Due to the US Government shutdown, the Smithsonian is temporarily closed. The Global Volcanism Program website will remain available but will not be monitored or updated. Status updates will be available on the Smithsonian homepage.



The Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) reported ongoing unrest at Ambrym during September. A weak thermal anomaly was detected in satellite images on 4 and 12 September. Seismic data confirmed ongoing unrest. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
New ash eruption with crater incandescence in late January 2022
Ambrym contains a 12-km-wide caldera and is part of the New Hebrides Arc, located in the Vanuatu archipelago. The two currently active craters within the caldera are Benbow and Marum, which have produced lava lakes, explosions, lava flows, ash, and gas emissions. The previous eruption period, which began in May 2008, ended in December 2018 with lava fountains, lava flows, a submarine fissure eruption, and drainage of the lava lake (BGVN 45:03). After those events no eruptive activity was reported until January 2022, which consisted of ash plumes and crater incandescence. This report updates information from April 2020 through March 2022 and describes a short eruption period during 25 January to the beginning of February 2022. Information comes from the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) and satellite data.
Activity during April 2020 through December 2021 was relatively low and consisted mainly of gas-and-steam emissions from both Benbow and Marum craters. On 25 January 2022 the Volcanic Alert Level (VAL) was raised from Level 1 to 2 (on a scale of 0-5) due to increased activity beginning around 0400. Significant gas-and-steam emissions were observed rising from Marum, and gas-and-ash emissions rose from Benbow at 0515 (figure 52). A sulfur dioxide plume that exceeded 2 DUs (Dobson Units) was detected on 25 January and drifted SE, following the ash plume, based on data from the Sentinel-5 instrument (figure 53). At night on 25 January, crater incandescence from Benbow was visible in webcam images, which represented a lava flow that had effused from a new vent on the NW part of the crater floor. Incandescence persisted through 27 January, according to VMGD (figure 54).
 |
Figure 52. Webcam image of Ambrym at 0645 on 25 January 2022 showing an ash plume rising above the Benbow crater. Courtesy of VMGD. |
By early February, crater incandescence was no longer visible. On 2 February sulfur dioxide emissions were still detected in satellite images and drifted E. According to VMGD, no gas-and-steam emissions were visible from Benbow during early February through April and seismicity had decreased. As a result, the VAL was lowered to Level 1 on 28 April.
Information Contacts: Geo-Hazards Division, Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD), Ministry of Climate Change Adaptation, Meteorology, Geo-Hazards, Energy, Environment and Disaster Management, Private Mail Bag 9054, Lini Highway, Port Vila, Vanuatu (URL: http://www.vmgd.gov.vu/, https://www.facebook.com/VanuatuGeohazardsObservatory/); NASA Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard, MD 20771, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/).
2025: January
| February
| April
| May
| June
| July
| August
| September
2024: January
| April
| May
| October
| November
| December
2023: October
2022: January
| February
| March
| April
2019: April
| October
2018: March
| April
| June
| August
| November
| December
2017: March
| August
| September
| October
| December
2016: June
2015: February
| April
| May
| July
| August
2014: September
| November
| December
2013: June
| July
| August
2011: June
| July
2010: March
| August
2009: March
| December
2007: March
| April
| May
2004: March
The Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) reported ongoing unrest at Ambrym during September. A weak thermal anomaly was detected in satellite images on 4 and 12 September. Seismic data confirmed ongoing unrest. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
The Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) reported ongoing unrest at Ambrym during August. A weak thermal anomaly was detected in satellite images on 2 August. Steam emissions rising from Marum Crater on 5 August were reported based on field observations and webcam images. Seismic data confirmed ongoing unrest. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
The Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) reported ongoing unrest at Ambrym during the month of July. Field observations and webcam images from 11 and 14 July confirmed continuous degassing at Marum crater. Low-level thermal anomalies were detected in satellite imagery from 14 and 27 July. Seismic data further confirmed ongoing unrest. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside the Permanent Exclusion Zone, which includes a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater, and Danger Zone A, a 2-km radius around Marum Crater (including Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu, and Mbwelesu), and to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 27 June the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) reported ongoing unrest at Ambrym during the month. Webcam images recorded steam emissions rising from both Benbow and Marum craters during 7, 10-11, and 24 June, and a weak thermal anomaly on 17 June. Seismic data confirmed ongoing unrest. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 28 May the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) reported ongoing unrest at Ambrym during the month of May. Webcam images recorded volcanic emissions rising from Benbow Crater on 9 May. Seismic data confirmed ongoing unrest. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 24 April the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) reported ongoing fumarolic activity at Ambrym from both Benbow and Marum craters based on webcam images. Seismic data confirmed ongoing unrest. A low-level thermal anomaly was identified in satellite data on 9 April indicative of increased surface temperatures. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 27 February the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) reported ongoing fumarolic activity at Ambrym from both Benbow and Marum craters based on webcam images. Seismic data confirmed ongoing unrest. A low-level thermal anomaly was identified in satellite data from 11 February indicting increased surface temperatures. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 30 January the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) reported ongoing fumarolic activity at Ambrym from both Benbow and Marum craters based on webcam images. Seismic data confirmed ongoing unrest. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 31 December the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) reported ongoing fumarolic activity at Ambrym from both Benbow and Marum craters based on webcam images. Thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images on 4, 18, and 27 December, indicating increased surface temperatures. Sulfur dioxide emissions were detected on 27 December. Seismic data confirmed ongoing unrest. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
The Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) reported eruptive activity at Ambrym during October and November. In October small steam emissions from both Benbow and Marum craters were visible in webcam images. A low-level thermal anomaly over the volcano was detected in satellite images on 3 October indicating the presence of lava at or near the surface. Low-to-moderate thermal anomalies were identified in satellite images during 1, 2, 5, and 11-12 November. Seismic data confirmed an ongoing volcanic activity. On 12 November interferometry analysis of satellite data indicated magma movement beneath the surface. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 1 November, the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) reported ongoing fumarolic activity at Ambrym from both Benbow and Marum craters based on webcam images, as well as satellite images acquired on 31 October. Satellite images also indicated moderate thermal anomalies. Incandescence was observed during the night of 31 October, and seismic activity continued. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 30 May the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) reported that ongoing small fumarolic steam emissions at Ambrym were coming from both Benbow and Marum craters based on both satellite and webcam images. Seismic data also confirmed ongoing unrest. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 25 April the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) reported that small fumarolic steam emissions were ongoing in both of Ambrym’s Benbow and Marum craters. A satellite image from 20 April showed minor amounts of gas emissions. Incandescence at Marum was visible at night during 20-21 April and a low- to moderate-intensity thermal anomaly was identified in a satellite image on 23 April. Seismic data also confirmed ongoing unrest. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
The Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) reported that lava effusion in Ambrym began on 13 January and lasted for four days, producing a lava flow in Benbow Crater. Since then, steam emissions were ongoing and observed through 31 January. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
The Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) reported that at 2217 on 13 January an eruption began at Ambrym’s Benbow Crater based on webcam and seismic data. The eruption was characterized by a loud explosion, intense incandescence at the crater, and gas-and-steam emissions. The Alert Level was raised from 1 to 3 (on a scale of 0-5) and the public to stay 2 km away from Benbow Crater and 4 km away from Marum Crater, and additionally to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption. Sulfur dioxide emissions measured using satellite data were 1,116 tons per day on 14 January. Activity decreased during 15-17 January based on webcam images, seismic data, and field observations. Gas, steam, and ash emissions had decreased, and crater incandescence was dim or not visible at all. The Alert Level was lowered to 2 on 17 January.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
The Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) reported ongoing volcanic earthquakes and tremors at Ambrym during October. Volcanic activity increased for a few hours during 22-23 October and diffuse gas emissions were detected in satellite data on 23 October. The Alert Level was lowered to 1 (on a scale of 0-5) on 28 April. VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and additionally to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
The Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) reported that incandescence from Ambrym’s Benbow Crater was visible during 25 January-3 February from a lava flow that had effused from a new vent on the NW part of the crater floor. Recent observations indicated that gas and ash was no longer being emitted from the crater, and seismicity had decreased and stabilized. The Alert Level was lowered to 1 (on a scale of 0-5) on 28 April. VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and additionally to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 31 March the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) reported that nighttime crater incandescence from Ambrym’s Benbow Crater was no longer visible, though steam emissions persisted. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and additionally to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 24 February the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) reported that nighttime crater incandescence from Ambrym’s Benbow Crater was no longer visible, though steam emissions persisted. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of the Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and additionally to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 2 February the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) reported that sulfur dioxide gas emissions from Ambrym were detected in satellite images drifting E. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of the Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and additionally to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 27 January the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) reported that steam-and-gas emissions rose from Ambrym’s Benbow Crater, and incandescence from the same crater was visible at night. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). VMGD warned the public to stay outside of the Permanent Danger Zone A, defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and additionally to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 25 January the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) raised the Alert Level for Ambrym to 2 (on a scale of 0-5) due to a significant increase in activity beginning at around 0400. Steam emissions rose from Marum Crater, and at 0515 a steam, gas, and ash plume rose from Benbow Crater. Satellite data recorded increased sulfur dioxide emissions from Benbow, and residents of Ambrym and surrounding islands reported seeing incandescence from crater overnight. VMGD warned the public to stay outside of the Permanent Danger Zone A defined as a 1-km radius around Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius around Marum Crater, and additionally to stay 500 m away from the ground cracks created by the December 2018 eruption.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) reported that data and observations during February-October indicated that conditions at Ambrym had become stable after the eruption in December 2018 that focused on the summit caldera and East Rift Zone. On 10 October the Alert Level was lowered to 1 (on a scale of 0-5) indicating minor unrest. VMGD warned the public to stay outside of the Permanent Danger Zone defined as a 1-km radius from Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius from Marum Crater, and additionally to stay away from the ground cracks resulting from the December 2019 eruption (a 500-m-radius around the major cracks at Paamal village).
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 24 April the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) reported ongoing seismic activity at Ambrym and steam emissions. The lava lakes in Benbow and Marum craters had ceased to be active on 16 December 2018, one day after a fissure eruption began in the ESE part of the summit caldera near the Lewlembwi crater, and continued to be inactive. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5); the report reminded the public to stay outside of the Permanent Danger Zone defined as a 1-km radius from Benbow Crater and a 2-km radius from Marum Crater. An additional Danger Zone was defined as a 1-km radius around the December 2018 fissures.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
The Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-hazards Department (VMGD) reported that a fissure eruption in the ESE part of the Ambrym summit caldera near the Lewlembwi crater (4 km SE of Marum) began at 0600 on 15 December, heralded by elevated seismicity detected by the seismic network and ash emissions visible in the webcam. A notice issued later that day by VMGD stated that lava flows and lava fountains were visible, and explosions were occurring. John Tasso, a local guide, visited the caldera a few hours after the new activity started and observed lava fountains from a fissure eruption; his video was posted to his website. The lava fountains were about 40 m high; lava flows spread to the E part of the caldera. Although partially obscured by a steam plume directly above the eruption site, infrared imagery from the Sentinel-2 satellite on 15 December showed lava filling much of the 500 x 900 m Lewlembwi crater and a lava flow almost as large a few hundred meters SW of that crater. VMGD raised the Alert Level to 3 and stated that the eruption was characterized as “small scale.” The eruption continued during 16-17 December, though reports on 17 December only described ongoing ash-and-gas emissions.
Sources: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD); John Tasso, Vanuatu Island Experience, Port Vatu, West Ambrym, Vanuatu; Sentinel Hub
On 15 November the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-hazards Department (VMGD) reported that the lava lakes in Ambrym’s Benbow and Marum craters continued to be active during October and November, and produced substantial and sustained gas-and-steam emissions. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5); the report reminded the public to stay outside of the Permanent Danger Zone defined as a 1-km radius from Benbow Crater and a 2.7-km radius from Marum Crater.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 22 August the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-hazards Department reported that the lava lakes in Ambrym’s Benbow and Marum craters continued to be active, and produced sustained and substantial gas-and-steam emissions. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5); the report reminded the public to stay outside of the Permanent Danger Zone defined as a 1-km radius from Benbow Crater and a 2.7-km radius from Marum Crater.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 7 June the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory (VGO) reported that the lava lakes in Ambrym’s Benbow and Marum craters continued to be active, and produced sustained and substantial gas-and-steam emissions. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5); the report reminded the public to stay outside of the Permanent Danger Zone defined as a 1-km radius from Benbow Crater and a 2.7-km radius from Marum Crater.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 25 April the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory (VGO) reported that the lava lakes in Ambrym’s Benbow and Marum craters continued to be active, and produced gas-and-steam emissions. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5); the report reminded the public to stay outside of the Permanent Danger Zone defined as a 1-km radius from Benbow Crater and a 2.7-km radius from Marum Crater.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 19 March the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory (VGO) reported that, based on photos taken during February-March, the lava lakes in Ambrym’s Benbow and Marum craters continued to be active and produced gas-and-steam emissions. Visitors occasionally reported smelling volcanic gases and hearing explosions. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5); the report reminded the public to stay outside of the Permanent Danger Zone defined as a 1-km radius from Benbow Crater and a 2.7-km radius from Marum Crater.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 7 December Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory (VGO) lowered the Alert Level for Ambrym to 2 (on a scale of 0-5), noting that activity had stabilized by the end of November and was characterized by gas-and-steam emissions. Seismicity had also declined. The report reminded the public to stay outside of the Permanent Danger Zone defined as a 1-km radius from Benbow Crater and a 2.7-km radius from Marum Crater.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
The Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory (VGO) reported that aerial observations of Ambrym on 24 and 30 September, and 1 and 6 October, and the analysis of seismic data, confirmed that minor eruptive activity within the caldera was characterized by hot volcanic gas and steam emissions. The Alert Level remained at 3 (on a scale of 0-5). Areas deemed hazardous were within a 2-km radius from Benbow Crater and a 3-km radius from Marum Crater.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 28 September the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory (VGO) reported that minor eruptive activity continued at Ambrym. The Alert Level remained at 3 (on a scale of 0-5). Areas deemed hazardous were within a 2-km radius from Benbow Crater and a 3-km radius from Marum Crater.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 30 August the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory (VGO) reported that “drastic changes” at Ambrym prompted an increase in the Alert Level from 2 to 3 (on a scale of 0-5). Areas deemed hazardous were near and around the active vents (Benbow, Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu and Mbwelesu), and in downwind areas prone to ashfall. According to a news article, a representative of VGO indicated that the Alert Level change was based on increased seismicity detected since the beginning of August but which became more notable on 25 August. Since monitoring of the volcano started around 20 years ago, the Alert Level had never been elevated past 2.
Sources: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD); Radio New Zealand
The Wellington VAAC reported that a low-level ash emission from Ambrym was identified in satellite images on 3 April.
Source: Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
On 27 May the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory issued a statement reminding residents and visitors that Ambrym remained active; the Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). Areas deemed hazardous were near and around the active vents (Benbow, Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu and Mbwelesu), and in downwind areas prone to ashfall.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 21 August the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory issued a statement reminding residents and visitors that Ambrym remained active; the Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). Areas deemed hazardous were near and around the active vents (Benbow, Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu and Mbwelesu), and in downwind areas prone to ashfall.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 22 July the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory issued a statement reminding residents and visitors that Ambrym remained active; the Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). Areas deemed hazardous were near and around the active vents (Benbow, Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu, and Mbwelesu), and in downwind areas prone to ashfall.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 18 May the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory issued a statement reminding residents and visitors that Ambrym remained active. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-5). Areas deemed hazardous were near and around the active vents (Benbow, Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu and Mbwelesu), and in downwind areas prone to ashfall.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 7 April the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory issued a statement reminding residents and visitors that Ambrym remained active. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a new scale of 0-5). Areas deemed hazardous were near and around the active vents (Benbow, Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu and Mbwelesu), and in downwind areas prone to ashfall.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 2 March the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory reported that activity at Ambrym had slightly decreased but remained elevated. The Alert Level was lowered to 2 (on a new scale of 0-5). Areas deemed hazardous were near and around the active vents (Benbow, Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu and Mbwelesu), and in downwind areas prone to ashfall.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 21 February the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory issued a notice reminding the public that a minor eruption was occurring at Ambrym from a new vent inside the caldera. The Alert Level was raised to 3 (on a new scale of 0-5). Hazardous areas were identified as being near and around the active vents (Benbow, Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu and Mbwelesu), and in downwind areas prone to ashfall.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 8 December the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory reported that observations and analyses of Ambrym conducted during November and early December showed that activity levels had slightly decreased. The Alert Level was lowered to 1 (on a scale of 0-4). VGO warned that the area in close proximity to the active vents (Benbow, Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu, and Mbwelesu) remained dangerous.
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 10 November the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory reported that activity at Ambrym remained elevated. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-4).
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 1 October the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory reported a slight increase in activity from Ambrym. The Alert Level remained at 2 (on a scale of 0-4).
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 11 September, the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory reported increased seismicity from Ambrym and raised the Alert Level from 1 to 2 (on a scale of 0-4).
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
According to NASA's Earth Observatory, a satellite image acquired on 9 August showed steam-and-gas plumes rising from Ambrym’s Benbow cone and from the active lava lake in Mbwelesu Crater (one of three active sub-craters of the Marun cone).
Source: NASA Earth Observatory
The Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory reported that activity at Ambrym slightly increased to a minor eruptive phase, and a seismic swarm was detected between 2400 and 0700 on 26 July. The Alert Level remained at 1 (on a scale of 0-4).
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
On 21 June the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory reported that satellite images on 2, 4, 11, 14, and 16 June detected gas emissions from Ambrym. Emissions of minor amounts of ash and substantial amounts of gas from the active vents had been detected during the previous week. The report warned that communities on the island, especially those downwind of Ambrym, may experience ashfall and acid rain that could damage to the environment and contaminate water. The Alert Level remained at 1 (on a scale of 0-4).
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
Based on pilot observations and analyses of satellite imagery, the Wellington VAAC reported that on 19 July an ash plume from Ambrym rose to an altitude of 3 km (10,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted 185 km NW.
Source: Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
On 27 June, the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory reported that data collected from Ambrym's monitoring network showed significant degassing daily and occasional explosions in the crater. Field observers noted that the level of the lava lakes was high. During June, villages reported minor ashfall and that acid rain affected vegetables in some areas W, S, and E. The Alert Level remained at 1 (on a scale of 0-4).
Source: Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD)
Based on pilot observations, analyses of satellite imagery, and information from the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory, the Wellington VAAC reported that on 8 and 10 August ash-and-steam plumes from Ambrym rose to an altitude 6.1 km (20,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted W and NW.
Source: Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
Based on pilot observations and analyses of satellite imagery, the Wellington VAAC reported that ash plumes from Ambrym rose to an altitude of 2.4 km (8,000 ft) a.s.l. on 5 March.
Source: Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
On 3 December, a diffuse plume from Ambrym, likely largely composed of sulfur dioxide, was visible on satellite imagery acquired by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and posted on NASA's Earth Observatory website.
Source: NASA Earth Observatory
Based on information from the Port Vila airport tower, the Wellington VAAC reported that on 25 March an ash plume from Ambrym rose to an altitude of 2.1 km (7,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted about 55 km S. The next day, a pilot reported that "smoke" rose to an altitude of 2.4 km (8,000 ft) a.s.l. Ash was not identified on satellite imagery.
Source: Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
The Wellington VAAC reported that a pilot observed an ash plume from Ambrym on 3 May. The plume rose to an altitude of 1.8 km (6,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted SE. Ash was visible on satellite imagery.
Source: Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
The Wellington VAAC reported that an ash plume from Ambrym was visible on satellite imagery on 1 May. The altitude and direction of the plume were not reported.
Source: Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
The Wellington VAAC reported that on 3 April pilots observed lava and ash emissions from Ambrym. Ash plumes rose to altitudes below 2.4 km (8,000 ft) a.s.l.
Source: Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC)
According to a report from John Seach, during March an active lava lake was present in Ambrym's Mbwelesu crater.
Source: Volcano Live
Reports are organized chronologically and indexed below by Month/Year (Publication Volume:Number), and include a one-line summary. Click on the index link or scroll down to read the reports.
Destructive acid rain caused by eruption
According to press reports, an eruption from Benbow Crater occurred on 10 February. Gases from the eruption caused acid rainfall on the SW portion of Ambrym Island, destroying most vegetation within 24 hours, contaminating water supplies, and burning some inhabitants. Jean-Luc Saos, Director of Mineral Resources for the New Hebrides government, reported a high concentration of HCl and sulfur compounds in the volcanic gases. Although heavy ashfalls have occurred in the area in the past, this is the first report of acid rains.
