam plume containing some ash that was associated with avalanches rose to 5-6 km altitude and extended 52-92 km W on 7 January. Explosions that same day produced ash plumes that rose to 7-7.5 km altitude and drifted 10 km W. According to a Volcano Observatory Notice for Aviation (VONA) issued at 1344 on 19 January, explosions produced an ash cloud that was 15 x 25 km in size and rose to 9.6-10 km altitude, drifting 21-25 km W; as a result, the Aviation Color Code (ACC) was raised to Red (the highest level on a four-color scale). Another VONA issued at 1635 reported that no more ash plumes were observed, and the ACC was lowered to Orange (the second highest level on a four-color scale). On 22 January an ash plume from collapses and avalanches rose to 5 km altitude and drifted 25 km NE and SW; ash plumes associated with collapses extended 70 km NE on 27 and 31 January.
Lava dome growth, fumarolic activity, dome incandescence, and occasional explosions and avalanches continued during February and March. A daily thermal anomaly was visible in satellite data. Explosions on 1 February generated ash plumes that rose to 6.3-6.5 km altitude and extended 15 km NE. Video data showed an ash cloud from avalanches rising to 5.5 km altitude and drifting 5 km SE on 2 February. Satellite data showed gas-and-steam plumes containing some ash rose to 5-5.5 km altitude and drifted 68-110 km ENE and NE on 6 February, to 4.5-5 km altitude and drifted 35 km WNW on 22 February, and to 3.7-4 km altitude and drifted 47 km NE on 28 February. Scientists from the Kamchatka Volcanological Station (KVS) went on a field excursion on 25 February to document the growing lava dome, and although it was cloudy most of the day, nighttime incandescence was visible. Satellite data showed an ash plume extending up to 118 km E during 4-5 March. Video data from 1150 showed an ash cloud from avalanches rose to 3.7-5.5 km altitude and drifted 5-10 km ENE and E on 5 March. On 11 March an ash plume drifted 62 km E. On 27 March ash plumes rose to 3.5 km altitude and drifted 100 km E. Avalanches and constant incandescence at the lava dome was focused on the E and NE slopes on 28 March. A gas-and-steam plume containing some ash rose to 3.5 km altitude and moved 40 km E on 29 March. Ash plumes on 30 March rose to 3.5-3.7 km altitude and drifted 70 km NE.
Similar activity continued during April, with lava dome growth, strong fumarolic activity, incandescence in the dome, occasional explosions, and avalanches. A thermal anomaly persisted throughout the month. During 1-4 April weak ash plumes rose to 2.5-3 km altitude and extended 13-65 km SE and E.
Activity during 11 April 2023. The Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS) reported a significant increase in seismicity around 0054 on 11 April, as reported by strong explosions detected on 11 April beginning at 0110 that sent ash plumes up to 7-10 km altitude and extended 100-435 km W, WNW, NNW, WSW, and SW. According to a Tokyo VAAC report the ash plume rose to 15.8 km altitude. By 0158 the plume extended over a 75 x 100 km area. According to an IVS FEB RAS report, the eruptive column was not vertical: the initial plume at 0120 on 11 April deviated to the NNE, at 0000 on 12 April, it drifted NW, and by 1900 it drifted SW. KVS reported that significant pulses of activity occurred at around 0200, 0320, and then a stronger phase around 0600. Levin Dmitry took a video from near Békés (3 km away) at around 0600 showing a rising plume; he also reported that a pyroclastic flow traveled across the road behind him as he left the area. According to IVS FEB RAS, the pyroclastic flow traveled several kilometers SSE, stopping a few hundred meters from a bridge on the road between Klyuchi and Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky.
Ashfall was first observed in Klyuchi (45 km SW) at 0630, and a large, black ash plume blocked light by 0700. At 0729 KVERT issued a Volcano Observatory Notice for Aviation (VONA) raising the Aviation Color Code to Red (the highest level on a four-color scale). It also stated that a large ash plume had risen to 10 km altitude and drifted 100 km W. Near-constant lightning strikes were reported in the plume and sounds like thunderclaps were heard until about 1000. According to IVS FEB RAS the cloud was 200 km long and 76 km wide by 0830, and was spreading W at altitudes of 6-12 km. In the Klyuchi Village, the layer of both ash and snow reached 8.5 cm (figure 96); ashfall was also reported in Kozyrevsk (112 km SW) at 0930, Mayskoye, Anavgay, Atlasovo, Lazo, and Esso. Residents in Klyuchi reported continued darkness and ashfall at 1100. In some areas, ashfall was 6 cm deep and some residents reported dirty water coming from their plumbing. According to IVS FEB RAS, an ash cloud at 1150 rose to 5-20 km altitude and was 400 km long and 250 km wide, extending W. A VONA issued at 1155 reported that ash had risen to 10 km and drifted 340 km NNW and 240 km WSW. According to Simon Carn (Michigan Technological University), about 0.2 Tg of sulfur dioxide in the plume was measured in a satellite image from the TROPOMI instrument on the Sentinel-5P satellite acquired at 1343 that covered an area of about 189,000 km2 (figure 97). Satellite data at 1748 showed an ash plume that rose to 8 km altitude and drifted 430 km WSW and S, according to a VONA.
 |
Figure 96. Photo of ash deposited in Klyuchi village on 11 April 2023 by the eruption of Sheveluch. About 8.5 cm of ash was measured. Courtesy of Kam 24 News Agency. |
Activity during 12-15 April 2023. On 12 April at 0730 satellite images showed ash plumes rose to 7-8 km altitude and extended 600 km SW, 1,050 km ESE, and 1,300-3,000 km E. By 1710 that day, the explosions weakened. According to news sources, the ash-and-gas plumes drifted E toward the Aleutian Islands and reached the Gulf of Alaska by 13 April, causing flight disruptions. More than 100 flights involving Alaska airspace were cancelled due to the plume. Satellite data showed ash plumes rising to 4-5.5 km altitude and drifted 400-415 km SE and ESE on 13 April. KVS volcanologists observed the pyroclastic flow deposits and noted that steam rose from downed, smoldering trees. They also noted that the deposits were thin with very few large fragments, which differed from previous flows. The ash clouds traveled across the Pacific Ocean. Flight cancellations were also reported in NW Canada (British Columbia) during 13-14 April. During 14-15 April ash plumes rose to 6 km altitude and drifted 700 km NW.
Alaskan flight schedules were mostly back to normal by 15 April, with only minor delays and far less cancellations; a few cancellations continued to be reported in Canada. Clear weather on 15 April showed that most of the previous lava-dome complex was gone and a new crater roughly 1 km in diameter was observed (figure 98); gas-and-steam emissions were rising from this crater. Evidence suggested that there had been a directed blast to the SE, and pyroclastic flows traveled more than 20 km. An ash plume rose to 4.5-5.2 km altitude and drifted 93-870 km NW on 15 April.
Activity during 16-30 April 2023. Resuspended ash was lifted by the wind from the slopes and rose to 4 km altitude and drifted 224 km NW on 17 April. KVERT reported a plume of resuspended ash from the activity during 10-13 April on 19 April that rose to 3.5-4 km altitude and drifted 146-204 km WNW. During 21-22 April a plume stretched over the Scandinavian Peninsula. A gas-and-steam plume containing some ash rose to 3-3.5 km altitude and drifted 60 km SE on 30 April. A possible new lava dome was visible on the W slope of the volcano on 29-30 April (figure 99); satellite data showed two thermal anomalies, a bright one over the existing lava dome and a weaker one over the possible new one.
References. Girina, O., Loupian, E., Horvath, A., Melnikov, D., Manevich, A., Nuzhdaev, A., Bril, A., Ozerov, A., Kramareva, L., Sorokin, A., 2023, Analysis of the development of the paroxysmal eruption of Sheveluch volcano on April 10–13, 2023, based on data from various satellite systems, Modern problems of remote sensing from space, 20(2).
Information Contacts: Kamchatka Volcanic Eruptions Response Team (KVERT), Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/kvert/); Institute of Volcanology and Seismology, Far Eastern Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences (IVS FEB RAS), 9 Piip Blvd., Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky 683006, Russia (URL: http://www.kscnet.ru/ivs/eng/); Kamchatka Volcanological Station, Kamchatka Branch of Geophysical Survey, (KB GS RAS), Klyuchi, Kamchatka Krai, Russia (URL: http://volkstat.ru/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Copernicus Browser, Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, European Space Agency (URL: https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/browser/); Kam 24 News Agency, 683032, Kamchatka Territory, Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, Vysotnaya St., 2A (URL: https://kam24.ru/news/main/20230411/96657.html#.Cj5Jrky6.dpuf); Simon Carn, Geological and Mining Engineering and Sciences, Michigan Technological University, 1400 Townsend Drive, Houghton, MI 49931, USA (URL: http://www.volcarno.com/, Twitter: @simoncarn).
This compilation of synonyms and subsidiary features may not be comprehensive. Features are organized into four major categories: Cones, Craters, Domes, and Thermal Features. Synonyms of features appear indented below the primary name. In some cases additional feature type, elevation, or location details are provided.