Information Contacts: A.L. Dahl, S Pacific Commission, Noumea; Les Nouvelles Caledoniennes, Noumea.
More information on February eruption and acid rain
The following report, written by A. Macfarlane using information from J-L. Saos, supplements the previous report.
"An increase in activity from Benbow Crater (in the SW portion of Ambrym's caldera) involving the copious emission of cinders, lapilli, and gases was first noted on 7 February. On the night of 10-11 February, ash and gas columns apparently combined with local rainstorms to produce a fallout of dilute sulfuric acid, which affected an area of some 90 km across SW Ambrym Island between and inland of the coastal villages of Baiap and Calinda (about 16 and 10 km SSW of Benbow Crater). The most extreme effects were observed in the Lalinda-Port Vato area (a 5 km zone along the coast) where there was extensive burning of pastures and yellowing of cash crops such as cocoa and coconut palms. In addition, the local population suffered from gastric upsets and from burning of the skin by contact with the acid rainwater. The local water supply was contaminated to the extent that pH values in cisterns had decreased to 5.2-5.5 when subsequently measured and were probably even lower at the time of the acid rains.
"Owing to heavy cloud cover, it has not been possible to determine whether these eruptions mark a significant change in the configuration of vents within Benbow Crater."
Information Contacts: A. Macfarlane, Geological Survey, Vanuatu; J.-L. Saos, Dept. of Mineral Resources and Rural Water Supply, Vanuatu.
Ash plume visible for 30 km
"On 8 March an ash-laden plume issued from Ambrym and reached an altitude estimated at 3,000 m (by aircraft altimeter), remaining visible 30 km or more downwind. The volcano's last violent activity had been reported 3 months earlier."
Information Contacts: R. Stoiber, Dartmouth College.
Ash cloud reported from aircraft
The crew of a Continental Airlines flight from Australia to Honolulu reported an eruption on 13 February at 0357, with ash clouds below 12 km altitude, moving SW. A NOTAM issued the next day at 2018 said that the eruption was from Benbow Crater, and forecast ash clouds to 10.5 km altitude, spreading ESE. A second NOTAM released 19 February at 0827 stated that volcanic activity had ceased. Geologists in Vanuatu reported that activity from Benbow was slightly stronger than usual for 2-3 days 12-14 February, but had since returned to normal. No damage was reported.
Information Contacts: J. Latter, DSIR Geophysics, Wellington, New Zealand; C. Clark, Dept of Geology, Mines, and Rural Water Supplies, Port-Vila.
Ash plume and lava flow; recent eruption history
On 31 April at 0730, the meteorological service in Wellington, New Zealand detected volcanic ash clouds near 16.1°S, 168.1°E on satellite images. The main cloud had an estimated diameter of 15-30 km, with streamers to 115 km NNE, and moved at a speed of ~30 km/hour. The plume height was estimated at ~6 km from an aircraft at 0350. The meteorological service in Darwin, Australia also located a steam/ash cloud on visible satellite images at 1030. NOAA infrared and visible images showed only a small cloud on 31 April at 1344 during clear weather. The following is a report from J.P. Eissen, M. Lardy, M. Monzier, L. Mollard, and D. Charley of ORSTOM (Nouméa and Port Vila).
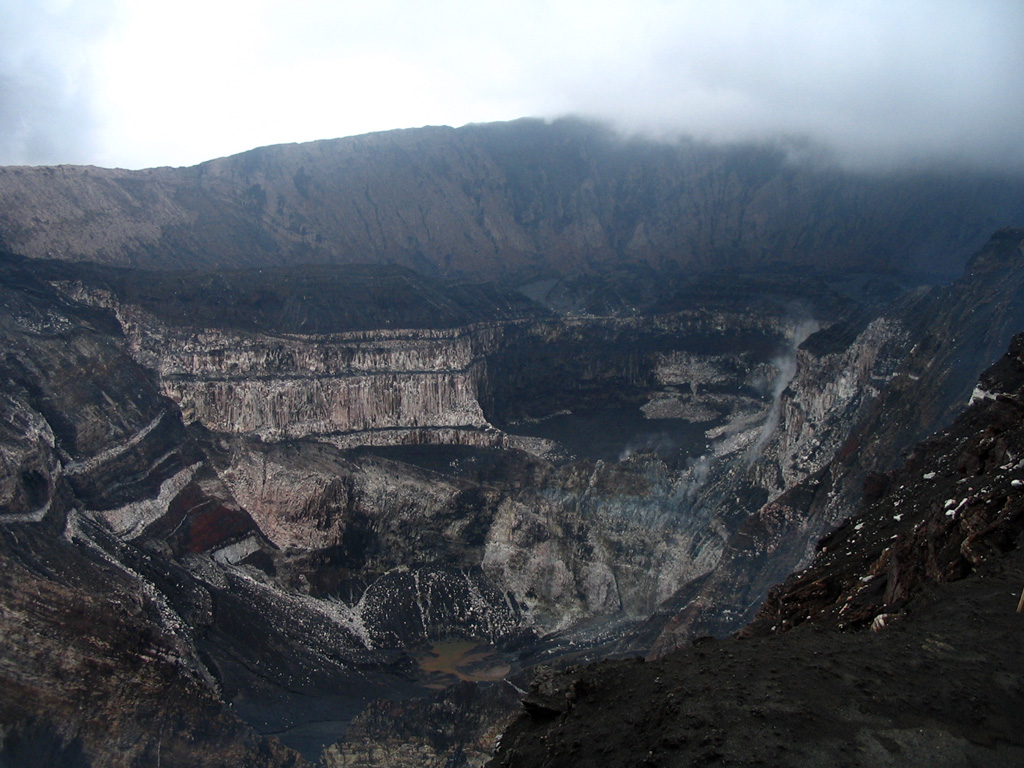
Description and history. "Ambrym, a large stratovolcano with a 15-km-wide caldera (figure 1), is one of the most active volcanoes of the New Hebrides arc, which includes Yasur (Tanna Island), Lopevi (Lopevi Island), and the shallow submarine volcano Karua (between Epi and Tongoa Islands).
". . . . In the historical period, at least five types of activity can be distinguished. From the most to least frequent, these are: 1) intra-caldera, intermittent, Strombolian-type activity with mild extra-caldera ashfalls, but without lava flows (occurs almost every year); 2) intracaldera eruption frequently preceded by lava lake formation in the crater — generally starts with emission of a Plinian column that produces extra-caldera ashfalls, followed by intra-caldera lava flows; 3) activity similar to (2) followed by lava overflowing from the caldera (1863 (?), 1913-14, 1942 eruptions); 4) extra-caldera lava emission from fissures (1894, 1913, 1929, 1936 eruptions) — sometimes evolves toward 5) formation of pyroclastic cones, sometimes accompanied by lava flows (1888, 1915, 1929 eruptions). Several of these types of actvity have occurred consecutively in the different phases of a single eruption (as in 1913-14 and 1929, the two major Ambrym eruptions).
"On 13 November 1986, an aircraft pilot reported an increase in activity at the volcano. Ash emission became significant 17 November, but activity decreased 19-20 November. A new cone formed (Cheney, 1986) 3 km E of the active Marum cone (figure 1) and produced an intra-caldera lava flow ~4 km long (Melchior, 1988).
May 1988 activity. "On 27 May 1988, a lava lake ~50 m in diameter was observed in Mbwelesu's crater. Benbow was emitting white clouds whereas Marum and Mbwelesu were emitting dark grey clouds (Melchior, 1988). On 10 August, intracaldera lava flowed S more than 1.5 km from what appeared to be a new cone, but was possibly an extension of Mbwelesu (Cheney, 1988). The flow (still warm) extended ~5 km S (Charley, 1988). This eruption had ended by 23 August.
April 1989 activity. "At 1000 on 24 April 1989, a pilot observed a large plume rising ~3,500 m above the volcano. A lava flow from the the 1988 cone was following the same path as the 1988 flow but was a few kilometers longer. It followed the creek near Endou village (figure 1) and may or may not have extended outside the caldera [but see 14:10]. About 1 km2 of Otas village was reported to be burned. On the night of 29 April, large areas of red glow were seen from boats cruising in the area, and winds carried ash NW. Young vegetation on the S flank was burned (possibly by acid rain), and rain water had a strong taste. Local inhabitants said that the eruption was normal for the volcano even though there were more loud roaring noises and small earthquakes than in 1986 or 1988. A local pilots' strike prevented further observation of the eruption, but on 10 May the volcano was still active." The eruption apparently stopped sometime before 14 May.
References. Charley, D., 1988, Rapport de Mission à Ambrym en Aout 1988: Document ORSTOM, Port Vila, 5 p.
Cheney, C.S., 1986, New volcanic eruption near Endu, SE Ambrym: Geology Dept Memo, 24 November 1986, 1 p.
Cheney, C.S., 1988, Volcanic activity report, Ambrym and Epi: Geology Dept Memo, 17 August 1988, 1 p.
Melchior, A.H., 1988, Rapport de Mission de Reconnaissance Volcanologique Ambrym (25-28 May 1988) et à Tanna (14 May 1988): Document ORSTOM, Nouméa, 10 p.
Quantin, P., 1978, Archipel des Nouvelles-Hébrides: Atlas des Sols et de quelques Données du Milieu: Cartes Pédologiques, des Formes du Relief, Géologiques et de la Végétation; ORSTOM (18 sheets).
Stephenson, P.J., McCall, G.J.H., Le Maitre, R.W., and Robinson, G.P., 1968, The Ambrym Island Research Project, in Warden, A.J., ed., New Hebrides Geological Survey Annual Report 1966: Port Vila, p. 9-15.
Information Contacts: J. Eissen, M. Lardy, M. Monzier, ORSTOM, New Caledonia; L. Mollard, and D. Chaney, ORSTOM, Vanuatu; J. Latter, DSIR Geophysics, Wellington; S. Kusselson, SAB; J. Temakon, Dept of Geology, Mines, and Rural Water Supply, Port Vila.
Lava lakes in two craters; changes since 1943 described
"After our previous report of the April-May 1989 eruption (14:04), activity apparently declined in early May to the normal level in the cone complex near Marum (figure 1). The previous report of a possible extra-caldera flow turned out to be erroneous, with the 1989 lava flows staying strictly confined inside the caldera. However, a pilot indicated that on 25 May a white plume was rising to 6,000 m, associated with an ash cloud that rose to 3,000 m, showing that the volcano remained active.
"There was no further report until two of us visited the volcano 26-30 September, gathering complementary information about the recent eruptions and the present level of activity (Monzier and Douglas, 1989). The 1988 and 1989 lava flows originated from an area on the S flank of Marum formed by one crater and two cones, one of which was already visible during a 1943 photographic survey. The flows are basaltic aa, 1-3 m thick, highly vesicular and aphyric in 1988, and slightly vesicular and plagioclase sub-aphyric in 1989. The lava contours have been mapped; one of the 1989 flows partially covered a 1988 flow, while the other (E) one rejoined the 1988 flow in the SE sector and extended farther E, but stayed inside the caldera. Observation of the main craters was limited by poor weather. The Benbow pit was occupied by a gently bubbling lava lake, evident at night by a red glow visible from Sesivi, on the S coast of Ambrym. Marum was slightly degassing. The Mbuelesu pit was also occupied by a strongly bubbling lava lake but no large explosions were observed. The crater just S of Mbuelesu was in a fumarolic stage, as were the craters from which the recent flows originated.
"The series of photographic surveys done periodically between 1943 and 1989 allows us to compare the evolution of the morphology of the craters (figure 2). Benbow, source of the major historic eruptions (figure 3), does not show any major morphological changes. In contrast, the morphology of Marum and adjacent cones changed substantially during this period. In 1943, Marum and its eastern neighbor Mbuelesu were both clogged with detrital material. Note that the small '892' cone, from which the recent flows originated, already existed in 1943. In 1953, Marum resumed its activity (Eissen, Blot, and Louat, 1991). On the 1954 photos, one new crater ('1953') underlain by fumaroles had formed across the edges of Marum and Mbuelesu Craters. Two smaller cones were also visible S of the 1953 crater. On the 1972 photos we can note: 1) the opening of a gently smoking pit in the center of Marum Crater; 2) the enlargement and division of 1953 crater, inactive at this time; 3) the formation of a new active crater S of 1953 crater, at the site of the two small cones visible in 1954. In 1986, the central pit of Marum and the W part of the 1972 double crater had merged and were slightly smoking. The E part of the 1972 double crater had enlarged at Mbuelesu and was strongly active and smoking. The 1989 situation is described above.
"Thus, whereas Benbow has remained almost unchanged morphologically during the last 46 years, Marum and its adjacent craters strongly evolved during the same period, and recent activity seems concentrated in this area, restricted to the caldera. Although testimony is fragmental since 1980, strong activity seems to have resumed, the presence of two lava lakes indicating that the magma column is presently very high. Ambrym has had at least seven eruptions accompanied by extra-caldera lava flows, sometimes with resulting destruction and casualties. Part of the population has been evacuated several times (in 1913-15, 1929, and 1951) on adjacent islands. Careful study, observation, and eventually monitoring of this volcano should be encouraged to help prevent further destruction due to extra-caldera lava flow(s) that could reasonably be expected within the next few years."
References. Eissen, J.P., Blot, C., and Louat, R., 1991, Chronology of the historic volcanic activity of the New Hebrides Island Arc from 1595 to 1991: ORSTOM Rapports Scientifiques et Technique, Sciences de la Terre, Géologie-Géophysique, no. 2, 69 p.
Monzier, M., and Douglas, C., 1989, Rapport de Mission à Ambrym (Vanuatu) du 26 au 30 Septembre 1989: Rapport de Mission Géologie-Géophysique no. 10, Document ORSTOM Nouméa, 30 p.
New Hebrides Geological Survey, 1976, Geology of Pentecost and Ambrym: 1:100,000, Sheet 6.
Quantin, P., 1978, Archipel des Nouvelles Hébrides; Atlas des Sols et de Quelques Donées du Milieu: Cartes Pédologíques (01:50,000-1:100,000), des Formes du Relief, Géologiques et de la Végétation (01:100,000-1:250,000), 18 feuilles et 11 notices; ed. ORSTOM.
Information Contacts: J. Eissen, M. Lardy, and M. Monzier, ORSTOM, New Caledonia; C. Douglas and L. Mollard, ORSTOM, Vanuatu.
Block and ash ejection; 1989 lava lake gone
The Vanuatu arc was visited by an ORSTOM mission 5-18 September. The following is modified from their report in the LAVE Bulletin.
Thick puffs of ash rose several hundred meters, and scattered blocks were ejected, from a vent 200 m below the rim of Niri Tamo, which formed adjacent to Mbuelesu crater in 1989 (14:10). The approach to the crater was sprinkled with blocks 10 cm to 1 m in diameter. One block, 2 m in diameter, was located near a possible new crater (Niri Taten) that was S of Mbuelesu, near the source of the 1988 lava flows and [~500 m] from Niri Tamo. A zone of intense degassing, with temperatures of at least 625°C, occurred within Niri Taten. Mbuelesu appeared more elongate to the NE than represented on 1989 maps and no longer contained a lava lake. One vent, sounding like a reactor, violently emitted ash, gas, lava blocks, and fragments. The plume rose vertically at 30 m/s, and projectiles frequently landed beyond the rim of the crater. Benbow crater emitted a strong bluish plume, suggesting a significant SO2 content.
Further Reference. Eissen, J.P., Monzier, M., Robin, C., Picard, C., and Douglas, C., 1990, Report on the volcanological field work on Ambrym and Tanna Islands (Vanuatu) from 2 to 25 September 1990: Rapport Missions Sci Terre Geologie-Geophysique – ORSTOM (Noumea), no. 22, p. 1-22.
Information Contacts: M. Lardy, ORSTOM, New Caledonia; B. Marty, CNRS, France; LAVE.
Ash plume extends 50 km
The control tower at Bauerfield airport (serving Port Vila, ~150 km SSE of Ambrym), reported a 2-km-high ash cloud stretching ~50 km from Marum Crater on 10 June.
Information Contacts: C. Mortimer, Dept of Geology, Mines, and Rural Water Supply, Vanuatu.
Ash emissions and lava lake activity continue
"Aerial surveys on 13 and 24 July (VANAIR flights) showed puffs of gas and ash rising several hundred meters above Mbuelesu crater, and weak degassing from Benbow crater. Mbuelesu's lava lake, ~100 m in diameter and very deep in the crater, was still present. Activity has remained more or less constant since 1990, and no new lava flows have been observed since 1989."
Information Contacts: C. Robin and M. Monzier, ORSTOM, New Caledonia; M. Lardy and C. Douglas, ORSTOM, Vanuatu; C. Mortimer, Dept of Geology, Mines, and Rural Water Supply, Vanuatu; J. Eissen, ORSTOM, France.
Lava lakes still present in Benbow and Marum craters
During an aerial reconnaissance on 7 December 1994, activity was at normal levels with lava lakes present in both Benbow and Marum craters. An intermediate-depth earthquake (185 km) occurred under Ambrym on 26 April 1994. Regular monitoring is done with a seismic station on Ambrym that transmits data via ARGOS satellite to the ORSTOM office in Port Vila.
Information Contacts: M. Monzier, ORSTOM and Vanuatu Dept of Geology, Mines and Water Resources, Vanuatu.
Lava lakes in both Benbow and Marum craters still active in July
A visit to the summit caldera on 8-9 July did not permit an approach to the lava lakes in the Benbow and Marum craters due to poor weather. An overflight on the night of 20 July permitted observations of surface bubbling in Marum's lava lake. Two other overflights, on 21 and 22 July, allowed observation of activity in both lakes for several minutes. During these observations, the surface of the Benbow lake was fairly calm. However, Marum's lava lake, ~100 m in diameter, exhibited occasional explosions that threw glowing magma fragments some meters above the surface; bubbling was clearly visible from the airplane.
Information Contacts: Henry Gaudru, C. Pittet, C. Bopp, and G. Borel, Société Volcanologique Européenne, C.P. 1, 1211 Genève 17, Switzerland (URL: http://www.sveurop.org/); Michel Lardy, Centre ORSTOM, B.P. 76, Port Vila, Vanuatu.
August visit reveals lava fountains, Strombolian explosions
During 5-13 August 1997, a team from the Société de Volcanologie Genève (SVG) observed Ambrym caldera and deployed an infrared (1.55 µm wavelength) optical pyrometer (Optix-G, Keller GMBH., Ibbenburen-Lagenbeck). Temperatures of lavas were estimated from the pyrometer by measuring emissivity factors of lavas heated to known temperatures in an oven. In some cases comparisons were also made with a thermocouple on the floor of Marum crater (contact the authors regarding procedures and results).
At Benbow cone, most activity, including lava fountaining, occurred inside the S part of the crater. A deep crater in the cone's N flank emitted a large amount of hot, very concentrated gas. The crater bottom was not visible; however, strong night glow revealed the proximity of magma.
At Marum cone, three different craters were active during the SVG visit. At Mbwelesu, the main crater, two closely spaced openings full of lava were visible from the rim. The lava surface was continuously overturned by fountains that were tens of meters high. The maximum temperature of the chimney opening was estimated with the optical pyrometer at 910°C. The pyrometer measurement was taken on the NNE side of the crater rim under conditions of good visibility and strong degassing.
At Niri Mbwelesu, a secondary crater close to Mbwelesu's rim, strong degassing was observed. Although the crater was often full of vapor, occasionally the bottom was visible. A small, elongated lake surrounded by fumaroles was seen in the crater near a glowing opening that was emitting pulses of hot gas; however, magma was not directly observed.
Inside Niri Mbwelesu Taten, a small collapse pit (169 x 185 m; 140 m deep) to the S of Niri Mbwelesu, Strombolian explosions were observed until 7 August. The explosions lasted a few hours, stopped, then resumed a few hours later. The explosions were caused by the bursting of magma bubbles 2-3 m in diameter as they reached the surface. The noise from the explosions could be heard a few kilometers away. Shock waves were sometimes observed in the cloud above the pit. The maximum temperature of liquid lava inside the pit was estimated with the optical pyrometer at 964°C. Pyrometer measurements were taken standing on the S border of the crater rim under conditions of good visibility. Maximum temperature estimates on liquid lava varied between ~935°C and 965°C.