Synonyms |
||||
| Shiveluch | Suelich | Schuvelutsch | Schiwelutsch | ||||
Cones |
||||
| Feature Name | Feature Type | Elevation | Latitude | Longitude |
| Stary Sheveluch | Stratovolcano | 3283 m | 56° 39' 0" N | 161° 21' 0" E |
Domes |
||||
| Feature Name | Feature Type | Elevation | Latitude | Longitude |
| Crater Top | Dome | |||
| Fourth Top | Dome | |||
| Karan | Dome | |||
| Krasnaya | Dome | |||
| Molodoy Sheveluch | Dome | 2800 m | ||
| Semkarok | Dome | |||
| Sherokhovataya | Dome | |||
|
Suelich
Suyelich |
Former dome | |||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
There is data available for 102 confirmed Holocene eruptive periods.
1999 Aug 15 - 2024 Jun 6 (continuing) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4 (?)
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1999 Aug 15 - 2024 Jun 6 (continuing) | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 19 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1999 Apr 3 - 1999 Apr 12 Confirmed Eruption VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1999 Apr 3 - 1999 Apr 12 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 8 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1998 May 30 - 1998 Sep 3 Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1998 May 30 - 1998 Sep 3 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 9 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1997 Mar 8 - 1997 Apr 4 Confirmed Eruption VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1997 Mar 8 - 1997 Apr 4 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1990 Jan 10 - 1995 Feb 16 ± 15 days Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 Jan 10 - 1995 Feb 16 ± 15 days | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 18 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1989 Apr 7 - 1989 Jun 26 Confirmed Eruption VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1989 Apr 7 - 1989 Jun 26 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 6 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1988 Dec 7 - 1988 Dec 7 Confirmed Eruption VEI: 2 (?)
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1988 Dec 7 - 1988 Dec 7 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1986 Mar 28 - 1988 Feb 28 Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1986 Mar 28 - 1988 Feb 28 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 10 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1985 May 26 - 1985 Oct 25 Confirmed Eruption VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1985 May 26 - 1985 Oct 25 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1984 Mar 17 - 1984 Sep 6 Confirmed Eruption VEI: 2 (?)
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1984 Mar 17 - 1984 Sep 6 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1980 Aug 23 - 1981 Dec 1 ± 30 days Confirmed Eruption VEI: 1
| Episode 1 | Eruption | Center of 1964 crater | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 Aug 23 - 1981 Dec 1 ± 30 days | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 9 Events for Episode 1 at Center of 1964 crater
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1964 Nov 12 - 1964 Nov 12 Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | Molodoy Sheveluch summit domes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1964 Nov 12 - 1964 Nov 12 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 15 Events for Episode 1 at Molodoy Sheveluch summit domes
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1944 Nov 5 - 1950 Apr 6 Confirmed Eruption VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption | Suelich | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1944 Nov 5 - 1950 Apr 6 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 6 Events for Episode 1 at Suelich
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1930 Feb 1 ± 30 days Confirmed Eruption VEI: 1
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1930 Feb 1 ± 30 days - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1928 Jan 27 - 1929 Apr 15 ± 45 days Confirmed Eruption VEI: 1
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1928 Jan 27 - 1929 Apr 15 ± 45 days | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 2 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||
1905 Confirmed Eruption
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1905 - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||
1897 - 1898 Confirmed Eruption VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1897 - 1898 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
1879 - 1883 Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1879 - 1883 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1854 Feb 18 Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1854 Feb 18 - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 6 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
[ 1800 ± 10 years ] Uncertain Eruption
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1800 ± 10 years - Unknown | Evidence from Unknown | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1739 Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1739 - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
1700 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1700 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1652 ± 11 years Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | Tephra layer SH1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1652 ± 11 years - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1 at Tephra layer SH1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
1550 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1550 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1430 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | Tephra layer SH2a | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1430 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at Tephra layer SH2a
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1150 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1150 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1034 ± 23 years Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | Tephra layer SH2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1034 ± 23 years - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1 at Tephra layer SH2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1020 (?) ± 40 years Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1020 (?) ± 40 years - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0970 (?) ± 80 years Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0970 (?) ± 80 years - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0750 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0750 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0700 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0700 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0650 ± 40 years Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | Tephra layer SH3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0650 ± 40 years - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at Tephra layer SH3
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0630 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | Western flank (Karan) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0630 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at Western flank (Karan)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0600 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0600 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
0580 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0580 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
0530 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0530 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
0500 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0500 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0380 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0380 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0250 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0250 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0230 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0230 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
0170 ± 20 years Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0170 ± 20 years - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0120 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0120 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0100 (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | Unit 21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0100 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1 at Unit 21
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
0010 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0010 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
[ 0050 BCE (?) ] Discredited Eruption
0150 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | West flank (Karan) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0150 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1 at West flank (Karan)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0300 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | West flank (Karan) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0300 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at West flank (Karan)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0400 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | West flank (Karan) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0400 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1 at West flank (Karan)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0500 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0500 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