In addition, the team measured rain acidity at different sites inside the caldera. A clear gradient was found: the rain had a pH of 2 on the Benbow crater rim and a pH of 4 close to the caldera's border.
Information Contacts: P. Vetch and S. Haefeli, Société de Volcanologie Genève (SVG), C.P. 298, CH-1225, Chene-bourg, Switzerland.
Long-active lava lake continues to hold bubbling lava
This long-active caldera was visited by John Seach during 4-7 September 1998. At Niri Mbwelesu Taten, a small collapse pit, strong degassing was observed as well as yellow sulfurous deposits on the NW wall. During the night, degassing was heard from a distance of 4 km and white vapor tinged with blue was constantly emitted from the pit.
Niri Mbelesu crater was constantly full of vapor resulting in poor visibility. But bubbling lava was heard and at night the clouds reflected a red glow from the crater.
At Mbwelesu crater, an active elongated lava lake (~100 x 30 m) was observed. The larger explosions threw lava high into the air and onto the crater wall. To the east of the lava lake a smaller elongated vent contained lava. On the NW wall of the crater was a circular vent 20 m in diameter from which no lava was extruded.
Benbow crater was climbed from the S. The sound of bubbling lava was heard but not observed, and there was a very intense night glow.
Information Contacts: John Seach, P.O. Box 16, Chatsworth Island, N.S.W. 2469, Australia.
Benbow lava lake disappears in avalanche
Ambrym Island was investigated by John Seach and Perry Judd during a climb into the caldera 1-8 January 1999. A lava lake in Benbow cone was present during 1-3 January but was covered by deposits from an avalanche that occurred overnight 4-5 January. Fumarolic and Strombolian activity was observed at other craters.
Activity at Benbow. Benbow crater was climbed from the S, after which observers lowered themselves using ropes 200 m down from the crater rim to a point where they could observe the crater interior. In the center of the crater, an active lava lake was seen 220 m below the observation point. The lava lake was ~40 m in diameter and constantly in motion. Large explosions caused lava fountains that reached 100 m high. Bombs glowed for up to one minute in daylight and radiated great heat. Bombs could be heard landing on the side of the pit where they caused glowing avalanches. At night a strong glow from the lava lake was visible in the sky over Benbow.
Elsewhere inside Benbow crater, Pele's hair covered the ground and fumaroles were active on the NE crater wall. Acid rain burned eyes and skin. Heavy rainfall caused many waterfalls to form inside the crater rim and a shallow brown pond formed on the floor of the first level.
During 4-5 January violent Strombolian explosions could be heard almost hourly. Each series of explosions lasted 5-10 minutes and produced dark ash columns above the crater. At some time during these explosions an avalanche on the W side of the lava lake crater completely covered the lava lake. No night glow was visible above the crater after the night of 5 January.
On 6 January Benbow crater was entered again. The wall collapse that covered the lava lake was confirmed visually. In the location of the former lava lake was a depression of rubble with two small, glowing vents nearby. The entire crater was clear of magmatic gases. Three violent Strombolian eruptions were viewed from the crater rim in the afternoon. Bombs were thrown 300 m into the air and dark ash clouds were emitted.
Activity at Niri Mbwelesu Taten. This small collapse pit continuously emitted white, brown, and blue vapors. Red deposits covered the crater walls. A small amount of yellow deposits covered the S wall. Fumarole temperatures were 66 to 69°C at a point 40 m SE of the pit. On 6-7 January numerous deep, loud degassings were heard from a distance of 4 km.
Activity at Niri Mbwelesu. Pungent, sulfurous-smelling white vapor was emitted from this crater. Periods of good visibility enabled views 200 m down from the crater rim, but the bottom could not be seen. Rockfalls were heard inside the crater.
Activity at Mbwelesu. Excellent visibility to the bottom of this crater enabled detailed observations of the lava lake. Night observations were also obtained. The lava lake was in constant motion and splashing lava out over the sides of the pit. The lake was at a lower level than during observations made three months earlier (BGVN 23:09). Large explosions sent lava fountains up to 100 m in height and threw lava onto the sides of the pit causing glowing avalanches. During one night observation a 20 x 5 m section of the crater wall broke off and fell into the lava lake. The 60-m-wide lake radiated heat that could be felt from the viewing area 380 m away. North of the lava lake was a circular vent 20 m in diameter that glowed brilliantly from magma inside and huffed out burning gasses every 20 seconds. Foul gas, smelling of rotten fish, was emitted from the crater. South of the lava lake was an elongated vent (40 x 10 m) that spattered lava every 5-10 seconds and sent showers of glowing orange lava spray 150 m high.
On the S side of Mbwelesu, fumarole temperatures averaged 43°C at 10 m from the crater edge. On the SE side, 40 m from the crater edge, fumaroles measured 57°C. On 4 January ashfall occurred on the S side of the caldera.
Information Contacts: John Seach, P.O. Box 16, Chatsworth Island, NSW, 2469, Australia.
Lava lake activity and ash emission from both Benbow and Marum craters
Observations within Ambrym's summit crater were made by John Seach during a 22-30 August 1999 climb. There are two active cones in the caldera complex, Benbow and Marum. The Marum cone has three active sub-craters: Mbwelesu, the main crater; Niri Mbwelesu, a secondary crater close to Mbwelesu's rim; and Niri Mbwelesu Taten, a small collapse pit to the S of Niri Mbwelesu. Seach found increased activity compared to a previous visit in January 1999 (BGVN 24:02), with one new vent inside the Benbow crater and a second lava lake in Mbwelesu crater. Temperature measurements were made with a hand-held digital thermometer with an 8-cm probe. All depth estimates are visual; distances were estimated in comparison to a climbing rope.
A Mw 6.5 earthquake on 22 August was centered ~18.6 km NW of Ambrym volcano. Seach reported that the earthquake was felt with an intensity of MM VI with large ground movements in a NW-SE direction for 10 seconds. The earthquake caused landslides in the caldera and opened large cracks in the rim of Benbow crater. Coconut trees were knocked down on the W coast of Ambrym Island, and there was infrastructure damage in southern Pentecost Island. Fourteen aftershocks were felt during the next 8 hours.
Activity at Benbow. The crater was full of vapor when climbed on 22 August, but bubbling lava sounds were heard. A brown ash emission at 1740 was followed that night by moderate glow. Occasional crater explosions were heard between 1400 and 2100 on 26 August. Good visibility into the crater the next day showed that a new vent had opened on the N crater floor that was continually emitting light brown ash that rose 1,500 m above the crater floor (~2,300 m altitude) before being blown to the SE. Thicker ash emissions about every 5 minutes were accompanied by vigorous degassing; these emissions rose at a rate of ~13.5 m/s. From 1615 to 1625 on 27 August there were 66 discrete explosions or loud venting noises heard from the crater. At one location on the NW rim of the central crater, 200 m from the new vent, a recent ash deposit was ~50 m thick. Fumaroles were active on the inside N wall of the central crater, with yellow and red deposits at their bases. The lava lake vent that was covered by an avalanche in January had reopened and exhibited orange glow from the pit at night; white vapor tinged with blue was emitted, and brown ash was ejected every 15-30 minutes. Both active vents glowed a brilliant orange color at night. Loud degassing was heard at 0620 on 28 August from a distance of 4 km.
Activity at Mbwelesu. Excellent visibility at times during 26-28 August allowed detailed observations of the crater bottom. Continuous load roaring and crashing sounds were heard coming from the pit. Explosions shook the ground and bombs could be heard striking inside the crater. An observer on the E edge of the crater, 350 m from the lava, felt radiant heat. Scattered blocks 20-30 cm in diameter and Pele's hair covered the edge of the crater. A fumarole field 60 m SE of the crater had a measured temperature of 53°C. A brown pond was present on the floor of the Marum crater. The central floor of the 1953 crater (in Marum adjacent to Mbwelesu) contained a green pond surrounded by active fumaroles. Intense night glow was visible on the evening of 26 August.
Three vents were active within the Mbwelesu crater. Vent A, in the SE part of the crater, was ~10 m wide and ejected sprays of lava 150 m high every 5-10 seconds. Occasional lava spatter fell onto the vent wall. Lava spray was generally directed S, and formed black marks on the wall of Mbwelesu crater.
Vent B, in the central part of the crater, was roughly circular and ~45 m in diameter. It was ~15 m from the rim to the lava lake. During this visit the lava lake exhibited 20-m-high waves moving across the pit. Vigorous boiling of the surface and incandescent lava fountaining to 150 m heights was observed. Some black bombs were ejected. At 1220 on 28 August a large part of the S rim of the pit fell into the lava lake, generating a large brown cloud that filled Mbwelesu crater and triggering Strombolian explosions for the next 10 minutes.
Vent C within the Mbwelesu crater (figure 4) was located NW of Vent B. When seen in January 1999 this vent emitted burning gas, but it had deepened, widened, and contained a lava lake by 28 August. The elongate ~75 x 45 m pit had a steep N wall (~75 m high), but was open to the S (rim ~15 m above the lava lake). The lava lake surface was directly visible and boiling violently, ejecting showers of dark bombs every 1-2 seconds. Lava fountaining occurred from a fixed point along the edge from the NE to the E side of the pit. Some bombs remained incandescent for 20 seconds in the daylight. Lava was splashing onto the SW walls and sides of the pit after emerging from the NW edge of the lake. Horizontal current flow was estimated at 8 m/s towards the SE shore across at least 75% of the diameter of the lake. Three simultaneous 20-m-diameter lava bubbles were seen that almost filled the entire lake surface.
 |
Figure 4. Photograph of Vent C in the Mbwelesu Crater at Ambrym, 28 August 1999. Courtesy of John Seach. |
Activity at Niri Mbwelesu. White sulfurous-smelling gas was emitted from the pit in late August. Mild degassing was observed from the south part of the crater, and fumaroles were active on the N crater wall.
Activity at Niri Mbwelesu Taten. Compared to January 1999, in late August there was an increase in activity and substantial morphological changes. On 25 August at 1045 a thick brown ash emission continued for 5 minutes, rising 300 m and then being carried 4 km NW by the wind. Similar ash emissions occurred at 10-20 minute intervals during the afternoon. The E rim was littered with new rocks. Recent cowpat bombs were present 10-20 m from the E side of the crater. Mild degassing and sloshing lava sounds were heard. Fumaroles were active in two small collapse pits on the SE side of the crater. The fumarole field 40 m SE of the main pit had a temperature measured at 67-69°C, the same as in January 1999. Views into the crater to a depth of 150 m were obtained on 28 August, but the bottom was not seen. The south inside wall was covered with yellow deposits. Red-brown ash was building a raised rim on the NW side of the pit. The pit was degassing every 1-2 seconds. Fumaroles on a sill 50 m down were venting in unison with the main pit. Bubbles of hot gas 20 m in diameter were observed rising from the vent at 30 m/s.
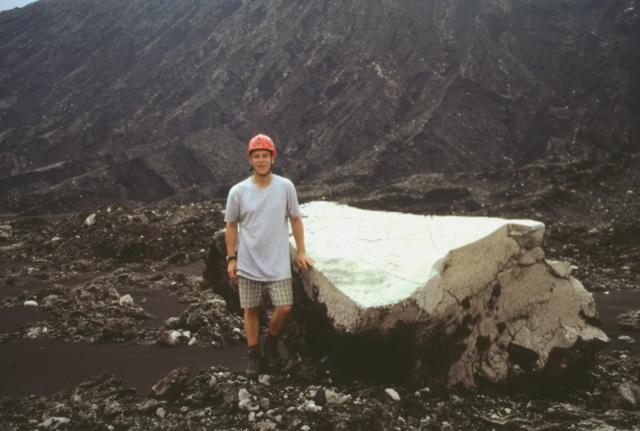 |
Figure 5. Lithic block ejected 100 m NE of the Niri Mbwelesu Taten collapse pit at Ambrym, August 1999. Courtesy of John Seach. |
Information Contacts: John Seach, P.O. Box 16, Chatsworth Island, NSW 2469, Australia.
Lava lakes disappear, but ash eruptions continue from many active vents
Eruptive activity continued at Ambrym in late 1999 and through January 2000. A volcanic ash advisory regarding this volcano was issued to aviators on 1 November 1999 reporting "smoke and ash" rising to ~1,500 m altitude. Similar notices were issued on 5 and 6 November. [Aviation reports on 9-10 December] described an ash cloud up to 2,700 m altitude.
John Search and Geoff Mackley investigated Ambrym caldera during a 19-28 January 2000 climb. Lava lakes had disappeared from both Benbow and Mbwelesu craters and a new vent had opened inside the previously inactive 1953 crater. A series of earthquakes were registered around Ambrym Island on 27 November 1999. The largest of these was magnitude 7.1. The earthquakes were followed by a month of reduced activity during which there were no reported observations of lava lakes. Landslides were visible in the caldera and ground cracking visible at Benbow, Mbwelesu, and Niri Mbwelesu craters.
Activity at Benbow Crater. Four vents were active inside Benbow. On 19 January a white plume tinged with blue and yellow rose 1,000 m above the crater rim. Twin plumes were visible the next day rising from the S end of the crater at 15 m/s and from the N end of the crater, where they were tinged with brown. Each time the crater was climbed from the S on 22, 23, and 24 January the pit was full of vapor and no sounds were heard. On 25 January the observers lowered themselves into Benbow using 200 m of rope. The floor of the first level was covered with fine brown ash and a shallow brown pond was present in the SW end of the crater. The inner crater was climbed and observations made from its rim. Below the observers was a ledge 120-140 m down covered with ash and containing a 10-m circular vent emitting white vapor. The main vent was 50 m farther down and 40 m in diameter. This was the vent that contained the lava lake in January 1999 (BGVN 24:02). No lava was observed inside this vent and it made no sound. At 1300 a large roar from the vent was followed by brown ash emission. At the NE end of the inner crater was a plume emission from an unseen vent.
The N end of Benbow crater (on the first level) contained another vent that could not be directly observed but regularly emitted light brown ash. On 26 January a loud continuous 30-second degassing heard from the N vent was followed by brown ash emission and rain of small cinders on observers at the S crater edge. From the central pit the vapor was rising at 5 m/s. During the late afternoon two visible atmospheric perturbations were observed above the main vent. The first followed a loud degassing sound and rose at 40 m/s to a height of 200 m above the vent. Rockfalls were also heard during the afternoon. During the night of 26 January twin skyglows of fluctuating intensity were visible above Benbow followed by a large brown ash emission that rose 1,400 m above the crater in 3 minutes.
Activity at Niri Mbwelesu Taten. On both 19 and 20 January light brown or red/brown ash was emitted from the collapse pit and rose 200-250 m. On 21 January a brown pond of water 150 m NE of the pit was bubbling from both fixed and random locations. Active fumaroles were present on a ledge 60 m down. There were large cracks on the SE side and evidence of wall collapse since August 1999. Ash fell on observers in the area N of the pit. On 23 January larger ash emissions occurred about every hour.
On 24 January the collapse pit was entered using ropes. Fumaroles on the ledge 60 m down averaged 64°C. The pit bottom was 120-140 m below the ledge covered in brown ash. Small clouds of ash were emitted occasionally from two large fissures. Bubbles of hot blue vapors, 6 m in diameter, rose past the observer. Continual degassing sounds were heard in the pit, like the sound of waves crashing on the beach. On 26 January from 0600 to 1100 dark gray ash clouds were continually being emitted from the pit. Plumes rose at 8 m/s to a height of 200 m above the pit, filling the caldera in all directions. During the afternoon the pit returned to a low level of activity. On 27 January a continuous emission of brown ash occurred all day to a height of 800 m above the pit.
Activity at Niri Mbwelesu. On 20 January white vapor tinged with blue was constantly emitted to 600 m above crater. During the evening a very intense pulsating night glow was visible. The glow would brighten (sometimes flicker), then rapidly drop to a lower level of illumination. The bright/dim cycle would repeat every 10-15 seconds. On 21 January in the afternoon degassing was heard from the crater rim and during the evening clouds were illuminated 250 m above the crater. Observers on the crater edge felt hot vapor. When the crater was climbed on the evening of 25 January a clearing of the vapor enabled the bottom to be seen 280 m down. A 40-m-diameter vent was visible emitting bright yellow burning gas, radiant heat was felt on the faces of observers, and moderate degassing was heard.
Activity at Mbwelesu. Observations were made of Mbwelesu crater on 21 January. The two lava lakes observed in August 1999 had disappeared (BGVN 24:08). A brown pond surrounded by fumaroles was in the Vent B location, with large amounts of ash and rock to the SE. The sill on the SE edge of the crater had large craters and several large sections (over 10 m) that had broken off and fallen into the crater. The fumarole field 40 m SE of the crater rim had a temperature of 72.7°C. Heavy rains caused waterfalls and rockfalls inside the crater. The crater was otherwise quiet with some vapor emissions from many fumaroles on the floor. Fumaroles were also present in the location of the former lava lake at Vent C.
Activity in the 1953 Crater. The 1953 crater contained two levels. The higher (W half) contained a brown pond. The lower (E half) had developed a deep smoking vent. This was in the location of the green pond observed in August 1999.
Information Contacts: John Seach, PO Box 16, Chatsworth Island, N.S.W. 2469, Australia; Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), MetService, PO Box 722, Wellington, New Zealand (URL: http://www.metservice.co.nz/).
Vapor emissions observed in February; pilots report seeing lava in vents
Ambrym was observed during an aircraft overflight on 25 February 2000. Pilot reports indicated that lava was beginning to reappear in some vents. As previously reported (BGVN 25:02), the long-standing lava lakes in Benbow and Mbwelesu craters had disappeared after the 26 November 1999 earthquake. Activity increased slightly from January indicating the magma column may be rising again.
Brown vapor was being emitted from Mbwelesu crater. The bottom of the crater could be seen but no lava was observed. Four craters, each ~8 m in diameter, were located on a 40 x 10 m section of the sill on the E rim of the crater. This rim had been weakened by the November 1999 earthquake and appeared ready to fall. Both vents inside Benbow crater emitted white vapor, which rose 1.5 km as one plume. The bottom of the vents could not be seen.
Information Contacts: John Seach, PO Box 16, Chatsworth Island, N.S.W. 2469, Australia.
Visits during 1999 and 2000 revealed variable lava lake and explosive activity
The following report discusses observations of Marum and Benbow craters (in the central and WSW portions of Ambrym's caldera, respectively). The observations were made in September-October 1999 and August-October 2000. Our previous Ambrym report discussed aerial observations made in late February 2000 (BGVN 25:04). Marum and Benbow host long-standing lava lakes with active surfaces (sometimes molten and sometimes chilled).
1999 Marum observations. On 24 September 1999 the lava lake was once again present at more or less the normal site. It measured ~60 m in diameter and underwent significant degassing accompanied by turbulent waves and the escape of incandescent fragments. On several occasions, observers witnessed large collapses on the periphery as well as rapid and sudden variations in the lake's surface level. At the foot of the SE face, perhaps three explosive vents ejected plumes of ash and cauliflower-shaped discharges of steam at irregular intervals varying from 8 to 30 minutes. At night, observers distinguished incandescence along concentric faults on the lava lake.
On 22 October 1999 observers camped on the crater's edge, on the ash-covered floor found to its ESE. They noted that the main lava lake had grown since September, and it displayed more violent, regular degassing. Its surface was continuously disrupted by waves and escaping incandescent fragments that rained all the way down the active terrace. Observers saw a second small elongate lake and reported that its surface too was sometimes very agitated. At night, several incandescent faults were seen on the bottom of the terrace. These spread open and then closed, indicating that the entire zone had a thin, partially solidified crust.
On 23 October bad weather prevented visual observations, but at night observers saw intense red glow, felt tremors, and heard rumblings. On 24 October, at sunrise, the meteorological conditions were excellent, but volcanic gas obscured the crater.
1999 Benbow observations. On 23 September 1999, observers looking toward Benbow crater from the sea saw a large column of ash and gas rising about 1,200 m above the crater. On two occasions at night, visitors saw brief instances of weak incandescence in the plume's interior.
A month later, on 23 October 1999, despite unstable weather conditions, observers reached summit crests and saw gas occupying the crater's interior. They saw the first terrace only for a brief moment and then only partially, making it impossible to say whether the lava lake was again molten at the surface. The characteristic rumblings that accompanied the regular degassing on the lake's surface were perceptible but weak, as if molten material lay beneath a thin chilled surface.