0650 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0650 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0780 BCE ± 300 years Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | Tephra layer SH5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0780 BCE ± 300 years - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 6 Events for Episode 1 at Tephra layer SH5
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0900 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0900 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0950 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0950 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
1010 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1010 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1330 BCE ± 200 years Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1330 BCE ± 200 years - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1500 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1500 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1650 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1650 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1700 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1700 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2000 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | Tephra layer SHsp | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at Tephra layer SHsp
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2100 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2100 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2150 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2150 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2200 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2200 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2490 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2490 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2530 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2530 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2620 BCE ± 300 years Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | Tephra layer SHdv | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2620 BCE ± 300 years - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1 at Tephra layer SHdv
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2750 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2750 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2900 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2900 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3050 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3050 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3200 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3200 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3500 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3500 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
3650 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3650 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4250 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4250 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4350 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4350 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4400 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4400 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4530 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4530 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
4900 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4900 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
[ 5050 BCE (?) ] Discredited Eruption
5400 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5400 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
5500 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5500 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6000 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6000 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6100 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6100 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6200 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6200 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6350 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6350 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
6380 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6380 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
6400 BCE ± 150 years Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6400 BCE ± 150 years - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
6500 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6500 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6600 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6600 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6800 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5 (?)
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6800 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7000 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7000 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7150 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7150 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7300 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7300 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7400 BCE ± 150 years Confirmed Eruption VEI: 5
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7400 BCE ± 150 years - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (calibrated) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7500 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7500 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7550 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7550 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7600 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7600 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7630 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7630 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
7700 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7700 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7750 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7750 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7850 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7850 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
7950 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7950 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
8100 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8100 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
8200 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8200 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
8350 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8350 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
8450 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8450 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
8500 BCE (?) Confirmed Eruption VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8500 BCE (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Correlation: Tephrochronology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
There is no Deformation History data available for Sheveluch.
There is data available for 4 emission periods. Expand each entry for additional details.
| Start Date: 2015 Feb 24 | Stop Date: 2015 Mar 16 | Method: Satellite (Aura OMI) |
| SO2 Altitude Min: 7 km | SO2 Altitude Max: 9 km | Total SO2 Mass: 15 kt |
Data Details
| Date Start | Date End | Assumed SO2 Altitude | SO2 Algorithm | SO2 Mass |
| 20150316 | 9.0 | 5.000 | ||
| 20150308 | 8.0 | 2.000 | ||
| 20150303 | 9.0 | 2.000 | ||
| 20150228 | 9.0 | 2.000 | ||
| 20150226 | 7.0 | 2.000 | ||
| 20150224 | 7.0 | 2.000 |
| Start Date: 2014 Sep 24 | Stop Date: 2014 Sep 24 | Method: Satellite (Aura OMI) |
| SO2 Altitude Min: 12 km | SO2 Altitude Max: 12 km | Total SO2 Mass: 5 kt |
Data Details
| Date Start | Date End | Assumed SO2 Altitude | SO2 Algorithm | SO2 Mass |
| 20140924 | 12.0 | 5.000 |
| Start Date: 2010 Oct 27 | Stop Date: 2010 Oct 27 | Method: Satellite (Aura OMI) |
| SO2 Altitude Min: 12 km | SO2 Altitude Max: 12 km | Total SO2 Mass: 11 kt |
Data Details
| Date Start | Date End | Assumed SO2 Altitude | SO2 Algorithm | SO2 Mass |
| 20101027 | 12.0 | 11.000 |
| Start Date: 2004 May 10 | Stop Date: 2004 May 10 | Method: Satellite (Earth Probe TOMS) |
| SO2 Altitude Min: 11 km | SO2 Altitude Max: 11 km | Total SO2 Mass: 1 kt |
Data Details
| Date Start | Date End | Assumed SO2 Altitude | SO2 Algorithm | SO2 Mass |
| 20040510 | 11.0 | 1.000 |
 Sheveluch towers above the Kamchatka River and is one of the largest volume volcanoes in Kamchatka. A large horseshoe-shaped crater, whose northern headwall is seen in this view, formed by collapse during the Pleistocene. Repeated edifice collapse events form a vast debris avalanche plain to the south, overlain by block-and-ash flow deposits from dome collapse events. The most recent edifice collapse occurred in 1964, and the resulting deposit forms the light-colored area below the volcano to the right.
Sheveluch towers above the Kamchatka River and is one of the largest volume volcanoes in Kamchatka. A large horseshoe-shaped crater, whose northern headwall is seen in this view, formed by collapse during the Pleistocene. Repeated edifice collapse events form a vast debris avalanche plain to the south, overlain by block-and-ash flow deposits from dome collapse events. The most recent edifice collapse occurred in 1964, and the resulting deposit forms the light-colored area below the volcano to the right. Following the 1964 eruption and debris avalanche, erosional canyons formed in the pyroclastic flow deposits that overlie debris avalanche deposits. The pyroclastic flows were produced during the explosive Plinian phase that followed catastrophic flank collapse.
Following the 1964 eruption and debris avalanche, erosional canyons formed in the pyroclastic flow deposits that overlie debris avalanche deposits. The pyroclastic flows were produced during the explosive Plinian phase that followed catastrophic flank collapse.  These paired photos show Sheveluch volcano from the south before (top) and after (bottom) a major eruption in 1964. A brief, but powerful eruption on 12 November 1964 resulted in collapse of the south summit of Sheveluch (Crater Top), forming a 1.5 x 3 km open crater seen in the bottom photo. A large debris avalanche swept to the south, after which a Plinian eruption with an ash plume 10-15 km high produced pumice fall and pumiceous pyroclastic flow deposits.
These paired photos show Sheveluch volcano from the south before (top) and after (bottom) a major eruption in 1964. A brief, but powerful eruption on 12 November 1964 resulted in collapse of the south summit of Sheveluch (Crater Top), forming a 1.5 x 3 km open crater seen in the bottom photo. A large debris avalanche swept to the south, after which a Plinian eruption with an ash plume 10-15 km high produced pumice fall and pumiceous pyroclastic flow deposits. Steam and gases rise from vents on the summit and flanks of a new lava dome that began to grow in 1980 within the 1964 crater of Sheveluch. The northern wall of the 1964 crater appears in the background. By the time the eruption ended in late 1981, the dome had grown to a height of 180 m.
Steam and gases rise from vents on the summit and flanks of a new lava dome that began to grow in 1980 within the 1964 crater of Sheveluch. The northern wall of the 1964 crater appears in the background. By the time the eruption ended in late 1981, the dome had grown to a height of 180 m. Nearly 16 years after the previous eruption of Sheveluch in 1964, lava dome extrusion began on 23 August 1980. Dome growth accompanied by minor explosions and avalanches took place at the location of an older dome in the 1964 crater, and continued until the end of 1981. This November 1980 photo shows gas rising from the base of the new dome, which by this time was about 170 m high and 300 m wide.
Nearly 16 years after the previous eruption of Sheveluch in 1964, lava dome extrusion began on 23 August 1980. Dome growth accompanied by minor explosions and avalanches took place at the location of an older dome in the 1964 crater, and continued until the end of 1981. This November 1980 photo shows gas rising from the base of the new dome, which by this time was about 170 m high and 300 m wide. A block-and-ash flow descends the lava dome in the crater of Sheveluch; it eventually reached 1.5 km from the dome. Growth of the dome recommenced on 23 August 1980. By the time the eruption ended in late 1981 the dome had reached a height of 180 m and a diameter of 350 m.
A block-and-ash flow descends the lava dome in the crater of Sheveluch; it eventually reached 1.5 km from the dome. Growth of the dome recommenced on 23 August 1980. By the time the eruption ended in late 1981 the dome had reached a height of 180 m and a diameter of 350 m.  Ash clouds rise in 1948 above a pyroclastic flow descending the flanks of a lava dome growing in the crater of Shiveluch volcano, seen here from the south. Explosive activity beginning in late 1944 became more frequent and powerful prior to the onset of dome growth in 1946. By the time dome growth ceased in 1949, the Suelich dome had a height of 500-600 m and a diameter of 1 km. Explosive eruptions continued intermittently until April 1950. This marked the last eruptive activity of Shiveluch prior to a catastrophic eruption in 1964.
Ash clouds rise in 1948 above a pyroclastic flow descending the flanks of a lava dome growing in the crater of Shiveluch volcano, seen here from the south. Explosive activity beginning in late 1944 became more frequent and powerful prior to the onset of dome growth in 1946. By the time dome growth ceased in 1949, the Suelich dome had a height of 500-600 m and a diameter of 1 km. Explosive eruptions continued intermittently until April 1950. This marked the last eruptive activity of Shiveluch prior to a catastrophic eruption in 1964. The lava dome in the Sheveluch crater is seen from the north on 2 February 1990, four days after a series of explosions began. The explosions created funnel-shaped vents at the dome summit up to a few tens of meters wide. Subsequent explosions occurred on 6 February, 2, 5, and 29-30 March, 26 and 29 April, and 4 August 1990. The latter eruption was the most vigorous since 1984, producing a 6-km-high ash plume, lahars, and block-and-ash flows that traveled 2 km.