2000 Marum observations. During the nights of 2 and 3 August 2000 a lava lake was clearly visible (about 100 x 60 m in size). Regular and sustained degassing agitated the surface with big waves. Showers of incandescent fragments rose to heights of ~50-70 m.
On the night of 16 August a tropical depression crossed the region affecting an area extending at least as far as the Banks Islands ~200 km N. Heavy rains fell on the Marum plateau. Thick "smoke" rose from the crater, impeding visual observations.
On the night of 30 September-1 October, incessant rain again fell on the Marum plateau. Very poor visibility in the crater stopped for a few minutes around 0100, enabling observers to confirm the absence of the lava lake's exposed molten surface. At that time, only two small and closely spaced circular vents emitted incandescent gases.
2000 Benbow observations. Observers descended to the first terrace level on 3 August 2000, crossing along the crests that encircled the central shaft. At this time, there was no exposed molten lava on the lake's surface. Still, violent and continuous explosions fed a darkly colored, dense ash plume. These outbursts came from a vent situated in the deepest part of the central opening. The excursion failed to get around the NE vent on the terrace level N1 due to a zone of mass wasting that left a scar ~160 m deep. On 17 August, torrential rains and excessively violent winds impeded attempts to approach Benbow.
On 1 September, people descending to terrace N1 felt sub-continuous tremor but found comparatively little gas. What gas there was looked blue in color and hung over the central opening. The lava lake was once again present (but difficult to see due to impeded access caused by the above-mentioned scar). Degassing accompanied by rumblings and strong detonations sent incandescent lava fragments to heights of ~100 m.
Information Contacts: G. de St. Cyr, c/o Bulletin of the Geneva Society of Volcanology, C.P. 6423, CH-1211, Geneva 6, Switzerland.
Lava lakes remain active in Mbwelesu and Benbow craters through December 2002
Observations of Ambrym were made by John Seach during a climb to the caldera during 11-15 December 2002. Lava lakes were visible in both Mbwelesu and Benbow craters that had been absent during a visit in February 2000 (BGVN 25:02) . Reports from local guides indicated that two lava lakes appeared in Mbwelesu crater during February 2001 and joined to form a single lava lake in August 2001. A lava lake reappeared in Benbow crater during June 2002. During November 2002 acid rain, for the third consecutive year, destroyed the mango crops between Sanesup and Lalinda on the W coast of Ambrym.
Activity at Mbwelesu Crater, 12 December 2002. Perfect visibility into the crater enabled detailed observations of the lava lake over 5 hours from the S side of the crater at an elevation of 950 m and over 300 m above the lava lake. The lava lake, located at the bottom of Mbwelesu Crater inside a circular pit (figures 6 and 7), had a diameter of 40-50 m, was in constant motion, and made continuous loud crashing sounds like waves at the beach. The lava lake was much more active than during previous visits in 1998 and 1999. Pele's hair littered the observation area, and white lithic blocks up to 30 cm in diameter were scattered on the rim.
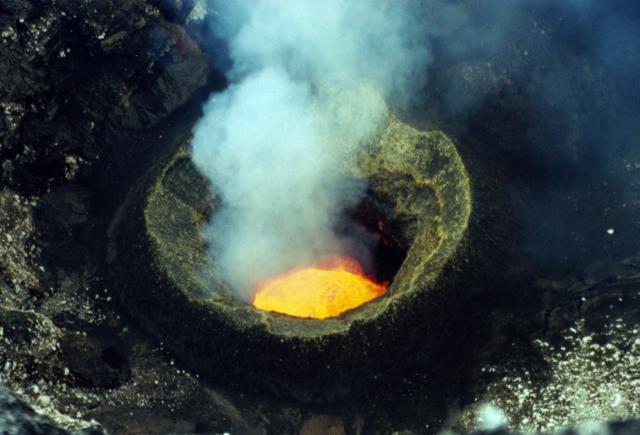 |
Figure 6. Photo of the lava lake inside a circular pit within Mbwelesu Crater at Ambrym, 12 December 2002. The diameter of the lava lake is 40-50 m. Courtesy of John Seach. |
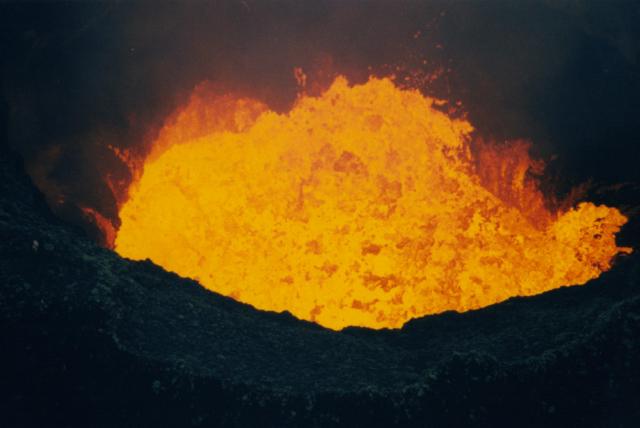 |
Figure 7. Photo showing the violent degassing from the lava lake in Mbwelesu Crater at Ambrym, 12 December 2002. Courtesy of John Seach. |
The surface of the lava lake was continuously disrupted by degassing. Bubbles caused the lake surface to blister and finally burst, splashing lava into the air. Up to eight large bubbles formed at any one time and covered over 80% of the lake surface. The cycle of bubble formation and rupture took about 3 seconds. Waves up to 10 m high formed due to the degassing and crashed onto the side of the pit. After lava waves hit the side of the pit there was a drain-back of lava into the main lake much like ocean waves receding off a beach. Jets of lava were regularly expelled from the lake surface and directed both vertically and at an angle towards the pit side. Fountains reached up to 40 m high. Blobs of molten lava spattered onto the side of the pit up to 20 m from the lava lake edge. This spatter was more erratic than lava fountains and sprayed over a greater area. When large amounts of lava were thrown onto the pit wall, some would cascade back into the lake via a lava stream, lava fall, or a wide curtain of orange flowing lava.
Crusting of the surface was observed when parts of the lake had a lower level of activity, most often in the NE part of the pit opposite the area of most vigorous degassing. Sometimes a lava fountain would burst through the crust, throwing darker pieces of lava high into the air. At times the orange lava lake surface was covered with black pieces of broken crust. Crusting lasted for only a few minutes at a time before it was disrupted by fountains or waves. Lava disappeared into the lava lake surface by subducting under layers of other lava. Some lava disappeared into overhangs on the side of the pit. Lava lake activity continued out of view for an unknown distance past these overhangs.
The lava lake level rose and fell over a period of less than an hour in response to changes in the surface degassing rate. When the rate of degassing was high the lake level was raised by 10 m. The changes appeared to be caused by inflation of the lake due to gas rather than any change in lava eruption rate. During a period of low lava lake activity, the whole lake surface tilted 5 m towards the N and then back to the S over a two-second period. Violent intra-crater winds were observed around the lava lake as reflected in their effects on gas emissions. These were also felt beside the lava lake in Benbow crater. Vapors emitted from the lake surface were white tinged with blue.
Two 15-m-diameter vents 100 m N of the lava lake and 60 m higher were separated by a thin wall. The W vent did not show any activity. The E vent made almost continuous loud degassing noises, and larger explosions ejected black ash 50 m into the air. Mbwelesu was approached again on 15 December, but rain the previous day and low clouds had filled the crater with white vapor, allowing only brief views of the still constantly active lava lake.
Activity at Mbogon Niri Mbwelesu, 12 December 2002. This small collapse pit has been re-named (formerly Niri Mbwelesu Taten) after a request by local residents. The new name comes from the local Port Vato language of W Ambrym, as did the previous name, but is more culturally appropriate. The translation of the new name is " mouth of the wild young pig" (Mbogon = mouth, Niri = son, Mbwelesu = wild pig).
On 12 December excellent visibility enabled detailed observations into Mbogon Niri Mbwelesu. Observations were made from the N side of the pit. Loud crashing, degassing sounds were heard inside the pit, and a 10-m-diameter vent was observed on the floor about 180 m below. The pit glowed bright orange, but lava was not directly observed. This was the first time in 2002 that guides had observed the presence of lava in this pit. Loud degassing occurred every few seconds, and the larger explosions were accompanied by light brown emissions and ground shaking. Pungent sulfurous fumes were emitted from the pit, forcing the observer to use a respirator at times. Strong degassing of brown vapors was coming from the E side of the pit, 50 m below the rim. The W inside wall of the pit was coated with red and yellow deposits.
Activity at Niri Mbwelesu Crater, 12 December 2002. On 12 December excellent views were obtained into Niri Mbwelesu. A recent large landslide on the W wall of the crater had covered the previously lava-filled vent. Rockfalls were heard regularly inside the crater and degassing occurred about every 30 seconds. About every 20 minutes larger explosions were heard at the crater; some were audible over 3 km away.
Activity at Benbow Crater, 13 December 2002. Benbow was climbed from the S on 13 December. The observer free-climbed 165 m down to the floor of the first level, and then another 45 m further down to the edge of the lava lake pit in the N of the crater. Inside Benbow there were two active pits. The larger pit, in the middle of the crater, contained a crusted lava lake and two active vents. The SW vent was 25 m in diameter and was full of vapor but emitted no sounds. The NW vent was 10 m in diameter, glowed red, and loudly degassed. The N crater in Benbow contained an active lava lake. The observer climbed to the rim and was able to view the lake surface, ~50 m below, for a few seconds before retreating. The lava lake was in constant motion and lava was ejected in to the air. Violent winds (over 80 km/hour) were generated inside the pit and made observations on the edge dangerous. At times the pit was filled with white and blue-tinged vapors which made breathing difficult. The lava lake made continuous rumbling and sloshing noises. On a wall next to the lava lake pit there was dripping water with a pH of 3.5 and 700 ppm total dissolved solids.
Visit to Ambrym, 15-20 August 2001. Jeff and Raine Williams, sailing aboard the S/Y Gryphon, visited Ambrym Island during 15-20 August 2001. One day was spent hiking to the Mbwelesu crater with a guide from the village of Ranvetlam. Their report has been reduced here to basic observations; a more poetic and complete description of their hike can be found on their website. After leaving Ranvetlam, they began a steep climb through jungle and gardens, continuing through coconut groves and thick woods of breadfruit trees and wild nut trees. After an hour they were still passing through the garden plots of villagers. At higher altitudes the vegetation changed to bananas, kava, and lap-lap plants; wild tree ferns and palm trees were abundant.
After about 90 minutes they emerged from the jungle onto a lava flow at the lower limit of the high central 'ash plain' plateau. They climbed along this "50-yard wide, black gravel road," also described as a "wild orchid-lined highway," through the jungle to the ash plain itself, where the tops of Marum and Benbow could be seen shrouded in clouds and mist. The hike continued across ~1.5 km of the ash plain before passing along a lava gully onto the final ridge, a 1-m-wide path of loose cinders and stone. They climbed to the rim and looked down the sheer, nearly vertical cliffs into the crater, where they heard rumbling and splashing sounds of the active lava lake. Although the weather was cold and windy, the fog cleared enough for the visitors to briefly observe bright red lava in the crater three times within 30 minutes. The 11-km-long hike to the crater took four hours, and another 3 hours to return.
Information Contacts: John Seach, PO Box 16, Chatsworth Island, NSW, 2469, Australia (URL: http://www.volcanolive.com/); Jeff and Raine Williams, P.O. Box 729, Funkstown, MD 21734, USA.
Infrared data indicate continued lava lake activity during 2001-2002
Although the current period of activity at Ambrym has been ongoing since June 1996, direct observations have been intermittent. Most recently, there have been reports of visits during January and February 2000 (BGVN 25:02 and 25:04), August-October 2000 (BGVN 26:02), and August 2001 and December 2002 (BGVN 27:12). Another report of scientific investigations from July 2000 is presented below. These observations are supplemented by MODIS data that indicate continued lava lake activity through much of 2001 and 2002.
Observations during July 2000. During 8-11 July 2000, David Nakedau and Douglas Charley reached Ambrym and camped in the caldera, after the necessary authorizations from local chiefs. On 11 July, French and Italian scientists joined the group. During the following days two stations were installed, one close to the village of Lalinda, the other on the E flank of Benbow cone. The first station, composed of a broadband STS2 seismometer, was installed on a basaltic lava flow with the aim of recording local volcano-related seismicity and tectonic earthquakes. The summit station was equipped with a short-period Mark seismometer to record the activity of the lava lake that used to be visible at Benbow until 1999 and now has drained back at a greater depth due to the Ms 7.1 earthquake of 26 November 1999. The first results from the analysis of these data are currently in press (Carniel and others, 2003).
On 11 July 2000 a visit was made to the Niri Taten Mbwelesu crater, where only fumarolic activity could be observed. The crater name means "the son of the female pig," given after its birth in 1989 near the existing Mbwelesu (the pig) and Niri Mbwelesu (the female pig). At the request of local residents, this crater was renamed Mbogon Niri Mbwelesu in December 2002 (BGVN 27:12). After more than a day of continuous rain, on 13 July the installation of the station on the Benbow rim was accomplished. During 13 July strong degassing noises were heard only sporadically from the Southern crater, which was otherwise showing low degassing rates and low-level noises. The southern crater has been observed since the first visits of Douglas Charley, and was the site where the lava lake was observed until 1999. The Northern crater, on the contrary, was not observed by Charley before 1997. Another small vent used to be present on its W side, but was completely buried by 1999 collapses. During 13 July, from the rim observations, this crater appeared to be the source of the strongest noises.
During the following days, two descents were made into Benbow using ropes, one on 14 July by Carniel and Fulle with local guides Jimmy and Isaac; the other was made on 16 July by Charley, Garaebiti, Wallez, and Jimmy. The Southern, older crater, was obstructed and conical in shape. From it's central part, significant blueish-colored degassing was observed, indicating sulfur dioxide. On 14 July visible degassing activity was not accompanied by noticeable sound. On 16 July some small explosions were observed at this vent, which ejected centimeter-sized fragments. On the N side, a fault full of sulfur deposits was visible. Numerous concentric faults were also visible around the vent on the n, E, and W sides. A significant zone of fumarolic activity was concentrated on the N flank of the vent, mainly composed of water vapor. Other small fumaroles were located around the vent. A number of pits were aligned in the W and S border, with the most significant fumarolic activity at the S side, where blueish sulfurous gas escaped continuously.
The Northern crater emitted significant water vapor plumes. To the N and to the S of the vent, two deep tracks were created by water runoff during strong rainfalls. To the E, the border of the vent was formed by rock debris, which, according to the guide Jimmy, was emplaced as a consequence of the strong 26 November 1999 earthquake. Both on 14 July and on 16 July the sound from the N crater appeared to be much lower than from the S crater, an observation opposite to the one made from the Benbow rim on 13 July. On 14 July scientists observed several more dense water vapor clouds, some of them accompanied by the fall of very small (less than 1 cm) light lithic fragments.
Marum, and the surrounding vents of Mbwelesu, Niri Mbwelesu, and Niri Taten Mbwelesu, were visited again on 16 July. Mbwelesu was intensely degassing, which often precluded direct observation of the crater. On the SE side, where a lava lake used to be, only a static mud pond could be seen. Also Taten Mbwelesu crater was showing intense degassing accompanied by strong noise, which made observation difficult. Niri Taten Mbwelesu showed intense degassing but no noise. The dropping of rocks into the pit confirmed the presence of a mud pond at the bottom, at an approximate depth of 200 m.
On 17 July the scientists left the volcano for the village of Lalinda, where they met with the custom chief and the population in order to inform them about the activity of the volcano and about the research. On the early morning of 19 July the two eruptive plumes from Ambrym's main cones were clearly visible at a distance from the island of Paama. However, only the plume produced by Marum was colored pink-orange; this observation suggests the presence of lava at shallow depth in one of its vents, although such a feature was not observed directly during the previous days.
MODVOLC Thermal Alerts, 2001-2002. MODIS detected quasi-continuous thermal alerts for Ambrym throughout 2001 and 2002 (figure 8). Moreover, these occur fairly equally in two clusters interpreted as representing Benbow and Marum (figure 9). These data provide strong evidence in favor of continued lava lake activity. The highest alert ratios for the period of -0.107 on 9 April 2001 in Marum and -0.116 on 3 November 2001 in Benbow may represent episodes of overturn. Marum appears to have been particularly active also during January-February 2002 when the anomaly usually consisted of either 4 or 6 alert-pixels (figure 9). Anomalies continued in January-February 2003.
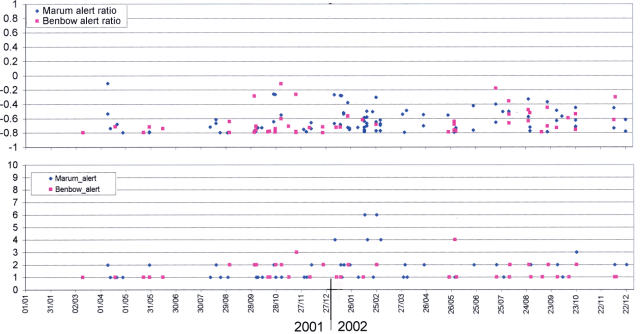 |
Figure 8. MODIS thermal alerts on Ambrym during 2001-2002. Courtesy of Diego Coppola and David Rothery, The Open University. |
References. Quantin, P., 1978, Archipel des Nouvelles-Hébrides: Atlas des Sols et de quelques Données du Milieu: Cartes Pédologiques, des Formes du Relief, Géologiques et de la Végétation; ORSTOM (18 sheets).
Carniel, R., Di Cecca, M., Rouland, D., accepted Feb 2003, Ambrym, Vanuatu (July-August 2000): Spectral and dynamical transitions on the hours-to-days timescale: JVGR.
Information Contacts: Diego Coppola and David A. Rothery, Department of Earth Sciences, The Open University, Milton Keynes, MK7 6AA, United Kingdom; Roberto Carniel, Università di Udine, Italy (URL: http://www.swisseduc.ch/stromboli/); Douglas Charley, Sandrine Wallez, and David Nakedau, Département de la Géologie, des Mines et des Ressources en eau, Vanuatu; Marco Fulle, Osservatorio Astronomico, Trieste, Italy (URL: http://www.swisseduc.ch/stromboli/); Esline Garaebiti, Université de Clermont-Ferrand, France; Daniel Rouland, E.O.S.T., Strasbourg, France; Geneviève Roult, I.P.G., Paris, France.
Lava visible in six vents during September; lava lake activity and ash emissions
John Seach previously reported his observations of the Ambrym caldera made during a visit in December 2002 (BGVN 27:12). This report contains his observations of the caldera during a 7-11 September 2003 visit and flyovers on 6 and 13 September. The level of activity during September 2003, with visible lava in six vents, was higher than that during his previous visit.
Observations of Benbow. During the 6 September flyover, two white plumes were rising 200 m above the crater rim and drifting NW. On the evening of 7 September, orange glows were seen from the caldera edge (3 km SE). A strong glow originated N of the crater and the central crater pit produced a less intense fluctuating glow. During the 13 September flyover, both pits continued to emit white and light-brown plumes to 200 m above the rim.
Observations of Mbogon Niri Mbwelesu. Large white vapor emissions from the collapse pit formed mushroom-shaped clouds on 6 September that drifted W and attained a height of 300 m. A visit to the S rim on 7 September showed a weak orange glow and copious gas emissions. On 8 September, observations from the N rim showed the pit full of swirling brown and white vapor. The NW wall was stained with yellow and red deposits, and pungent sulfurous gases were being emitted. Loud, rhythmic degassing sounds were heard every few seconds. The bottom of the pit was visible on 10 September, allowing views of two glowing red holes 150 m below the rim separated by a small wall a few meters wide. The two vents degassed simultaneously, but the E vent emitted larger amounts of brown ash.
Observations of Niri Mbwelesu. During the 6 September overflight, the pit of Niri Mbwelesu crater was filled with white vapor. The crater was climbed on 8 September and observations from the S rim showed the crater still filled with vapor; no sounds were heard. During that evening, an orange glow was observed. Excellent visibility on 10 September enabled sighting of a 10-m-diameter, crusted lava pond. Red lava was visible through surface cracks, and lava spatter rose 10 m above them at infrequent intervals.