The lava dome in the Sheveluch crater is seen from the north on 2 February 1990, four days after a series of explosions began. The explosions created funnel-shaped vents at the dome summit up to a few tens of meters wide. Subsequent explosions occurred on 6 February, 2, 5, and 29-30 March, 26 and 29 April, and 4 August 1990. The latter eruption was the most vigorous since 1984, producing a 6-km-high ash plume, lahars, and block-and-ash flows that traveled 2 km. An ash plume at Sheveluch volcano is observed in 1984 from the town of Klyuchi, 50 km to the SW. The eruption originated from a lava dome that began growing in 1980 within a crater that formed during flank collapse in 1964. No change in the geometry of the lava dome was noticed from 1983 until the onset of the 1984 eruption.
An ash plume at Sheveluch volcano is observed in 1984 from the town of Klyuchi, 50 km to the SW. The eruption originated from a lava dome that began growing in 1980 within a crater that formed during flank collapse in 1964. No change in the geometry of the lava dome was noticed from 1983 until the onset of the 1984 eruption. The light-colored deposits were produced by a debris avalanche resulting from a major flank collapse at Sheveluch in 1964. The debris avalanche traveled up to 15 km from its source at very high velocities before stopping abruptly, leaving trees just beyond its terminus unaffected.
The light-colored deposits were produced by a debris avalanche resulting from a major flank collapse at Sheveluch in 1964. The debris avalanche traveled up to 15 km from its source at very high velocities before stopping abruptly, leaving trees just beyond its terminus unaffected.  Sheveluch has undergone several large flank collapse events to shape the edifice we see today. The frequent collapses of lava-dome complexes have produced numerous debris avalanches whose deposits cover much of the area south of the volcano. The light-colored hummocky deposits in the foreground were produced during the latest collapse in 1964.
Sheveluch has undergone several large flank collapse events to shape the edifice we see today. The frequent collapses of lava-dome complexes have produced numerous debris avalanches whose deposits cover much of the area south of the volcano. The light-colored hummocky deposits in the foreground were produced during the latest collapse in 1964. Small plumes rise above rockfalls accompanying renewed lava-dome growth at Sheveluch volcano on 22 August 1993. Intermittent mild explosions with a maximum cloud height of 5 km began on 11 April 1992. A large explosive eruption on 22 April produced an 18-km-high ash plume and pyroclastic flows. Renewed dome growth began that month, and by 27 May the lava dome had doubled its pre-eruption height to 400 m. Dome growth along with intermittent mild explosive activity continued until at least July 1994.
Small plumes rise above rockfalls accompanying renewed lava-dome growth at Sheveluch volcano on 22 August 1993. Intermittent mild explosions with a maximum cloud height of 5 km began on 11 April 1992. A large explosive eruption on 22 April produced an 18-km-high ash plume and pyroclastic flows. Renewed dome growth began that month, and by 27 May the lava dome had doubled its pre-eruption height to 400 m. Dome growth along with intermittent mild explosive activity continued until at least July 1994. The Kinenin maar lies at the eastern foot of the Sredinny Range, about 80 km NW of Sheveluch seen in the background. The eruption took place about 1,100 years ago, and the maar is now partially filled by a 1-km-wide lake whose surface is at 400 m elevation.
The Kinenin maar lies at the eastern foot of the Sredinny Range, about 80 km NW of Sheveluch seen in the background. The eruption took place about 1,100 years ago, and the maar is now partially filled by a 1-km-wide lake whose surface is at 400 m elevation. An ash plume from Sheveluch was photographed by NASA astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) around 21 March 2007. Dome growth had recommenced in 1999 and resulted in ash plumes, avalanches, and occasional block-and-ash flows.
An ash plume from Sheveluch was photographed by NASA astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) around 21 March 2007. Dome growth had recommenced in 1999 and resulted in ash plumes, avalanches, and occasional block-and-ash flows. An avalanche descends the NE flank of the Sheveluch lava dome on 6 July 2015, seen above the 1964 flank collapse scarp rim. Fragmentation of the hot dome rock produces the beginning of an ash plume above it and degassing is also visible across the dome.
An avalanche descends the NE flank of the Sheveluch lava dome on 6 July 2015, seen above the 1964 flank collapse scarp rim. Fragmentation of the hot dome rock produces the beginning of an ash plume above it and degassing is also visible across the dome. This closeup view of the eastern flank of the Sheveluch lava dome shows degassing across the surface on 6 July 2015. In the lower right is the top of the 1964 flank collapse scarp that encloses the dome.
This closeup view of the eastern flank of the Sheveluch lava dome shows degassing across the surface on 6 July 2015. In the lower right is the top of the 1964 flank collapse scarp that encloses the dome. This 6 July 2015 photo of Sheveluch is from the Baidarnaya river channel to the SE. The higher edifice to the right is Old Sheveluch, and the rest of the edifice shown here is “Young Sheveluch”. An ash plume is rising from the lava dome, seen beyond the 1964 collapse scarp.
This 6 July 2015 photo of Sheveluch is from the Baidarnaya river channel to the SE. The higher edifice to the right is Old Sheveluch, and the rest of the edifice shown here is “Young Sheveluch”. An ash plume is rising from the lava dome, seen beyond the 1964 collapse scarp. This large boulder is dome rock that was carried by and emplaced within the 27-28 February 2005 Sheveluch block-and-ash flow, 15 km away from its source. It has been exposed in an eroded channel, surrounded by highly fragmented dome remnants.
This large boulder is dome rock that was carried by and emplaced within the 27-28 February 2005 Sheveluch block-and-ash flow, 15 km away from its source. It has been exposed in an eroded channel, surrounded by highly fragmented dome remnants. This July 2015 photo looks across the 2010 Sheveluch block-and-ash flow towards the 1964 debris avalanche deposit. Klyuchevskoy (left) and Ushkovsky (right) are in the background, with a gas plume emitting from the former. The section of deposit in the foreground is darker because of cloud cover.
This July 2015 photo looks across the 2010 Sheveluch block-and-ash flow towards the 1964 debris avalanche deposit. Klyuchevskoy (left) and Ushkovsky (right) are in the background, with a gas plume emitting from the former. The section of deposit in the foreground is darker because of cloud cover. This section within the Sheveluch the block-and-ash flow deposit from 27-28 February 2005 was exposed by the new Baidarnaya river channel along the northern edge of the deposit. The deposit is composed of fragmented lava dome rock and overlies older laminated deposits, seen here in July 2015.
This section within the Sheveluch the block-and-ash flow deposit from 27-28 February 2005 was exposed by the new Baidarnaya river channel along the northern edge of the deposit. The deposit is composed of fragmented lava dome rock and overlies older laminated deposits, seen here in July 2015. The trees in this dam were entrained by the 27-28 February 2005 block-and-ash flow and emplaced over 13 km from the dome, near the end of the deposit. The flow destroyed around 10 km2 of forest and emplaced material reaching over 20 m thick in places.
The trees in this dam were entrained by the 27-28 February 2005 block-and-ash flow and emplaced over 13 km from the dome, near the end of the deposit. The flow destroyed around 10 km2 of forest and emplaced material reaching over 20 m thick in places.  The trees along the Baidarnaya river channel walls in this 2015 view towards the W were killed by the October 2010 block-and-ash flow, around 14 km from the lava dome where the flow originated. By the time this photo was taken, extensive erosion had occurred through the deposit across the channel floor.
The trees along the Baidarnaya river channel walls in this 2015 view towards the W were killed by the October 2010 block-and-ash flow, around 14 km from the lava dome where the flow originated. By the time this photo was taken, extensive erosion had occurred through the deposit across the channel floor. This boulder was part of the lava dome at Sheveluch before a collapse produced the 27 October 2010 block-and-ash-flow that emplaced it 13 km away. The hot dome rock fragmented as it travelled, producing a large amount of ash with a large range of block sizes within the ash matrix.
This boulder was part of the lava dome at Sheveluch before a collapse produced the 27 October 2010 block-and-ash-flow that emplaced it 13 km away. The hot dome rock fragmented as it travelled, producing a large amount of ash with a large range of block sizes within the ash matrix.Maps are not currently available due to technical issues.
The maps shown below have been scanned from the GVP map archives and include the volcano on this page. Clicking on the small images will load the full 300 dpi map. Very small-scale maps (such as world maps) are not included.