Loud cannon-like explosions about every 20 minutes shook the ground and were accompanied by the sounds of cracking rock. During the evening, glowing projectiles were ejected into the air, although none fell outside the crater. Loud, roaring degassing noises like a jet engine at take-off were also heard. The roar would gain intensity over 30 seconds, cease for 15 seconds and then re-start. During periods of intense roaring, red lava was observed through cracks in the crusted surface.
Both types of intense degassing were accompanied by gentle emissions of brown vapor. A pit, 6 m in diameter, located N of the crusted pond in the crater wall, emitted brown ash. Fumaroles were high on the N inner crater wall. Brown ash was emitted from the S crater floor.
Observations of Mbwelesu. Mbwelesu crater was observed for 3 hours during mid-day on 8 September from a position on the SW rim. At times, the crater was filled with vapor, but observation of the lake surface was only possible about 60% of the time. The lava lake showed remarkable similarities in location, size, and dynamics compared to December 2002. The 50-m-diameter lava lake was contained inside a circular funnel-shaped pit 100-120 m in diameter. Violent agitation of the surface occurred most of the time. Lava splashed onto the pit walls and drained back vertically 25 m into the pit.
Large 10-m-diameter gas bubbles burst in the SE half of the lava lake with up to eight bubbles visible at the same time. Jets of lava were ejected every few seconds, created by wave intersections from the bursting bubbles. During periods of low activity, lasting tens of seconds, lava drained back into the middle of the pit. Surface crusting occurred after as little as one minute during quiet periods. Subsequently, the crust was broken up by a resumption of degassing from the SW side of the pit. On several occasions, up to 80% of the lava lake surface was covered by darker crust.
Acid rain was experienced on the edge of the crater and observers felt minor burning on the face. White, light-brown, and blue-tinged vapors smelling of sulfur were emitted from the crater.
Mbwelesu was scaled again on 10 September and observations of the lava lake (figure 10) were made over eight hours. The crater was clear, enabling detailed observations. At times 80% of the lake surface was deformed by bubbling. The SE portion of the pit contained the most degassing. Violent explosions regularly sprayed orange lava mixed with black crust in all directions. At one point the whole lake surface rotated clockwise and lava drained back into the middle of the pit. This whirlpool was followed by an avalanche on the W side of the pit that threw black material into the lake. A second pit with a diameter of 75 m NE of the lava lake was separated by an unstable 10-m-wide wall from which numerous avalanches occurred during the day; red lava spatter was ejected once.
 |
Figure 10. Lava lake inside Mbwelesu crater at Ambrym on 10 September 2003. Surface crusting and degassing are clear, note new crater at top of photo. Courtesy of John Seach. |
An afternoon flyover on 13 September enabled excellent views of the active lava lake. The smaller pit NE of the lava lake contained a small lava pond with a diameter of ~ 8-10 m.
Observations of Marum. Two areas of fumarolic activity were seen at the edge of the 1953 crater (between Marum and Mbwelesu). Brown ash was being emitted from the ground at these locations.
Information Contacts: John Seach, PO Box 4025, Port Vila, Vanuatu (URL: http://www.volcanolive.com/).
Abundant MODIS thermal alerts during March 2003-February 2004
Ambrym was last reported in BGVN 28:09, when details of activity observed during September 2003 visits were published. A daily summary of MODIS thermal alerts for the year ending February 2004 (table 1) suggests, subject to the limitations of thermal imaging (e.g. in times of heavy cloud), regular activity over the course of the year. No corroborative reports of activity have been received from the [Départment de la Géologie, des Mines et des Ressources,] or the Darwin Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre.
Table 1. Nights on which MODIS thermal alerts were recorded for Ambrym, for the year ending February 2004 . Thermal alerts recorded in daylight hours have been omitted for data reliability reasons (four cases). Data courtesy HIGP MODIS Thermal Alert System.
| Month | Days with Thermal Alerts |
| Mar 2003 | 7, 21, 30 |
| Apr 2003 | 15, 17 |
| May 2003 | 1, 3, 17, 19, 20, 28 |
| Jun 2003 | 9, 15, 16, 29 |
| Jul 2003 | 29 |
| Aug 2003 | 21, 25 |
| Sep 2003 | 13, 15, 24 |
| Oct 2003 | 1, 3, 8, 10, 22, 24, 31 |
| Nov 2003 | 2 |
| Dec 2003 | 25, 27 |
| Jan 2004 | 7, 9, 12, 28 |
| Feb 2004 | 1, 3, 4, 10, 17, 19, 22, 28 |
Information Contacts: HIGP MODIS Thermal Alert System, Hawaii Institute of Geophysics and Planetology, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology, University of Hawaii at Manoa (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/).
Lava lake active; ash plume in MODIS images
Ambrym (last reported in BGVN 29:03) exhibited high levels of activity in March and April 2004. During March, an active lava lake was present in Mbwelesu crater, one of the active summit craters. As of 27 March, there were reports that the people of Craig Cove in West Ambrym were suffering from the effects of the ongoing volcanic eruption on the island. Gas and acidic rainfall from the active vents on the volcano were threatening to destroy the local food gardens. The island was still recovering from the effects of Cyclone Ivy, which caused widespread damage two weeks earlier; the added affects of the eruption prompted Vanuatu's leaders to request emergency relief assistance from national and local authorities.
As of 3 April, reports confirmed by the Darwin VAAC and J. Seach described continuing lava lake activity at Ambrym. On 27 April, a large ash plume was recorded drifting 150 km NW of the volcano, passing the northern tip of Malekula Island and almost reaching Malo Island. Eruptions were still continuing up to 2 May.
NASA's Earth Observatory posted two images of Ambrym and its plume as they appeared on 27 April 2004 (figure 11). The pair of images came from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on the Terra satellite. A large plume of volcanic ash blew westward from the volcano, which appears at the center right edge of figure 11 (top). The plume was mixing with clouds, and was more apparent as a bright, reddish orange color in the false-color image (below). Figure 11 (bottom) shows a wider area at the same spatial resolution.
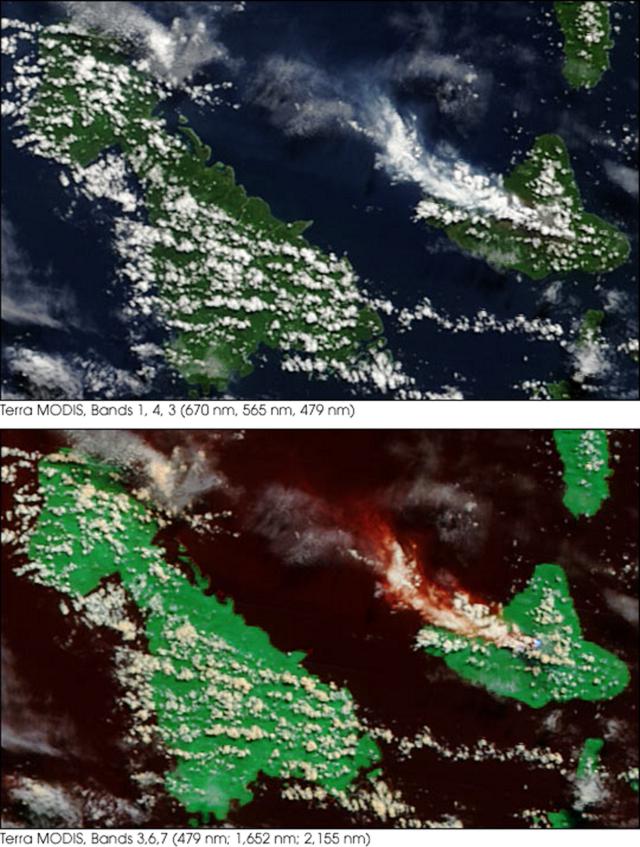 |
Figure 11. Ambrym volcano in two MODIS images (top and bottom). See text for discussion. Image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team, NASA-GSFC. |
Information Contacts: John Seach, PO Box 4025, Port Vila, Vanuatu (URL: http://www.volcanolive.com/); Darwin VAAC (URL: http://www.bom.gov.au/info/vaac/); Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team, NASA-GSFC; Holli Riebeek, NASA Earth Observatory (URL: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/).
Continued MODVOLC thermal alerts indicating activity, January 2003-May 2004
Ambrym triggered continued alerts during 2003 and 2004 at both Marum and Benbow craters, with Marum alerts being the slightly more common (figures 12 and 13). Activity appeared less intense than in previous years, but more alerts were issued due to the availability of Aqua data starting from January 2004. The highest alert ratio (-0.088) (see BGVN 28:01 for a discussion of the alert ration) was detected by Aqua on 14 May 2004 and the highest number of alert pixels detected for any one pass was four, a situation repeated on 29 June, 21 August, and 2 November 2003. Visual observations during September 2003 (BGVN 28:09) confirmed that there was activity at these craters.
Data acquisition and analysis. Reports from Diego Coppola and David A. Rothery provided analyses of MODIS thermal alerts during 2001 and 2002 (using the MODVOLC alert-detection algorithm) extracted from the MODIS Thermal Alerts website (http://modis.hgip.hawaii.edu/) maintained by the University of Hawaii HIGP MODIS Thermal Alerts team (BGVN 28:01). Rothery and Charlotte Saunders provided updates to 31 May 2004. MODVOLC data are now routinely available from the Aqua satellite (equator crossing times 0230 and 1430 local time) in addition to the original Terra satellite (equator crossing times 1030 and 2230 local time).
Information Contacts: David A. Rothery and Charlotte Saunders, Department of Earth Sciences, The Open University, Milton Keynes, MK7 6AA, United Kingdom.
Steady emissions of SO2 create health problems, destroy crops, and contaminate water
Jenifer Piatt, a meteorologist with the Air Force Weather Agency in the Satellite Applications Branch, notified Bulletin staff on 17 June 2005 that haze had appeared near Ambrym on MODIS imagery over the past few days. Over the past several months, this volcano had been emitting SO2 and sometimes light ash. She informed us of several recent news articles that addressed this event and provided several satellite images (figure 14).
Tony Ligo wrote on 1 June 2005 in the Port Villa Presse that acid rain continued to fall in W Ambrym Island in Vanuatu, even after ash from the volcano had stopped falling. This prompted the provincial secretary general to discuss the need for new water sources. The Vanuatu government, through the department of Rural Water Supply, agreed to provide a drilling rig to the Malampa provincial government to drill on W Ambrym as soon as possible.
The government also recognized the value of scientific and technical data; in order to effectively respond to such environmental problems the government needs to get more young people studying in this area. The article noted that Vanuatu only has one volcanologist, Charley Douglas, with enough background to give accurate data on current activity.
Aid and food have been sent to affected areas on the western coast of the island, and a contingency evacuation plan is required for resettling people should this be necessary in the future. Health issues have been raised regarding hygiene, respiratory problems, asthma, and malnutrition over the past couple of months. Of great concern are health problems particular to children, including exposure to excess fluoride and the consequent risk of bone disease.
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Earth Observatory web site reported that Ambrym volcano was the strongest point source of SO2 on the planet for the first months of 2005; it had been steadily emitting SO2 for at least 6 months, and satellite images produced using data collected by the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) on NASA's Aura satellite during the first 10 days of March 2005 show high concentrations of SO2 drifting NW.
The web site article noted that "Ambrym is not erupting in the traditional sense with thick ash plumes and explosive bursts of lava, rather it is leaking SO2 gas from active lava lakes in what scientists call 'passive' or 'non-eruptive' emissions. Despite these gentle names, the volcano still threatens the local population. SO2 has a strong smell and can irritate the eyes and nose and make breathing difficult. Higher in the atmosphere, SO2 combines with water to create rain laced with sulfuric acid. On Ambrym, acid rain has destroyed staple crops and contaminated the water supply, leaving communities in need of food aid." In the past, satellites have been able to monitor SO2 emissions only from large eruptions or the most powerful passive degassing. All other SO2 emissions remain at low altitudes and have low SO2 concentrations that were hard to see from space.
On 15 July 2004, NASA launched its Aura satellite carrying the OMI, which is part of a collaboration between the Netherlands' Agency for Aerospace Programs, the Finnish Meteorological Institute, and NASA. With greater spatial resolution (the ability to "zoom-in" to see greater detail) and higher sensitivity to SO2 than any previous space-borne sensor, OMI allows scientists to study passive volcanic degassing on a daily basis for the first time.
The image in figure 15 is an example of the instrument's preliminary, uncalibrated, and unvalidated data. This new view of passive volcanic emissions could lead to significant advances in understanding both volcanic eruptions and the impact of SO2 on climate. Changes in passive emissions can be a precursor to explosive eruptions, and thus provide a warning signal that activity may be changing.
Information Contacts: Jenifer E. Piatt, HQ Air Force Weather Agency Satellite Applications Branch; Simon Carn, TOMS Volcanic Emissions Group, University of Maryland, 1000 Hilltop Circle, Baltimore, MD 21250, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/); NASA Earth Observatory Natural Hazards web page (URL: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/).
Lava lakes active again starting in January 2007; ash plumes
Thermal anomalies detected by the MODIS satellite instrument showed that the lava lakes present in Benbow and Marum craters, which have been almost continuously active since early 2001 (BGVN 29:06), continued until 19 June 2005. Ash had apparently stopped falling on 1 June, though a haze of SO2 was noted on 17 June (BGVN 30:05). Thermal anomalies were not regularly seen again until 11 January 2007. The only exceptions occurred from Benbow on 14 April 2006 (one pixel) and from Marum on 8 and 15 November 2006 (one and two pixels, respectively). Thermal anomalies were seen on 11 and 15 January, again during 3-19 February, and then almost daily after 9 March through at least the end of May. The current lava-lake activity, as determined by MODIS data, seems to be confined to the Marum crater area.
The Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) reported that on 3 April 2007 pilots observed lava and ash emissions from Ambrym; ash plumes rose to altitudes below 2.4 km. On 1 May at 1330 satellite imagery showed an ash cloud with NE winds at the surface turning to NW above an altitude of 3 km. On next day at 0715 a pilot observed a vertical plume extending 37 km NW at an altitude of 4 km. On 3 May at 0900 a pilot identified an ash cloud below an atmospheric temperature inversion at an altitude of -1.8 km drifting SE. Ash was visible on satellite imagery at 1310 on 3 May.
Steven Clegg and Kelby Hicks reported that the volcano continued to exhibit strong degassing from both Marum (figure 16) and Benbow vents from 26 May to 12 June 2007. Within the Mbwelesu crater a lava lake appeared in May 2007, while the group was there, and continued to be visible through 12 June (figure 17). Fumarolic activity was visible throughout the interior of Mbwelesu Crater with intermittent ash eruptions and light tephra emissions. Extra-crater tephra fall included Pele's Hair, reticulite, spatter, and scoria-sized ejecta. Both Niri Mbwelesu and Mbogon Niri Mbwelesu (formerly Niri Mbwelesu Taten) craters exhibited notable fumarolic degassing, but no other observable activity. No lava lake could be seen from the rim of Benbow crater; however, a strong glow above Benbow was visible during night observations.
 |
Figure 16. View of the Marum cone at Ambrym looking SW, 7 June 2007. Incandescence from the active lava lakes can be seen reflected in the clouds (left). Courtesy of Steven Clegg. |
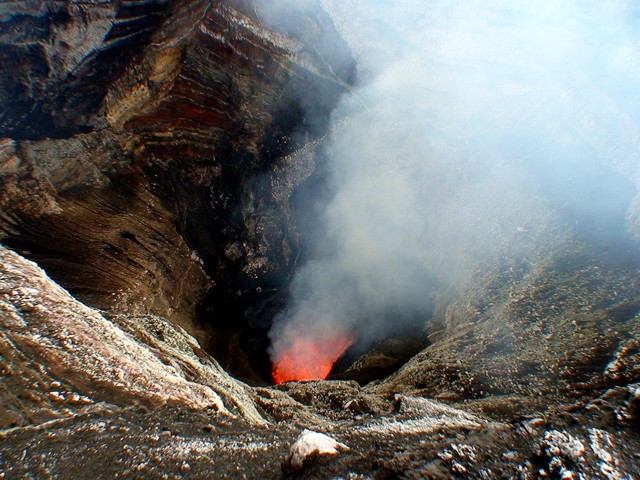 |
Figure 17. Lava lake inside Mbwelesu crater within Marum cone at Ambrym, 7 June 2007. Courtesy of Steven Clegg. |
Information Contacts: Steven G. Clegg and Kelby E. Hicks, Volcan, Inc., P.O. Box 1287, Austin, TX 78767, USA (URL: http://www.volcan.org/); Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Meteorological Service of New Zealand Ltd (MetService), PO Box 722, Wellington, New Zealand (URL: http://www.metservice.com/vaac/, http://vaac.metservice.com/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/).
Lava lakes at least intermittently active during 2006 into 2009
Thermal anomalies detected by MODIS instruments and processed by MODVOLC indicated that lava lakes in both summit craters at Ambrym have been at least intermittently active during November 2006 through February 2009 (figure 18). After MODVOLC alerts were detected on 8 and 15 November 2006 (BGVN32:05), they were again frequently identified from 12 January until 11 July 2007. Another cluster occurred between 31 October and 27 December 2007. A single alert occurred on 23 May 2008. Alerts resumed again on 21 October 2008 and continued through 15 February 2009.
Observations during 31 August-8 September 2008.Arnold Binas reached the summit and observed lava lake activity during 31 August-8 September 2008, an interval without thermal alerts. Binas also reported that the lake was largely crusted over, abundant steam was emitted, and poor weather conditions often prevented views into the craters. Such factors may have prevented satellite detection of low-level activity during those, and possibly other, times.
Binas climbed to the Benbow crater rim once, but thick steam prevented visual observation of the inner cone; however, strong degassing was noted, often in pulses. At Marum, low rain clouds on the SE side limited observations to periods of a few seconds at a time.
The Marum cone has three active sub-craters with distinct names. The name Mbwelesu describes the main crater; Niri Mbwelesu, a secondary crater close to Mbwelesu's rim; and Mbogon Niri Mbwelesu, a small collapse-pit to the S of Niri Mbwelesu. (The collapse pit Mbogon Niri Mbwelesu is also sometimes called Niri Mbwelesu Taten.)
During the visit, partial views into the Mbwelesu crater were rare through small gaps in constant rain clouds and strong steam emissions. A small lava lake was visible in the main vent, and another nearby opening often spattered small chunks of lava (figure 19). It appeared that both openings were holes through a crusted-over lava lake. The width of the visible portion of the larger opening, measured in digital image pixels at a given focal length and an assumed distance of 350-400 m, was determined to be on the order of 7.5-8.5 m. Waves rolled back and forth along the surface of the covered lake almost constantly, splashing lava through the holes, to a maximum height of about 30-35 m. Degassing also caused small explosions. Noises from the lava lake could be heard throughout the night from within the tent ~ 15 m from the crater rim, despite strong winds and rain.
Strong gas emissions took place in Niri Mbwelesu, with only very rare views of the crater floor, on which a small lake of brownish water was present next to a steaming vent. Mbogon Niri Mbwelesu displayed mostly strong but silent gas emissions from fumaroles on the crater floor, occasionally clearing enough to enable views of the bottom. Sometimes small rockfalls were heard, but not seen, inside the crater.
Information Contacts: Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Arnold Binas, Toronto, Canada (URL: http://www.summitpost.org/user_page.php?user_id=42443, http://www.flickr.com/photos/hshdude/collections/72157600584144439/).
Frequent thermal anomalies from lava lakes during October 2008-September 2009
Lava lake activity in both summit craters at Ambrym has been documented by the frequent presence of thermal anomalies, detected by MODIS instruments and processed by MODVOLC, between 21 October 2008 and 24 September 2009 (figure 20). Prior to this eruptive episode, the active lava lakes caused detectible thermal anomalies in November 2006 (BGVN 32:05), January-July 2007 (BGVN 34:01), and October-December 2007 (BGVN 34:01).
Ash plumes reported on 25-26 March 2009 resulted in advisories to aviators issued by the Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC). The airport control tower in Port Vila, Vanuatu, informed the VAAC on 25 March of an ash plume that rose to an altitude of 2.1 km and drifted about 55 km S. A pilot report the next day noted "smoke" rising to 2.4 km altitude. Although ash was not visible on satellite imagery analyzed by the VAAC on those days, thermal anomalies were seen in MODIS data on 25 March.
Additional plumes described by the NASA Earth Observatory were seen in visible MODIS imagery on 6 October and 3 December 2009. On both days the light-colored plume initially drifted 65 km WNW towards Malekula island. On 6 October the plume became a broad diffuse plume that spread hundreds of kilometers NW across the Coral Sea.
Information Contacts: Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Meteorological Service of New Zealand Ltd (MetService), PO Box 722, Wellington, New Zealand (URL: http://www.metservice.com/vaac/, http://vaac.metservice.com/); NASA Earth Observatory (URL: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/).
Ongoing plumes, some bearing ash and to over 6 km altitude
In our last report on Ambrym (BGVN: 3411), we described the frequent thermal anomalies from the volcano's active lava lakes during October 2008-September 2009. Satellite imagery in 2009 and 2010 suggested ongoing visible plumes and thermal alerts consistent with active lava lakes. Several satellite images of Vanuatu appear below (figures 21-22).
Based on observations by aircraft pilots, analyses of satellite imagery, and information from the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory (VGO), the Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) reported that on 8 and 10 August 2010 ash and steam plumes from Ambrym volcano rose to an altitude 6.1 km and drifted W and NW.
Ambrym is a major source of SO2 in the Vanuatu Republic. The VGO web site shows daily Vanuatu volcanic sulfur dioxide (SO2) fluxes through a partnership with GNS Science Institute (Taupo, New Zealand) using OMI satellite images.
Figure 23 shows a 22 May 2011 satellite image of Ambrym. Similar images were acquired by NASA satellites on 28 March 2011 and on 7 June 2011. On figure 23, a blue-tinged volcanic plume emissions extends from Ambrym to the W. The plume contains vog, a mix of gases and aerosols that is formed when SO2 and other volcanic gases react with sunlight, oxygen, and moisture.
Information Contacts: Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory, Department of Geology, Mines and Water Resources of Vanuatu (URL: http://www.vmgd.gov.vu/vmgd/); NASA Earth Observatory (URL: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/); MODIS/MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP), School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Meteorological Service of New Zealand Ltd (MetService), PO Box 722, Wellington, New Zealand (URL: http://www.metservice.com/vaac/, URL: http://vaac.metservice.com/).
Roiling lava lake and related observations through mid-2013
In our previous Ambrym report, we described ongoing plumes, some bearing ash rising to over 6 km altitude through early June 2011 (BGVN 36:05). The volcano has been known to contain two molten, turbulent lava lakes since August 1999, and that continues at least through June 2011, which was the last time lava-lake activity was noted in a report by the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory (VGO). Our reporting observations drew heavily on government reports of 3 April 2009 and 29 July 2013. The former report also discussed water supply and other issues of public health and safety associated with inhabiting an active volcano. Vanuatu is located in the South Pacific NE of Australia (figures 24 and 25).
Reynolds (2010) posted videos of lava lake behavior seen in September 2010. Figure 26 is a screenshot taken from the Reynolds' video of the turbulent lava lake with a climber in the foreground. The high definition videos showed an exceedingly agitated lake surface, everywhere disturbed and molten, without any chilled material in evidence. Violent upwellings of lava occurred continuously. Some fraction of the videos show climbers in the foreground, at one point descending a steep slope or vertical drop by a single rope secured from above (abseiling or rappelling).
 |
Figure 26. A screen capture from a video of Marum, one of Ambrym's two active lava lakes, taken on unstated day in September 2010. Courtesy of James Reynolds (typhoonfury.com and earthuncut.tv). |
On 27 June 2011, the VGO reported that data collected from Ambrym's monitoring network showed significant daily degassing and occasional explosions in the crater. Field observers noted that the level of the lava lakes was high. During June, villages reported minor ashfall and that acid rain affected agriculture in general in some areas W, S, and E. The Alert Level remained at 1 (on a scale of 0-4).
During the previous 12 months prior to mid-July 2013, MODVOLC thermal alerts were frequent, on the order of several a week to multiple per day, as would be expected for a volcano with active lava lakes. The alerts referred to the lava lakes in Benbow and Marum craters (figure 25).
On 21 June 2013, VGO reported that satellite images on 2, 4, 11, 14, and 16 June detected gas emissions from Ambrym. Emissions of minor amounts of ash and substantial amounts of gas from the active vents had been detected during the previous week. The report warned that communities on the island, especially those downwind of Ambrym, may experience ashfall and acid rain that could damage the environment and contaminate water. The Alert Level remained at 1. Based on pilot observations and analyses of satellite imagery, the Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) reported that on 19 July 2013 an ash plume rose to an altitude of 3 km a.s.l. and drifted 185 km NW.
VGO reported that activity at Ambrym slightly increased to a minor eruptive phase, and a seismic swarm was detected between 2400 and 0700 on 26 July 2013. The Alert Level remained at 1.
Gas fluxes are generally high for Vanuatu volcanoes and have been the subject of regular reporting online and several recent reports in the literature (for example, Bani and others, 2009; Bani and others, 2012).
References. Bani, P., C. Oppenheimer, V.I. Tsanev, S.A. Carn, S.J. Cronin, R. Crimp, J.A. Calkins, D. Charley, M. Lardy, and T.R. Roberts, 2009, Surge in sulfur and halogen degassing from Ambrym volcano, Vanuatu, Bulletin of Volcanology, 71(10), 1159-1168, doi:10.1007/s00445-009-0293-7.
Bani, P., C. Oppenheimer, P. Allard, H. Shinohara, V. Tsanev, S. Carn, M. Lardy, and E. Garaebeti, 2012, First arc-scale volcanic SO2 budget for the Vanuatu archipelago, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 211-212, 36-46, doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2011.10.005.
Polacci, M, Baker, D, La Rue, A., Mancini, L., Allard, P., 2012, Degassing behaviour of vesiculated basaltic magmas: an example from Ambrym volcano, Vanuatu Arc, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, Vol. 233-234, 1 July 2012, pp. 55-64.
Reynolds, J., 2010, (Video) Abseiling towards a lava lake--extreme video From Marum volcano, Ambrym, Vanuatu (September 2010) YouTube (URL: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AtGT-_7Xoal) [also available at typhoonfury.com and earthuncut.tv].
Information Contacts: Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory, Department of Geology, Mines and Water Resources of Vanuatu (URL: http://geohazards.gov.vu/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP), MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Sciences and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http//hotspot.higp.hawaii.edu/); Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC) (URL: http://vaac.metservice.com/); and NASA Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Home Page, Goddard Space Flight Center, Sciences and Exploration Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, Code 614 (URL: http://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/, http://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/pix/daily/0813/vanuatu_0813z.html).
Frequent thermal alerts and gas emissions continue
Our previous report on Ambrym (BGVN 38:05) indicated that daily degassing and an infrequent ash plume occurred through July 2013, along with frequent MODVOLC thermal alerts, consistent with the hot molten surface of the volcano's active lava lakes. The volcano, whose location was shown in the previous report in figure 27, consists of two craters, Marum and Benbow, each with a lava lake. According to the Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory (VGO), the last known eruption was in 2009. The island of Ambrym has ~7,000 inhabitants, many of whom live within the hazard zone (see figure 28 in BGVN 38:05). This report updates information through July 2014.
According to NASA's Earth Observatory, a satellite image acquired on 9 August 2013 showed steam-and-gas plumes rising from Ambrym's Benbow cone and from the active lava lake in Mbwelesu Crater (one of three active sub-craters of the Marum cone) (figure 27). Another Earth Observatory image on 7 January 2014 showed a plume from Ambrym spreading across the South Pacific Ocean (figure 28). The strong reflection of the sun off the sea surface is called "sunglint."
As in previous years, MODVOLC thermal alerts during the reporting period were frequent, ranging from several per week to multiple times per day. This activity is consistent with the presence of active lava lakes.
According to VGO, the current alert level remains in mid-2014 at 1 (increased activity, danger near crater only).
Information Contacts: MODVOLC - HIGP, Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP), MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); NASA Earth Observatory, EOS Project Science Office, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/); and Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory (VGO) (URL: http://www.geohazards.gov.vu).
New eruption with lava flow on 20 February 2015
Ambrym is a large basaltic volcano, with two lava lakes (figure 29) that have been almost continuously active since May 2008 contained in the 12-km-wide summit crater; MODIS data shows that they have remained active through at least June 2015. The Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory (VGO) issues periodic updates for the population of ~7000 island residents, and monitors seismicity using one permanent station. It also regularly emits ash plumes affecting air navigation, spreads clouds of vog across the island (BGVN 39:04), and occasionally has reported lava flows. The dramatic nature of the lava lakes makes it a popular destination with volcano tourists.
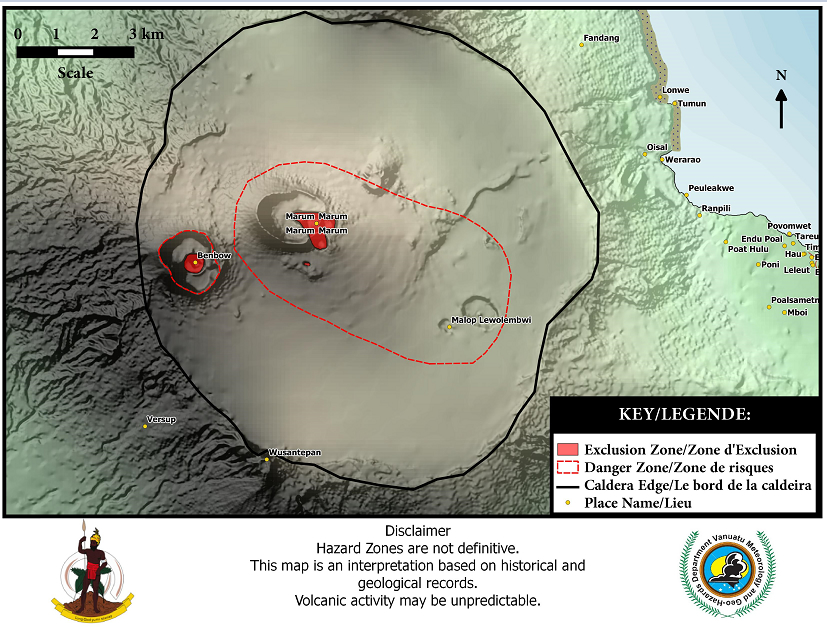 |
Figure 29. Main crater area of Ambrym volcano showing smaller craters and lava lakes as well as the danger and exclusion zones. Image courtesy of VGO. |
Steam-and-gas plumes were previously detected in satellite imagery on 9 August 2013 and 7 January 2014 (BGVN 39:04). On 11 September 2014, VGO reported increased seismicity and raised the Alert Level from 1 to 2 (on a scale of 0-4). On 8 December 2014, VGO reported that observations and analyses of Ambrym conducted during November and early December showed that activity levels had slightly decreased and consequently, the Alert Level was lowered to 1. An expedition to the Benbow lava lake by Volcano Discovery in September 2014 confirmed active lava fountaining from the lake.
On 21 February 2015, VGO issued a notice reporting an eruption from a new vent; the Alert Level was raised to 3 (on a scale of 0-5, see figure 30). Aura.OMI SO2 data from NASA first shows an anomaly between 0113 and 0255 UTC on 21 February. By 23 February an SO2 plume extending about 800 km WSW past northern New Caledonia is recorded. The plume then drifts ~600 km to the SSE by 25 February as it dissipates. Only the slightest trace is still visible to the SE of the volcano on 26 February. Satellite images indicated that the eruption location was southwest of Lewolembwi crater inside the caldera (figures 29, 31). The LANDSAT images taken in February and March 2015, and compared with an image from May 2014, annotated by Culture Volcan, show the eruption in progress and the extent and distribution of the new lava flow.
Culture Volcan reported that the Vanuatu National Disaster Management Office (NDMO) visited Ambrym on 22 February 2015. Ben Clark, Chief Pilot for Vanuatu Helicopters, photographed the new lava flow (figure 32), and lava fountains from the eruption in progress (figure 33).
MODVOLC data from 21 February shows a large thermal anomaly in the SE quadrant of the large crater which was no longer visible by 23 February. This could be from vegetation fires associated with the new lava flow, and suggests that it only flowed actively for ~ 2 days. Culture Volcan reported that the Wellington VAAC had noted a 2-km-high ash plume on 21 February.
On 2 March 2015, VGO reported that activity at Ambrym had slightly decreased but remained elevated, and the Alert Level was lowered to 2. By 25 April 2015 Satellite imagery showed only a steam-and-ash plume drifting W from the two active craters (figure 34).
Information Contacts: Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory (VGO), Geo-Hazards office, Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (URL: http://www.vmgd.gov.vu/vmgd/); Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Meteorological Service of New Zealand Ltd (MetService), PO Box 722, Wellington, New Zealand (URL: http://vaac.metservice.com/); Volcano Discovery (URL: https://www.volcano-adventures.com/photos/vanuatu/tour/2014/marum-bembow-lavalakes.html); NASA Global Sufur Dioxide Monitoring Page (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/); Culture Volcan: Journal d'un volcanophile (URL: http://laculturevolcan.blogspot.fr/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP), MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); NASA Earth Observatory, EOS Project Science Office, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/).
Occasional low-level ash emissions; lava lakes in Benbow and Marum craters active into April 2017
Ambrym, a volcanic island in the archipelago of Vanuatu with a large caldera (figure 35) is frequently active. Since at least 2001 the caldera has been the site of two lava lakes (BGVN 29:06, 32:05, and 40:06). The Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory (VGO) is responsible for monitoring the volcano, and the Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) tracks ash plumes to provide aviation warnings.
On 21 February 2015 the VGO issued a notice reminding the public that a minor eruption was occurring from a new vent inside the caldera. The Alert Level was raised from 2 to 3 (on a new scale of 0-5; see figure 30 in BGVN 40:06). Hazardous areas were near and around the active vents (Benbow, Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu and Mbwelesu), and downwind areas prone to ashfall. VGO reported both on 2 March 2015 and 27 May 2016 that activity at Ambrym had slightly decreased but remained elevated. The Alert Level was lowered to 2. Areas deemed hazardous were near and around the active vents, and in downwind areas prone to ashfall.
The Wellington VAAC reported that low-level ash emissions from Ambrym were identified in satellite images on 12 July 2016, 11-13 October 2016, and 3 April 2017. MODIS satellite thermal sensors have measured nearly continuous thermal anomalies over the past year ending in mid-April 2017, evident in both MIROVA (figure 36) and MODVOLC data (figure 37); similar levels of thermal anomalies are present in MODVOLC records since 2009.
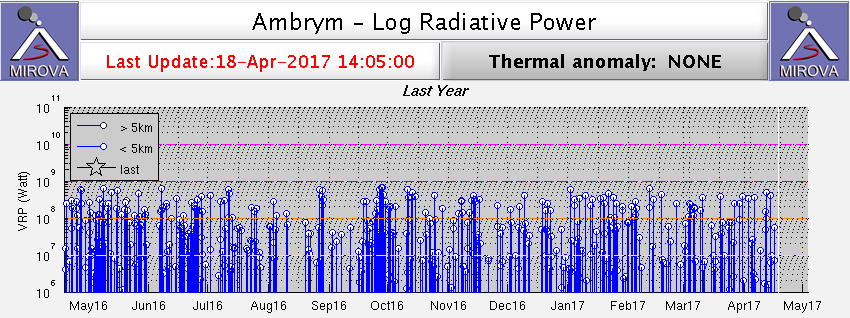 |
Figure 36. Plot of MODIS thermal infrared data analyzed by MIROVA showing log radiative power for Ambrym for the year ending 18 April 2017. Courtesy of MIROVA. |
Information Contacts: Vanuatu Geohazards Observatory (VGO), Geo-Hazards office, Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (URL: http://www.vmgd.gov.vu/vmgd/); Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre (VAAC), Meteorological Service of New Zealand Ltd (MetService), PO Box 722, Wellington, New Zealand (URL: http://vaac.metservice.com/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP), MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Stromboli Online (URL: http://www.swisseduc.ch/stromboli/perm/van/links-en.html).
Elevated seismicity in early August 2017-early November 2017, lava lakes remain
Occasional weak eruptions and low-level ash emissions are typical of activity at Ambrym. The most recent ash emission was on 3 April 2017 (BGVN 42:05). The current report summarizes activity from late April through December 2017.
On 30 August 2017, the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) reported that "drastic changes" at Ambrym prompted an increase in the Alert Level from 2 to 3 (on a scale of 0-5). Areas deemed hazardous were near and around the active vents (Benbow, Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu and Mbwelesu), and in downwind areas prone to ashfall. According to a news report (Radio New Zealand), a representative of VMGD indicated that the Alert Level change was based on increased seismicity detected since the beginning of August, but which became more notable on 25 August.
According to VMGD, aerial observations on 24 and 30 September, and 1 and 6 October, combined with analysis of seismic data, confirmed that minor eruptive activity within the caldera was characterized by hot volcanic gas and steam emissions. Areas deemed hazardous were within a 2-km radius from Benbow Crater and a 3-km radius from Marum Crater.
A news report (The Vanuatu Independent) quoted an official from VMGD as stating that on 8 November 2017 at 0500, the Niri-Mbwelesu eruptive vent emitted a minor ash plume. On 7 December 2017, VGO lowered the Alert Level to 2, noting that activity had stabilized by the end of November and was characterized by gas-and-steam emissions. Seismicity had also declined. The report reminded the public to stay outside of the Permanent Danger Zone, defined as a 1-km radius from Benbow Crater and a 2.7-km radius from Marum Crater.
During the reporting period, thermal anomalies based on MODIS satellite instruments and analyzed using the MODVOLC algorithm, continued to be numerous every month, possibly reflecting lava lakes in Benbow and Marum craters. The MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) system also detected numerous hotspots every month within 5 km of the volcano.
Information Contacts: Geo-Hazards Division, Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department, Ministry of Climate Change Adaptation, Meteorology, Geo-Hazards, Energy, Environment and Disaster Management, Private Mail Bag 9054, Lini Highway, Port Vila, Vanuatu (URL: http://www.vmgd.gov.vu/, https://www.facebook.com/VanuatuGeohazardsObservatory/); Radio New Zealand (URL: https://www.radionz.co.nz); The Vanuatu Independent (URL: https://vanuatuindependent.com/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP), MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity (MIROVA), Mirova (collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence, Italy)(URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it).
Benbow and Marum lava lake activity continues with steam and gas emissions through June 2018
Ambrym volcano, located in Vanuatu along the New Hebrides Island Arc, consists of a large 12-km-diameter caldera with two active craters, Marum and Benbow. Historical activity has occurred at summit and flank vents, producing moderate explosive eruptions and lava flows that reach the coast. Historically important eruptions date back two centuries, including extra-caldera W-flank lava flows that caused destruction in coastal areas in 1820, 1894, 1913, and 1929. Since then, there have not been extra-caldera lava eruptions, although the areas around Marum and Benbow craters remain hazardous. The Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD) located in Port Vila, Vanuatu, is responsible for monitoring ongoing activity at Ambrym.
During January through June 2018, volcanic activity was confined to the eruptive vents of Benbow and Marum craters, including ongoing lava lake activity inside the active vents, substantial degassing, and emission of steam clouds. The Volcanic Alert Level remained at Level 2 on a scale from 0 to 5 with five being the highest (figure 30). At Level 2 ('Major Unrest') the danger is restricted to the active craters and the Permanent Exclusion Zones, which are located within a 1 km radius around Benbow crater and about a 2.7 km radius around Marum crater (figure 38).
VMGD reported that the lava lakes in Benbow and Marum craters continued to be active and produced gas and steam emissions on 30 January, 19 March, and 25 April 2018. More sustained and substantial emissions were reported on 7 June.
During the reporting period, numerous thermal anomalies were detected by the MODIS satellite instruments and subsequently analyzed using the MODVOLC algorithm, possibly reflecting lava lake activity in Benbow and Marum craters (figures 39 and 40). The MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) system also detected numerous hotspots almost every day (figure 41).