The following 2 samples associated with this volcano can be found in the Smithsonian's NMNH Department of Mineral Sciences collections, and may be availble for research (contact the Rock and Ore Collections Manager). Catalog number links will open a window with more information.
| Catalog Number | Sample Description | Lava Source | Collection Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| NMNH 116556-8 | Dacitic Andesite | -- | -- |
| NMNH 116556-9 | Dacitic Andesite | -- | -- |
| Copernicus Browser | The Copernicus Browser replaced the Sentinel Hub Playground browser in 2023, to provide access to Earth observation archives from the Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, the main distribution platform for data from the EU Copernicus missions. |
| MIROVA | Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity (MIROVA) is a near real time volcanic hot-spot detection system based on the analysis of MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) data. In particular, MIROVA uses the Middle InfraRed Radiation (MIR), measured over target volcanoes, in order to detect, locate and measure the heat radiation sourced from volcanic activity. |
| MODVOLC Thermal Alerts | Using infrared satellite Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) data, scientists at the Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology, University of Hawai'i, developed an automated system called MODVOLC to map thermal hot-spots in near real time. For each MODIS image, the algorithm automatically scans each 1 km pixel within it to check for high-temperature hot-spots. When one is found the date, time, location, and intensity are recorded. MODIS looks at every square km of the Earth every 48 hours, once during the day and once during the night, and the presence of two MODIS sensors in space allows at least four hot-spot observations every two days. Each day updated global maps are compiled to display the locations of all hot spots detected in the previous 24 hours. There is a drop-down list with volcano names which allow users to 'zoom-in' and examine the distribution of hot-spots at a variety of spatial scales. |
|
WOVOdat
Single Volcano View Temporal Evolution of Unrest Side by Side Volcanoes |
WOVOdat is a database of volcanic unrest; instrumentally and visually recorded changes in seismicity, ground deformation, gas emission, and other parameters from their normal baselines. It is sponsored by the World Organization of Volcano Observatories (WOVO) and presently hosted at the Earth Observatory of Singapore.
GVMID Data on Volcano Monitoring Infrastructure The Global Volcano Monitoring Infrastructure Database GVMID, is aimed at documenting and improving capabilities of volcano monitoring from the ground and space. GVMID should provide a snapshot and baseline view of the techniques and instrumentation that are in place at various volcanoes, which can be use by volcano observatories as reference to setup new monitoring system or improving networks at a specific volcano. These data will allow identification of what monitoring gaps exist, which can be then targeted by remote sensing infrastructure and future instrument deployments. |
| Volcanic Hazard Maps | The IAVCEI Commission on Volcanic Hazards and Risk has a Volcanic Hazard Maps database designed to serve as a resource for hazard mappers (or other interested parties) to explore how common issues in hazard map development have been addressed at different volcanoes, in different countries, for different hazards, and for different intended audiences. In addition to the comprehensive, searchable Volcanic Hazard Maps Database, this website contains information about diversity of volcanic hazard maps, illustrated using examples from the database. This site is for educational purposes related to volcanic hazard maps. Hazard maps found on this website should not be used for emergency purposes. For the most recent, official hazard map for a particular volcano, please seek out the proper institutional authorities on the matter. |
| IRIS seismic stations/networks | Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology (IRIS) Data Services map showing the location of seismic stations from all available networks (permanent or temporary) within a radius of 0.18° (about 20 km at mid-latitudes) from the given location of Sheveluch. Users can customize a variety of filters and options in the left panel. Note that if there are no stations are known the map will default to show the entire world with a "No data matched request" error notice. |
| UNAVCO GPS/GNSS stations | Geodetic Data Services map from UNAVCO showing the location of GPS/GNSS stations from all available networks (permanent or temporary) within a radius of 20 km from the given location of Sheveluch. Users can customize the data search based on station or network names, location, and time window. Requires Adobe Flash Player. |
| DECADE Data | The DECADE portal, still in the developmental stage, serves as an example of the proposed interoperability between The Smithsonian Institution's Global Volcanism Program, the Mapping Gas Emissions (MaGa) Database, and the EarthChem Geochemical Portal. The Deep Earth Carbon Degassing (DECADE) initiative seeks to use new and established technologies to determine accurate global fluxes of volcanic CO2 to the atmosphere, but installing CO2 monitoring networks on 20 of the world's 150 most actively degassing volcanoes. The group uses related laboratory-based studies (direct gas sampling and analysis, melt inclusions) to provide new data for direct degassing of deep earth carbon to the atmosphere. |
| Large Eruptions of Sheveluch | Information about large Quaternary eruptions (VEI >= 4) is cataloged in the Large Magnitude Explosive Volcanic Eruptions (LaMEVE) database of the Volcano Global Risk Identification and Analysis Project (VOGRIPA). |
| EarthChem | EarthChem develops and maintains databases, software, and services that support the preservation, discovery, access and analysis of geochemical data, and facilitate their integration with the broad array of other available earth science parameters. EarthChem is operated by a joint team of disciplinary scientists, data scientists, data managers and information technology developers who are part of the NSF-funded data facility Integrated Earth Data Applications (IEDA). IEDA is a collaborative effort of EarthChem and the Marine Geoscience Data System (MGDS). |