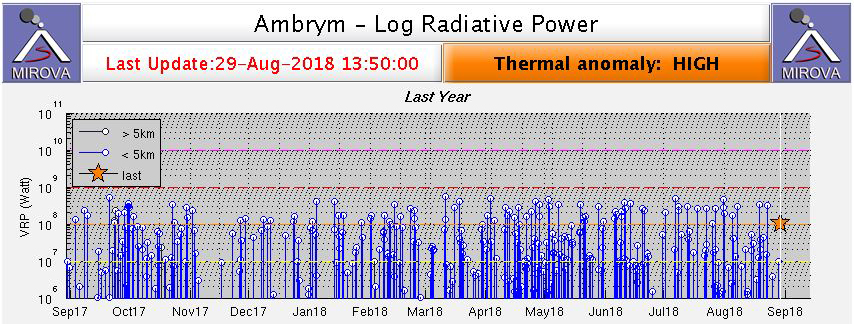 |
Figure 41. Plot of MODIS thermal infrared data analyzed by MIROVA showing the log radiative power of thermal anomalies at Ambrym for the year ending on 29 August 2018. Courtesy of MIROVA. |
Information Contacts: Geo-Hazards Division, Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD), Ministry of Climate Change Adaptation, Meteorology, Geo-Hazards, Energy, Environment and Disaster Management, Private Mail Bag 9054, Lini Highway, Port Vila, Vanuatu (URL: http://www.vmgd.gov.vu/, https://www.facebook.com/VanuatuGeohazardsObservatory/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/).
Fissure eruption in mid-December 2018 produces fountaining and lava flows; no activity evident in caldera after 17 December
Ambrym is a shield volcano in the Vanuatu archipelago with a 12-km-wide summit caldera containing the persistently active Benbow and Marum craters. These craters are home to multiple active vents that produce episodic lava lakes, explosions, lava flows, ash, and gas emissions. Occasional fissure eruptions occur outside of these main craters. This report covers July to December 2018 and summarizes reports by the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD), the Wellington Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC), and multiple sources of satellite data.
As of the beginning of the reporting period, the hazard status at Ambrym had remained at Volcanic Alert Level 2 ("Major unrest") since 7 December 2017. Monthly VMGD activity reports describe the continued activity within the two main craters, consisting of multiple lava lakes, sustained substantial degassing and steam emission, and seismic unrest. Frequent thermal anomalies were detected throughout the reporting period (figure 42). The danger areas were confined to the Permanent Exclusion Zone within a 1 km radius of Benbow crater, and the Permanent Exclusion Zone and Danger Zone A within about a 2.7 km radius of Marum crater (including Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu and Mbwelesu, see BGVN 43:07, figure 38).
Observations and seismic data analysis by VMGD confirmed the onset of a small-scale intra-caldera fissure eruption at 0600 local time on 15 December. This new fissure produced lava fountains and lava flows with ash and gas plumes (figure 43). Footage of the eruption by John Tasso shows the fissure eruption to the SE of Marum crater producing lava fountaining. A Sentinel-2 satellite image shows a white eruption plume and two new lava flow lobes (figure 44); the actual fissure vent was hidden by the plume. The northernmost lava flow filled in the 500 x 900 m Lewolembwi crater and a smaller lobe continued to flow towards the E (figure 44). Due to this elevated activity, the Volcanic Alert Level was raised to 3 ("Minor eruption"), with the danger zones increased to a 2 km radius around Benbow crater and a 4 km radius around Marum crater. VMGD warned of additional risk within 3 km of eruptive fissures in the SE caldera area.
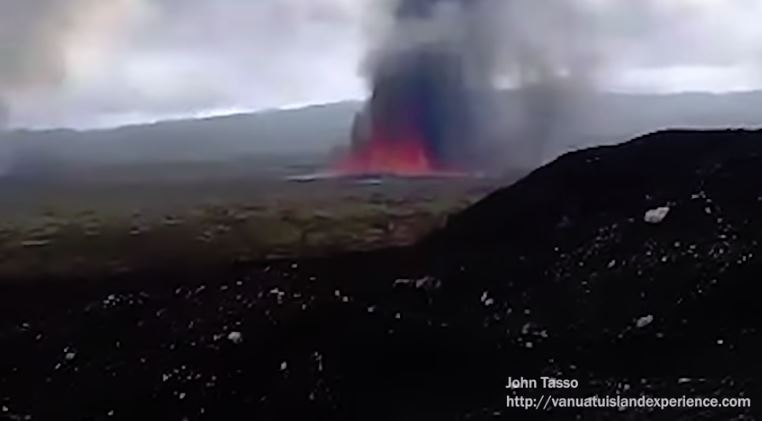 |
Figure 43. Image of the fissure eruption producing lava fountaining at Ambrym volcano, taken from a video recorded by John Tasso on 16 December 2018. |
Through 16-17 December, ash and gas emission continued from Benbow and Marum craters (figures 45 and 46), accompanied by ongoing localized seismicity; earthquakes with a magnitude greater than five were felt on neighboring islands. The Wellington VAAC issued ash advisories on 16 and 17 December noting maximum cloud altitudes of approximately 8 km.
 |
Figure 45. Ash emission from Ambrym volcano at 1600 on 16 December 2018. Webcam image courtesy of, and annotated by, VMGD. |
From 14 to 26 December, the National Volcano Monitoring Network detected over 4,500 earthquakes related to the eruptive activity, but locally felt seismicity decreased. Analysis of satellite imagery confirmed surface deformation associated with the increase in activity. Media reports from Radio New Zealand indicated that seismic activity during December resulted in ground rupture and damage to homes on the island and residents were moved to evacuation centers.
During the reporting period, thermal anomalies were frequently detected by the MODIS satellite instruments and subsequently analyzed using the MODVOLC algorithm, reflecting the lava lake activity in Benbow and Marum craters, as well additional thermal anomalies during the December 2018 fissure eruption and subsequent lava flows to the SE of the main crater area (figures 47 and 48).
As of 7 January 2019, Ambrym remains on Alert Level 3 with continued seismic activity. The MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity) system has not detected any recent thermal anomalies, indicating the end of the fissure eruption and a reduction in activity at the main craters.
Information Contacts: Geo-Hazards Division, Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD), Ministry of Climate Change Adaptation, Meteorology, Geo-Hazards, Energy, Environment and Disaster Management, Private Mail Bag 9054, Lini Highway, Port Vila, Vanuatu (URL: http://www.vmgd.gov.vu/, https://www.facebook.com/VanuatuGeohazardsObservatory/); Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology (HIGP) - MODVOLC Thermal Alerts System, School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), Univ. of Hawai'i, 2525 Correa Road, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA (URL: http://modis.higp.hawaii.edu/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/); Radio New Zealand, 155 The Terrace, Wellington 6011, New Zealand (URL: https://www.radionz.co.nz/); Sentinel Hub Playground (URL: https://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/sentinel-playground); John Tasso, Vanuatu Island Experience, Port Vatu, West Ambrym, Vanuatu (URL: http://vanuatuislandexperience.com/).
Fissure eruption in December 2018 produces an offshore pumice eruption after lava lakes drain
Ambrym is an active volcanic island in the Vanuatu archipelago consisting of a 12 km-wide summit caldera. Benbow and Marum are two currently active craters within the caldera that have produced lava lakes, explosions, lava flows, ash, and gas emissions, in addition to fissure eruptions. More recently, a submarine fissure eruption in December 2018 produced lava fountains and lava flows, which resulted in the drainage of the active lava lakes in both the Benbow and Marum craters (BGVN 44:01). This report updates information from January 2019 through March 2020, including the submarine pumice eruption during December 2018 using information from the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) and research by Shreve et al. (2019).
Activity on 14 December 2018 consisted of thermal anomalies located in the lava lake that disappeared over a 12-hour time period; a helicopter flight on 16 December confirmed the drainage of the summit lava lakes as well as a partial collapse of the Benbow and Marum craters (figure 49). During 14-15 December, a lava flow (figure 49), accompanied by lava fountaining, was observed originating from the SE flank of Marum, producing SO2 and ash emissions. A Mw 5.6 earthquake at 2021 on 15 December marked the beginning of a dike intrusion into the SE rift zone as well as a sharp increase in seismicity (Shreve et al., 2019). This intrusion extended more than 30 km from within the caldera to beyond the east coast, with a total volume of 419-532 x 106 m3 of magma. More than 2 m of coastal uplift was observed along the SE coast due to the asymmetry of the dike from December, resulting in onshore fractures.
Shreve et al. (2019) state that although the dike almost reached the surface, magma did not erupt from the onshore fractures; only minor gas emissions were detected until 17 December. An abrupt decrease in the seismic moment release on 17 December at 1600 marked the end of the dike propagation (figure 50). InSAR-derived models suggested an offshore eruption (Shreve et al., 2019). This was confirmed on 18-19 December when basaltic pumice, indicating a subaqueous eruption, was collected on the beach near Pamal and Ulei. Though the depth and exact location of the fissure has not been mapped, the nature of the basaltic pumice would suggest it was a relatively shallow offshore eruption, according to Shreve et al. (2019).
In the weeks following the dike emplacement, there was more than 2 m of subsidence measured at both summit craters identified using ALOS-2 and Sentinel-1 InSAR data. After 22 December, no additional large-scale deformation was observed, though a localized discontinuity (less than 12 cm) measured across the fractures along the SE coast in addition to seismicity suggested a continuation of the distal submarine eruption into late 2019. Additional pumice was observed on 3 February 2019 near Pamal village, suggesting possible ongoing activity. These surveys also noted that no gas-and-steam emissions, lava flows, or volcanic gases were emitted from the recently active cracks and faults on the SE cost of Ambrym.
During February-October 2019, onshore activity at Ambrym declined to low levels of unrest, according to VMGD. The only activity within the summit caldera consisted of gas-and-steam emissions, with no evidence of the previous lava lakes (figure 51). Intermittent seismicity and gas-and-steam emissions continued to be observed at Ambrym and offshore of the SE coast. Mével et al. (2019) installed three Trillium Compact 120s posthole seismometers in the S and E part of Ambrym from 25 May to 5 June 2019. They found that there were multiple seismic events, including a Deep-Long Period event and mixed up/down first motions at two stations near the tip of the dike intrusion and offshore of Pamal at depths of 15-20 km below sea level. Based on a preliminary analysis of these data, Mével et al. (2019) interpreted the observations as indicative of ongoing volcanic seismicity in the region of the offshore dike intrusion and eruption.
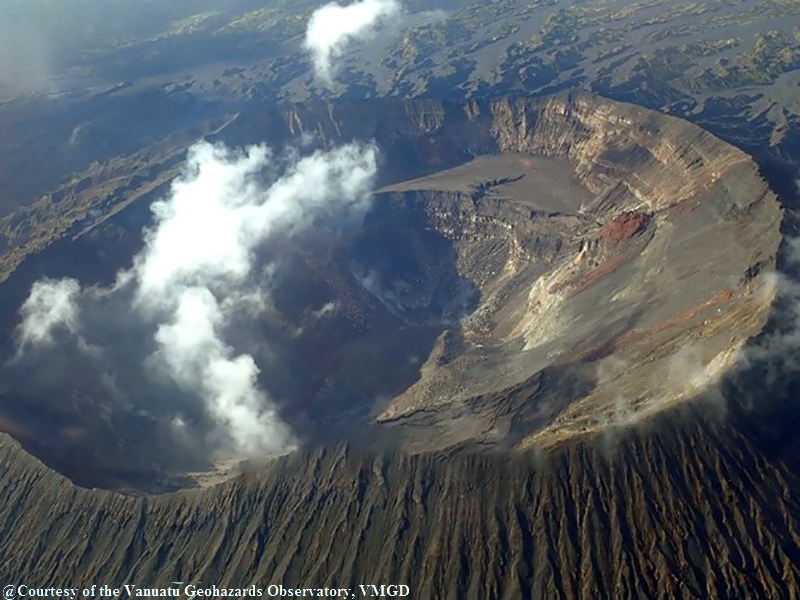 |
Figure 51. Aerial photograph of Ambrym on 12 August 2019 showing gas-and-steam emissions rising from the summit caldera. Courtesy of VMGD. |
Seismicity was no longer reported from 10 October 2019 through March 2020. Thermal anomalies were not detected in satellite data except for one in late April and one in early September 2019, according to MODIS thermal infrared data analyzed by the MIROVA system. The most recent report from VMGD was issued on 27 March 2020, which noted low-level unrest consisting of dominantly gas-and-steam emissions.
References:
Shreve T, Grandin R, Boichu M, Garaebiti E, Moussallam Y, Ballu V, Delgado F, Leclerc F, Vallée M, Henriot N, Cevuard S, Tari D, Lebellegard P, Pelletier B, 2019. From prodigious volcanic degassing to caldera subsidence and quiescence at Ambrym (Vanuatu): the influence of regional tectonics. Sci. Rep. 9, 18868. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-55141-7.
Mével H, Roman D, Brothelande E, Shimizu K, William R, Cevuard S, Garaebiti E, 2019. The CAVA (Carnegie Ambrym Volcano Analysis) Project - a Multidisciplinary Characterization of the Structure and Dynamics of Ambrym Volcano, Vanuatu. American Geophysical Union, Fall 2019 Meeting, Abstract and Poster V43C-0201.
Information Contacts: Geo-Hazards Division, Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD), Ministry of Climate Change Adaptation, Meteorology, Geo-Hazards, Energy, Environment and Disaster Management, Private Mail Bag 9054, Lini Highway, Port Vila, Vanuatu (URL: http://www.vmgd.gov.vu/, https://www.facebook.com/VanuatuGeohazardsObservatory/); MIROVA (Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity), a collaborative project between the Universities of Turin and Florence (Italy) supported by the Centre for Volcanic Risk of the Italian Civil Protection Department (URL: http://www.mirovaweb.it/); Sentinel Hub Playground (URL: https://www.sentinel-hub.com/explore/sentinel-playground); Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard, Maryland, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/).
New ash eruption with crater incandescence in late January 2022
Ambrym contains a 12-km-wide caldera and is part of the New Hebrides Arc, located in the Vanuatu archipelago. The two currently active craters within the caldera are Benbow and Marum, which have produced lava lakes, explosions, lava flows, ash, and gas emissions. The previous eruption period, which began in May 2008, ended in December 2018 with lava fountains, lava flows, a submarine fissure eruption, and drainage of the lava lake (BGVN 45:03). After those events no eruptive activity was reported until January 2022, which consisted of ash plumes and crater incandescence. This report updates information from April 2020 through March 2022 and describes a short eruption period during 25 January to the beginning of February 2022. Information comes from the Vanuatu Meteorology and Geohazards Department (VMGD) and satellite data.
Activity during April 2020 through December 2021 was relatively low and consisted mainly of gas-and-steam emissions from both Benbow and Marum craters. On 25 January 2022 the Volcanic Alert Level (VAL) was raised from Level 1 to 2 (on a scale of 0-5) due to increased activity beginning around 0400. Significant gas-and-steam emissions were observed rising from Marum, and gas-and-ash emissions rose from Benbow at 0515 (figure 52). A sulfur dioxide plume that exceeded 2 DUs (Dobson Units) was detected on 25 January and drifted SE, following the ash plume, based on data from the Sentinel-5 instrument (figure 53). At night on 25 January, crater incandescence from Benbow was visible in webcam images, which represented a lava flow that had effused from a new vent on the NW part of the crater floor. Incandescence persisted through 27 January, according to VMGD (figure 54).
 |
Figure 52. Webcam image of Ambrym at 0645 on 25 January 2022 showing an ash plume rising above the Benbow crater. Courtesy of VMGD. |
By early February, crater incandescence was no longer visible. On 2 February sulfur dioxide emissions were still detected in satellite images and drifted E. According to VMGD, no gas-and-steam emissions were visible from Benbow during early February through April and seismicity had decreased. As a result, the VAL was lowered to Level 1 on 28 April.
Information Contacts: Geo-Hazards Division, Vanuatu Meteorology and Geo-Hazards Department (VMGD), Ministry of Climate Change Adaptation, Meteorology, Geo-Hazards, Energy, Environment and Disaster Management, Private Mail Bag 9054, Lini Highway, Port Vila, Vanuatu (URL: http://www.vmgd.gov.vu/, https://www.facebook.com/VanuatuGeohazardsObservatory/); NASA Global Sulfur Dioxide Monitoring Page, Atmospheric Chemistry and Dynamics Laboratory, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (NASA/GSFC), 8800 Greenbelt Road, Goddard, MD 20771, USA (URL: https://so2.gsfc.nasa.gov/).
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
There is data available for 56 confirmed eruptive periods.
[ 2024 Oct 31 - 2024 Nov 2 ] Uncertain Eruption
| Episode 1 | Uncertain | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 Oct 31 - 2024 Nov 2 | Evidence from Observations: Satellite (infrared) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VMGD reported that incandescence was observed during the night of 31 October, and a large SO2 plume was detected by TROPOMI. Stronger thermal anomalies were detected in MODIS data by the MODVOLC system during 1-2 November. Lower power thermal anomalies were detected by VIIRS into mid-April 2025. No hotspots have been visible in any of the craters in Sentinel-2 data. As of July 2025 the VMGD webpage listed the short January 2024 activity as the last eruption at Ambrym. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2024 Jan 13 - 2024 Jan 16 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 0
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 Jan 13 - 2024 Jan 16 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 2 Events for Episode 1
|
|||||||||||||||||||
2022 Jan 25 - 2022 Feb 2 ± 1 days Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 1
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow Crater | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 Jan 25 - 2022 Feb 2 ± 1 days | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| On 25 January 2022 significant gas-and-steam emissions were observed rising from Marum, and gas-and-ash emissions rose from Benbow at 0515. Satellite data recorded increased sulfur dioxide emissions from Benbow. Crater incandescence from Benbow was visible in webcam images, due to a lava flow that had effused from a new vent on the NW part of the crater floor. Incandescence persisted through 27 January. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow Crater
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2008 May 23 - 2018 Dec 17 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow and Marum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 May 23 - 2018 Dec 17 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow and Marum
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2006 Nov 8 - 2007 Dec 27 (on or after) Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Marum (Mbwelesu) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 Nov 8 - 2007 Dec 27 (on or after) | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at Marum (Mbwelesu)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1996 Jun 16 (on or before) ± 15 days - 2005 Aug 16 (on or after) ± 15 days Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 1
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow, Marum, Niri Mbelesu, Mbwelesu | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1996 Jun 16 (on or before) ± 15 days - 2005 Aug 16 (on or after) ± 15 days | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 7 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow, Marum, Niri Mbelesu, Mbwelesu
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1994 Dec 16 (on or before) ± 15 days Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 1 (?)
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow and Marum | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1994 Dec 16 (on or before) ± 15 days - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow and Marum
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
1990 Sep 16 (on or before) ± 15 days - 1991 Jul 16 (on or after) ± 15 days Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Mbwelesu, Niri Mbwelesu, Niri Taten | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 Sep 16 (on or before) ± 15 days - 1991 Jul 16 (on or after) ± 15 days | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 6 Events for Episode 1 at Mbwelesu, Niri Mbwelesu, Niri Taten
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1989 Apr 24 - 1989 Dec 23 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Marum, Benbow, Niri Mbwelesu Taten | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1989 Apr 24 - 1989 Dec 23 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 6 Events for Episode 1 at Marum, Benbow, Niri Mbwelesu Taten
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1988 Feb 12 (?) - 1988 Aug 23 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow, Mbwelesu, Marum, Niri Taten | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1988 Feb 12 (?) - 1988 Aug 23 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow, Mbwelesu, Marum, Niri Taten
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1986 Nov 13 - 1986 Nov 19 (?) Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | New cone 3 km east of Marum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1986 Nov 13 - 1986 Nov 19 (?) | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at New cone 3 km east of Marum
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1984 Jul 2 ± 182 days - 1986 Mar 8 (on or after) Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1984 Jul 2 ± 182 days - 1986 Mar 8 (on or after) | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
1983 Jul 2 ± 182 days Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Marum | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1983 Jul 2 ± 182 days - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 2 Events for Episode 1 at Marum
|
|||||||||||||||||||
1981 Feb 20 - 1981 Sep 30 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow, Marum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1981 Feb 20 - 1981 Sep 30 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 6 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow, Marum
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1980 May 16 - 1980 Aug 18 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Marum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980 May 16 - 1980 Aug 18 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at Marum
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1979 Jun 6 - 1979 Sep 16 (?) ± 15 days Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow, Marum | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1979 Jun 6 - 1979 Sep 16 (?) ± 15 days | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 2 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow, Marum
|
|||||||||||||||||||
1979 Jan 26 ± 5 days - 1979 Feb 18 (?) Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1979 Jan 26 ± 5 days - 1979 Feb 18 (?) | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1977 Aug 16 ± 15 days - 1977 Sep 30 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1977 Aug 16 ± 15 days - 1977 Sep 30 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
1977 Jan 20 ± 5 days - 1977 Jan 28 (?) Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1977 Jan 20 ± 5 days - 1977 Jan 28 (?) | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1973 Apr 15 ± 5 days - 1976 Oct 14 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow, Mbuelesu, Marum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1973 Apr 15 ± 5 days - 1976 Oct 14 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 6 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow, Mbuelesu, Marum
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1972 Apr 15 - 1972 Aug 15 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow, Marum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1972 Apr 15 - 1972 Aug 15 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 9 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow, Marum
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1971 Feb 3 - 1971 Nov 5 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Marum, Benbow | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1971 Feb 3 - 1971 Nov 5 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 6 Events for Episode 1 at Marum, Benbow
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1967 Jul 16 ± 15 days - 1970 Aug 29 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Marum, Benbow, Mbuelesu | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1967 Jul 16 ± 15 days - 1970 Aug 29 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at Marum, Benbow, Mbuelesu
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1964 Feb 16 (?) ± 15 days - 1966 Sep 16 (on or after) ± 15 days Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Marum, Benbow | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1964 Feb 16 (?) ± 15 days - 1966 Sep 16 (on or after) ± 15 days | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 6 Events for Episode 1 at Marum, Benbow
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1963 Aug 30 - 1963 Sep 23 (on or after) Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow, Marum | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1963 Aug 30 - 1963 Sep 23 (on or after) | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow, Marum
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
1961 Aug 15 - 1963 Apr 3 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow, Marum, south of Marum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1961 Aug 15 - 1963 Apr 3 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 9 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow, Marum, south of Marum
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1960 Sep 17 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 1 (?)
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Mbuelesu, Benbow, near Marum | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1960 Sep 17 - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1 at Mbuelesu, Benbow, near Marum
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
1959 Apr 16 ± 15 days Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Marum | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1959 Apr 16 ± 15 days - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 2 Events for Episode 1 at Marum
|
|||||||||||||||||||
1958 Nov 18 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2 (?)
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow and Marum | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1958 Nov 18 - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 2 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow and Marum
|
|||||||||||||||||||
1957 Aug 26 ± 5 days - 1957 Oct 16 ± 15 days Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 1 (?)
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow, Marum | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1957 Aug 26 ± 5 days - 1957 Oct 16 ± 15 days | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow, Marum
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
1955 Jul 2 ± 182 days Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1955 Jul 2 ± 182 days - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1954 Jul 2 ± 182 days Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1954 Jul 2 ± 182 days - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 2 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow
|
|||||||||||||||||||
1953 May 16 ± 15 days - 1953 Oct 13 (?) Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow, Mbuelesu, S flank of Benbow | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1953 May 16 ± 15 days - 1953 Oct 13 (?) | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow, Mbuelesu, S flank of Benbow
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
1952 Aug 10 - 1952 Dec 26 ± 5 days Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1952 Aug 10 - 1952 Dec 26 ± 5 days | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1950 Dec 6 - 1951 Nov 25 ± 5 days Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 4
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 Dec 6 - 1951 Nov 25 ± 5 days | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 11 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1942 Jun 6 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | NW flank of Benbow | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1942 Jun 6 - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1 at NW flank of Benbow
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1938 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow, Marum ? | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1938 - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 2 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow, Marum ?
|
|||||||||||||||||||
1937 Mar 27 - 1937 Apr Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow and west flank | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1937 Mar 27 - 1937 Apr | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow and west flank
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1935 Sep - 1936 Jan Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1935 Sep - 1936 Jan | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
1929 Jun 28 - 1929 Jul 1 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow, west flank, Marum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1929 Jun 28 - 1929 Jul 1 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 6 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow, west flank, Marum
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1915 Oct 20 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Marum, crater at SE point | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1915 Oct 20 - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1 at Marum, crater at SE point
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1913 Oct 14 - 1914 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow, west flank, Marum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1913 Oct 14 - 1914 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 10 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow, west flank, Marum
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1912 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive)
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Marum ?, west flank ? | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1912 - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||
|
List of 1 Events for Episode 1 at Marum ?, west flank ?
|
||||||||||||||
1910 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 0 (?)
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Base of Marum | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1910 - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1 at Base of Marum
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
1909 Jul 28 (?) Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2 (?)
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1909 Jul 28 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1908 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2 (?)
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1908 - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 2 Events for Episode 1
|
|||||||||||||||||||
1898 Mar 26 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 1 (?)
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1898 Mar 26 - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
1894 Oct 15 - 1895 Feb 10 (on or after) Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 3
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Benbow and west flank | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1894 Oct 15 - 1895 Feb 10 (on or after) | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 9 Events for Episode 1 at Benbow and west flank
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1888 Feb 24 ± 4 days - 1888 Apr (?) Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | SE flank (6 km from SE Point), Marum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1888 Feb 24 ± 4 days - 1888 Apr (?) | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 5 Events for Episode 1 at SE flank (6 km from SE Point), Marum
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1886 Jul Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1886 Jul - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
1884 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2 (?)
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Marum and/or Benbow | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1884 - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 2 Events for Episode 1 at Marum and/or Benbow
|
|||||||||||||||||||
1883 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | Marum | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1883 - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1 at Marum
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
1871 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1871 - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
[ 1870 ] Uncertain Eruption
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1870 - Unknown | Evidence from Unknown | |||||||||||||
|
List of 1 Events for Episode 1
|
||||||||||||||
1863 - 1864 Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1863 - 1864 | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
1820 (?) Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive)
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | West flank | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1820 (?) - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 3 Events for Episode 1 at West flank
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
1774 Jul 2 ± 182 days Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 2
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1774 Jul 2 ± 182 days - Unknown | Evidence from Observations: Reported | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Two columns of smoke were reported by Captain Cook in 1774. This is considered to have been accompanied by heavy ashfall by Eissen and Louat (1989, table in SEAN Bull. 14:10). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 4 Events for Episode 1
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0050 ± 100 years Confirmed Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) VEI: 6
| Episode 1 | Eruption (Explosive / Effusive) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0050 ± 100 years - Unknown | Evidence from Isotopic: 14C (uncalibrated) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
List of 7 Events for Episode 1
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This compilation of synonyms and subsidiary features may not be comprehensive. Features are organized into four major categories: Cones, Craters, Domes, and Thermal Features. Synonyms of features appear indented below the primary name. In some cases additional feature type, elevation, or location details are provided.
Synonyms |
||||
| Ambrim | ||||
Cones |
||||
| Feature Name | Feature Type | Elevation | Latitude | Longitude |
| Dalahum
Rahoum Ohalahoum |
Cone | 1067 m | 16° 12' 0.00" S | 168° 9' 0.00" E |
| Tuvio, Mont
Tuyio |
Cone | 1141 m | 16° 10' 0.00" S | 168° 9' 0.00" E |
| Vetlam
Vietlam |
Cone | 1175 m | 16° 10' 0.00" S | 168° 9' 0.00" E |
| Woosantapaliplip
Tower Peak Tour, La Touo, Le |
Cone | 999 m | 16° 19' 0.00" S | 168° 7' 0.00" E |
Craters |
||||
| Feature Name | Feature Type | Elevation | Latitude | Longitude |
| Benbow | Crater - Cone | 1159 m | 16° 16' 0.00" S | 168° 6' 0.00" E |
| Lewolembwi | Maar | 16° 17' 0.00" S | 168° 10' 0.00" E | |
| Marum
Maroum Puelamarum |
Crater - Cone | 1270 m | 16° 15' 0.00" S | 168° 7' 0.00" E |
| Marumliglar
Heienliglar |
Crater | 957 m | 16° 15' 0.00" S | 168° 8' 0.00" E |
| Mbwelesu
Mbuelesu |
Crater | 16° 15' 0.00" S | 168° 8' 0.00" E | |
| Minnei | Crater | 375 m | 16° 15' 0.00" S | 167° 55' 0.00" E |
| Niri Mbwelesu | Crater | 16° 15' 0.00" S | 168° 8' 0.00" E | |
| Niri Mbwelesu Taten | Crater | 16° 10' 0.00" S | 168° 8' 0.00" E | |
| Niri Taten | Crater | 16° 10' 0.00" S | 168° 8' 0.00" E | |
 This vertical aerial photo shows part of the 12-km-wide summit caldera of Ambrym. The craters emitting plumes to the lower left are Marum (top) and Benbow (bottom). The caldera formed during a major Plinian eruption that included pyroclastic flows about 1,900 years ago. Post-caldera eruptions, primarily from Marum and Benbow cones, have partially filled the caldera floor and also formed a series of cones and maars along a fissure system oriented ENE-WSW.
This vertical aerial photo shows part of the 12-km-wide summit caldera of Ambrym. The craters emitting plumes to the lower left are Marum (top) and Benbow (bottom). The caldera formed during a major Plinian eruption that included pyroclastic flows about 1,900 years ago. Post-caldera eruptions, primarily from Marum and Benbow cones, have partially filled the caldera floor and also formed a series of cones and maars along a fissure system oriented ENE-WSW. During 5-18 September 1990 Ambrym was observed to be ejecting ash and blocks from Niri Mbwelesu crater, which formed adjacent to Mbwelesu crater in 1989 when Mbwelesu was also active. It no longer contained an active lava lake. Mbwelesu, Niri Mbwelesu, and Niri Mbwelesu Taten craters remained almost constantly active into 1991.
During 5-18 September 1990 Ambrym was observed to be ejecting ash and blocks from Niri Mbwelesu crater, which formed adjacent to Mbwelesu crater in 1989 when Mbwelesu was also active. It no longer contained an active lava lake. Mbwelesu, Niri Mbwelesu, and Niri Mbwelesu Taten craters remained almost constantly active into 1991. Explosive activity that ejected ash and blocks from Niri Mbwelesu crater was observed on 16 September 1990. The Niri Mbwelesu crater formed adjacent to Mbwelesu crater in 1989 when Mbwelesu was also active but no longer contained a lava lake. During 1990 activity was concentrated in Mbwelesu, Niri Mbwelesu and Niri Mbwelesu Taten craters. Activity remained more or less constant into 1991.
Explosive activity that ejected ash and blocks from Niri Mbwelesu crater was observed on 16 September 1990. The Niri Mbwelesu crater formed adjacent to Mbwelesu crater in 1989 when Mbwelesu was also active but no longer contained a lava lake. During 1990 activity was concentrated in Mbwelesu, Niri Mbwelesu and Niri Mbwelesu Taten craters. Activity remained more or less constant into 1991. A series of basaltic tuff rings and a scoria cone occupy the western tip of Ambrym, at the subaerial end of a fissure system that cuts across the length of the island. The largest tuff ring is about 1 km in diameter. The tuff rings were produced by phreatic eruptions when magma interacted with the water table or near-surface, water-saturated sediments along the coast. At higher elevations along the rift zone, scoria cones predominate.
A series of basaltic tuff rings and a scoria cone occupy the western tip of Ambrym, at the subaerial end of a fissure system that cuts across the length of the island. The largest tuff ring is about 1 km in diameter. The tuff rings were produced by phreatic eruptions when magma interacted with the water table or near-surface, water-saturated sediments along the coast. At higher elevations along the rift zone, scoria cones predominate. On 27 May 1988 this lava lake was observed in Mbwelesu's crater, which along with Marum, was emitting ash plumes. Airline pilots had reported ash plumes below 12 km altitude from Benbow on 13 February. Vanuatu geologists reported increased activity from Benbow during 12-14 February, after which the volcano returned to normal. On 9-10 August lava flows were emitted from a new cone along the S flank, Niri Taten, and traveled towards the southern caldera wall. This eruption ended on 23 August.
On 27 May 1988 this lava lake was observed in Mbwelesu's crater, which along with Marum, was emitting ash plumes. Airline pilots had reported ash plumes below 12 km altitude from Benbow on 13 February. Vanuatu geologists reported increased activity from Benbow during 12-14 February, after which the volcano returned to normal. On 9-10 August lava flows were emitted from a new cone along the S flank, Niri Taten, and traveled towards the southern caldera wall. This eruption ended on 23 August. Incandescent spatter ejected from a new lava lake at vent C of Mbwelesu crater at Ambrym volcano on 28 August 1999. Mbwelesu was constructed at the eastern rim of Marum crater in the west-central part of the 12-km-wide summit caldera. More frequent lava lake activity had been reported from several craters within the caldera since at least 1996. Lava lake activity had also been previously noted by infrequent visitors to the summit caldera during the late 1980s and early 1990s.
Incandescent spatter ejected from a new lava lake at vent C of Mbwelesu crater at Ambrym volcano on 28 August 1999. Mbwelesu was constructed at the eastern rim of Marum crater in the west-central part of the 12-km-wide summit caldera. More frequent lava lake activity had been reported from several craters within the caldera since at least 1996. Lava lake activity had also been previously noted by infrequent visitors to the summit caldera during the late 1980s and early 1990s. The ash-mantled slopes of the northern side of Marum cone are cut by erosional furrows. Marum is one of several historically active cones constructed within the 12-km-wide caldera of Ambrym. The cone lies in the west-central part of the caldera and is the highest of the post-caldera cones.
The ash-mantled slopes of the northern side of Marum cone are cut by erosional furrows. Marum is one of several historically active cones constructed within the 12-km-wide caldera of Ambrym. The cone lies in the west-central part of the caldera and is the highest of the post-caldera cones. Erosional gullies in fresh tephra deposits across the northern slopes of Benbow, one of the tuff cones in the Ambrym summit caldera. The 12-km-wide caldera formed during a major Plinian eruption with dacitic pyroclastic flows about 1,900 years ago. Post-caldera eruptions, primarily from the Marum and Benbow cones, have partially filled the caldera floor and produced lava flows that ponded on the caldera floor or overflowed through gaps in the caldera rim.
Erosional gullies in fresh tephra deposits across the northern slopes of Benbow, one of the tuff cones in the Ambrym summit caldera. The 12-km-wide caldera formed during a major Plinian eruption with dacitic pyroclastic flows about 1,900 years ago. Post-caldera eruptions, primarily from the Marum and Benbow cones, have partially filled the caldera floor and produced lava flows that ponded on the caldera floor or overflowed through gaps in the caldera rim. The steep-walled craters of the Marum cone complex at the summit of Ambrym volcano, seen from the east. Ambrym contains a 12-km-wide caldera and is one of the most active volcanoes of the New Hebrides arc. A thick pyroclastic sequence, initially dacitic, then basaltic, overlies lava flows of a pre-caldera shield volcano. Post-caldera eruptions, primarily from Marum and Benbow cones, have partially filled the caldera floor and produced lava flows that ponded on the caldera floor or overflowed through gaps in the caldera rim.
The steep-walled craters of the Marum cone complex at the summit of Ambrym volcano, seen from the east. Ambrym contains a 12-km-wide caldera and is one of the most active volcanoes of the New Hebrides arc. A thick pyroclastic sequence, initially dacitic, then basaltic, overlies lava flows of a pre-caldera shield volcano. Post-caldera eruptions, primarily from Marum and Benbow cones, have partially filled the caldera floor and produced lava flows that ponded on the caldera floor or overflowed through gaps in the caldera rim. A lava lake is visible inside Mbwelesu crater within Marum cone at Ambrym on 7 June 2007. Lava lake activity was observed during a field expedition from May to June. MODIS thermal alerts had resumed at Ambrym since November 2006 and eruptions took place in April and March 2007.
A lava lake is visible inside Mbwelesu crater within Marum cone at Ambrym on 7 June 2007. Lava lake activity was observed during a field expedition from May to June. MODIS thermal alerts had resumed at Ambrym since November 2006 and eruptions took place in April and March 2007.There are no samples for Ambrym in the Smithsonian's NMNH Department of Mineral Sciences Rock and Ore collection.
| Copernicus Browser | The Copernicus Browser replaced the Sentinel Hub Playground browser in 2023, to provide access to Earth observation archives from the Copernicus Data Space Ecosystem, the main distribution platform for data from the EU Copernicus missions. |
| MIROVA | Middle InfraRed Observation of Volcanic Activity (MIROVA) is a near real time volcanic hot-spot detection system based on the analysis of MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) data. In particular, MIROVA uses the Middle InfraRed Radiation (MIR), measured over target volcanoes, in order to detect, locate and measure the heat radiation sourced from volcanic activity. |
| MODVOLC Thermal Alerts | Using infrared satellite Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) data, scientists at the Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology, University of Hawai'i, developed an automated system called MODVOLC to map thermal hot-spots in near real time. For each MODIS image, the algorithm automatically scans each 1 km pixel within it to check for high-temperature hot-spots. When one is found the date, time, location, and intensity are recorded. MODIS looks at every square km of the Earth every 48 hours, once during the day and once during the night, and the presence of two MODIS sensors in space allows at least four hot-spot observations every two days. Each day updated global maps are compiled to display the locations of all hot spots detected in the previous 24 hours. There is a drop-down list with volcano names which allow users to 'zoom-in' and examine the distribution of hot-spots at a variety of spatial scales. |
|
WOVOdat
Single Volcano View Temporal Evolution of Unrest Side by Side Volcanoes |
WOVOdat is a database of volcanic unrest; instrumentally and visually recorded changes in seismicity, ground deformation, gas emission, and other parameters from their normal baselines. It is sponsored by the World Organization of Volcano Observatories (WOVO) and presently hosted at the Earth Observatory of Singapore.
GVMID Data on Volcano Monitoring Infrastructure The Global Volcano Monitoring Infrastructure Database GVMID, is aimed at documenting and improving capabilities of volcano monitoring from the ground and space. GVMID should provide a snapshot and baseline view of the techniques and instrumentation that are in place at various volcanoes, which can be use by volcano observatories as reference to setup new monitoring system or improving networks at a specific volcano. These data will allow identification of what monitoring gaps exist, which can be then targeted by remote sensing infrastructure and future instrument deployments. |
| Volcanic Hazard Maps | The IAVCEI Commission on Volcanic Hazards and Risk has a Volcanic Hazard Maps database designed to serve as a resource for hazard mappers (or other interested parties) to explore how common issues in hazard map development have been addressed at different volcanoes, in different countries, for different hazards, and for different intended audiences. In addition to the comprehensive, searchable Volcanic Hazard Maps Database, this website contains information about diversity of volcanic hazard maps, illustrated using examples from the database. This site is for educational purposes related to volcanic hazard maps. Hazard maps found on this website should not be used for emergency purposes. For the most recent, official hazard map for a particular volcano, please seek out the proper institutional authorities on the matter. |
| IRIS seismic stations/networks | Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology (IRIS) Data Services map showing the location of seismic stations from all available networks (permanent or temporary) within a radius of 0.18° (about 20 km at mid-latitudes) from the given location of Ambrym. Users can customize a variety of filters and options in the left panel. Note that if there are no stations are known the map will default to show the entire world with a "No data matched request" error notice. |
| UNAVCO GPS/GNSS stations | Geodetic Data Services map from UNAVCO showing the location of GPS/GNSS stations from all available networks (permanent or temporary) within a radius of 20 km from the given location of Ambrym. Users can customize the data search based on station or network names, location, and time window. Requires Adobe Flash Player. |
| DECADE Data | The DECADE portal, still in the developmental stage, serves as an example of the proposed interoperability between The Smithsonian Institution's Global Volcanism Program, the Mapping Gas Emissions (MaGa) Database, and the EarthChem Geochemical Portal. The Deep Earth Carbon Degassing (DECADE) initiative seeks to use new and established technologies to determine accurate global fluxes of volcanic CO2 to the atmosphere, but installing CO2 monitoring networks on 20 of the world's 150 most actively degassing volcanoes. The group uses related laboratory-based studies (direct gas sampling and analysis, melt inclusions) to provide new data for direct degassing of deep earth carbon to the atmosphere. |
| Large Eruptions of Ambrym | Information about large Quaternary eruptions (VEI >= 4) is cataloged in the Large Magnitude Explosive Volcanic Eruptions (LaMEVE) database of the Volcano Global Risk Identification and Analysis Project (VOGRIPA). |
| EarthChem | EarthChem develops and maintains databases, software, and services that support the preservation, discovery, access and analysis of geochemical data, and facilitate their integration with the broad array of other available earth science parameters. EarthChem is operated by a joint team of disciplinary scientists, data scientists, data managers and information technology developers who are part of the NSF-funded data facility Integrated Earth Data Applications (IEDA). IEDA is a collaborative effort of EarthChem and the Marine Geoscience Data System (MGDS). |